Segmentation Algorithm of Breast Tumor in Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Based on Network with Multi-scale Residuals and Dual-domain Attention
-
摘要: 针对乳腺肿瘤大小形态多变、边界模糊以及前景与背景间严重类不平衡的问题,该文提出一种多尺度残差双域注意力融合网络。该网络以多尺度卷积构成的多尺度残差块作为基本搭建模块,通过提取多尺度特征和优化梯度传播通道提高其识别不同尺寸目标的能力,同时融入双域注意力单元,提高网络的边缘识别和边界保持能力。另外该文提出一种混合自适应权重损失函数改善网络优化方向,缓解正负样本极度不均衡的影响。实验结果表明,该文所提方法的平均骰子相似系数(Dice)值达到0.8063,较U形网络(UNet)提高5.3%,参数量下降73.36%,具有更优的分割性能。
-
关键词:
- 乳腺肿瘤分割 /
- 多尺度残差块 /
- 双域注意力 /
- 混合自适应权重损失函数
Abstract: Considering the problems of breast tumor size and shape change, blurred boundary and severe class imbalance between foreground and background, a multi-scale residual dual-domain attention fusion network is proposed. In this network, multi-scale residual blocks composed of multi-scale convolution are used as the basic building modules. Multi-scale residual block improves the network's ability to recognize targets of different sizes and the model’s robustness by extracting multi-scale features and optimizing gradient propagation. Meanwhile, the dual-domain attention units are integrated into the network to improve the ability of edge recognition and boundary preservation. The hybrid loss function with adaptive weight is proposed, it can improve the optimization direction of the network, alleviate the influence of the extreme imbalance of positive and negative samples. The experimental results show that the average Dice value of the method proposed in this paper reaches 0.8063, which is 5.3% higher than that of U-shaped Network (UNet), and the number of parameters is reduced by 73.36%, which has better segmentation performance. -
表 1 多尺度残差块在UNet基础网络中的表现
UNet MSRUNet_C MSRUNet_S MSRUNet_SS DSC 0.7533±0.0937 0.7729±0.0634 0.7717±0.0688 0.771±0.0653 IOU 0.6115±0.1207 0.6336±0.0855 0.6324±0.0934 0.6311±0.0883 TPR 0.7036±0.1801 0.7343±0.1273 0.7304±0.0945 0.7284±0.1125 PPV 0.8484±0.0783 0.8334±0.0616 0.822±0.0522 0.8313±0.06 ACC 0.9975±0.001 0.9977±0.0009 0.9976±0.0011 0.9976±0.0009 HD 114.7123±52.7682 99.5655±48.1704 98.8848±48.3012 99.8627±48.4836 总参数 31044162 7321474 7091586 6869058 参数占比(%) 100 23.58 22.84 22.13 表 2 多尺度残差块在UNetPP基础网络中的表现
UNetPP MSRUNetPP_C MSRUNetPP_S MSRUNetPP_SS DSC 0.7654±0.0904 0.773±0.075 0.7757±0.0726 0.7773±0.0824 IOU 0.627±0.121 0.6349±0.101 0.6382±0.0981 0.6417±0.1103 TPR 0.7182±0.1617 0.7675±0.143 0.7241±0.1151 0.7281±0.1353 PPV 0.8436±0.051 0.8033±0.0956 0.8449±0.0433 0.8479±0.0403 ACC 0.9976±0.001 0.9976±0.0009 0.9977±0.001 0.9978±0.0011 HD 102.8907±50.2464 98.5523±44.3852 96.3007±49.4064 96.6875±50.0719 总参数 36173186 8865602 8619074 8381666 参数占比(%) 100 24.51 23.83 23.17 表 3 不同注意力机制表现对比
方法 MSRNet MSRAUNet MSRDANet DSC 0.771±0.0653 0.7784±0.0723 0.7839±0.0665 IOU 0.6311±0.0883 0.6419±0.0987 0.6485±0.0902 TPR 0.7284±0.1125 0.7203±0.1153 0.7273±0.1089 PPV 0.8313±0.06 0.8549±0.0205 0.8593±0.0267 ACC 0.9976±0.0009 0.9978±0.001 0.9978±0.0009 HD 99.8627±48.4836 96.1847±47.1049 95.5195±42.2526 表 4 不同损失函数表现对比
方法 UNet_CD MSRNet_CD MSRDANet_CD DSC 0.7541±0.0763 0.7767±0.0675 0.7848±0.0736 IOU 0.6119±0.1043 0.6391±0.0933 0.6507±0.1007 TPR 0.7104±0.1278 0.7209±0.1201 0.7364±0.1313 PPV 0.8394±0.0923 0.8537±0.0296 0.8545±0.035 ACC 0.9975±0.0009 0.9978±0.0009 0.9978±0.0009 HD 108.9456±44.1965 98.6967±50.8693 93.7069±45.4647 方法 UNet_HL MSRNet_HL MSRDANet_HL DSC 0.7722±0.0792 0.788±0.0653 0.8063±0.0538 IOU 0.6345±0.1078 0.654±0.0883 0.6781±0.0752 TPR 0.716±0.1427 0.7449±0.1166 0.7765±0.0939 PPV 0.8556±0.0401 0.8479±0.0323 0.8452±0.0338 ACC 0.9977±0.0009 0.9978±0.0009 0.998±0.0007 HD 106.7584±44.9645 87.6175±47.1643 77.9541±37.3557 表 5 各网络分割指标对比
SegNet UNet CPFNet AUNet DSC 0.7399±0.0957 0.7533±0.0937 0.7602±0.0583 0.7653±0.0758 IOU 0.5946±0.1237 0.6115±0.1207 0.6159±0.0754 0.6249±0.1031 TPR 0.6678±0.1548 0.7036±0.1801 0.6955±0.0707 0.7178±0.1472 PPV 0.8489±0.0022 0.8484±0.0783 0.8429±0.0721 0.8445±0.0734 ACC 0.9975±0.0011 0.9975±0.001 0.9975±0.0011 0.9976±0.0009 HD 117.6852±66.3663 114.7123±52.7682 109.1354±51.5033 100.1426±47.0054 总参数 29444738 31044162 89369286 31745286 参数占比(%) 94.85 100 287.88 102.26 UNetPP UNet3+ MSRNet MSRDANet MSRDANet_HL DSC 0.7654±0.0904 0.7697±0.0828 0.771±0.0653 0.7839±0.0665 0.8063±0.0538 IOU 0.627±0.121 0.6315±0.1112 0.6311±0.0883 0.6485±0.0902 0.6781±0.0752 TPR 0.7182±0.1617 0.7096±0.1408 0.7284±0.1125 0.7273±0.1089 0.7765±0.0939 PPV 0.8436±0.051 0.8577±0.0334 0.8313±0.06 0.8593±0.0267 0.8452±0.0338 ACC 0.9976±0.001 0.9977±0.001 0.9976±0.0008 0.9978±0.0009 0.998±0.0007 HD 102.8907±50.2464 95.8319±45.0312 99.8627±48.4836 95.5195±42.2526 77.9541±37.3557 总参数 36173186 26975234 6869058 8271562 8271562 参数占比(%) 116.52 86.89 22.13 26.64 26.64 -
[1] SUNG H, FERLAY J, SIEGEL R L, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA:A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2021, 71(3): 209–249. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660 [2] WILD C P, WEIDERPASS E, STEWART B W, et al. World Cancer Report: Cancer Research for Cancer Prevention[M]. Lyon: IARC Press, 2020: 25–27. [3] ROMEO V, CAVALIERE C, IMBRIACO M, et al. Tumor segmentation analysis at different post-contrast time points: A possible source of variability of quantitative DCE-MRI parameters in locally advanced breast cancer[J]. European Journal of Radiology, 2020, 126: 108907. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108907 [4] WANG Shuai, SUN Kun, WANG Li, et al. Breast tumor segmentation in DCE-MRI with tumor sensitive synthesis[J/OL]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021. [5] CARVALHO E D, SILVA R R V, MATHEW M J, et al. Tumor segmentation in breast DCE-MRI slice using deep learning methods[C]. 2021 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC), Athens, Greece, 2021: 1–6. [6] ZHANG Jun, SAHA A, ZHU Zhe, et al. Hierarchical convolutional neural networks for segmentation of breast tumors in MRI with application to radiogenomics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(2): 435–447. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2865671 [7] MENCATTINI A, RABOTTINO G, SALMERI M, et al. Breast mass segmentation in mammographic images by an effective region growing algorithm[C]. 10th International Conference on Advanced Concepts for Intelligent Vision Systems, Juan-les-Pins, France, 2008: 948–957. [8] SHAN Juan, CHENG Hengda, and WANG Yuxuan. A novel automatic seed point selection algorithm for breast ultrasound images[C]. IEEE 2008 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Tampa, USA, 2008: 1–4. [9] PRAKASH R M, BHUVANESHWARI K, DIVYA M, et al. Segmentation of thermal infrared breast images using K-means, FCM and EM algorithms for breast cancer detection[C]. 2017 International Conference on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems (ICIIECS), Coimbatore, India, 2017: 1–4. [10] LIU Hui, LIU Yiping, ZHAO Zuowei, et al. A new background distribution-based active contour model for three-dimensional lesion segmentation in breast DCE-MRI[J]. Medical Physics, 2014, 41(8): 082303. doi: 10.1118/1.4886295 [11] ZHOU Zhuhuang, WU Weiwei, WU Shuicai, et al. Semi-automatic breast ultrasound image segmentation based on mean shift and graph cuts[J]. Ultrasonic Imaging, 2014, 36(4): 256–276. doi: 10.1177/0161734614524735 [12] LIU Liangliang, CHENG Jianhong, QUAN Quan, et al. A survey on U-shaped networks in medical image segmentations[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 409: 244–258. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.070 [13] AL-FARIS A Q, NGAH U K, ISA N A M, et al. Breast MRI tumour segmentation using modified automatic seeded region growing based on particle swarm optimization image clustering[M]. SNÁŠEL V, KRÖMER P, KÖPPEN M, et al. Soft Computing in Industrial Applications. Cham: Springer, 2014: 49–60. [14] CHAKRABORTY J, MUKHOPADHYAY S, SINGLA V, et al. Detection of masses in mammograms using region growing controlled by multilevel thresholding[C]. 2012 25th IEEE International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Rome, Italy, 2012: 1–6. [15] SHARMA J, RAI J K, and TEWARI R P. A combined watershed segmentation approach using K-means clustering for mammograms[C]. 2015 2nd International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 2015: 109–113. [16] 冯宝, 陈业航, 刘壮盛, 等. 结合MRF能量和模糊速度的乳腺癌图像分割方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1188–1199. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180759FENG Bao, CHEN Yehang, LIU Zhuangsheng, et al. Segmentation of breast cancer on DCE-MRI images with MRF energy and fuzzy speed function[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1188–1199. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180759 [17] XIAN Min, ZHANG Yingtao, CHENG H D, et al. Automatic breast ultrasound image segmentation: A survey[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 79: 340–355. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.02.012 [18] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, and BROX T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]. 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 2015: 234–241. [19] ZHOU Zongwei, SIDDIQUEE M M R, TAJBAKHSH N, et al. Unet++: Redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(6): 1856–1867. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2959609 [20] SCHLEMPER J, OKTAY O, SCHAAP M, et al. Attention gated networks: Learning to leverage salient regions in medical images[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2019, 53: 197–207. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.01.012 [21] HUANG Huimin, LIN Lanfen, TONG Ruofeng, et al. UNet 3+: A full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation[C]. ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 2020: 1055–1059. [22] FENG Shuanglang, ZHAO Heming, SHI Fei, et al. CPFNet: Context pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2020, 39(10): 3008–3018. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.2983721 [23] BENJELLOUN M, EL ADOUI M, LARHMAM M A, et al. Automated breast tumor segmentation in DCE-MRI using deep learning[C]. 2018 4th International Conference on Cloud Computing Technologies and Applications (Cloudtech), Brussels, Belgium, 2018: 1–6. [24] JIAO Han, JIANG Xinhua, PANG Zhiyong, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks-based automatic breast segmentation and mass detection in DCE-MRI[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2020, 2020: 2413706. doi: 10.1155/2020/2413706 [25] WANG Hongyu, CAO Jiaqi, FENG Jun, et al. Mixed 2D and 3D convolutional network with multi-scale context for lesion segmentation in breast DCE-MRI[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2021, 68: 102607. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102607 [26] SINGH V K, ABDEL-NASSER M, AKRAM F, et al. Breast tumor segmentation in ultrasound images using contextual-information-aware deep adversarial learning framework[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2020, 162: 113870. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113870 -





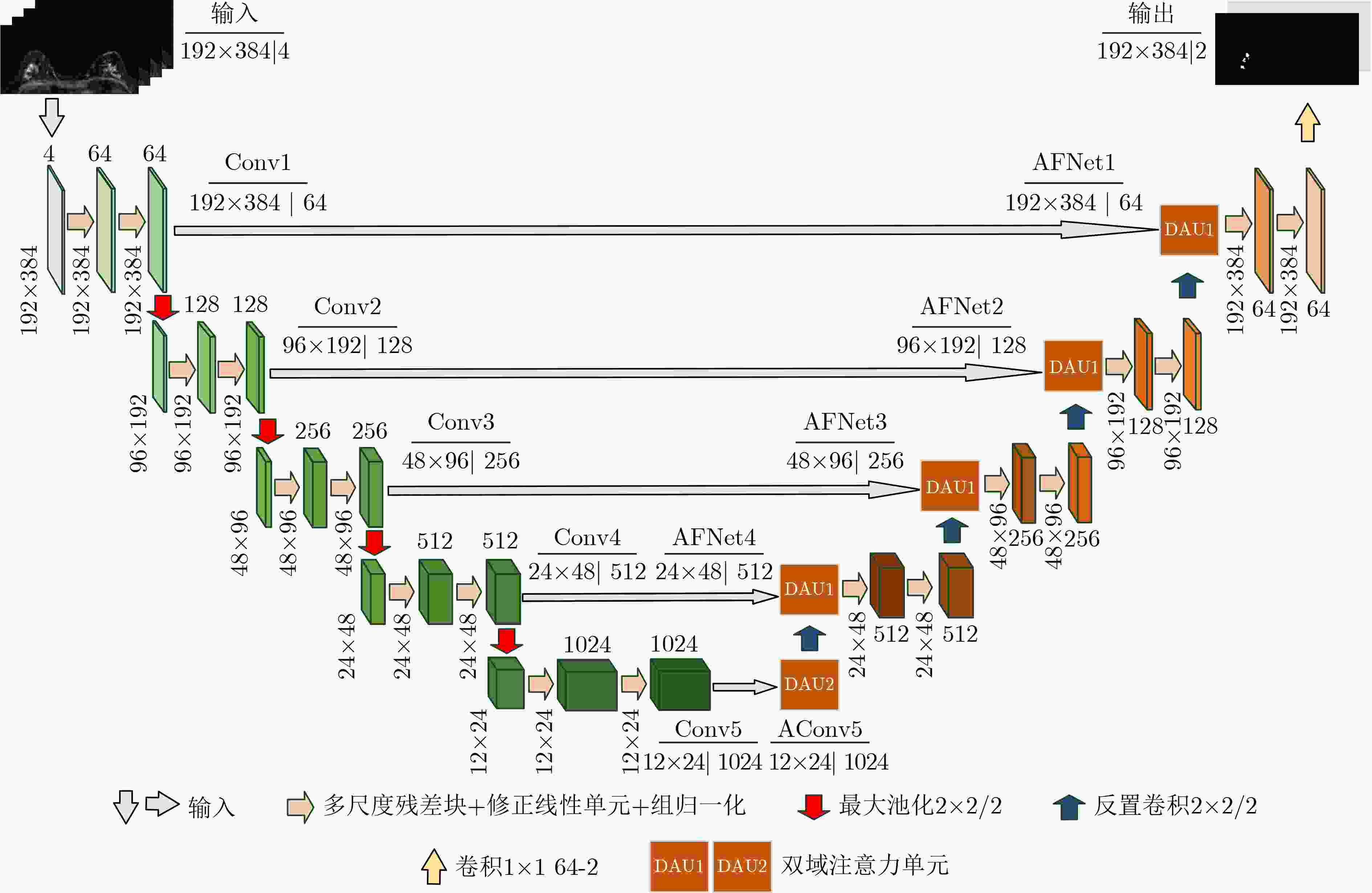
 下载:
下载:
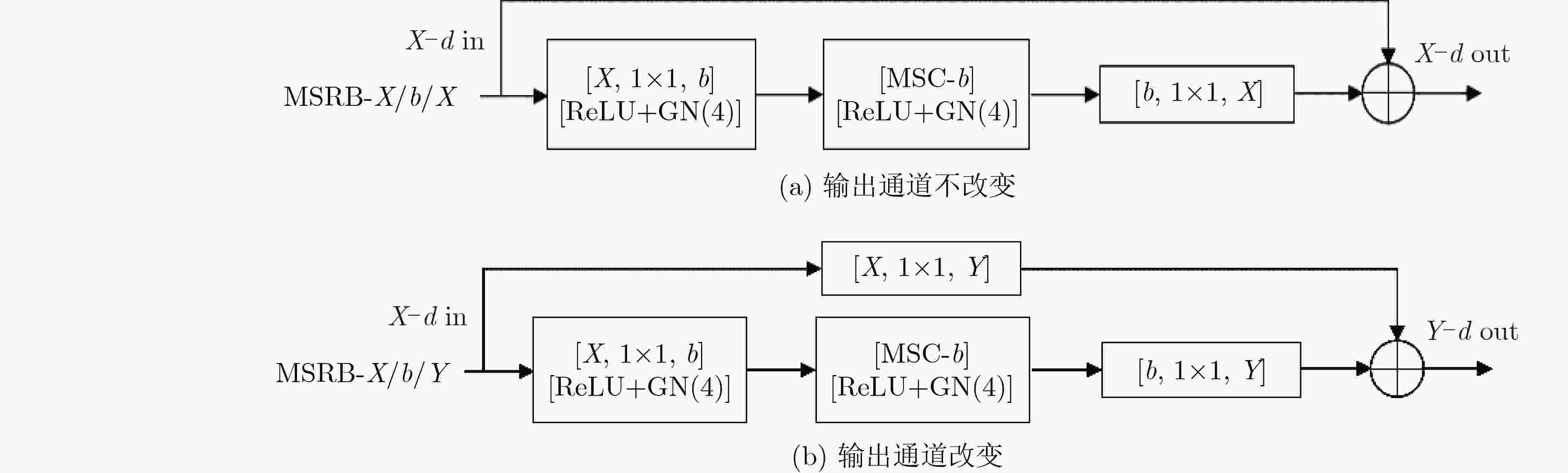
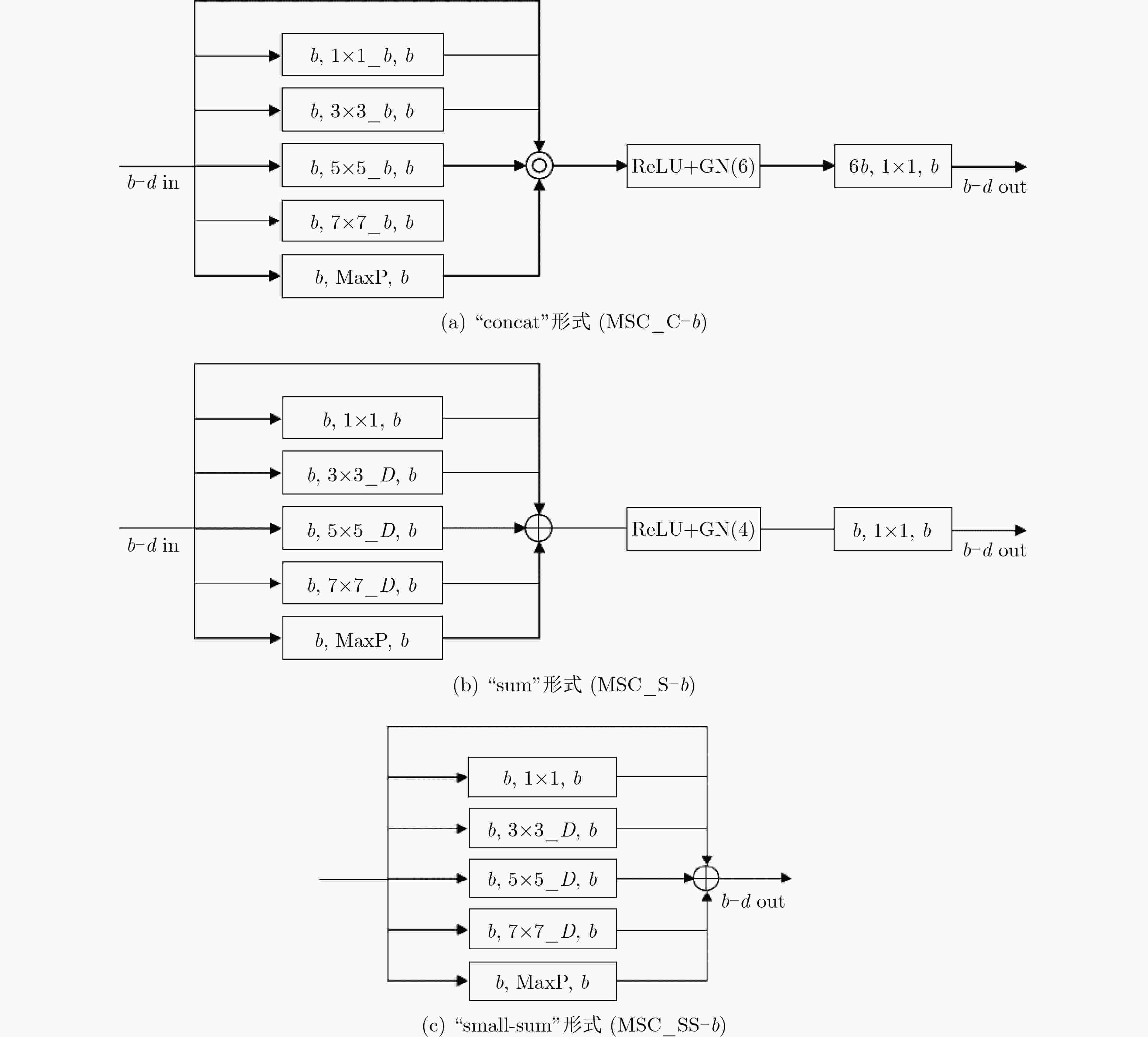
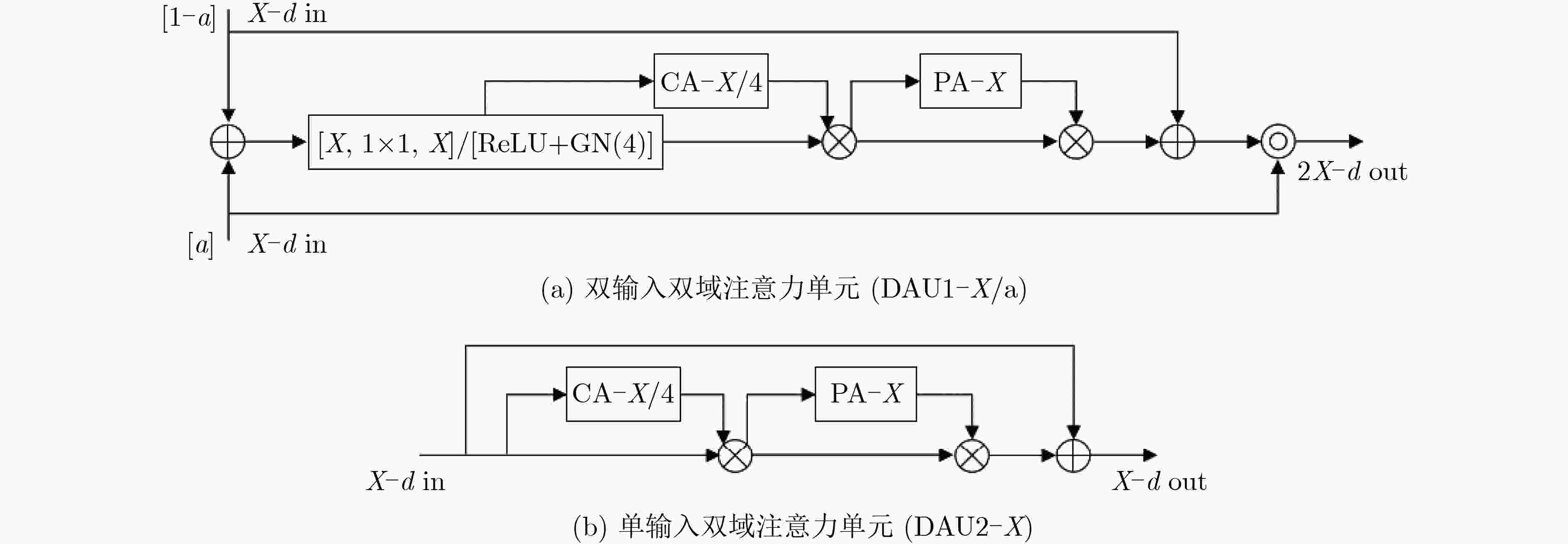
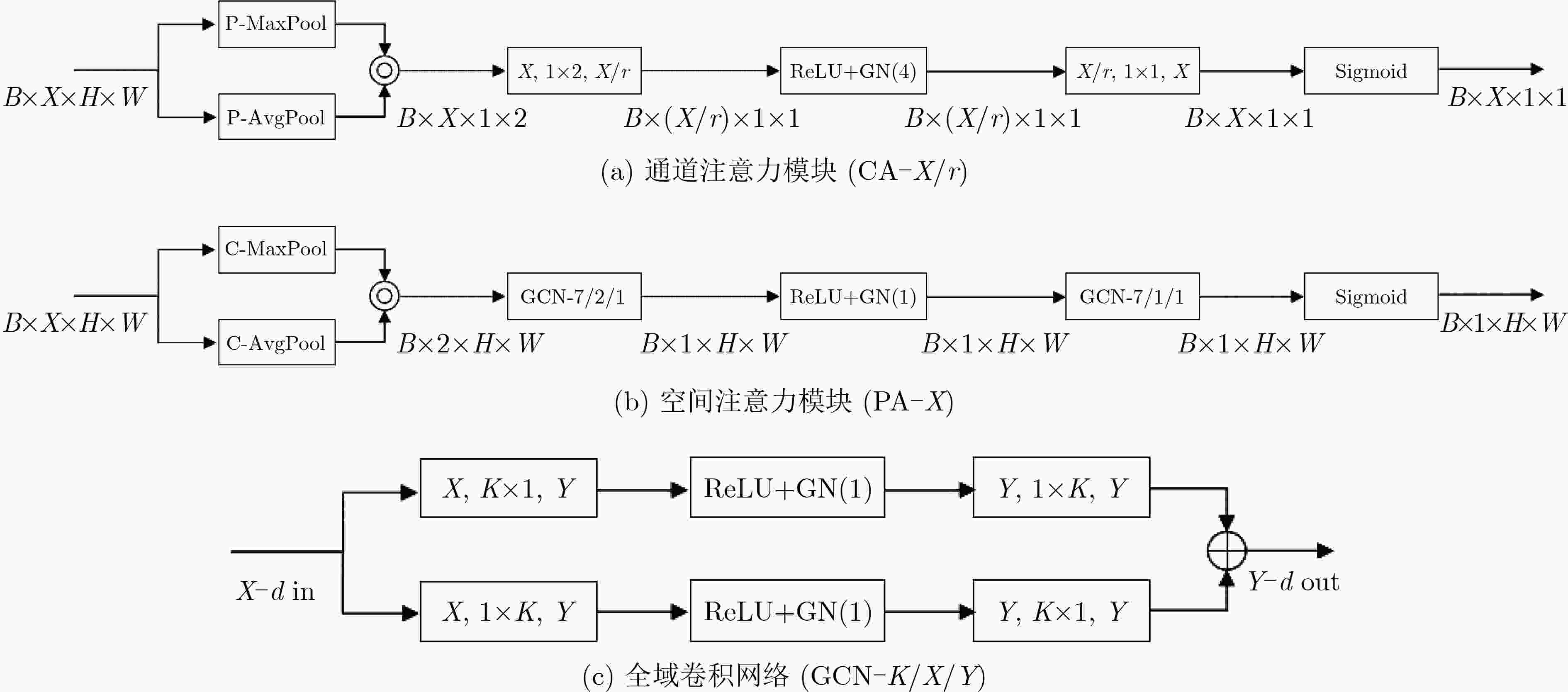
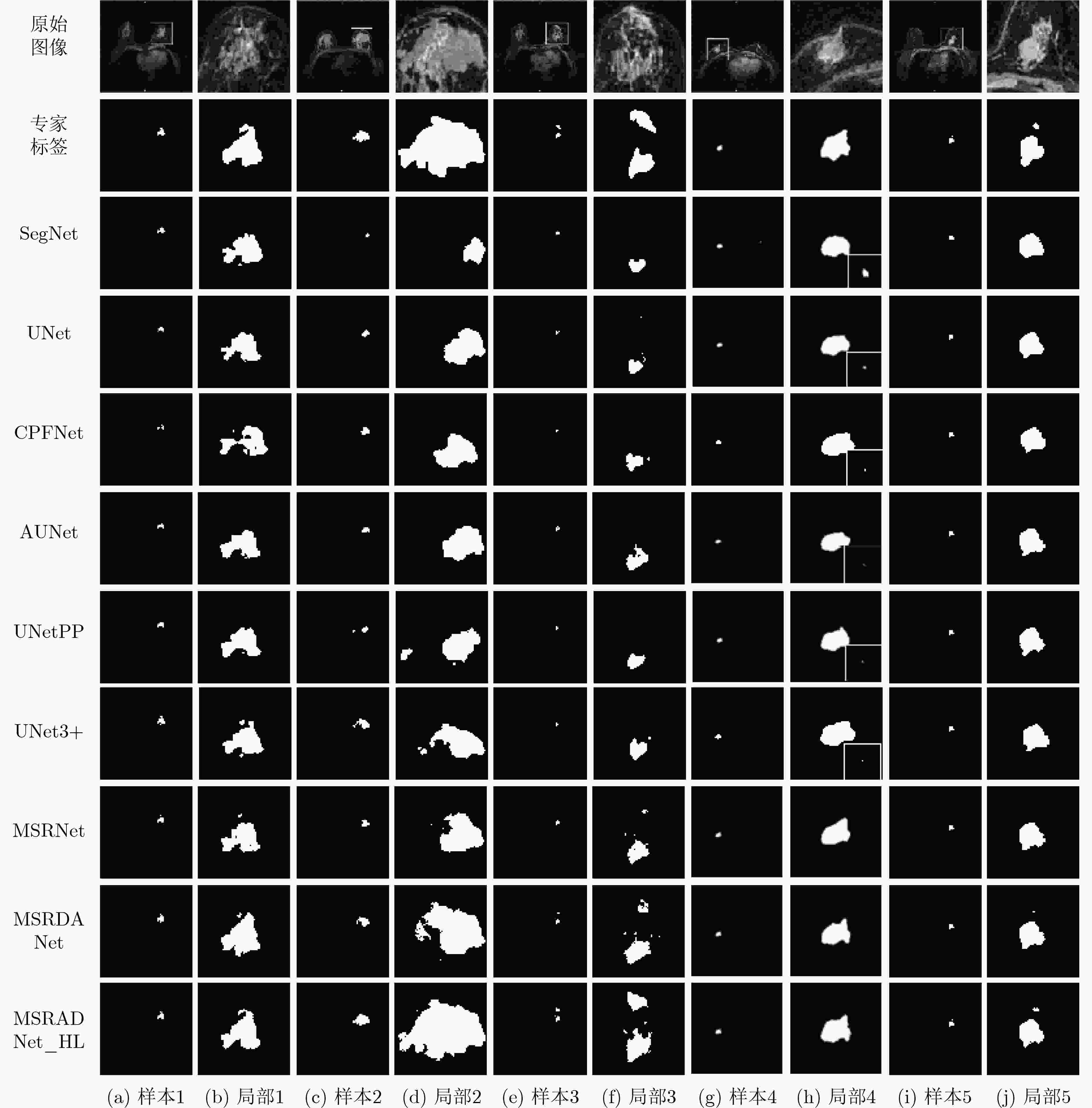
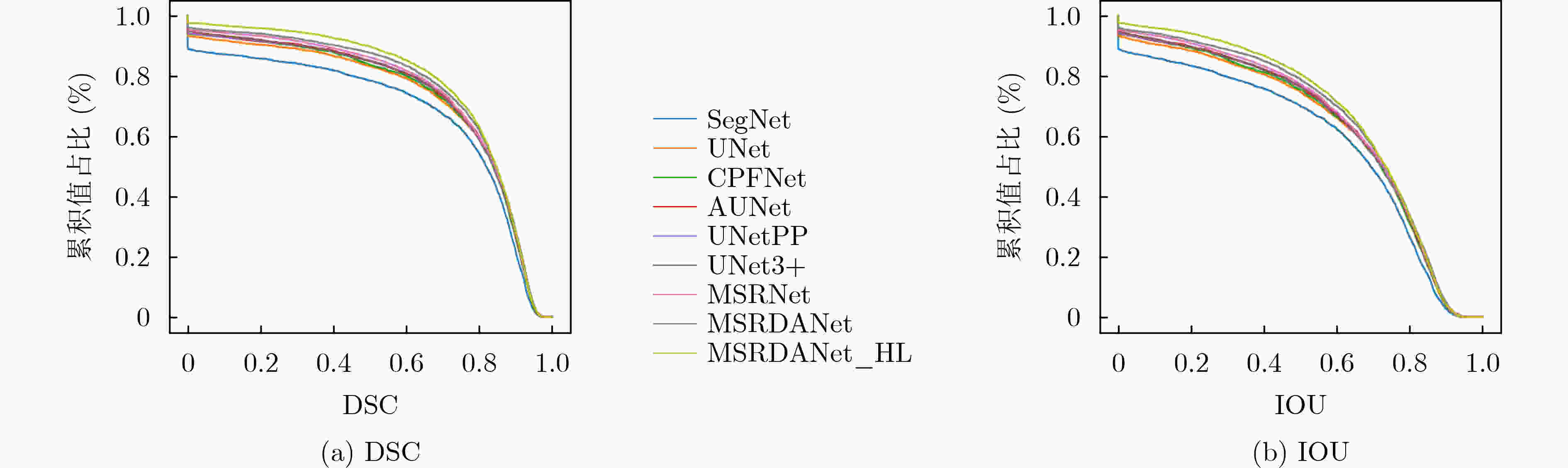
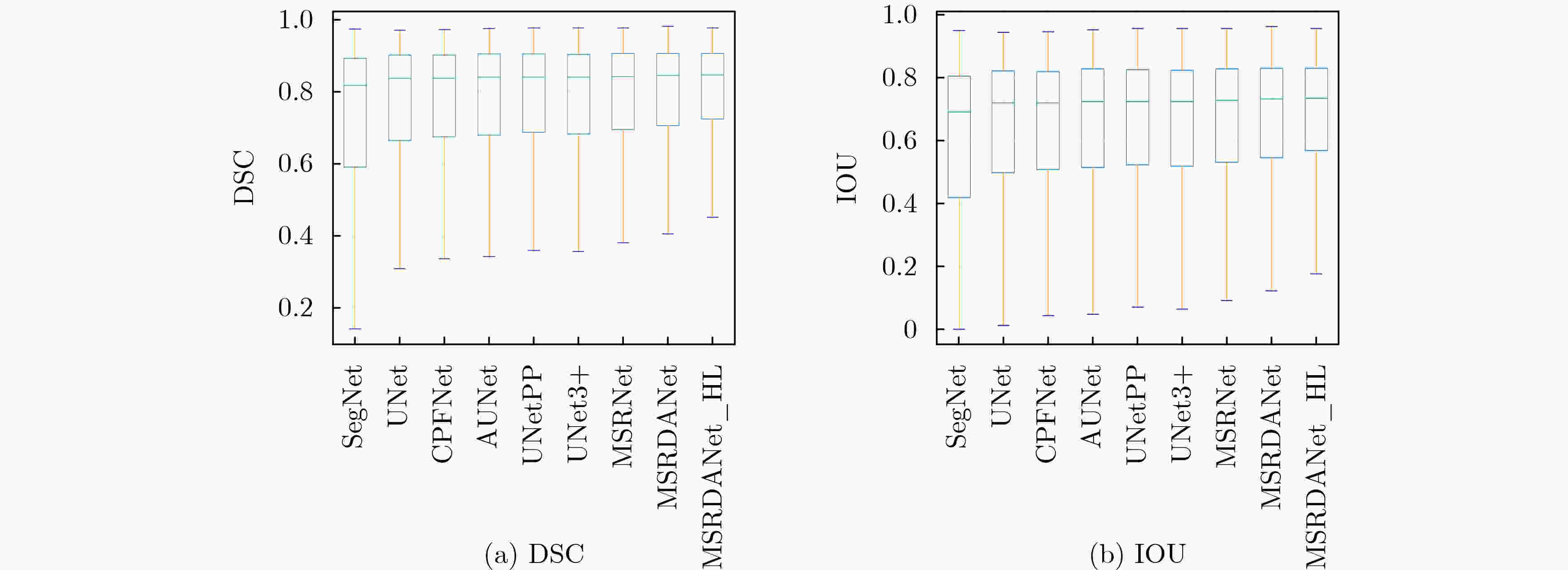


 下载:
下载:
