Collision Avoidance Algorithm for UAV Formation Reconfiguration under UV Non-uniform Virtual Potential Field
-
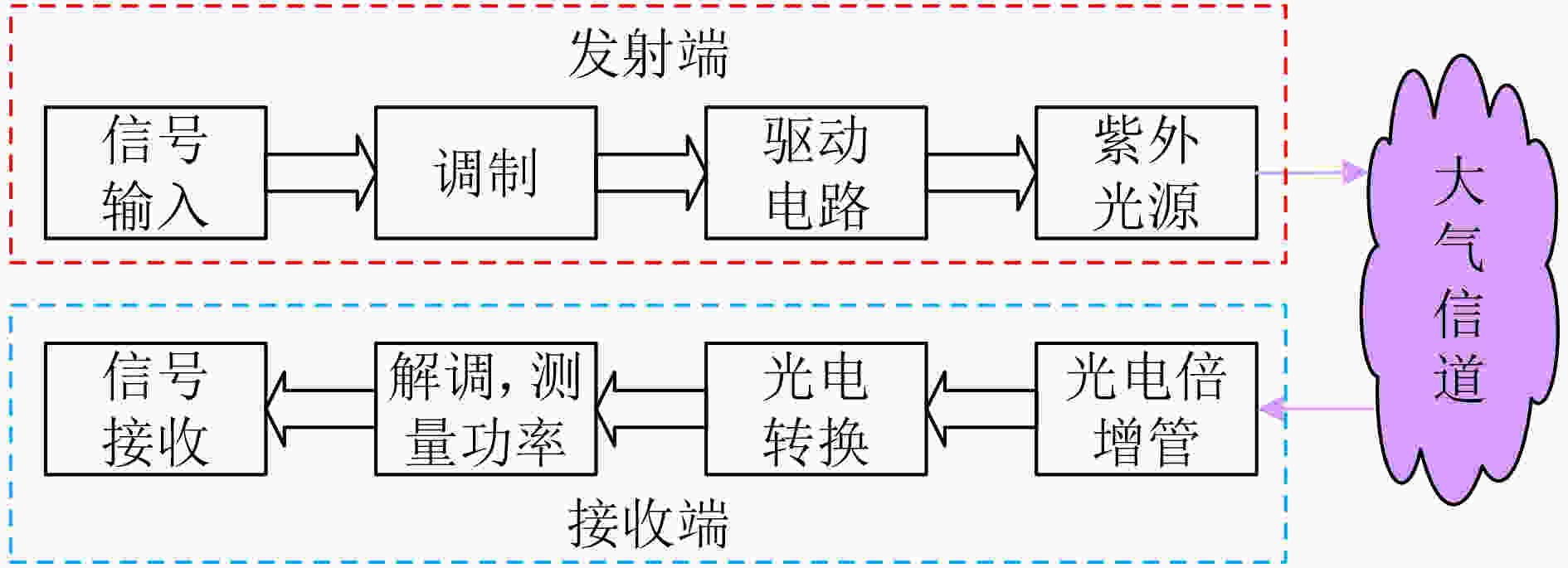
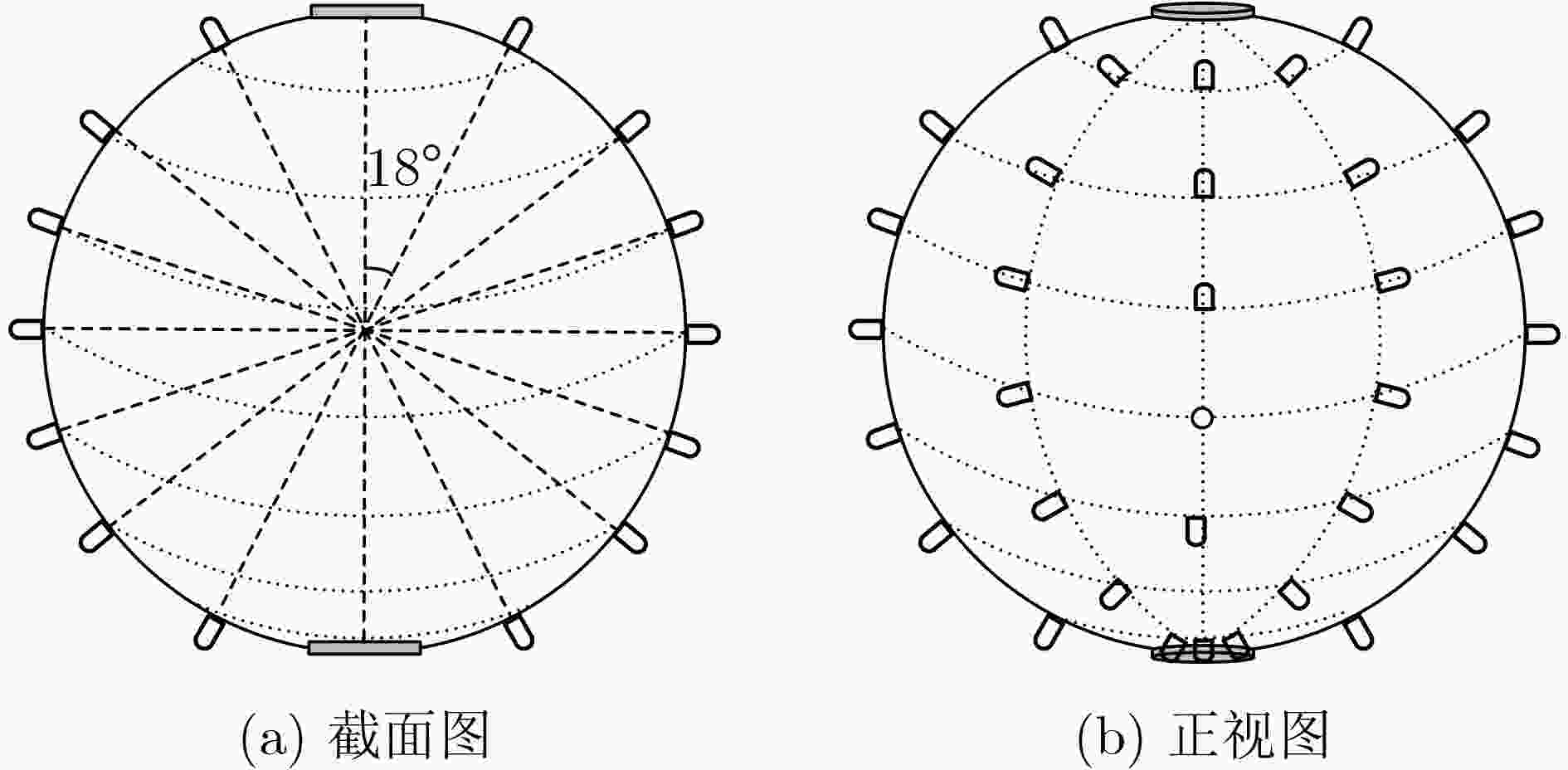
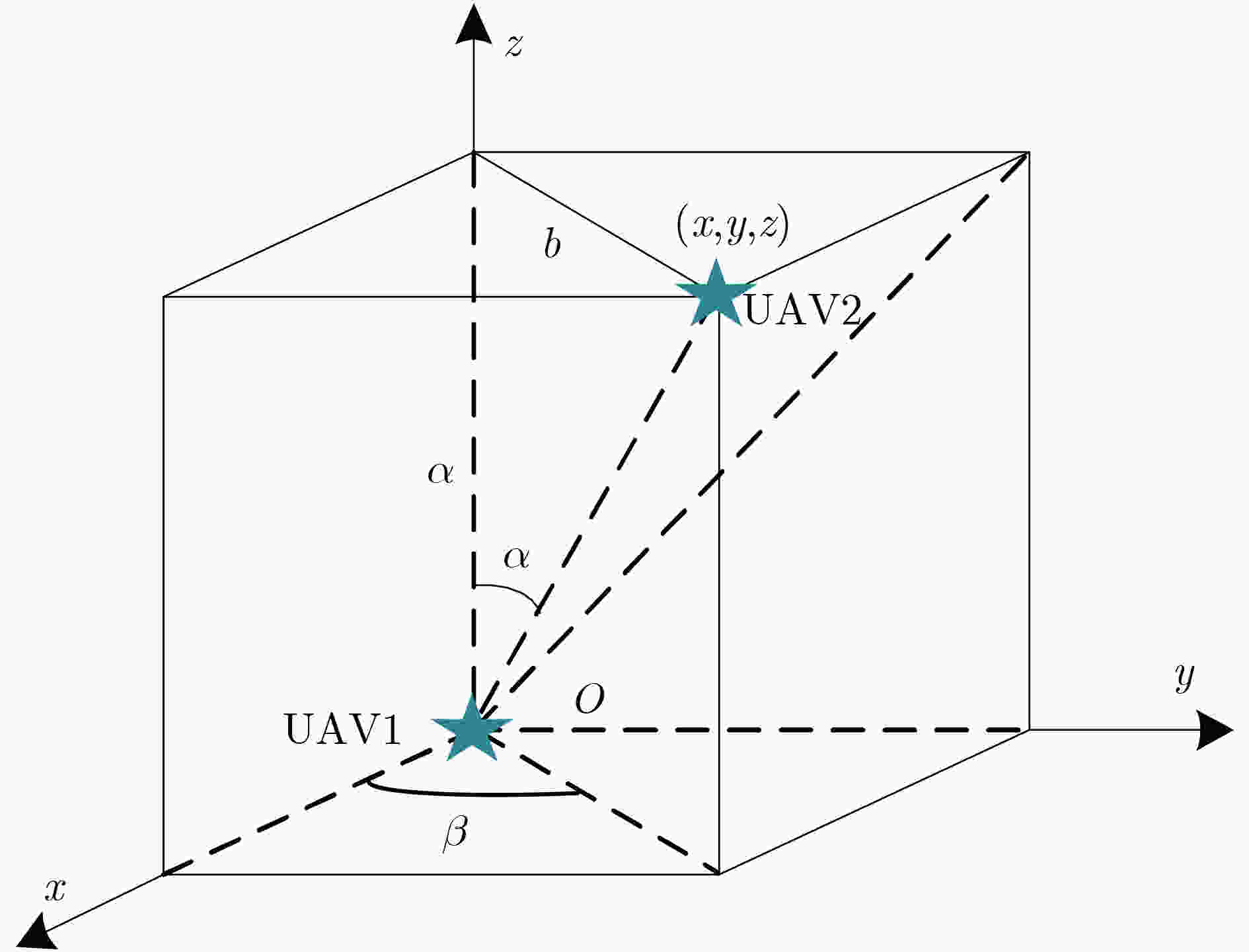
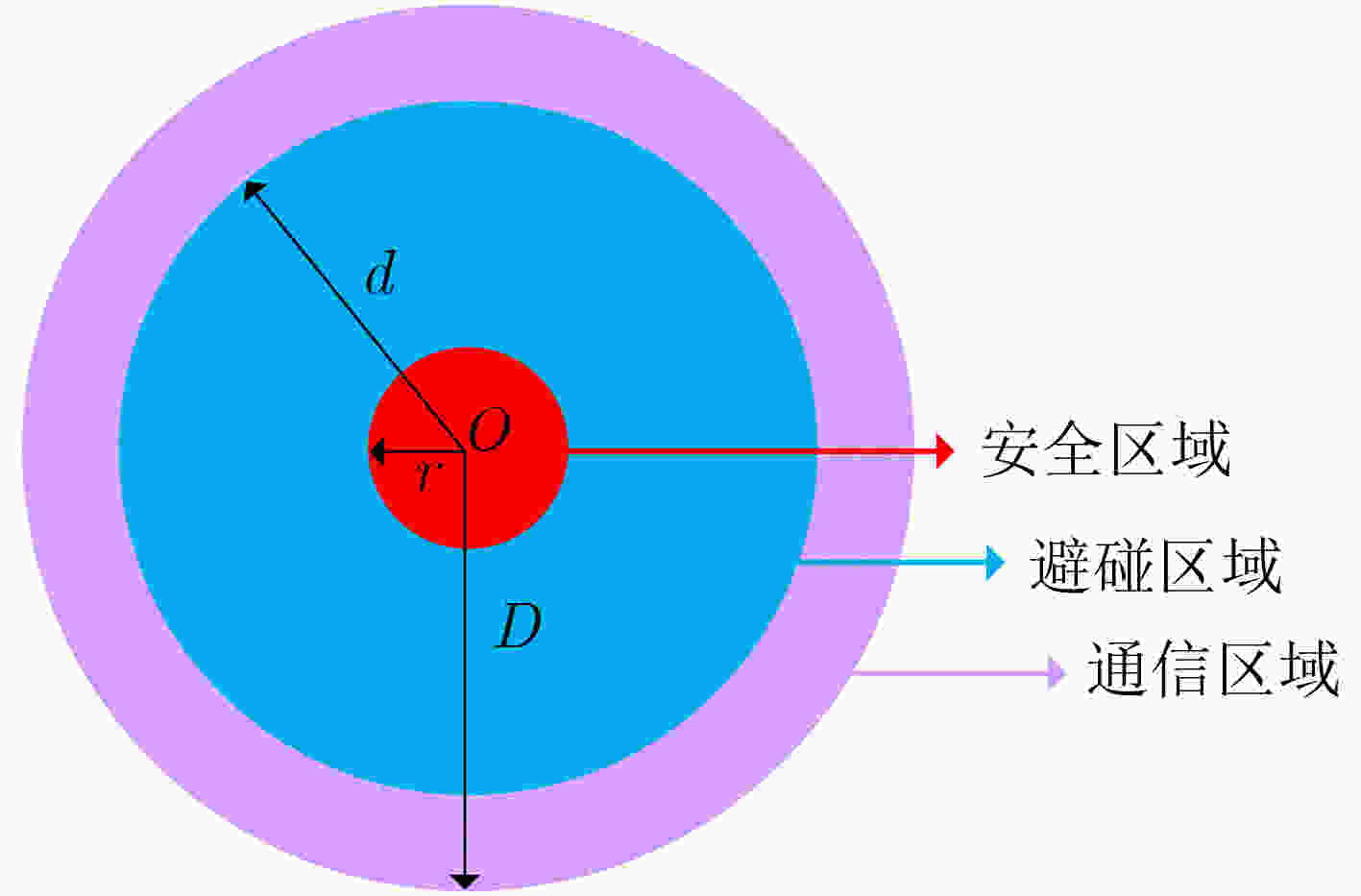
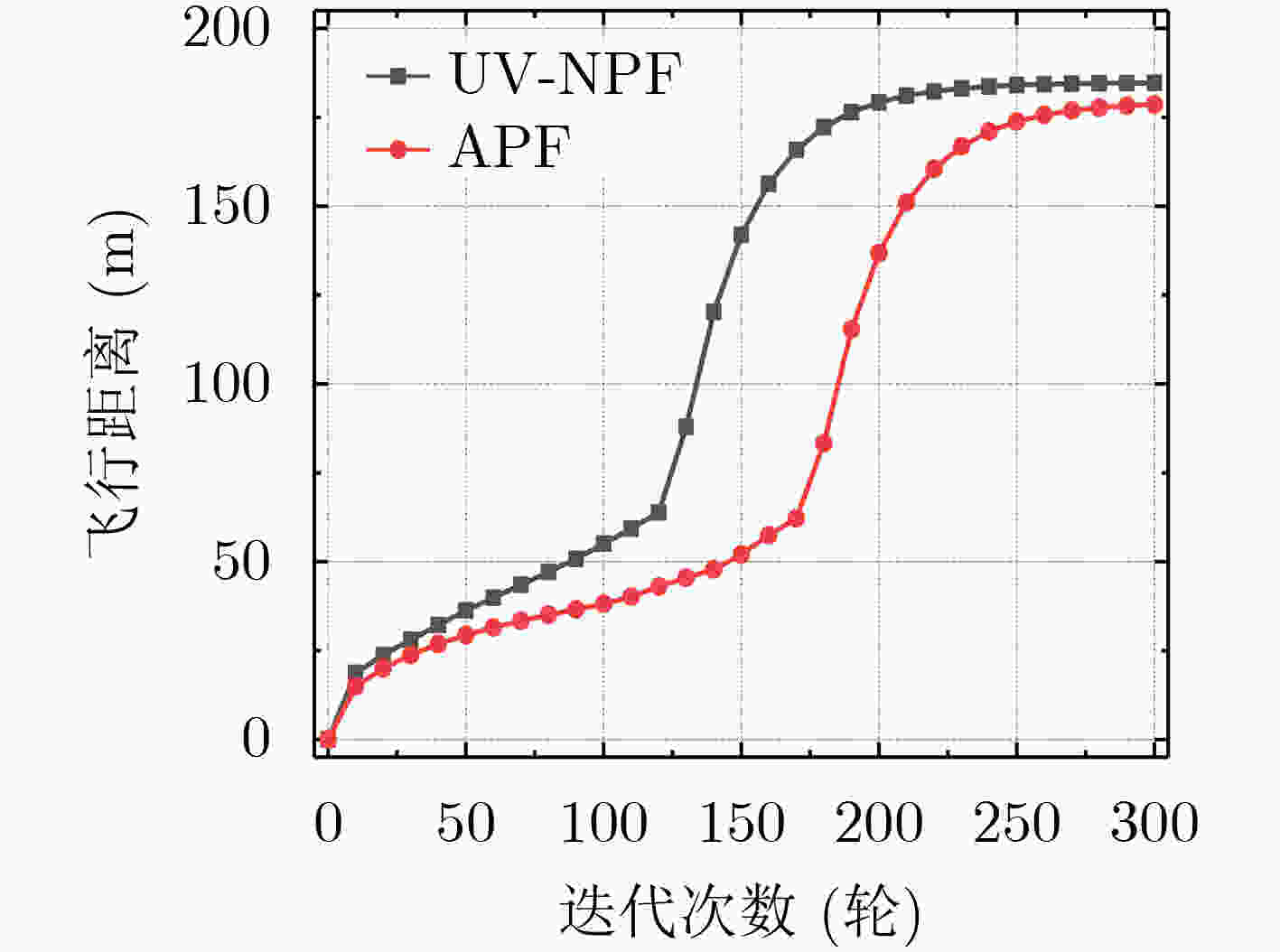
摘要: 针对复杂电磁环境下无人机编队重构过程中的路径规划和机间避碰问题,该文在传统紫外虚拟势场基础上,利用距离因子对斥力函数进行了改进,构建了一种紫外非均匀虚拟势场来协助无人机进行机间避碰。改进的紫外非均匀虚拟势场可以使得无人机避碰路径更加平滑,相同时间内,无人机可以飞行更远的距离。此外,通过无线紫外光测距方法计算无人机机间距离,并结合紫外非均匀势场对传统的人工势场法进行改进,实现无人机编队重构。仿真结果表明,该文算法可以有效解决传统算法下路径振荡和局部最小值问题,同时避碰效率相比传统人工势场算法有明显提升,在预设环境中该文算法路程缩短6%,到达目标点的时间提前40%。最后在两种不同的队形重构场景下,对该文算法进行了验证,结果表明该文算法可以有效实现无人机队形重构中预期的机间避碰效果。Abstract: To address the path planning and inter-aircraft collision avoidance problems in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) formation reconstruction in complex electromagnetic environment, the repulsion function is improved by using distance factor on the basis of traditional UV virtual potential field, and a non-uniform UV virtual potential field is constructed to assist UAVs in collision avoidance in this paper. The improved UV non-uniform virtual potential field can make the collision avoidance path of UAV smoother, and the UAV can fly a longer distance in the same time. In addition, the distance between UAVs is calculated by the wireless ultraviolet ranging method, and the traditional artificial potential field method is improved by combining the ultraviolet non-uniform potential field to realize the formation reconstruction of UAVs. Simulation results show that this algorithm can effectively solve the path oscillation and local minimum problems under the traditional algorithm, while the collision avoidance efficiency is significantly improved compared with the traditional artificial potential field algorithm, and the distance is shortened by 6% in the preset environment while the time to reach the target point is advanced by 40%. The results show that the algorithm can effectively achieve the expected inter-aircraft collision avoidance effect in UAV formation reconstruction.
-
表 1 坐标参数(m)
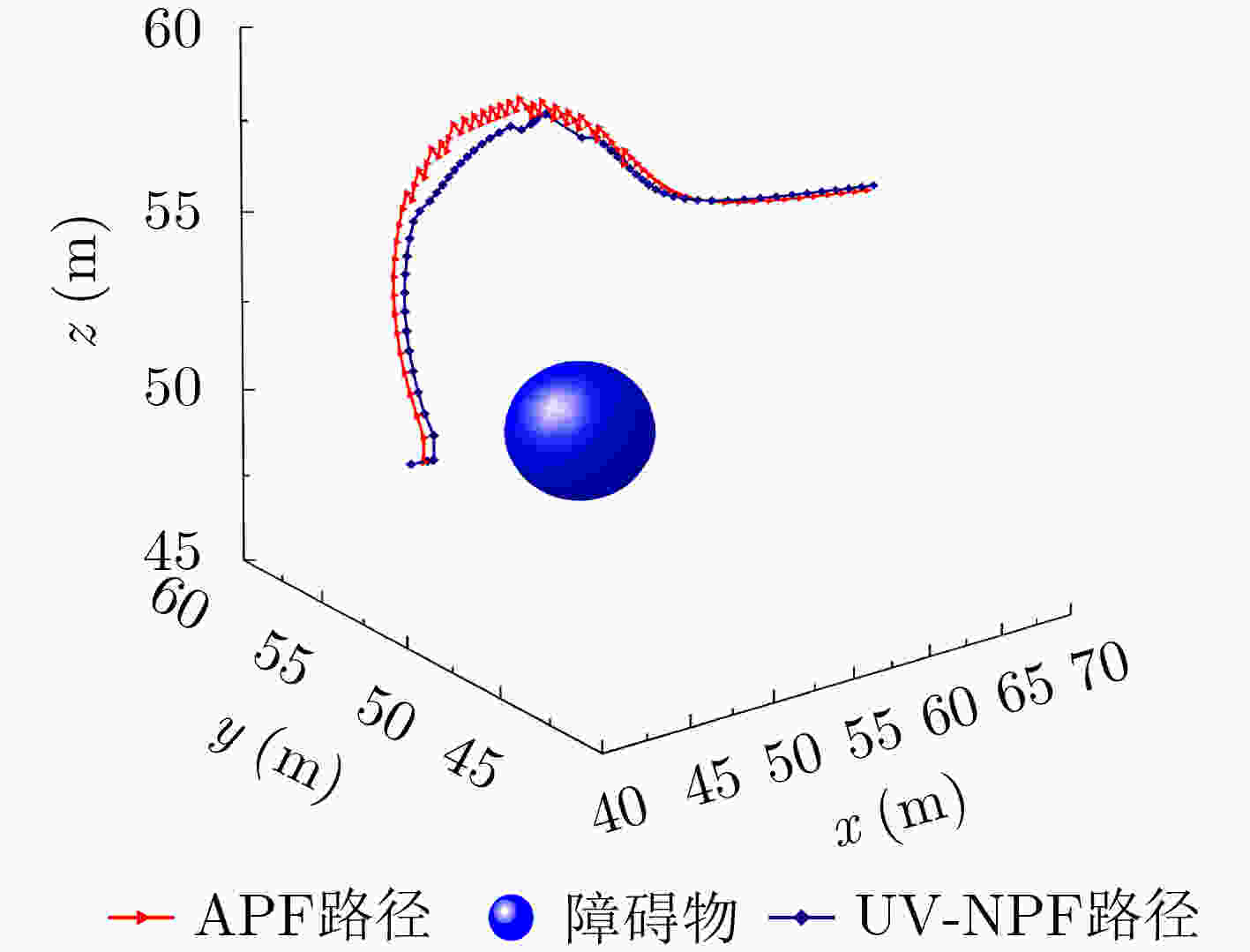
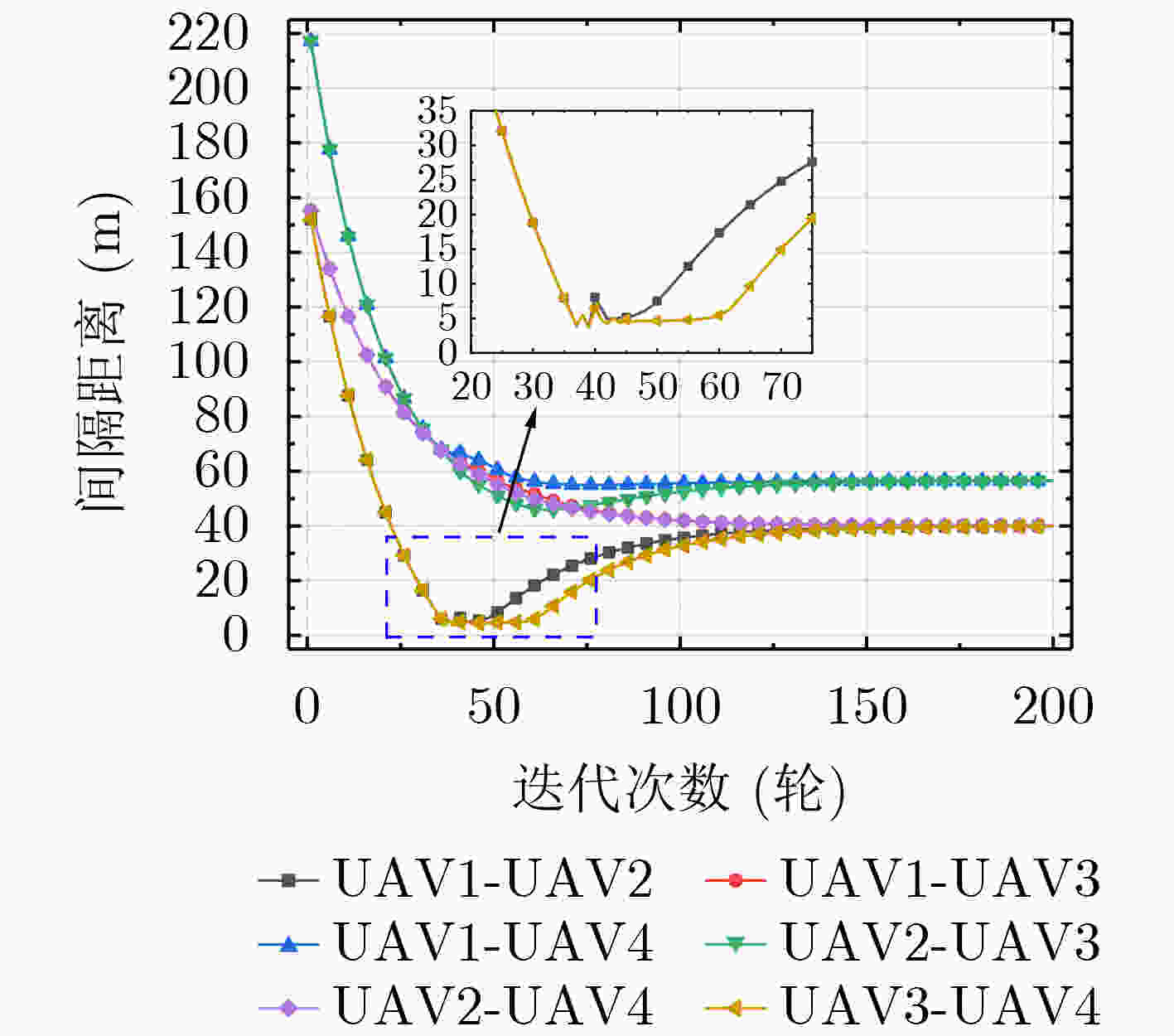
起点 目标点 障碍物1 障碍物2 障碍物3 障碍物4 障碍物5 坐标 (10,100) (190,120) (130,95) (100,110) (80,130) (160,80) (50,100) 半径(m) / / 7 5 10 5 10 表 2 编队队形设计1 (m)
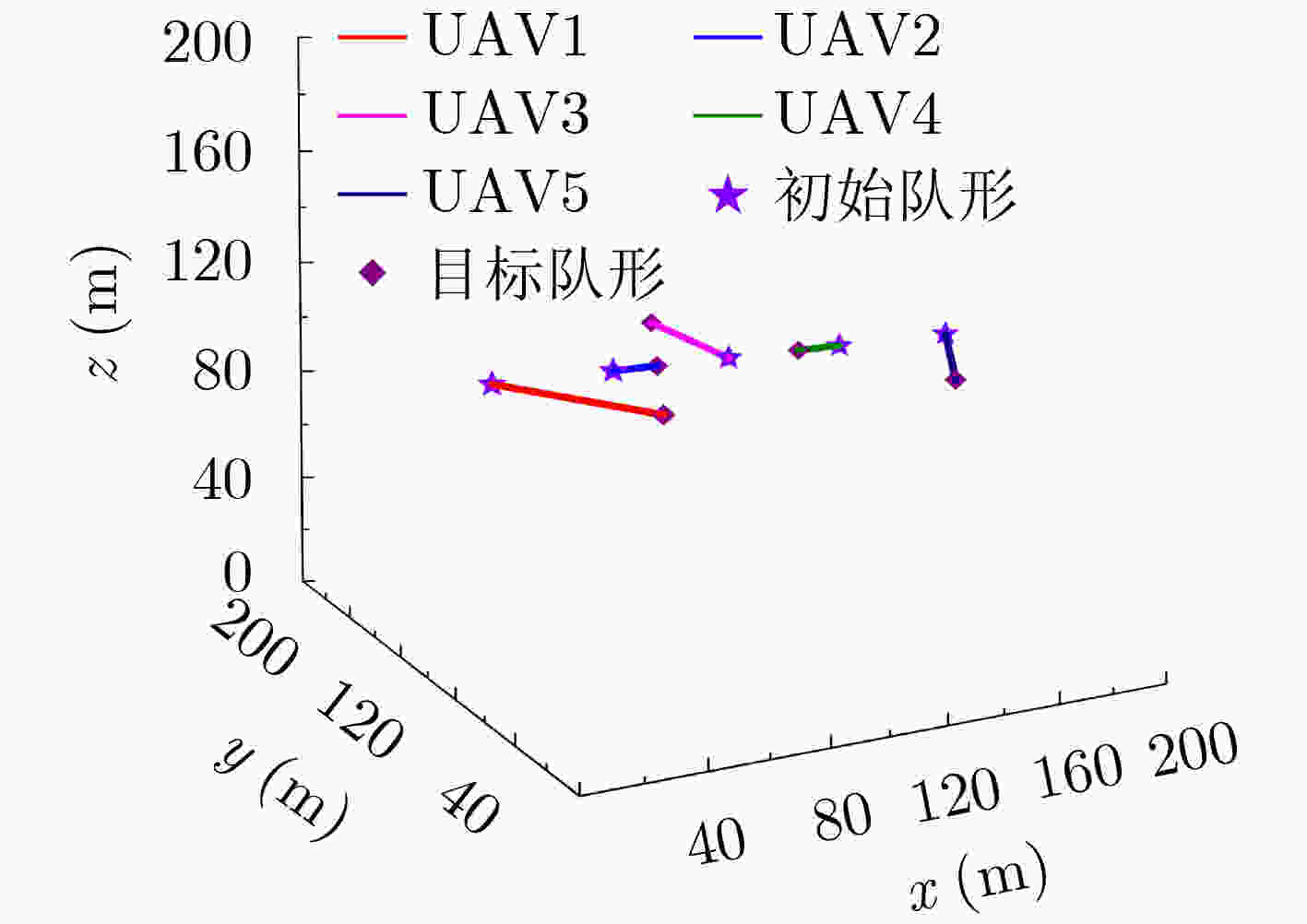
UAV1 UAV2 UAV3 UAV4 UAV5 起始队形 (20,100,100) (60,100,100) (100,100,100) (125,100,100) (180,100,100) 目标队形 (50,50,100) (75,100,100) (100,150,100) (125,100,100) (150,50,100) 表 3 编队队形设计2 (m)
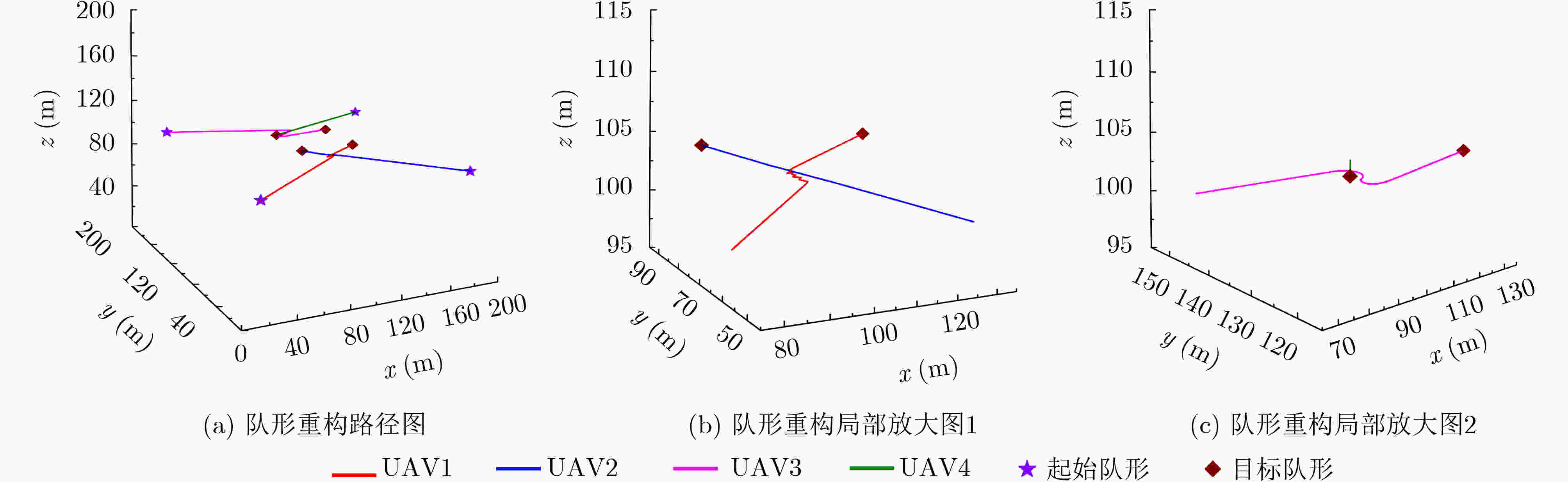
UAV1 UAV2 UAV3 UAV4 起始队形 (20,20,95) (180,20,95) (20,180,95) (180,180,95) 目标队形 (120,80,105) (80,80,105) (120,120,105) (80,120,105) -
[1] 沈林成, 牛轶峰, 朱华勇. 多无人机自主协同控制理论与方法[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013: 1–9.SHEN Lincheng, NIU Yifeng, and ZHU Huayong. Theories and Methods of Autonomous Cooperative Control for Multiple UAVs[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013: 1–9. [2] KANG Yuhang, KUANG Yu, CHENG Jun, et al. Robust leaderless time-varying formation control for unmanned aerial vehicle swarm system with Lipschitz nonlinear dynamics and directed switching topologies[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(1): 124–136. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.05.017 [3] CHUNG S J, PARANJAPE A A, DAMES P, et al. A survey on aerial swarm robotics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 837–855. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2857475 [4] AYAWLI B B K, MEI Xue, SHEN Mouquan, et al. Mobile robot path planning in dynamic environment using Voronoi diagram and computation geometry technique[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 86026–86040. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2925623 [5] BAYILI S and POLAT F. Limited-Damage A*: A path search algorithm that considers damage as a feasibility criterion[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2011, 24(4): 501–512. [6] BANSAL J C, GOPAL A, and NAGAR A K. Stability analysis of Artificial Bee Colony optimization algorithm[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2018, 41: 9–19. doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2018.01.003 [7] GAO Chen, ZHEN Ziyang, and GONG Huajun. A self-organized search and attack algorithm for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2016, 54: 229–240. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2016.03.022 [8] SHAO S, PENG Y, HE C, et al. Efficient path planning for UAV formation via comprehensively improved particle swarm optimization[J]. ISA transactions, 2020, 97: 415–430. [9] WU E, SUN Y, HUANG J, et al. Multi uav cluster control method based on virtual core in improved artificial potential field[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 131647–131661. [10] SUN Hang, QI Juntong, WU Chong, et al. Path planning for dense drone formation based on modified artificial potential fields[C]. The 39th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 2020: 4658–4664. [11] GARG K K, SHAIK P, and BHATIA V. Performance analysis of cooperative relaying technique for non-line-of-sight UV communication system in the presence of turbulence[J]. Optical Engineering, 2020, 59(5): 055101. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.59.5.055101 [12] ZHENG Xuan, TANG Yanfeng, DU Jingyi. Analysis of transmission characteristics of non-line-of-sight ultraviolet light under complex channel conditions[J]. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2021, 336(2): 1–7. [13] 赵太飞, 王晶, 张杰, 等. 蛙人协作中的水下无线光通信邻居发现方法[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(12): 1206002.ZHAO Taifei, WANG Jing, ZHANG Jie, et al. Neighbor Discovery Method for Frogmen Cooperation in Underwater Wireless Optical Communication[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(12): 1206002. [14] ZHAO Taifei, XIE Ying, XU Shan, et al. Flocking of UAV formation with wireless ultraviolet communication[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2020, 114(3): 2551–2568. doi: 10.1007/s11277-020-07489-7 [15] XU Zhengyuan. Approximate performance analysis of wireless ultraviolet links[C]. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing-ICASSP'07, Honolulu, USA, 2007: III-577–III-580. [16] 赵太飞, 余叙叙, 包鹤, 等. 无线日盲紫外光测距定位方法[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2017, 25(9): 2324–2332. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172509.2324ZHAO Taifei, YU Xuxu, BAO He, et al. Ranging and positioning method using wireless solar blind ultraviolet[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2017, 25(9): 2324–2332. doi: 10.3788/OPE.20172509.2324 [17] Vasilyev G S, Kuzichkin O R, Surzhik D I. Performance analysis of MIMO communication system with NLOS UV channel[J]. Photonics Letters of Poland, 2020, 12(4): 91–93. [18] ZHAO Taifei, XIE Ying, LIU Xue, et al. Research on novel fountain code for UAV formation flight control in UV communication[C]. The 7th IEEE International Symposium on Microwave, Antenna, Propagation, and EMC Technologies (MAPE), Xi'an, China, 2017: 120–123. [19] 邓婉, 王新民, 王晓燕, 等. 无人机编队队形保持变换控制器设计[J]. 计算机仿真, 2011, 28(10): 73–77.DENG Wan, WANG Xinmin,WANG Xiaoyan, et al. Controller design of UAVs formation keep and change[J]. Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems, 2011, 28(10): 73–77. -





 下载:
下载:

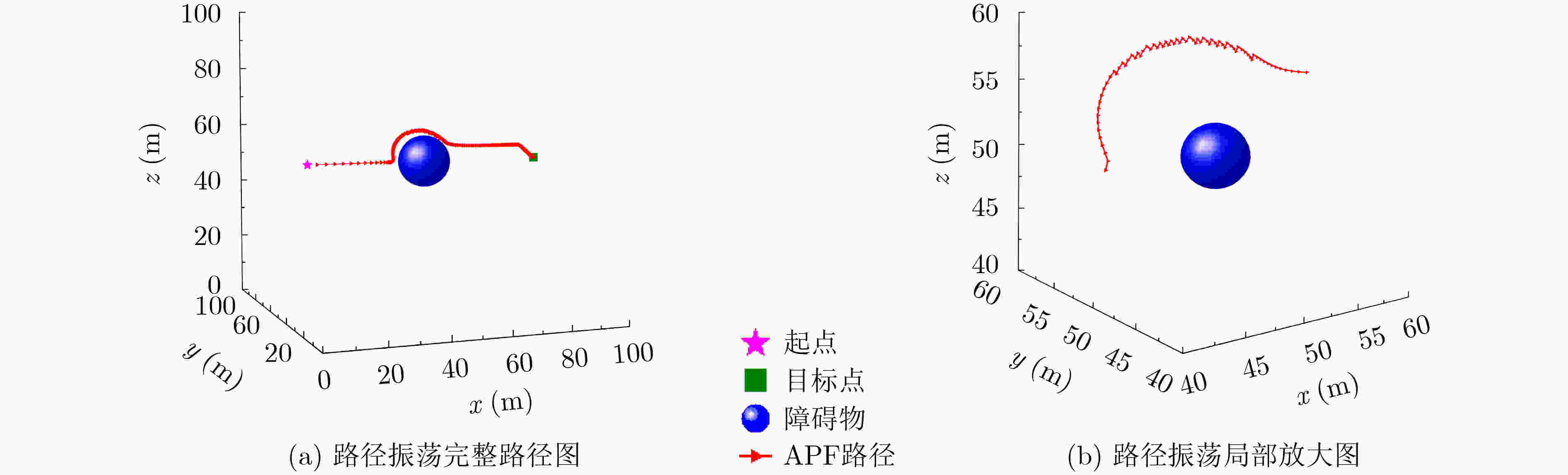
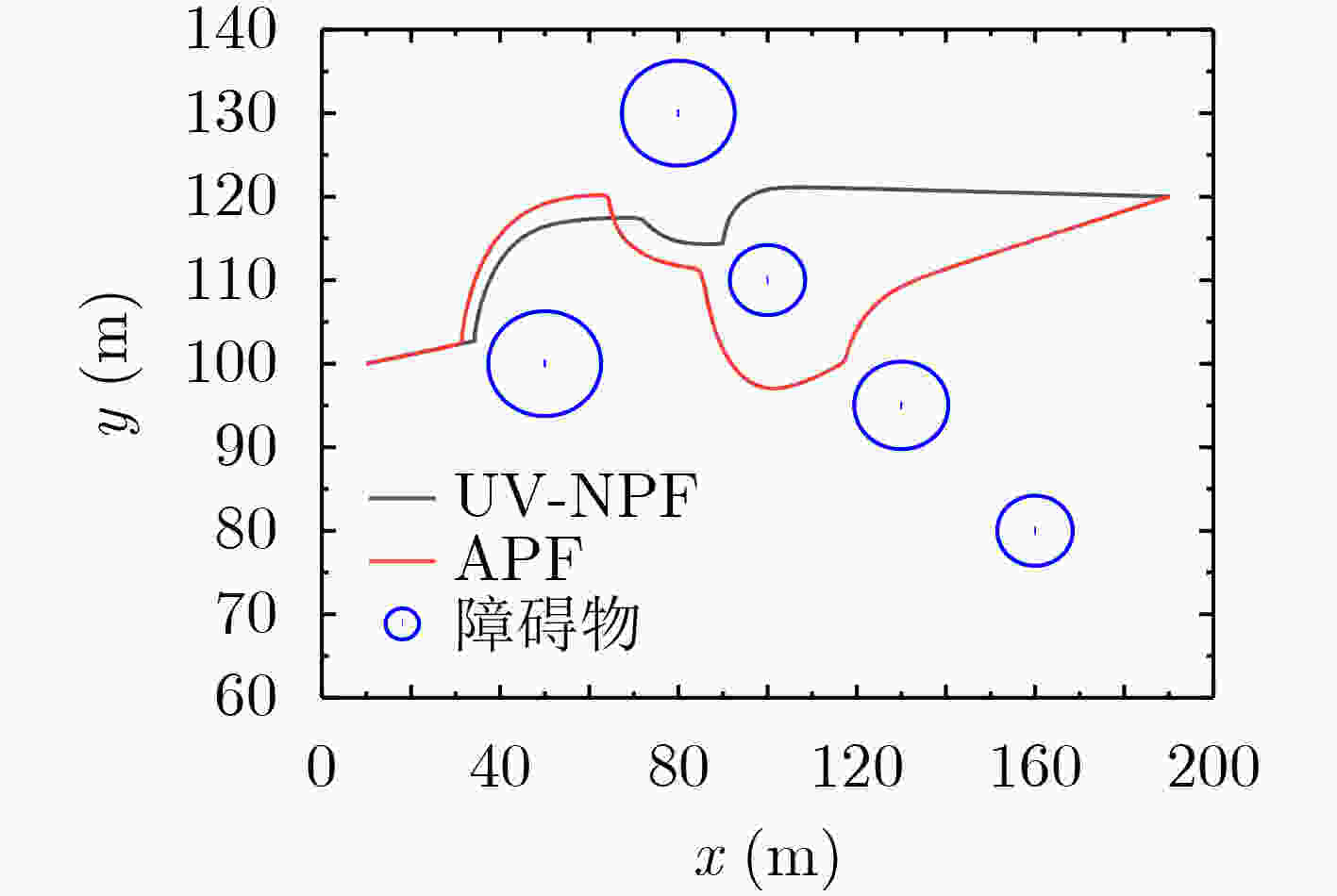
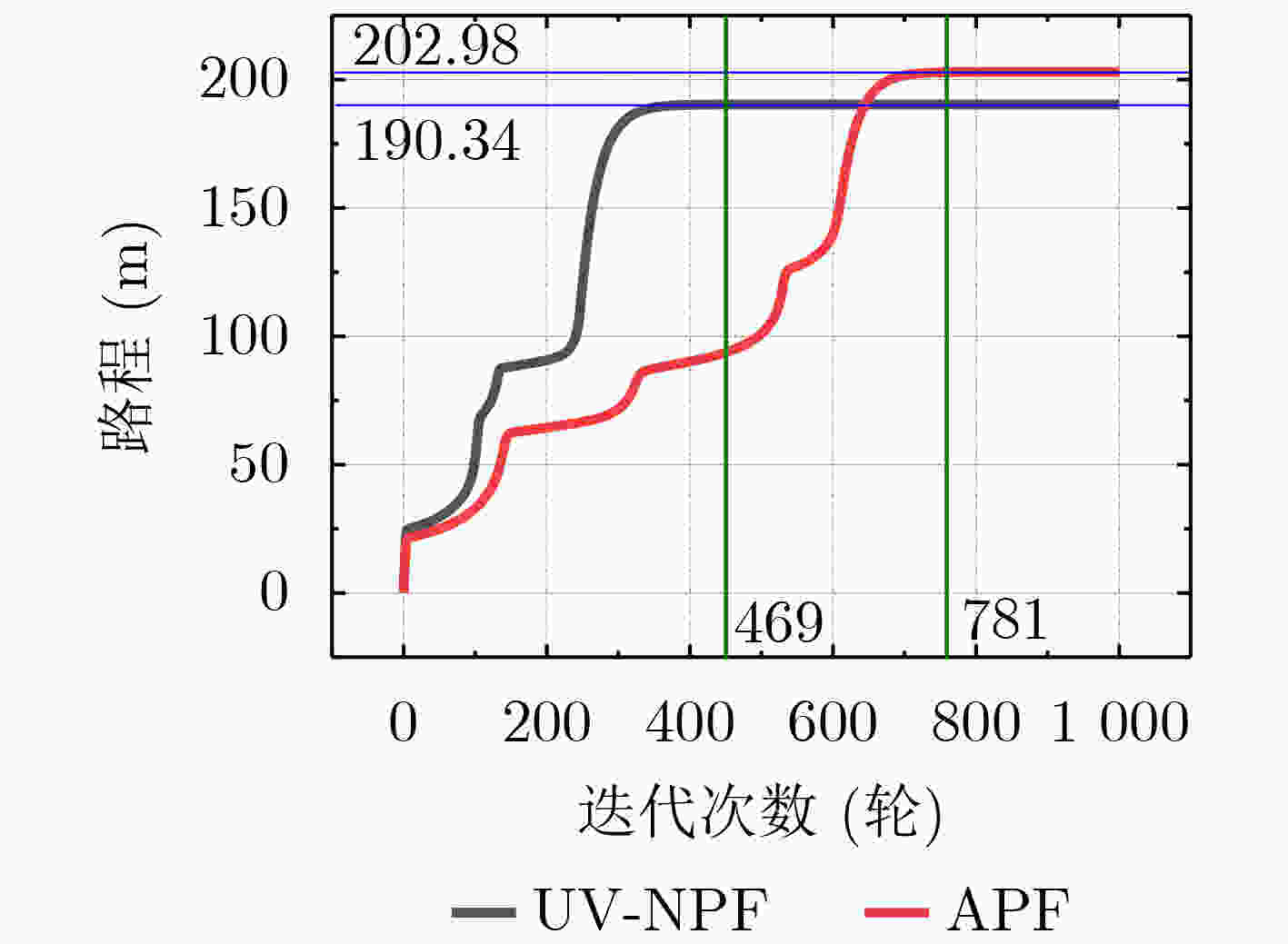
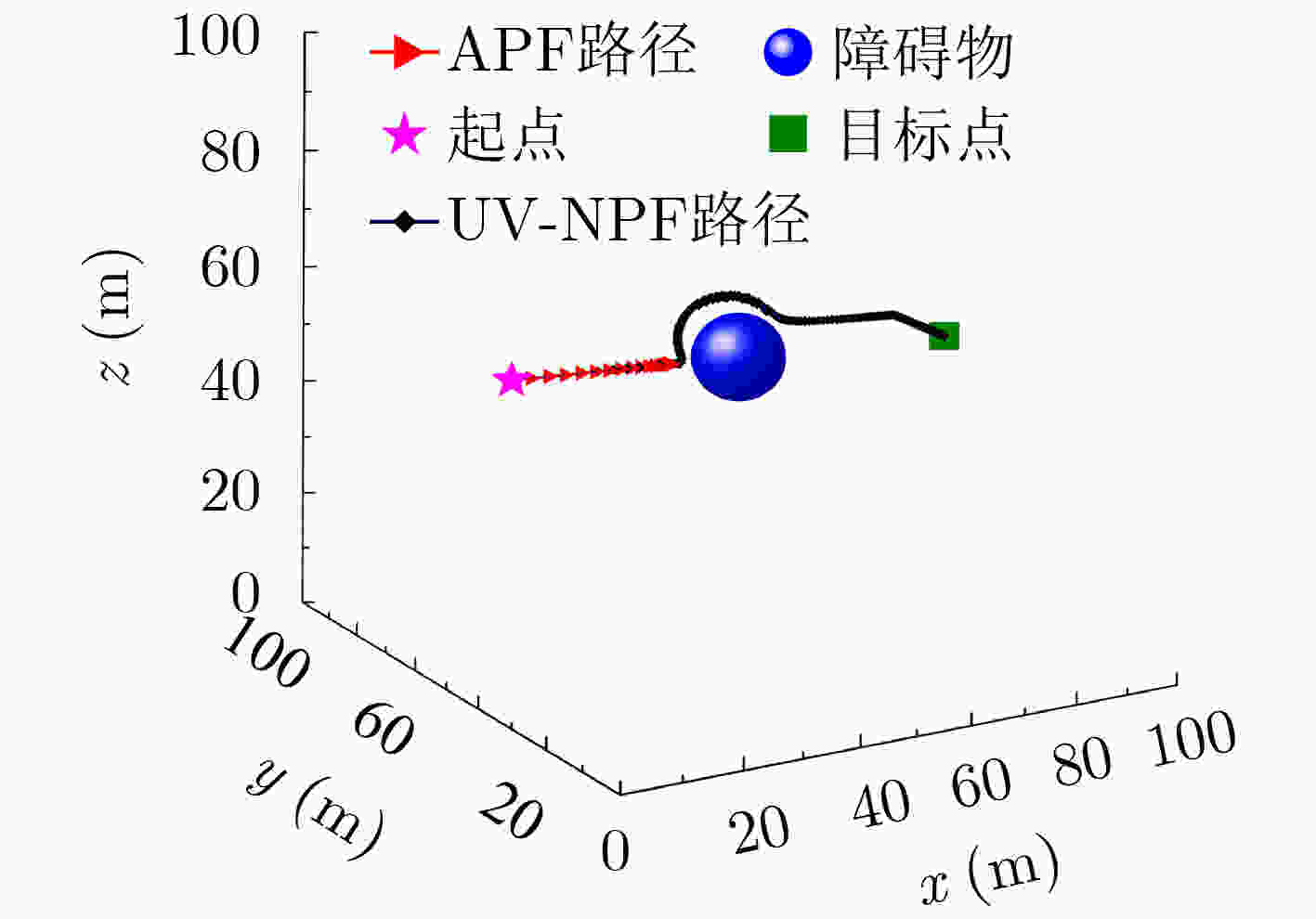


 下载:
下载:
