Lightweight Indoor Personnel Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv4-tiny
-
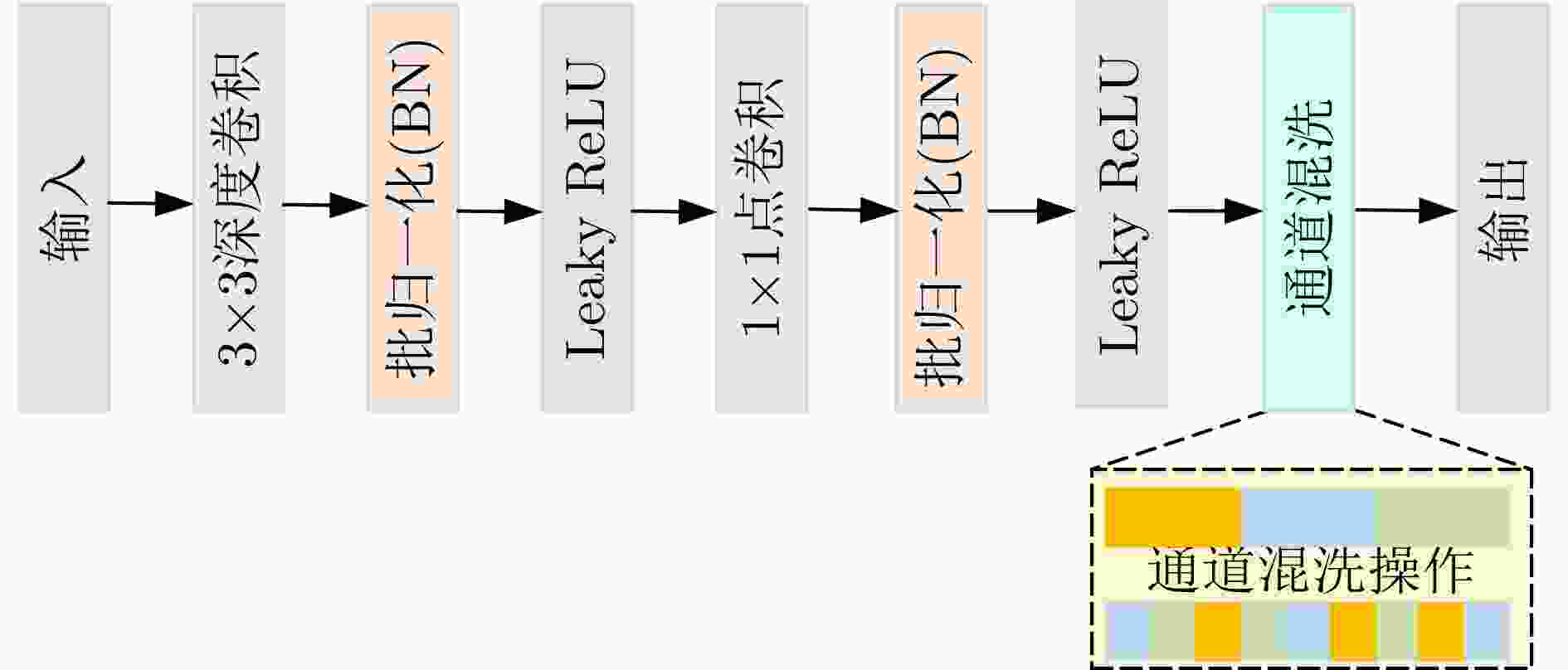
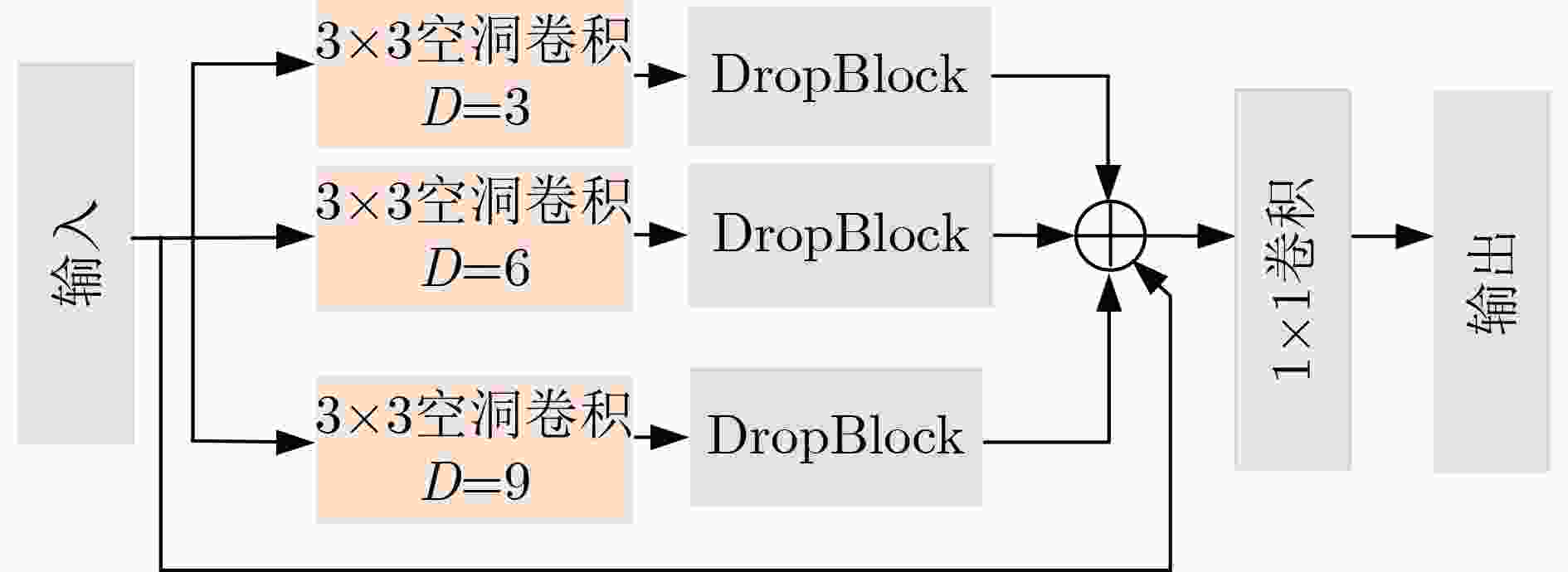
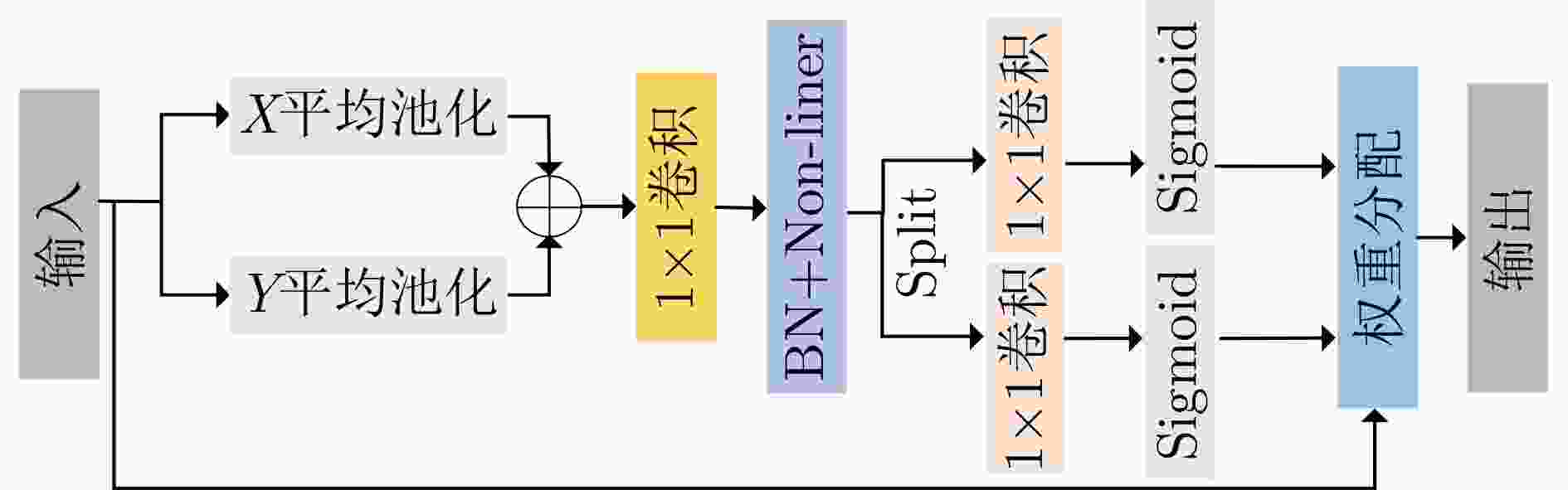
摘要: 深度学习在室内人员检测领域应用广泛,但是传统的卷积神经网络复杂度大且需要高算力GPU的支持,很难实现在嵌入式设备上的部署。针对上述问题,该文提出一种基于改进YOLOv4-tiny的轻量化室内人员目标检测算法。首先,设计一种改进的Ghost卷积特征提取模块,有效减少了模型的复杂度;同时,该文通过采用带有通道混洗机制的深度可分离卷积进一步减少网络参数;其次,该文构建了一种多尺度空洞卷积模块以获得更多具有判别性的特征信息,并结合改进的空洞空间金字塔池化结构和具有位置信息的注意力机制进行有效的特征融合,在提升准确率的同时提高推理速度。在多个数据集和多种硬件平台上的实验表明,该文算法在精度、速度、模型参数和体积等方面优于原YOLOv4-tiny网络,更适合部署于资源有限的嵌入式设备。
-
关键词:
- 室内人员检测 /
- 深度学习 /
- YOLOv4-tiny /
- Ghost卷积
Abstract: Deep learning has been widely applied to the field of indoor personnel detection. However, the traditional convolutional neural networks have a high complexity and require the support of highly computational GPU. It is difficult to accomplish the implementation in the embedded devices. For the above problems, a lightweight network model based on improved YOLOv4-tiny network is proposed for indoor personnel detection. Firstly, an improved Ghost convolution feature extraction module is designed to reduce effectively the model complexity. Simultaneously, to reduce network parameters, a depth-wise separable convolution with channel shuffle mechanism is adopted in this paper. Secondly, a multi-scale dilated convolution module is developed in this paper to obtain more discriminative feature information, which combines the improved dilated space pyramid pooling module and the attention mechanism with location information for effective feature fusion, thereby improving inference accuracy and inference speed, simultaneously. The experiments on multiple datasets and hardware platforms show that the proposed model is superior to the original YOLOv4-tiny network in terms of accuracy, speed, model parameters and volume. Therefore, the proposed model is more suitable for deployment in resource-limited embedded devices.-
Key words:
- Indoor personnel detection /
- Deep learning /
- YOLOv4-tiny /
- Ghost convolution
-
表 1 不同扩张率下实验结果
多尺度空洞卷积融合模块 空洞空间金字塔池化特征融合模块 扩张率 精确率(%) 召回率(%) mAP(%) 扩张率 精确率(%) 召回率(%) mAP(%) [2,2,2] 79.69 68.29 81.75 [3,3,3] 79.49 78.97 82.91 [4,4,4] 79.55 67.95 81.15 [9,9,9] 78.95 79.21 82.49 [2,3,4] 76.18 80.43 82.93 [2,4,6] 80.32 78.56 82.66 [3,2,4] 79.33 78.96 82.52 [3,6,9] 76.18 80.43 82.93 [4,5,6] 79.35 78.62 82.12 [12,14,18] 79.46 77.66 82.46 表 2 模块验证结果
ghost block CBLCS ASPP CA dilated conv block 参数量(M) FLOPs(G) 模型体积(MB) 精确率(%) 召回率(%) mAP(%) 模型A √ 1.23 0.92 5.5 80.76 57.92 75.28 模型B √ √ 1.22 1.02 5.6 79.68 62.74 77.14 模型C √ √ √ 1.44 1.05 6.3 81.34 64.28 79.33 模型D √ √ √ √ 1.44 1.05 6.5 80.09 69.19 81.13 模型E √ √ √ √ √ 1.61 1.46 6.4 76.18 80.43 82.93 表 3 多个数据集下检测效果对比(%)
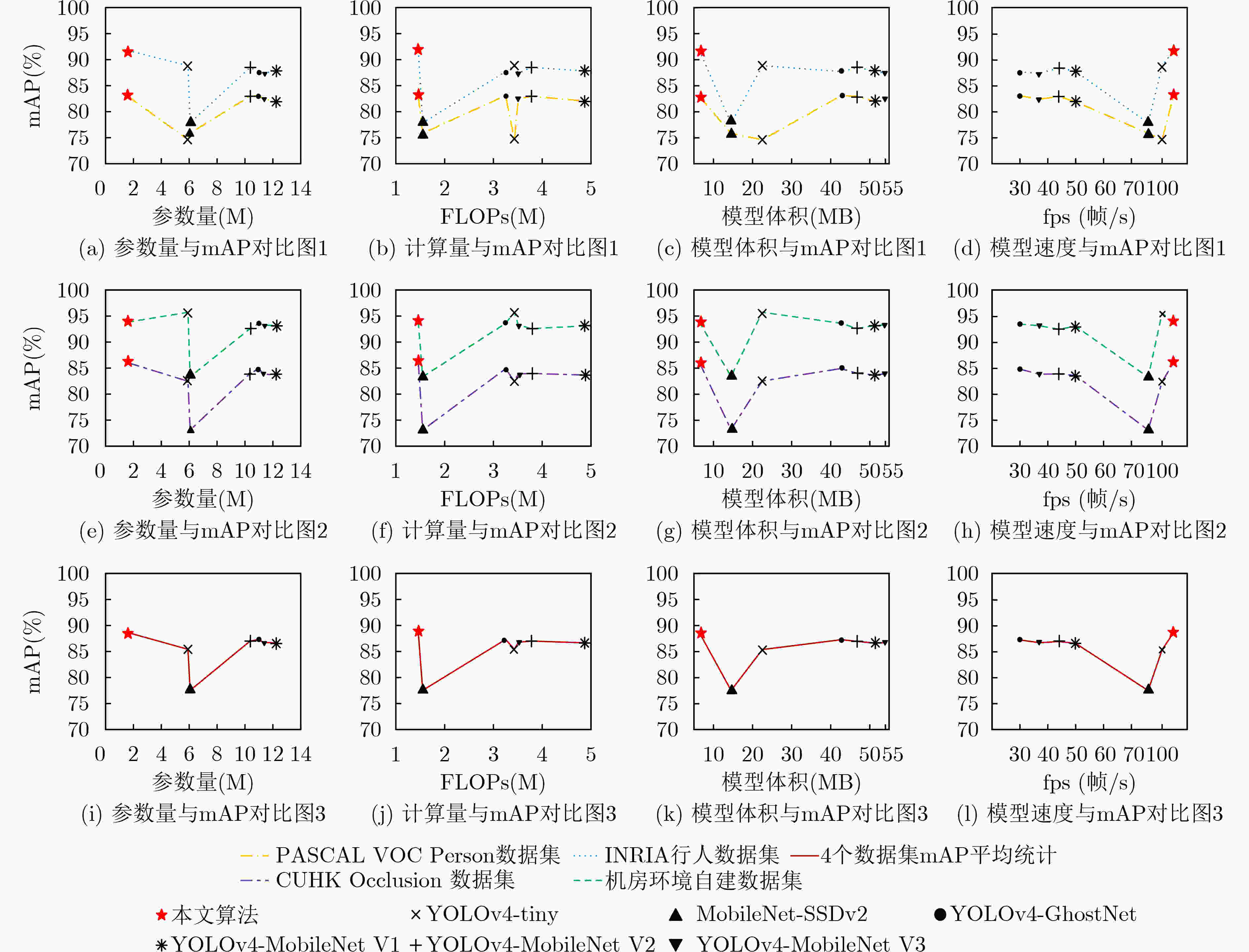
数据集名称 评价指标 YOLOv4-tiny 本文算法 PASCAL VOC Person数据集 精确率 76.73 76.18 召回率 62.83 80.43 mAP 74.63 82.93 INRIA数据集 精确率 90.81 98.13 召回率 75.00 79.23 mAP 88.86 91.74 CUHK Occlusion 数据集 精确率 90.97 89.71 召回率 73.85 72.82 mAP 82.47 86.03 机房环境自建数据集 精确率 74.68 95.82 召回率 96.31 88.36 mAP 95.72 93.84 表 4 不同网络模型结果对比
模型类型 模型名称 参数量(M) FLOPs(G) 模型体积(MB) 精确率(%) 召回率(%) mAP(%) 通用目标检测网络 YOLOv4[10] 64.36 30.16 277.7 76.21 84.53 86.63 SSD[3] 26.15 59.52 90.7 69.37 71.18 72.15 EfficientDet[4] 3.87 2.55 14.9 79.84 70.82 82.17 轻量化网络 YOLOv4-tiny[9] 5.91 3.43 22.5 76.73 62.83 74.63 MobileNet-SSDv2[22] 6.07 1.55 14.5 76.31 64.55 75.86 YOLOv4-MobileNet v1[23] 12.26 4.98 51.4 75.12 80.26 81.96 YOLOv4-MobileNet v2[24] 10.37 3.78 46.8 75.97 80.00 82.96 YOLOv4-MobileNet v3[25] 11.30 3.51 54.1 70.97 73.85 82.47 YOLOv4-GhostNet[26] 11.00 3.25 42.7 77.45 78.01 83.10 本文算法 1.61 1.46 6.4 76.18 80.43 82.93 表 5 不同性能设备推理速度对比
模型类型 模型名称 fps(帧/s) 帧图片推理耗时(ms) GPU环境
RTX2070CPU环境
I5-8200UJetson Nx Jetson Nano GPU环境
RTX2070CPU环境
I5-8200UJetson Nx Jetson Nano 通用目标检测网络 YOLOv4[10] 26 0.02 5.17 1.46 38 49710 193 680 SSD[3] 69 0.35 10.80 2.86 14 2853 917 349 EfficientDet[4] 18 0.14 4.80 3.46 54 7022 207 288 轻量化网络 YOLOv4-tiny[9] 101 4.01 24.00 12.48 9.90 249 40 80 Mobilenet-SSDv2[22] 76 2.33 19.00 14.47 13 425 504 69 YOLOv4-MobileNet v1[23] 50 1.20 15.30 5.03 19 827 65 198 YOLOv4-MobileNet v2[24] 44 1.17 13.20 5.25 22 849 75 190 YOLOv4-MobileNet v3[25] 37 1.26 11.90 5.51 26 792 83 181 YOLOv4-GhostNet[26] 30 1.27 9.70 4.20 33 786 102 238 本文算法 105 9.01 27.00 16.01 9.52 115 37 62 -
[1] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]. 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, USA, 2014: 580–587. [2] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 779–788. [3] LIU Wei, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]. The 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 21–37. [4] TAN Mingxing, PANG Ruoming, and LE Q V. Efficientdet: Scalable and efficient object detection[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10778–10787. [5] LIU Wei, LIAO Shengcai, HU Weidong, et al. Learning efficient single-stage pedestrian detectors by asymptotic localization fitting[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 643–659. [6] 张明伟, 蔡坚勇, 李科, 等. 基于DE-YOLO的室内人员检测方法[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2020, 29(1): 203–208. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.007240ZHANG Mingwei, CAI Jianyong, LI Ke, et al. Indoor personnels detection method based on DE-YOLO[J]. Computer Systems &Applications, 2020, 29(1): 203–208. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.007240 [7] 董小伟, 韩悦, 张正, 等. 基于多尺度加权特征融合网络的地铁行人目标检测算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 2113–2120. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200450DONG Xiaowei, HAN Yue, ZHANG Zheng, et al. Metro pedestrian detection algorithm based on multi-scale weighted feature fusion network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 2113–2120. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200450 [8] 苏杨, 卢翔, 李琨, 等. 基于轻量深度学习网络的机房人物检测研究[J]. 工业仪表与自动化装置, 2021(1): 100–103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0682.2021.01.024SU Yang, LU Xiang, LI Kun, et al. Research on computer room human detection based on lightweight deep learning network[J]. Industrial Instrumentation &Automation, 2021(1): 100–103. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0682.2021.01.024 [9] WANG C Y, BOCHKOVSKIY A, and LIAO H Y M. Scaled-YOLOv4: Scaling cross stage partial network[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13024–13033. [10] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934v1, 2020. [11] HAN Kai, WANG Yunhe, TIAN Qi, et al. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations[C]. 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 1577–1586. [12] ZHANG Xiangyu, ZHOU Xinyu, LIN Mengxiao, et al. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6848–6856. [13] YU F, KOLTUN V, and FUNKHOUSER T. Dilated residual networks[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 636–644. [14] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 40(4): 834–848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [15] HOU Qibin, ZHOU Daquan, and FENG Jiashi. Coordinate attention for efficient mobile network design[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, USA, 2021: 13708–13717. [16] SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU Menglong, et al. MobileNetV2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks[C]. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 4510–4520. [17] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904–1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [18] GHIASI G, LIN T Y, and LE Q V. DropBlock: A regularization method for convolutional networks[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 10750–10760. [19] EVERINGHAM M, VAN GOOL L, WILLIAMS C K I, et al. The PASCAL visual object classes (VOC) challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 88(2): 303–338. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0275-4 [20] DALAL N and TRIGGS B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, USA, 2005: 886–893. [21] OUYANG Wanli and WANG Xiaogang. A discriminative deep model for pedestrian detection with occlusion handling[C]. 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, USA, 2012: 3258–3265. [22] CHIU Y C, TSAI C Y, RUAN M D, et al. Mobilenet-SSDv2: An improved object detection model for embedded systems[C]. 2020 International Conference on System Science and Engineering, Kagawa, Japan, 2020: 1–5. [23] LIU Jie and LIU Lizhi. Helmet wearing detection based on YOLOv4-MT[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 4th International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation Engineering, Wuhan, China, 2021: 1–5. [24] FANG Lifa, WU Yanqiang, LI Yuhua, et al. Ginger seeding detection and shoot orientation discrimination using an improved YOLOv4-LITE network[J]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(11): 2328. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11112328 [25] WANG Shengying, CHEN Tao, LV Xinyu, et al. Forest fire detection based on lightweight Yolo[C]. The 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference, Kunming, China, 2021: 1560–1565. [26] WANG Huixuan, GE Huayong, and LI Muxian. PFG-YOLO: A safety helmet detection based on YOLOv4[C]. The 2021 IEEE 5th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, Xi'an, China, 2021: 1242–1246. -





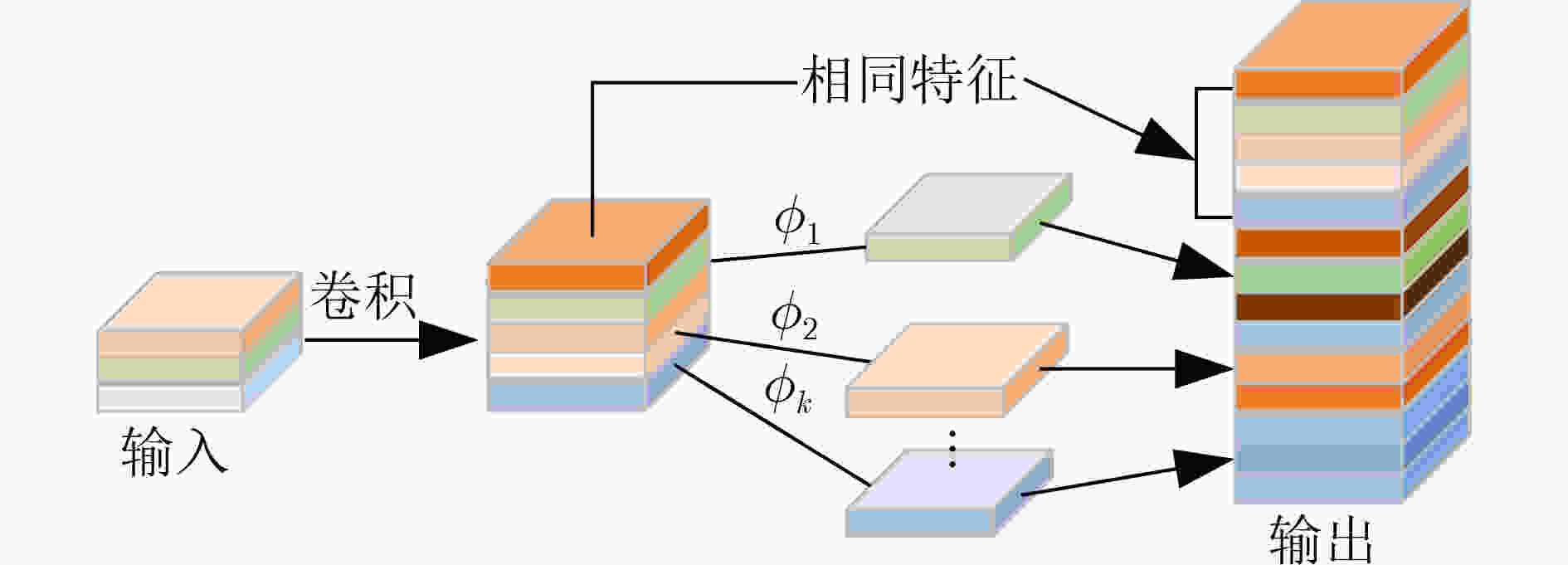
 下载:
下载:
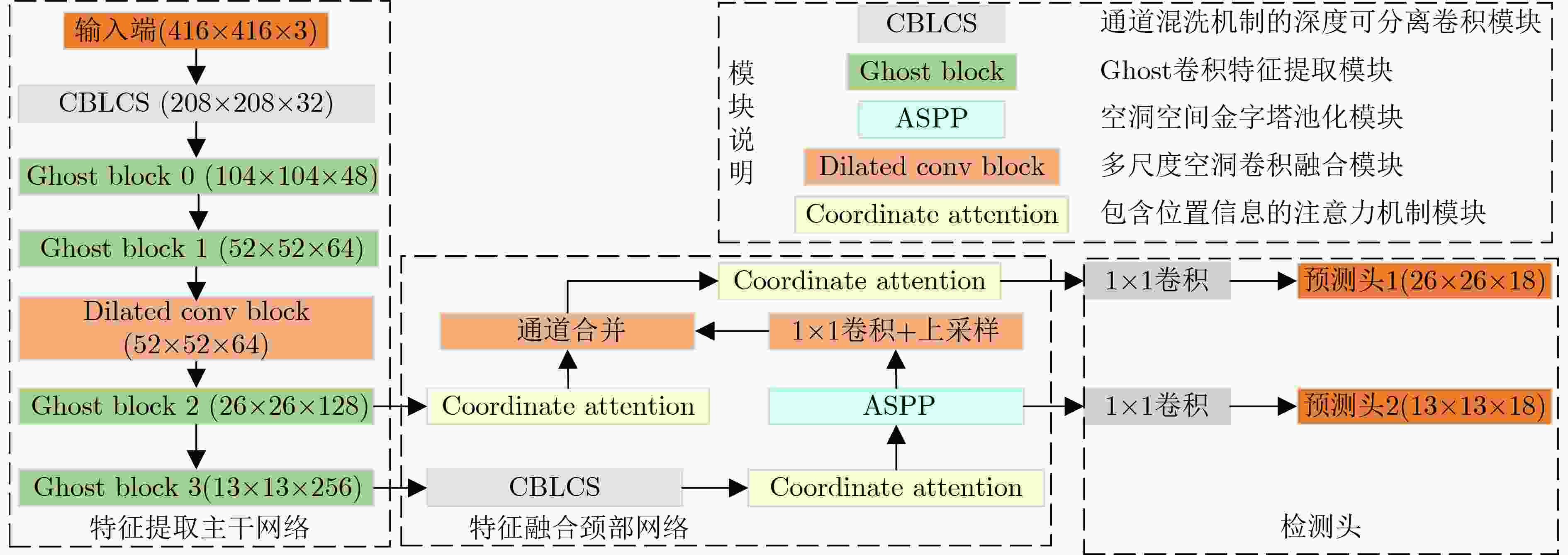
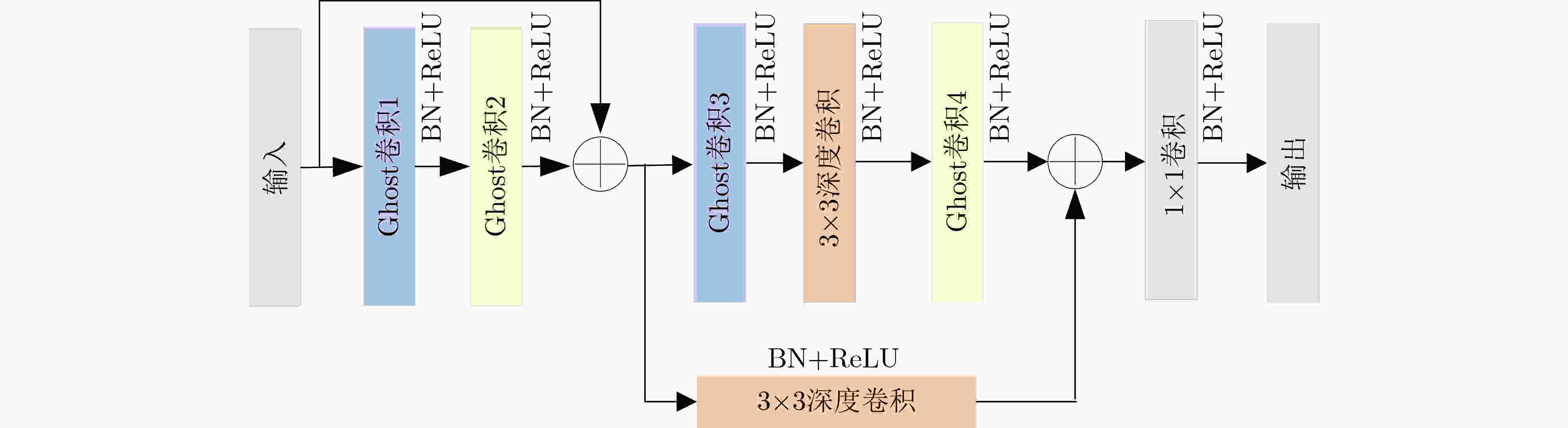
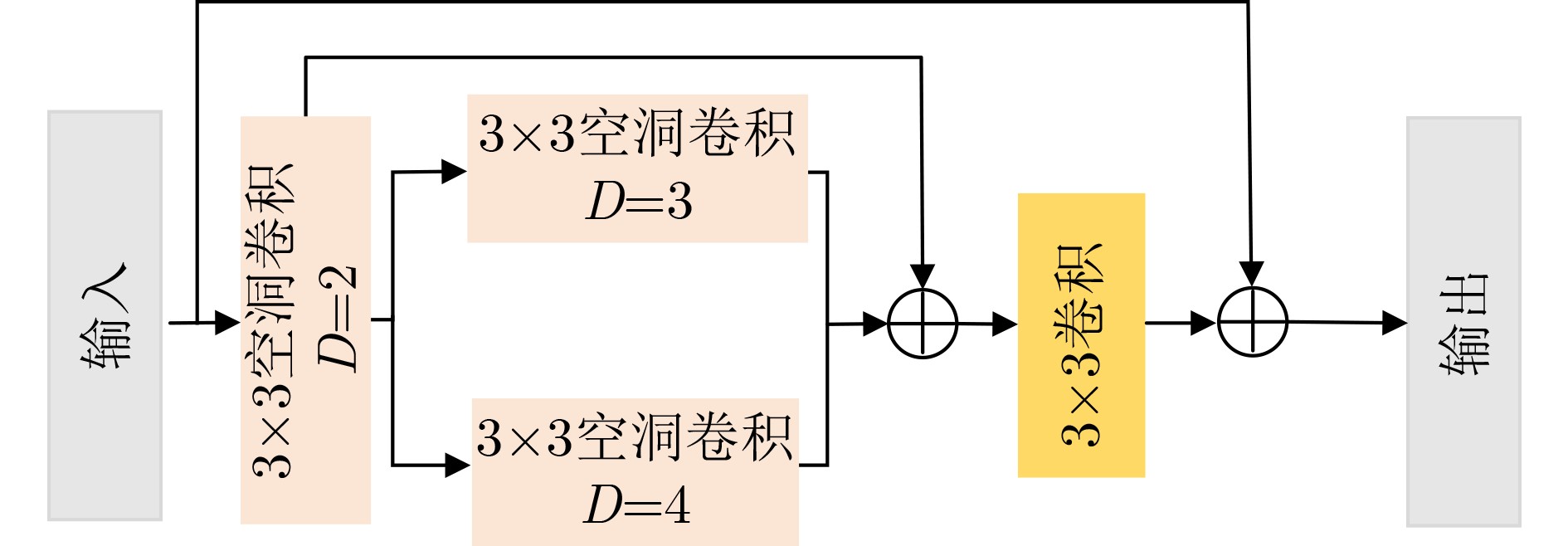



 下载:
下载:
