Research on Microwave Frequency Shift Method Based on Photonics
-
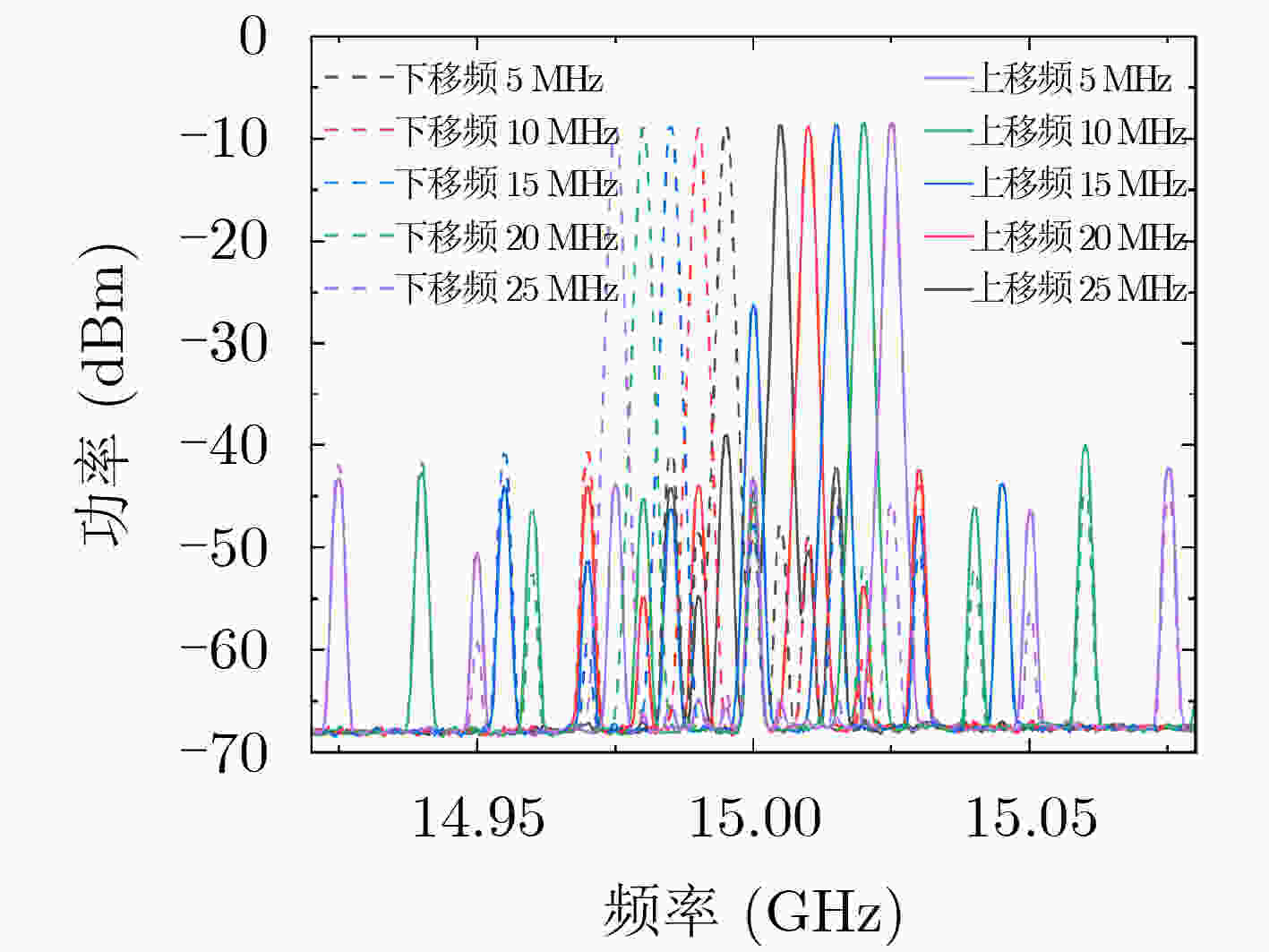
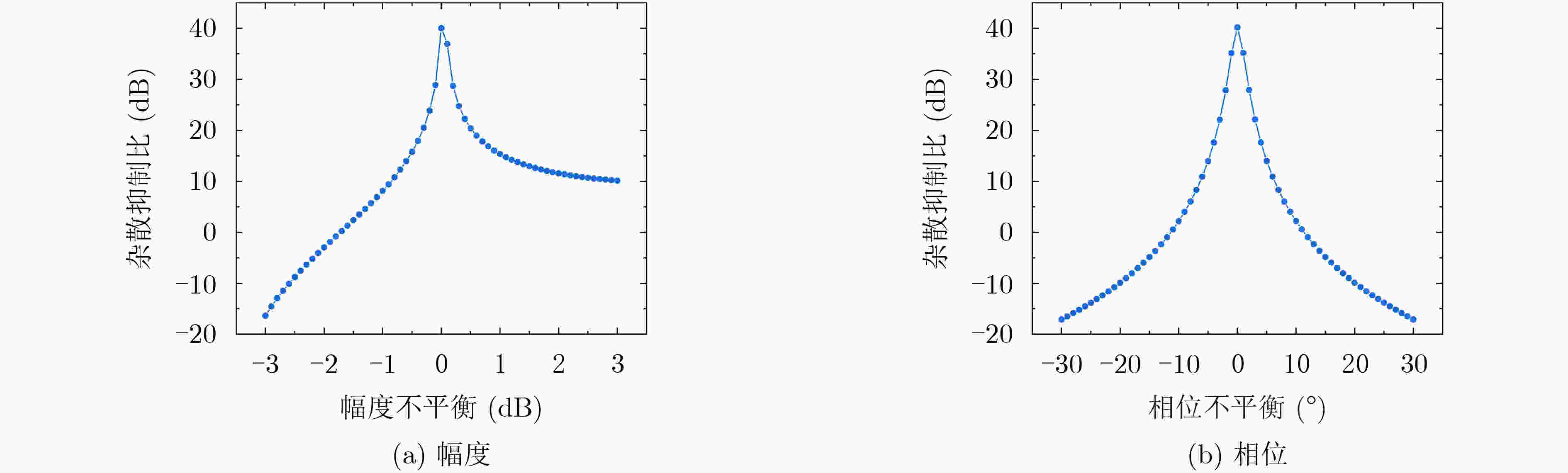
摘要: 微波移频技术(MFS)广泛应用于电子对抗、卫星通信、频控阵雷达等系统。基于光子学的微波移频方法具有带宽大、频谱纯净等优点。为了探索基于光子学的微波移频性能,该文对比研究了基于声光移频(AOFS)、锯齿波相位调制(SPM)和I/Q调制3种微波光子移频方法,阐释了3种方法的原理,搭建了对应的原理验证系统,对不同的移频方法进行了实验与分析。结果表明,3种移频方法都可以实现精准的微波信号移频,实现大于30 dB的杂散抑制比。但3种移频方法也存在各自的局限性:AOFS的工作频率、带宽和移频方向较为固定,可调谐性低;SPM移频与I/Q调制对输入驱动信号要求严格,系统稳定性较差。Abstract: Microwave Frequency Shift (MFS) technology is widely used in electronic countermeasures, satellite communications and frequency diverse array radar. The MFS method based on photonics has the advantages of large bandwidth and pure spectrum. In order to explore the performance, three MFS methods based on Acousto-Optic Frequency Shifter (AOFS), Sawtooth Phase Modulation (SPM) and I/Q modulation are compared in this paper. The principles of the three methods are illustrated and the corresponding verification systems are built for experiments and analysis. The results show that the three methods can achieve accurate MFS whose spurious suppression ratios are greater than 30 dB. However, the three methods simultaneously have different limitations: the operating frequency, bandwidth, and frequency shift direction of AOFS are relatively fixed which means the tunability is low; methods based on SPM and I/Q modulation have strict requirements on the input driving signal which leads to poor stability.
-
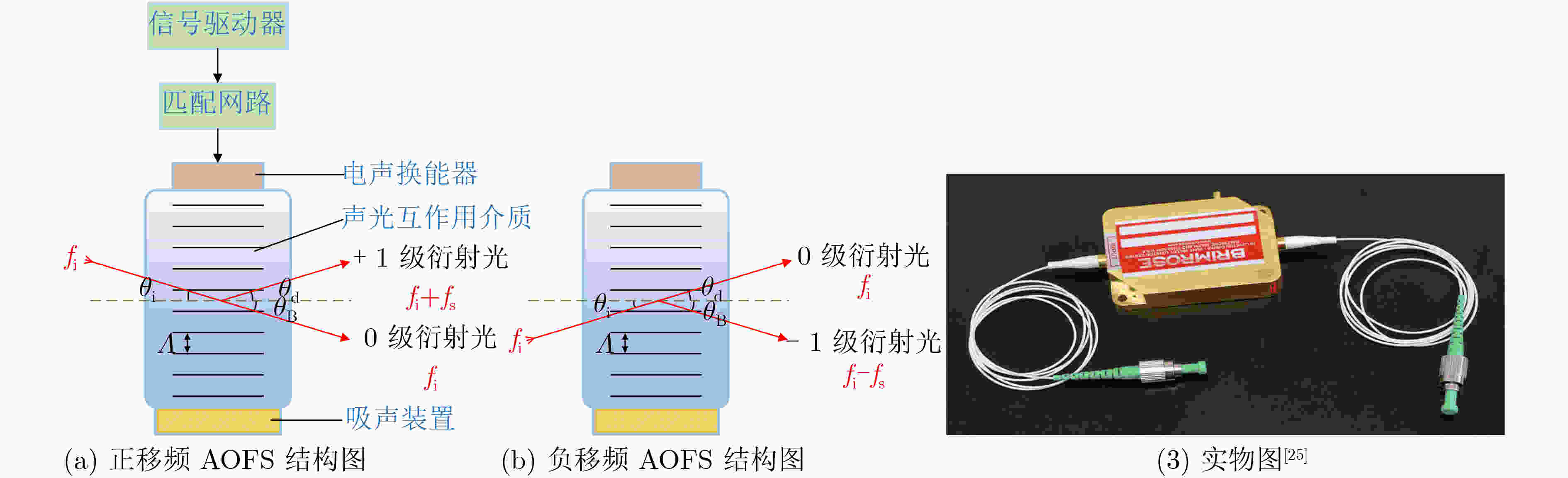
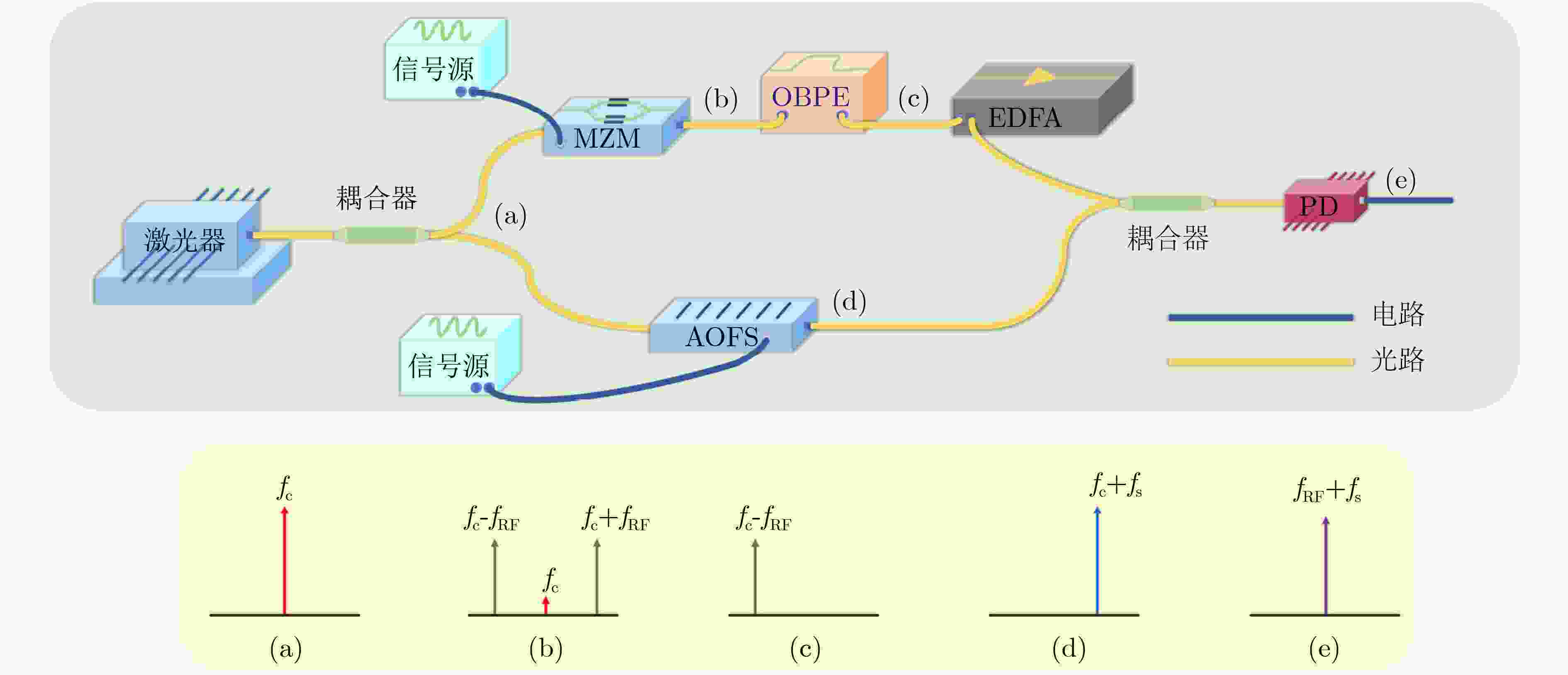
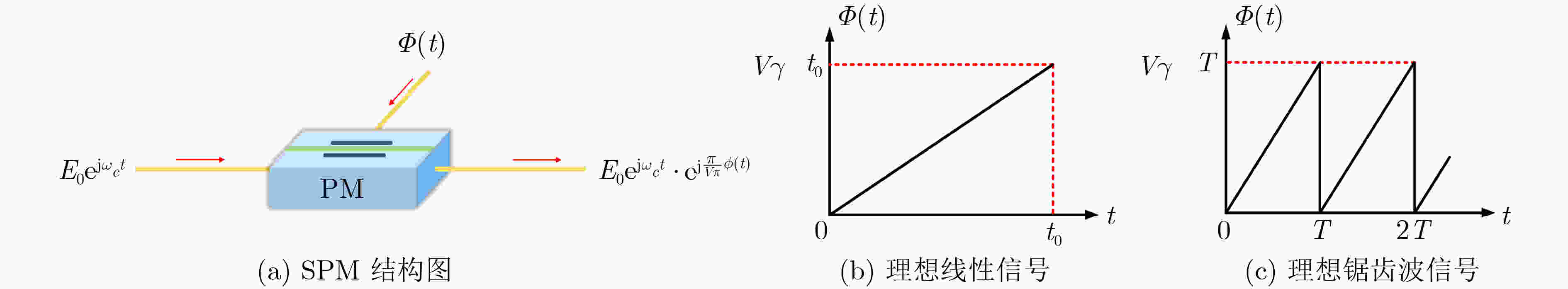
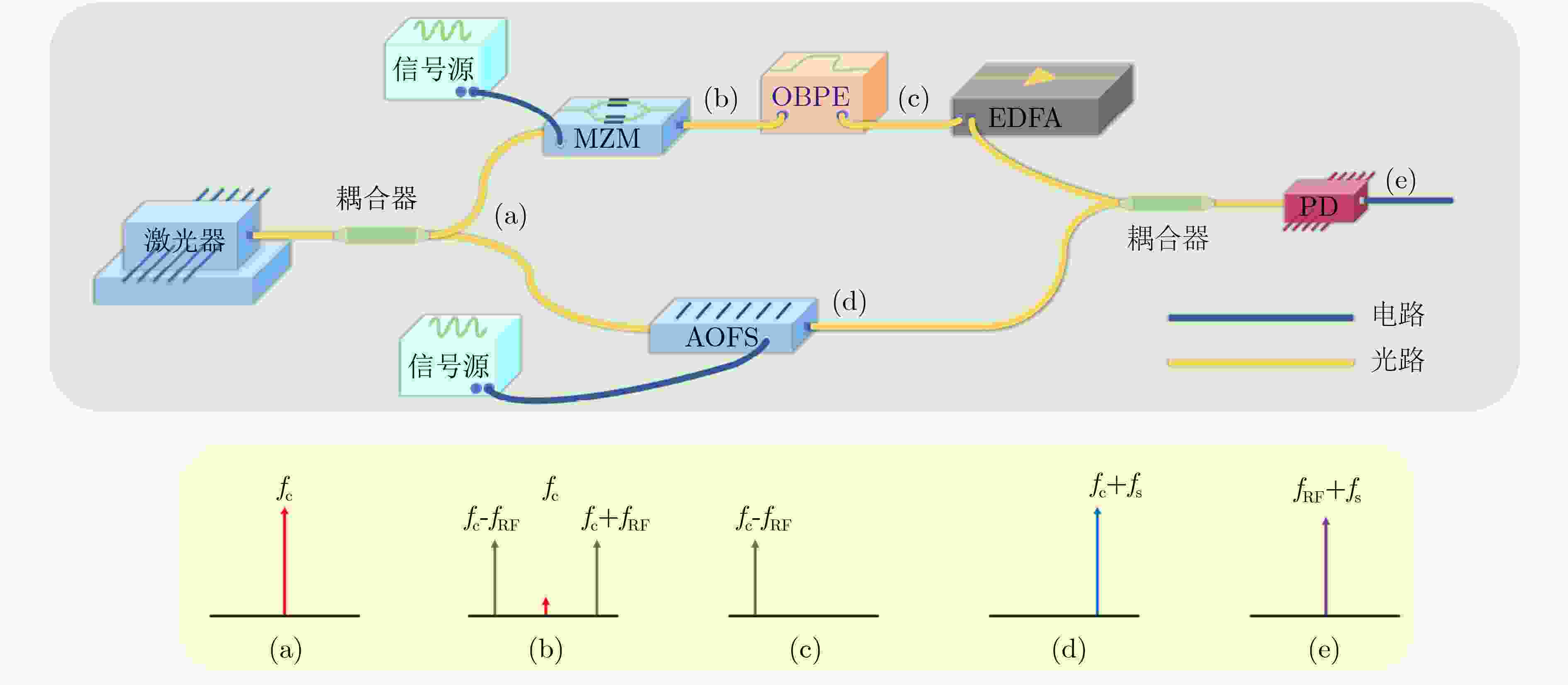
图 1 AOFS结构图、工作模式及实物图[25]
表 1 实验器材型号和参数表
器件名称 型号 器件名称 型号 激光器 KG-DFB-40-C32 微波信号源 Agilent, E8256D MZM AZ-DV5-65-PFA-PFA-SSZ818 OBPF EXFO XTM-50 AOFS IPF-500-50-1550-2FP PD Finisar BPDV2150R PM
功率放大器PM-DV5-40-PFA-PFA-LV
CMP-0.122G-3329-K直流源
光谱仪Gwinstek GDP-4303S
BOSA BOSA400C+LPDM-DPMZM Fujitsu FTM7977HQA 频谱仪 R&S FSQ40 函数发生器 Junctek PSG 9060 表 2 3种移频方式对比
移频方式 工作频率范围(GHz) 瞬时带宽 移频量 杂散抑制比(dB) 稳定性 可调谐性 AOFS 8~65 GHz量级 <1 >45 稳定 差 SPM 8~65 GHz量级 取决于DDS或DAC 20~35 较差 优 I/Q调制 8~40 GHz量级 DC~40 30~40 中 优 -
[1] PENG Zhang. Realization of DRFM radar target simulator based on general instruments[C]. IET International Radar Conference 2015, Hangzhou, China, 2015: 1–8. [2] 曹康, 姜成昊, 朱精果, 等. 激光多普勒移频特性研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(11): 20210116. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210116CAO Kang, JIANG Chenghao, ZHU Jingguo, et al. Frequency shift characteristics of laser Doppler effect[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(11): 20210116. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20210116 [3] ENGELHARDT M, PFEIFFER F, and BIEBL E. A high bandwidth radar target simulator for automotive radar sensors[C]. 2016 European Radar Conference, London, UK, 2016: 245–248. [4] JIANG Wei, ZHAO Shanghong, TAN Qinggui, et al. Wideband photonic microwave channelization and image-reject down-conversion[J]. Optics Communications, 2019, 445: 41–49. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.04.013 [5] 伍振海, 刘静娴, 李晓辉. 基于微波光子变频的发射频率分集阵列实现装置及方法[P]. 中国专利, 202010434080.7, 2020.WU Zhenhai, LIU Jingxian, and LI Xiaohui. Device and method for realizing transmit frequency diversity array based on microwave photonic frequency conversion [P]. China Patent, 202010434080.7, 2020. [6] HAO Tengfei, CEN Qizhuang, DAI Yitang, et al. Breaking the limitation of mode building time in an optoelectronic oscillator[J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1839. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04240-6 [7] 杨利超, 邢孟道, 孙光才, 等. 一种微波光子雷达ISAR成像新方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(6): 1271–1279. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180661YANG Lichao, XING Mengdao, SUN Guangcai, et al. A novel ISAR imaging algorithm for microwave photonics radar[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(6): 1271–1279. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180661 [8] 高永胜. 微波光子混频技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021.GAO Yongsheng. Photonics Microwave Mixing Technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. [9] GREENHALGH P A, FOORD A P, and DA VIES P A. All-fibre frequency shifter using piezoceramic SAW device[J]. Electronics Letters, 1989, 25(18): 1206–1207. doi: 10.1049/el:19890809 [10] DING Zhidan, YANG Fei, ZHAO Jiejun, et al. Photonic high-fidelity storage and Doppler frequency shift of broadband RF pulse signals[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(23): 34359–34369. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.034359 [11] 吴彭生, 吴冉, 魏正武, 等. 基于声光调制的微波信号多普勒移频技术[J]. 压电与声光, 2020, 42(3): 296–298.WU Pengsheng, WU Ran, WEI Zhengwu, et al. A microwave doppler frequency shift technology based on acousto-optic modulation[J]. Piezoelectrics &Acoustooptics, 2020, 42(3): 296–298. [12] PAGÁN V R and MURPHY T E. Electro-optic millimeter-wave harmonic downconversion and vector demodulation using cascaded phase modulation and optical filtering[J]. Optics Letters, 2015, 40(11): 2481–2484. doi: 10.1364/OL.40.002481 [13] EMAMI H, SARKHOSH N, BUI L A, et al. Wideband RF photonic in-phase and quadrature-phase generation[J]. Optics Letters, 2008, 33(2): 98–100. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.000098 [14] ZHU Dan, HU Xiaopeng, CHEN Wenjuan, et al. Photonics-enabled simultaneous self-interference cancellation and image-reject mixing[J]. Optics Letters, 2019, 44(22): 5541–5544. doi: 10.1364/OL.44.005541 [15] LI Jianqiang, XIAO Jia, SONG Xiaoxiong, et al. Full-band direct-conversion receiver with enhanced port isolation and I/Q phase balance using microwave photonic I/Q mixer (Invited Paper)[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2017, 15(1): 010014. doi: 10.3788/COL201715.010014 [16] JIANG Tianwei, WU Ruihuan, YU Song, et al. Microwave photonic phase-tunable mixer[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(4): 4519–4527. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.004519 [17] LI Peixuan, PAN Wei, ZOU Xihua, et al. Image-free microwave photonic down-conversion approach for fiber-optic antenna remoting[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2017, 53(4): 9100208. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2017.2704929 [18] LIN Tao, ZHAO Shanghong, ZHU Zihang, et al. Microwave photonic image rejection mixer based on a DP-QPSK modulator[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 2017, 64(17): 1699–1707. doi: 10.1080/09500340.2017.1310321 [19] HUANG Long, TANG Zhenzhou, XIANG Peng, et al. Photonic generation of equivalent single sideband vector signals for RoF systems[J]. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters, 2016, 28(22): 2633–2636. doi: 10.1109/LPT.2016.2612240 [20] GAO Yongsheng, WEN Aijun, JIANG Wei, et al. Wideband photonic microwave SSB up-converter and I/Q modulator[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2017, 35(18): 4023–4032. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2017.2726532 [21] GAO Yongsheng, WANG Xinyuan, WANG Wuying, et al. Wideband and low-spur Doppler simulator based on photonic microwave I/Q up-converter[C]. 2020 Asia Communications and Photonics Conference (ACP) and International Conference on Information Photonics and Optical Communications (IPOC), Beijing, China, 2020: 1–3. [22] JOHNSON L M and COX C H. Serrodyne optical frequency translation with high sideband suppression[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 1988, 6(1): 109–112. doi: 10.1109/50.3974 [23] POBEREZHSKIY I Y, BORTNIK B, CHOU J, et al. Serrodyne frequency translation of continuous optical signals using ultrawide-band electrical sawtooth waveforms[J]. IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, 2005, 41(12): 1533–1539. doi: 10.1109/JQE.2005.858467 [24] HUANG Chongjia and CHAN E H W. Photonics-based serrodyne microwave frequency translator with large spurious suppression and phase shifting capability[J]. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 2021, 39(7): 2052–2058. doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.3046280 [25] Brimrose. Acousto-optic frequency shifter[EB/OL]. https://www.brimrose.com/free-space-ao/acousto-optic-frequency-shifters, 2021. [26] 樊星, 张伟, 郭光辉, 等. 晶体与电极位置失配对声光移频器性能的影响研究[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(22): 2223001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.2223001FAN Xing, ZHANG Wei, GUO Guanghui, et al. Impact of position mismatch between crystal and electrode on performance of acousto-optic frequency shifter[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(22): 2223001. doi: 10.3788/AOS202141.2223001 -





 下载:
下载:
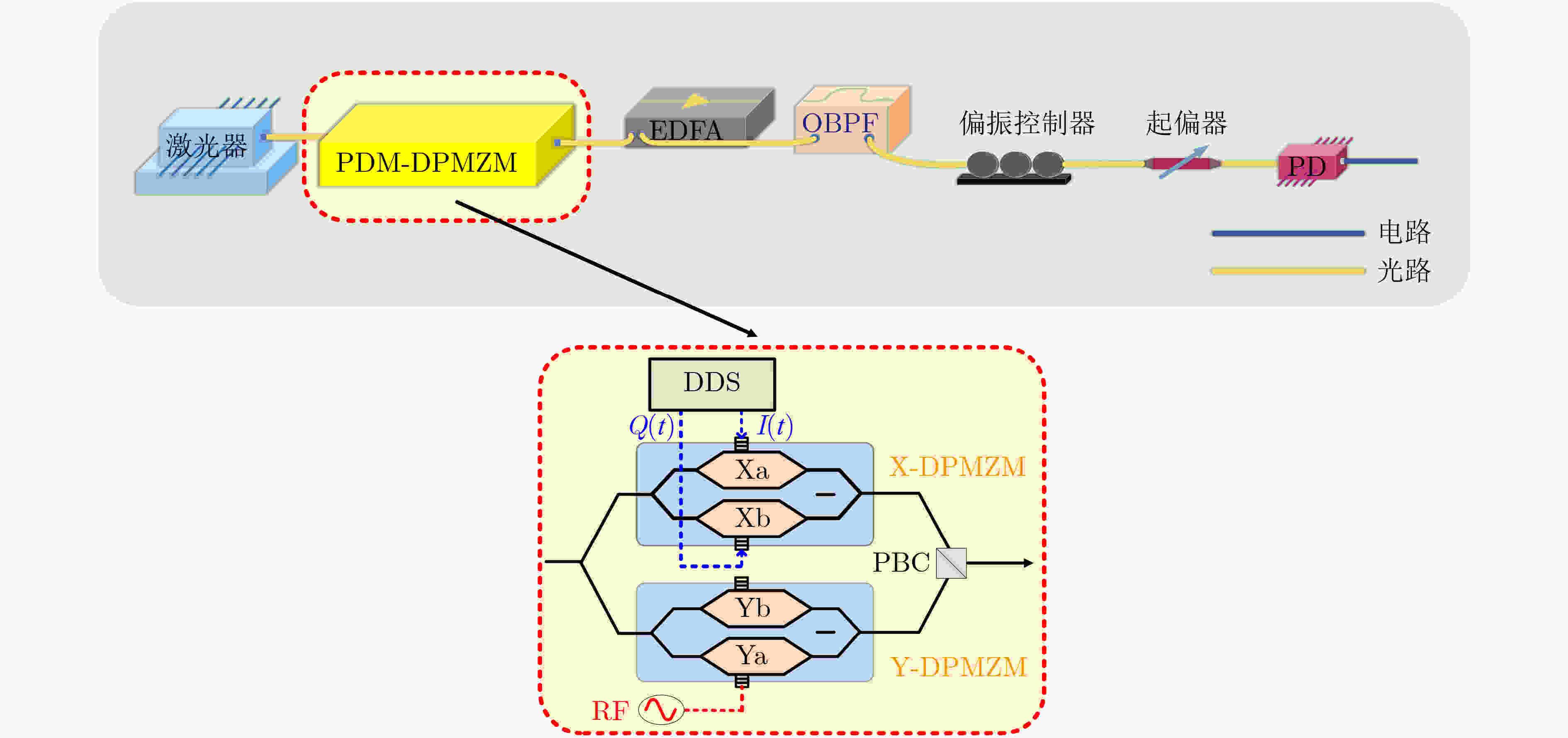

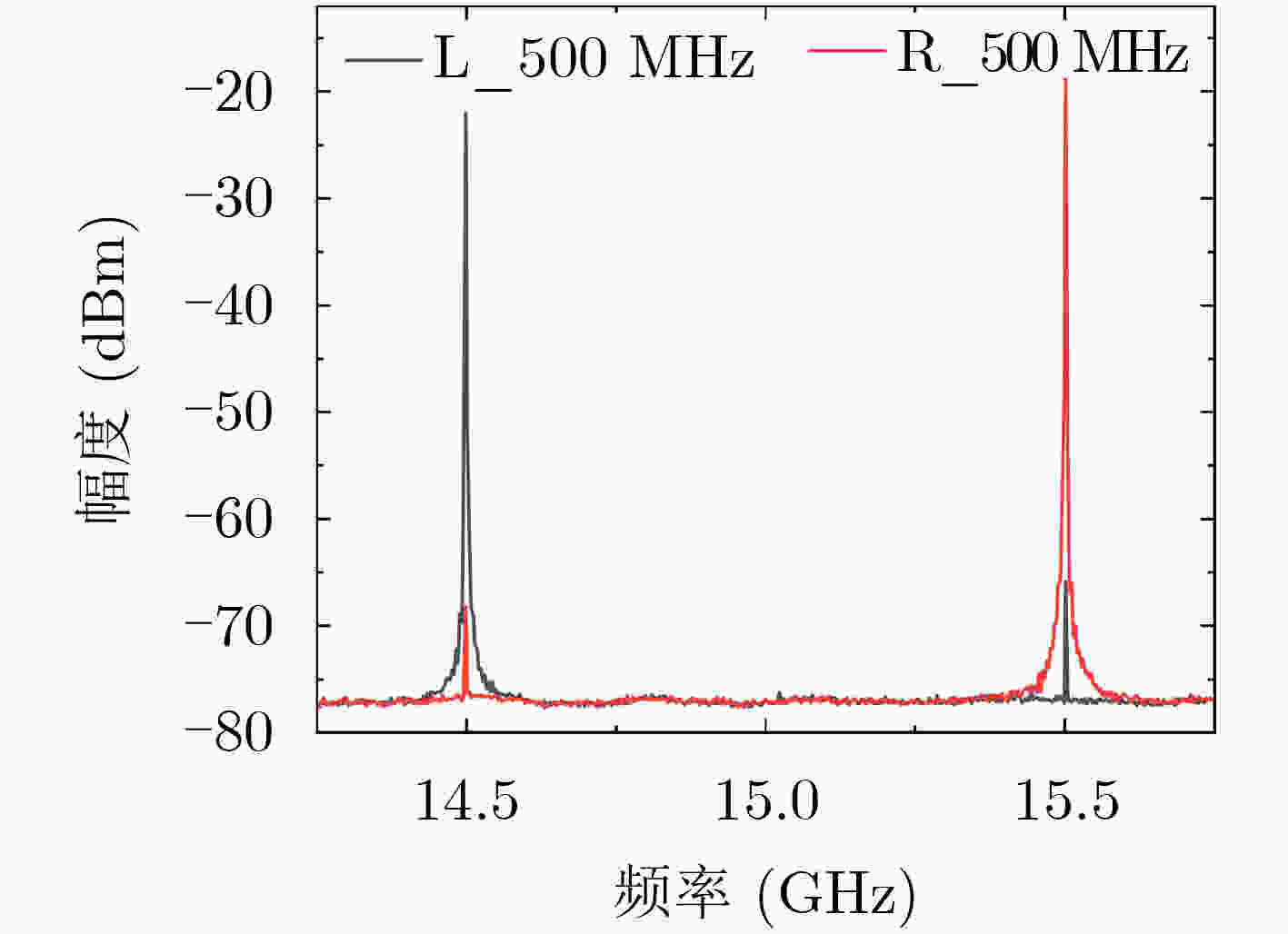
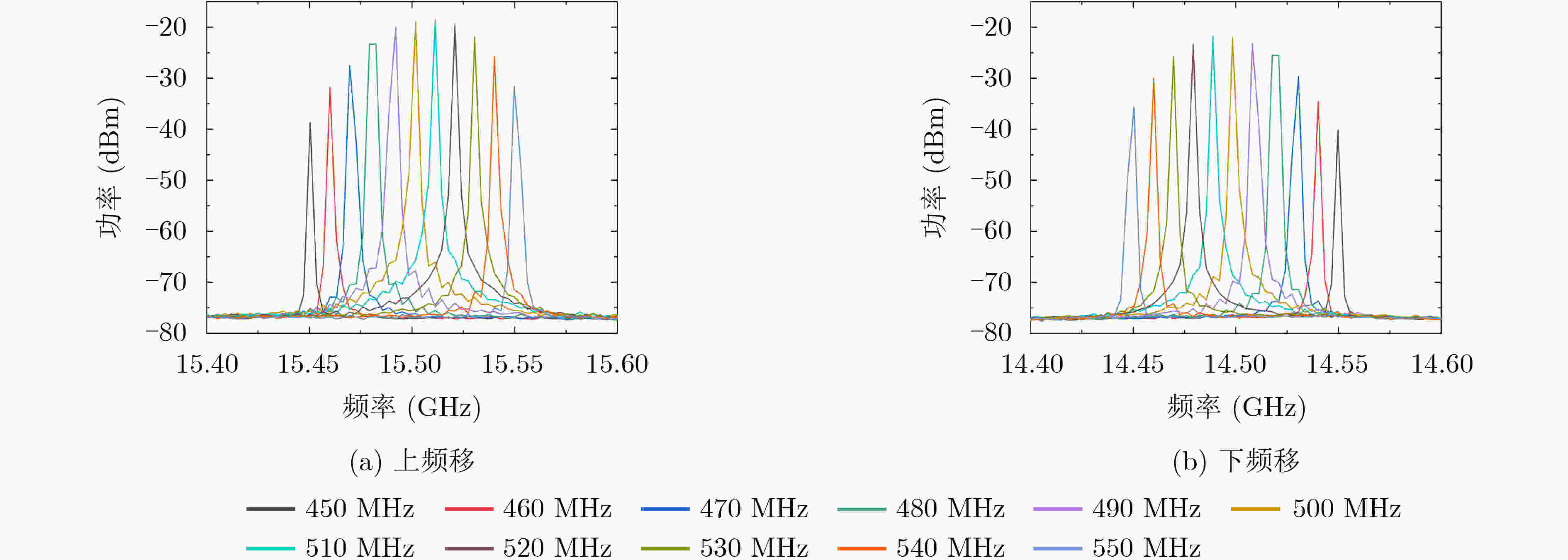
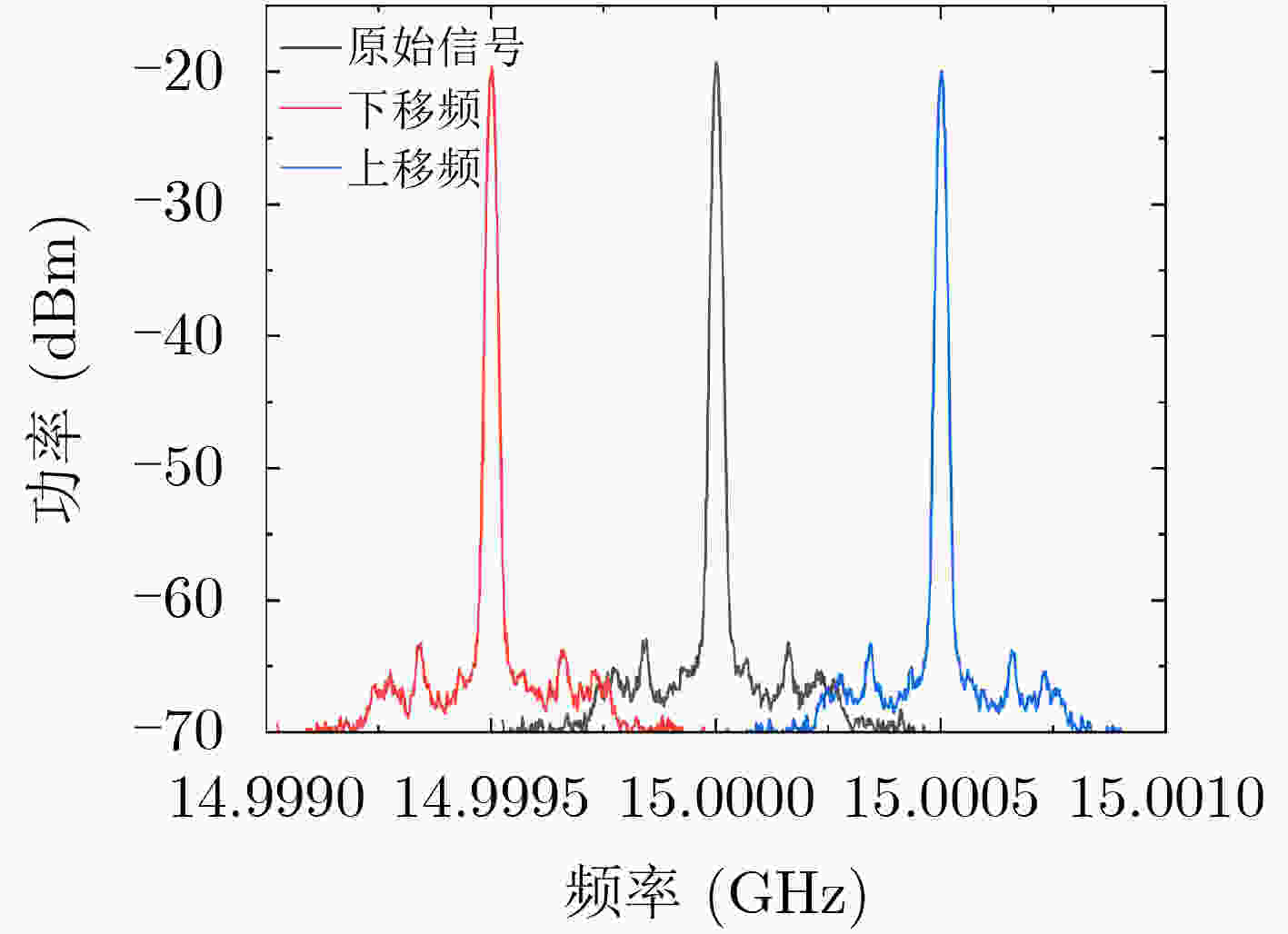
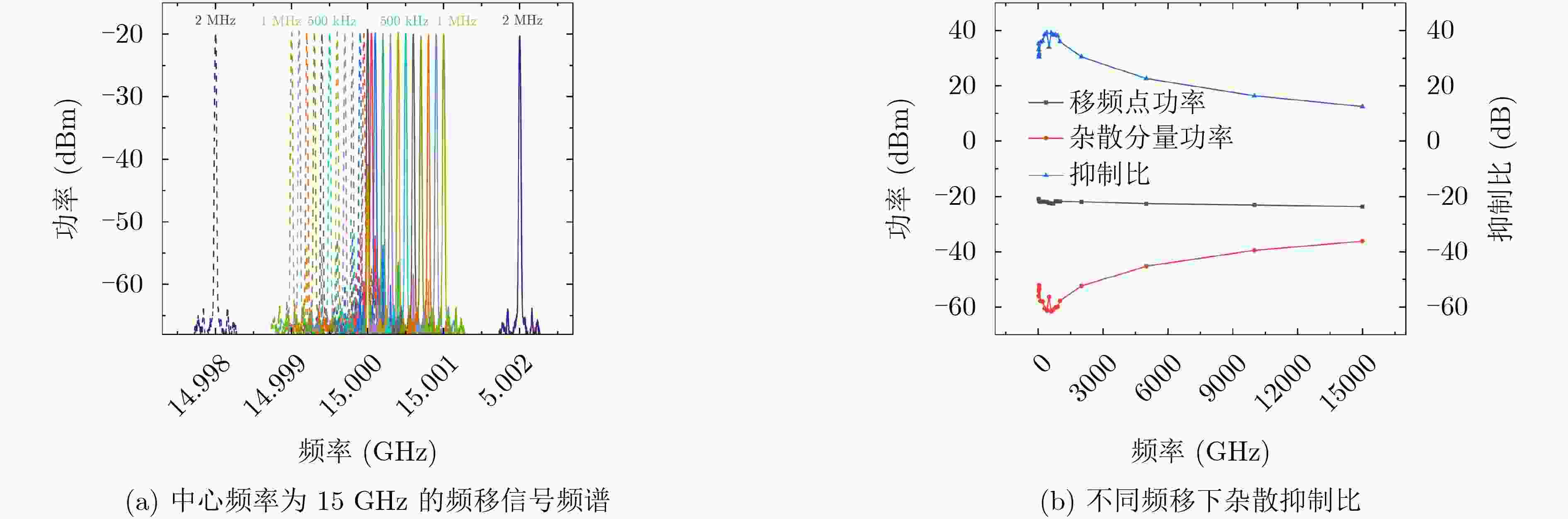

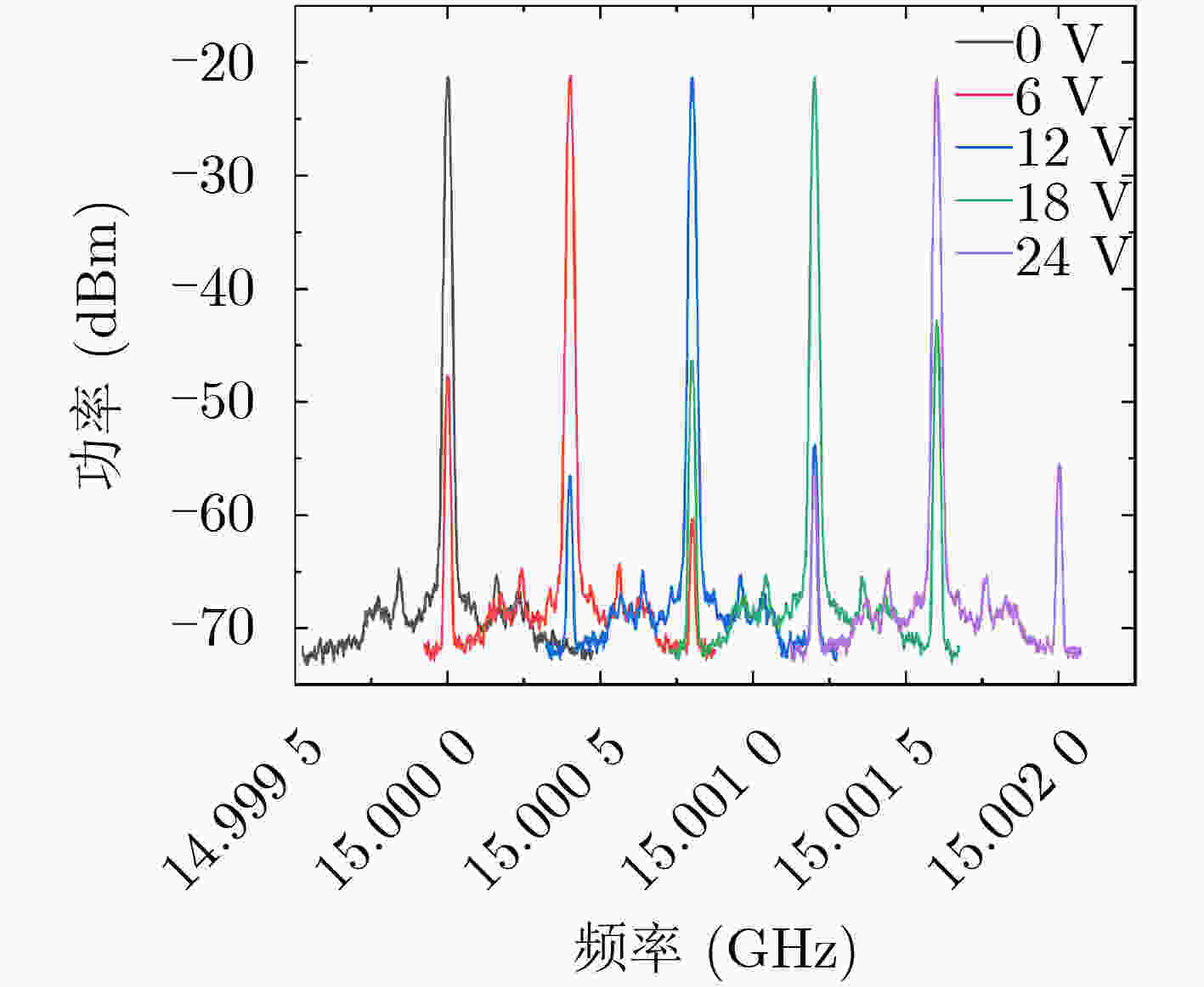
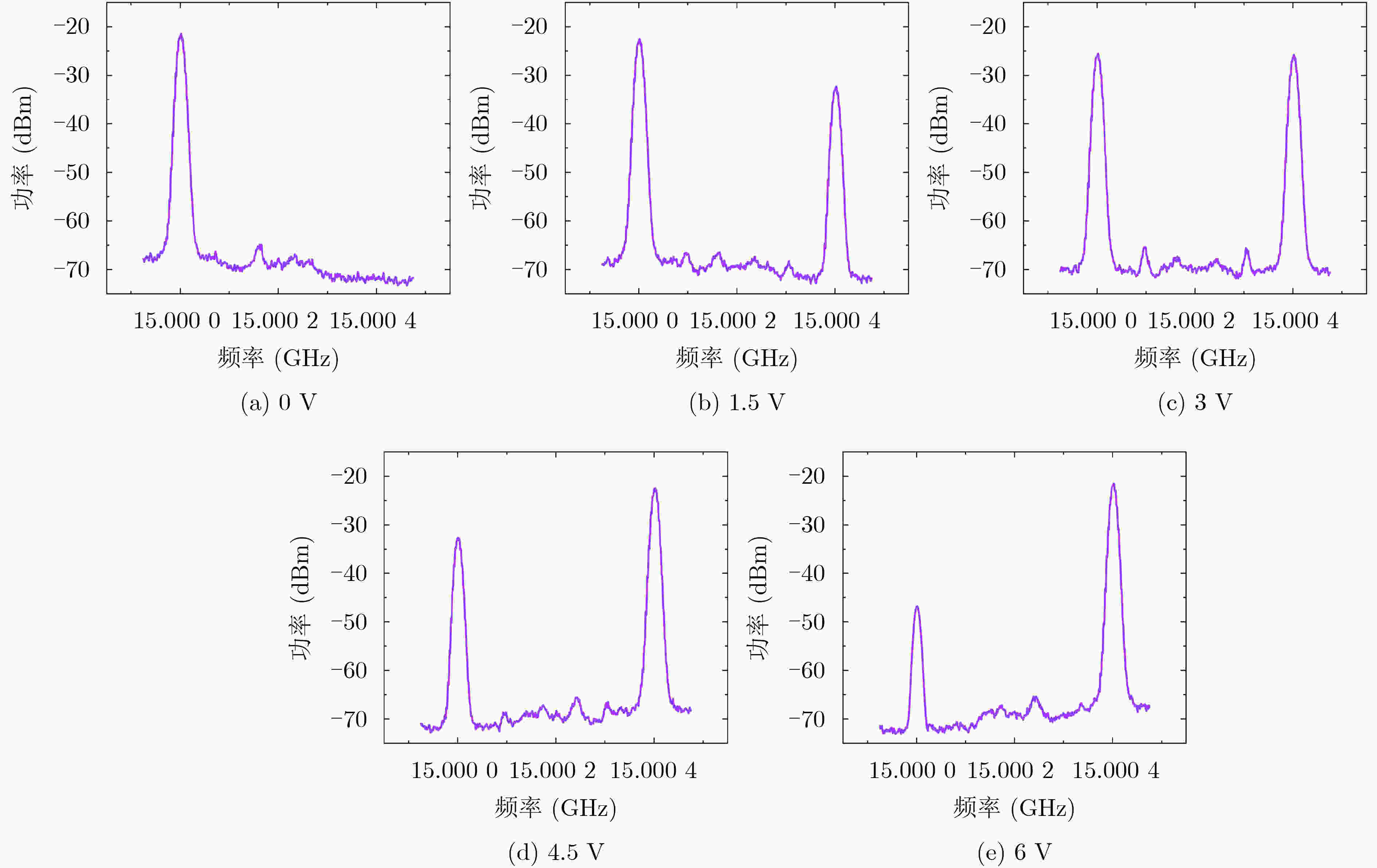
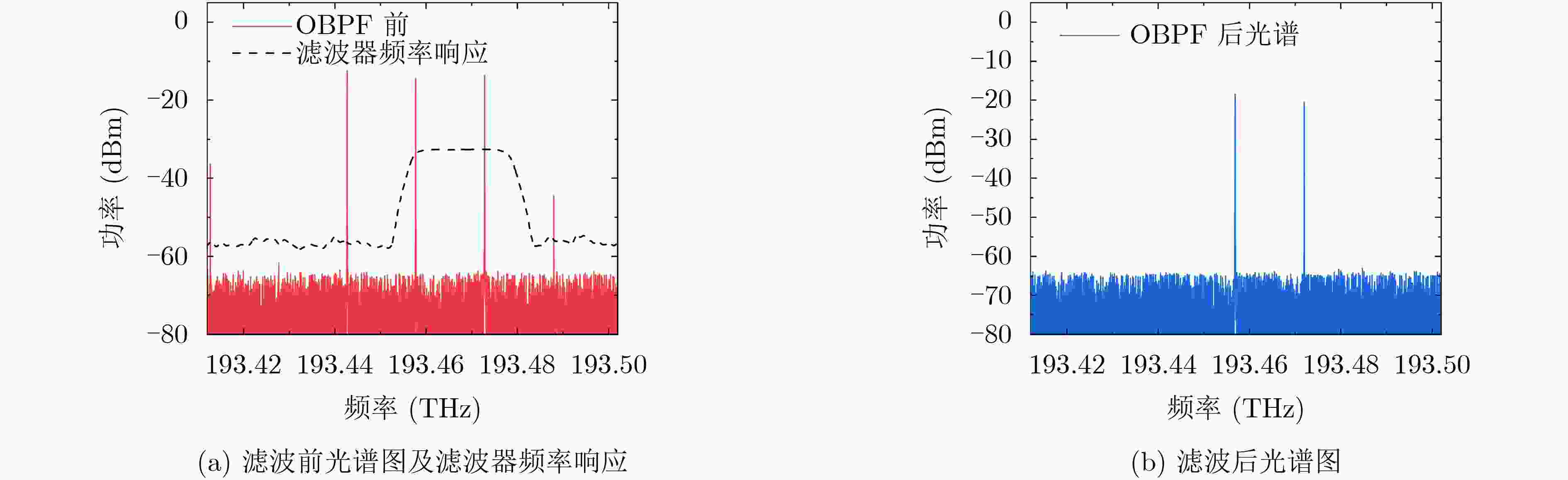


 下载:
下载:
