Deep Disease MicroRNA Association Prediction via Variational Gated Graph Autoencoders
-
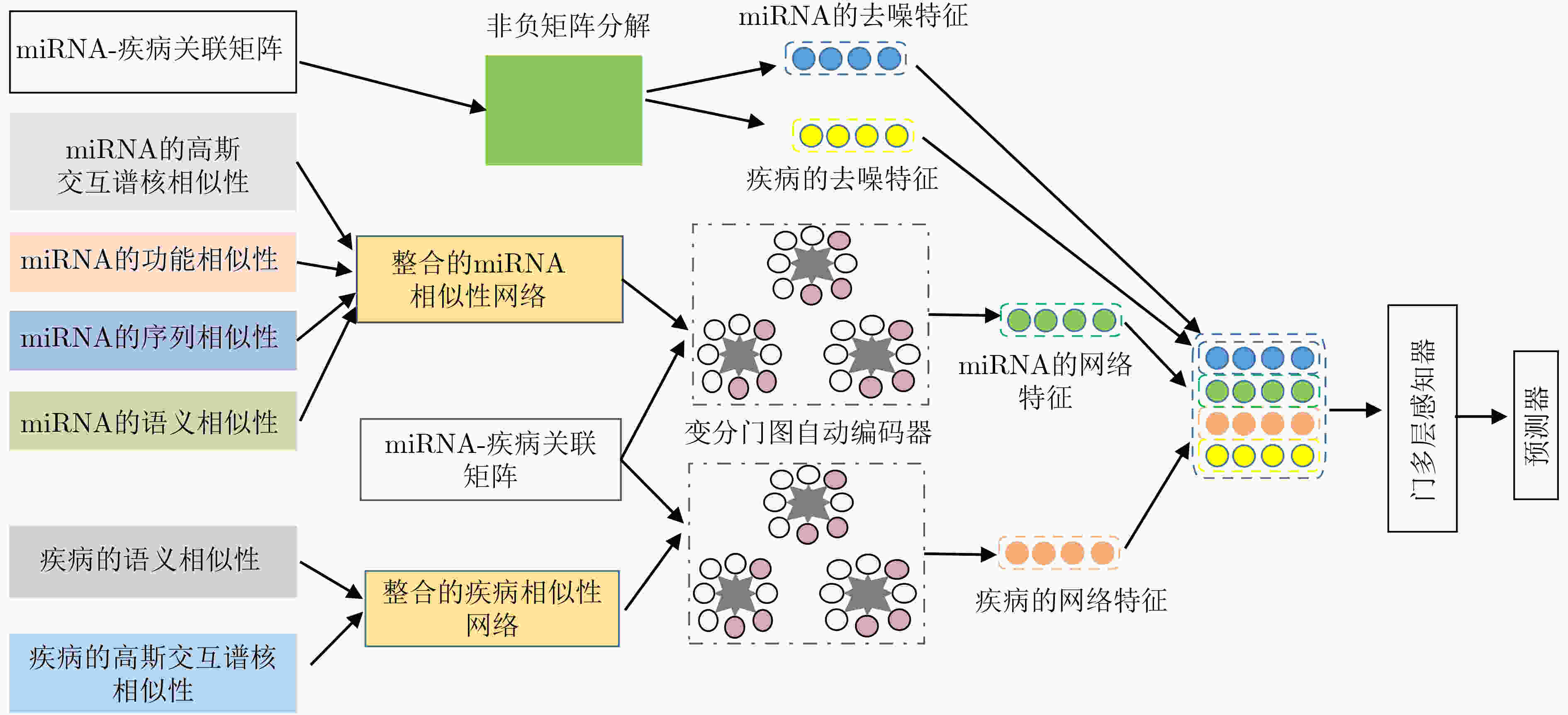
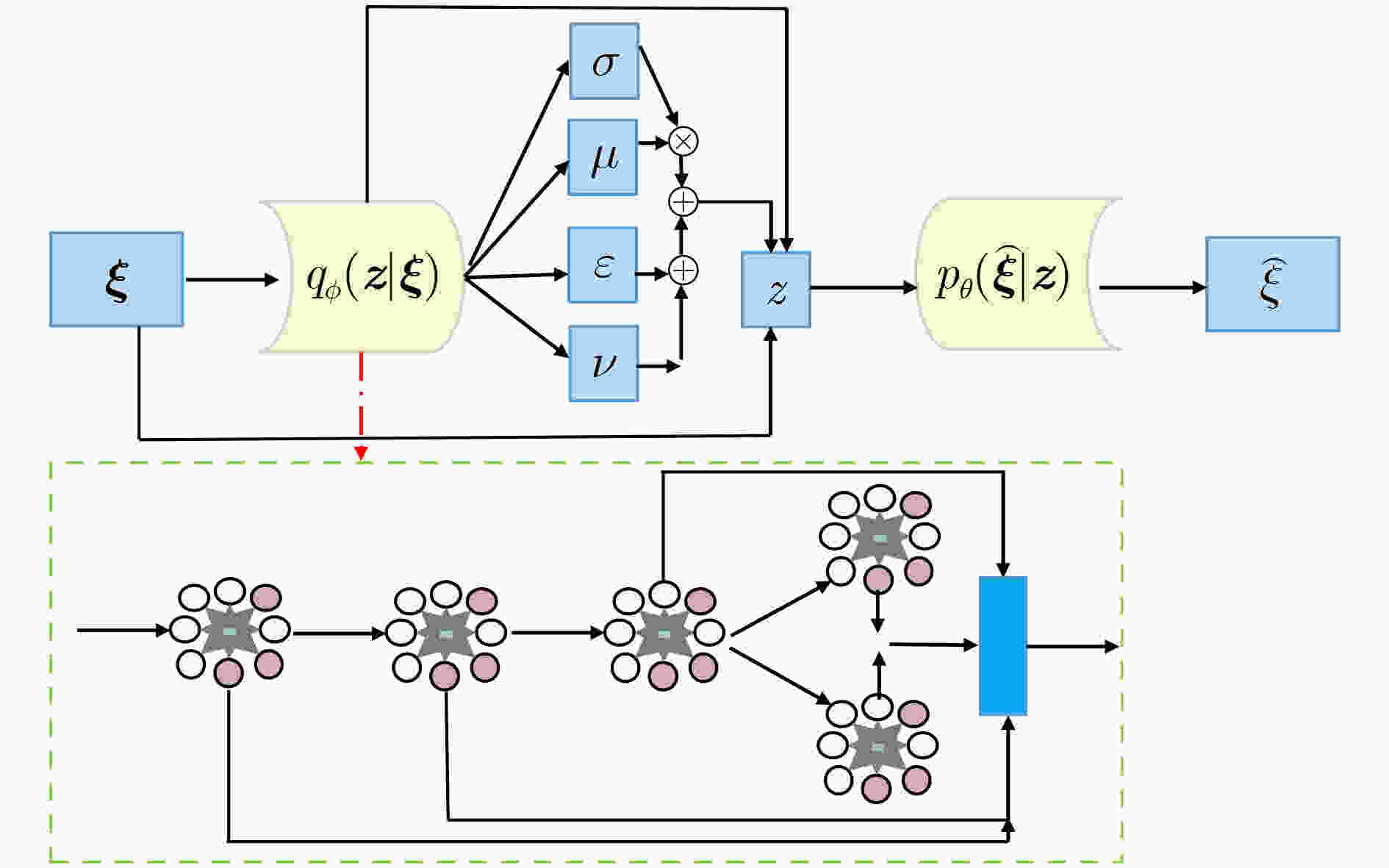
摘要: 小核糖核酸(miRNA)在基因表达和转录等过程中具有重要作用,与疾病的产生有着密切关联。对于疾病miRNA关联识别,生物鉴定方法代价高、耗时长和效率低。为快速自适应提取疾病和miRNA构成的异质网络信息,该文基于通道型注意力设计变分门图自编码器和门多层感知器,构建一种深度变分门神经网络模型(VGAE-N)并用于疾病miRNA关联预测任务。该模型整合miRNA及疾病的多种相似度信息得到miRNA和疾病的整合相似性特征,然后基于多数据融合的整合相似性网络和疾病miRNA邻接信息,利用变分门图自编码器提取miRNA和疾病网络的拓扑信息和语义信息;其次基于疾病miRNA关联矩阵,利用非负矩阵分解提取miRNA和疾病的低维线性去噪特征;最后,利用门多层感知器融合miRNA和疾病特征,预测其关联关系。实验结果表明VGAE-N模型能更有效地预测疾病miRNA关联,可为生物实验提供可靠的技术支撑。
-
关键词:
- 变分自编码器 /
- 矩阵分解 /
- 门机制 /
- 疾病小核糖核酸关联预测
Abstract: micro RiboNucleic Acid (miRNA) plays an important role in the process of gene expression and transcription, and is closely related to the production of diseases. Biological experimental methods for disease miRNA association prediction are costly and time-consuming. To extract contextual information in heterogeneous networks of diseases and miRNAs, a high-performance Variational Gated AutoEncoder Network (VGAE-N) and a gated multi-layer perceptron are designed based on gated mechanisms and convolutions, and then a deep variational gated neural model is constructed for inferring disease miRNA associations. Multisource information first is integrated between miRNAs and diseases, and then the comprehensive similarity matrix is obtained between miRNAs and diseases. Based on a comprehensive network and the miRNA disease adjacency matrix, topological information is further extracted for miRNAs and diseases, respectively. Based on the miRNA disease adjacency matrix, the nonnegative matrix decomposition is used to extract low dimensional denoising features of miRNA and diseases. The experimental results show that the proposed model can effectively conduct miRNA disease association prediction, and provide reliable technical support for biological experiments. -
表 1 VGAE-N模型的消融实验研究(%)
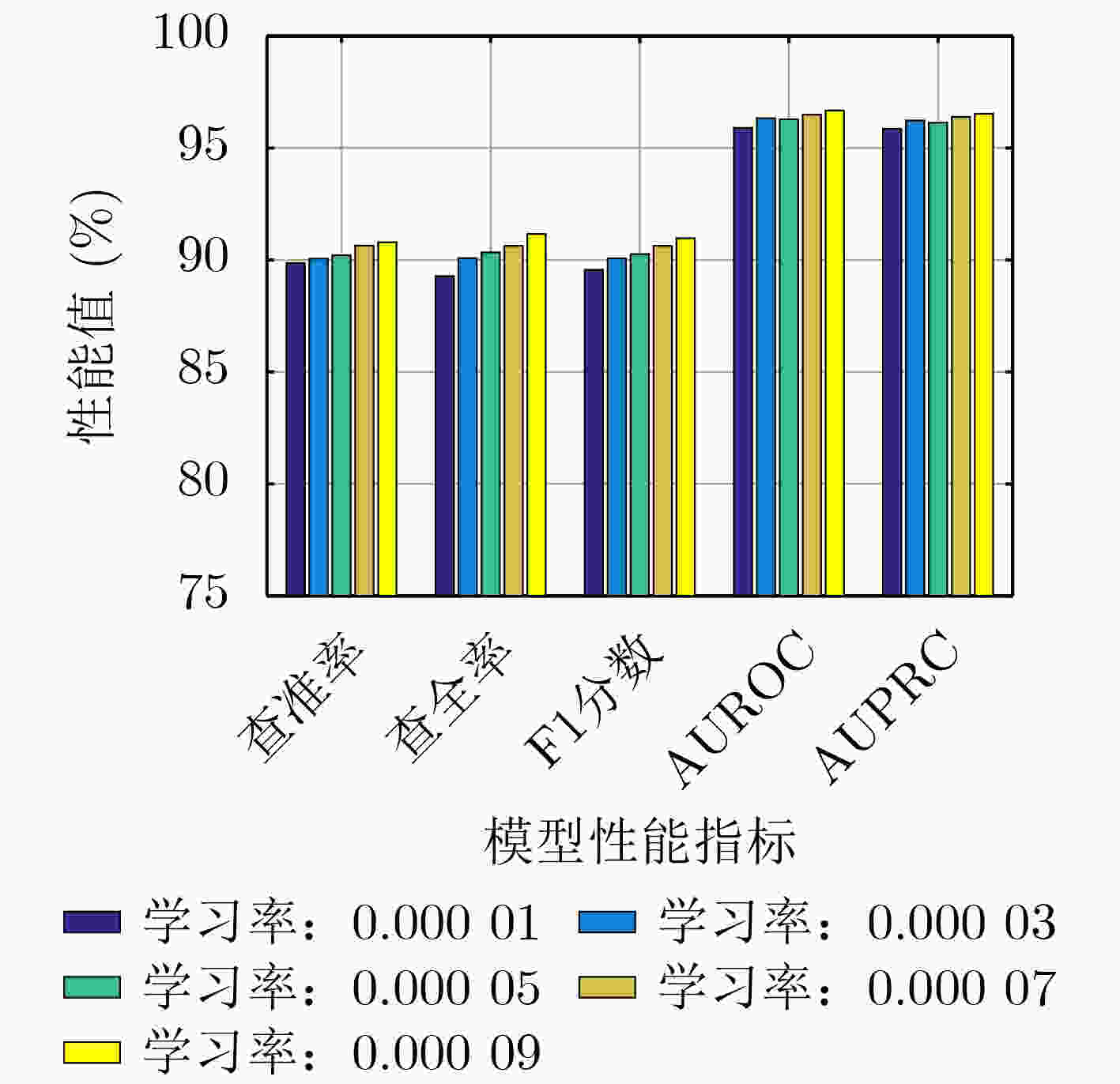
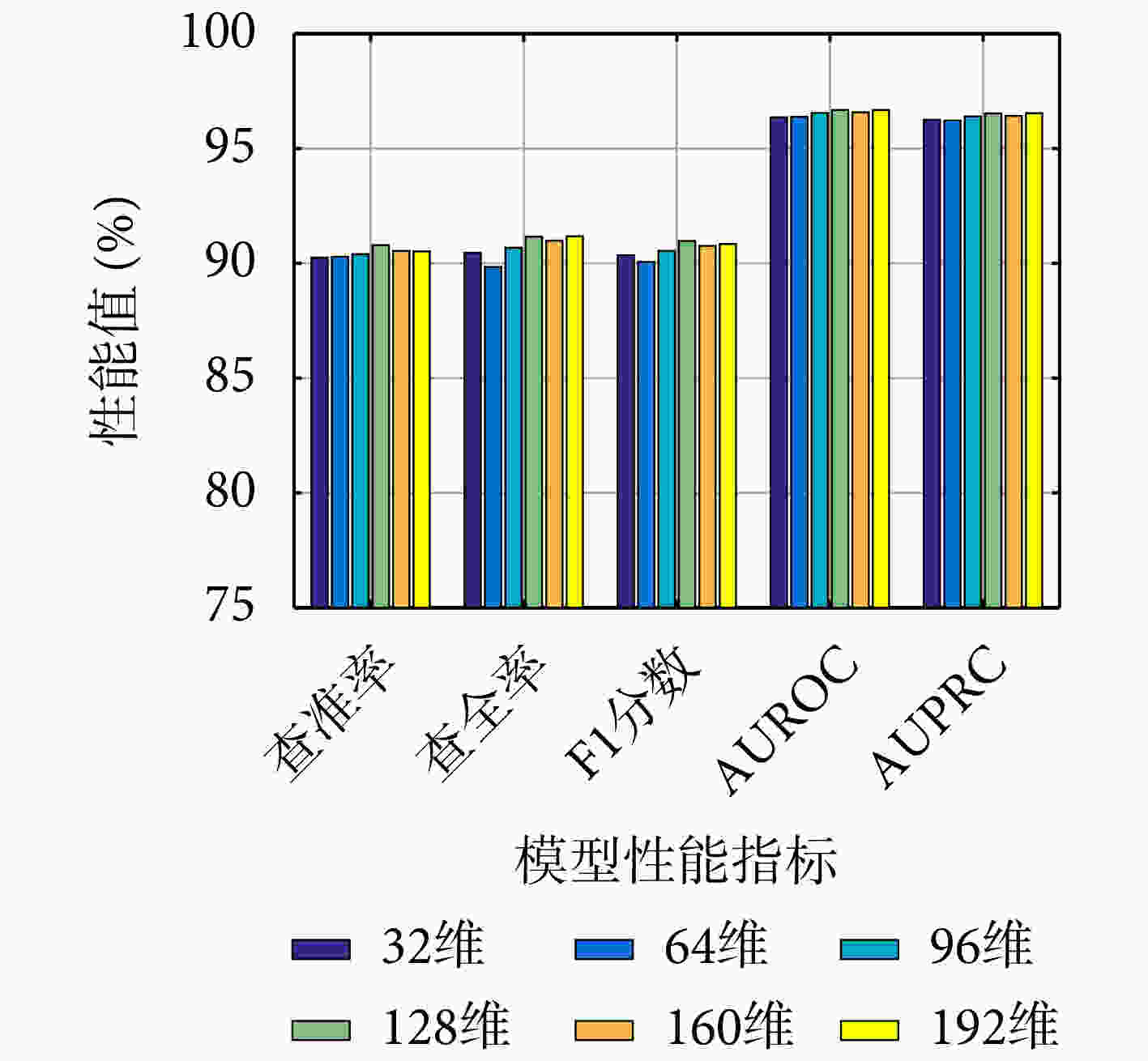
模型 查准率 查全率 F1分数 AUROC AUPRC VGAE-N 90.79 91.16 90.97 96.68 96.53 -BN 90.42 90.11 90.25 96.35 96.24 -FF 89.78 91.00 90.38 96.49 96.33 -GM 89.62 92.15 90.86 96.61 96.42 表 2 在HMDDv3.2数据集上VGAE-N和基准模型的性能(%)
-
[1] 刘文斌, 吴倩, 杜玉改, 等. 基于个性化网络标志物的药物推荐方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1340–1347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190837LIU Wenbin, WU Qian, DU Yugai, et al. Drug recommendation based on individual specific biomarkers[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1340–1347. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190837 [2] 郭茂祖, 王诗鸣, 刘晓燕, 等. miRNA与疾病关联关系预测算法[J]. 软件学报, 2017, 28(11): 3094–3102. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005351GUO Maozu, WANG Shiming, LIU Xiaoyan, et al. Algorithm for predicting the associations between MiRNAs and diseases[J]. Journal of Software, 2017, 28(11): 3094–3102. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005351 [3] 王磊, 徐涛, 宋传东, 等. 基于深度学习的miRNA与疾病相关性预测算法[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(5): 870–877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.05.006WANG Lei, XU Tao, SONG Chuandong, et al. Prediction algorithm of association between miRNAs and diseases based on deep learning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(5): 870–877. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.05.006 [4] ZHENG Kai, YOU Zhuhong, WANG Lei, et al. MISSIM: An incremental learning-based model with applications to the prediction of miRNA-disease association[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2021, 18(5): 1733–1742. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2020.3013837 [5] GUO Leiming, SHI Kun, and WANG Lin. MLPMDA: Multi-layer linear projection for predicting miRNA-disease association[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 214: 106718. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106718 [6] SHI Hongbo, XU Juan, ZHANG Guangde, et al. Walking the interactome to identify human miRNA-disease associations through the functional link between miRNA targets and disease genes[J]. BMC Systems Biology, 2013, 7(1): 101. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-101 [7] 高鹏, 陈智华. 一种基于拓扑信息的预测疾病相关的MicroRNAs方法[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(2): 333–340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.02.016GAO Peng and CHEN Zhihua. A method for predicting disease-related MicroRNAs based on topological information[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(2): 333–340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.02.016 [8] LIU Yuansheng, ZENG Xiangxiang, HE Zengyou, et al. Inferring microRNA-disease associations by random walk on a heterogeneous network with multiple data sources[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2017, 14(4): 905–915. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2016.2550432 [9] YAN Cheng, WANG Jianxin, NI Peng, et al. DNRLMF-MDA: Predicting microRNA-disease associations based on similarities of microRNAs and diseases[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2019, 16(1): 233–243. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2017.2776101 [10] CHEN Xing, HUANG Li, XIE Di, et al. EGBMMDA: Extreme gradient boosting machine for miRNA-disease association prediction[J]. Cell Death & Disease, 2018, 9(1): 3. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0003-x [11] XUAN Ping, SHEN Tonghui, WANG Xiao, et al. Inferring disease-associated microRNAs in heterogeneous networks with node attributes[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2020, 17(3): 1019–1031. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2018.2872574 [12] NIU Yawei, WANG Guanghui, YAN Guiying, et al. Integrating random walk and binary regression to identify novel miRNA-disease association[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2019, 20(1): 59. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2640-9 [13] LUO Jiawei, DING Pingjian, LIANG Cheng, et al. Collective prediction of disease-associated miRNAs based on transduction learning[J]. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2017, 14(6): 1468–1475. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2016.2599866 [14] CHEN Xing and HUANG Li. LRSSLMDA: Laplacian regularized sparse subspace learning for miRNA-disease association prediction[J]. PLoS Computational Biology, 2017, 13(12): e1005912. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005912 [15] PENG Jiajie, HUI Weiwei, LI Qianqian, et al. A learning-based framework for miRNA-disease association identification using neural networks[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(21): 4364–4371. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz254 [16] CHEN Xing, GONG Yao, ZHANG Dehong, et al. DRMDA: Deep representations-based miRNA-disease association prediction[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 2018, 22(1): 472–485. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13336 [17] LI Jin, ZHANG Sai, LIU Tao, et al. Neural inductive matrix completion with graph convolutional networks for miRNA-disease association prediction[J]. Bioinformatics, 2020, 36(8): 2538–2546. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz965 [18] ZHENG Kai, YOU Zhuhong, WANG Lei, et al. iMDA-BN: Identification of miRNA-disease associations based on the biological network and graph embedding algorithm[J]. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18: 2391–2400. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.08.023 [19] DING Yulian, TIAN Liping, LEI Xiujuan, et al. Variational graph auto-encoders for miRNA-disease association prediction[J]. Methods, 2021, 192: 25–34. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.08.004 [20] DING Yulian, LEI Xiujuan, LIAO Bo, et al. Predicting miRNA-disease associations based on multi-view variational graph auto-encoder with matrix factorization[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2022, 26(1): 446–457. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3088342 [21] 袁野, 贾克斌, 刘鹏宇. 基于深度卷积神经网络的多元医学信号多级上下文自编码器[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 371–378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190135YUAN Ye, JIA Kebin, and LIU Pengyu. Multi-context autoencoders for multivariate medical signals based on deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 371–378. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190135 [22] DAUPHIN Y N, FAN A, AULI M, et al. Language modeling with gated convolutional networks[C]. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 2017: 933–941. [23] LI Yang, QIU Chengxiang, TU Jian, et al. HMDD v2.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA and disease associations[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(D1): D1070–D1074. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1023 [24] HUANG Zhou, SHI Jiangcheng, GAO Yuanxu, et al. HMDD v3.0: A database for experimentally supported human microRNA-disease associations[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2019, 47(D1): D1013–D1017. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1010 [25] KOZOMARA A and GRIFFITHS-JONES S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2014, 42(D1): D68–D73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1181 [26] CHOU C H, SHRESTHA S, YANG C D, et al. miRTarBase update 2018: A resource for experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2018, 46(D1): D296–D302. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1067 [27] WANG Dong, WANG Juan, LU Ming, et al. Inferring the human microRNA functional similarity and functional network based on microRNA-associated diseases[J]. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(13): 1644–1650. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq241 [28] VAN LAARHOVEN T, NABUURS S B, and MARCHIORI E. Gaussian interaction profile kernels for predicting drug–target interaction[J]. Bioinformatics, 2011, 27(21): 3036–3043. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr500 [29] WANG Bo, MEZLINI A M, DEMIR F, et al. Similarity network fusion for aggregating data types on a genomic scale[J]. Nature Methods, 2014, 11(3): 333–337. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2810 [30] LI Yanghao, WANG Naiyan, SHI Jianping, et al. Adaptive batch normalization for practical domain adaptation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2018, 80: 109–117. doi: 10.1016/J.patcog.2018.03.005 [31] XIAO Qiu, DAI Jianhua, LUO Jiawei, et al. Multi-view manifold regularized learning-based method for prioritizing candidate disease miRNAs[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 175: 118–129. doi: 10.1016/J.knosys.2019.03.023 [32] ZHAO Yan, CHEN Xing, and YIN Jun. Adaptive boosting-based computational model for predicting potential miRNA-disease associations[J]. Bioinformatics, 2019, 35(22): 4730–4738. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz297 [33] ZHANG Li, CHEN Xing, and YIN Jun. Prediction of potential mirna–disease associations through a novel unsupervised deep learning framework with variational autoencoder[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(9): 1040. doi: 10.3390/cells8091040 [34] DING Yulian, WANF Fei, LEI Xiujuan, et al. Deep belief network–based matrix factorization model for MicroRNA-disease associations prediction[J]. Evolutionary Bioinformatics, 2020, 16: 17693432091970. doi: 10.1177/1176934320919707 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
