Accurate and Fast ElectroCardioGram Classification Method Based on Adaptive Fast S-Transform and XGBoost
-
摘要: 针对心电信号(ECG)传统分类方法效率较低的问题,该文提出一种基于自适应快速S变换(AFST)和XGBoost的心电信号精确快速分类方法。该方法首先通过快速定位算法确定心电信号特征频率点,再根据特征频率点自适应调节S变换窗宽因子,增强S变换的时频分辨率的同时避免迭代计算,大大减少运行时间。其次,基于自适应快速S变换的时频矩阵提取12个特征量来表征5种心电信号的特征信息,特征向量维数低,识别能力强。最后,利用XGBoost算法对特征向量进行识别。MIT-BIH心律失常数据库和患者实测数据验证表明,该方法显著地缩短了分类时间,对5种心电信号的分类准确率分别为99.59%和97.32%,适用于实际检测系统中心律失常疾病的快速诊断。Abstract: Considering the low efficiency of traditional ElectroCardioGram(ECG) classification methods, an accurate and fast ElectroCardioGram classification method based on Adaptive Fast S-Transform (AFST) and XGBoost is proposed. Firstly, the main feature points of the ECG signals are determined through a fast positioning algorithm, and then the S-Transform window width factor is adjusted adaptively according to the main feature points to enhance the time-frequency resolution of the S-transform while avoiding iterative calculation and reducing the running time greatly; Secondly, based on the time-frequency matrix of AFST, 12 eigenvalues are extracted to represent the characteristic information of 5 kinds of ECG signals, with low eigenvector dimension and strong recognition ability. Finally, XGBoost is used to identify the eigenvectors. The experimental studies based on the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database and the verification of patient measurement data show that, with the proposed method, the classification time of ECG signals is significantly shortened and classification accuracy of 99.59%, 97.32% is obtained respectively, which is suitable for the rapid diagnosis of abnormal diseases in the center rate of the actual detection system.
-
表 1 不同算法运算量分析
算法 运算量 复数乘法 复数加法 时间复杂度 ST $ ({N^2} + {N^3})/2 $ $ ({N^3} - {N^2})/2 $ $ O({N^3}) $ FST $ (2{N^2} + {N^2}{\log _2}N)/4 $ $ ({N^2}{\log _2}N)/2 $ $ O({N^2}\log {}_2N) $ AFST $ q(2N + N{\log _2}N)/2 $ $ qN{\log _2}N $ $ O(qN\log {}_2N) $ 表 2 分类结果(%)
心电类型 $ {\text{Acc}} $ $ {\text{Sen}} $ $ {\text{Spe}} $ $ {\text{PPV}} $ NORM 99.68 99.06 99.30 98.95 LBBB 99.43 98.83 99.58 99.64 RBBB 99.52 99.54 99.90 99.96 APC 99.70 99.36 98.86 99.43 PVC 99.61 99.48 99.71 99.29 总计 99.59 99.25 99.47 99.45 表 3 各算法性能对比
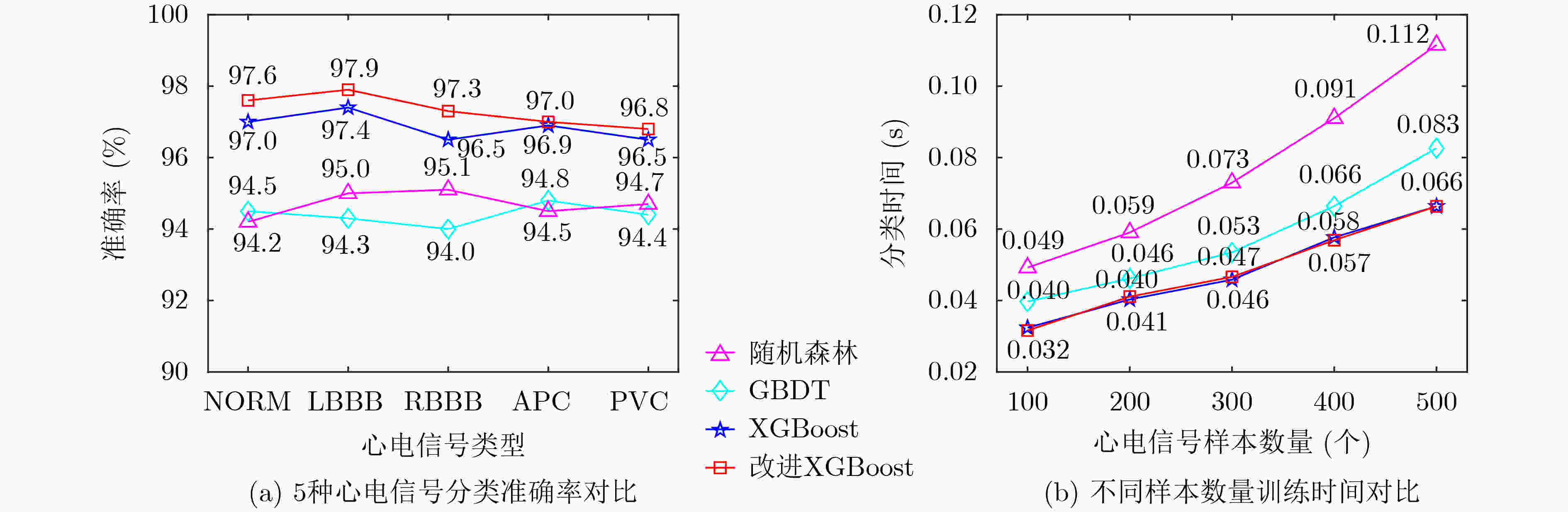
特征提取方法 分类器 特征提取
时间(s)分类器运行
时间(s)准确率
(%)ST 随机森林 389.10 6.42 84.14 GBDT 4.98 80.29 XGBoost 4.35 85.95 改进XGBoost 4.35 88.53 AFST 随机森林 152.07 6.47 98.42 GBDT 4.98 97.74 XGBoost 4.36 99.06 改进XGBoost 4.36 99.59 表 4 不同分类方法对比(%)
方法 分类器 ECG特征 Acc Sen Spe PPV Wavelet[24] E-SVM 小波系数、R-R间期、形态特征 94.50 94.70 93.90 – Wavelet[8] RNN-LSTM 小波系数、R-R间期、形态特征 97.10 85.70 94.28 98.35 TSFEL[16] RT+SVM 统计学特征、时频特征 98.21 84.21 95.95 92.81 XWT[8] SVM 小波系数、R-R间期、时域特征 98.50 99.69 98.80 – SST[25] SVM SST系数、R-R间期、形态特征 84.71 80.43 70.75 – ST[11] GA-SVM R-R间期、时频特征、形态特征 99.74 99.42 99.83 – AFST 改进XGBoost 时频特征 99.59 99.25 99.47 99.45 -
[1] KREATSOUS C and ANAND S S. The impact of social determinants on cardiovascular disease[J]. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 2010, 26 Suppl C: 8C–13C. [2] World Health Organization. Cardiovascular disease (CVDs)[EB/OL].https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds), 2021. [3] AMORIM P, MORAES T, FAZANARO D, et al. Shearlet and contourlet transforms for analysis of electrocardiogram signals[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2018, 161: 125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.04.021 [4] 吴志勇, 丁香乾, 许晓伟, 等. 基于深度学习和模糊C均值的心电信号分类方法[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1913–1920. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170417WU Zhiyong, DING Xiangqian, XU Xiaowei, et al. A method for ECG classification using deep learning and fuzzy C-means[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1913–1920. doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170417 [5] DE CHAZAL P, O’DWYER M, and REILLY R B. Automatic classification of heartbeats using ECG morphology and heartbeat interval features[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2004, 51(7): 1196–1206. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2004.827359 [6] MAR T, ZAUNSEDER S, MARTÍNEZ J P, et al. Optimization of ECG classification by means of feature selection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 58(8): 2168–2177. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2113395 [7] 王金海, 史梦颖, 张兴华. 基于EMD和ApEn特征提取的心律失常分类研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2016, 37(S1): 168–173. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2016.s1.028WANG Jinhai, SHI Mengying, and ZHANG Xinghua. Classification of arrhythmias based on EMD and ApEn feature extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2016, 37(S1): 168–173. doi: 10.19650/j.cnki.cjsi.2016.s1.028 [8] JACOB N and JOSEPH L A. Classification of ECG beats using cross wavelet transform and support vector machines[C]. 2015 IEEE Recent Advances in Intelligent Computational Systems (RAICS), Trivandrum, India, 2015. [9] 尹柏强, 邓影, 王署东, 等. 时频广义S变换和VL-MOBP神经网络在人体动作识别中的应用[J]. 电子测量与仪器学报, 2020, 34(11): 1–9. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2003032YIN Baiqiang, DENG Ying, WANG Shudong, et al. Application of time-frequency generalized S transform and VL-MOBP neural network in human motion recognition[J]. Journal of Electronic Measurement and Instrumentation, 2020, 34(11): 1–9. doi: 10.13382/j.jemi.B2003032 [10] DAS M K and ARI S. Electrocardiogram beat classification using S-transform based feature set[J]. Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology, 2014, 14(5): 1450066. doi: 10.1142/S0219519414500663 [11] YANG Jianyong and YAN Ruqiang. A multidimensional feature extraction and selection method for ECG arrhythmias classification[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(13): 14180–14190. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3047962 [12] RAJ S and RAY K C. ECG signal analysis using DCT-Based DOST and PSO optimized SVM[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(3): 470–478. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2016.2642758 [13] SINHA N and DAS A. Identification and localization of myocardial infarction based on analysis of ECG signal in cross spectral domain using boosted SVM classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 4007409. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2021.3117663 [14] HOU Borui, YANG Jianyong, WANG Pu, et al. LSTM-based auto-encoder model for ECG arrhythmias classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(4): 1232–1240. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2910342 [15] 柯丽, 王丹妮, 杜强, 等. 基于卷积长短时记忆网络的心律失常分类方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(8): 1990–1998. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190712KE Li, WANG Danni, DU Qiang, et al. Arrhythmia classification based on convolutional long short term memory network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(8): 1990–1998. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190712 [16] BHATTACHARYYA S, MAJUMDER S, DEBNATH P, et al. Arrhythmic heartbeat classification using ensemble of random forest and support vector machine algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 2(3): 260–268. doi: 10.1109/TAI.2021.3083689 [17] KUNG B H, HU P Y, HUANG C C, et al. An efficient ECG classification system using resource-saving architecture and random forest[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2021, 25(6): 1904–1914. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3035191 [18] 王帅, 赵钟瑶, 张翔宇, 等. 穿戴式心电信号质量的三分类评估方法[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 2020, 39(5): 550–556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2020.05.005WANG Shuai, ZHAO Zhongyao, ZHANG Xiangyu, et al. Three-type classification method for wearable ECG signal quality[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2020, 39(5): 550–556. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-8021.2020.05.005 [19] 喻玲, 符玲, 熊思宇, 等. 基于最优Kaiser窗的动态同步相量测量算法[J]. 电网技术, 2022, 46(3): 1100–1108. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2021.0602YU Ling, FU Ling, XIONG Siyu, et al. A dynamic synchrophasor estimation algorithm based on optimal Kaiser window[J]. Power System Technology, 2022, 46(3): 1100–1108. doi: 10.13335/j.1000-3673.pst.2021.0602 [20] 尹柏强, 何怡刚, 朱彦卿. 一种广义S变换及模糊SOM网络的电能质量多扰动检测和识别方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2015, 35(4): 866–872. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.04.013YIN Baiqiang, HE Yigang, and ZHU Yanqing. Detection and classification of power quality multi-disturbances based on generalized s-transform and fuzzy SOM neural network[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2015, 35(4): 866–872. doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2015.04.013 [21] 王奕森, 夏树涛. 集成学习之随机森林算法综述[J]. 信息通信技术, 2018, 12(1): 49–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1285.2018.01.009WANG Yisen and XIA Shutao. A survey of random forests algorithms[J]. Information and Communications Technologies, 2018, 12(1): 49–55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1285.2018.01.009 [22] 赵洪山, 闫西慧, 王桂兰, 等. 应用深度自编码网络和XGBoost的风电机组发电机故障诊断[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(1): 81–86. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180708001ZHAO Hongshan, YAN Xihui, WANG Guilan, et al. Fault diagnosis of wind turbine generator based on deep autoencoder network and XGBoost[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(1): 81–86. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180708001 [23] PAN Jiapu and TOMPKINS W J. A real-time QRS detection algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 1985, BME-32(3): 230–236. doi: 10.1109/TBME.1985.325532 [24] CHIA N G, HAU Y W, and JAMALUDIN M N. Robust arrhythmia classifier using wavelet transform and support vector machine classification[C]. The 13th International Colloquium on Signal Processing & its Applications (CSPA), Penang, Malaysia, 2017. [25] HERRY C L, FRASCH M, SEELY A J, et al. Heart beat classification from single-lead ECG using the synchrosqueezing transform[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2017, 38(2): 171–187. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/aa5070 -





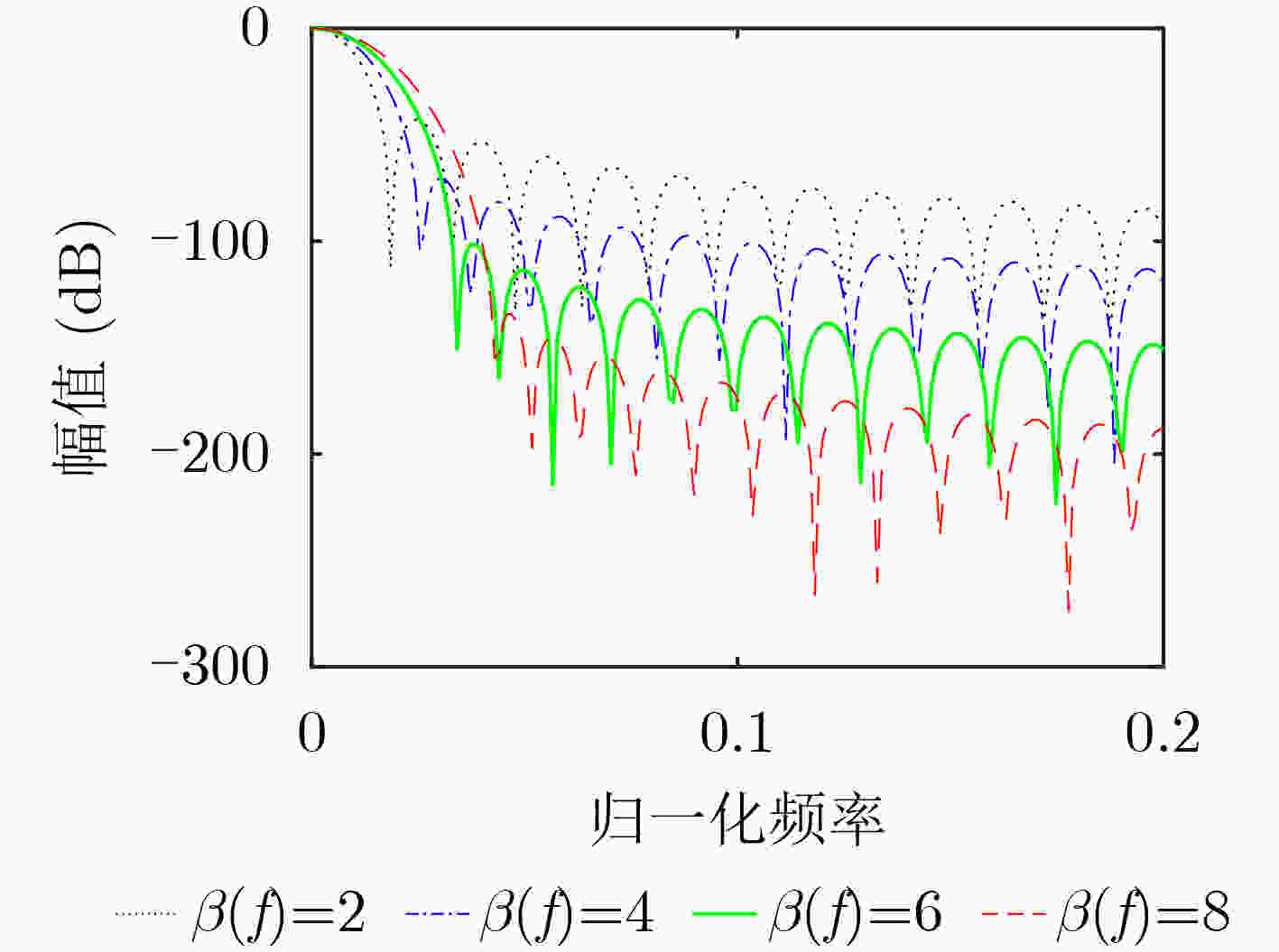

 下载:
下载:
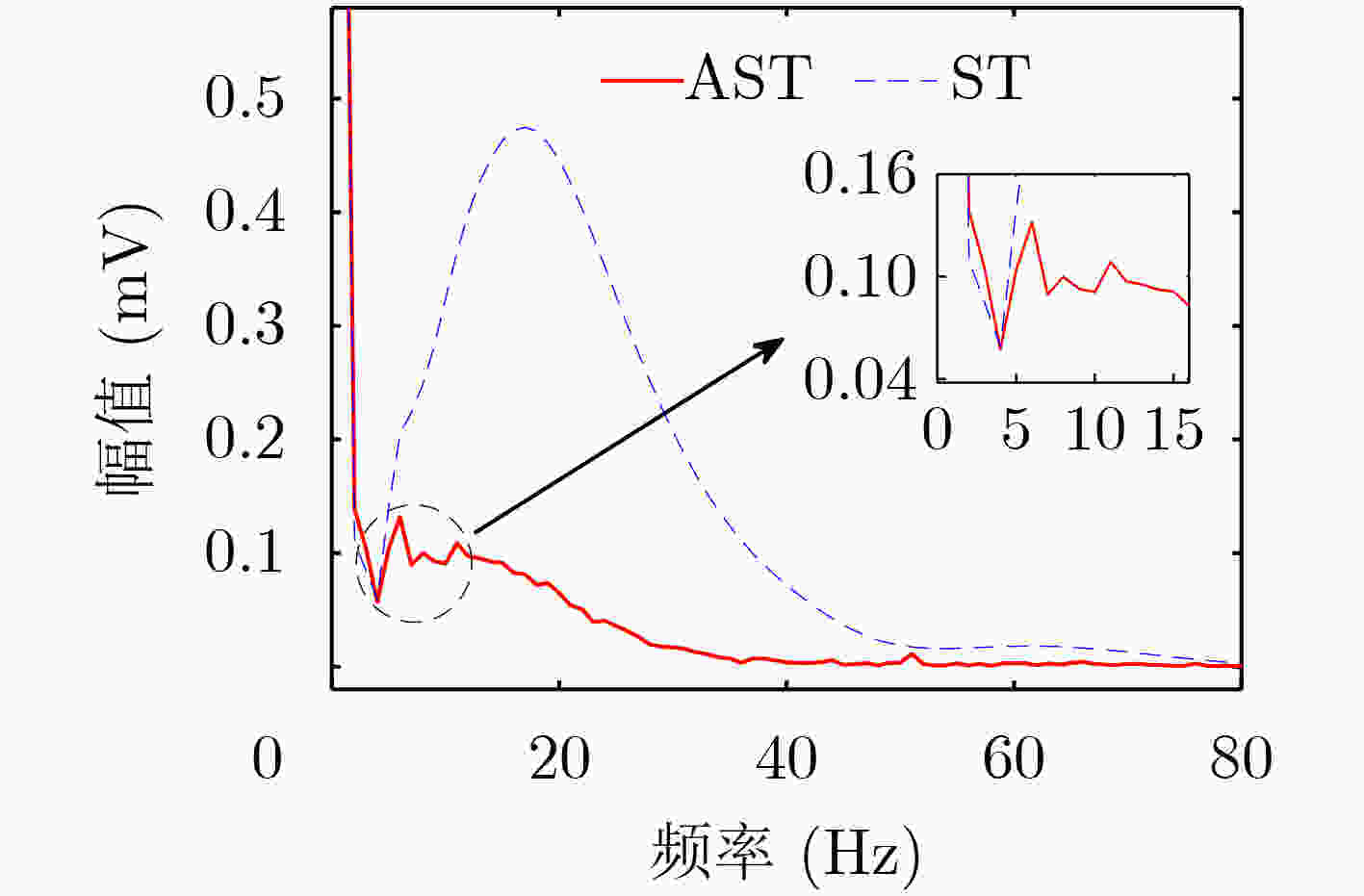
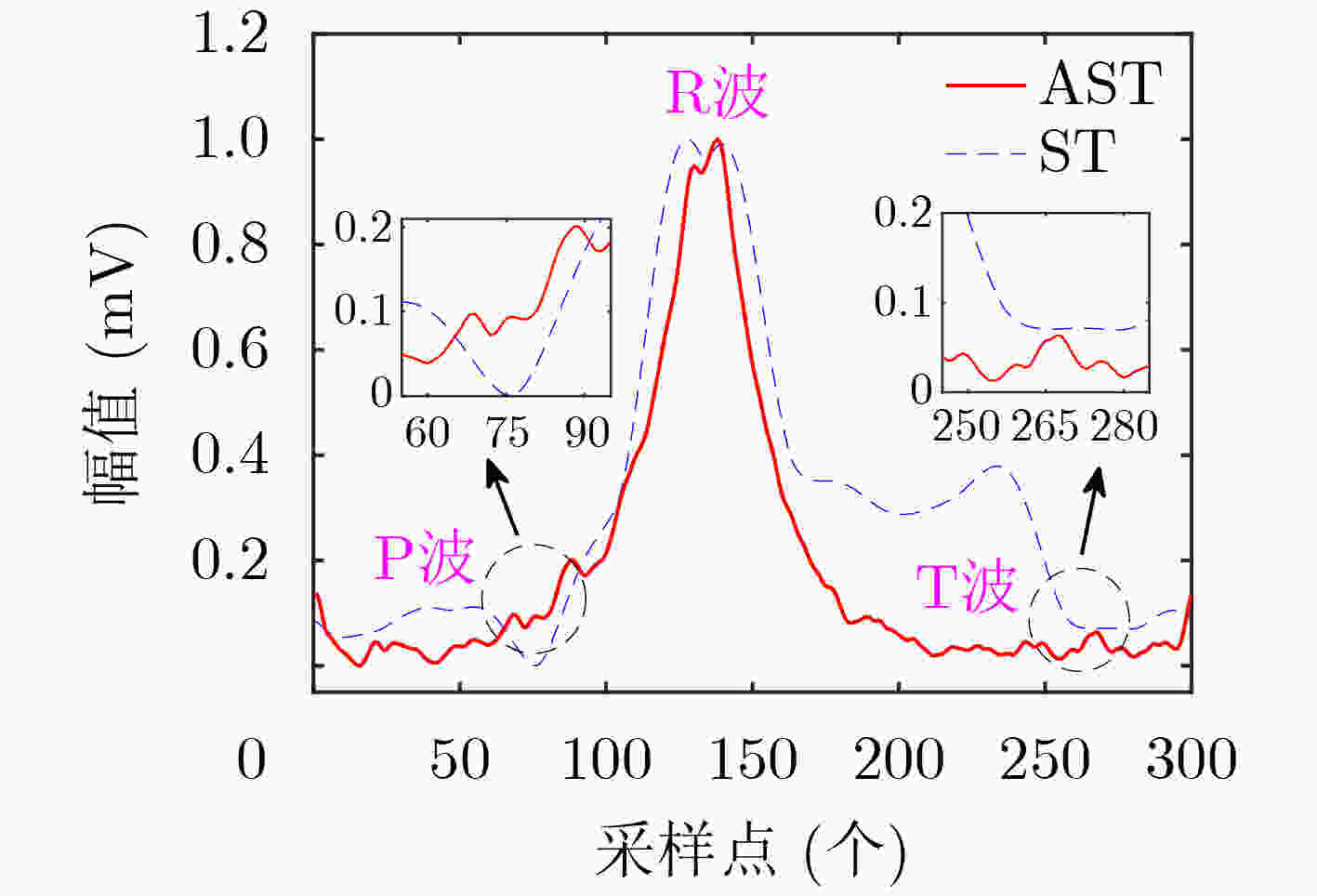
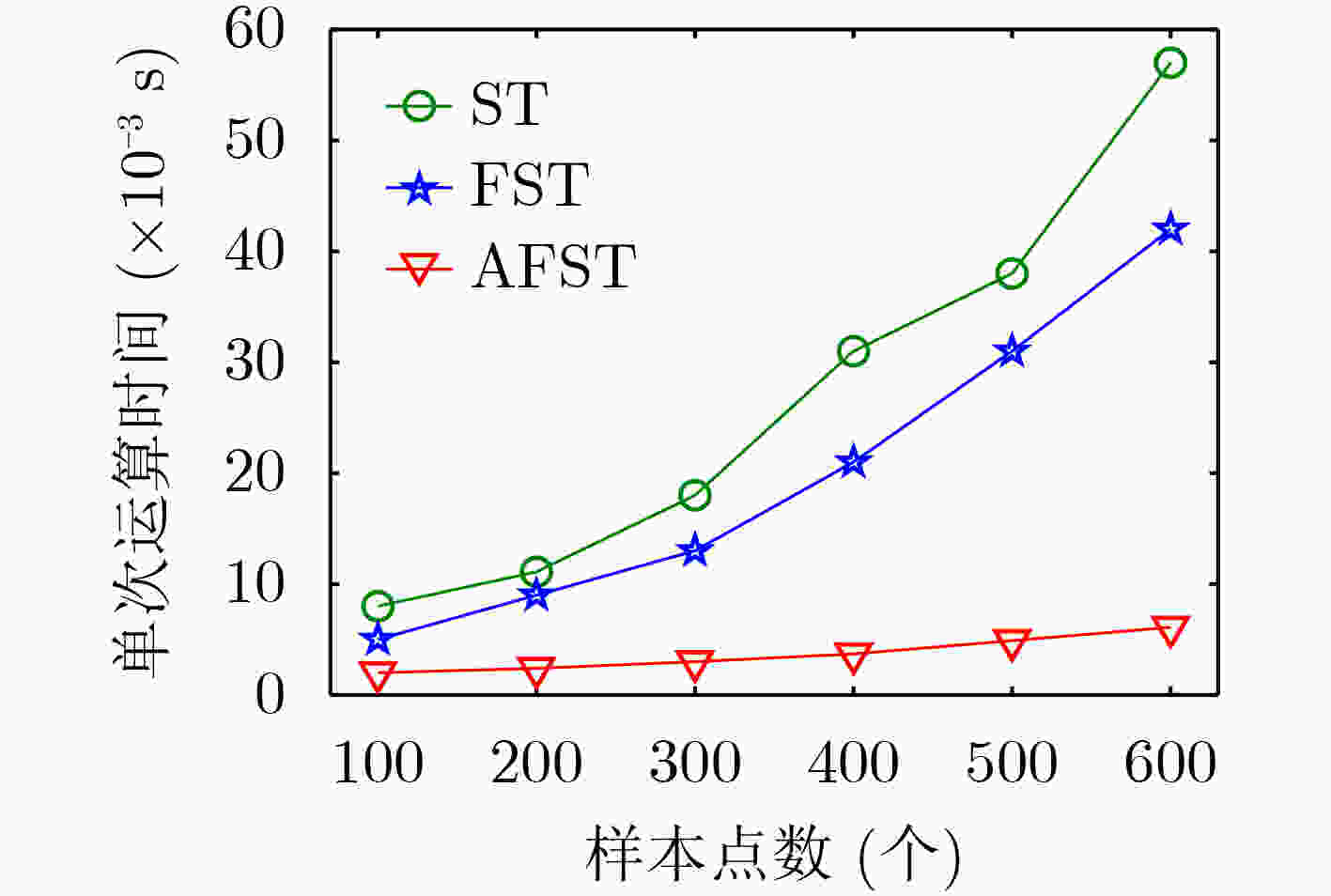
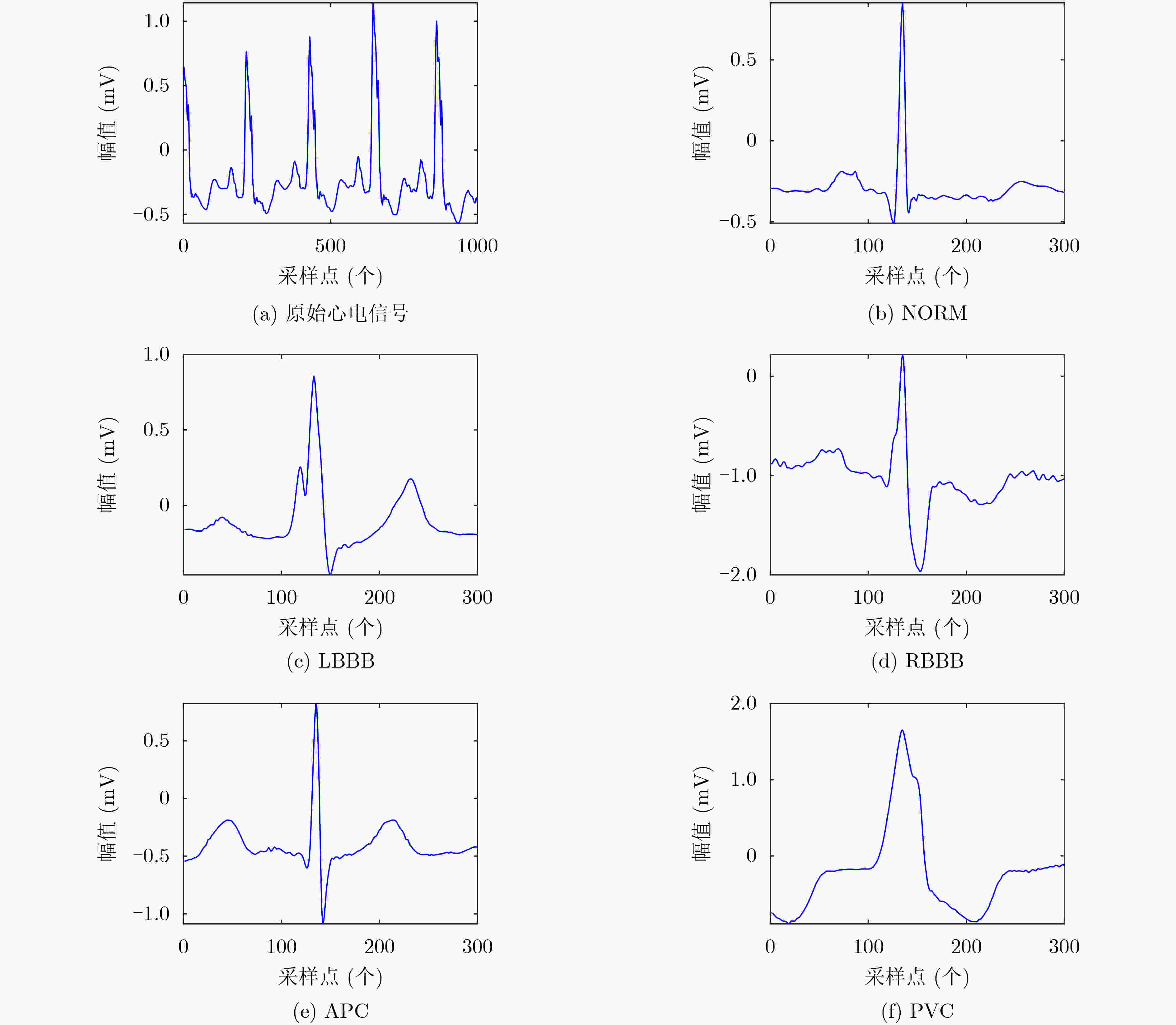
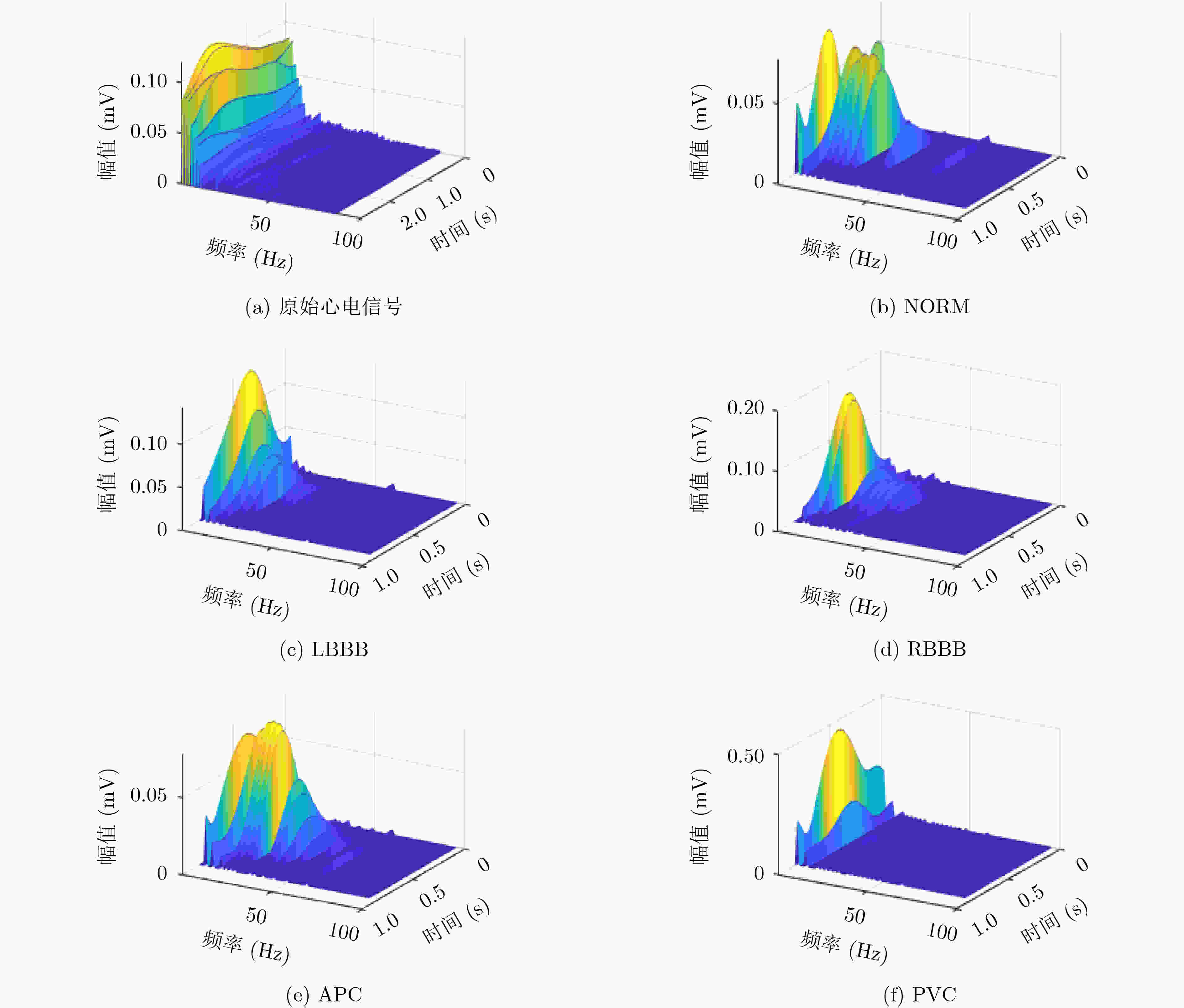
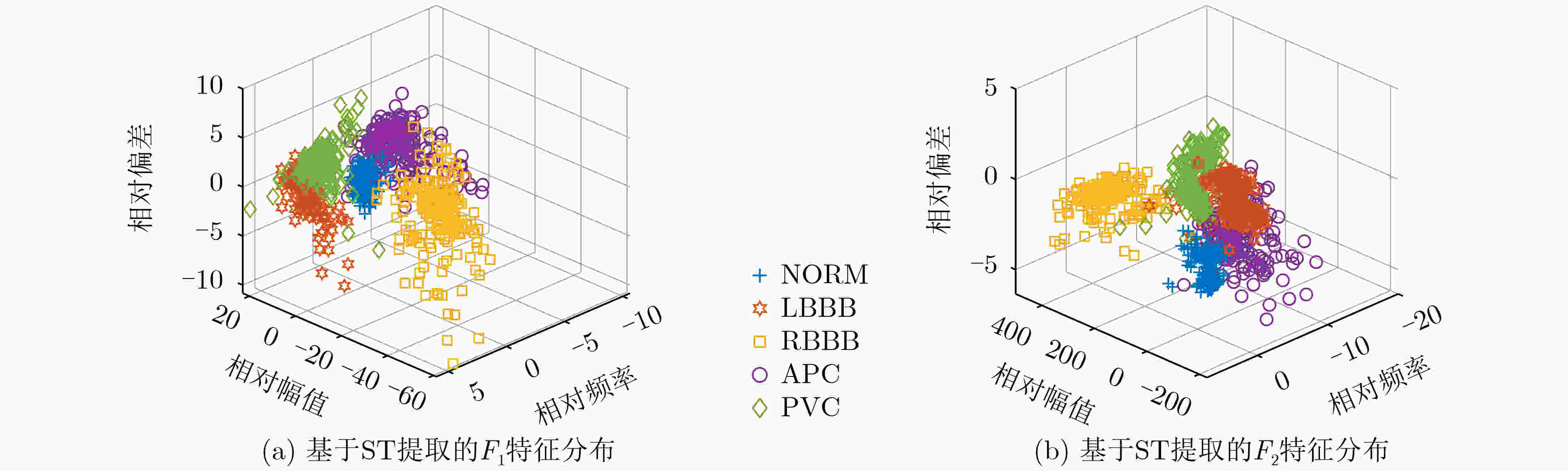

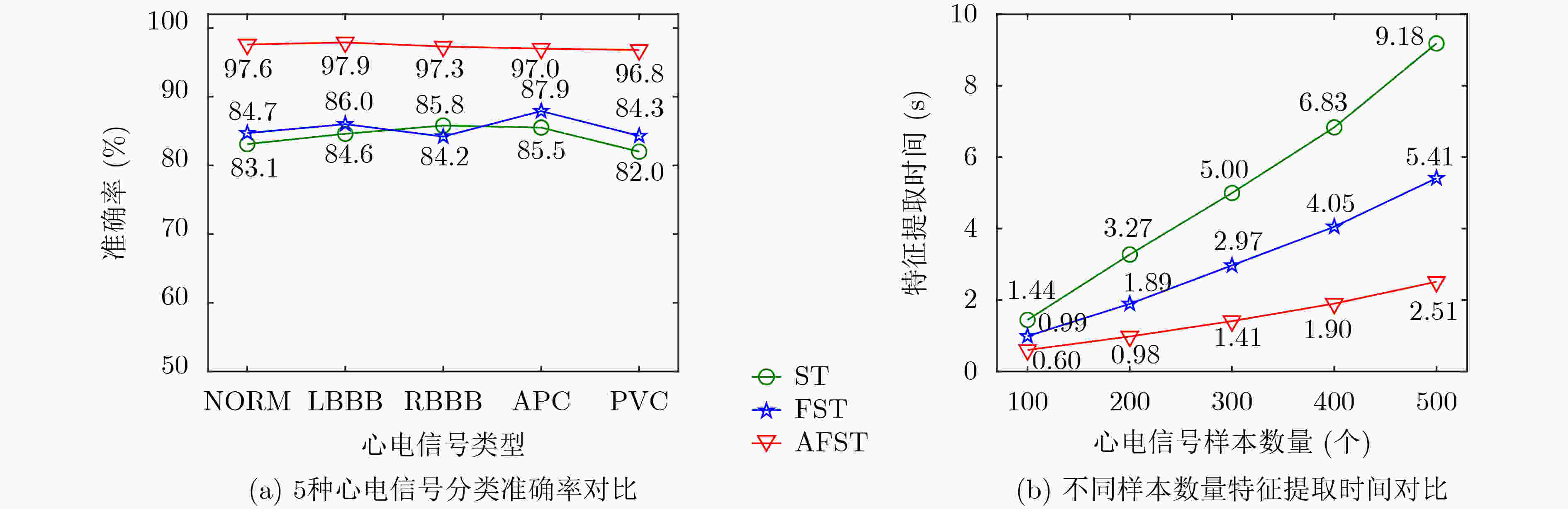


 下载:
下载:
