Energy-efficient Beamforming Design for Simultaneous Lightwave Information and Power Transfer in VLC systems
-
摘要: 物联网是6G的核心应用场景,然而由于射频频谱资源稀缺,为数以百亿计的物联网设备提供高质量无线覆盖服务面临挑战。可见光通信(Visible Light Communication, VLC)作为射频通信的补充,提供了丰富的高频频谱资源。该文研究多用户VLC无线信能同传网络的可达能量效率(Energy Efficiency, EE)性能界,即在用户信息和能量需求、避免LED谐波失真以及VLC发射机总功率约束下最大化EE。为求解所考虑的问题,结合Dinkelbach方法和连续凸近似方法构建迭代算法优化波束赋形向量和直流偏置。从理论上证明了所提算法的收敛性,并讨论了避免LED谐波失真的工作条件对EE的影响。仿真结果验证了所提方法的有效性,分析了信息需求、能量需求和VLC发射机总功率对EE的影响规律,并讨论了LED视野对EE和VLC信号传播的影响。Abstract: Internet of Things (IoT) is a key application of future 6G. However, it is challenging to provide high-quality wireless coverage for billions of IoT devices with limited Radio Frequency (RF) bandwidth. Visible Light Communication (VLC) utilizes abundant ultrahigh bandwidths as complement to RF communication. This paper investigates the Energy Efficiency (EE) of a Simultaneous Lightwave Information and Power Transfer (SLIPT) enabled multi-user VLC system. An EE maximization problem is formulated under constraints of Quality of Service (QoS) requirements of energy harvesting and information rate at users, avoiding clipping distortion by the nonlinearity of the LED and the power budget at VLC transmitter. To solve the considered problem, an iterative algorithm is proposed based on Dinkelbach and successive convex approximation methods to optimize the beamforming vectors and the direct current offset. The convergence of the proposed algorithm is theoretically proved. The impact of the constraint of avoiding clipping distortion by the nonlinearity of the LED on EE is discussed. Simulation results verify the analysis. Moreover, the impacts of QoS requirements of users, the power budget at VLC transmitter and the filed of view of LED on EE are illustrated and analyzed.
-
表 1 所提出算法
算法1 求解问题${ {\bf{P} }_1}$的迭代算法 (1) 初始化$ {\bar \alpha _n}[t] $和$ {\bar \beta _n}[t] $; (2) 设置$ t = 1 $; (3) While 连续两次迭代的最优解之差大于$ \varepsilon $ do (4) 初始化$ \lambda [0] $且$ F(\lambda [0]) > 0 $; (5) $ q = 0 $; (6) While $ F(\lambda [q]) \le \varepsilon $ do (7) 基于给定的$ \lambda [q] $求解凸问题${ {\bf{P} }_5}$得到
$ \{ {\mathbf{w}}_n^ * [q],I_{\text{D}}^ * [q],\theta _n^ * [q]\} $;更新
(8) $ F(\lambda [q]) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{n = 1}^N {\theta _n^ * [q]} - \lambda [q]{P_{{\text{Total}}}}(\{ {\mathbf{w}}_n^ * [q],I_{\text{D}}^ * [q]\} ) $;(9) 根据式(19)更新$ \lambda [q + 1] $; (10) 设置$ q = q + 1 $; (11) end while (12) 设置$ {\mathbf{w}}_n^ * [t] = {\mathbf{w}}_n^ * [q] $和$ \theta _n^ * [t] = \theta _n^ * [q] $; (13) 根据式(20)和式(21)分别更新$ {\bar \alpha _n}[t] $和$ {\bar \beta _n}[t] $; (14) 设置$ t = t + 1 $; (15) end while 表 2 仿真参数
变量 值(m) 变量 值(m) 变量 值 变量 值 LED1坐标 (4.9,4.9,3.0) LED7坐标 (5.1,4.9,3.0) $ A $ 2V $ {A_{\text{R}}} $ 1cm2 LED2坐标 (4.9,5.0,3.0) LED8坐标 (5.1,5.0,3.0) $ [{I_{\text{L}}},{I_{\text{H}}}] $ [0,5]A $ T({\varphi _{ni}}) $ 1 LED3坐标 (4.9,5.1,3.0) LED9坐标 (5.1,5.1,3.0) $ {P_{{\text{Max}}}} $ 50W $\varPsi$ 60° LED4坐标 (5.0,4.9,3.0) 用户1坐标 (5.1,6.0,1.5) $ {I_{\text{0}}} $ ${10^{ - 9} }$A $ \mu $ 1 LED5坐标 (5.0,5.0,3.0) 用户2坐标 (5.1,4.9,1.5) $ V $ 25mV $ \theta _{ni}^{1/2} $ 60° LED6坐标 (5.0,5.1,3.0) 用户3坐标 (4.9,4.9,1.5) $ f $ 0.75 $ \sigma _{}^2 $ $ {10^{ - 15}} $ -
[1] 袁伟杰, 李双洋, 种若汐, 等. 面向6G物联网的分布式译码技术[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 21–27. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200343YUAN Weijie, LI Shuangyang, CHONG Ruoxi, et al. A distributed decoding algorithm for 6G Internet-of-Things networks[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 21–27. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200343 [2] ZHANG Rui and HO C K. MIMO broadcasting for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2013, 12(5): 1989–2001. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.031813.120224 [3] 尤肖虎, 尹浩, 邬贺铨. 6G与广域物联网[J]. 物联网学报, 2020, 4(1): 3–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00158YOU Xiaohu, YIN Hao, and WU Hequan. On 6G and wide-area IoT[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2020, 4(1): 3–11. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2020.00158 [4] 栾宁, 熊轲, 张煜, 等. 6G: 典型应用、关键技术与面临挑战[J]. 物联网学报, 2022, 6(1): 29–43. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2022.00253LUAN Ning, XIONG Ke, ZHANG Yu, et al. 6G: Typical applications, key technologies and challenges[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2022, 6(1): 29–43. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-3750.2022.00253 [5] CHI Nan, ZHOU Yingjun, WEI Yiran, et al. Visible light communication in 6G: Advances, challenges, and prospects[J]. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 2020, 15(4): 93–102. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2020.3017153 [6] WANG Jinyuan, FU Xiantao, LU Rongrong, et al. Tight capacity bounds for indoor visible light communications with signal-dependent noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(3): 1700–1713. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3035615 [7] PAN Gaofeng, YE Jie, ZHANG Chao, et al. Secure cooperative hybrid VLC-RF systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(11): 7097–7107. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3007937 [8] PAN Gaofeng, DIAMANTOULAKIS P D, MA Zheng, et al. Simultaneous lightwave information and power transfer: Policies, techniques, and future directions[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 28250–28257. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901855 [9] NDJIONGUE A R, NGATCHED T M N, DOBRE O A, et al. Toward the use of re-configurable intelligent surfaces in VLC systems: Beam steering[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(3): 156–162. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000365 [10] LU Yang, XIONG Ke, FAN Pingyi, et al. Global energy efficiency in secure MISO SWIPT systems with non-linear power-Splitting EH model[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37(1): 216–232. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2872369 [11] YANG Helin, ALPHONES A, ZHONG Wende, et al. Learning-based energy-efficient resource management by heterogeneous RF/VLC for ultra-reliable low-latency industrial IoT networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(8): 5565–5576. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2933867 [12] ABDELHADY A M, AMIN O, SHIHADA B, et al. Spectral efficiency and energy harvesting in multi-cell SLIPT systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(5): 3304–3318. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2972314 [13] XIAO Yue, DIAMANTOULAKIS P, FANG Zequn, et al. Cooperative hybrid VLC/RF systems with SLIPT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(4): 2532–2545. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3051908 [14] GUO Yangbo, XIONG Ke, LU Yang, et al. Achievable information rate in hybrid VLC-RF networks with lighting energy harvesting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(10): 6852–6864. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3098030 [15] AL HAMMADI A, SOFOTASIOS P C, MUHAIDAT S, et al. Non-orthogonal multiple access for hybrid VLC-RF networks with imperfect channel state information[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(1): 398–411. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3044837 [16] LIU Xiaodong, WANG Yuhao, ZHOU Fuhui, et al. Beamforming design for secure MISO visible light communication networks with SLIPT[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(12): 7795–7809. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3019818 [17] MA Shuai, ZHANG Fan, LI Hang, et al. Simultaneous lightwave information and power transfer in visible light communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(12): 5818–5830. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2939242 [18] ARFAOUI M A, ZAID H, REZKI Z, et al. Artificial noise-based beamforming for the MISO VLC wiretap channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2019, 67(4): 2866–2879. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2889649 [19] HSIAO Y C, WU Y C, and LIN Che. Energy-efficient beamforming design for MU-MISO mixed RF/VLC heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(14): 3770–3784. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2920612 [20] ZHANG Haijun, LIU Na, LONG Keping, et al. Energy efficient subchannel and power allocation for software-defined heterogeneous VLC and RF networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2018, 36(3): 658–670. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2018.2815478 [21] DIAMANTOULAKIS P D, KARAGIANNIDIS G K, and DING Zhiguo. Simultaneous lightwave information and power transfer (SLIPT)[J]. IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, 2018, 2(3): 764–773. doi: 10.1109/TGCN.2018.2818325 [22] WANG Kunyu, SO A M C, CHANG T H, et al. Outage constrained robust transmit optimization for multiuser MISO downlinks: Tractable approximations by conic optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(21): 5690–5705. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2354312 -





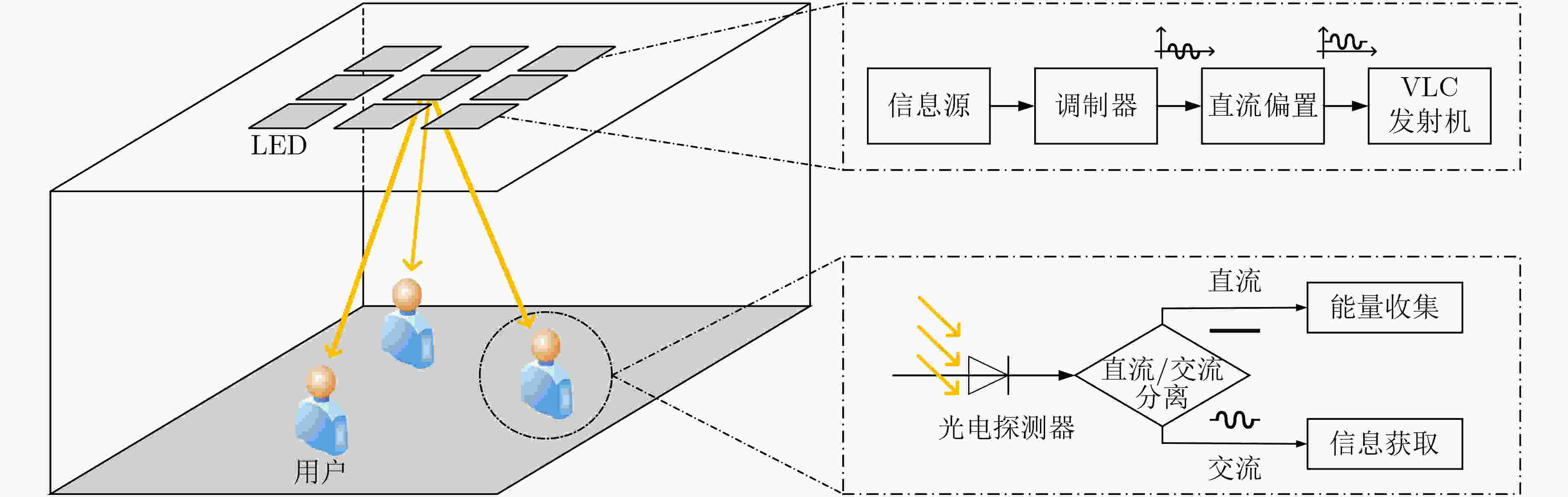
 下载:
下载:

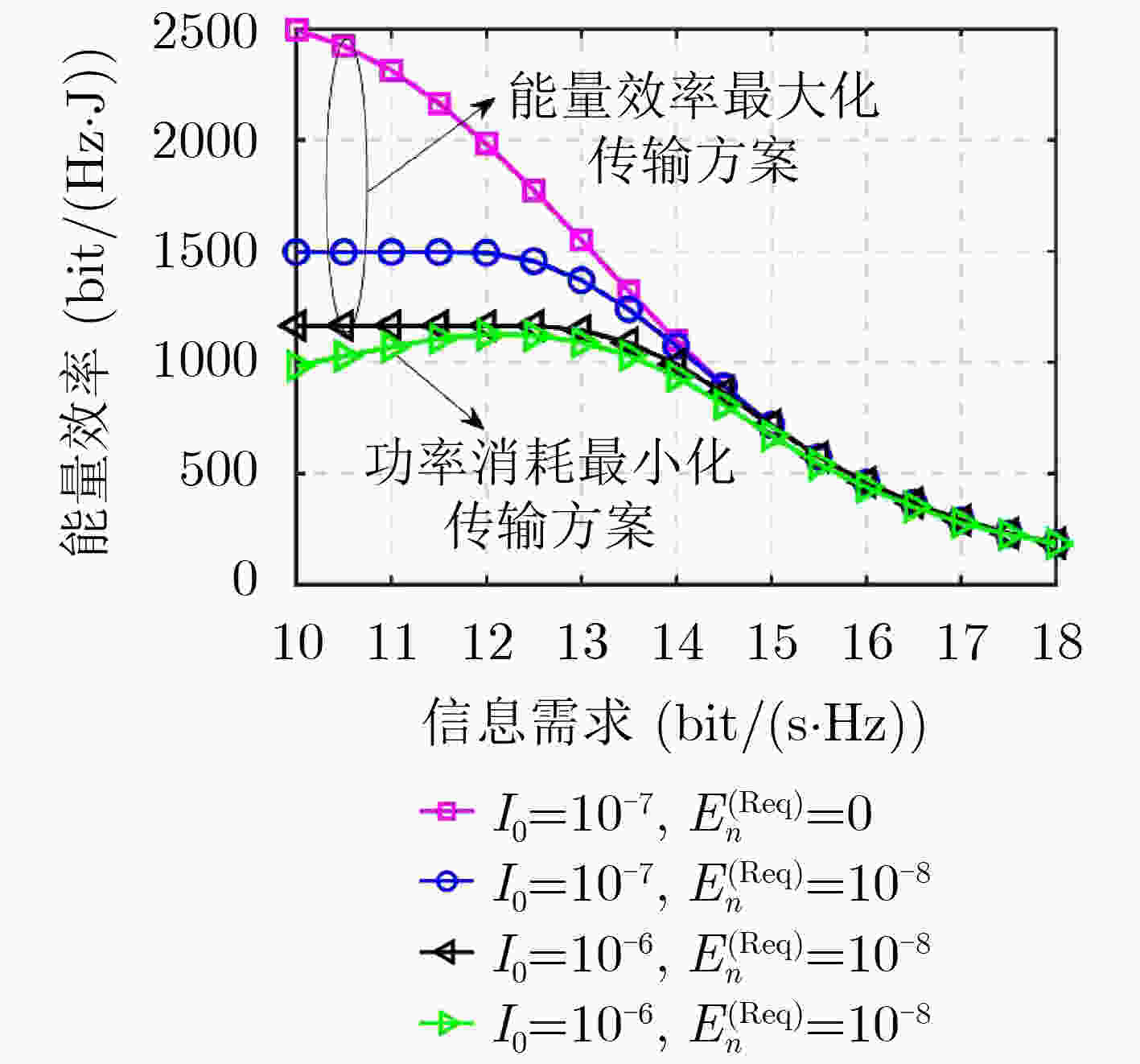
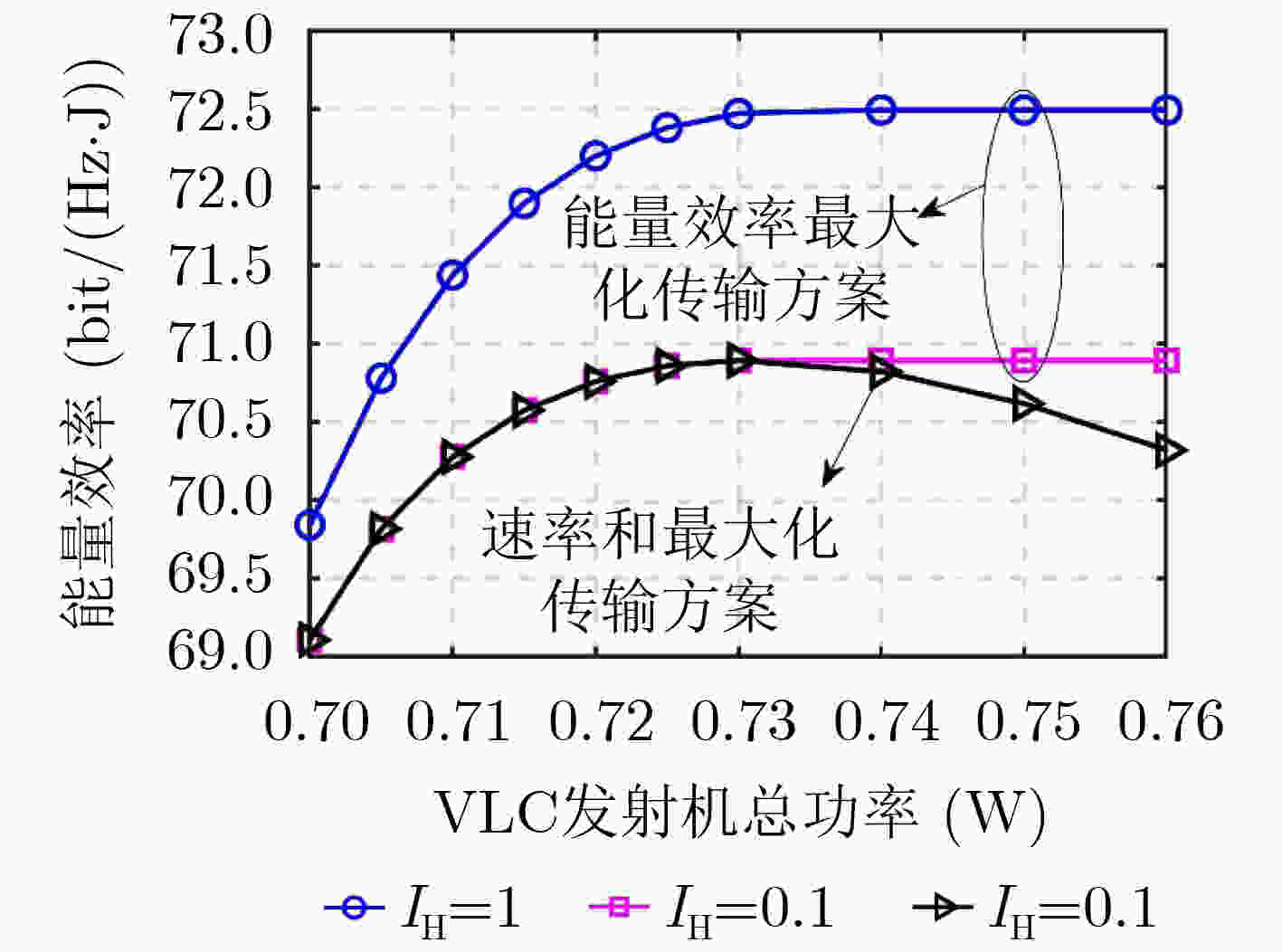
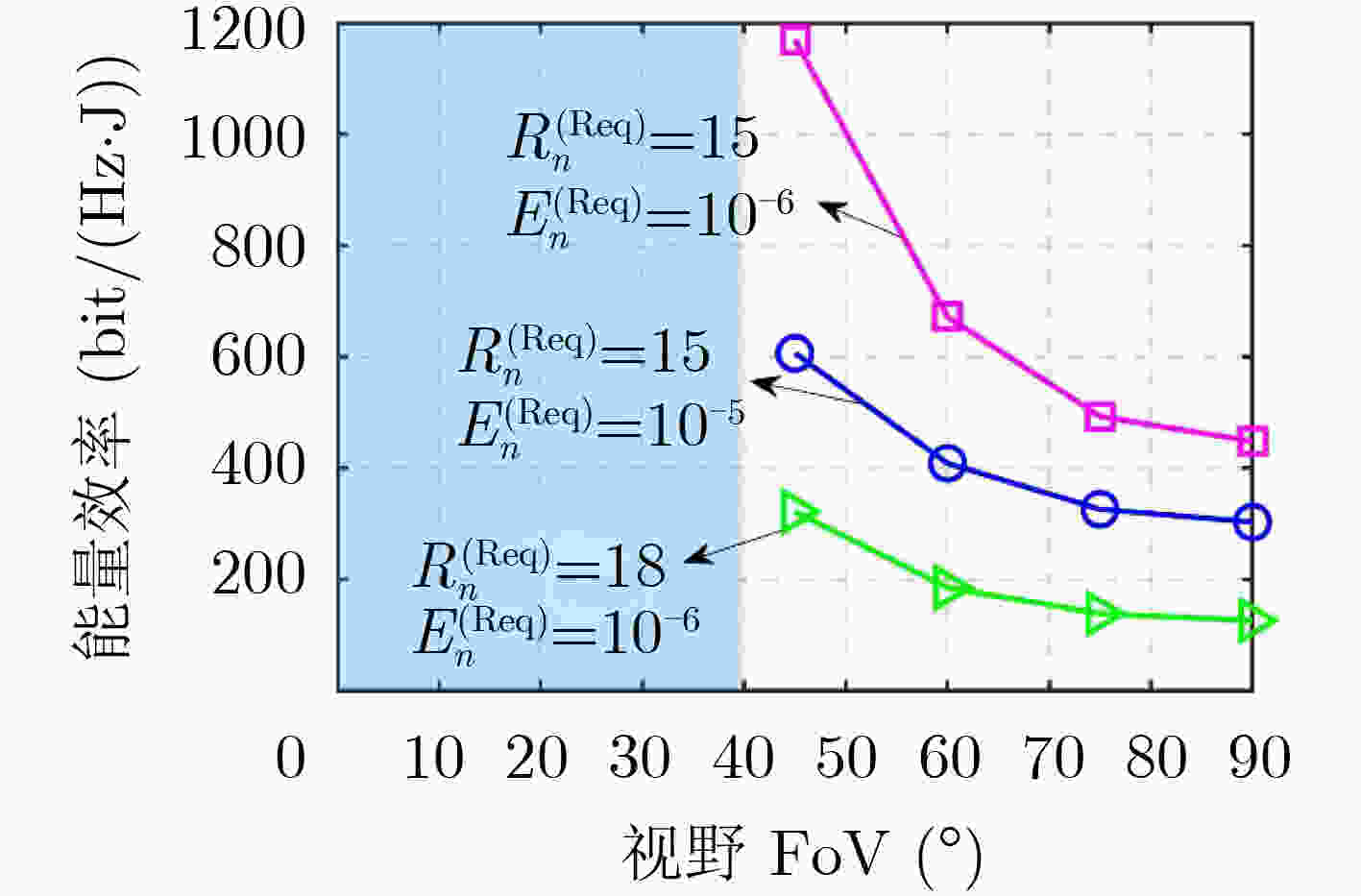


 下载:
下载:
