Error Analysis and Processing Method of Non-stationary Airborne Fully Polarimetric SAR Quantitative Measurement
-
摘要: 即使SAR系统内外定标非常准确,在不同飞行条件下,机载全极化SAR测量精度仍然存在一定的变化,特别在非平稳及高波段时,精度恶化较为严重。针对该问题,该文首先建立了非平稳环境下全极化SAR误差模型,然后分析了分时收发体制下通道间轨迹的微弱变化对极化相位不平衡度的影响,指出随着波段的提升,相同运动误差导致的相位不平衡度相应加重,据此给出了相应的处理方法。最后通过仿真及高分航空专项S波段SAR获取的数据对该方法进行了检验,开展的多次应用示范,也验证了方法的有效性和稳定性。Abstract: Even though the internal and external SAR system calibration is very accurate, the accuracy of airborne fully polarimetric SAR measurement still changes to some extent under different flight conditions. In the condition of non-stationary and high frequency, the accuracy deteriorates seriously. In order to solve this problem, an error model of fully polarimetric SAR in non-stationary environment is proposed, and then the influence of the slight variation of trajectory between channels on the polarization phase imbalance degree in time-sharing transceiver system is analyzed. It is pointed out that the same motion error will aggravate the phase imbalance with the increase of the band. The corresponding processing method is proposed accordingly. Finally, the effectiveness of this method is verified by simulation and S-band SAR data. The effectiveness and stability of this method are also verified by several application demonstrations.
-
表 1 国内外典型SAR系统定标精度
平台 SAR 绝对定标精度(dB) 相对辐射定标精度(dB) 极化隔离度(dB) 通道不平衡度(dB) 相位不平衡度(°) 机载 毫米波SAR[15] $ \le 2 $ $ \le 1 $ – – – X-SAR[16] $ \le 2$ $ \le 1$ – $ \pm 0.2$ $ \pm 11$ UAVSAR[20] $ \le 1$ $ \le 0.7$ $ - 30$ $ \pm 0.04$ $ \pm 6$ F-SAR[21] $ \le 2$ $ \le 0.3$ $ - 37$ – $ \pm 2$ Pi-SAR-L2[22] $ \le 1$ – $ - 35$ $ \pm 0.2$ $ \pm 5$ 星载 SIR-C[23] $ \le 3 $ $ \le 1.5 $ $ - 30$ $ \pm 0.4$ $ \pm 10$ Tandem-X[24] $ \le 0.5$ $ \le 0.2$ – – – Sentinel-1A[25] $ \le 1$ $ \le 0.5$ $ - 33.2$ $ \pm 0.2$ $ \pm 13$ AlSO-2[26] $ \le 1$ $ \le 0.5$ $ - 40$ $ \pm 1$ $ \pm 5$ GF-3[27,28] $ \le 1.5$ $ \le 1$ $ - 45$ $ \pm 0.5$ $ \pm 10$ 表 2 雷达及飞行参数表
参数 数值 载频(GHz) 3,9,35 采样频率(MHz) 400 中心视角(°) 60 带宽(MHz) 300 中心斜距(m) 5000 数据积累时间(s) 11.1 航向速度(m/s) 70 Y和Z方向速度(m/s) 0.1 Y和Z方向加速度(m/s2) 0.01 表 3 S波段飞行参数
参数 数值 机场 测区 载频(GHz) 3.240040~55300 采样频率(MHz) 视角(°) 带宽(MHz) 中心斜距(m) 2817 5818 飞行高度(m) 1993 4206 飞机速度(m/s) 71 76 表 4 机场角反射器补偿前后性能指标(°)
补偿前 补偿后 同极化通道相位不平衡度 3.47 3.19 交叉极化通道相位不平衡度 3.07 1.17 表 5 裸土同极化通道相位测量(°)
区域 入射角 补偿前 补偿后 1 41.93 2.15 1.46 2 42.83 3.26 1.71 3 44.39 2.31 1.51 4 47.03 3.75 2.22 5 50.31 3.99 2.77 6 51.93 4.16 3.61 7 52.51 6.17 3.9 相位不平衡度 3.89 2.62 -
[1] LEE J S and POTTIER E. Polarimetric Radar Imaging: From Basics to Applications[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2009. [2] DAI Yanhui, FENG Lian, HOU Xuejiao, et al. Policy-driven changes in enclosure fisheries of large lakes in the Yangtze plain: Evidence from satellite imagery[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 688: 1286–1297. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.06.179 [3] KOSTINSKI A and BOERNER W. On foundations of radar polarimetry[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 1986, 34(12): 1395–1404. doi: 10.1109/TAP.1986.1143771 [4] GIULI D. Polarization diversity in radars[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1986, 74(2): 245–269. doi: 10.1109/PROC.1986.13457 [5] 李宏宇, 李坤, 杨知. 基于时间序列全极化合成孔径雷达的水稻物候期反演[J]. 浙江大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 2021, 47(3): 404–414.LI Hongyu, LI Kun, and YANG Zhi. Retrieval of rice phenological stages based on time-series full-polarization synthetic aperture radar data[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Agriculture and Life Sciences, 2021, 47(3): 404–414. [6] SHI Jiancheng, WANG J, HSU A, et al. Estimation of soil moisture and surface roughness parameters using L-band SAR measurements[C]. 1995 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS '95. Quantitative Remote Sensing for Science and Applications, Firenze, Italy, 1995: 507–509. [7] 李凉海, 刘善伟, 周鹏, 等. SAR卫星组网观测技术与海洋应用研究进展[J]. 海洋科学, 2021, 45(5): 145–156. doi: 10.11759/hykx20210415002LI Lianghai, LIU Shanwei, ZHOU Peng, et al. Research progress of SAR satellite network observation technology and ocean application[J]. Marine Sciences, 2021, 45(5): 145–156. doi: 10.11759/hykx20210415002 [8] 郭倩, 王海鹏, 徐丰. SAR图像飞机目标检测识别进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020GUO Qian, WANG Haipeng, and XU Feng. Research progress on aircraft detection and recognition in SAR imagery[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 497–513. doi: 10.12000/JR20020 [9] 刘之榆, 刘忠, 万炜, 等. SAR与光学遥感影像的玉米秸秆覆盖度估算[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(6): 1308–1323. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210053LIU Zhiyu, LIU Zhong, WAN Wei, et al. Estimation of maize residue cover on the basis of SAR and optical remote sensing image[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 25(6): 1308–1323. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20210053 [10] SCHWERDT M, HOUNAM D, BRAUTIGAM B, et al. TerraSAR-X: Calibration concept of a multiple mode high resolution SAR[C]. 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Korea (South), 2005: 4874–4877. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2005.1526766. [11] SCHWARTZ M A and GINSBERG M H. Networks and crosstalk: Integrin signalling spreads[J]. Nature Cell Biology, 2002, 4(4): E65–E68. doi: 10.1038/ncb0402-e65 [12] VAN ZYL J J. Calibration of polarimetric radar images using only image parameters and trihedral corner reflector responses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1990, 28(3): 337–348. doi: 10.1109/36.54360 [13] 涂尚坦, 许丽颖, 王芳, 等. 基于极化定标的极化隔离度空变分析[J]. 现代雷达, 2020, 42(2): 12–15. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2020.02.003TU Shangtan, XU Liying, WANG Fang, et al. Analysis of polarization isolation spatial variation based on polarimetric calibration[J]. Modern Radar, 2020, 42(2): 12–15. doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2020.02.003 [14] FREEMAN A. SAR calibration: An overview[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1992, 30(6): 1107–1121. doi: 10.1109/36.193786 [15] 汪伟, 李军, 胡庆荣. 基于点目标的机载毫米波SAR辐射定标[C]. 第三届高分辨率对地观测学术年会优秀论文集, 北京, 中国, 2014: 502–513. [16] SHEN Ting, LI Jun, WANG Zhirui, et al. The airborne X-SAR calibration with high resolution[C]. 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar, Guangzhou, China, 2017: 1–5. doi: 10.1109/RADAR.2016.8059209. [17] 刘亚波, 刘霖, 童智勇, 等. S波段高分辨宽幅SAR辐射定标及误差分析方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(8): 1946–1951. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180983LIU Yabo, LIU Lin, TONG Zhiyong, et al. A radiometric calibration and error analysis method for HWRS SAR at S-band[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(8): 1946–1951. doi: 10.11999/JEIT180983 [18] CURLANDER J C and MCDONOUGH R N. Synthetic Aperture Radar: Systems and Signal Processing[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1991. [19] 张过, 蒋永华, 李立涛, 等. 高分辨率光学/SAR卫星几何辐射定标研究进展[J]. 测绘学报, 2019, 48(12): 1604–1623. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20190469ZHANG Guo, JIANG Yonghua, LI Litao, et al. Research progress of high-resolution optical/SAR satellite geometric radiometric calibration[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2019, 48(12): 1604–1623. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2019.20190469 [20] FORE A G, CHAPMAN B D, HAWKINS B P, et al. UAVSAR polarimetric calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(6): 3481–3491. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2377637 [21] REIGBER A, SCHEIBER R, JAGER M, et al. Very-high-resolution airborne synthetic aperture radar imaging: Signal processing and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2013, 101(3): 759–783. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2012.2220511 [22] SHIMADA M, KAWANO N, WATANABE M, et al. Calibration and validation of the Pi-SAR-L2[C]. Conference Proceedings of 2013 Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Tsukuba, Japan, 2013: 194–197. [23] FREEMAN A, ALVES M, CHAPMAN B, et al. SIR-C data quality and calibration results[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1995, 33(4): 848–857. doi: 10.1109/36.406671 [24] SCHWERDT M, GONZALEZ J H, BACHMANN M, et al. In-orbit calibration of the TanDEM-X system[C]. 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, Canada, 2011: 2420–2423. [25] SCHWERDT M, SCHMIDT K, RAMON N T, et al. Independent verification of the sentinel-1A system calibration-first results[C]. The 10th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Berlin, Germany, 2014: 1–4. [26] MORIYAMA T. Polarimetric calibration of PALSAR2[C]. 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Milan, Italy, 2015: 1284–1287. [27] 张庆君. 高分三号卫星总体设计与关键技术[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(3): 269–277. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170049ZHANG Qingjun. System design and key technologies of the GF-3 satellite[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(3): 269–277. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170049 [28] 李亮, 洪峻, 陈琦, 等. 基于极化有源定标器的高分三号SAR在轨测试分析[J]. 电子学报, 2018, 46(9): 2157–2164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.09.016LI Liang, HONG Jun, CHEN Qi, et al. In-orbit calibration of GF-3 SAR using quad-polarized transponder[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(9): 2157–2164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.09.016 [29] 张王菲, 陈尔学, 李增元, 等. 雷达遥感农业应用综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(3): 444–461. doi: 10.12000/JR20051ZHANG Wangfei, CHEN Erxue, LI Zengyuan, et al. Review of applications of radar remote sensing in agriculture[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(3): 444–461. doi: 10.12000/JR20051 [30] 刘健, 郭交, 韩文霆. 基于合成孔径雷达的土壤水分反演研究进展[J]. 三峡生态环境监测, 2020, 5(2): 44–53. doi: 10.19478/j.cnki.2096-2347.2020.02.07LIU Jian, GUO Jiao, and HAN Wenting. Advances in re-search on soil moisture retrieval using synthetic aperture radar[J]. Ecology and Environmental Monitoring of Three Gorges, 2020, 5(2): 44–53. doi: 10.19478/j.cnki.2096-2347.2020.02.07 [31] QUEGAN S, LOMAS M, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, et al. Calibration challenges for the biomass P-Band SAR instrument[C]. 2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 2018: 8575–8578. doi: 10.1109/IGARSS.2018.8518646. [32] CUMMING I G, 洪文, 胡东辉, 译. 合成孔径雷达成像: 算法与实现[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2007: 64.CUMMING I G, HONG Wen, and HU Donghui, translation. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2007: 64. [33] 张海瀛. 全极化SAR/InSAR数据定标技术研究[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2018.ZHANG Haiying. Study on fully polarimetric SAR/InSAR data calibration technology[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2018. [34] 杨杰, 常永雷, 李平湘, 等. 采用螺旋散射的SAR极化定标参考地物提取方法[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2018, 43(12): 2023–2029.YANG Jie, CHANG Yonglei, LI Pingxiang, et al. Distributed targets extraction for SAR polarimetric calibration using helix scattering[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 2023–2029. [35] GUISSARD A. Phase calibration of polarimetric radars from slightly rough surfaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 1994, 32(3): 712–715. doi: 10.1109/36.297991 -





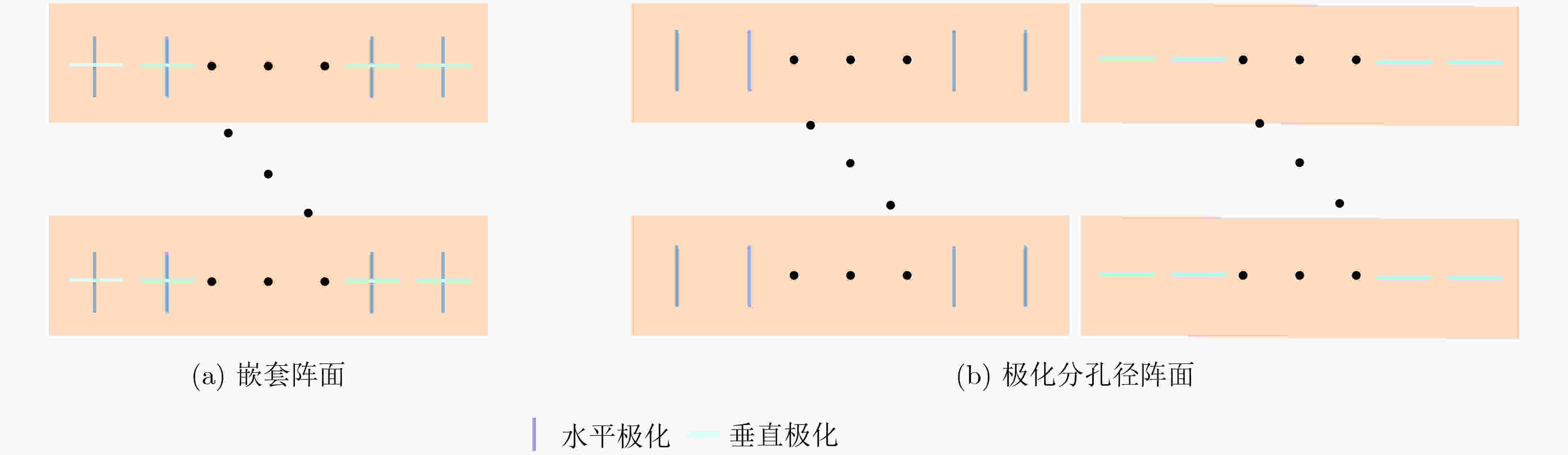
 下载:
下载:
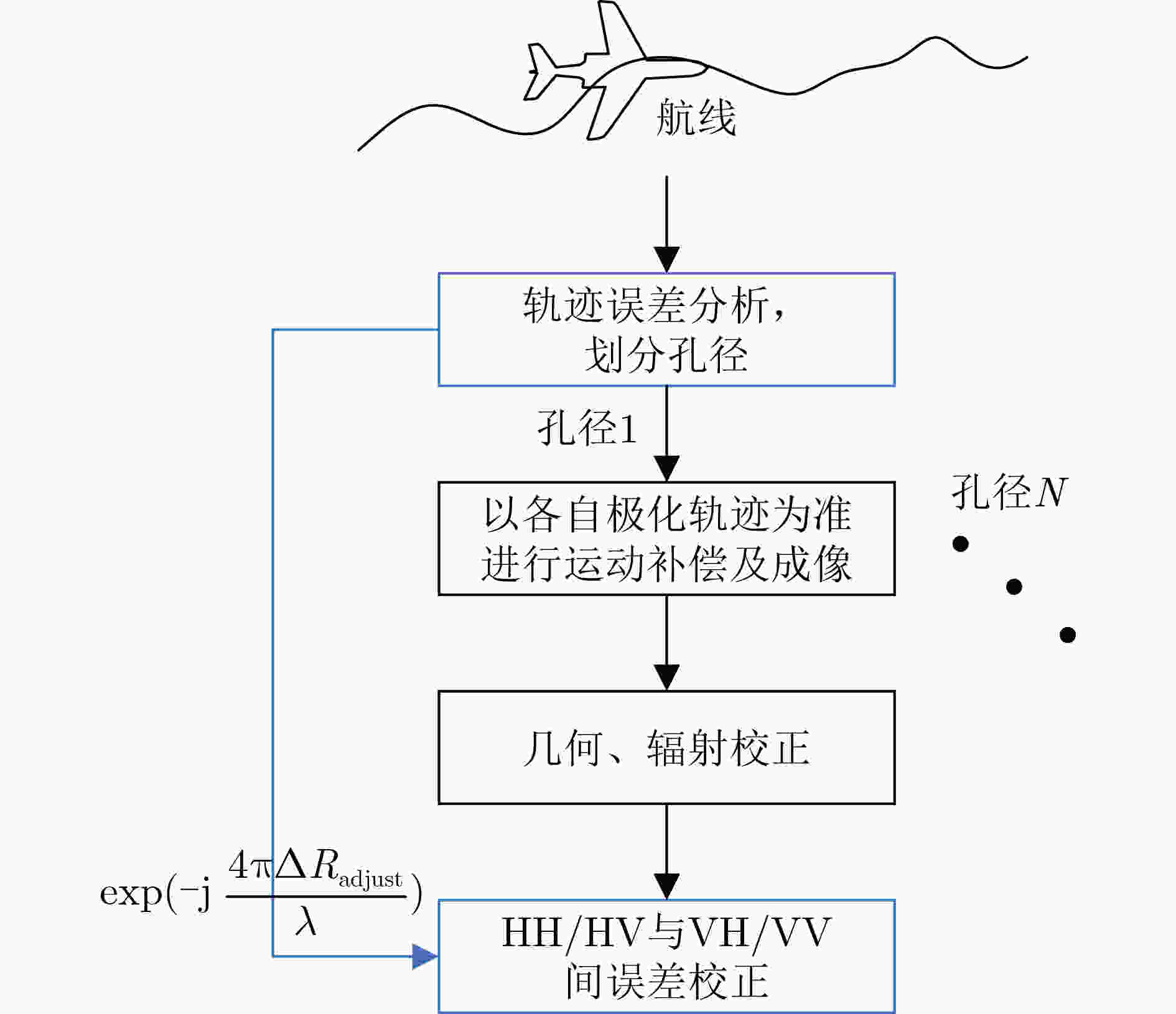

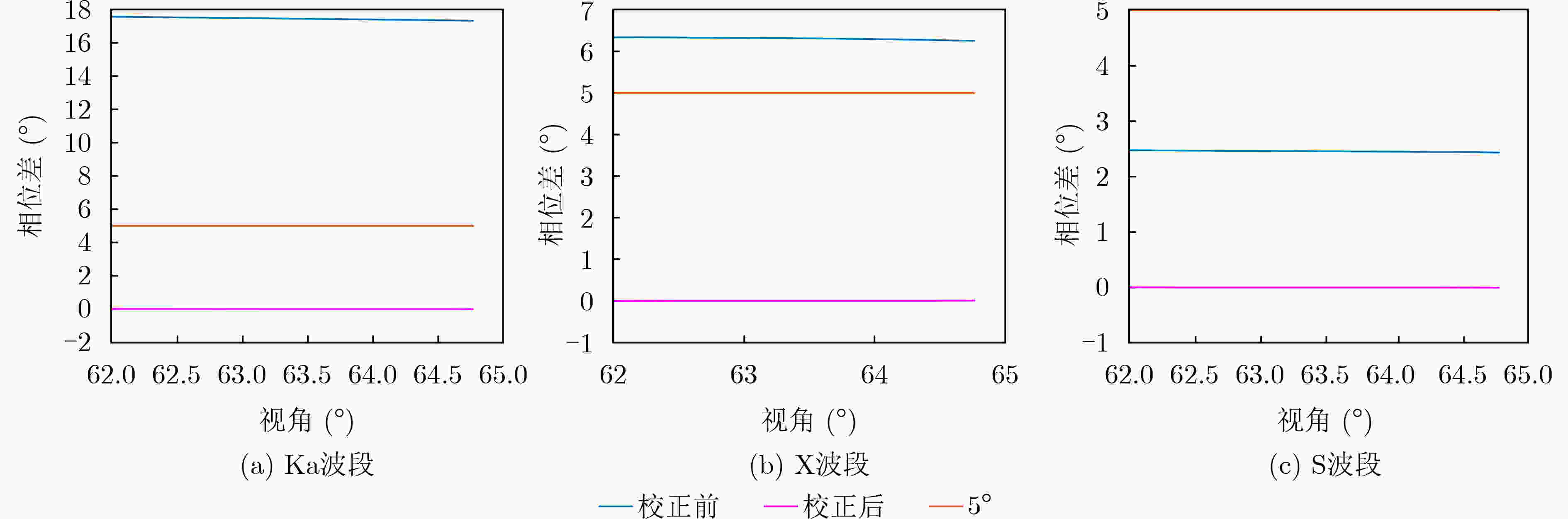


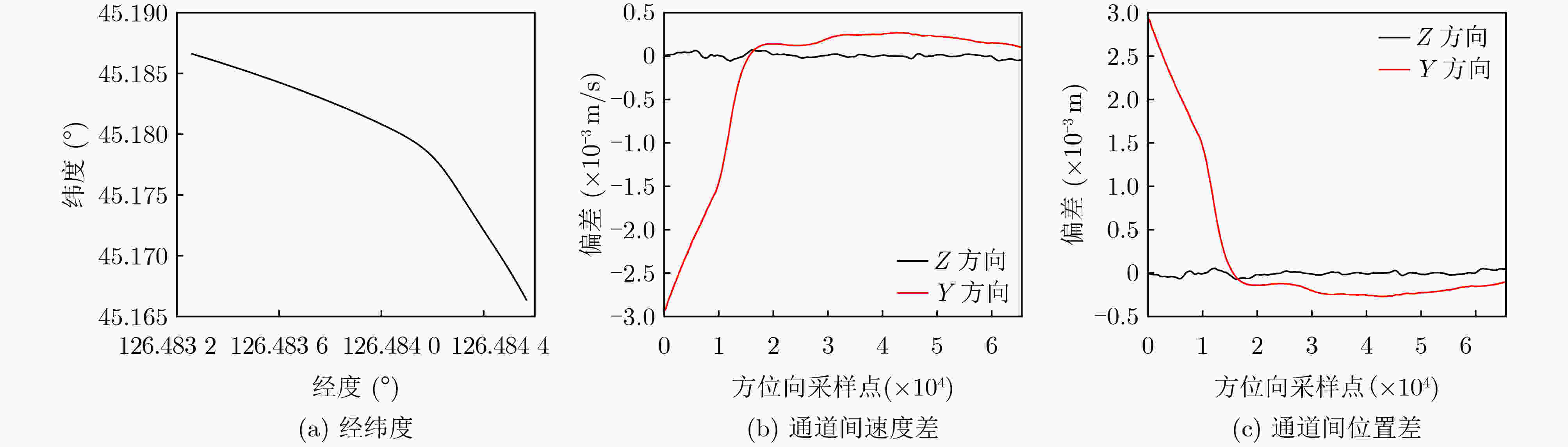


 下载:
下载:
