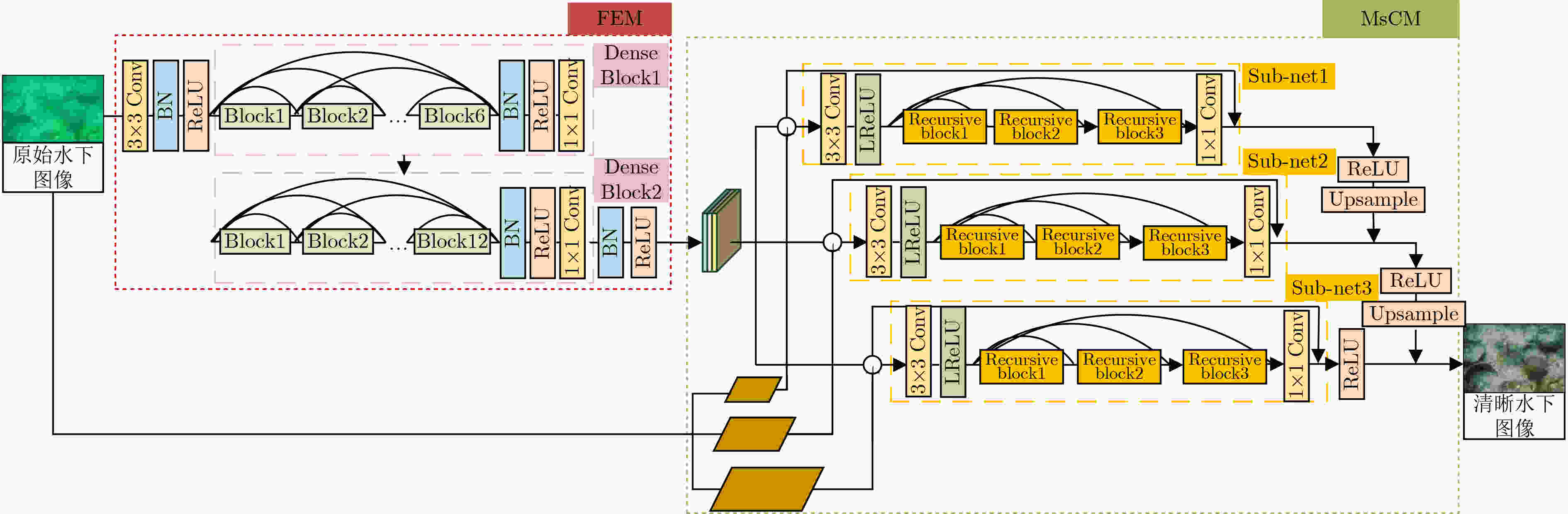
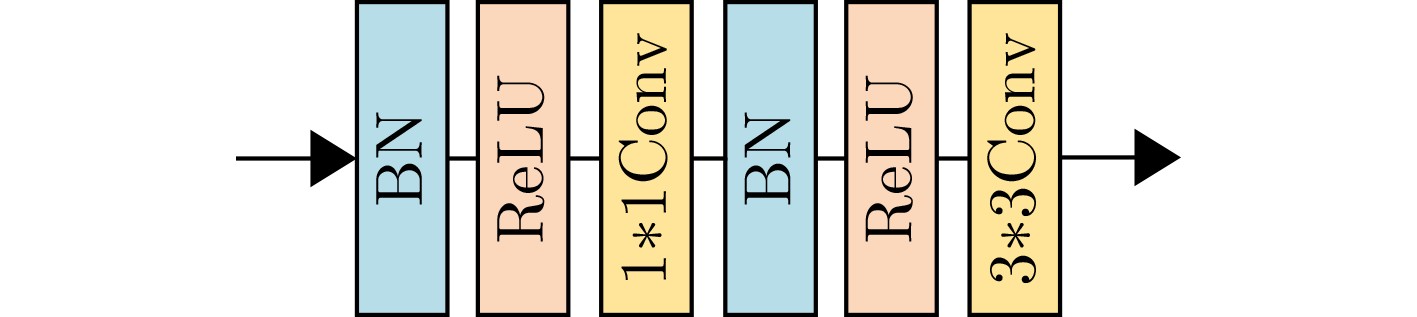
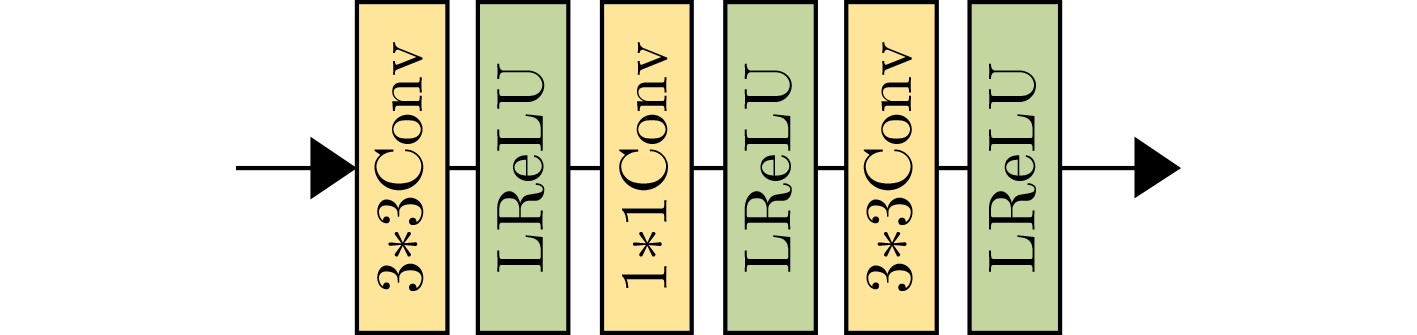
Underwater Image Enhancement Method Based on Multi-scale Cascade Network
-
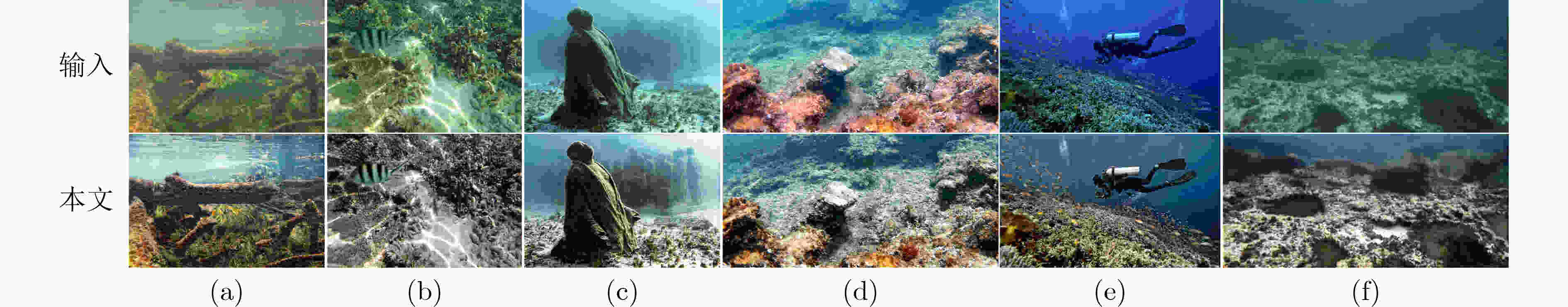
摘要: 针对水下图像由于光吸收、后向散射等因素导致的严重色偏、细节丢失等问题,该文提出一种基于多尺度级联网络的水下图像增强方法。针对单一网络特征利用不全面导致的图像梯度消失问题,该方法通过级联多尺度原始图像与相应的特征图像,以获得更优异的细节保持效果,并实现从较浅层到较深层快速预测残差的能力。此外,引入联合密集网络块和递归块,通过特征重用有效解决多尺度网络参数过多的问题。为有效解决单一损失造成的图像细节恢复不均的问题,提出Charbonnier和结构相似度 (SSIM) 联合损失函数。经仿真实验分析,所提网络在处理水下图像严重色偏、细节丢失等方面都取得了显著的效果。Abstract: Focusing on the serious color shift and loss of details caused by light absorption, backscattering and other factors in underwater images, an underwater image enhancement method based on multi-scale cascaded network is proposed in this paper. For the image gradient dissipation caused by incomplete utilization of features via single network, better details are preserved by cascading multi-scale original images and corresponding feature images, and rapid prediction of residuals from shallower layers to deeper layers can be realized at the same time. In addition, joint dense network block and recursive block are introduced to avoid effectively the problem of excessive parameters introduced by conventional multi-scale network through feature reuse. A joint loss function of Charbonnier and the Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) is proposed to solve effectively the problem of uneven restoration of image details caused by a single loss. The simulation experiments show that the proposed network has achieved excellent results in dealing with severe color shift and loss of details.
-
表 1 4种不同水下数据集的划分
UIEB EUVP1 EUVP2 EUVP3 训练图像对 790 4995 3330 1966 测试图像对 100 555 370 219 总图像对 890 5550 3700 2185 表 2 对网络框架结构的定量评价
PSNR SSIM Blur PCQI A + C 21.1980 0.6925 0.2742 0.9553 A + B + C 21.1722 0.7017 0.2702 0.9385 表 3 对多尺度子网络层数的定量评价
PSNR SSIM Blur PCQI 2层 20.3955 0.6789 0.2653 0.9370 3层(本文) 21.1722 0.7017 0.2702 0.9385 4层 20.6914 0.6981 0.2777 0.9628 5层 19.6474 0.6290 0.2741 0.9220 表 4 对多尺度子网络中递归块的定量评价
块数 PSNR SSIM Blur PCQI 2 20.3971 0.6776 0.2733 0.9551 3(本文) 21.1722 0.7017 0.2702 0.9385 4 21.4235 0.7000 0.2799 0.9435 表 5 对损失函数的定量评价
PSNR SSIM Blur PCQI l1 7.1387 0.0028 NaN 0.1345 Charbonnier 21.2840 0.6687 0.2707 0.9194 l1 + SSIM 7.1387 0.0028 NaN 0.1345 Charbonnier + SSIM(本文) 21.1722 0.7017 0.2702 0.9385 表 6 在4种数据集上的PSNR定量评价(dB)
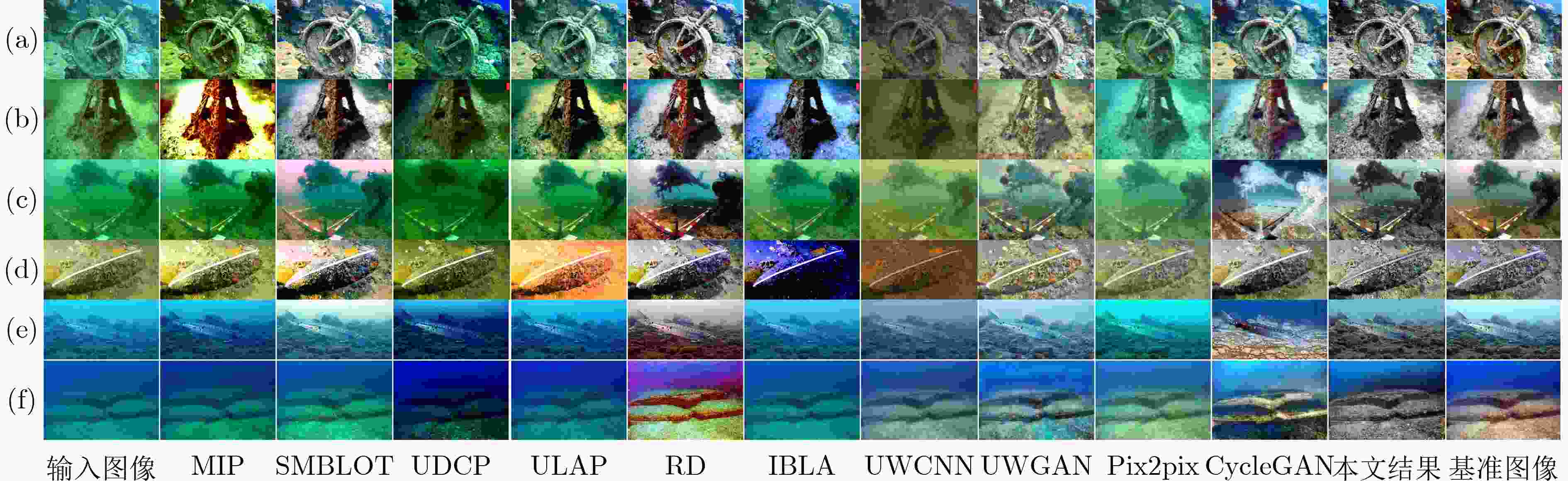
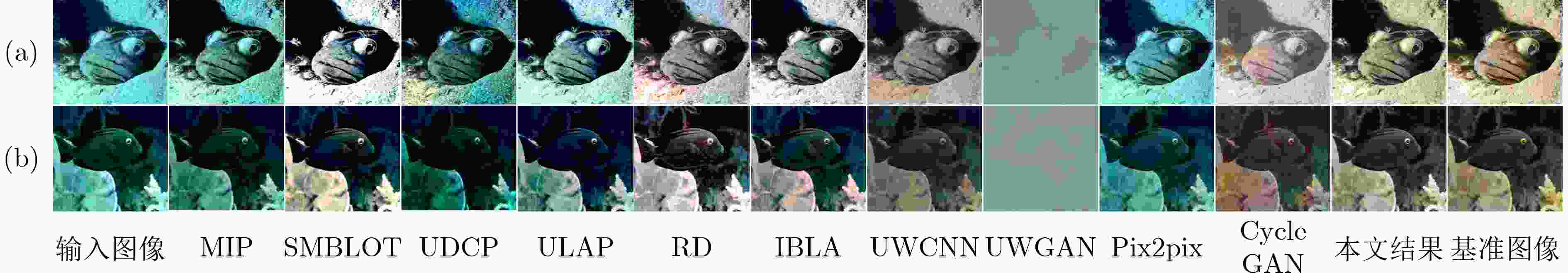
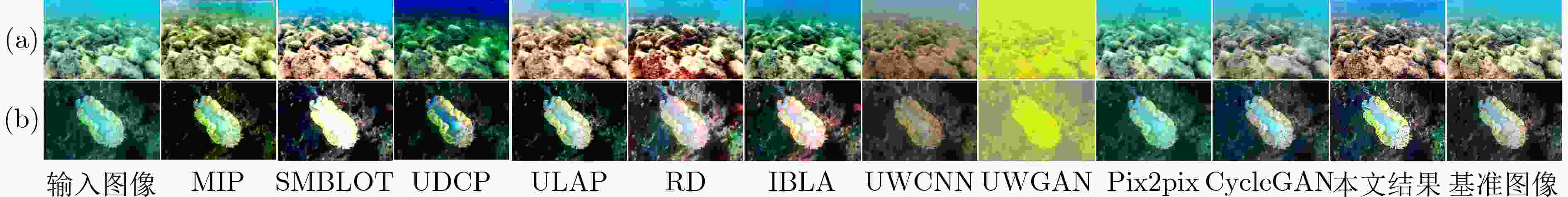
UIEB EUVP1 EUVP2 EUVP3 MIP 17.7824 23.2208 19.0353 19.6164 SMBLOT 20.4385 19.9150 20.3344 19.2797 UDCP 12.5706 16.6085 18.6297 16.8542 ULAP 20.8729 23.8800 22.4006 22.8187 RD 20.9269 20.2605 19.2846 18.1743 IBLA 17.0296 23.7864 21.7833 22.7280 UWCNN 15.3285 23.2881 18.6631 20.0642 UWGAN 21.6163 13.3417 13.0353 10.5894 Pix2pix 23.0141 30.1325 25.1247 28.1732 CycleGAN 8.6081 22.0597 8.6905 25.1744 本文 21.1722 28.5354 23.3623 22.9755 表 7 在4种数据集上的SSIM定量评价
UIEB EUVP1 EUVP2 EUVP3 MIP 0.4868 0.4155 0.4879 0.5424 SMBLOT 0.6571 0.4999 0.5637 0.6393 UDCP 0.4753 0.3282 0.4597 0.5401 ULAP 0.5373 0.4940 0.6054 0.7138 RD 0.6428 0.5116 0.5375 0.5079 IBLA 0.5188 0.4463 0.4585 0.6662 UWCNN 0.4660 0.5747 0.6421 0.6065 UWGAN 0.7428 0.0384 0.1218 -0.0232 Pix2pix 0.6512 0.3390 0.3858 0.6748 CycleGAN 0.1084 0.4879 0.0318 0.7761 本文 0.7017 0.6976 0.7410 0.7307 表 8 在4种数据集上的PCQI定量评价
UIEB EUVP1 EUVP2 EUVP3 MIP 0.6981 0.9358 0.6637 0.6033 SMBLOT 0.7830 1.0196 0.7697 0.6867 UDCP 0.5646 0.8061 0.5988 0.5058 ULAP 0.7359 0.9941 0.7159 0.6484 RD 0.8435 1.0176 0.7684 0.6724 IBLA 0.6453 0.9681 0.6911 0.6212 UWCNN 0.4277 0.7683 0.4445 0.4423 UWGAN 0.7686 0.0448 0.0499 0.1272 Pix2pix 0.5379 0.8915 0.5498 0.5996 CycleGAN 0.2957 0.5093 0.3557 0.5901 本文 0.9385 0.9209 0.7483 0.7753 表 9 在4种数据集上的Blur定量评价
UIEB EUVP1 EUVP2 EUVP3 MIP 0.2840 0.2513 0.3228 0.3737 SMBLOT 0.2881 0.2397 0.3347 0.3778 UDCP 0.2844 0.2405 0.3424 0.3814 ULAP 0.2898 0.2518 0.3398 0.3858 RD 0.2746 0.2427 0.3252 0.3577 IBLA 0.2870 0.2525 0.3403 0.3884 UWCNN 0.2956 0.2518 0.3428 0.3876 UWGAN 0.3315 0.1664 0.1794 0.2880 Pix2pix 0.3319 0.2613 0.3769 0.4057 CycleGAN 0.3148 0.3086 0.3548 0.3305 本文 0.2702 0.2682 0.3362 0.2784 表 10 不同卷积神经网络模型参数量分析
DenseNet121 CycleGAN UWCNN Pix2pix UWGAN MFFN UMUEN 本文 参数量(M) 7.98 107.95 0.15 54.41 1.93 11.97 29.2 1.42 -
[1] PIZER S M, AMBURN E P, AUSTIN J D, et al. Adaptive histogram equalization and its variations[J]. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, 1987, 39(3): 355–368. doi: 10.1016/s0734-189x(87)80186-x [2] PIZER S M, JOHNSTON R E, ERICKSEN J P, et al. Contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization: Speed and effectiveness[C]. The First Conference on Visualization in Biomedical Computing, Atlanta, USA, 1990: 337–345. [3] RIZZI A, GATTA C, and MARINI D. Color correction between gray world and white patch[J]. SPIE, 2002, 4662: 1–10. [4] VAN DE WEIJER J, GEVERS T, and GIJSENIJ A. Edge-based color constancy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2007, 16(9): 2207–2214. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2007.901808 [5] SINGH G, JAGGI N, VASAMSETTI S, et al. Underwater image/video enhancement using wavelet based color correction (WBCC) method[C]. 2015 IEEE Underwater Technology, Chennai, India, 2015: 1–5. [6] MUNIRAJ M and DHANDAPANI V. Underwater image enhancement by combining color constancy and dehazing based on depth estimation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 460: 211–230. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.07.003 [7] ZHUANG Peixian, LI Chongyi, and WU Jiamin. Bayesian retinex underwater image enhancement[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 101: 104171. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2021.104171 [8] GALDRAN A, PARDO D, PICÓN A, et al. Automatic Red-Channel underwater image restoration[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 26: 132–145. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.11.006 [9] LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, CONG Runmin, et al. Underwater image enhancement by Dehazing with minimum information loss and histogram distribution prior[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(12): 5664–5677. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2612882 [10] LI Chongyi, ANWAR S, and PORIKLI F. Underwater scene prior inspired deep underwater image and video enhancement[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 98: 107038. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107038 [11] WANG Nan, ZHOU Yabin, HAN Fenglei, et al. UWGAN: Underwater GAN for real-world underwater color restoration and Dehazing[J/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.10269, 2019. [12] ZHU Junyan, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2242–2251. [13] GUO Yecai, LI Hanyu, and ZHUANG Peixian. Underwater image enhancement using a multiscale dense generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45(3): 862–870. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2911447 [14] HUANG Gao, LIU Zhuang, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 2261–2269. [15] LAI Weisong, HUANG Jiabin, AHUJA N, et al. Fast and accurate image super-resolution with deep Laplacian pyramid networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 41(11): 2599–2613. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2865304 [16] WANG Zhou, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600–612. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [17] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, REN Wenqi, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 4376–4389. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2955241 [18] ISLAM M J, XIA Youya, and SATTAR J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227–3234. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [19] WANG Shiqi, MA Kede, YEGANEH H, et al. A patch-structure representation method for quality assessment of contrast changed images[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(12): 2387–2390. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2487369 [20] CRETE F, DOLMIERE T, LADRET P, et al. The blur effect: Perception and estimation with a new no-reference perceptual blur metric[J]. SPIE, 2007, 6492, 64920I. [21] CARLEVARIS-BIANCO N, MOHAN A, and EUSTICE R M. Initial results in underwater single image dehazing[C]. OCEANS 2010 MTS/IEEE Seattle, Seattle, USA, 2010: 1–8. [22] SONG Wei, WANG Yan, HUANG Dongmei, et al. Enhancement of underwater images with statistical model of background light and optimization of transmission map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2020, 66(1): 153–169. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2019.2960942 [23] DREWS P, DO NASCIMENTO E, MORAES F, et al. Transmission estimation in underwater single images[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 825–830. [24] SONG Wei, WANG Yan, HUANG Dongmei, et al. A rapid scene depth estimation model based on underwater light attenuation prior for underwater image restoration[C]. 19th Pacific-Rim Conference on Advances in Multimedia Information Processing, Hefei, China, 2018: 678–688. [25] GHANI A S A and ISA N A. Underwater image quality enhancement through composition of dual-intensity images and Rayleigh-stretching[J]. SpringerPlus, 2014, 3: 757. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-757 [26] PENG Y T and COSMAN P C. Underwater image restoration based on image blurriness and light absorption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1579–1594. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2663846 [27] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. [28] CHEN Renzhang, CAI Zhanchuan, and CAO Wei. MFFN: An underwater sensing scene image enhancement method based on multiscale feature fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 4205612. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2021.3134762 [29] DING Xuan, DONG Hang, GUO Yu, et al. Uncertainly guided multi-scale underwater image enhancement network with tone mapping block[C]. 2021 China Automation Congress (CAC), Beijing, China, 2021: 7172–7176. -





 下载:
下载:


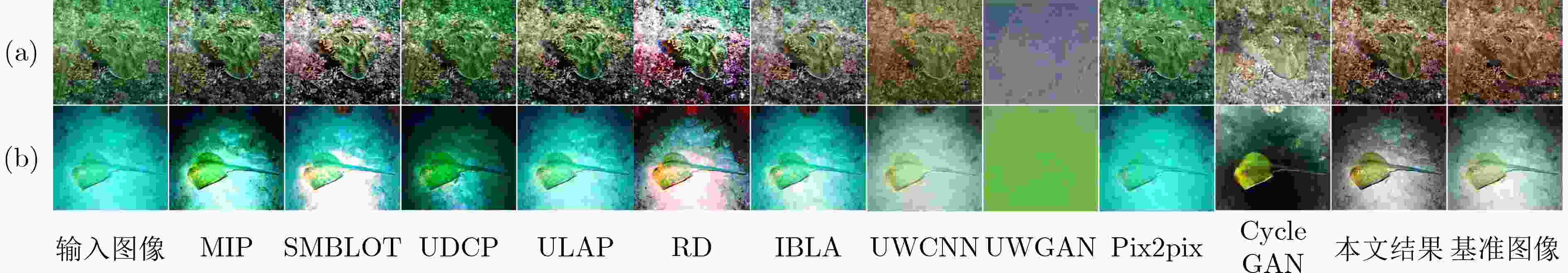


 下载:
下载:
