A Survey on User-centric Networks for 6G
-
摘要: 与第5代移动通信网络(5G)相比,第6代移动通信网络(6G)有望引入新的性能指标和应用方案,如全球覆盖、更高的频谱/能源/成本效率、更高的智能和安全水平。用户为中心网络(UCN)将成为实现6G的关键推动者,因为其突破了传统基站为中心网络并与信息产业的新兴技术形成了有效融合。该文将从物理层的信道估计和预测、网络上层的性能分析以及链路层的无线资源管理等方面综述这一新型网络的研究现状。首先,讨论和分析UCN的概念和总体网络架构;其次,总结UCN网络中信道估计预测方法、性能分析策略和无线资源管理(RRM)方案;最后,在广泛的调研基础上,探讨UCN网络中的开放性问题,为今后的研究方向提供思路。此综述旨在使读者快速而全面地了解UCN的当前技术状况,从而吸引更多的研究人员进入这一领域。Abstract: Compared with the Fifth Generation mobile network (5G), the Sixth Generation mobile network (6G) is expected to introduce new performance indicators and application scenarios. Global coverage, high spectrum/energy/cost efficiency, high level of intelligence and security are leading features in 6G era. Different from traditional Base Station (BS)-centric network, the User-Centric Network (UCN) emerges as a key enabler for 6G by combining emerging technologies from information industries. In this novel framework, a comprehensive overview of physical layer, network layer and link layer is provided. As a starting point, the concepts and general architecture of the UCNs are surveied and discussed. Then, the survey is classified as: channel estimation and prediction; performance analysis with diverse performance metrics; different types of RRM (Radio Resource Management). Finally, based on extensive discussions, open issues are provided to guide future scholarly research directions. It is anticipated that this survey will provide a quick and comprehensive understanding of the current state of the arts for UCNs which attracting more researchers into this area.
-
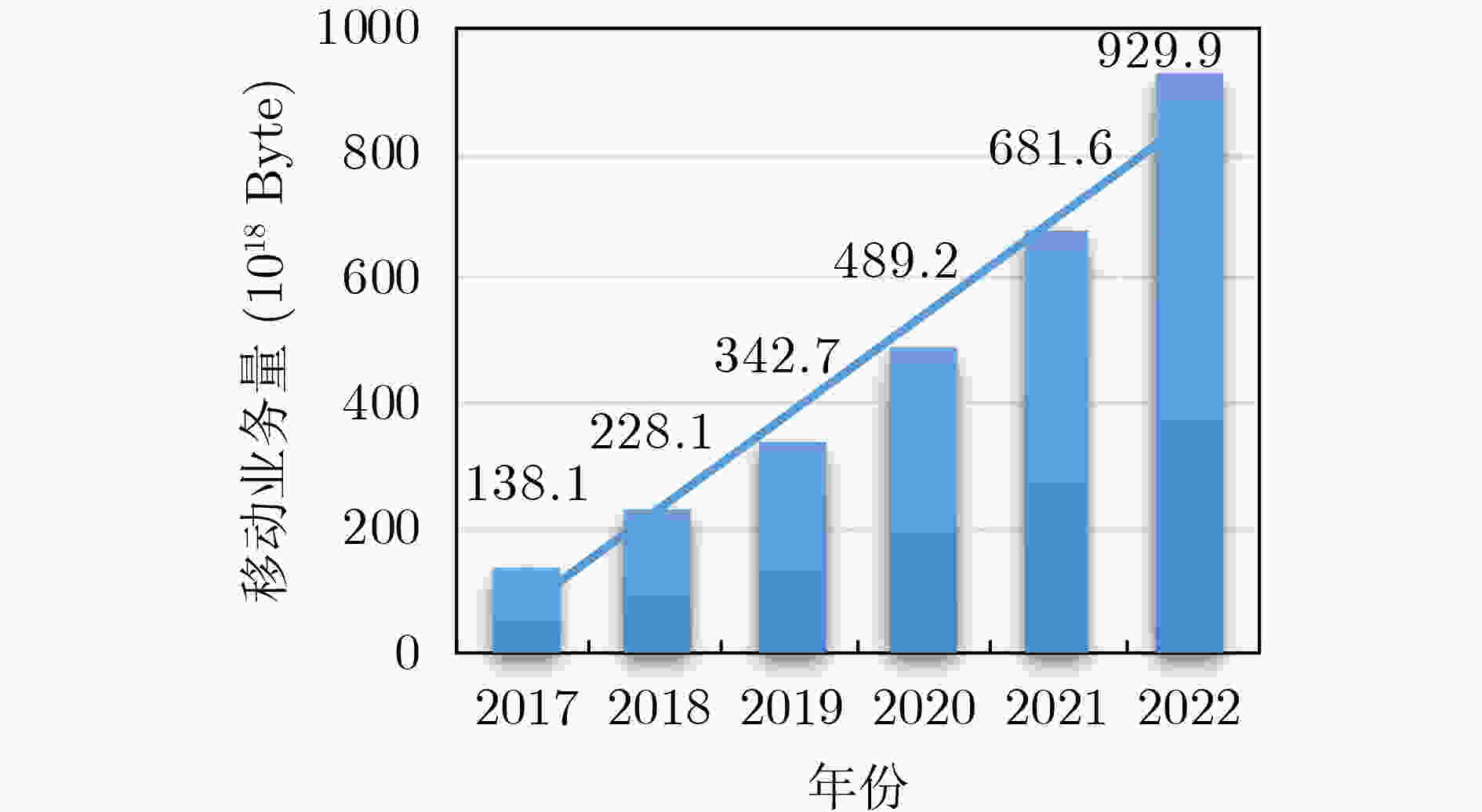
图 1 近几年全球移动数据量增长趋势[1]
表 1 已有综述工作对比
表 2 缩略词
缩写 全拼 含义 3GPP the Third-Generation Partnership Project 第3代伙伴计划 5G the Fifth Generation mobile network 第5代移动通信网络 6G the Sixth Generation mobile network 第6代移动通信网络 AP Access Point 接入节点 BCD Block Coordinate Descent 块坐标下降 BINLP Binary Integer Non-Linear Programming 二进制整数非线性优化 CRAN Cloud Radio Access Network 云接入网 CSI Channel State Information 信道状态信息 CVSINR Cluster Virtual Signal-to-Interference-plus-Noise Ratio 群虚拟信干燥比 DeDU Decoupled Downlink and Uplink 上下行解耦 MISO Multiple Input Single Output 多输入单输出 MIMO Multiple Input Multiple Output 多输入多输出 MINLP Mixed-Integer Non-Linear Programming 混合整型非线性优化 SISO Single Input Single Output 单输入单输出 TCN Traditional Cellular Network 传统蜂窝网络 UCN User-Centric Network 用户为中心网络 UDN Ultra-Dense Network 超密集网络 WMMSE Weighted Minimum Mean Square Error 权重最小均方误差 表 3 UCN与TCN之间的对比
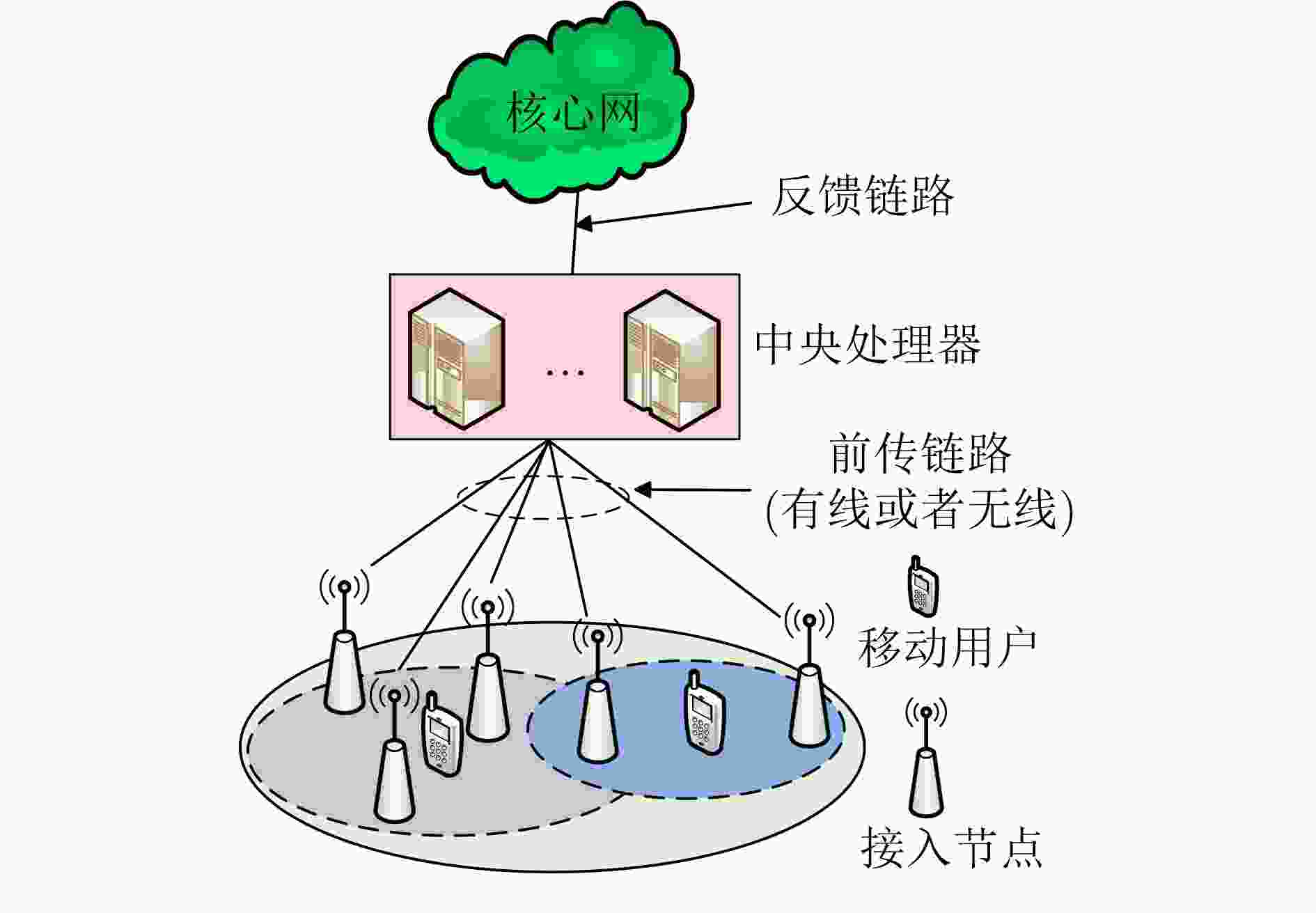
对比内容 网络 TCN UCN 部署范围 较大范围 室内/热点区域 AP密度 低 高 用户密度 远高于AP密度 与AP密度相仿 覆盖特点 异构,不规则形状 单层,规则的蜂窝形状 用户移动性 高 低 速率 中低 高 前传链路 理想的有线链路 理想的有线链路/非理想的无线链路 表 4 信道估计与预测研究工作总结
表 5 性能分析研究工作总结
表 6 无线资源管理研究工作总结
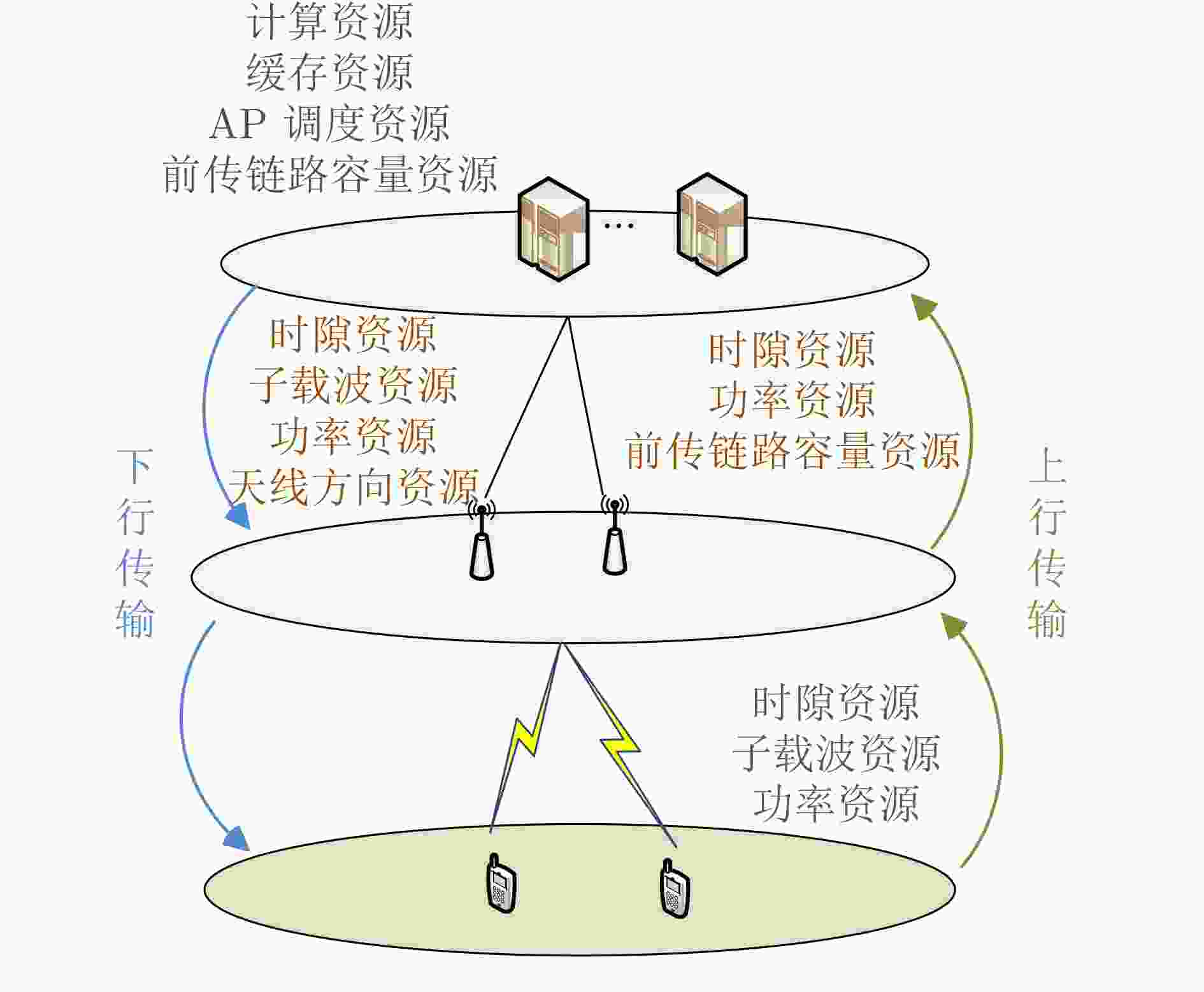
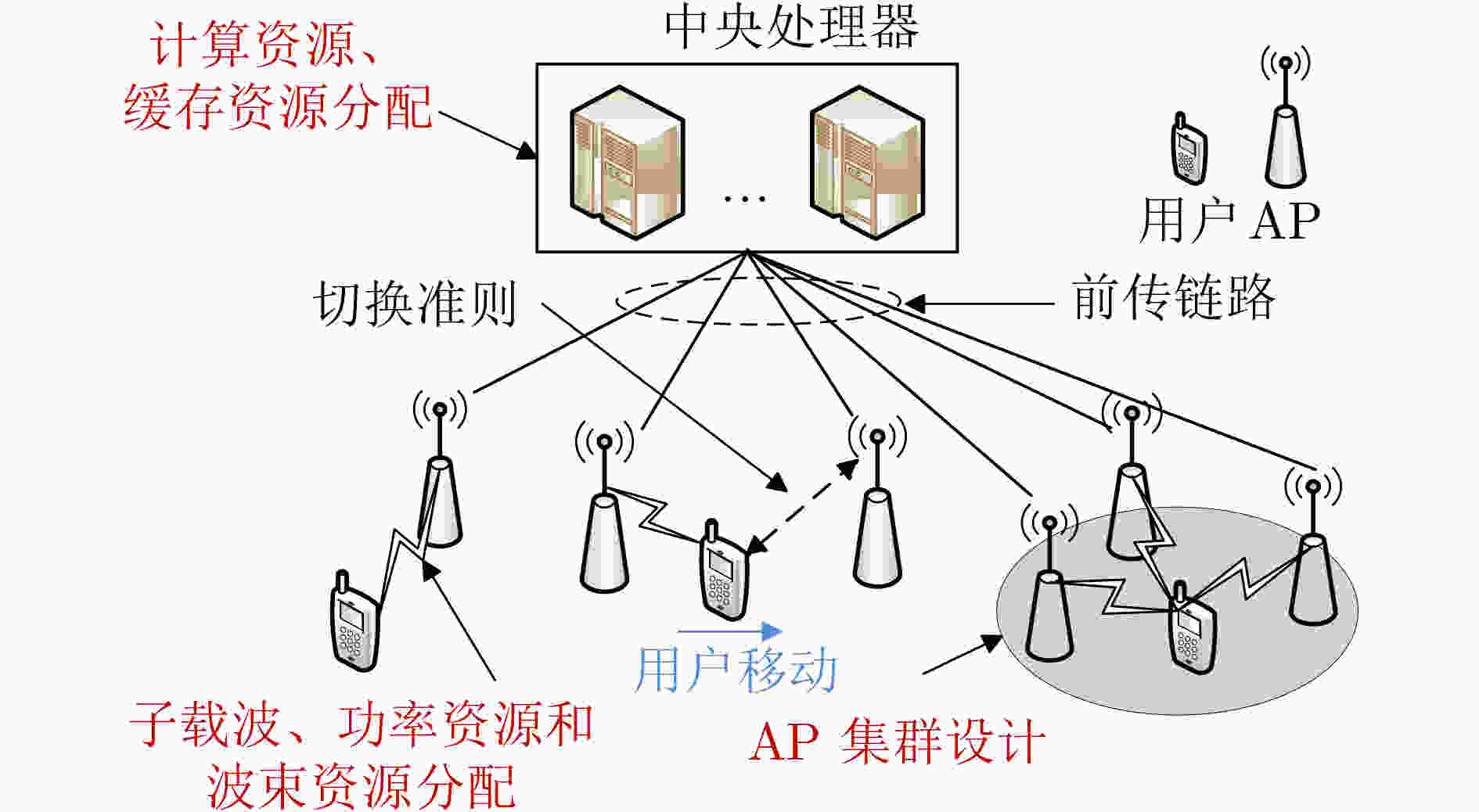
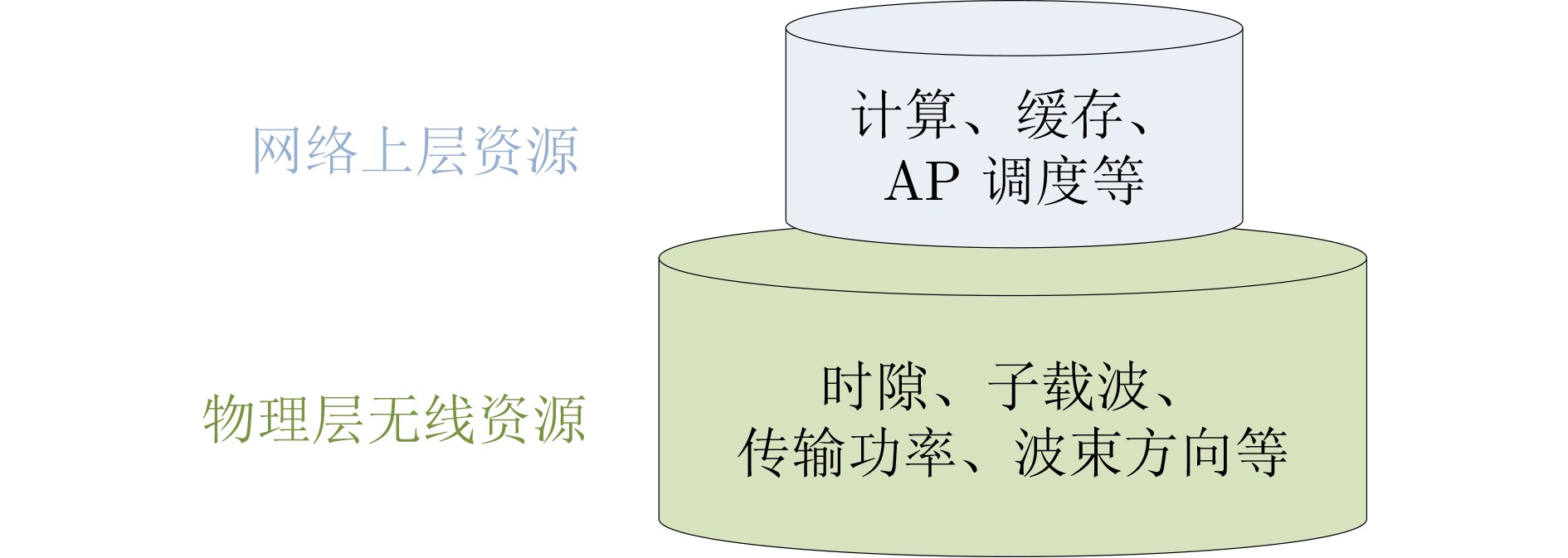
类别 资源种类 文献 方法 单维资源管理 功率资源 文献[49-52] 交替迭代、凸优化理论、深度Q学习网络 计算资源 文献[54,55] 深度强化学习、合作博弈理论 训练资源 文献[53] 图论 2维资源管理 子载波&功率 文献[56,57] 分支切割、交替迭代 链路容量&计算 文献[58] 松弛近似、罚函数 比特&计算 文献[58,59] 线性优化理论、循环神经网络 波束方向&功率 文献[60-62] 松弛近似、深度Q学习网络 3维资源管理 子载波、功率&比特 文献[63] 交替迭代 用户调度、子载波&功率 文献[64,65] 交替迭代、粒子群算法、松弛近似 比特、波束方向&功率 文献[66] 深度学习神经网络 AP集群、波束方向&功率 文献[67-72] 粒子群算法、凸优化理论、松弛近似、WMMSE、
深度残差学习网络、深度神经网络导频、波束方向&功率 文献[73] 信号处理理论、松弛近似 4维资源管理 计算、存储、波束方向&功率 文献[74] 松弛近似、交替迭代 AP集群、传输时隙、波束方向&功率 文献[75] 松弛近似、凸优化理论 AP集群、前传链路压缩比、波束方向&功率 文献[76] 范数最小化、凸优化理论 用户调度、AP集群、子载波&功率 文献[77] 交替迭代、协同优化理论 -
[1] Cisco Visual Networking Index. Global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2017–2022[R]. White Paper, 2019. [2] FEHSKE A, FETTWEIS G, MALMODIN J, et al. The global footprint of mobile communications: The ecological and economic perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2011, 49(8): 55–62. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2011.5978416 [3] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896 [4] XU Yongjun, XIE Hao, WU Qingqing, et al. Robust max-min energy efficiency for RIS-aided HetNets with distortion noises[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(2): 1457–1471. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3141798 [5] XU Yongjun, ZHAO Xiaohui, and LIANG Yingchang. Robust power control and beamforming in cognitive radio networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(4): 1834–1857. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2425040 [6] YOU Xiaohu, WANG Chengxiang, HUANG Jie, et al. Towards 6G wireless communication networks: Vision, enabling technologies, and new paradigm shifts[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(1): 110301. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-2955-6 [7] KASI S K, HASHMI U S, NABEEL M, et al. Analysis of area spectral & energy efficiency in a CoMP-enabled user-centric cloud RAN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2021, 5(4): 1999–2015. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2021.3093390 [8] PENG Mugen, SUN Yaohua, LI Xuelong, et al. Recent advances in cloud radio access networks: System architectures, key techniques, and open issues[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2016, 18(3): 2282–2308. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2016.2548658 [9] CHECKO A, CHRISTIANSEN H L, YAN Ying, et al. Cloud RAN for mobile networks-A technology overview[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(1): 405–426. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2355255 [10] BOCCARDI F, HEANTH R W, LOZANO A, et al. Five disruptive technology directions for 5G[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 74–80. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6736746 [11] 3GPP Technical Specification 36.401–2020. Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access Network (E-UTRAN): Architecture description[TS]. (Release 16), 2020. [12] BOCCARDI F, ANDREWS J, ELSHAER H, et al. Why to decouple the uplink and downlink in cellular networks and how to do it[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(3): 110–117. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7432156 [13] SHARMA T, CHEHRI A, and FORTIER P. Review of optical and wireless backhaul networks and emerging trends of next generation 5G and 6G technologies[J]. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 2021, 32(2): e4155. doi: 10.1002/ett.4155 [14] TEZERGIL B and ONUR E. Wireless backhaul in 5G and beyond: Issues, challenges and opportunities[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2103.08234, 2021. [15] XU Xiao, RAO Xiongbin, and LAU V K N. Active user detection and channel estimation in uplink CRAN systems[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 2015: 2727–2732. [16] HE Qi, QUEK T Q S, CHEN Zhi, et al. . Compressive channel estimation and multi-user detection in C-RAN[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. [17] HE Qi, QUEK T Q S, CHEN Zhi, et al. Compressive channel estimation and multi-user detection in C-RAN with low-complexity methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(6): 3931–3944. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2818125 [18] ZHANG Jianwen, YUAN Xiaojun, and ZHANG Yingjun. Locally orthogonal training design in cloud-RANs[C]. 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, USA, 2016: 1–6. [19] ZHANG Jianwen, YUAN Xiaojun, and ZHANG Yingjun. Locally orthogonal training design for cloud-RANs based on graph coloring[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(10): 6426–6437. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2723471 [20] STEPHEN R G and ZHANG Rui. Uplink channel estimation and data transmission in millimeter-wave CRAN with lens antenna arrays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(12): 6542–6555. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2859996 [21] WANG Jingchao, YI Jie, HAN Rui, et al. Variational Bayesian inference for channel estimation and user activity detection in C-RAN[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(7): 953–956. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2975785 [22] LIU Xuan, SHI Yuanming, ZHANG Jun, et al. Massive CSI acquisition for dense cloud-RANs with spatial-temporal dynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(4): 2557–2570. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2797969 [23] YANG Yuwen, GAO Feifei, MA Xiaoli, et al. Deep learning-based channel estimation for doubly selective fading channels[J]. IEEE Access, 2019: 36579–36589. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901066 [24] BAI Qinbo, WANG Jintao, ZHANG Yue, et al. Deep learning-based channel estimation algorithm over time selective fading channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2020, 6(1): 125–134. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2019.2943455 [25] XU Zhinan, HOFER M, and ZEMEN T. A time-variant channel prediction and feedback framework for interference alignment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(7): 5961–5973. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2017.2647880 [26] UEHASHI S, OGAWA Y, NISHIMURA T, et al. Prediction of time-varying multi-user MIMO channels based on DOA estimation using compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 565–577. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2882214 [27] CAREEM M A A and DUTTA A. Real-time prediction of non-stationary wireless channels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(12): 7836–7850. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3016962 [28] HERATH J D, SEETHARAM A, and RAMESH A. A deep learning model for wireless channel quality prediction[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. [29] JIANG Wei and SCHOTTEN H D. Recurrent neural networks with long short-term memory for fading channel prediction[C]. 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 2020: 1–5. [30] JIANG Wei and SCHOTTEN H D. Neural network-based fading channel prediction: A comprehensive overview[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 118112–118124. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2937588 [31] JIANG Wei, STRUFE M, and SCHOTTEN H D. Long-range MIMO channel prediction using recurrent neural networks[C]. 2020 IEEE 17th Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, USA, 2020: 1–6. doi: CCNC46108.2020.9045219. [32] JIANG Wei and SCHOTTEN H D. A deep learning method to predict fading channel in multi-antenna systems[C]. 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2020-Spring), Antwerp, Belgium, 2020: 1–5. [33] JIANG Wei and SCHOTTEN H D. Deep learning for fading channel prediction[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2020, 1: 320–332. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2020.2982513 [34] LUO Changqing, JI Jinlong, WANG Qianlong, et al. Channel state information prediction for 5G wireless communications: A deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2020, 7(1): 227–236. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2018.2848960 [35] EOM C and LEE C. Hybrid neural network-based fading channel prediction for link adaptation[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 117257–117266. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3106739 [36] CHEN Ying and ZHANG Hongtao. Outage probability and average rate analysis of user-centric ultra-dense networks[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. [37] ABBAS Z H, ULLAH A, ABBAS G, et al. Outage probability analysis of user-centric SBS-based HCNets under hybrid rician/rayleigh fading[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(2): 297–301. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2959578 [38] YANG Zheng, DING Zhiguo, and FAN Pingzhi. Performance analysis of cloud radio access networks with uniformly distributed base stations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(1): 472–477. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2394458 [39] ZHANG Yingxiao and ZHANG Yingjun. User-centric virtual cell design for cloud radio access networks[C]. 2014 IEEE 15th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), Toronto, Canada, 2014: 249–253. [40] LIN Yicheng and YU Wei. Ergodic capacity analysis of downlink distributed antenna systems using stochastic geometry[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Budapest, Hungary, 2013: 3338–3343. [41] ZHAO Zhongyuan, PENG Mugen, DING Zhiguo, et al. Cluster formation in cloud-radio access networks: Performance analysis and algorithms design[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), London, UK, 2015: 3903–3908. [42] HUMADI K, TRIGUI I, ZHU Weiping, et al. Coverage analysis of user-centric dense terahertz networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(9): 2864–2868. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3091596 [43] KHAN F A, HE Huasen, XUE Jiang, et al. Performance analysis of cloud radio access networks with distributed multiple antenna remote radio heads[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(18): 4784–4799. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2446440 [44] PENG Mugen, YAN Shi, and POOR H V. Ergodic capacity analysis of remote radio head associations in cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2014, 3(4): 365–368. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2014.2317476 [45] ZHU Caiyi and YU Wei. Stochastic modeling and analysis of user-centric network MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(12): 6176–6189. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2867458 [46] MO Yijun, XIE Juan, and HUANG Benxiong. Handoff in virtual cell system based on distributed antenna[C]. 2006 International Conference on Wireless Communications, Networking and Mobile Computing, Wuhan, China, 2006: 1–4. [47] BAO Wei and LIANG Ben. Optimizing cluster size through handoff analysis in user-centric cooperative wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(2): 766–778. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2771343 [48] ULLAH A, ABBAS Z H, MUHAMMAD F, et al. Uplink performance analysis of user-centric small cell aided dense HCNets with uplink-downlink decoupling[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 148460–148474. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3015915 [49] ALONZO M, BUZZI S, ZAPPONE A, et al. Energy-efficient power control in cell-free and user-centric massive MIMO at millimeter wave[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2019, 3(3): 651–663. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2019.2908228 [50] MAKHANBET M and LV T. User-centric online learning of power allocation in H-CRAN[C]. 2019 IEEE 30th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications (PIMRC), Istanbul, Turkey, 2019: 1–6. [51] IQBAL A, THAM M L, and CHANG Y C. Double deep Q-network for power allocation in cloud radio access network[C]. 2020 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Computer and Communication Engineering Technology (CCET), Beijing, China, 2020: 272–277. [52] IQBAL A, THAM M L, and CHANG Y C. Double deep Q-network-based energy-efficient resource allocation in cloud radio access network[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 20440–20449. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3054909 [53] SINGH R, SALUJA D, and KUMAR S. Graph based training resource allocation scheme for CoMP transmission in CRAN: A low complexity solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(3): 2402–2411. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2021.3093311 [54] RODOSHI R T, KIM T, and CHOI W. Deep reinforcement learning based dynamic resource allocation in cloud radio access networks[C]. 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju, Korea (South), 2020: 618–623. [55] BARAHMAN M, CORREIA L M, and FERREIRA L S. An efficient QoS-aware computational resource allocation scheme in C-RAN[C]. 2020 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Seoul, Korea (South), 2020: 1–6. [56] MOOSAVI N, SINAIE M, AZMI P, et al. Delay aware resource allocation with radio remote head cooperation in user-centric C-RAN[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(7): 2343–2347. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3069235 [57] HE Chunlong, LI G Y, ZHENG Fuchun, et al. Energy-efficient resource allocation in OFDM systems with distributed antennas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2014, 63(3): 1223–1231. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2013.2282373 [58] SHARARA M, HOTEIT S, BROWN P, et al. Coordination between radio and computing schedulers in Cloud-RAN[C]. IFIP/IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Network Management (IM), Bordeaux, France, 2021: 37–44. [59] SHARARA M, HOTEIT S, and VÈQUE V. A recurrent neural network based approach for coordinating radio and computing resources allocation in Cloud-RAN[C]. 2021 IEEE 22nd International Conference on High Performance Switching and Routing (HPSR), Paris, France, 2021: 1–7. [60] KADAN F E and YILMAZ A Ö. Beamformer design with smooth constraint-free approximation in downlink cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 36399–36416. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3063668 [61] TAN Fangqing, WU Peiran, WU Y C, et al. Cooperative beamforming for wireless fronthaul and access links in ultra-dense C-RANs with SWIPT: A first-order approach[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15(5): 1242–1257. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3086982 [62] LUO Yifan, YANG Jiawei, XU Wei, et al. Power consumption optimization using gradient boosting aided deep Q-network in C-RANs[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 46811–46823. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2978935 [63] ZHU Huiling and WANG Jiangzhou. Radio resource allocation in multiuser distributed antenna systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2013, 31(10): 2058–2066. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2013.131008 [64] ZHANG Guobin, KE Feng, ZHANG Haijun, et al. User access and resource allocation in full-duplex user-centric ultra-dense networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 12015–12030. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3010364 [65] ZHANG Long, ZHANG Guobin, ZHAO Xiaofang, et al. Energy efficient resource optimization in user-centric UDNs with NOMA and beamforming[C]. 2020 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 2020: 115–121. [66] YU D, LEE H, PARK S H, et al. Deep learning methods for joint optimization of beamforming and fronthaul quantization in cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(10): 2180–2184. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3095500 [67] SHI Jianfeng, XU Hao, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Energy efficient beamforming for user-centric virtual cell networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2019, 3(3): 575–590. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2019.2910827 [68] ZHAO Mingmin, CAI Yunlong, ZHAO Minjian, et al. Improving caching efficiency in content-aware C-RAN-based cooperative beamforming: A joint design approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(6): 4125–4140. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2979958 [69] ZHAO Mingmin, CAI Yunlong, ZHAO Minjian, et al. Joint content placement, RRH clustering and beamforming for cache-enabled Cloud-RAN[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. [70] ZHOU Yanglin, CI Song, and YANG Yang. Energy-aware joint clustering and scheduling for multicast beamforming in Cloud-RAN downlink[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(4): 461–464. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2019.2958929 [71] HE Yuan, DAI Lingcheng, and ZHANG Hongtao. Multi-branch deep residual learning for clustering and beamforming in user-centric network[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(10): 2221–2225. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3005947 [72] DU Gehui, WANG Luhan, LIAO Qing, et al. Deep neural network based cell sleeping control and beamforming optimization in Cloud-RAN[C]. 2019 IEEE 90th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2019-Fall), Honolulu, USA, 2019: 1–5. [73] PAN Cunhua, REN Hong, ELKASHLAN M, et al. Robust beamforming design for ultra-dense user-centric C-RAN in the face of realistic pilot contamination and limited feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(2): 780–795. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2882442 [74] TANG Jianhua, QUEK T Q S, CHANG T H, et al. Systematic resource allocation in cloud RAN with caching as a service under two timescales[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(11): 7755–7770. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2934854 [75] SHI Jianfeng, CHEN Xiao, HUANG Nuo, et al. Power-efficient transmission for user-centric networks with limited fronthaul capacity and computation resource[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(9): 5649–5660. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3002942 [76] TANG Weijun and FENG Suili. User selection and power minimization in full-duplex cloud radio access networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(9): 2426–2438. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2905804 [77] LI Nan, YAO Zhenjie, TU Yanhui, et al. Cooperative optimization for OFDMA resource allocation in multi-RRH millimeter-wave CRAN[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 8: 164035–164044. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3022363 [78] RODOSHI R T, KIM T, and CHOI W. Resource management in cloud radio access network: Conventional and new approaches[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(9): 2708. doi: 10.3390/s20092708 -





 下载:
下载:



 下载:
下载:
