A Joint Resource Allocation Method of D2D Communication Resources Based on Multi-agent Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
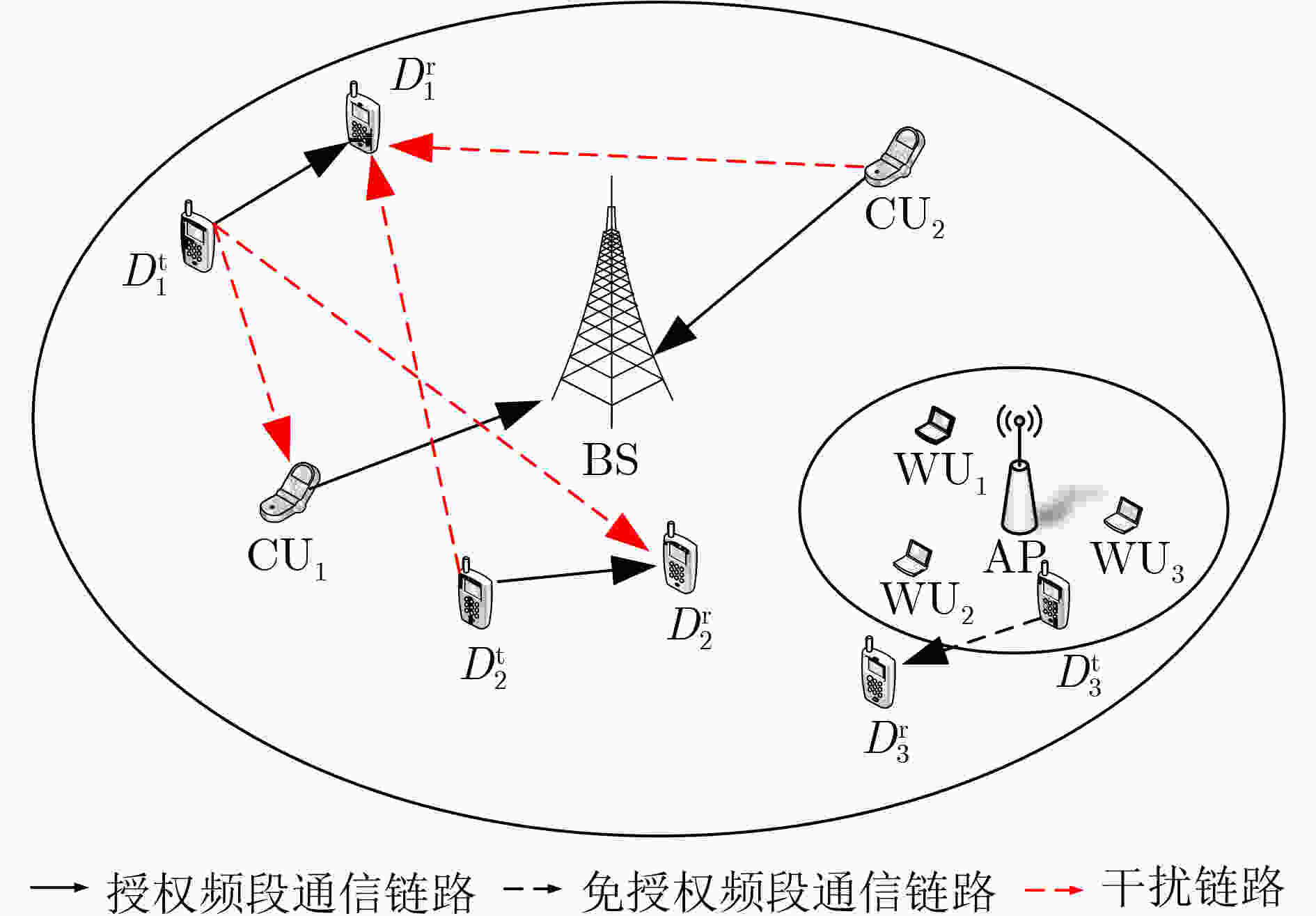
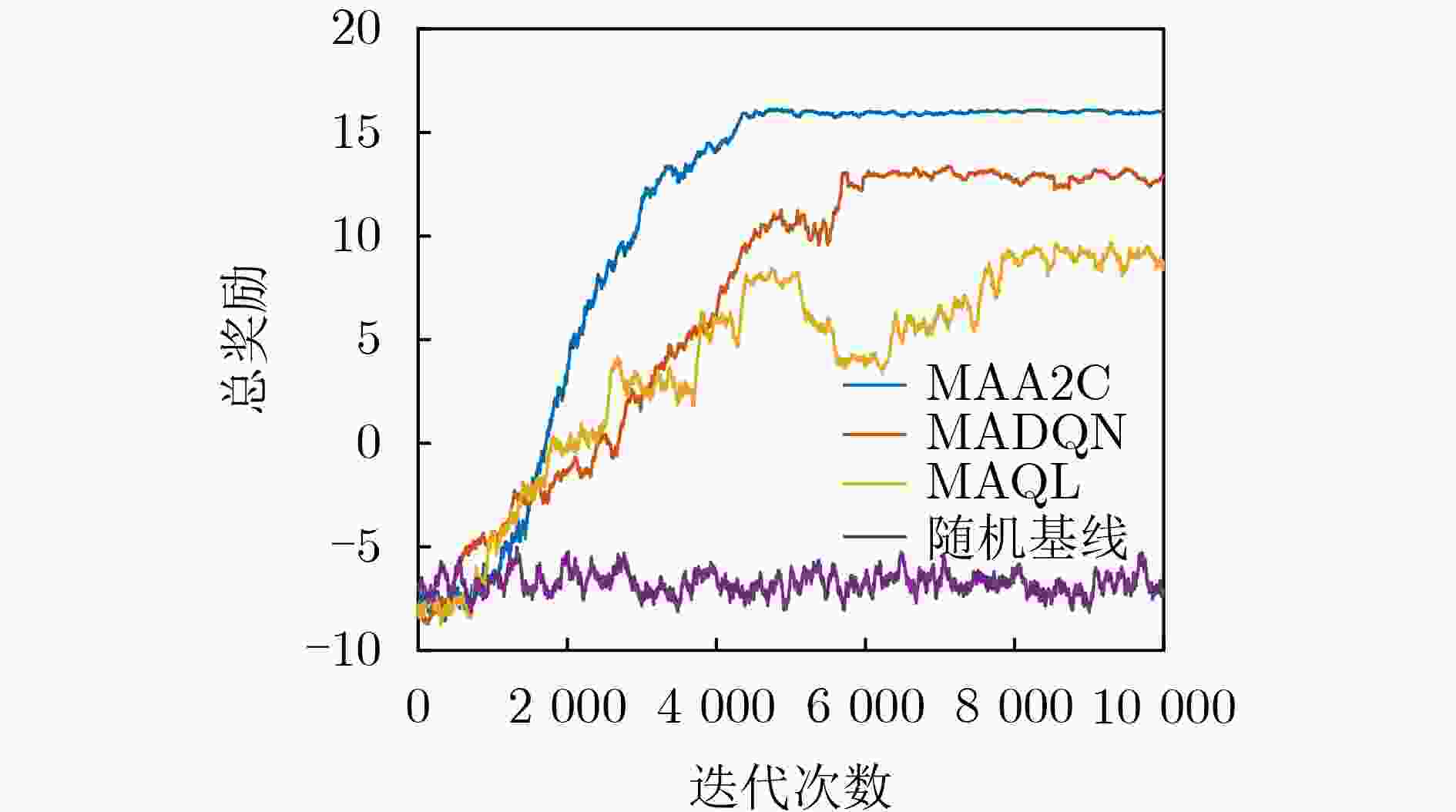
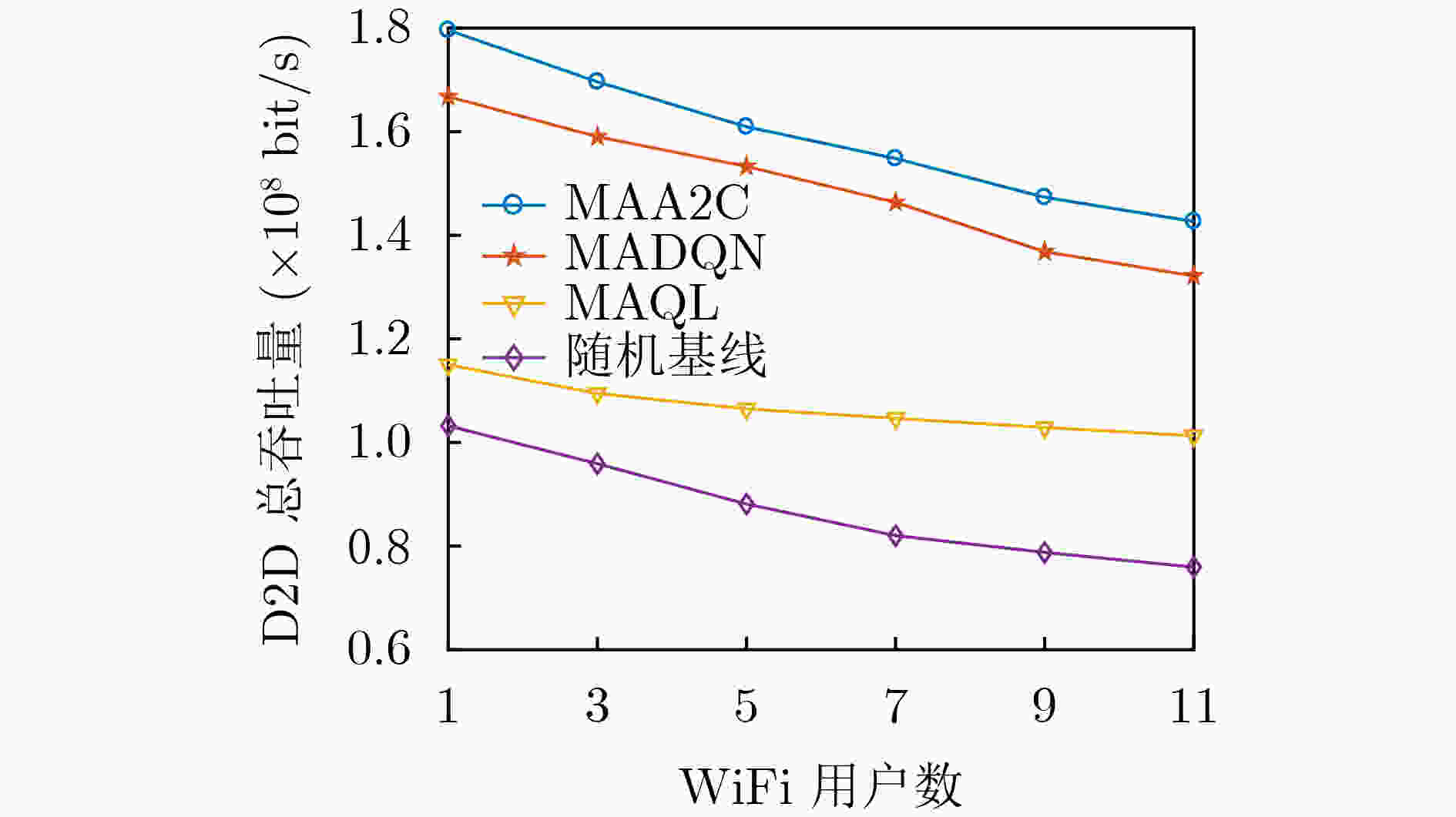
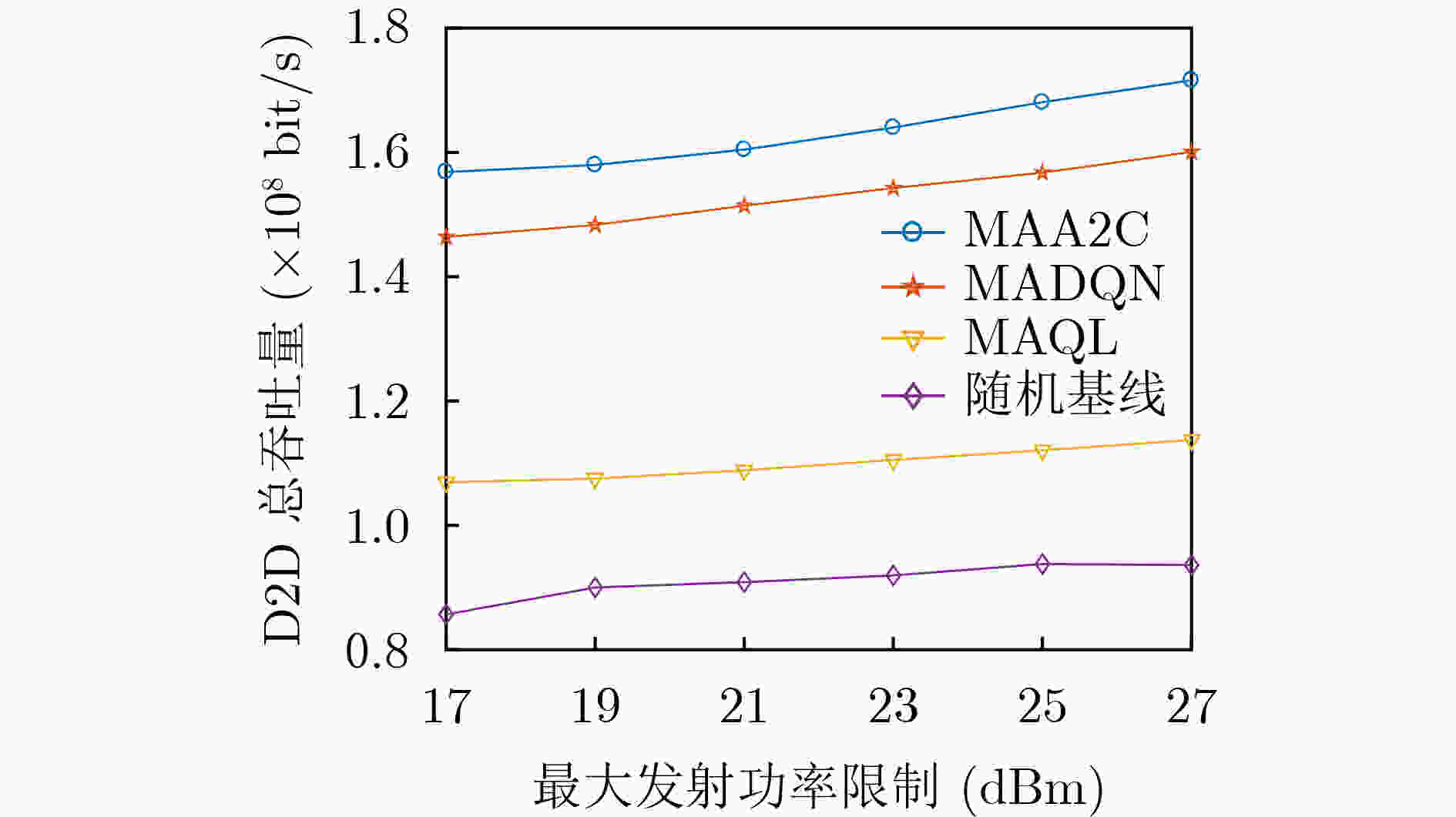
摘要: 设备对设备(D2D)通信作为一种短距离通信技术,能够极大地减轻蜂窝基站的负载压力和提高频谱利用率。然而将D2D直接部署在授权频段或者免授权频段必然导致与现有用户的严重干扰。当前联合部署在授权和免授权频段的D2D通信的资源分配通常被建模为混合整数非线性约束的组合优化问题,传统优化方法难以解决。针对这个挑战性问题,该文提出一种基于多智能体深度强化学习的D2D通信资源联合分配方法。在该算法中,将蜂窝网络中的每个D2D发射端作为智能体,智能体能够通过深度强化学习方法智能地选择接入免授权信道或者最优的授权信道并发射功率。通过选择使用免授权信道的D2D对(基于“先听后说”机制)向蜂窝基站的信息反馈,蜂窝基站能够在非协作的情况下获得WiFi网络吞吐量信息,使得算法能够在异构环境中执行并能够确保WiFi用户的QoS。与多智能体深度Q网络(MADQN)、多智能体Q学习(MAQL)和随机算法相比,所提算法在保证WiFi用户和蜂窝用户的QoS的情况下能够获得最大的吞吐量。Abstract: As a short-range communication technology, Device-to-Device (D2D) communication can greatly reduce the load pressure on cellular base stations and improve spectrum utilization. However, the direct deployment of D2D to licensed or unlicensed bands will inevitably lead to serious interference with existing users. At present, the resource allocation of D2D communication jointly deployed in licensed and unlicensed bands is usually modeled as a mixed-integer nonlinear constraint combinatorial optimization problem, which is difficult to solve by traditional optimization methods. To address this challenging problem, a multi-agent deep reinforcement learning based joint resource allocation D2D communication method is proposed. In this algorithm, each D2D transmitter in the cellular network acts as an agent, which can intelligently select access to the unlicensed channel or the optimal licensed channel and it transmits power through the deep reinforcement learning method. Through the feedback of D2D pairs that compete for the unlicensed channels based on the Listen Before Talk (LBT) mechanism, WiFi network throughput information can be obtained by cellular base station in a non-cooperative manner, so that the algorithm can be executed in a heterogeneous environment and QoS of WiFi users is guaranteed. Compared with Multi Agent Deep Q Network (MADQN), Multi Agent Q Learning (MAQL) and Random Baseline algorithms, the proposed algorithm can achieve the maximum throughput while the QoS is guaranteed for both WiFi users and cellular users.
-
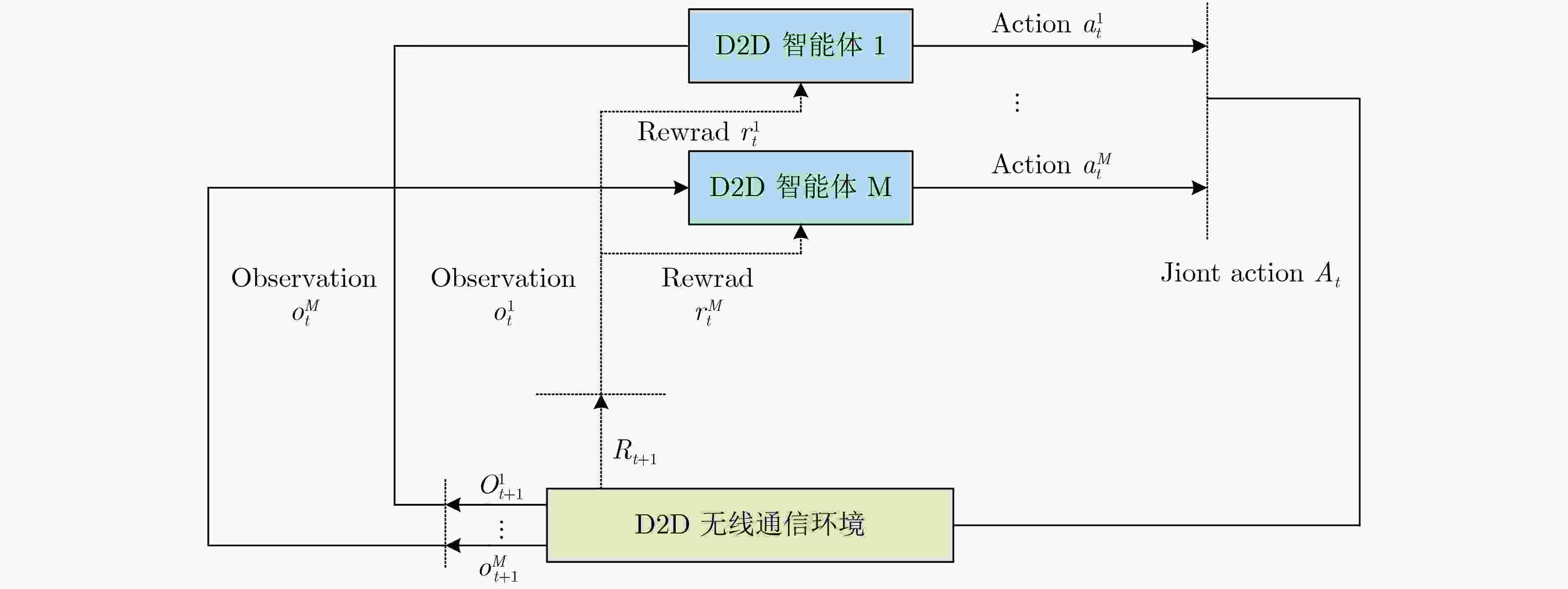
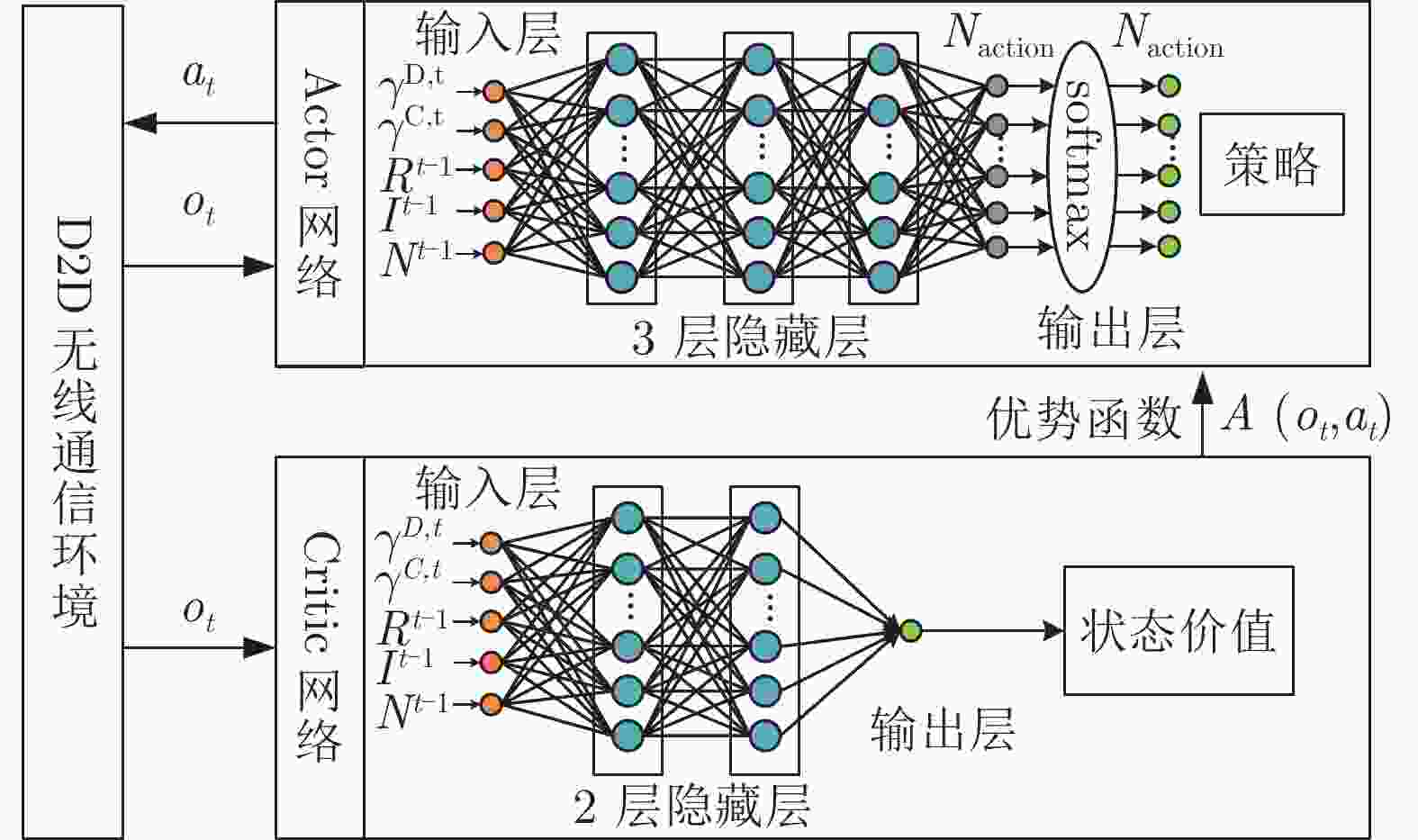
算法1 基于多智能体深度强化学习的D2D通信资源联合分配方法 (1) 设置超参数:折扣因子$ \gamma $,演员网络的学习率$ {\alpha _{\text{a}}} $,评论家网络的学习率$ {\alpha _{\text{c}}} $; (2) 随机初始化演员网络参数$ {\theta ^0},{\theta ^1}, \cdots ,{\theta ^M} $和评论家网络参数$ {\omega ^0},{\omega ^1}, \cdots ,{\omega ^M} $; (3) 所有的智能体(D2D对)获得初始状态${S_0} = \left\{ {s_0^1,s_0^2, \cdots ,s_0^M} \right\}$; (4) for $t = 1,2, \cdots ,T$do (5) for $i = 1,2, \cdots ,M$ do (6) 第$i$对D2D用户将自身的观测$o_t^i$作为策略网络的输入,根据当前策略函数$ {\pi _{\theta _t^i}}\left( {a_t^i\left| {o_t^i;\theta _t^i} \right.} \right) $选取动作$a_t^i$; (7) end for (8) 所有D2D发射端执行动作${A_t} = \left\{ {a_t^1,a_t^2, \cdots ,a_t^M} \right\}$,获得奖励${R_t} = \left\{ {r_t^1,r_t^2, \cdots ,r_t^M} \right\}$以及下一个状态
${S_{t + 1}} = \left\{ {o_{t + 1}^1,o_{t + 1}^2, \cdots ,o_{t + 1}^M} \right\}$;(9) for $i = 1,2, \cdots ,M$ do (10) 第$i$对D2D用户将自身观测$o_{t + 1}^i$作为Critic网络的输入并计算$ {V^i}\left( {o_{t + 1}^i} \right) $; 计算TD误差$ \delta _t^i(o_t^i) = r_t^i + \gamma {V^i}\left( {o_{t + 1}^i} \right) - {V^i}(o_t^i) $; 更新评论家网络参数$\omega _{t + 1}^i = \omega _t^i + {\alpha _{\text{c} } }{{\text{∇}} _{ {\omega ^i} } }V_{ {\omega ^i} }^i\left( {o_t^i} \right){\delta ^i}(o_t^i)$; 更新演员网络参数$\theta _{t + 1}^i = \theta _t^i + {\alpha _{\text{a} } }{{\text{∇}} _{ {\theta ^i} } }\ln \pi _{ {\theta ^i} }^i\left( {a_t^i\left| {o_t^i} \right.} \right){\delta ^i}(o_t^i)$; (11) end for (12) 所有D2D用户更新自身状态${S_t} = {S_{t + 1}}$; (13) end for 表 1 参数配置
参数 取值 参数 取值 参数 取值 参数 取值 蜂窝半径 500 m 噪声功率谱密度 –174 dBm/Hz 蜂窝用户的最大发射功率 23 dBm 阴影衰落标准差 8 dB 蜂窝用户数 5 D2D用户传输功率级别 5 D2D用户距离 25 m 蜂窝用户QoS的信噪比阈值 6 dB D2D用户数 5~45 路径损耗的衰减因子 4 授权上行信道带宽 5 MHz D2D用户QoS的
信噪比阈值6 dB WiFi用户数 1-11 D2D用户的最大发射功率 23 dBm 免授权信道带宽 20 MHz $ S_{\min }^W $ 6 Mbit/s -
[1] CISCO. Cisco annual internet report (2018–2023) white paper[EB/OL]. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/executive-perspectives/annual-internet-report/white-paper-c11-741490.html, 2021. [2] MACH P, BECVAR Z, and VANEK T. In-band device-to-device communication in OFDMA cellular networks: A survey and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2015, 17(4): 1885–1922. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2447036 [3] AHMED M, LI Yong, WAQAS M, et al. A survey on socially aware device-to-device communications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2018, 20(3): 2169–2197. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2820069 [4] ZHANG Hongliang, LIAO Yun, and SONG Lingyang. D2D-U: Device-to-device communications in unlicensed bands for 5G system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2017, 16(6): 3507–3519. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2017.2683479 [5] WU Yue, GUO Weisi, YUAN Hu, et al. Device-to-device meets LTE-unlicensed[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(5): 154–159. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7470950 [6] KO H, LEE J, and PACK S. A fair listen-before-talk algorithm for coexistence of LTE-U and WLAN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(12): 10116–10120. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2533627 [7] 张达敏, 张绘娟, 闫威, 等. 异构网络中基于能效优化的D2D资源分配机制[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 480–487. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190042ZHANG Damin, ZHANG Huijuan, YAN Wei, et al. D2D resource allocation mechanism based on energy efficiency optimization in heterogeneous networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 480–487. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190042 [8] KHUNTIA P and HAZRA R. An efficient channel and power allocation scheme for D2D enabled cellular communication system: An IoT application[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(22): 25340–25351. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3060616 [9] TANG Huan and ZHI Ding. Mixed mode transmission and resource allocation for D2D communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(1): 162–175. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2468725 [10] PAWAR P and TRIVEDI A. Joint uplink-downlink resource allocation for D2D underlaying cellular network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(12): 8352–8362. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3116947 [11] 徐勇军, 谷博文, 杨洋, 等. 基于不完美CSI的D2D通信网络鲁棒能效资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, YANG Yang, et al. Robust energy-efficient resource allocation algorithm in D2D communication networks with imperfect CSI[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(8): 2189–2198. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200587 [12] SHANG Bodong, ZHAO Liqiang, and CHEN K C. Enabling device-to-device communications in LTE-unlicensed spectrum[C]. Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 2017: 1–6. [13] YIN Rui, WU Zheli, LIU Shengli, et al. Decentralized radio resource adaptation in D2D-U networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(8): 6720–6732. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3016019 [14] XING Chigang and LI Fangmin. Unlicensed spectrum-sharing mechanism based on Wi-Fi security requirements implemented using device to device communication technology[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 135025–135036. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3011134 [15] WANG Ganggui, WU C, YOSHINAGA T, et al. Coexistence analysis of D2D-unlicensed and Wi-Fi communications[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2021, 2021: 5523273. doi: 10.1155/2021/5523273 [16] AMIRI R, MEHRPOUYAN H, FRIDMAN L, et al. A machine learning approach for power allocation in HetNets considering QoS[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, USA, 2018. [17] MASADEH A, WANG Zhengdao, and KAMAL A E. Reinforcement learning exploration algorithms for energy harvesting communications systems[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kansas City, USA, 2018. [18] LUO Yong, SHI Zhiping, ZHOU Xin, et al. Dynamic resource allocations based on Q-learning for D2D communication in cellular networks[C]. The 2014 11th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Actiev Media Technology and Information Processing (ICCWAMTIP), Chengdu, China, 2014: 385–388. [19] ZIA K, JAVED N, SIAL M N, et al. A distributed multi-agent RL-based autonomous spectrum allocation scheme in D2D enabled multi-tier HetNets[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 6733–6745. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2890210 [20] PEI Eerong, ZHU Bingbing, and LI Yun. A Q-learning based resource allocation algorithm for D2D-unlicensed communications[C]. The 2021 IEEE 93rd Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2021-Spring), Helsinki, Finland, 2021: 1–6. [21] LI Zheng and GUO Caili. Multi-agent deep reinforcement learning based spectrum allocation for D2D underlay communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(2): 1828–1840. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2961405 [22] 3GPP. 3GPP TR 36.814 V9.0. 0 Further advancements for E-UTRA physical layer aspects[S]. Valbonne: 3GPP, 2010. -





 下载:
下载:
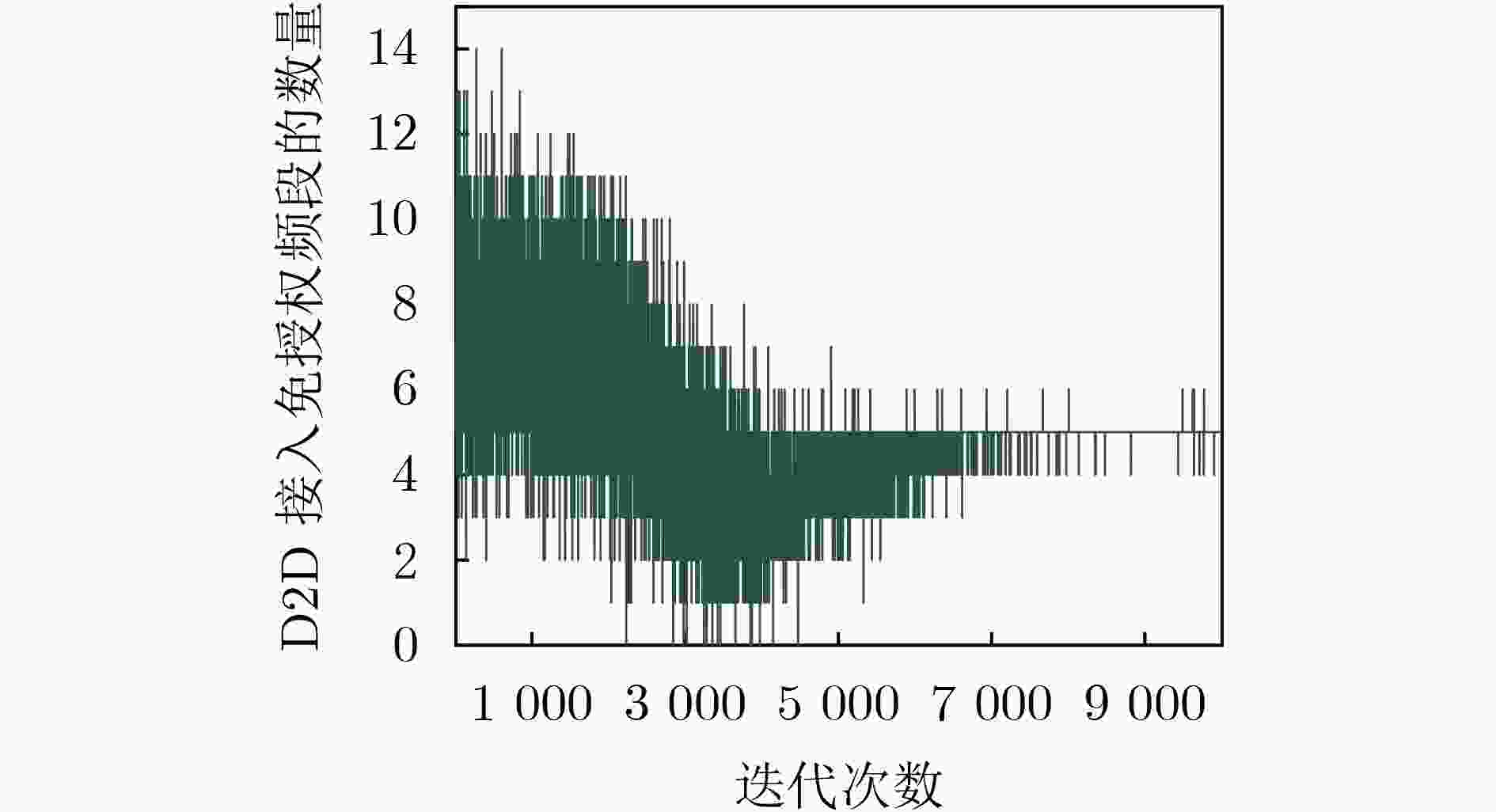
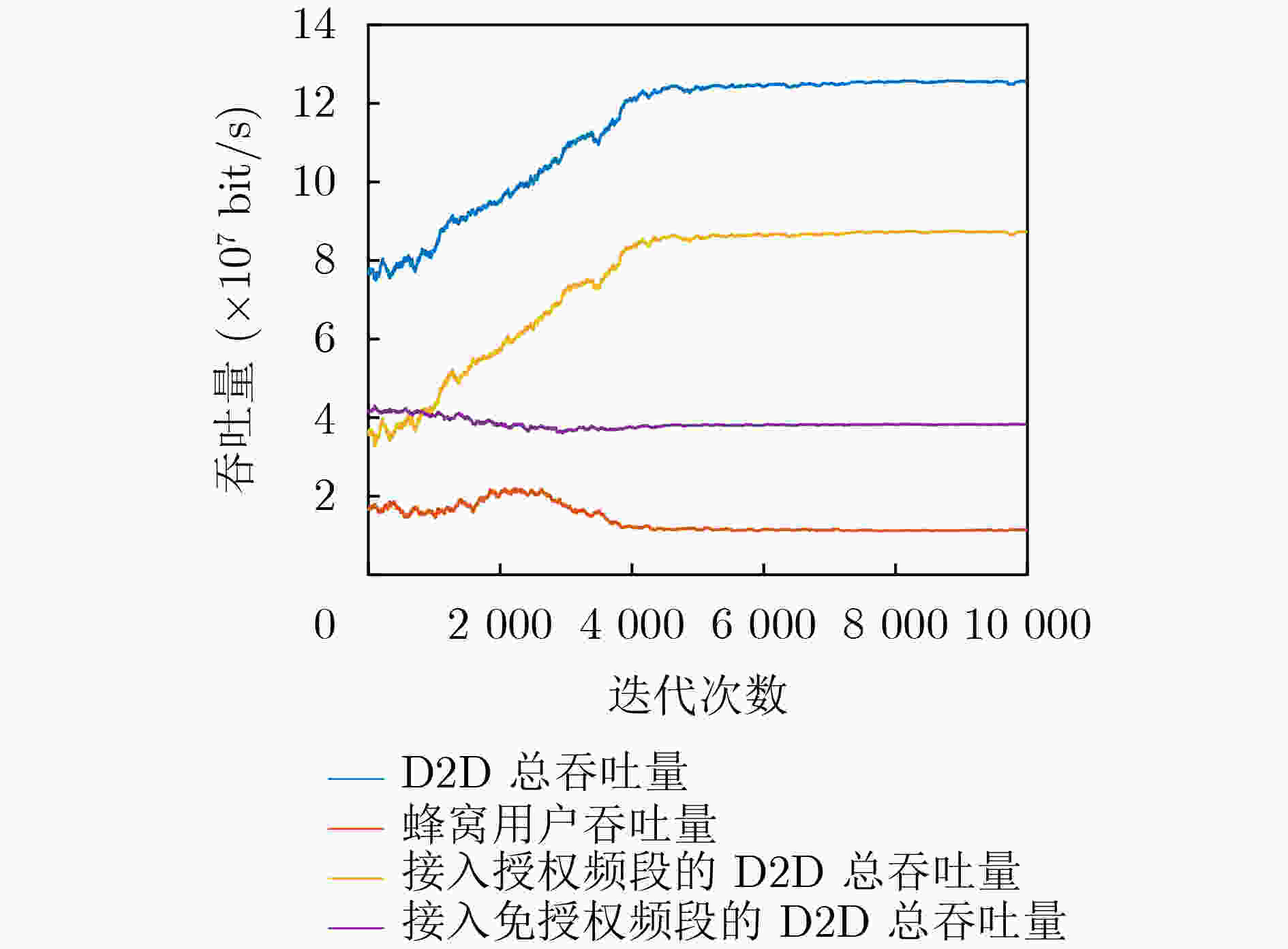
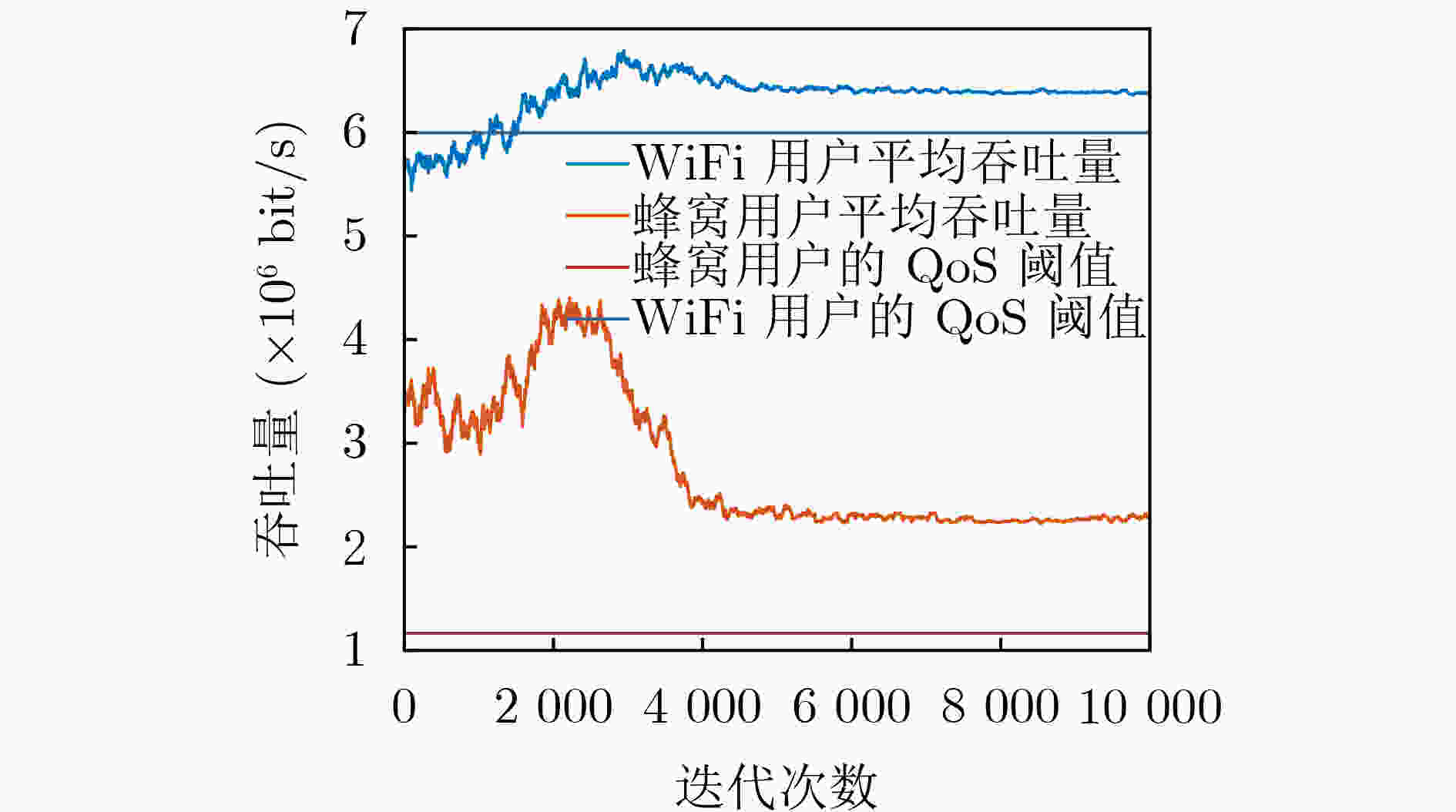
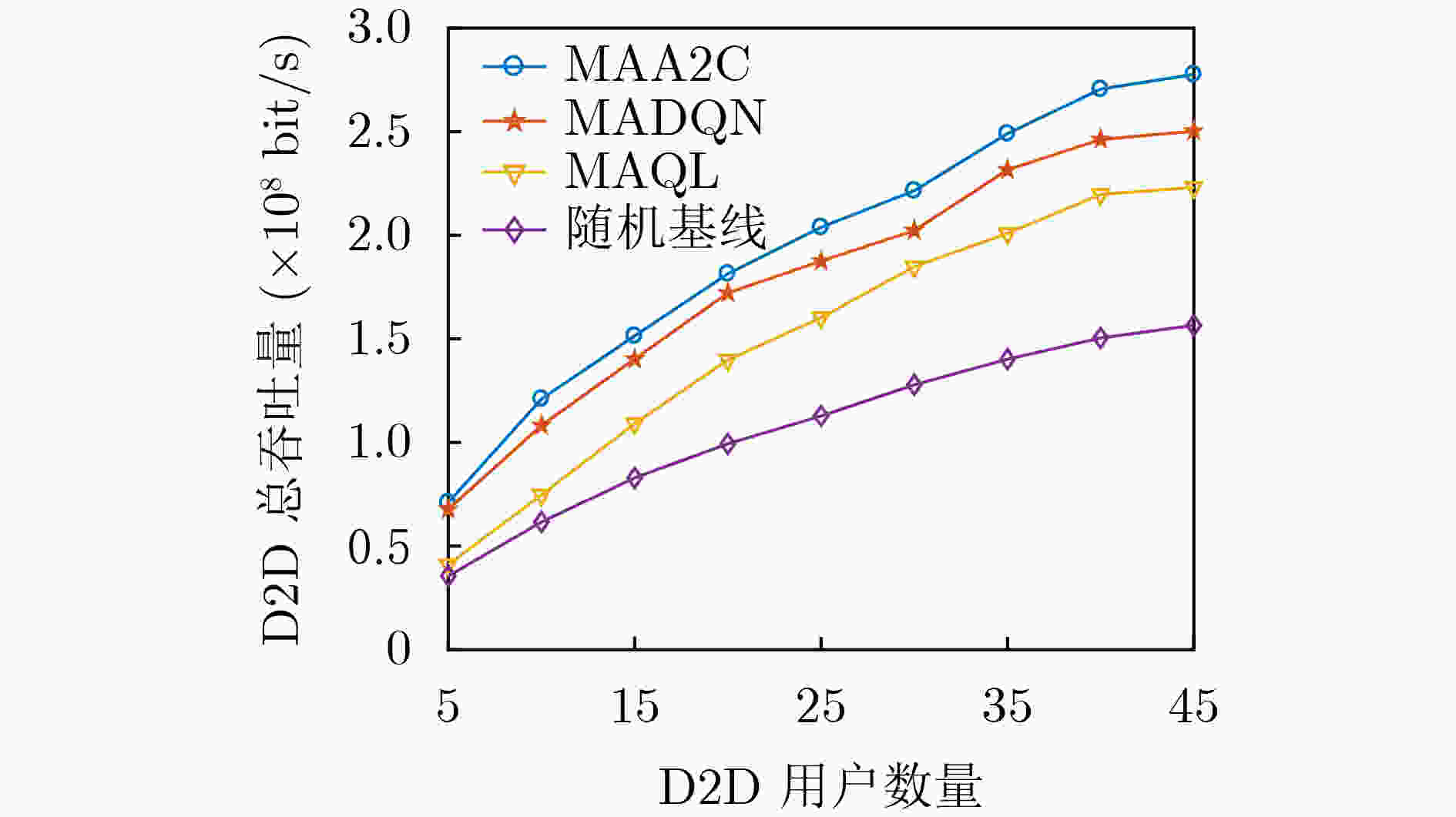



 下载:
下载:
