C2 Transformer U-Net: A Medical Image Segmentation Model for Cross-modality and Contextual Semantics
-
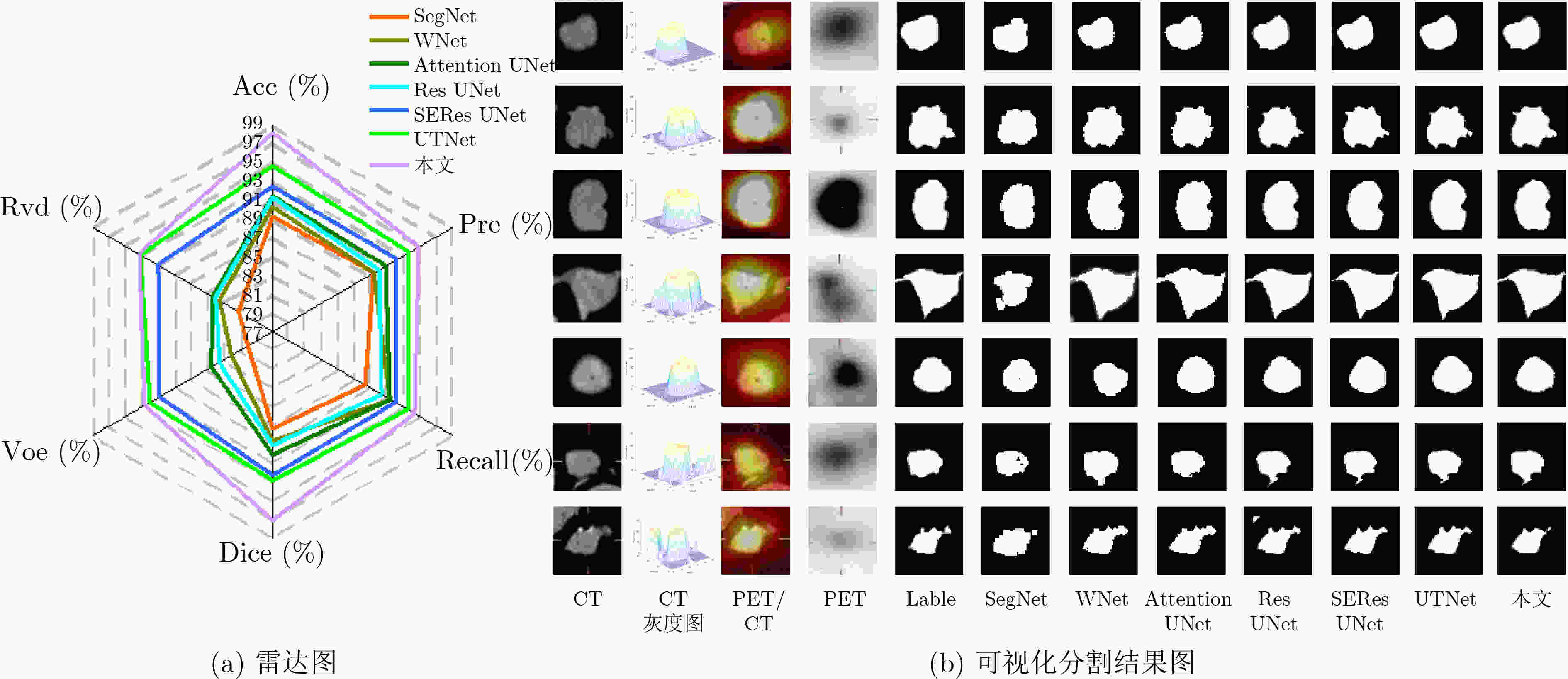
摘要: 跨模态的医学图像可以在同一病灶处提供更多的语义信息,针对U-Net网络主要使用单模态图像用于分割,未充分考虑跨模态、上下文语义相关性的问题,该文提出面向跨模态和上下文语义的医学图像分割C2 Transformer U-Net模型。该模型的主要思想是:首先,在编码器部分提出主干、辅助U-Net网络结构,来提取不同模态的语义信息;然后,设计了多模态上下文语义感知处理器(MCAP),有效地提取同一病灶跨模态的语义信息,跳跃连接中使用主网络的两种模态图像相加后传入Transformer解码器,增强模型对病灶的表达能力;其次,在编-解码器中采用预激活残差单元和Transformer架构,一方面提取病灶的上下文特征信息,另一方面使网络在充分利用低层和高层特征时更加关注病灶的位置信息;最后,使用临床多模态肺部医学图像数据集验证算法的有效性,对比实验结果表明所提模型对于肺部病灶分割的Acc, Pre, Recall, Dice, Voe与Rvd分别为:97.95%, 94.94%, 94.31%, 96.98%, 92.57%与93.35%。对于形状复杂肺部病灶的分割,具有较高的精度和相对较低的冗余度,总体上优于现有的先进方法。
-
关键词:
- 医学图像分割 /
- 跨模态语义 /
- 上下文语义 /
- Transformer /
- U-Net
Abstract: Cross-modal medical images can provide more semantic information at the same lesion. In view of the U-Net network uses mainly single-modal images for segmentation, the cross-modal and contextual semantic correlations are not fully considered. Therefore, a cross-modal and contextual semantic-oriented medical image segmentation C2 Transformer U-Net model is proposed. The main idea of this model is: first, a backbone and auxiliary U-Net network structure is proposed in the encoder part to extract semantic information of different modalities; Then, the Multi-modal Context semantic Awareness Processor (MCAP) is designed to extract effectively the semantic information of the same lesion across modalities. After adding the two modal images using the backbone network in the skip connection, it is passed to the Transformer decoder. This enhances the expression ability of the model to the lesion; Secondly, the pre-activated residual unit and Transformer architecture are used in the encoder-decoder. On the one hand, the contextual feature information of the lesion is extracted, and on the other hand, the network pays more attention to the location information of the lesion when making full use of low-level and high-level features; Finally, the effectiveness of the algorithm is verified by using a clinical multi-modal lung medical image dataset. Comparative experimental results show that the Acc, Pre, Recall, Dice, Voe and Rvd of the proposed model for lung lesion segmentation are: 97.95%, 94.94%, 94.31%, 96.98%, 92.57% and 93.35%. For the segmentation of lung lesions with complex shapes, it has high accuracy and relatively low redundancy. Overall, it outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.-
Key words:
- Medical image segmentation /
- Cross-modality semantics /
- Contextual semantics /
- Transformer /
- U-Net
-
表 1 评价指标定义
评价指标 定义 评价指标 定义 Acc $ {\text{Acc = }}\dfrac{{{\text{TP + TN}}}}{{{\text{TP + FP + FN + TN}}}} $ Pre $ {\text{Pre = }}\dfrac{{{\text{TP}}}}{{{\text{TP + FP}}}} $ Dice ${\rm{Dice}} = \dfrac{ {2 \times \left| {P \cap G} \right|} }{ {\left| P \right| + \left| G \right|} }$ Recall ${\text{Recall = }}\dfrac{{{\text{TP}}}}{{{\text{TP + FN}}}}$ Voe ${\rm{Voe} } = {\rm{abs} }\left(1 - \left| {\dfrac{ {P \cap G} }{ {P \cup G} } } \right|\right)$ Rvd $ {\text{Rvd}} = \dfrac{{{\text{abs}}(P{{ - }}G)}}{G} $ 表 2 跨模态语义相关性的不同编码器分割结果(%)
表 3 不同分割网络的分割结果(%)
模型 ACC Pre Recall Dice VOE RVD SegNet[18] 89.23 89.38 88.33 87.28 79.97 81.13 WNet[19] 90.16 89.49 91.28 88.59 82.08 83.45 Attention UNet[20] 91.30 90.94 91.31 89.98 84.57 84.35 ResUNet[21] 91.23 90.08 90.32 89.01 83.45 84.02 SEResUNet[22] 92.38 92.17 92.07 92.20 90.93 91.04 UTNet[23] 94.58 93.86 93.44 92.83 92.07 93.20 本文 97.95 94.94 94.31 96.98 92.57 93.35 表 4 上下文语义相关的分割结果(%)
模型 Acc Pre Recall Dice Voe Rvd RMUNet 93.26 90.69 91.14 92.68 89.45 91.10 RTMUNet 94.59 92.80 92.55 93.50 89.87 91.37 RTMMUNet 95.18 93.13 92.69 94.01 90.02 92.04 RTMMSUNet 96.62 93.60 93.15 94.40 90.09 92.05 本文 97.95 94.94 94.31 96.98 92.57 93.35 -
[1] DALCA A V, GUTTAG J, and SABUNCU M R. Anatomical priors in convolutional networks for unsupervised biomedical segmentation[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, USA, 2018: 9290–9299. [2] ZHOU Tao, LU Huiling, YANG Zaoli, et al. The ensemble deep learning model for novel COVID-19 on CT images[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2021, 98: 106885. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106885 [3] JAMES A P and DASARATHY B V. Medical image fusion: A survey of the state of the art[J]. Information Fusion, 2014, 19: 4–19. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2013.12.002 [4] LI Haoming, JIANG Huiyan, LI Siqi, et al. DenseX-Net: An end-to-end model for lymphoma segmentation in whole-body PET/CT Images[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 8004–8018. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963254 [5] HUSSEIN S, GREEN A, WATANE A, et al. Automatic segmentation and quantification of white and brown adipose tissues from PET/CT Scans[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2017, 36(3): 734–744. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2016.2636188 [6] MU Wei, CHEN Zhe, SHEN Wei, et al. A segmentation algorithm for quantitative analysis of heterogeneous tumors of the cervix with 18F-FDG PET/CT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 62(10): 2465–2479. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2015.2433397 [7] ZHOU Tao, DONG YaLi, LU HuiLing, et al. APU-Net: An attention mechanism parallel U-Net for lung tumor segmentation[J]. BioMed Research International, 2022, 2022: 5303651. doi: 10.1155/2022/5303651 [8] CUI Hui, WANG Xiuying, LIN W, et al. Primary lung tumor segmentation from PET-CT volumes with spatial-topological constraint[J]. International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery, 2016, 11(1): 19–29. doi: 10.1007/s11548-015-1231-0 [9] ZHAO Hengshuang, SHI Jianping, QI Xiaojuan, et al. Pyramid scene parsing network[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6230–6239. [10] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 630–645. [11] HAN Guang, ZHU Mengcheng, ZHAO Xuechen, et al. Method based on the cross-layer attention mechanism and multiscale perception for safety helmet-wearing detection[J]. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2021, 95: 107458. doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2021.107458 [12] WANG Sinong, LI B Z, KHABSA M, et al. Linformer: Self-attention with linear complexity[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.04768, 2020. [13] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS'17), Long Beach, USA, 2017: 6000–6010. [14] BELLO L, ZOPH B, LE Q, et al. Attention augmented convolutional networks[C]. 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 3285–3294. [15] PARMAR N, VASWANI A, USZKOREIT J, et al. Image transformer[C]. The 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 2018: 4052–4061. [16] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. The 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234−241. [17] LAN Hengrong, JIANG Daohuai, YANG Changchun, et al. Y-Net: Hybrid deep learning image reconstruction for photoacoustic tomography in vivo[J]. Photoacoustics, 2020, 20: 100197. doi: 10.1016/j.pacs.2020.100197 [18] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, and CIPOLLA R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481–2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [19] XU Lina, TETTEH G, LIPKOVA J, et al. Automated whole-body bone lesion detection for multiple myeloma on 68Ga-pentixafor PET/CT imaging using deep learning methods[J]. Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging, 2018, 2018: 2391925. doi: 10.1155/2018/2391925 [20] OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, LE FOLGOC L, et al. Attention U-Net: Learning where to look for the pancreas[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.03999, 2018. [21] LIU Jin, KANG Yanqin, QIANG Jun, et al. Low-dose CT imaging via cascaded ResUnet with spectrum loss[J]. Methods, 2022, 202: 78–87. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2021.05.005 [22] CAO Zheng, YU Bohan, LEI Biwen, et al. Cascaded SE-ResUnet for segmentation of thoracic organs at risk[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 453: 357–368. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.08.086 [23] GAO Yunhe, ZHOU Mu, and METAXAS D. UTNet: A hybrid transformer architecture for medical image segmentation[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.00781, 2021. -






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
