A Fast Classification Method of Rolling Bearing State Under Different Loads Based on Improved Broad Model Transfer Learning
-
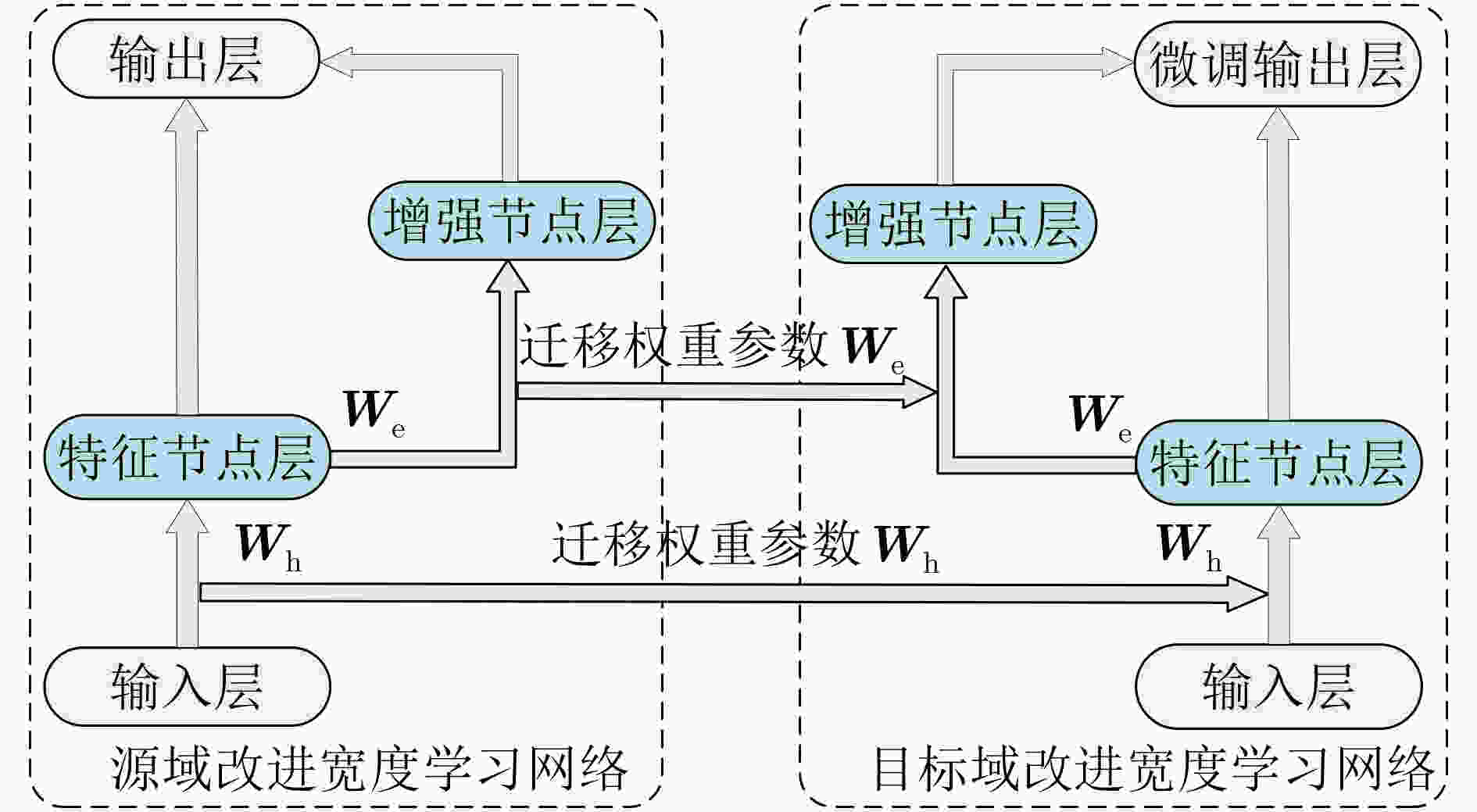
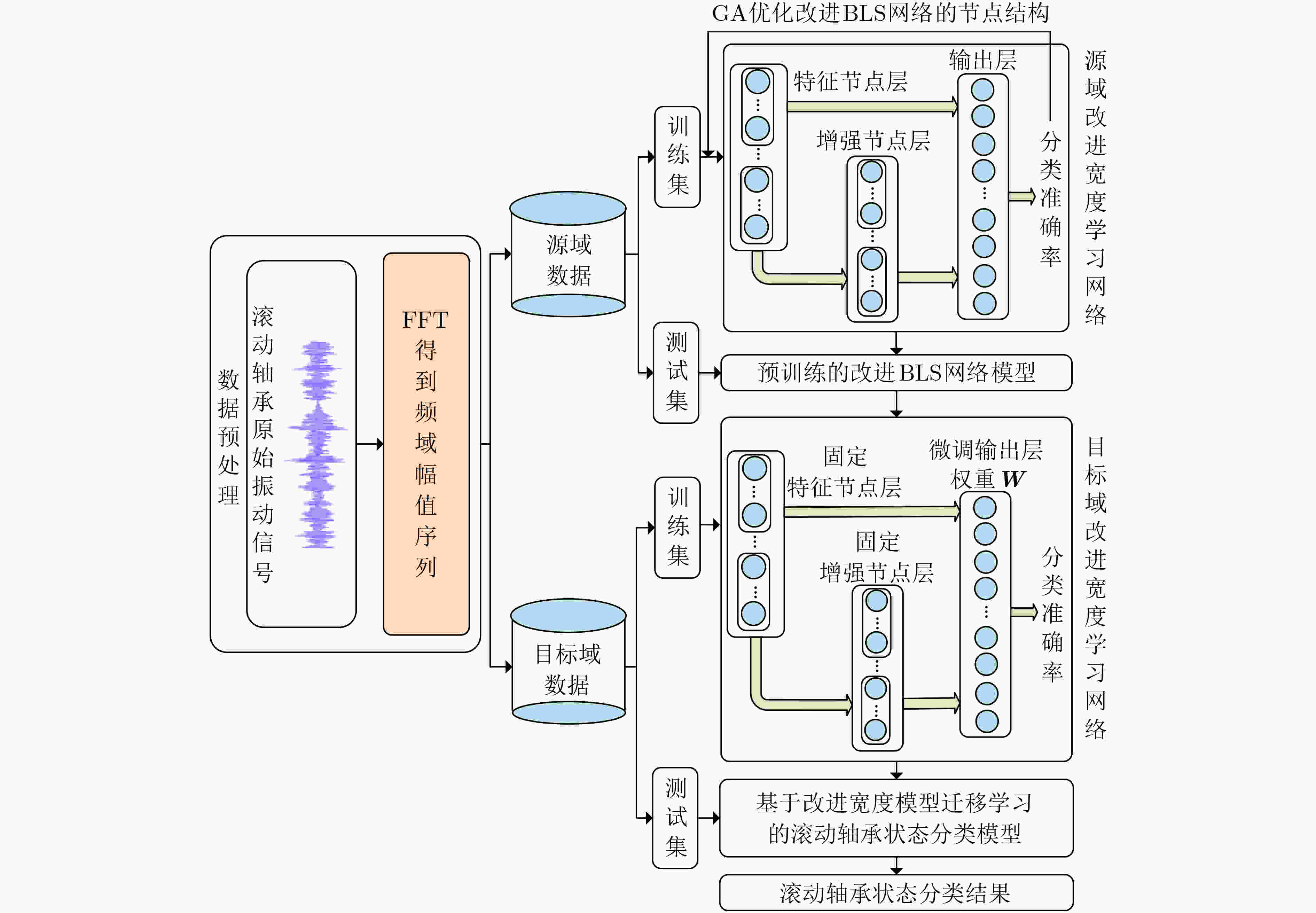
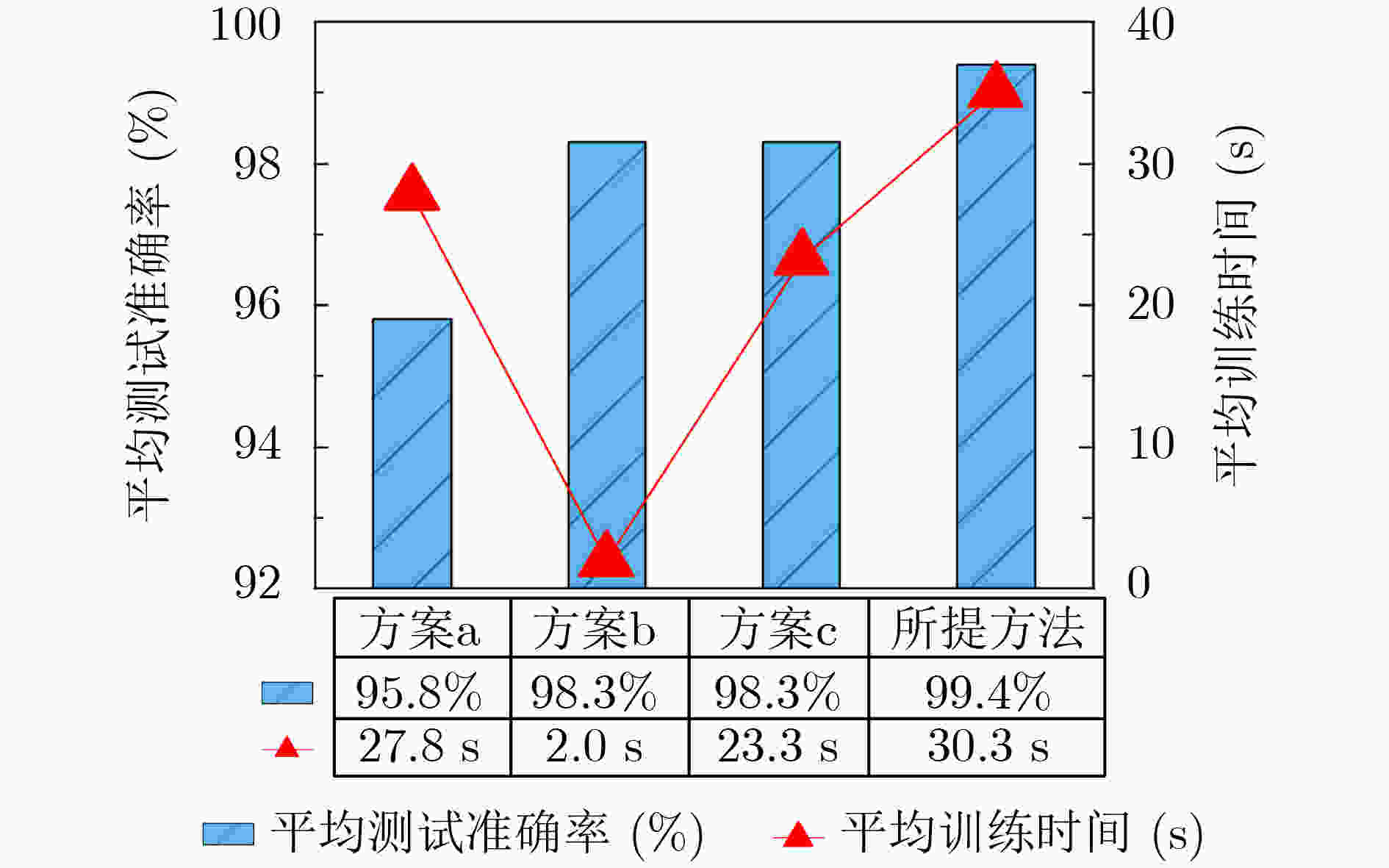
摘要: 针对深度学习网络训练耗时以及不同负载下滚动轴承的源域数据和目标域数据分布差异较大的问题,该文提出一种基于改进宽度模型迁移学习的滚动轴承状态快速分类方法。该方法首先对不同负载下滚动轴承振动信号进行快速傅里叶变换,构建频域幅值序列数据集,并选取某种或某些负载数据集作为源域,其他负载数据集作为目标域;其次以循环扩展的方式建立宽度学习系统(BLS)的增强节点窗口,并在增强层引入Maxout激活函数构建改进的BLS网络,同时引入遗传算法优化网络节点结构,建立基于源域数据的预训练模型;最后将预训练模型的网络参数、特征层和增强层的权重参数迁移至目标域网络,并利用少量目标域样本微调网络建立状态分类模型。实验结果表明,所提方法平均训练时间为32.6 s,平均测试准确率为98.9%。对比其他方法,所提方法可以在更短的时间内建立分类模型并获得良好的分类准确率。Abstract: For the training time of deep learning network is long, as well as larger distribution difference between source domain and target domain data of rolling bearings under different loads, a fast classification method of rolling bearing state based on improved broad model transfer learning is proposed. Fast Fourier transform is used to process the vibration signal of rolling bearing under different loads to construct frequency domain amplitude sequence data sets, from which a certain or some load data set is selected as the source domain, and other load data set is selected as the target domain. Secondly, an improved Broad Learning System (BLS) network is constructed by improving the way of building enhanced nodes windows of BLS in a cyclic extended way and introducing the Maxout activation function into the enhancement layer. At the same time, genetic algorithm is introduced to optimize the node structure of the improved BLS network. Then a pre-trained model based on source domain data is built. Finally, the network parameters, the weight parameters in feature layer and enhancement layer of the pre-trained model are transfered to target domain network, and a small amount target domain samples are used to fine-tune the network to build the state classification model. The experimental results show that the average training time of the proposed method is 32.6 s, and the average test accuracy is 98.9%. Compared with other methods, it could build a classification model in a shorter time and obtain good classification accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Rolling bearing /
- Fast classification /
- Broad Learning System (BLS) /
- Model transfer
-
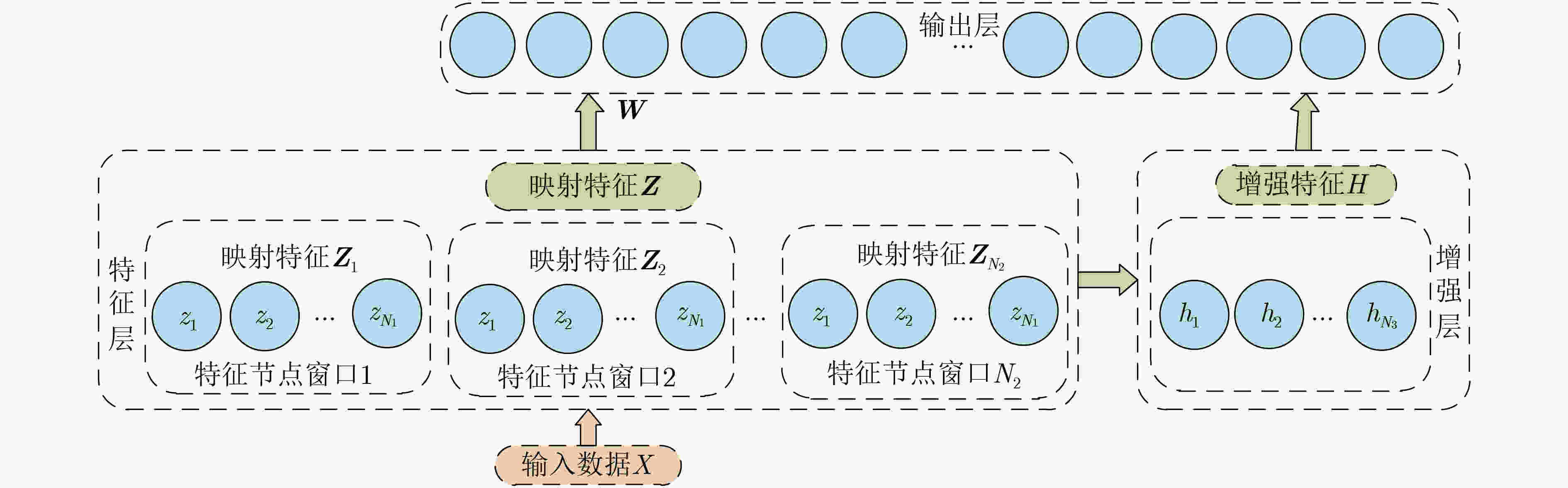
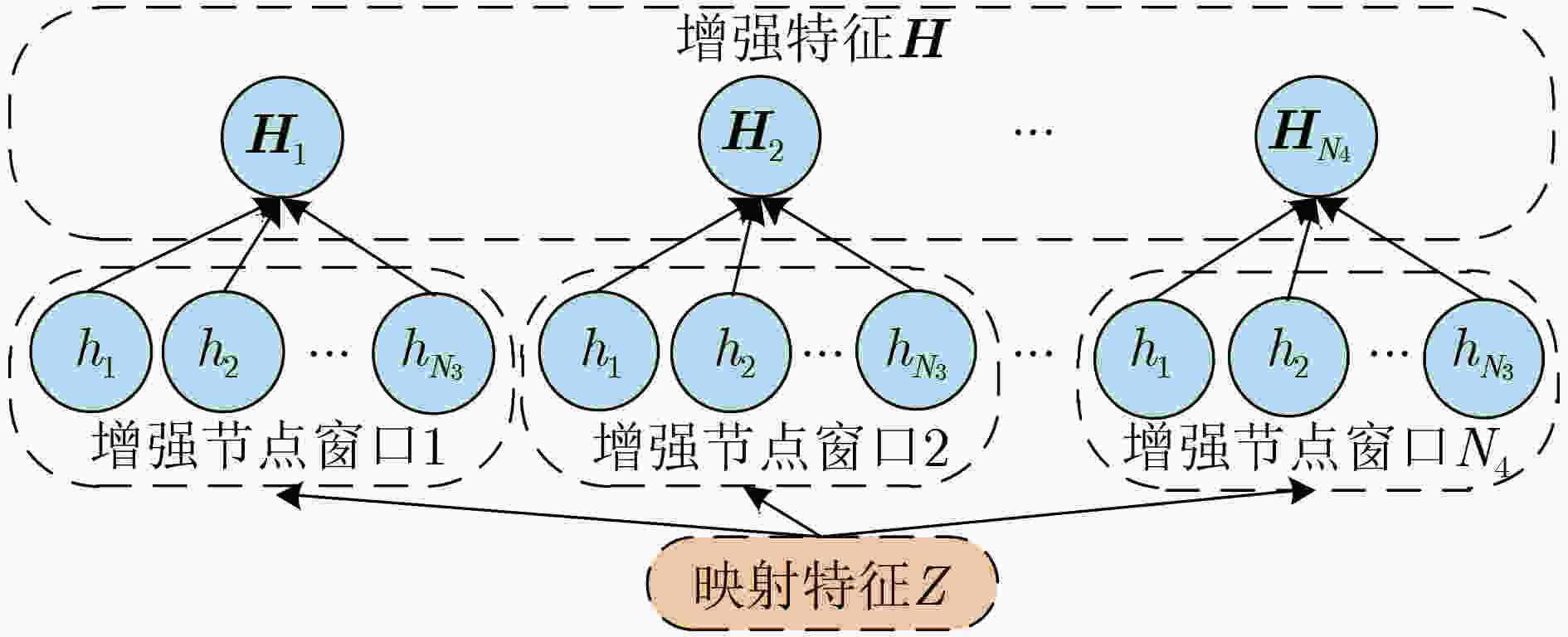
算法1 改进BLS网络获得增强特征算法 输入:映射特征Z 输出:增强特征H (1) for n = 1 to N4 //n表示增强节点窗口数目,N4表示增强节
点窗口的最大数目(2) 随机生成${W_{{h_k}}}$并对${W_{{h_k}}}$进行正交规范化 (3) OutofEachWindow←np.dot(Z×${{\boldsymbol{W}}_{{h_k}}}$+$ {{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _{{h_k}}} $) //$ {{\boldsymbol{\beta}} _{{h_k}}} $表示偏
置,随机生成(4) OutofAllWindow[:,n:n+1]←np.max
(OutofEachWindow, axis=1)(5) end for (6) H←OutofAllWindow 表 1 迁移任务构成
迁移任务 源域样本集负载 (kW) 目标域样本集负载 (kW) 源域样本数 (个) 目标域样本数 (个) 总样本数 (个) 2_3 1.50 2.25 600 600 1200 2_13 1.50 1.50, 2.25 600 1200 1800 3_012 2.25 0, 0.75, 1.50 600 1800 2400 13_2 0.75, 2.25 1.50 1200 600 1800 02_13 0, 1.50 0.75, 2.25 1200 1200 2400 023_1 0, 1.50, 2.25 0.75 1800 600 2400 表 2 BLS网络改进前后实验结果
网络模型 平均测试准确率 (%) 平均训练时间 (s) 基于BLS网络的迁移模型 97.0 27.4 基于改进BLS网络的
迁移模型98.4 35.1 表 3 随机设置的5组网络参数
组数 N1 N2 N3 N4 1 5 1 30 10 2 30 40 5 20 3 50 20 40 30 4 20 5 10 40 5 10 30 20 50 表 4 模型迁移前后实验结果
是否迁移 平均测试准确率 (%) 平均训练时间 (s) 是 98.4 35.1 否 90.1 29.1 表 5 迁移任务构成 (MFPT数据库)
迁移任务 源域样本集 目标域样本集 源域样本数 (个) 目标域样本数 (个) 总样本数 (个) A_C A C 180 180 360 A_CD A C D 180 360 540 D_ABC D A B C 180 540 720 CD_B C D B 360 180 540 AB_CD A B C D 360 360 720 ACD_B A C D B 540 180 720 -
[1] SOHAIB M and KIM J M. Fault diagnosis of rotary machine bearings under inconsistent working conditions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(6): 3334–3347. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2933342 [2] 孙瑾铃, 张伟涛, 楼顺天. 基于等变化自适应源分离算法的滚动轴承故障信号自适应盲提取[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(10): 2471–2477. doi: 10.11999/JEJT190722SUN Jinling, ZHANG Weitao, and LOU Shuntian. Adaptive blind extraction of rolling bearing fault signal based on equivariant adaptive separation via independence[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(10): 2471–2477. doi: 10.11999/JEJT190722 [3] 王玉静, 康守强, 张云, 等. 基于集合经验模态分解敏感固有模态函数选择算法的滚动轴承状态识别方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(3): 595–600. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00434WANG Yujing, KANG Shouqiang, ZHANG Yun, et al. Condition recognition method of rolling bearing based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition sensitive intrinsic mode function selection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(3): 595–600. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2013.00434 [4] WANG Jianyu, MO Zhenling, ZHANG Heng, et al. A deep learning method for bearing fault diagnosis based on time-frequency image[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 42373–42383. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907131 [5] 文成林, 吕菲亚. 基于深度学习的故障诊断方法综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(1): 234–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190715WEN Chenglin and LÜ Feiya. Review on deep learning based fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(1): 234–248. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190715 [6] GAO Shuzhi, XU Lintao, ZHANG Yimin, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis based on intelligent optimized self-adaptive deep belief network[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2020, 31(5): 055009. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab50f0 [7] WANG Huan, LIU Zhiliang, PENG Dandan, et al. Understanding and learning discriminant features based on multiattention 1DCNN for wheelset bearing fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(9): 5735–5745. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2955540 [8] ZHANG Ran, TAO Hongyang, WU Lifeng, et al. Transfer learning with neural networks for bearing fault diagnosis in changing working conditions[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 14347–14357. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2720965 [9] 康守强, 邢颖怡, 王玉静, 等. 基于无监督深度模型迁移的滚动轴承寿命预测方法[J]. 自动化学报, 待发表.KANG Shouqiang, XING Yingyi, WANG Yujing, et al. Rolling bearing life prediction based on unsupervised deep model transfer[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, To be published. [10] 于洋, 何明, 刘博, 等. 基于TL-LSTM的轴承故障声发射信号识别研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2019, 40(5): 51–59. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1904766YU Yang, HE Ming, LIU Bo, et al. Research on acoustic emission signal recognition of bearing fault based on TL-LSTM[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2019, 40(5): 51–59. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.J1904766 [11] CHEN C L Philip and LIU Zhulin. Broad learning system: An effective and efficient incremental learning system without the need for deep architecture[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(1): 10–24. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2716952 [12] FENG Jian, YAO Yu, LU Senxiang, et al. Domain knowledge-based deep-broad learning framework for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 68(4): 3454–3464. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2020.2982085 [13] FU Yang, CAO Hongrui, and CHEN Xuefeng. Adaptive broad learning system for high-efficiency fault diagnosis of rotating machinery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1–11. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3085940 [14] YAN Ruqiang, SHEN Fei, SUN Chuang, et al. Knowledge transfer for rotary machine fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20(15): 8374–8393. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2019.2949057 [15] YOSINSKI J, CLUNE J, BENGIO Y, et al. How transferable are features in deep neural networks?[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2014: 3320–3328. [16] LOPARO K A. Bearing data center[EB/OL]. https://engineering.case.edu/bearingdatacenter, 2019. [17] 王玉静, 那晓栋, 康守强, 等. 基于EEMD-Hilbert包络谱和DBN的变负载下滚动轴承状态识别方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2017, 37(23): 6943–6950. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.162418WANG Yujing, NA Xiaodong, KANG Shouqiang, et al. State recognition method of a rolling bearing based on EEMD-Hilbert envelope spectrum and DBN under variable load[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2017, 37(23): 6943–6950. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.162418 [18] KANG Shouqiang, CHEN Weiwei, WANG Yujing, et al. Method of state identification of rolling bearings based on deep domain adaptation under varying loads[J]. IET Science, Measurement & Technology, 2020, 14(3): 303–313. doi: 10.1049/iet-smt.2019.0043 [19] WANG Yujing, WANG Chao, KANG Shouqiang, et al. Network-combined broad learning and transfer learning: A new intelligent fault diagnosis method for rolling bearings[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2020, 31(11): 115013. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab8fee [20] BECHHOEFER E. Bearing fault dataset[EB/OL]. https://mfpt.org/fault-data-sets/, 2019. -





 下载:
下载:
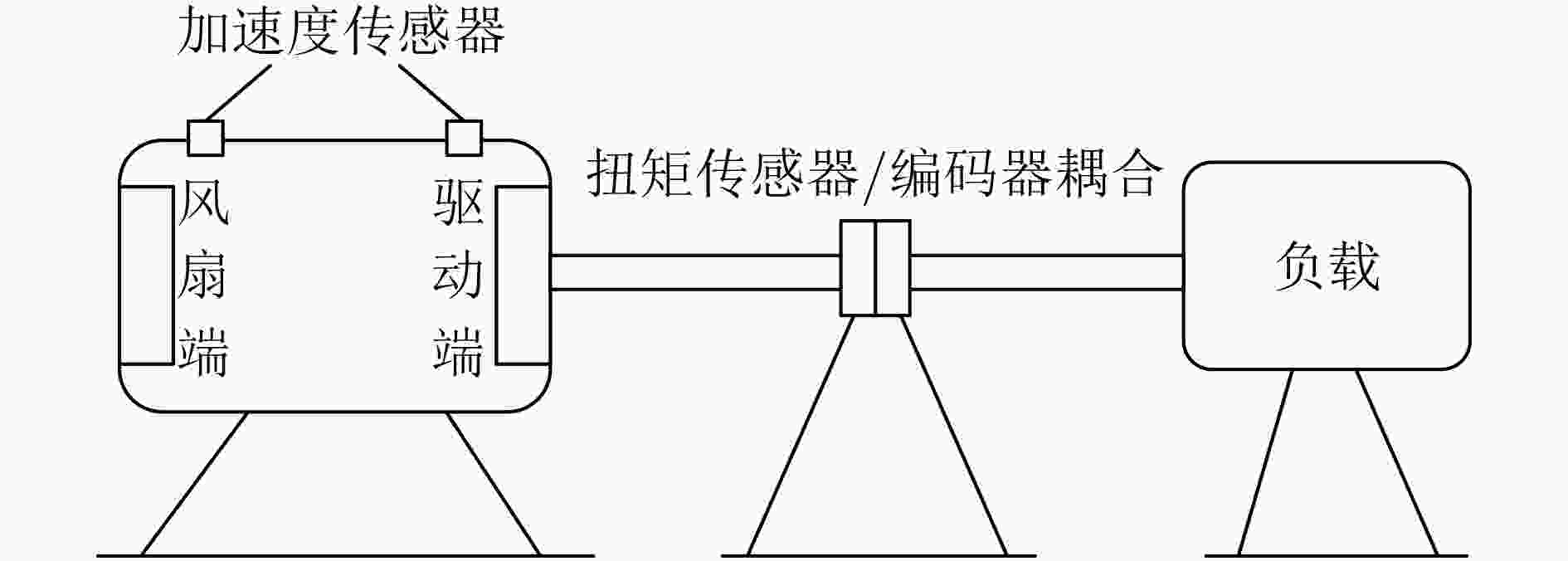
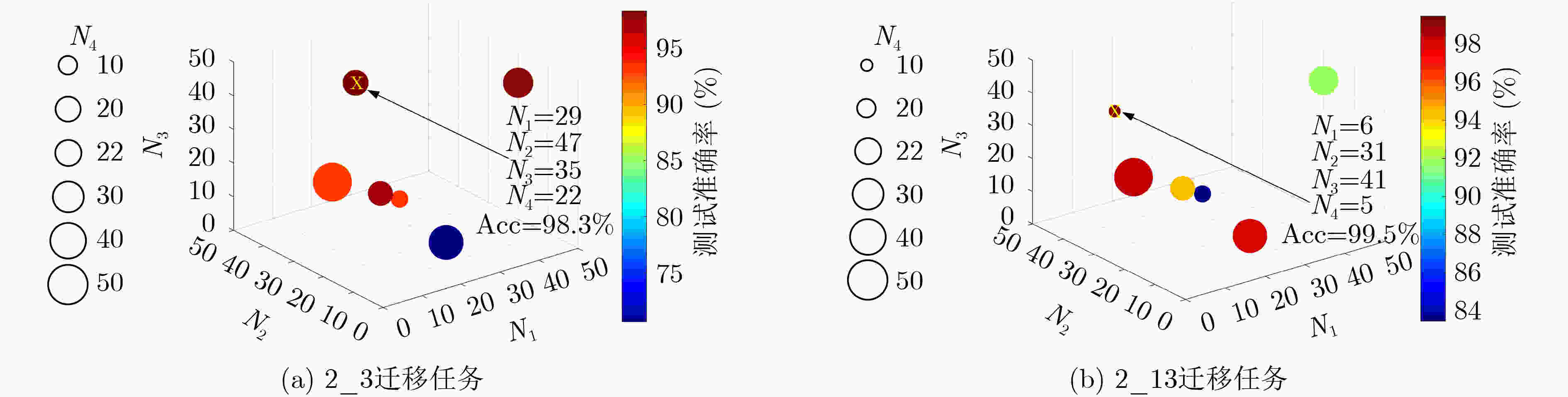
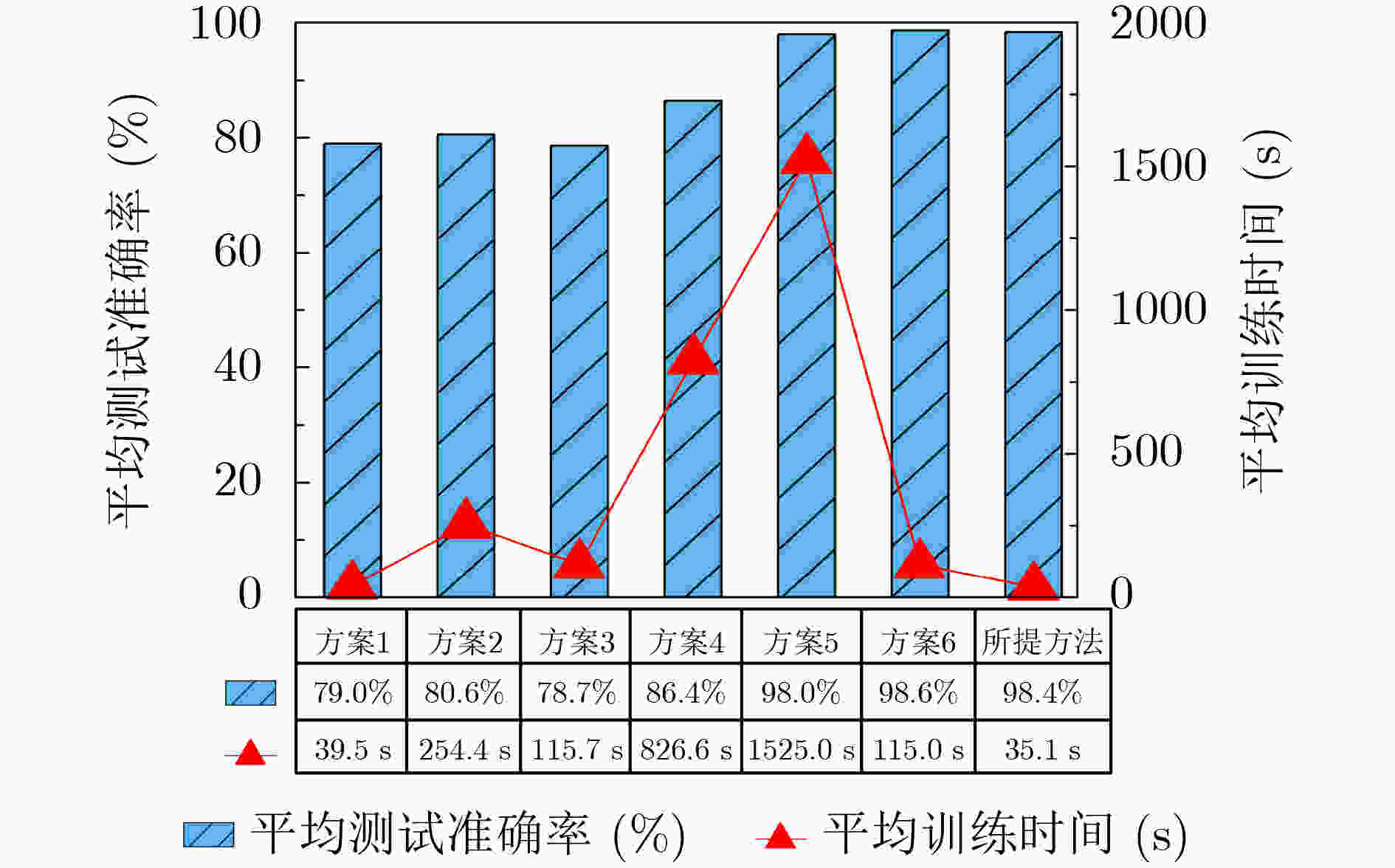
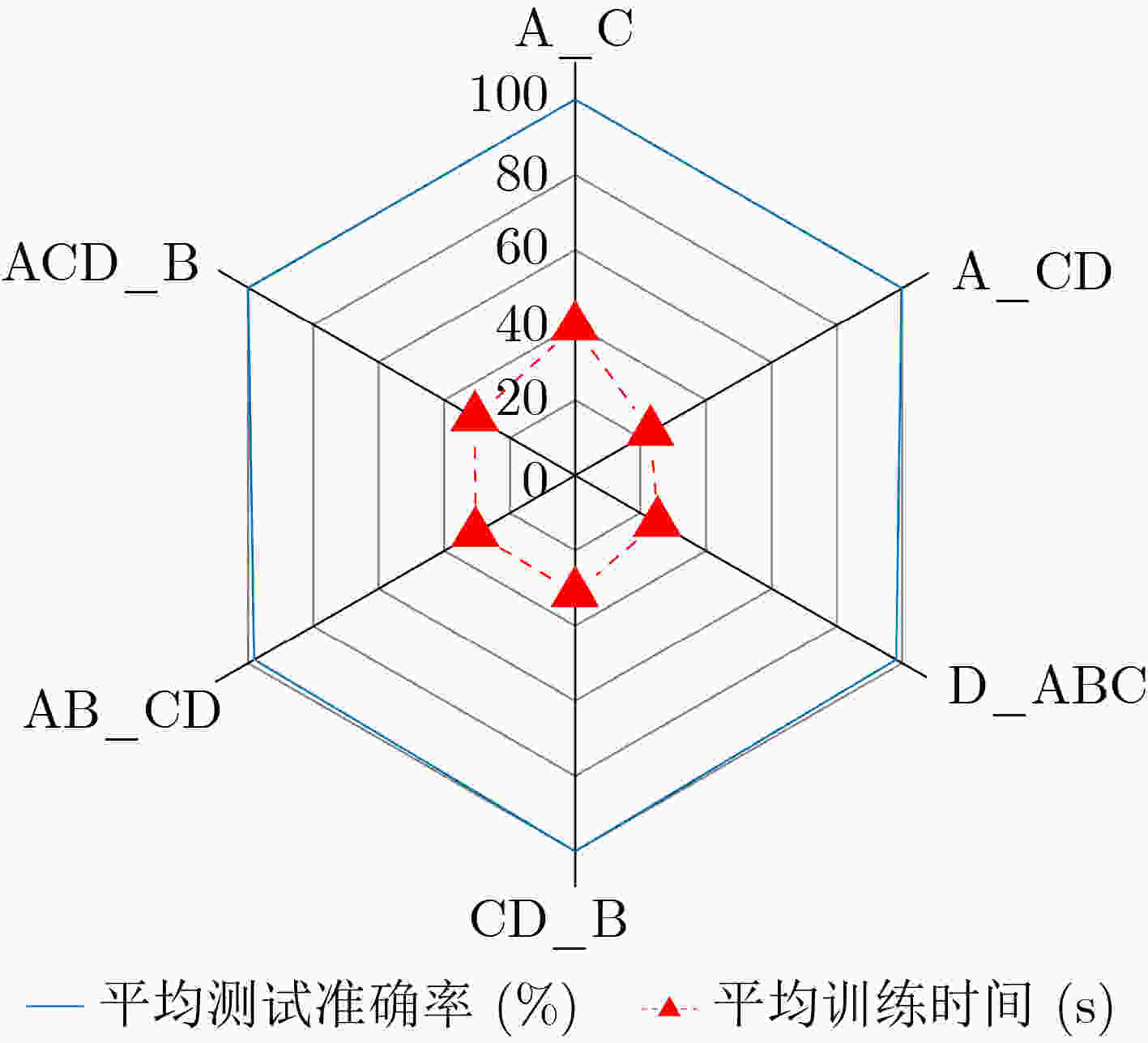


 下载:
下载:
