An Performance Optimization Scheme for Flash Memory System in 6G Mobile Network: Bit Remapping
-
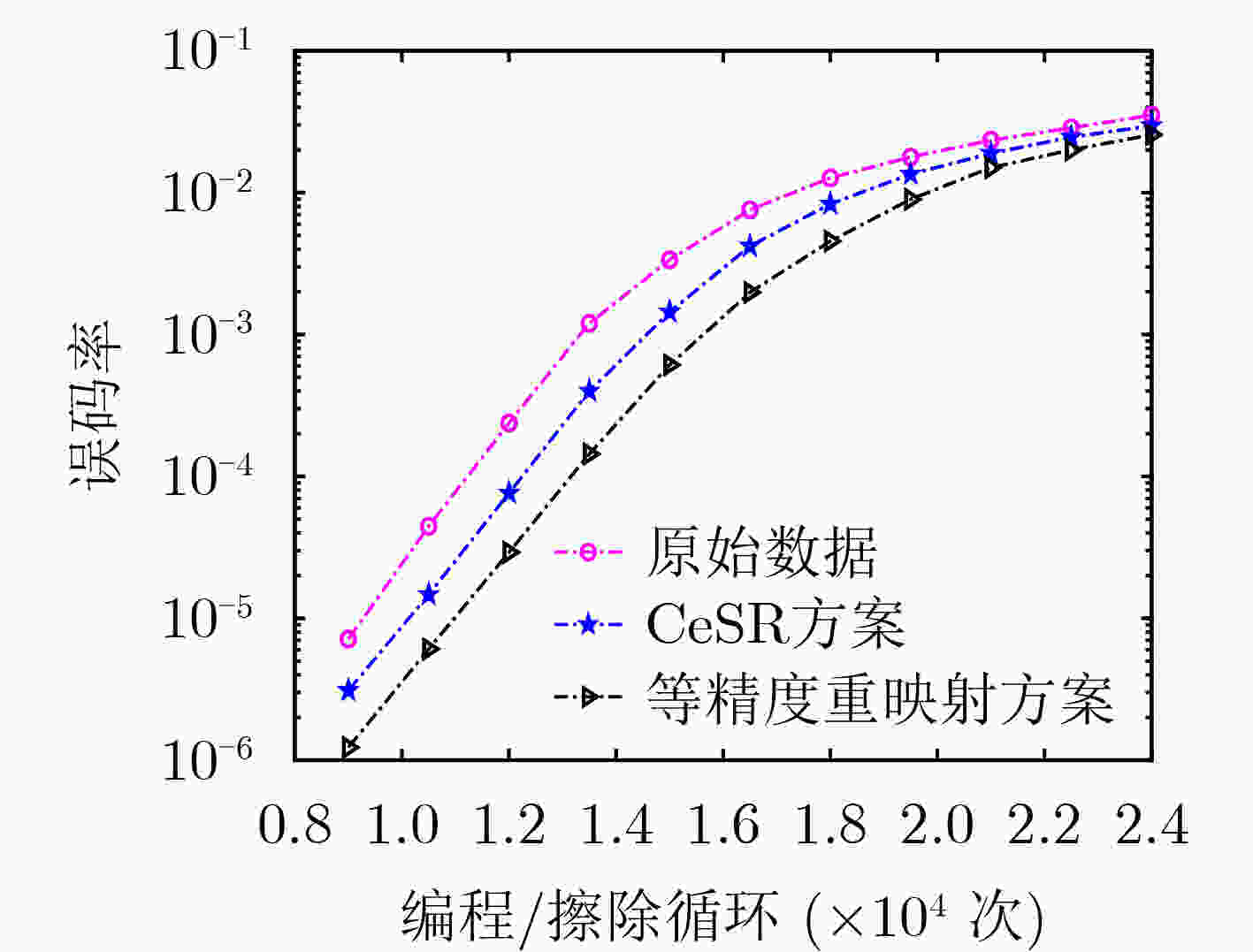
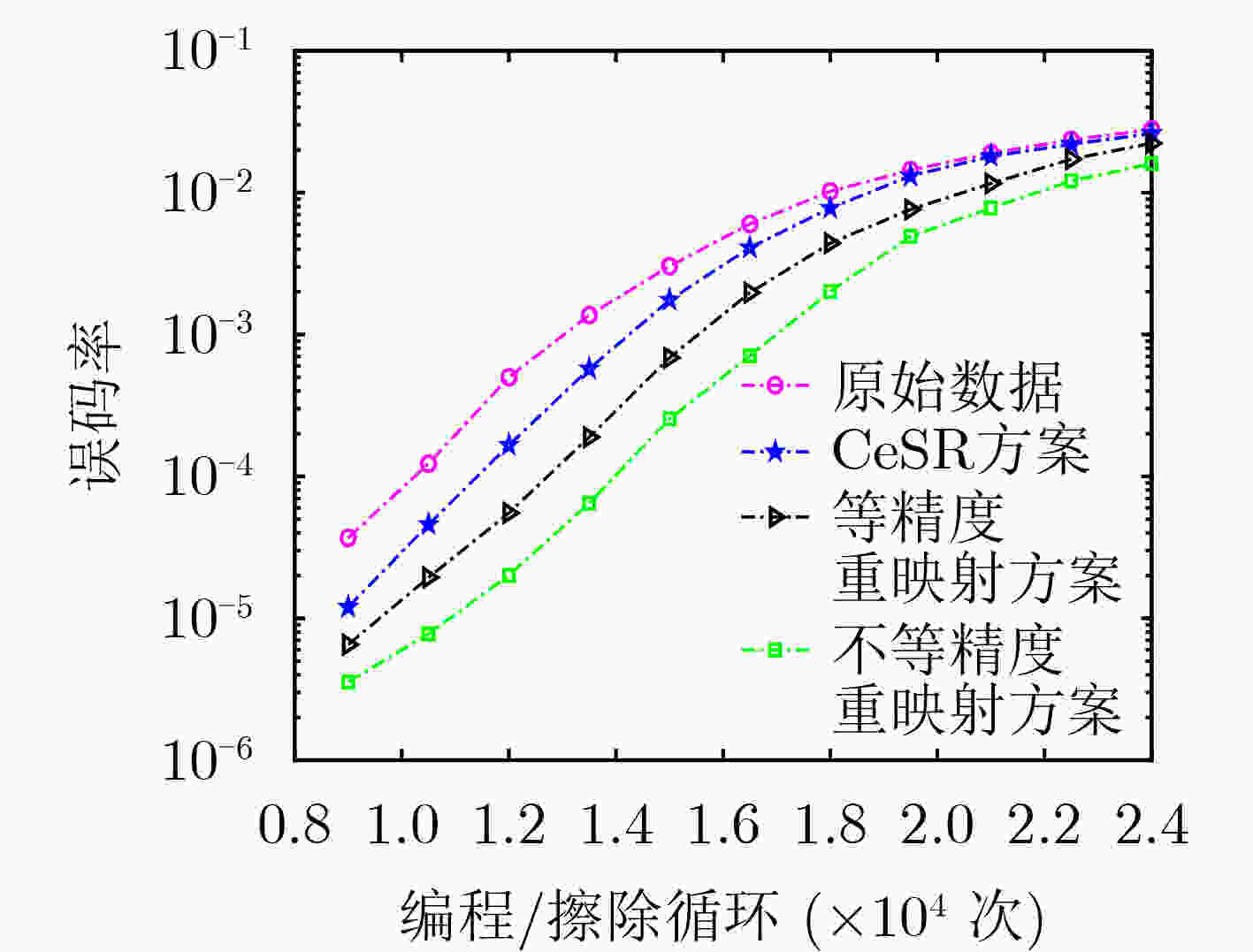
摘要: 第6代移动通信技术(6G)网络所产生的海量数据对数据存储带来了全新挑战,推动着存储技术的迅猛发展。与非门(NAND)闪存存储器具有读写速度快,可靠性高等优点,故在6G网络中具有广泛的应用前景。为了提高NAND闪存的可靠性,针对两种不同位线结构的错误特性,该文分别提出基于全位线结构的等精度重映射方案和基于奇偶位线结构的不等精度的重映射方案。仿真结果表明,两种新型比特重映射方案有效提升了闪存的误码性能。基于此,该文所提重映射技术可被视作6G网络中可靠而高效的存储优化技术。Abstract: The massive data generated by the sixth generation mobile communication technology (6G) network brings new challenges to data storage, which promotes further the rapid development of storage technology. Not AND (NAND) flash memory has the advantages of fast reading/writing speed and high reliability, and hence it possesses a wide application prospect in the 6G network. To improve the reliability of NAND flash memory, according to the error characteristics of two different bit-line structures, an all-bit-line-structure-aided equal-precision remapping scheme and an odd-even-bit-line-structure-aided unequal-precision remapping scheme are proposed. Simulation results show that the two new remapping schemes improve effectively the bit error performance of flash memory. Therefore, the remapping technology proposed in this paper can be regarded as a reliable and efficient storage optimization technology for 6G network.
-
Key words:
- 6G network /
- Data storage /
- All bit-line structure /
- Odd-even bit-line structure /
- Bit remapping
-
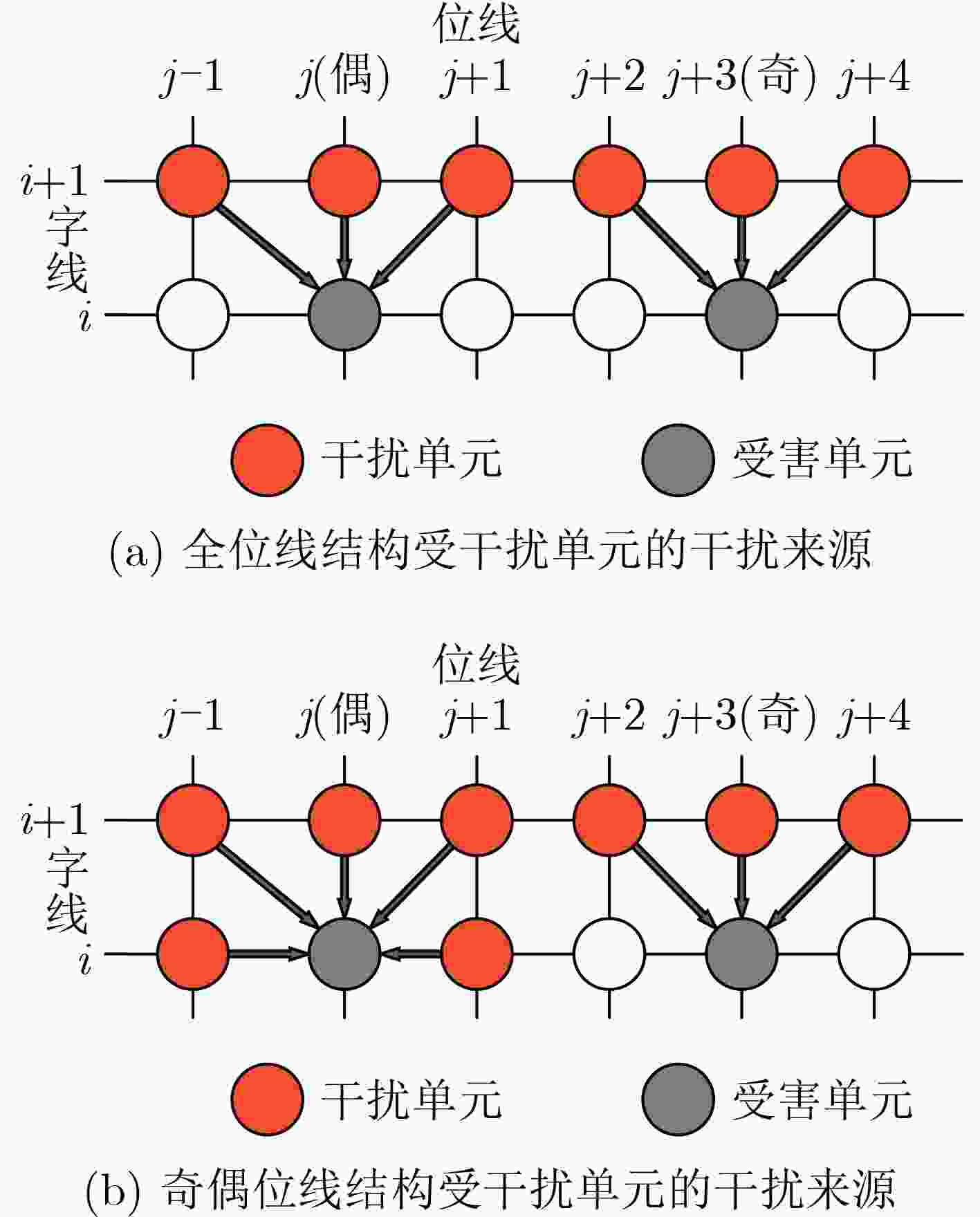
表 1 新型全位线结构重映射方案(算法1)
输入:原始数据${D_{\text{R}}}$ 输出:重映射后的数据$ D_{\text{R}}' $ (1) 获取原始数据${D_{\text{R}}}$; (2) 将${D_{\text{R}}}$划分成$N$个数据段${S_1},{\text{ }}{S_2},\cdots,{\text{ }}{S_N}$; (3) for 数据段${S_n}{\text{ (}}n \in \{ 1,{\text{ }}2,\cdots,{\text{ }}N\} {\text{)}}$ do (4) 统计MSB页上1的比例:${R_{{\text{MSB}}}}$; (5) if ${R_{{\text{MSB}}}} < 50\% $,then (6) 对MSB页上的数据执行比特翻转操作; (7) 分别统计对应MSB页为1和0时LSB页上1的比例:
${L^{{\text{MSB = 1}}}},{L^{{\text{MSB = 0}}}}$;(8) if ${L^{{\text{MSB = 1}}}} < 50\% $,then (9) 对$ {\text{MSB}} = 1 $对应的LSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (10) if ${L^{{\text{MSB = 0}}}} > 50\% $,then (11) 对$ {\text{MSB}} = 0 $对应的LSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (12) 记录标志位 (13) end (14) 输出重映射后的数据$ D_{\text{R}}' $; (15) 结束 表 2 新型奇偶位线结构重映射方案(算法2)
输入:原始数据${D_{\text{R}}}$ 输出:重映射后的数据$ D_{\text{R}}' $ (1) 获取原始数据${D_{\text{R}}}$,其中偶单元中的数据为$ D_{\text{R}}^{{\text{even}}} $,奇单元的
数据为$ D_{\text{R}}^{{\text{odd}}} $;(2) 将$ D_{\text{R}}^{{\text{even}}} $划分成$N$个数据段:$S_1^{{\text{even}}},{\text{ }}S_2^{{\text{even}}},\cdots,{\text{ }}S_N^{{\text{even}}}$,将
$ D_{\text{R}}^{{\text{odd}}} $划分成$M$ ($ M > N $)个数据段$S_1^{{\text{odd}}},{\text{ }}S_2^{{\text{odd}}},\cdots,{\text{ }}S_M^{{\text{odd}}}$;(3) for $ S_n^{{\text{even}}}{\text{ (}}n \in \{ 1,{\text{ }}2,\cdots,{\text{ }}N\} ) $ do (4) 统计MSB页上1的比例$M_n^{{\text{even}}}$; (5) if $M_n^{{\text{even}}} < 50\% $,then (6) 对MSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (7) 统计对应MSB页为1和0时LSB页上1的比例
${L^{{\text{MSB = 1}}}},{L^{{\text{MSB = 0}}}}$(8) if ${L^{{\text{MSB = 1}}}} < 50\% $,then (9) 对$ {\text{MSB = 1}} $对应的LSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (10) if ${L^{{\text{MSB = 0}}}} > 50\% $,then (11) 对$ {\text{MSB = 0}} $对应的LSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (12) 记录标志位 (13) end (14) for $S_m^{{\text{odd}}}{\text{ (}}m \in \{ 1,{\text{ }}2,\cdots,{\text{ }}M\} )$ do (15) 统计MSB页上1的比例$M_m^{{\text{odd}}}$; (16) if $M_m^{{\text{odd}}} < 50\% $,then (17) 对MSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (18) 统计对应MSB页为1和0时LSB页上1的比例
${L^{{\text{MSB = 1}}}},{L^{{\text{MSB = 0}}}}$(19) if ${L^{{\text{MSB = 1}}}} < 50\% $,then (20) 对$ {\text{MSB = 1}} $对应的LSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (21) if ${L^{{\text{MSB = 0}}}} > 50\% $,then (22) 对$ {\text{MSB = 0}} $对应的LSB页数据执行比特翻转操作; (23) 记录标志位 (24) end (25) 输出重映射后的数据$ D_{\text{R}}' $; (26) 结束 -
[1] SANDELL M and ISMAIL A. Machine learning for LLR estimation in flash memory with LDPC codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2021, 68(2): 792–796. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2020.3016979 [2] LEE W, KANG M, HONG S, et al. Interpage-based endurance-enhancing lower state encoding for MLC and TLC flash memory storages[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2019, 27(9): 2033–2045. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2912228 [3] YU D K H and HSIEH J W. A management scheme of multi-level retention-time queues for improving the endurance of flash-memory storage devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 2020, 69(4): 549–562. doi: 10.1109/TC.2019.2954398 [4] LEE H C, SHY J H, CHEN Y M, et al. LDPC coded modulation for TLC flash memory[C]. 2017 IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW), Kaohsiung, China, 2017: 204–208. [5] SHI Zhifang, FANG Yi, BU Yingcheng, et al. Convolutional neural network (CNN)-based detection for multi-level-cell NAND flash memory[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(12): 3883–3887. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3112908 [6] CUI Lanlan, WU Fei, LIU Xiaojian, et al. Improving LDPC decoding performance for 3D TLC NAND flash by LLR optimization scheme for hard and soft decision[J]. ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems, 2022, 27(1): 5. doi: 10.1145/3473305 [7] ASLAM C A, GUAN Yongliang, and CAI Kui. Retention-aware belief-propagation decoding for NAND flash memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2017, 64(6): 725–729. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2016.2602359 [8] ZHANG Meng, WU Fei, DU Yajuan, et al. CooECC: A cooperative error correction scheme to reduce LDPC decoding latency in NAND flash[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Boston, USA, 2017: 657–664. [9] PARK Y, LEE J, CHO S S, et al. Scaling and reliability of NAND flash devices[C]. 2014 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, Waikoloa, USA, 2014: 2E. 1.1–2E. 1.4. [10] CAI Yu, HARATSCH E F, MUTLU O, et al. Threshold voltage distribution in MLC NAND flash memory: Characterization, analysis, and modeling[C]. 2013 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Grenoble, France, 2013: 1285–1290. [11] GUO Jie, WANG Danghui, SHAO Zili, et al. Data-pattern-aware error prevention technique to improve system reliability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2017, 25(4): 1433–1443. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2016.2642055 [12] WEI Debao, DENG Libao, ZHANG Peng, et al. NRC: A nibble remapping coding strategy for NAND flash reliability extension[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2016, 35(11): 1942–1946. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2016.2533861 [13] QIN Hongwei, ZHAO Yutong, FENG Dan, et al. CeSR + assisted LDPC: A holistic strategy to improve MLC NAND flash reliability[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 63239–63254. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2985291 [14] BU Yingcheng, FANG Yi, ZHANG Guohua, et al. Achievable-rate-aware retention-error correction for multi-level-cell NAND flash memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, To be published. [15] MEI Zhen, CAI Kui, and HE Xuan. Deep learning-aided dynamic read thresholds design for multi-level-cell flash memories[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(5): 2850–2862. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2974723 [16] SUN Wenhao and ZHENG Jianping. A low-complexity retention noise parameter estimation for MLC NAND flash memory[C]. The ICC 2019-2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. [17] 张司琪, 孔令军, 张顺外, 等. MLC型NAND闪存中基于MI异构的Polar码优化[J]. 应用科学学报, 2020, 38(3): 431–440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0255-8297.2020.03.009ZHANG Siqi, KONG Lingjun, ZHANG Shunwai, et al. Optimization design of polar codes based on MI heterogeneity in MLC NAND flash channel[J]. Journal of Applied Sciences, 2020, 38(3): 431–440. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0255-8297.2020.03.009 [18] KIM T, KONG G, XI Weiya, et al. Cell-to-cell interference compensation schemes using reduced symbol pattern of interfering cells for MLC NAND flash memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, 2013, 49(6): 2569–2573. doi: 10.1109/TMAG.2013.2251417 [19] DONG Guiqiang, LI Shu, and ZHANG Tong. Using data postcompensation and predistortion to tolerate cell-to-cell interference in MLC NAND flash memory[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I:Regular Papers, 2010, 57(10): 2718–2728. doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2010.2046966 [20] FANG Yi, BU Yingcheng, CHEN Pingping, et al. Irregular-mapped protograph LDPC-coded modulation: A bandwidth-efficient solution for 6G-enabled mobile networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, To be published. [21] CAI Yu, HARATSCH E F, MUTLU O, et al. Error patterns in MLC NAND flash memory: Measurement, characterization, and analysis[C]. 2012 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 2012: 521–526. [22] DAI Lin, FANG Yi, YANG Zhaojie, et al. Protograph LDPC-coded BICM-ID with irregular CSK mapping in visible light communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(10): 11033–11038. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3106053 -





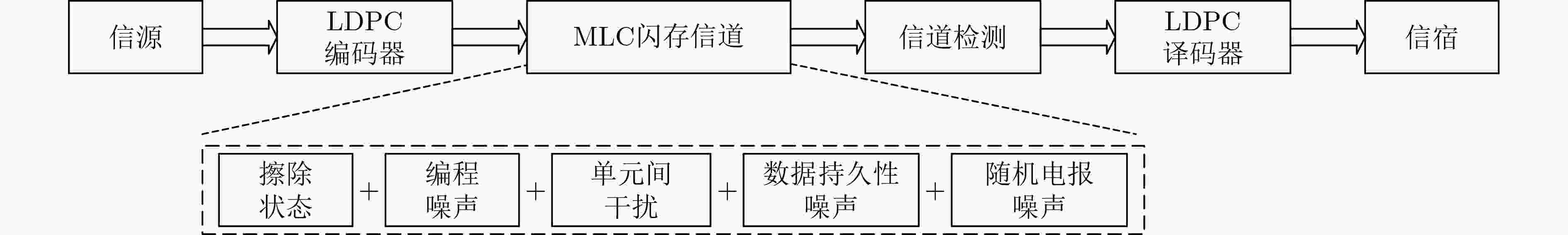
 下载:
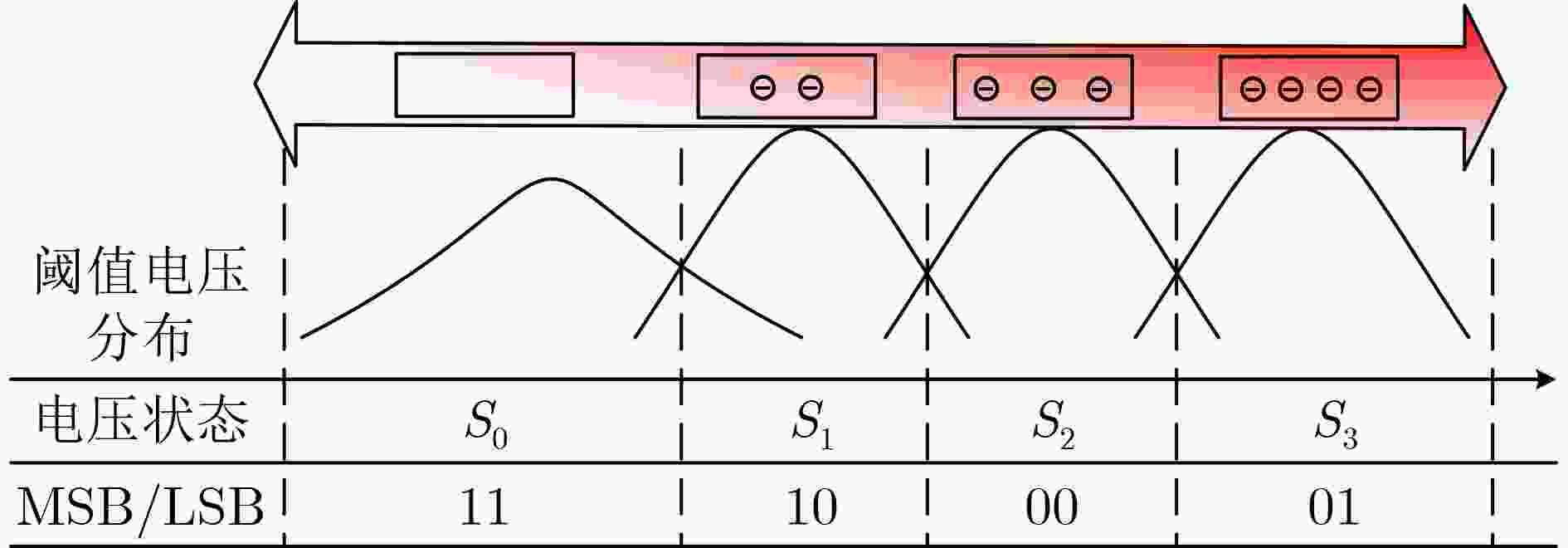
下载:
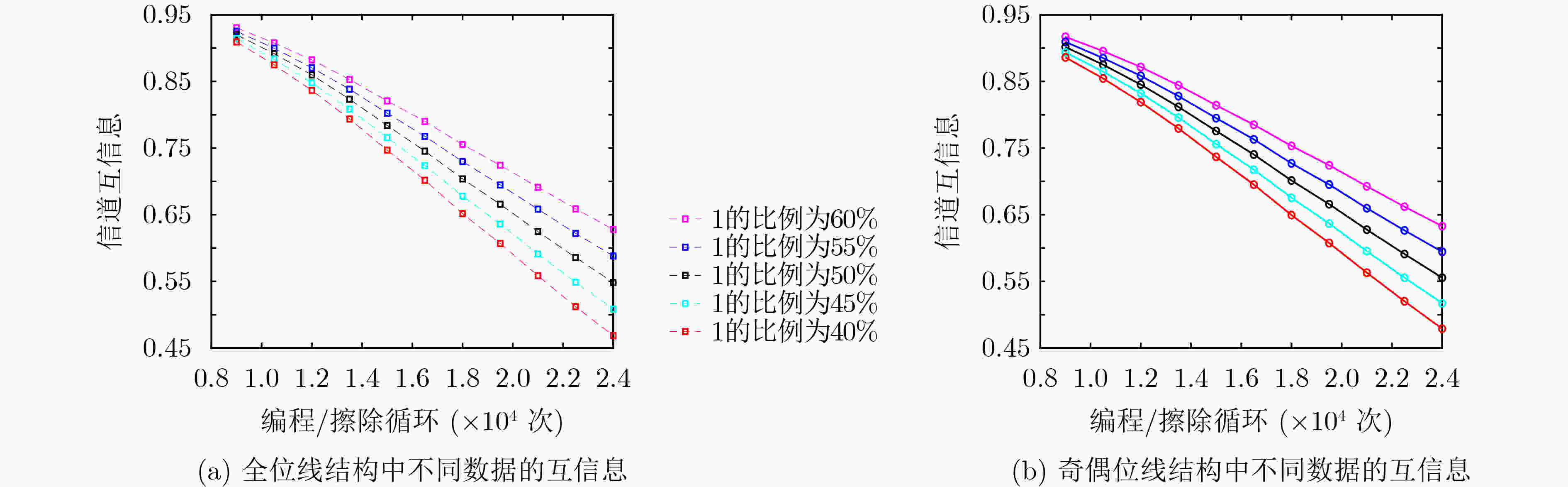


 下载:
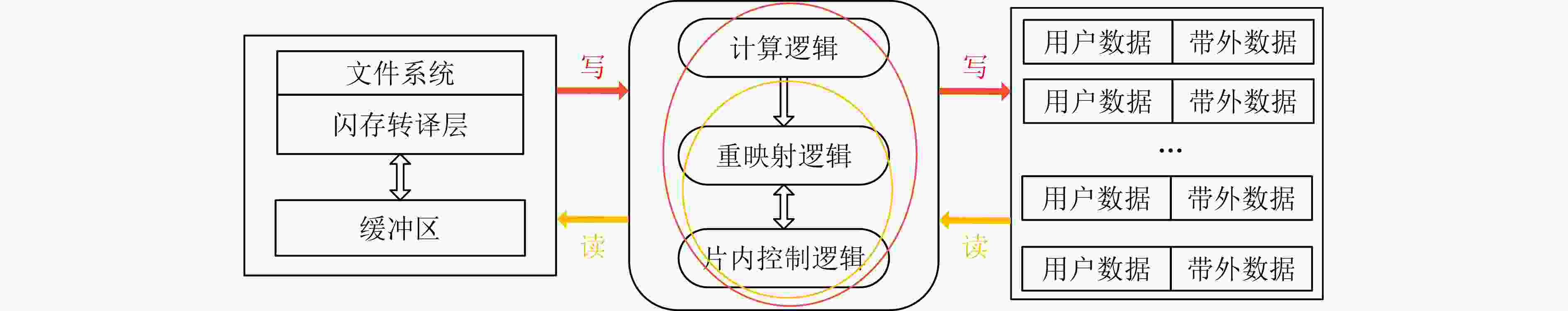
下载:
