Design of Physical Layer Security Scheme for Intelligent Reflecting Surface Assisted Multi-User System with Imperfect CSI
-
摘要: 该文研究智能反射表面(Intelligent Reflecting Surface, IRS)辅助的多用户下行系统中的物理层安全的优化问题。多个用户之间的信息需要相互保密,每个时隙,非信息传输的目标用户视为窃听者,因此这是一个多窃听者的安全传输系统。由于信道的时变性,基站拥有窃听信道的信道状态信息(Channel State Information, CSI)为与真实的CSI间存在误差的过时信息。在此条件下,以系统最坏情况下的保密速率最大化为目标,对基站发射信息信号和人工噪声波束成形矢量,以及IRS的相移矩阵进行联合优化。原始优化问题为非凸半正定规划问题,利用松弛变量、惩罚函数、Charnes-Cooper变换和交替迭代优化等方法将原问题转化为凸问题并求解。仿真结果显示,相较于基准方案,该文所提出的优化算法能有效提高系统的保密速率。Abstract: This paper investigates the optimization problem of physical layer security for an Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS) assisted multi-user downlink system. In each time slot, the information is sent to one user and is kept confidential from to other users, so it is a secure transmission system with multiple eavesdroppers. The target user of the information is the legitimate receiver and the others are regarded as eavesdroppers. The Channel State Information (CSI) of the eavesdropping channels owned by the base station is outdated because of the time variability of the channels, and there is error between the outdated CSI and the real CSI. To maximize system security rate in the worst case, the beamforming vectors of the signal and the artificial noise, and the IRS phase shifts are jointly optimized. The original optimization problem is a non-convex positive semi-definite programming problem.The problem is transformed into a convex problem and solved by using slack variables, penalty-based, Charnes-Cooper transformation, alternating optimization and other methods. The simulation results show that the proposed optimization algorithm can effectively improve the system security rate compared with other benchmark schemes.
-
表 1 优化问题式(9)的求解算法(算法1)
(1)初始化参数:步长$\delta $,$i = 1$,$\varOmega = \varnothing$,${\beta ^{(1)}} = 1$. (2)while: (3)给定${\beta ^{(i)}}$,求解问题(16),得到解$ \varphi ({\beta ^{(i)}}) $. (4)$\varOmega = \varOmega \cup \varphi ({\beta ^{(i)} })$,$i = i + 1$. (5)更新${\beta ^{(i)}} = {\beta ^{(i - 1)}} + \delta $. (6)until${\beta ^{(i)}} > 1 + \sigma _{\text{B}}^{ - 2}P\left\| {{{\mathbf{h}}_{{\text{AB}}}}} \right\|_{\text{F}}^2$. (7)输出$\varOmega$中最大值$ \varphi ({\beta ^{{\text{opt}}}}) $及其对应的${\beta ^{{\text{opt}}}}$. 表 2 第2层优化问题(16)的求解算法(算法2)
(1)初始化参数:迭代次数$m = 0$,${{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{(0)} }$,$ \zeta $. (2)while: (3)$m = m + 1$. (4)令${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} = {{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{(m - 1)} }$,求解问题式(18),得到$ {{\boldsymbol{Q}}^{(m)}} $, ${{\boldsymbol{Z}}^{(m)}}$与$ {\xi ^{(m)}} $. (5)利用公式$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_1} = {{\boldsymbol{Q}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\boldsymbol{Q}} \xi }} \right. } \xi } $与$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_2} = {{\boldsymbol{Z}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\boldsymbol{Z}} \xi }} \right. } \xi } $得到$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_1}^{(m)} $与$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_2}^{(m)} $. (6)令$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_1} = {\boldsymbol{W}}_1^{(m)} $与$ {{\boldsymbol{W}}_2} = {\boldsymbol{W}}_2^{(m)} $,求解问题式(25),得到
$ {{\boldsymbol{E}}^{(m)}} $与$ {\xi ^{(m)}} $.(7)利用公式$ {\boldsymbol{V}} = {{\boldsymbol{E}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{\boldsymbol{E}} \xi }} \right. } \xi } $,得到$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}^{(m)}} $,再对$ {{\boldsymbol{V}}^{(m)}} $进行特征值分解
得到特征向量$ {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(m)}} $,由$ {{\boldsymbol{v}}^{(m)}} $得到对角化矩阵${{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{(m)} }$.(8)until${ {\left( {R_{\text{S} }^{(m)} - R_{\text{S} }^{(m - 1)} } \right)}/ {R_{\text{S} }^{(m)} } } \le \zeta$. (9)对$ {\boldsymbol{W}}_1^{(m)} $、$ {\boldsymbol{W}}_2^{(m)} $进行特征值分解可得${{\boldsymbol{w}}_1}^{(m)}$, ${{\boldsymbol{w}}_2}^{(m)}$. (10)输出$ {\boldsymbol{w}}_{\text{1}}^{{\text{opt}}} = {\boldsymbol{w}}_1^{(m)} $,$ {\boldsymbol{w}}_2^{{\text{opt}}} = {\boldsymbol{w}}_2^{(m)} $,${{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{ {\text{opt} } } } = {{\boldsymbol{\varPhi}} ^{(m)} }$. -
[1] ZHANG Shunqing, WU Qingqing, XU Shugong, et al. Fundamental green tradeoffs: Progresses, challenges, and impacts on 5G networks[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(1): 33–56. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2594120 [2] 雷维嘉, 林秀珍, 杨小燕, 等. 利用人工噪声提高合法接收者性能的物理层安全方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(11): 2887–2892. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160054LEI Weijia, LIN Xiuzhen, YANG Xiaoyan, et al. Physical layer security scheme exploiting artificial noise to improve the performance of legitimate user[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2016, 38(11): 2887–2892. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160054 [3] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107 [4] GUAN Xinrong, WU Qingqing, and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted secrecy communication: Is artificial noise helpful or not?[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(6): 778–782. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2969629 [5] HONG Sheng, PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, et al. Artificial-noise-aided secure MIMO wireless communications via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(12): 7851–7866. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3024621 [6] CUI Miao, ZHANG Guangchi, and ZHANG Rui. Secure wireless communication via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2019, 8(5): 1410–1414. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2919685 [7] DE ARAÚJO G T and DE ALMEIDA A L F. PARAFAC-based channel estimation for intelligent reflective surface assisted MIMO system[C]. 2020 IEEE 11th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Hangzhou, China, 2020: 1–5. [8] ZHENG Beixiong and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface-enhanced OFDM: Channel estimation and reflection optimization[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(4): 518–522. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2961357 [9] YU Xianghao, XU Dongfang, SUN Ying, et al. Robust and secure wireless communications via intelligent reflecting surfaces[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2637–2652. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007043 [10] HONG Sheng, PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, et al. Robust transmission design for intelligent reflecting surface-aided secure communication systems with imperfect cascaded CSI[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(4): 2487–2501. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3042828 [11] DONG Limeng, WANG Huiming, and XIAO Haitao. Secure cognitive radio communication via intelligent reflecting surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(7): 4678–4690. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3073028 [12] BOYD S and VANDENBERGHE L. Convex Optimization[M]. Britain: Cambridge University Press, 2004: 131–133. [13] LI Qiang and MA W K. Spatially selective artificial-noise aided transmit optimization for MISO multi-eves secrecy rate maximization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(10): 2704–2717. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2013.2253771 [14] LUO Zhiquan, STURM J F, and ZHANG Shuzhong. Multivariate nonnegative quadratic mappings[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2004, 14(4): 1140–1162. doi: 10.1137/S1052623403421498 [15] MICHAEL C, STEPHEN B. The CVX users’ guide[EB/OL]. http://cvxr.com/cvx/, 2020. [16] LI Qiang and MA W K. Optimal and robust transmit designs for MISO channel secrecy by semidefinite programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(8): 3799–3812. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2146775 [17] YAN Wenjing, YUAN Xiaojun, HE Zhenqing, et al. Passive beamforming and information transfer design for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces aided multiuser MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(8): 1793–1808. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000811 [18] LIAO Weicheng, CHANG Tsunghui, MA Wingkin, et al. QoS-based transmit beamforming in the presence of eavesdroppers: An optimized artificial-noise-aided approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(3): 1202–1216. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2094610 -





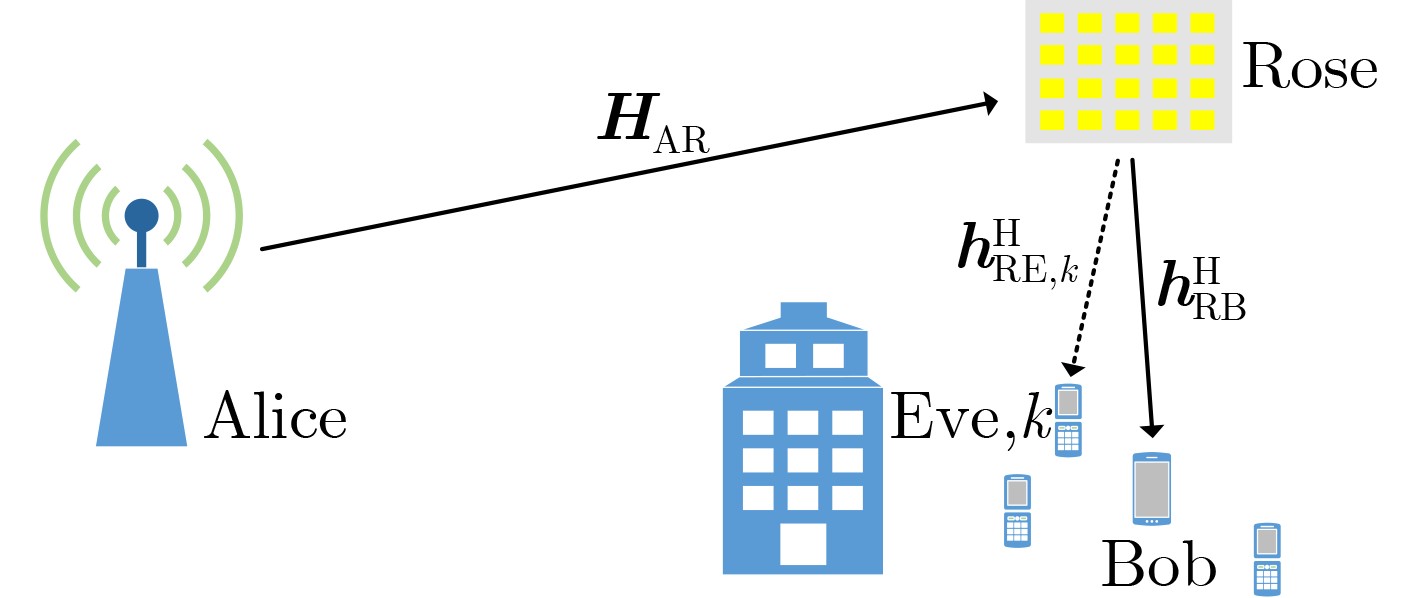
 下载:
下载:
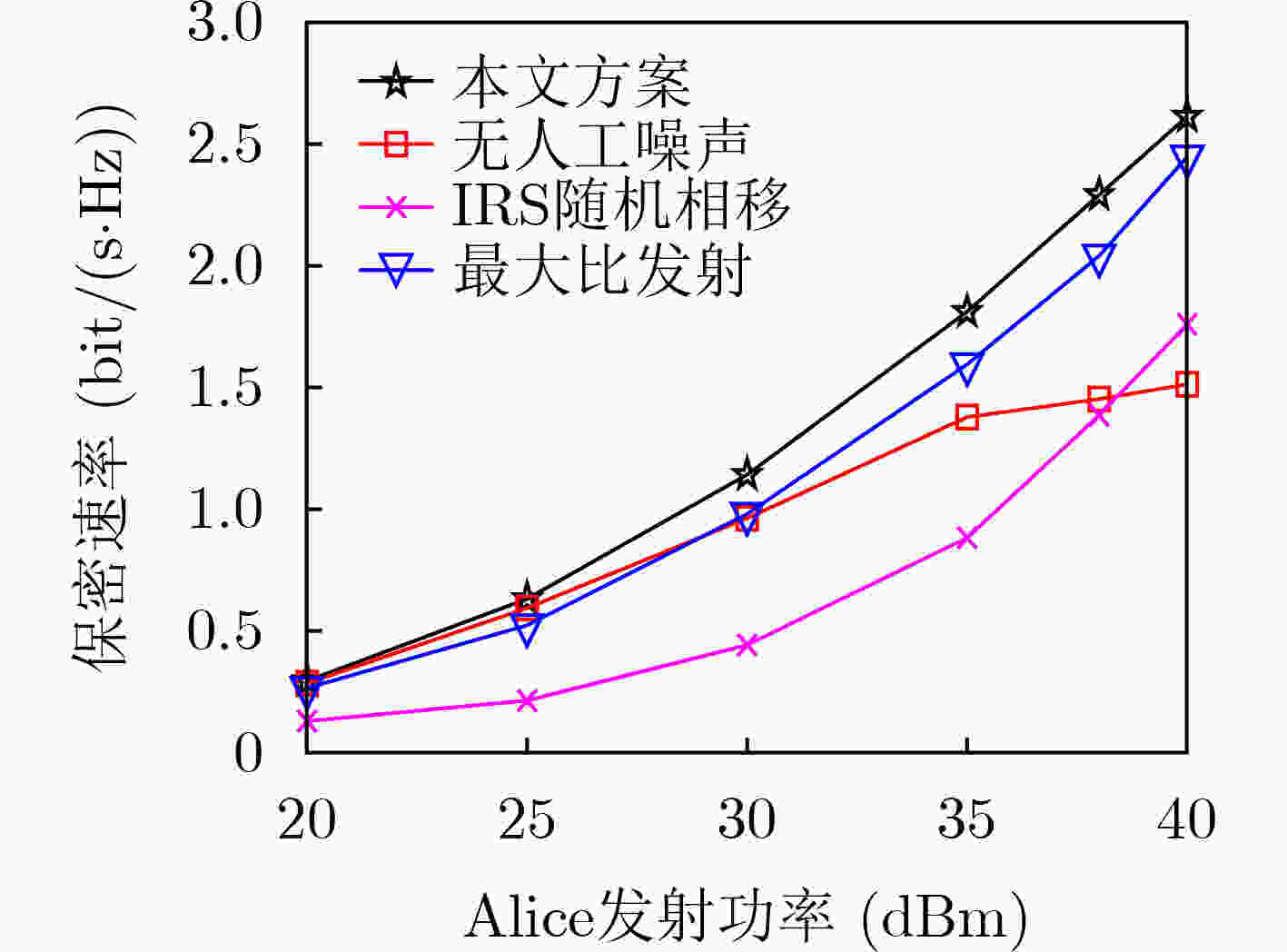
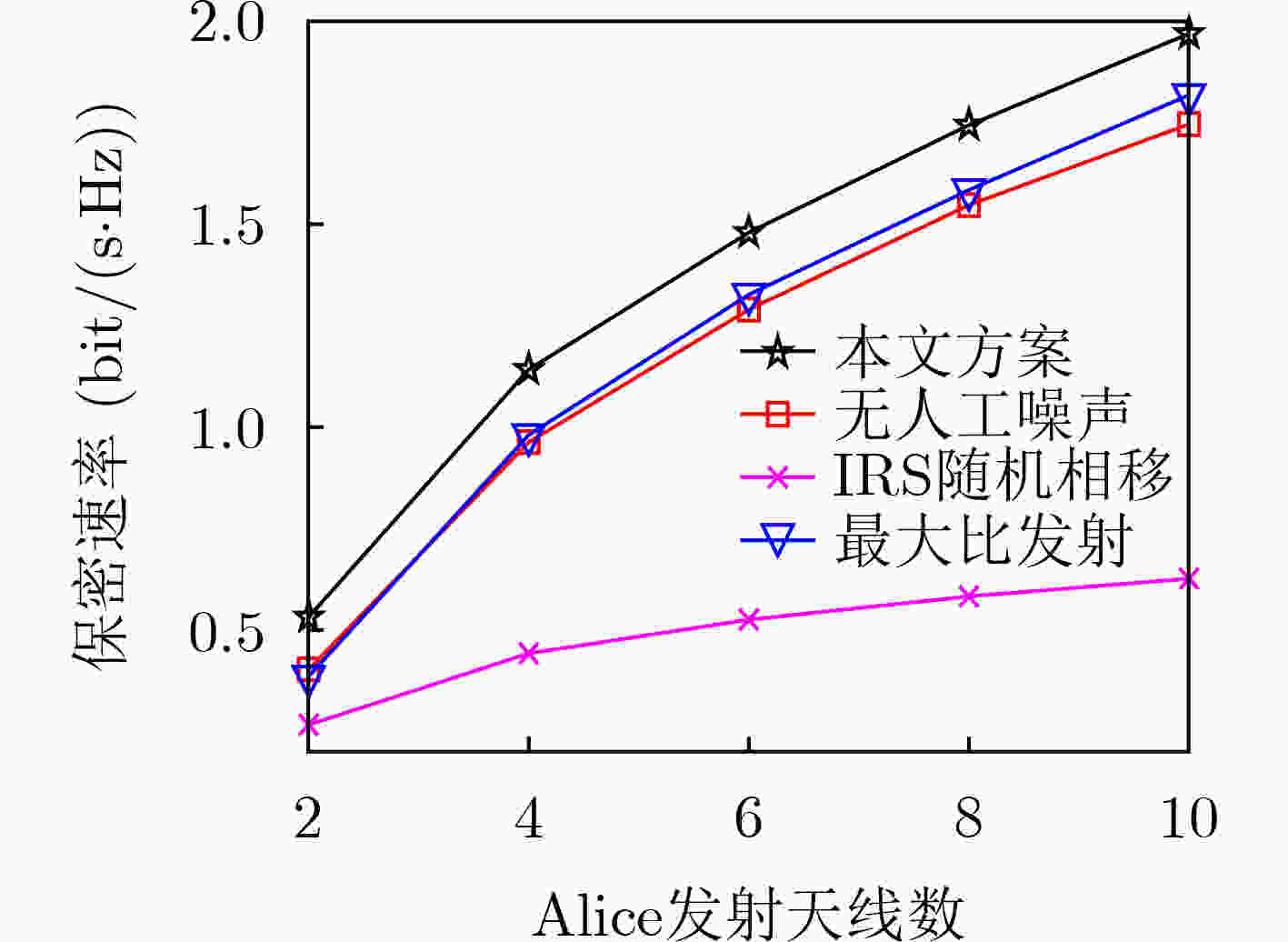
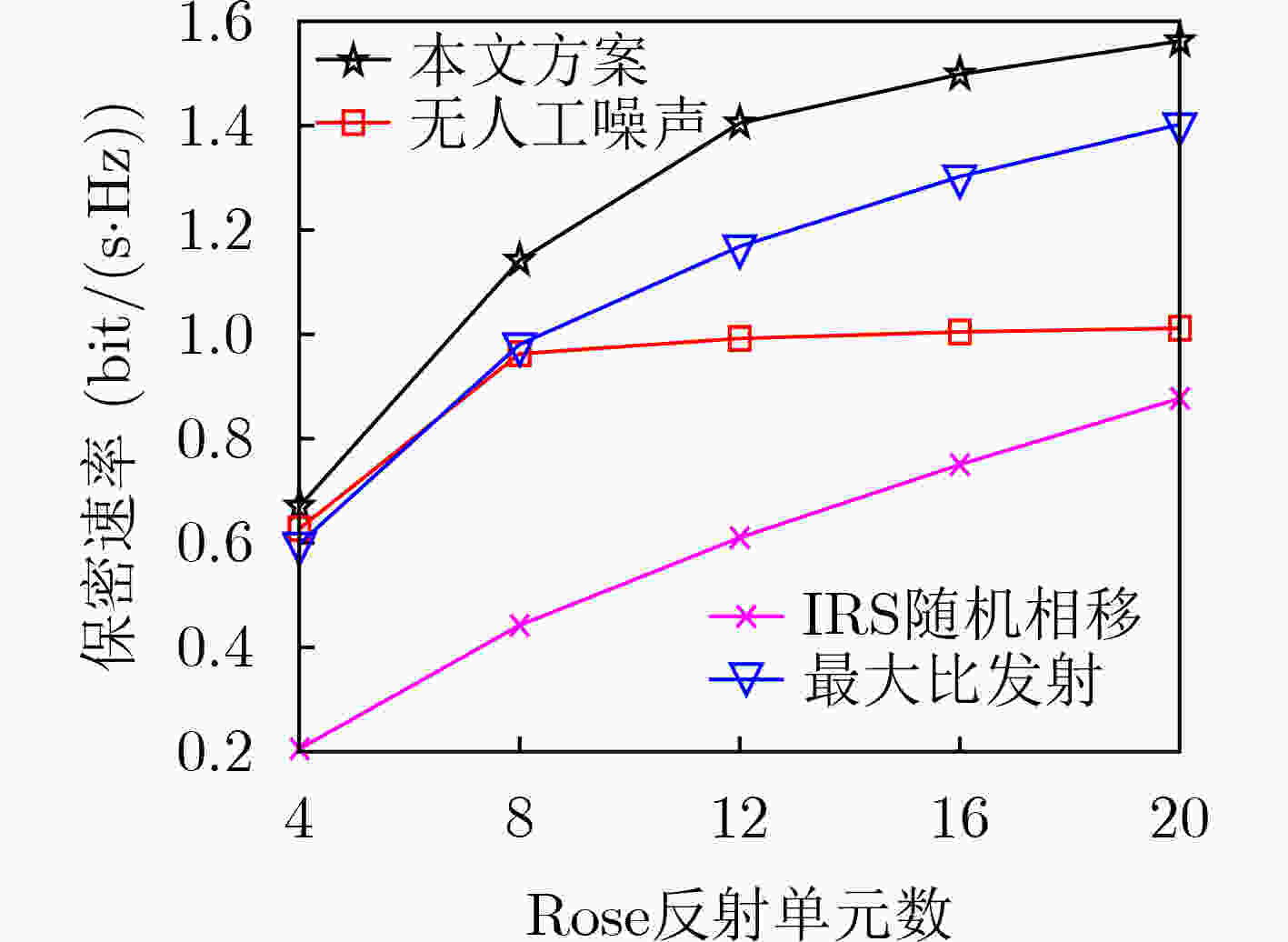
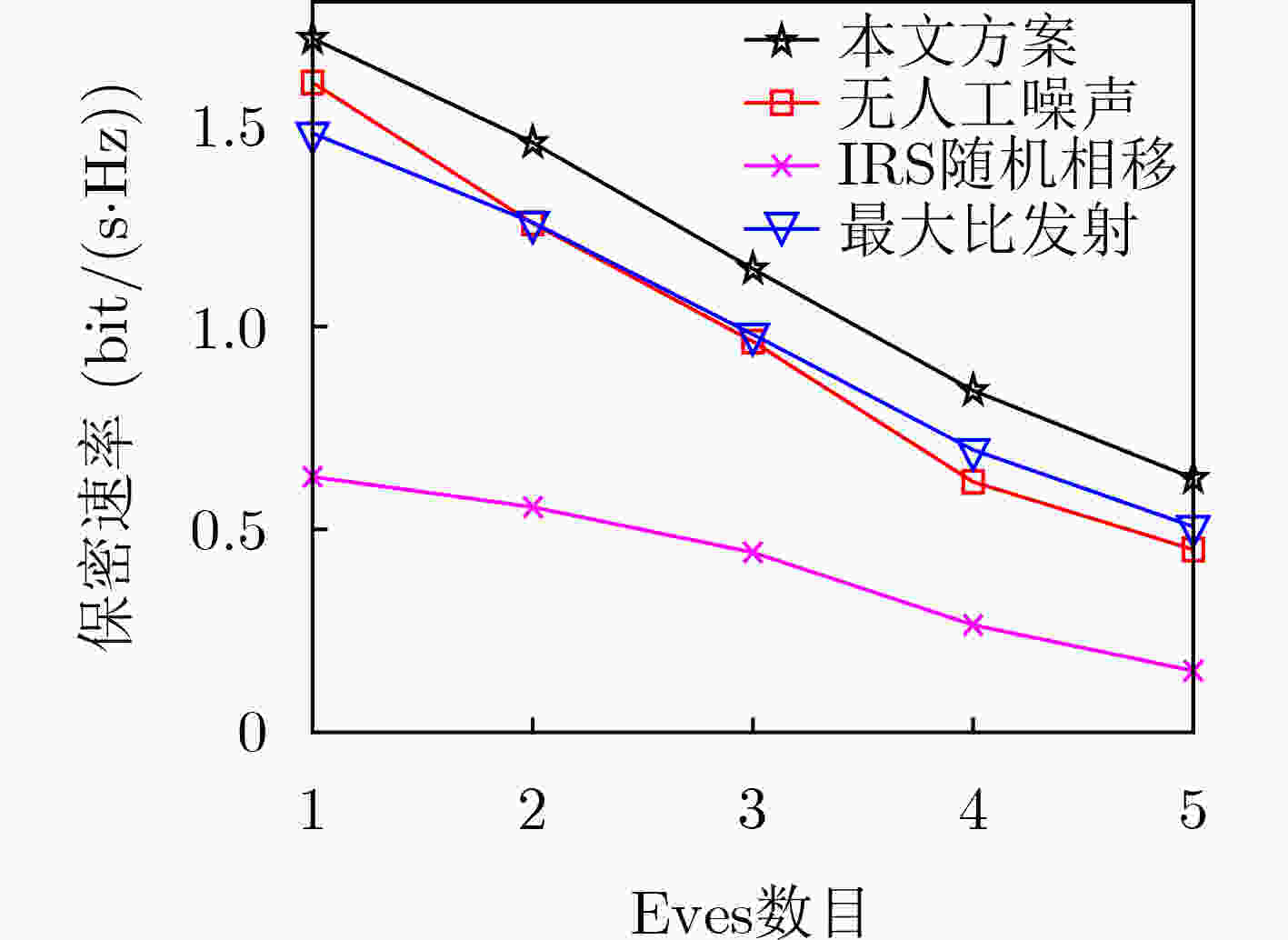
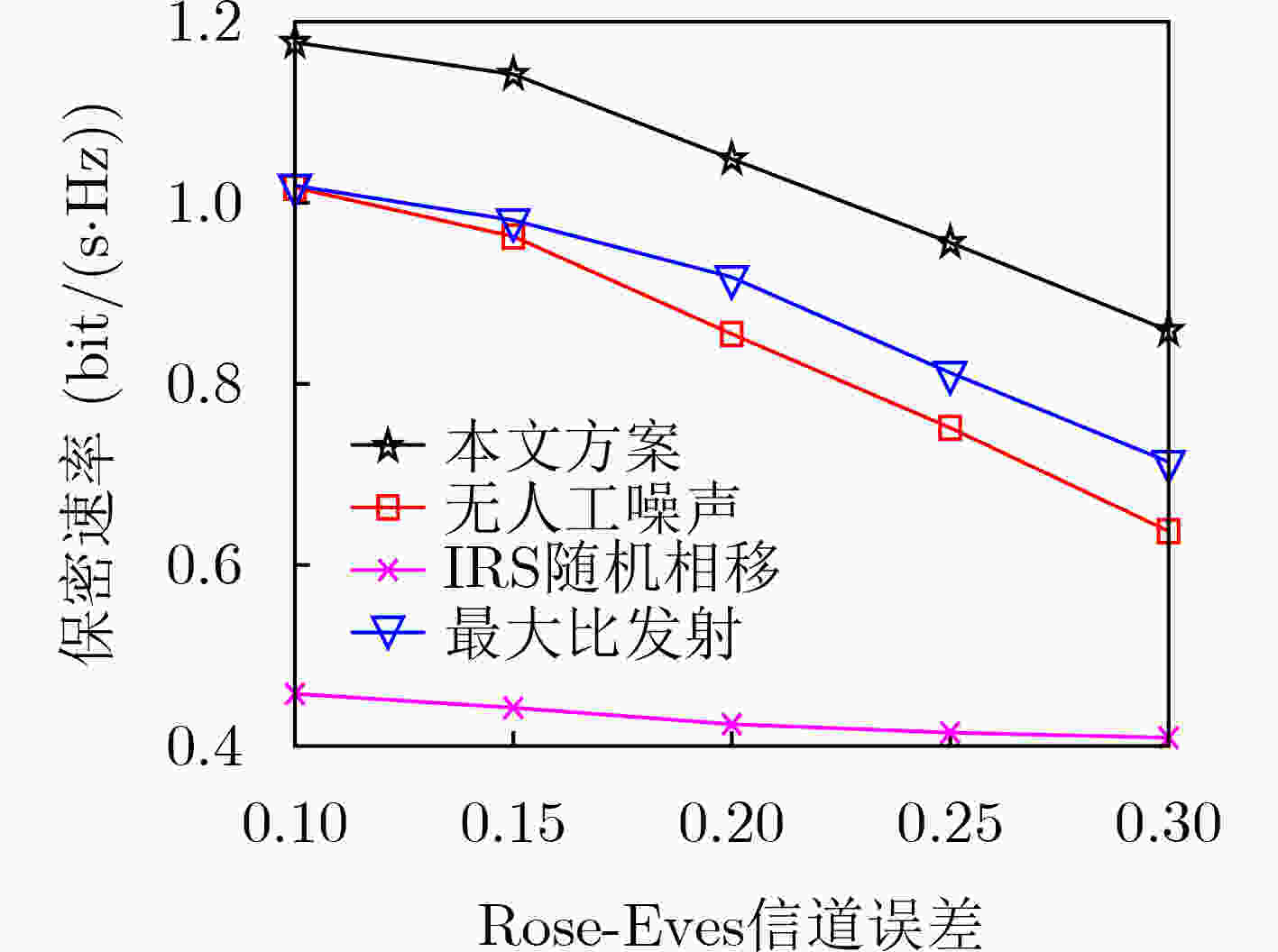



 下载:
下载:
