Blind Image Super-resolution Reconstruction via Iterative and Alternative Optimization
-
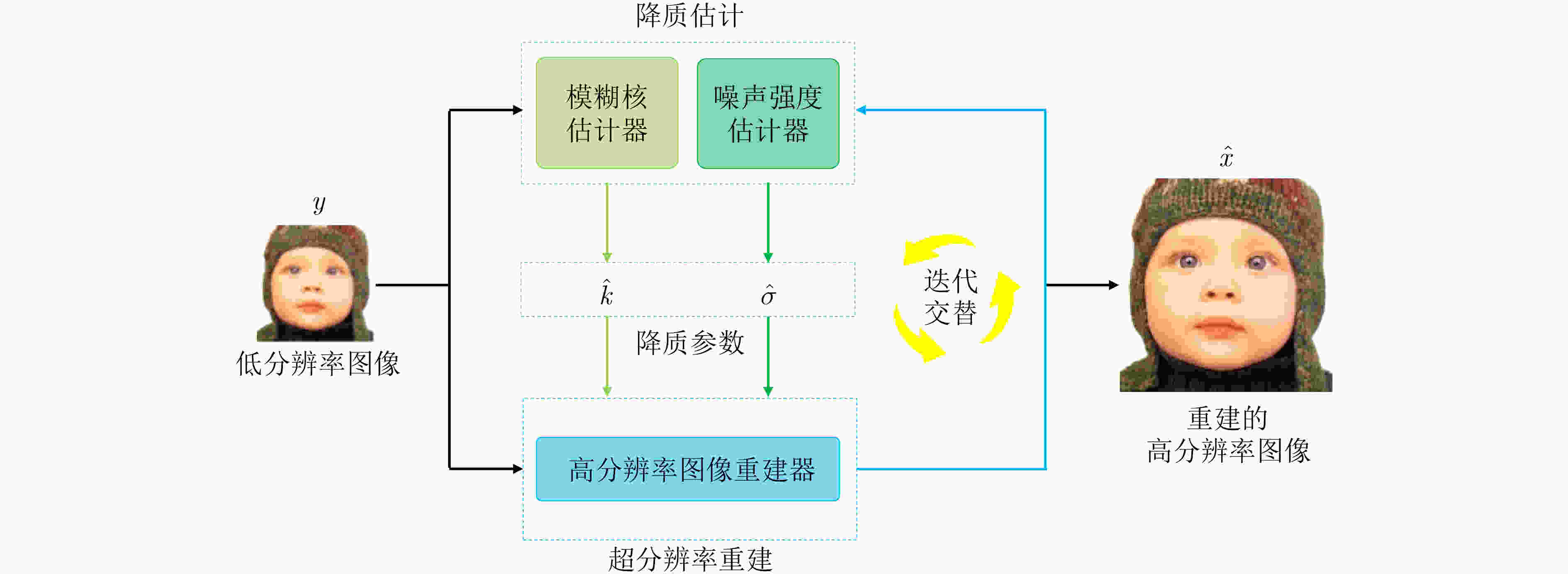
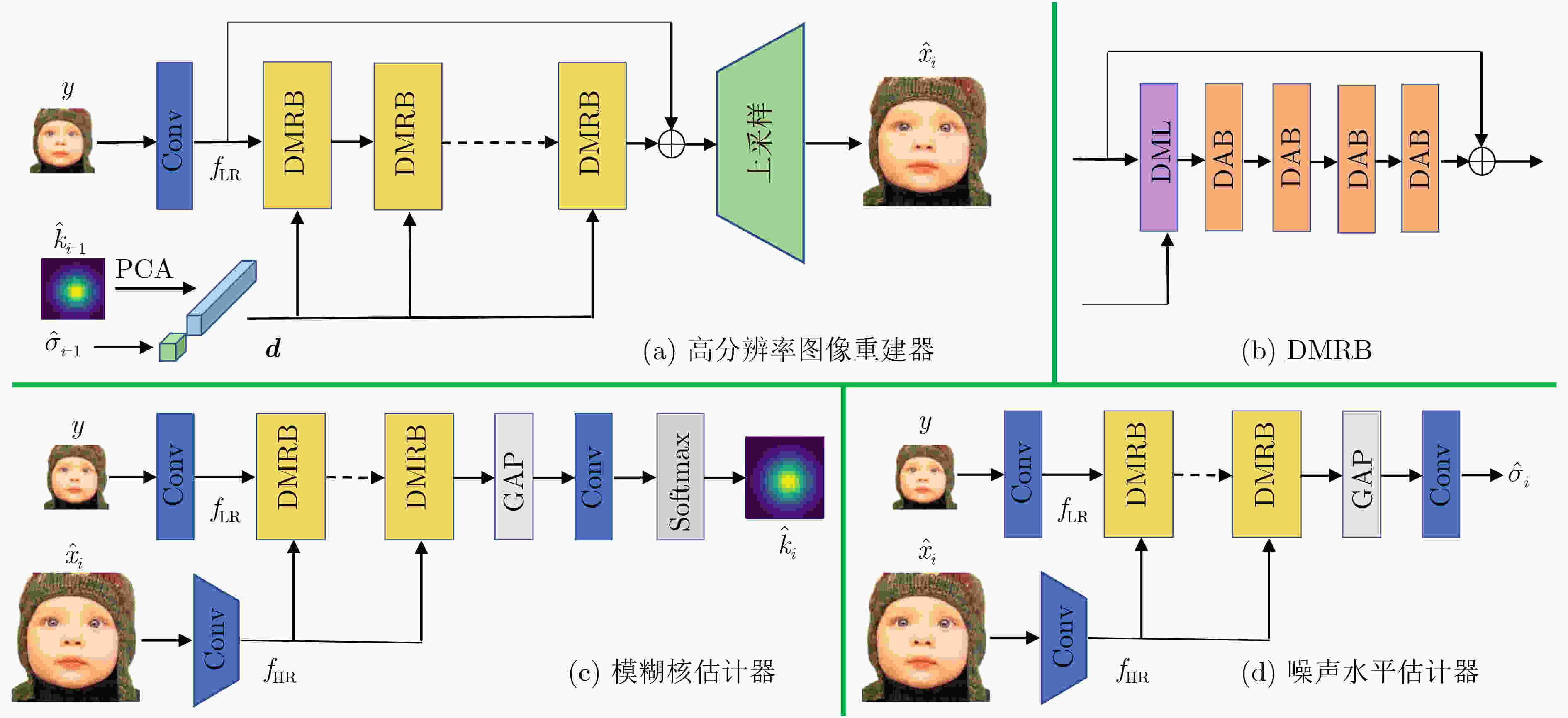
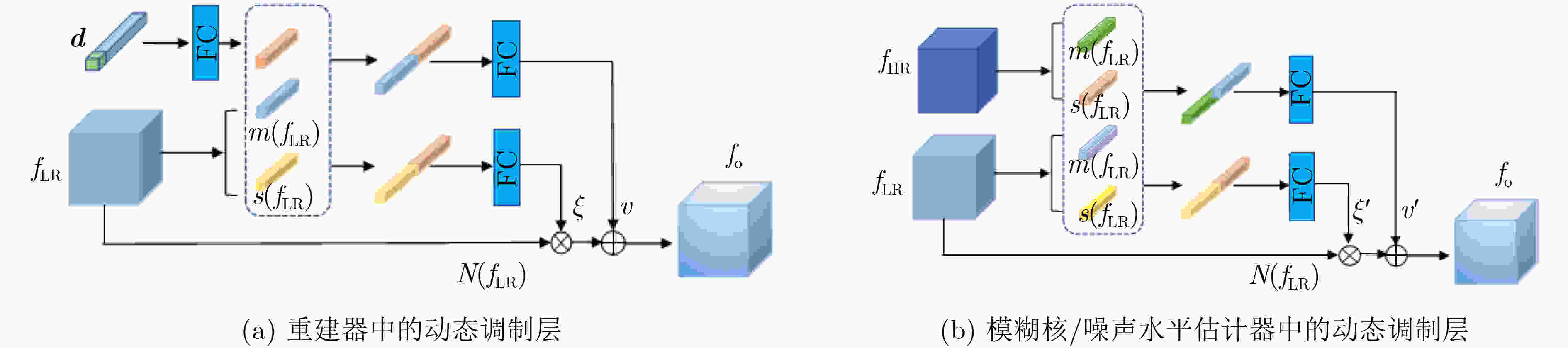
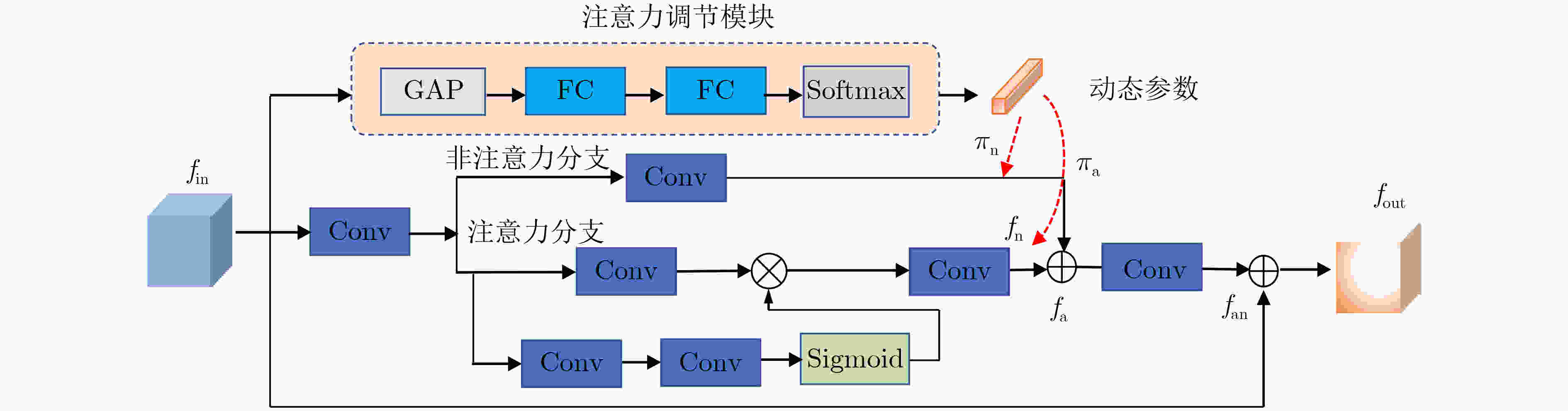
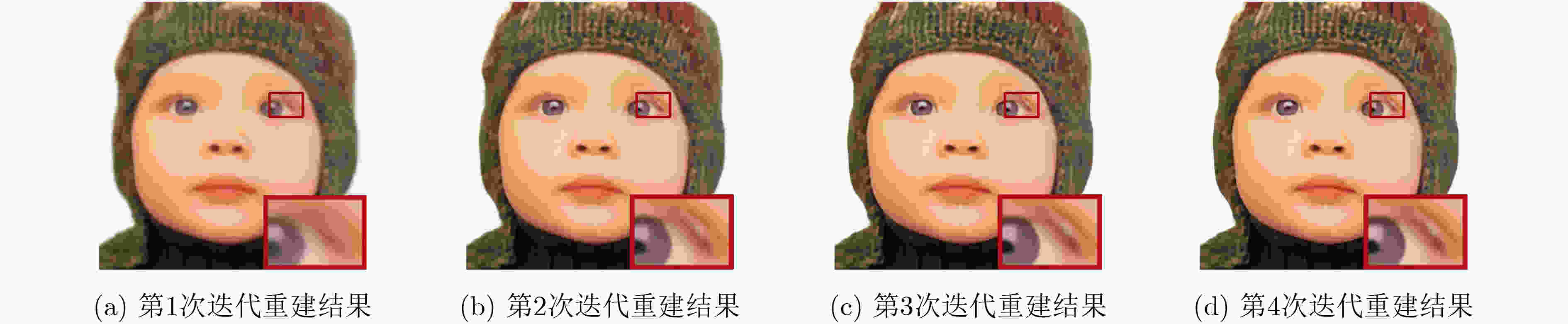
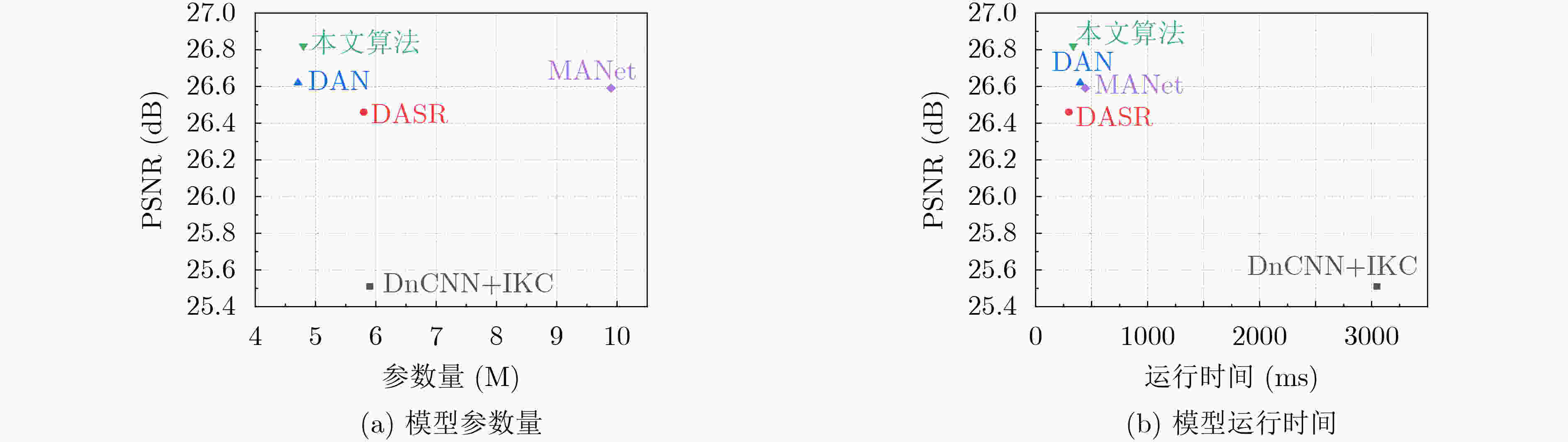
摘要: 基于深度卷积神经网络的图像超分辨率重建算法通常假设低分辨率图像的降质是固定且已知的,如双3次下采样等,因此难以处理降质(如模糊核及噪声水平)未知的图像。针对此问题,该文提出联合估计模糊核、噪声水平和高分辨率图像,设计了一种基于迭代交替优化的图像盲超分辨率重建网络。在所提网络中,图像重建器以估计的模糊核和噪声水平作为先验信息,由低分辨率图像重建出高分辨率图像;同时,综合低分辨率图像和估计的高分辨率图像,模糊核及噪声水平估计器分别实现模糊核和噪声水平的估计。进一步地,该文提出对模糊核/噪声水平估计器及图像重建器进行迭代交替的端对端优化,以提高它们的兼容性并使其相互促进。实验结果表明,与IKC, DASR, MANet, DAN等现有算法相比,提出方法在常用公开测试集(Set5, Set14, B100, Urban100)及真实场景图像上都取得了更优的性能,能够更好地对降质未知的图像进行重建;同时,提出方法在参数量或处理效率上也有一定的优势。Abstract: Deep convolutional neural network-based image Super-Resolution (SR) methods assume generally that the degradations of Low-Resolution (LR) images are fixed and known (e.g., bicubic downsampling). Thus, they are almost unable to super-resolve images with unknown degradations (e.g., blur kernel and noise level). To address this problem, an iterative and alternative optimization-based blind image SR network is proposed, in which the blur kernel, noise level, and High-Resolution (HR) image are jointly estimated. Specifically, in the proposed method, the image reconstruction network reconstructs an HR image from the given LR image using the estimated blur kernel and noise level as prior knowledge. Correspondingly, the blur kernel and noise level estimators estimate the blur kernel and noise level respectively from the given LR image and the reconstructed HR image. To improve compatibility and promote each other mutually, the blur kernel estimator, noise level estimator, and image reconstruction network are iteratively and alternatively optimized in an end-to-end manner. The proposed network is compared with state-of-the-art methods (i.e., IKC, DASR, MANet, DAN) on commonly used benchmarks (i.e., Set5, Set14, B100, and Urban100) and real-world images. Results show that the proposed method achieves better performance on LR images with unknown degradations. Moreover, the proposed method has advantages in model size or processing efficiency.
-
表 1 2倍重建结果的客观参数PSNR(dB)/SSIM比较
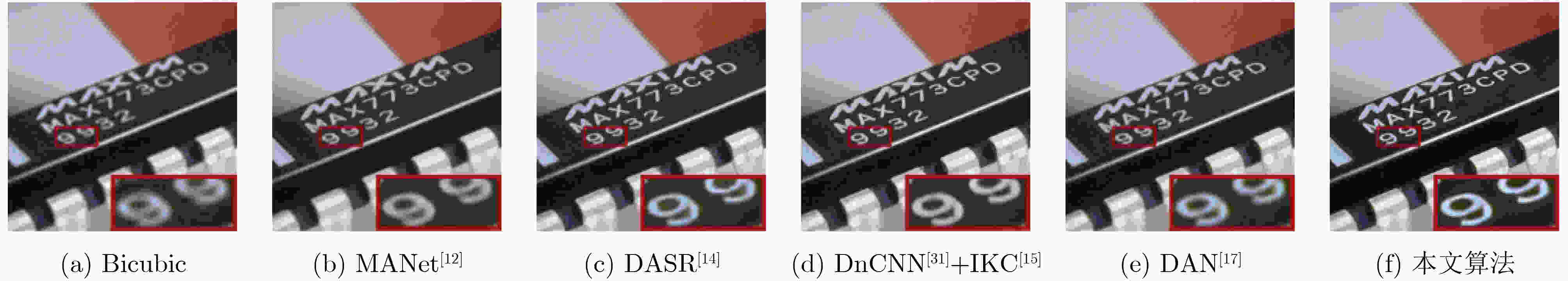
方法 噪声水平 Set5[27] Set14[28] B100[29] Urban100[30] Bicubic 5 30.07/0.8442 27.61/0.7620 27.23/0.7262 24.61/0.7253 10 28.85/0.7709 26.85/0.6979 26.51/0.6601 24.19/0.6637 MANet[12] 5 33.60/0.9101 30.53/0.8407 29.45/0.8056 28.31/0.8513 10 32.15/0.8871 29.42/0.8048 28.40/0.7629 27.31/0.8202 DASR[14] 5 33.35/0.9078 30.22/0.8325 29.12/0.7947 27.66/0.8364 10 31.95/0.8855 29.21/0.8003 28.21/0.7563 26.89/0.8107 DnCNN[31]+IKC[15] 5 31.69/0.8824 29.27/0.8118 28.67/0.7826 26.79/0.8089 10 30.85/0.8652 28.53/0.7817 27.90/0.7463 26.12/0.7830 DAN[17] 5 33.83/0.9132 30.69/0.8430 29.52/0.8081 28.62/0.8566 10 32.32/0.8902 29.53/0.8072 28.45/0.7650 27.56/0.8256 本文算法 5 33.98/0.9153 30.85/0.8492 29.66/0.8140 28.79/0.8609 10 32.39/0.8912 29.64/0.8110 28.54/0.7683 27.68/0.8283 表 2 4倍重建结果的客观参数PSNR(dB)/SSIM比较
方法 噪声水平 Set5[27] Set14[28] B100[29] Urban100[30] Bicubic 5 25.84/0.7162 24.29/0.6144 24.53/0.5825 21.70/0.5644 10 25.30/0.6728 23.91/0.5768 24.12/0.5438 21.48/0.5286 MANet[12] 5 29.01/0.8242 26.59/0.6983 26.01/0.6507 24.01/0.6922 10 27.77/0.7928 25.74/0.6672 25.37/0.6207 23.36/0.6605 DASR[14] 5 28.85/0.8214 26.46/0.6966 25.94/0.6494 23.72/0.6880 10 27.73/0.7921 25.69/0.6676 25.32/0.6207 23.16/0.6605 DnCNN[31]+IKC[15] 5 27.26/0.7619 25.51/0.6604 25.38/0.6218 22.92/0.6332 10 26.65/0.7493 25.03/0.6390 24.96/0.6008 22.53/0.6140 DAN[17] 5 29.01/0.8238 26.62/0.6980 26.02/0.6507 24.02/0.6903 10 27.84/0.7947 25.85/0.6698 25.39/0.6223 23.44/0.6630 本文算法 5 29.32/0.8300 26.82/0.7060 26.16/0.6584 24.29/0.7036 10 28.05/0.7999 25.98/0.6738 25.48/0.6260 23.61/0.6712 -
[1] 蔡文郁, 张美燕, 吴岩, 等. 基于循环生成对抗网络的超分辨率重建算法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 178–186. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201046CAI Wenyu, ZHANG Meiyan, WU Yan, et al. Research on cyclic generation countermeasure network based super-resolution image reconstruction algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 178–186. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201046 [2] ZHANG Xiangjun and WU Xiaolin. Image interpolation by adaptive 2-D autoregressive modeling and soft-decision estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(6): 887–896. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2008.924279 [3] ZHANG Kaibing, GAO Xinbo, TAO Dacheng, et al. Single image super-resolution with non-local means and steering kernel regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(11): 4544–4556. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2208977 [4] DONG Chao, LOY C C, HE Kaiming, et al. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 2014: 184–199. [5] CHEN Hanting, WANG Yunhe, GUO Tianyu, et al. Pre-trained image processing transformer[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 12299–12310. [6] LIANG Jingyun, CAO Jiezhang, SUN Guolei, et al. SwinIR: Image restoration using swin transformer[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1833–1844. [7] ZHANG Kai, LIANG Jingyun, VAN GOOL L, et al. Designing a practical degradation model for deep blind image super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 4791–4800. [8] WANG Xintao, XIE Liangbin, DONG Chao, et al. Real-ESRGAN: Training real-world blind super-resolution with pure synthetic data[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 1905–1914. [9] BELL-KLIGLER S, SHOCHER A, and IRANI M. Blind super-resolution kernel estimation using an internal-GAN[C]. Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, Canada, 2019: 284–293. [10] LIANG Jingyun, ZHANG Kai, GU Shuhang, et al. Flow-based kernel prior with application to blind super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10601–10610. [11] TAO Guangpin, JI Xiaozhong, WANG Wenzhuo, et al. Spectrum-to-kernel translation for accurate blind image super-resolution[C/OL]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021: 34. [12] LIANG Jingyun, SUN Guolei, ZHANG Kai, et al. Mutual affine network for spatially variant kernel estimation in blind image super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, Canada, 2021: 4096–4105. [13] KIM J, JUNG C, and KIM C. Dual back-projection-based internal learning for blind super-resolution[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 1190–1194. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.3005043 [14] WANG Longguang, WANG Yingqian, DONG Xiaoyu, et al. Unsupervised degradation representation learning for blind super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 10581–10590. [15] GU Jinjin, LU Hannan, ZUO Wangmeng, et al. Blind super-resolution with iterative kernel correction[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1604–1613. [16] LUO Zhengxiong, HUANG Yan, LI Shang, et al. Unfolding the alternating optimization for blind super resolution[C/OL]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020: 5632–5643. [17] LUO Zhengxiong, HUANG Yan, LI Shang, et al. End-to-end alternating optimization for blind super resolution[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.06878v1, 2021. [18] WANG Zhihao, CHEN Jian, and HOI S C H. Deep learning for image super-resolution: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(10): 3365–3387. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2982166 [19] CHEN Honggang, HE Xiaohai, QING Linbo, et al. Real-world single image super-resolution: A brief review[J]. Information Fusion, 2022, 79: 124–145. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.09.005 [20] LIU Anran, LIU Yihao, GU Jinjin, et al. Blind image super-resolution: A survey and beyond[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.03055, 2021. [21] HUI Zheng, LI Jie, WANG Xiumei, et al. Learning the non-differentiable optimization for blind super-resolution[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 2093–2102. [22] CHEN Haoyu, GU Jinjin, and ZHANG Zhi. Attention in attention network for image super-resolution[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09497v3, 2021. [23] GUO Shi, YAN Zifei, ZHANG Kai, et al. Toward convolutional blind denoising of real photographs[C]. Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1712–1722. [24] AGUSTSSON E and TIMOFTE R. NTIRE 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Dataset and study[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 126–135. [25] TIMOFTE R, AGUSTSSON E, VAN GOOL L, et al. NTIRE 2017 challenge on single image super-resolution: Methods and results[C]. Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 114–125. [26] KINGMA D P and BA J. ADAM: A method for stochastic optimization[C]. 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations, San Diego, USA, 2014. [27] BEVILACQUA M, ROUMY A, GUILLEMOT C, et al. Low-complexity single-image super-resolution based on nonnegative neighbor embedding[C]. British Machine Vision Conference, Surrey, United Kingdom, 2012. [28] ZEYDE R, ELAD M, and PROTTER M. On single image scale-up using sparse-representations[C]. 7th International Conference on Curves and Surfaces, Avignon, France, 2010: 711–730. [29] MARTIN D, FOWLKES C, TAL D, et al. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics[C]. Proceedings Eighth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Vancouver, Canada, 2001: 416–423. [30] HUANG J B, SINGH A, and AHUJA N. Single image super-resolution from transformed self-exemplars[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 5197–5206. [31] ZHANG Kai, ZUO Wangmeng, CHEN Yunjin, et al. Beyond a gaussian denoiser: Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7): 3142–3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
