Research on Effective Capacity of Multi-Source Visible Light Communication Systems Supporting Terminal Rotation
-
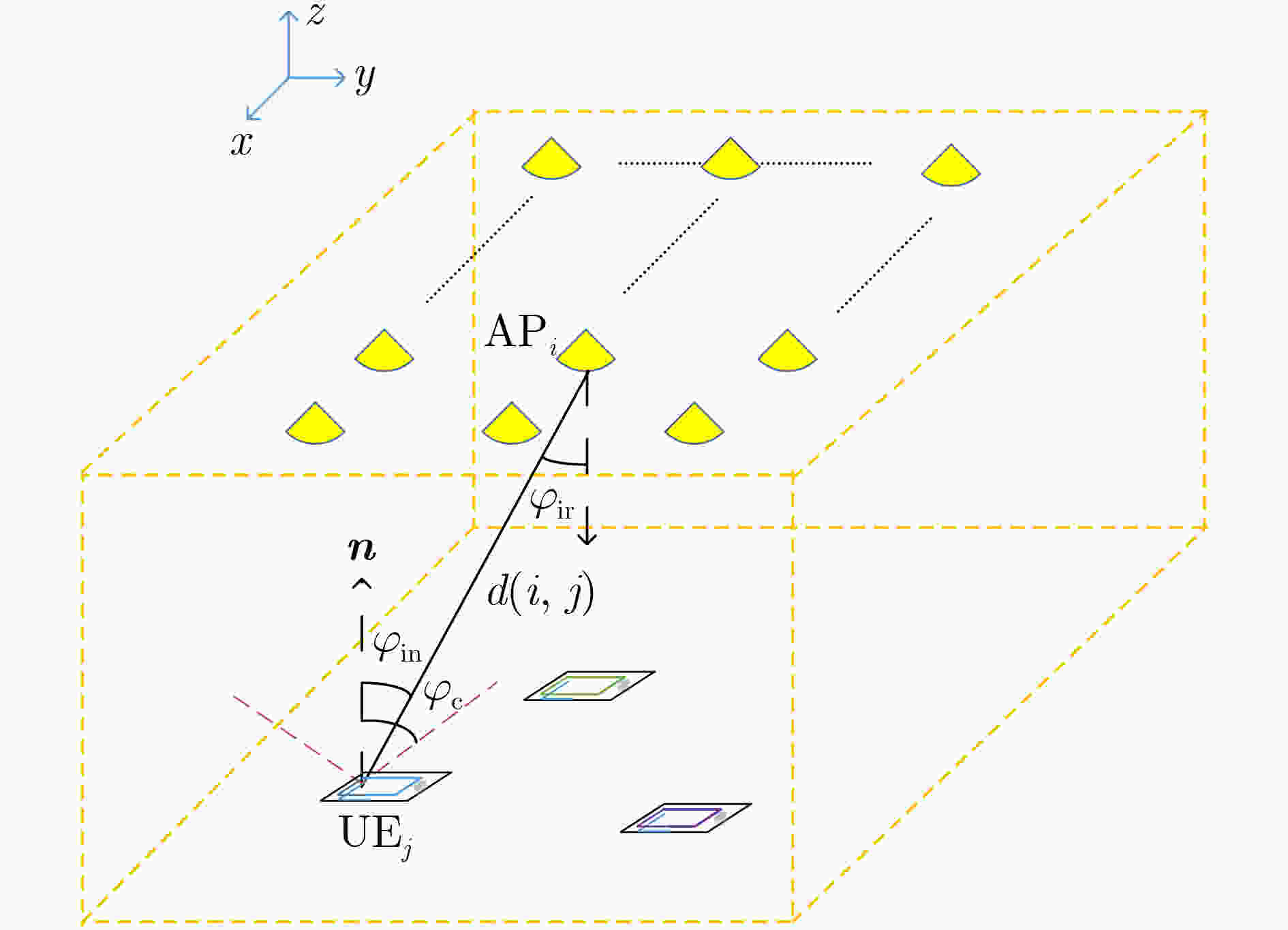
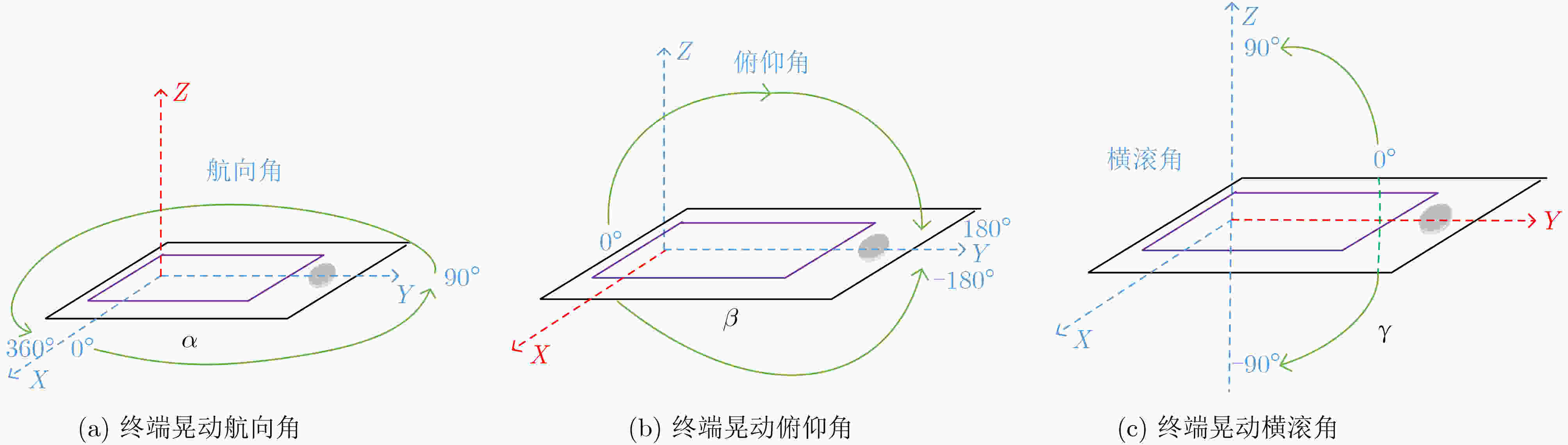
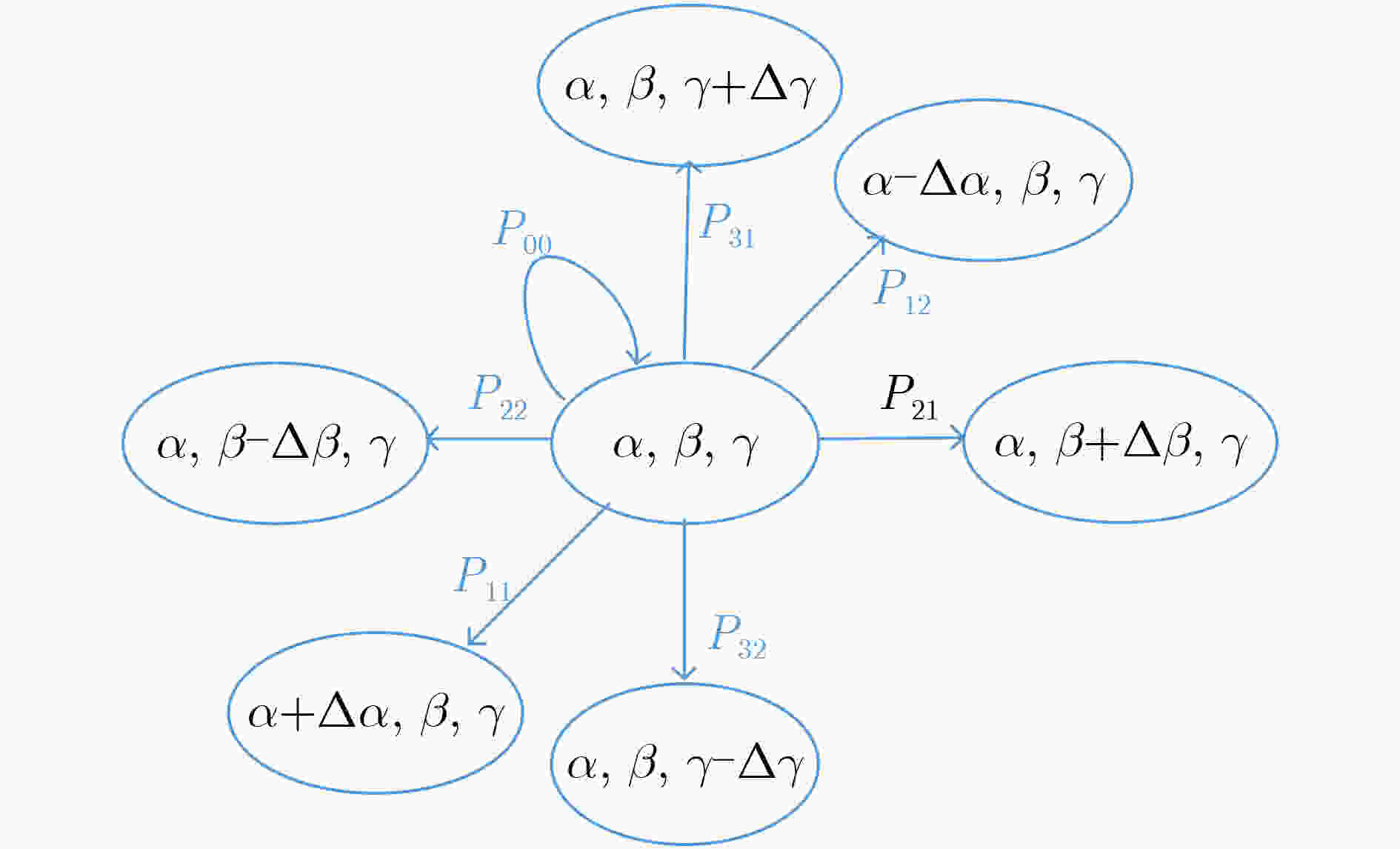
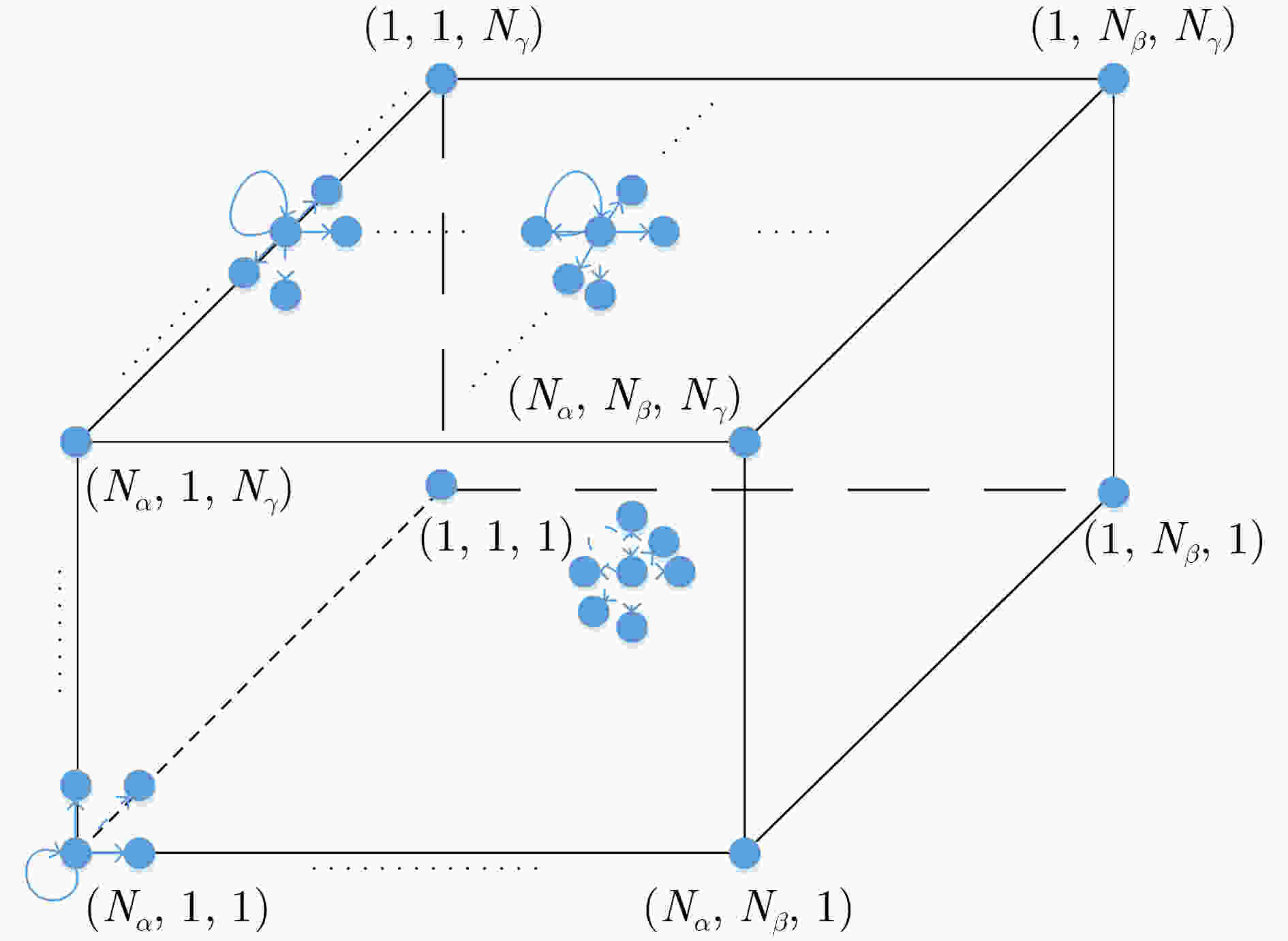
摘要: 作为下一代网络的重点候选技术,可见光通信(VLC)以其超高的传输速率有望提供严格的时延服务质量(QoS)保障。现有VLC研究大多假设终端在接收信号过程中始终保持垂直向上。然而,在实际VLC系统中,终端晃动将对接收端入射角产生较大的影响,从而对VLC的信道增益与传输速率产生影响。该文针对统计时延QoS约束下多光源VLC系统晃动终端的可达传输速率展开研究。首先,基于3维离散时间马尔可夫链,提出VLC终端3自由度晃动模型,从时间相关性的角度刻画了VLC终端的随机晃动过程;其次,将终端晃动下多光源VLC系统的矢量传输过程映射为马尔可夫式服务过程,基于有效容量理论,研究支持终端晃动的VLC系统在统计时延QoS约束下的可达传输速率;最后,通过仿真实验说明了终端晃动对VLC系统容量的影响并验证了所推导有效容量的准确性。Abstract: As one of the promising candidates of the next-generation network, Visible Light Communication (VLC) is expected to provide a strict delay QoS guarantee because of its high transmission rate. In the existing research of the VLC field, most of them assume that the direction of terminals is always vertically upward during the whole process of receiving signals. However, in a practical VLC system, the terminal rotation has considerable impacts on the angle of incidence and then affects the channel gain and transmission rate of VLC. In this paper, the achievable transmission rate of rotated terminals with the delay QoS constraint for the multi-source VLC system is investigated. Firstly, based on the three-dimension discrete-time Markov chain, a rotation model for the VLC terminal is proposed, which depicts the random rotation process of the VLC terminal from the perspective of temporal correlation. Secondly, the vectored transmission process of rotated terminals is mapped into Markov service process. Based on the effective capacity theory, the achievable transmission rate with the statistical delay QoS constraint for VLC system supporting terminal rotation is investigated. Finally, simulation results manifest significant rotation impacts on the VLC system capacity and the accuracy of the derived effective capacity.
-
表 1 VLC系统仿真参数
参数 符号 取值 单位 LED半功率角 $ {\phi _{1/2}} $ 70 ° 接收端的FoV $ {\varphi _{\text{c}}} $ 90 ° 光电检测器的物理面积 A 1 cm2 可用带宽 B 20 MHz 光电检测器的响应率 $ \tau $ 0.54 A/W 噪声功率谱密度 N0 10–21 A2/Hz 发送的光功率 Pt 20 W 终端和AP的垂直距离 hd 3 m -
[1] 尤肖虎. Shannon信息论与未来6G技术潜能[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2020, 50(9): 1377–1394. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0086YOU Xiaohu. Shannon theory and future 6G's technique potentials[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2020, 50(9): 1377–1394. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0086 [2] IMT-2030(6G)推进组. 6G 网络架构愿景与关键技术展望白皮书[R]. 2021.IMT-2030(6G) Promotion Group. White paper of network architecture vision and key technology of 6G[R]. 2021. [3] ARFAOUI M A, SOLTANI M D, TAVAKKOLNIA I, et al. Invoking deep learning for joint estimation of indoor LiFi user position and orientation[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2021, 39(9): 2890–2905. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2021.3064637 [4] SOLTANI M D, WU Xiping, SAFARI M, et al. Access point selection in Li-Fi cellular networks with arbitrary receiver orientation[C]. 2016 IEEE 27th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Valencia, Spain, 2016: 1–6. [5] EROĞLU Y S, YAPICI Y, GÜVENÇ I, et al. Impact of random receiver orientation on visible light communications channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(2): 1313–1325. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2879093 [6] WANG Jinyuan, LI Qinglin, ZHU Jianxia, et al. Impact of receiver’s tilted angle on channel capacity in VLCs[J]. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(6): 421–423. doi: 10.1049/el.2016.4657 [7] WANG Jinyuan, WANG Junbo, ZHU Bingcheng, et al. Improvement of BER performance by tilting receiver plane for indoor visible light communications with input-dependent noise[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. [8] SOLTANI M D, PURWITA A A, ZENG Zhihong, et al. Modeling the random orientation of mobile devices: Measurement, analysis and LiFi use case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(3): 2157–2172. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2882213 [9] SOLTANI M D, PURWITA A A, TAVAKKOLNIA I, et al. Impact of device orientation on error performance of LiFi systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 41690–41701. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907463 [10] ABUMARSHOUD H, SOLTANI M D, SAFARI M, et al. Realistic secrecy performance analysis for LiFi systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 120675–120688. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3108727 [11] ARFAOUI M A, SOLTANI M D, TAVAKKOLNIA I, et al. Measurements-based channel models for indoor LiFi systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(2): 827–842. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3028456 [12] YOO S K, COTTON S L, SOFOTASIOS P C, et al. Effective capacity analysis over generalized composite fading channels[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 123756–123764. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3003207 [13] WU Dapeng and NEGI R. Effective capacity: A wireless link model for support of quality of service[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2003, 2(4): 630–643. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2003.814353 [14] JIN Fan, ZHANG Rong, and HANZO L. Resource allocation under delay-guarantee constraints for heterogeneous visible-light and RF femtocell[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14(2): 1020–1034. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.2363451 [15] HAMMOUDA M, AKIN S, VEGNI A M, et al. Link selection in hybrid RF/VLC systems under statistical queueing constraints[J]. IEEE transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2738–2754. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2802937 [16] LI Xuan, JIN Fan, ZHANG Rong, et al. Joint cluster formation and user association under delay guarantees in visible-light networks[C]. 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, USA, 2016: 1–6. [17] ZHAO Linlin, CHI Xuefen, and YANG Shaoshi. Optimal ALOHA-like random access with heterogeneous QoS guarantees for multi-packet reception aided visible light communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(11): 7872–7884. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2016.2608956 [18] QIAN Lei, CHI Xuefen, ZHAO Linlin, et al. User-centric secure cell formation for visible light networks with statistical delay guarantees[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(3): 1831–1846. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3036907 [19] KOMINE T and NAKAGAWA M. Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights[J]. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 2004, 50(1): 100–107. doi: 10.1109/TCE.2004.1277847 [20] CHANG Chengshang. Stability, queue length and delay. II. Stochastic queueing networks[C]. The 31st IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Tucson, USA, 1992: 1005–1010. [21] KESIDIS G, WALRAND J, and CHANG Chengshang. Effective bandwidths for multiclass Markov fluids and other ATM sources[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 1993, 1(4): 424–428. doi: 10.1109/90.251894 -





 下载:
下载:
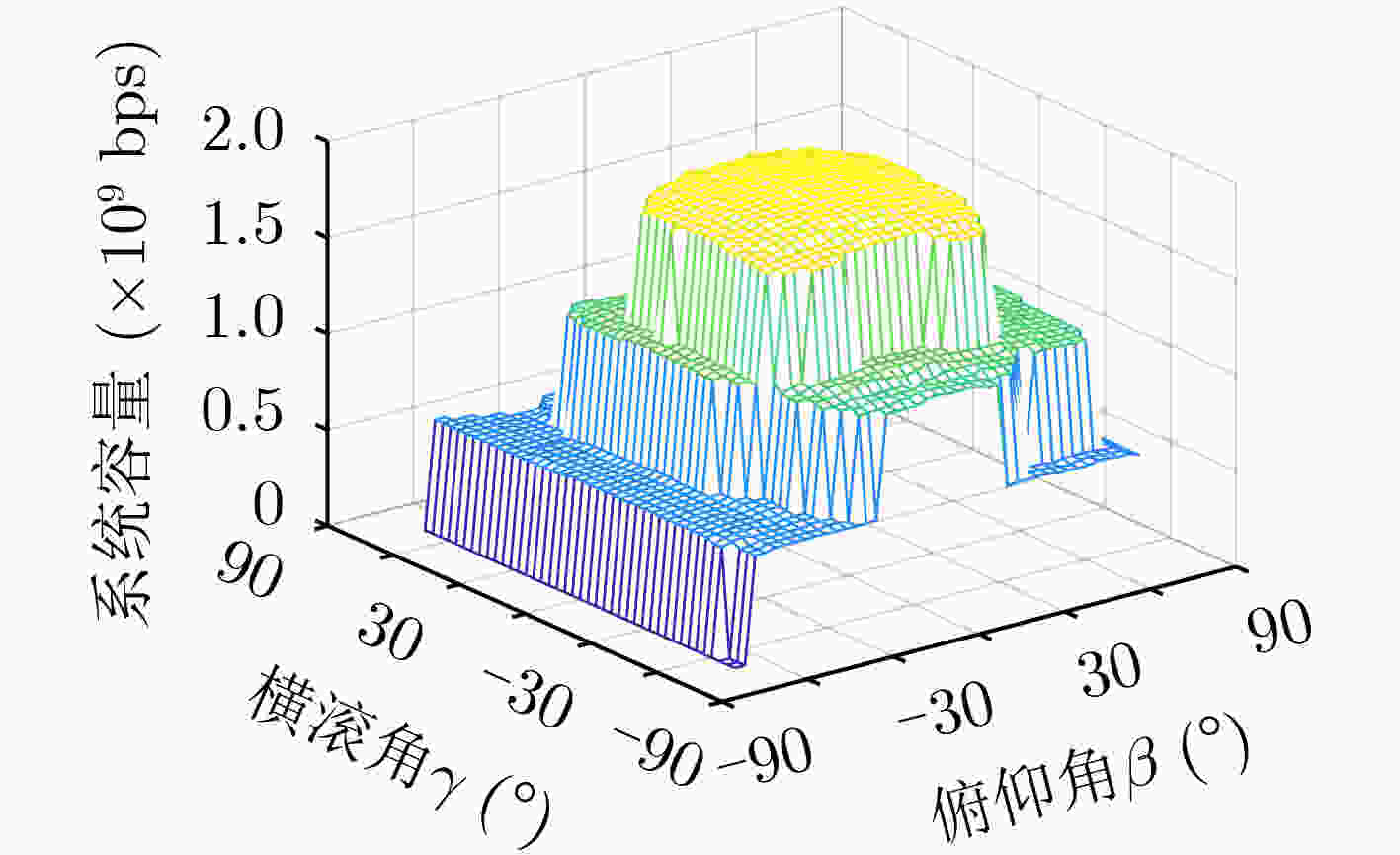
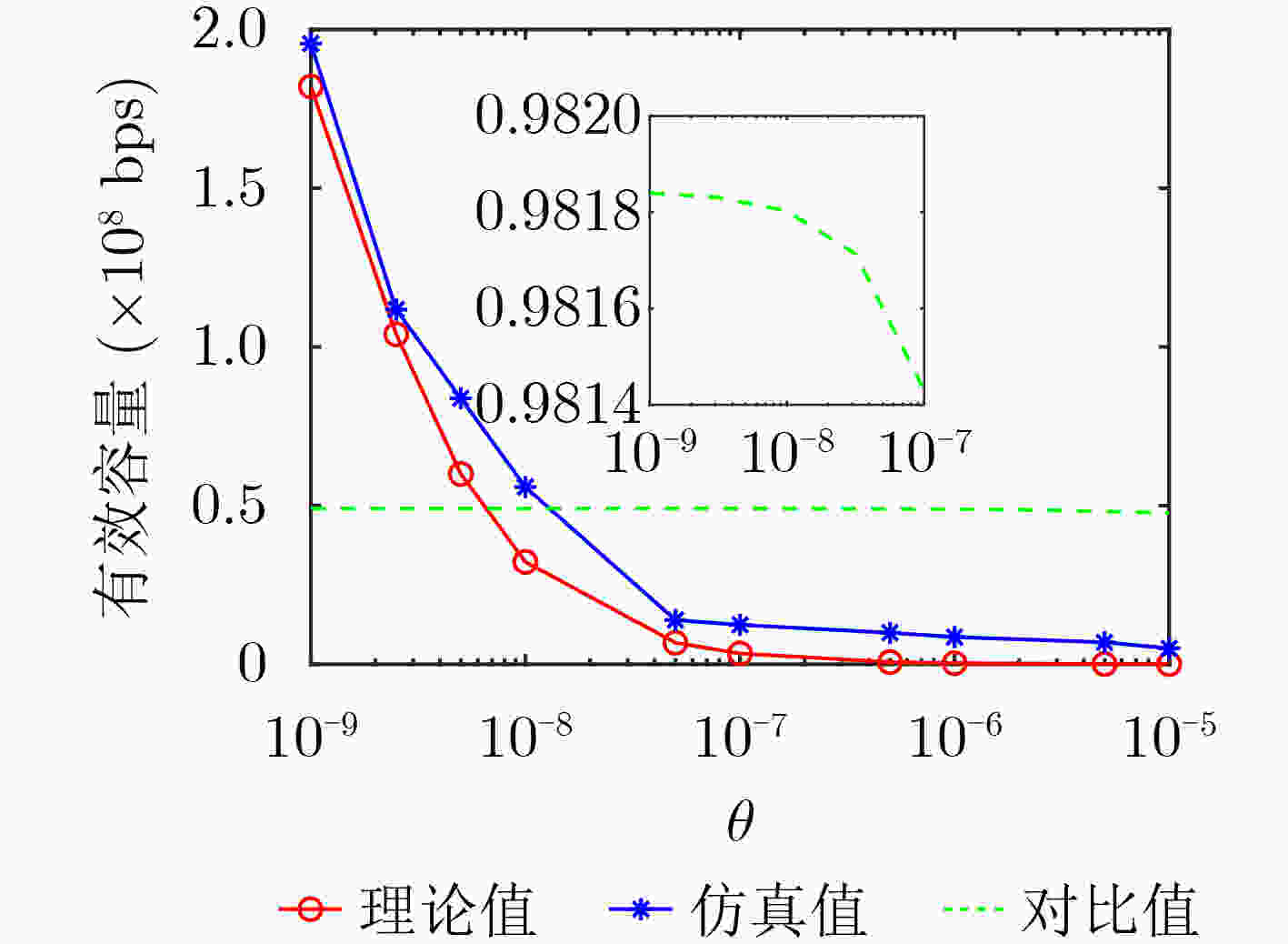
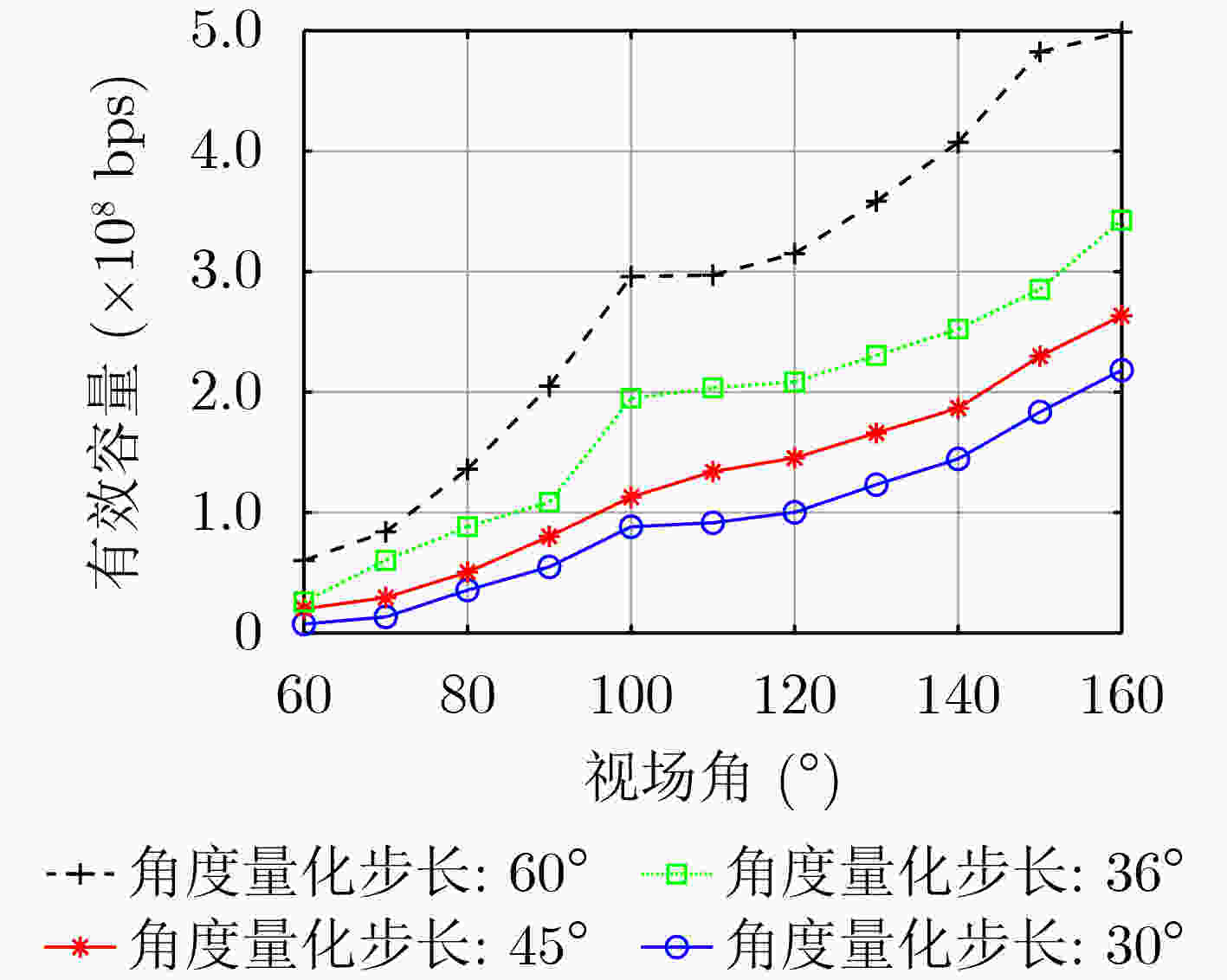


 下载:
下载:
