Small Target Detection Based on Frequency Domain Multichannel Graph Feature Perception on Sea Surface
-
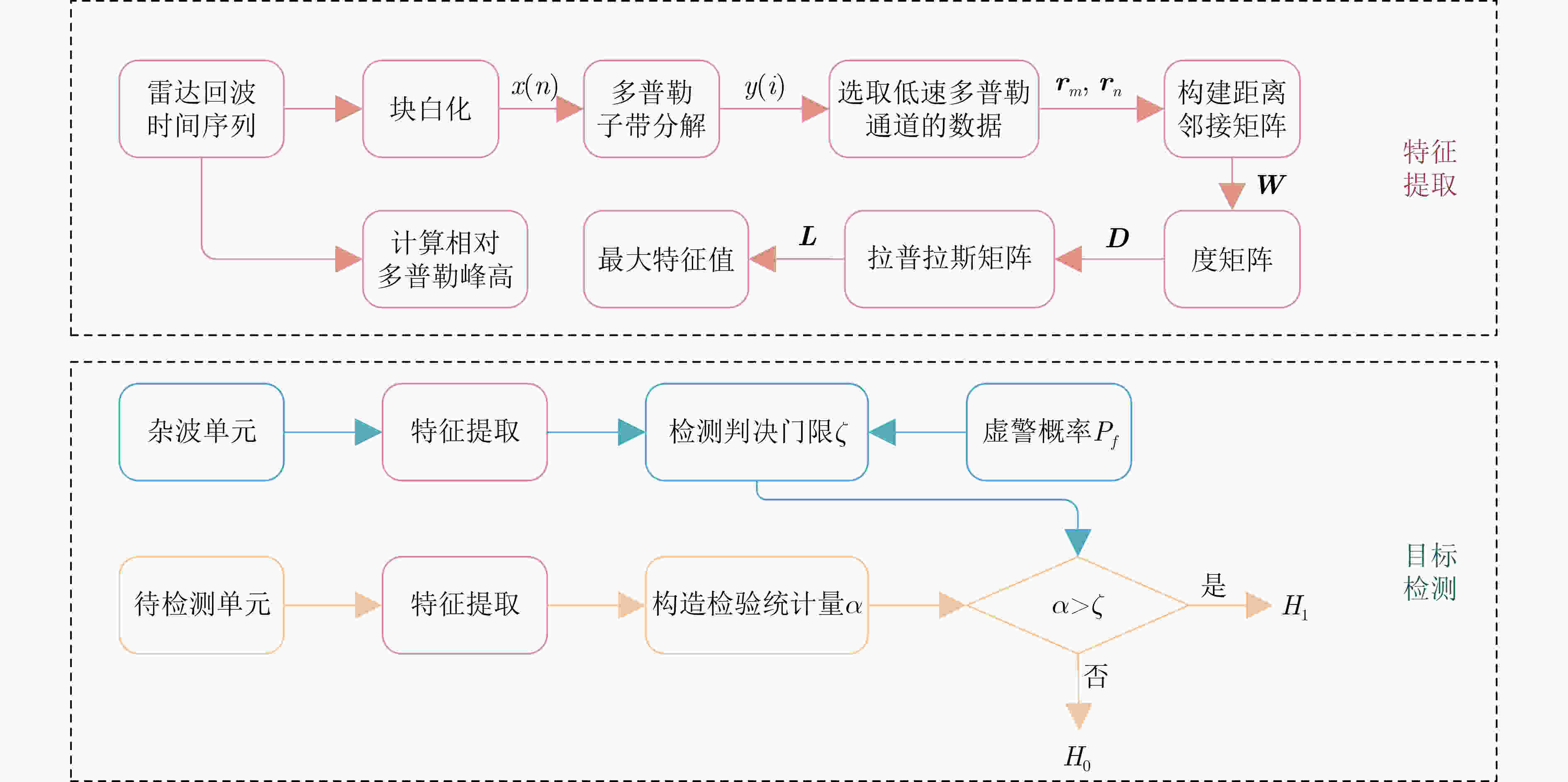
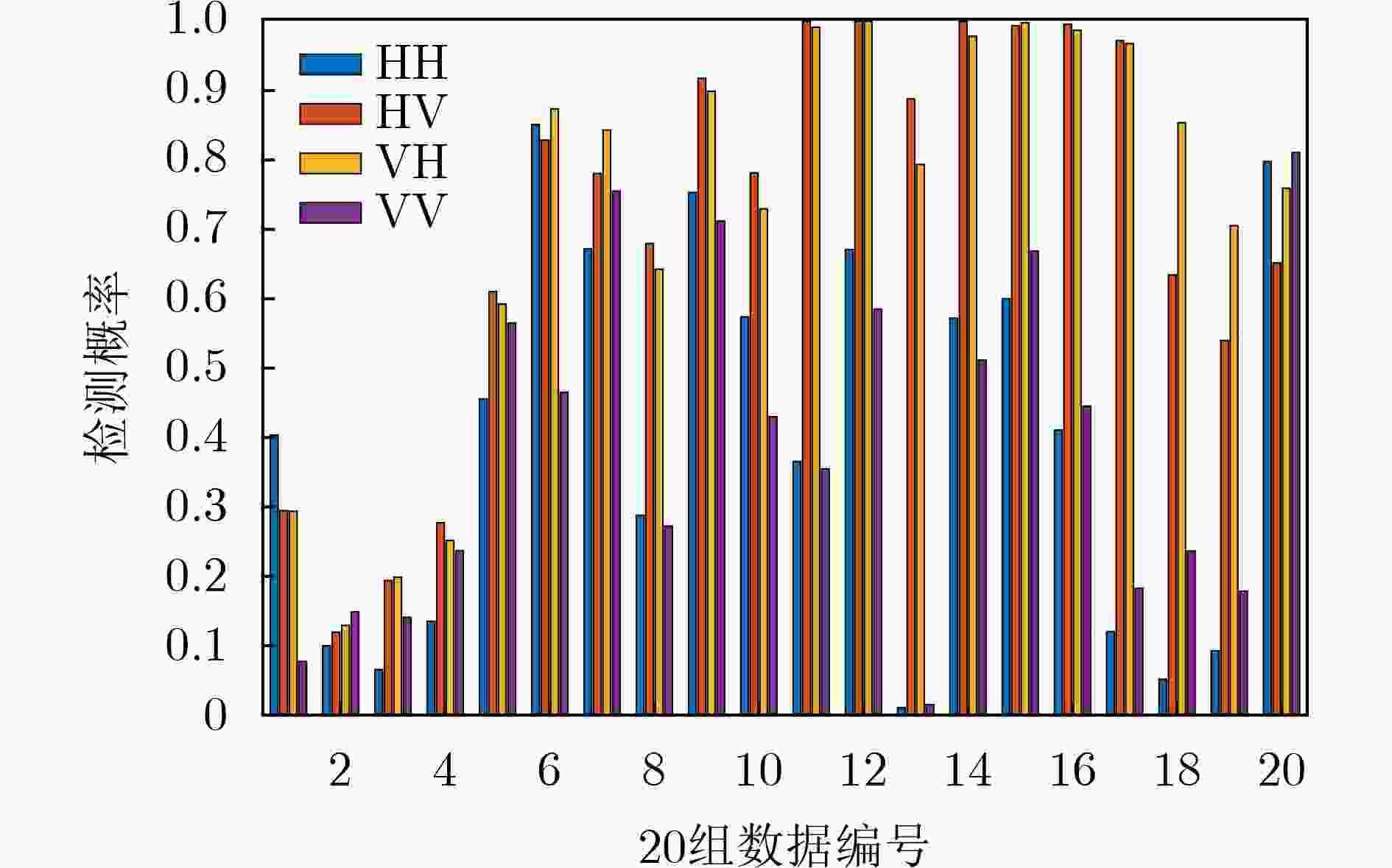
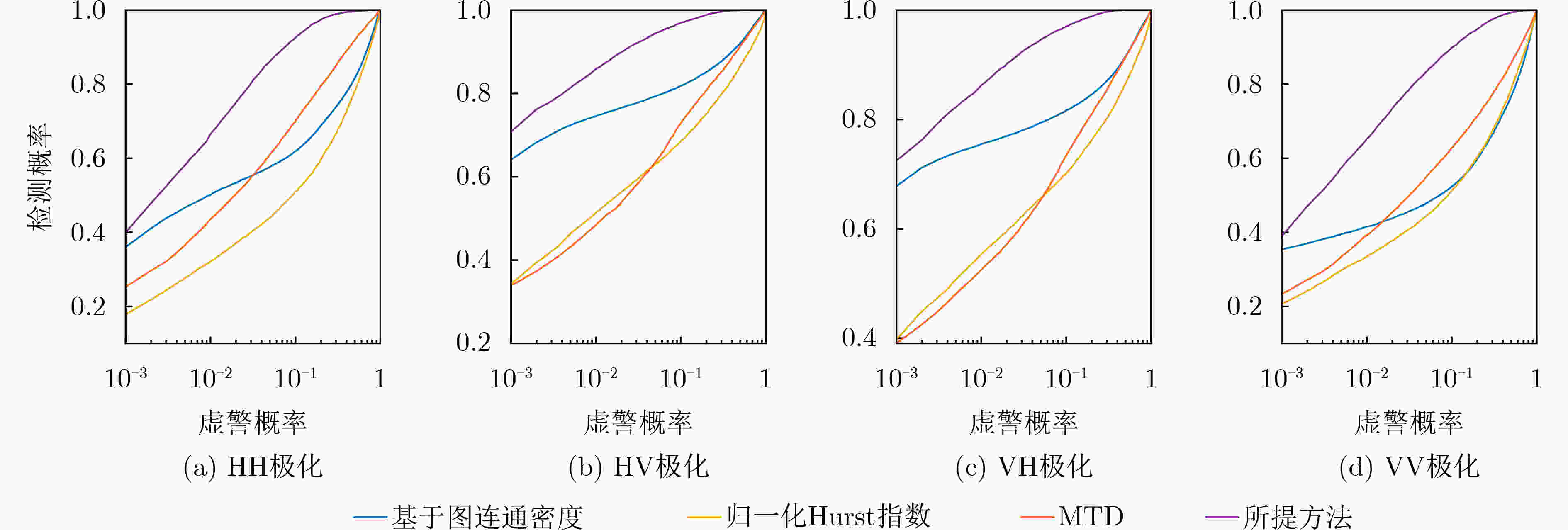
摘要: 海洋物理环境和电磁环境日趋复杂,海杂波背景下的微弱慢速小目标检测始终是一个研究难点和重点。海面小目标的雷达散射截面积小、回波能量低,传统基于能量的检测方法存在性能瓶颈。基于特征的检测方法聚焦于提取纯杂波和目标回波的差异性特征来实现目标检测,且有效提升了检测性能。该文利用回波数据间频域中幅度的关联性,将图论的方法引入到特征检测中。首先将实测数据进行块白化处理,对海杂波进行一定的抑制,然后在频域提取各多普勒通道下的数据,借助图的处理方法,构建所提取数据的距离邻接矩阵,再转换为拉普拉斯矩阵。该方法计算不同时间序列下拉普拉斯矩阵的最大特征值,并将其与刻画频域能量信息的相对多普勒峰高进行融合,得到新的检验统计量来区分纯杂波和含有目标的回波。通过全相参的X波段(IPIX)实测数据验证,该文所提方法的检测性能更为优越。Abstract: The marine physical environment and electromagnetic environment are becoming increasingly complex, making the weak and slow small target detection in the sea clutter background be both emphasis and difficulty of radar target detection research. Due to small radar cross sections and low energy of small targets on the sea surface, traditional energy-based detection methods have a performance bottleneck. Feature-based detection methods focus on extracting distinguishing features between pure sea clutter and target returns to achieve target detection, which improve effectively the detection performance. Using the correlation of amplitude of radar returns in frequency domain, the graph theory method to feature-based detection is introduced. Firstly, measured sea clutter data are block-whitened to suppress sea clutter. Then, the data from Doppler channels are extracted in the frequency domain. With the help of graph processing methods, a distance adjacency matrix of the extracted data is constructed, and then it is converted into a Laplacian matrix. The maximum eigenvalue of Laplacian matrix under different radar returns is calculated, and fused with the relative Doppler peak height, then a new test statistic is obtained. By comparing the value of test statistics, sea clutter and returns with targets can be distinguished. Verified by the measured Ice multiParameter Imaging X-band (IPIX) database, the proposed detector attains better detection performance.
-
Key words:
- Target detection /
- Sea clutter /
- Feature-based detection /
- Graph feature /
- Doppler channel
-
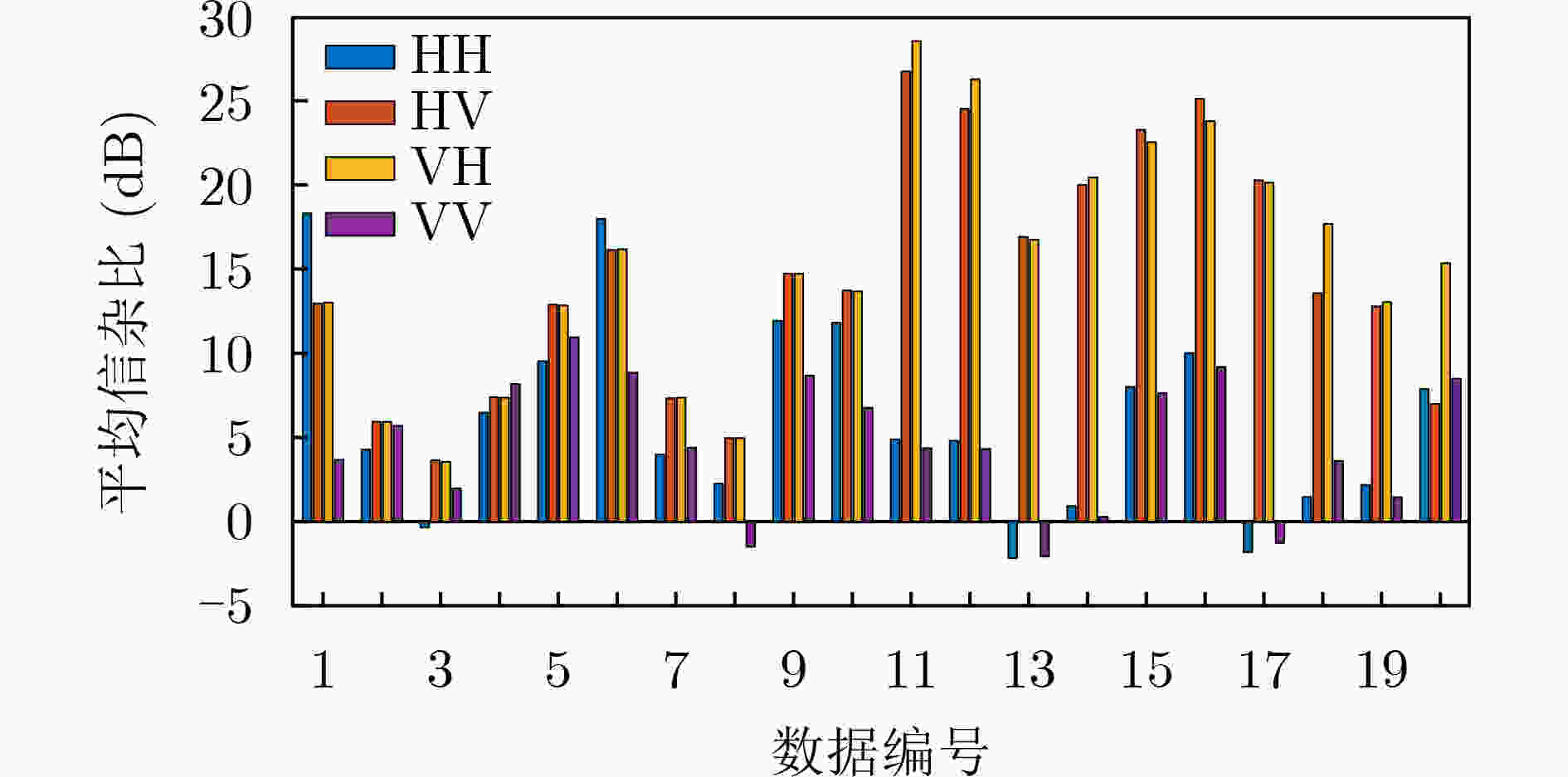
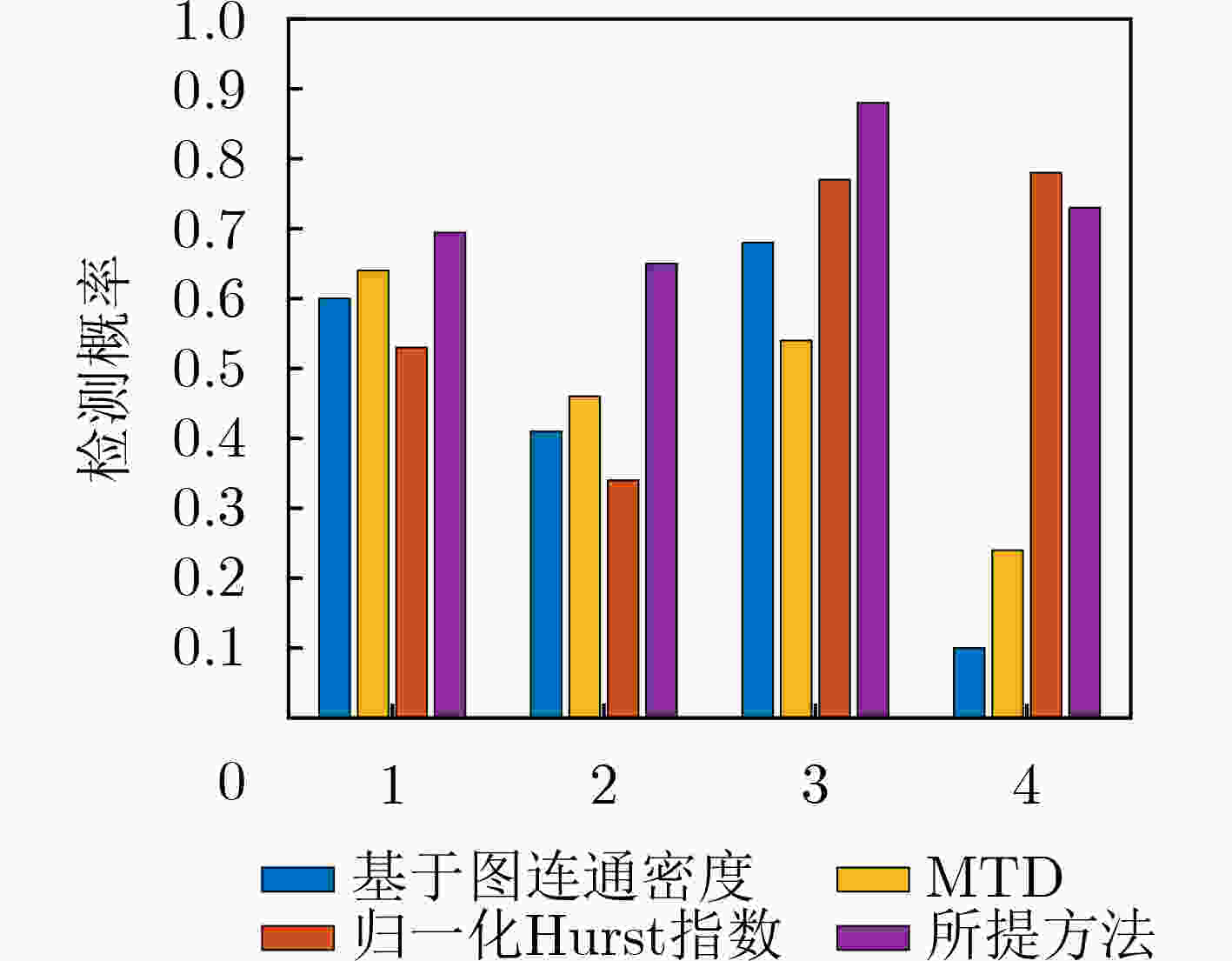
表 1 海航数据的信杂比(dB)
目标 单载频 LFM 浮标 13.23 14.16 船只 12.23 7.35 -
[1] HU Jing, TUNG W W, and GAO Jianbo. Detection of low observable targets within sea clutter by structure function based multifractal analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2006, 54(1): 136–143. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2005.861541 [2] GUAN Jian, LIU N B, HUANG Y, et al. Fractal characteristic in frequency domain for target detection within sea clutter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2012, 6(5): 293–306. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2011.0250 [3] 陈小龙, 刘宁波, 宋杰, 等. 海杂波FRFT域分形特征判别及动目标检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2011, 33(4): 823–830. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00486CHEN Xiaolong, LIU Ningbo, SONG Jie, et al. Fractal feature discriminant of sea clutter in FRFT domain and moving target detection algorithm[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2011, 33(4): 823–830. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2010.00486 [4] WOOD J C and BARRY D T. Radon transformation of time-frequency distributions for analysis of multicomponent signals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1994, 42(11): 3166–3177. doi: 10.1109/78.330375 [5] SHUI Penglang, BAO Zheng, and SU Hongtao. Nonparametric detection of FM signals using time-frequency ridge energy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(5): 1749–1760. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.909322 [6] MEI J and MOURA J M F. Signal processing on graphs: Estimating the structure of a graph[C]. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, South Brisbane, Australia, 2015: 5495–5499. [7] 殷剑宏, 吴开亚. 图论及其算法[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2003.YIN Jianhong and WU Kaiya. Graph Theory and Its Algorithm[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2003. [8] SU Ningyuan, CHEN Xiaolong, GUAN Jian, et al. Maritime target detection based on radar graph data and graph convolutional network[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2022, 19: 4019705. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2021.3133473 [9] YAN Kun, BAI Yu, WU H C, et al. Robust target detection within sea clutter based on graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 7093–7103. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2911451 [10] 时艳玲, 姚婷婷, 郭亚星. 基于图连通密度的海面漂浮小目标检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(11): 3185–3192. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201028SHI Yanling, YAO Tingting, and GUO Yaxing. Floating small target detection based on graph connected density in sea surface[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(11): 3185–3192. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201028 [11] 李炯生, 张晓东, 潘永亮. 图的Laplace特征值[J]. 数学进展, 2003, 32(2): 157–165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0917.2003.02.003LI Jiongsheng, ZHANG Xiaodong, and PAN Yongliang. Laplacian eigenvalues of graphs[J]. Advances in Mathematics, 2003, 32(2): 157–165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0917.2003.02.003 [12] 张海霞. 关于图的Laplace特征值[D]. [硕士论文], 大连理工大学, 2005.ZHANG Haixia. On Laplace eigenvalues of graph[D]. [Master dissertation], Dalian University of Technology, 2005. [13] 李东宸. 海杂波中小目标的特征检测方法[D]. [博士论文], 西安电子科技大学, 2016.LI Dongchen. Feature-based detection methods of small targets in sea clutter[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Xidian University, 2016. [14] STANKOVIĆ L, MANDIC D, DAKOVIĆ M, et al. Data analytics on graphs part III: Machine learning on graphs, from graph topology to applications[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2020, 13(4): 332–530. doi: 10.1561/2200000078-3 [15] ORTEGA A, FROSSARD P, KOVAČEVIĆ J, et al. Graph signal processing: Overview, challenges, and applications[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2018, 106(5): 808–828. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2018.2820126 [16] SHUI Penglang, LI Dongchen, and XU Shuwen. Tri-feature-based detection of floating small targets in sea clutter[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(2): 1416–1430. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120657 [17] 许述文, 白晓惠, 郭子薰, 等. 海杂波背景下雷达目标特征检测方法的现状与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084XU Shuwen, BAI Xiaohui, GUO Zixun, et al. Status and prospects of feature-based detection methods for floating targets on the sea surface[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(4): 684–714. doi: 10.12000/JR20084 [18] 丁昊, 刘宁波, 董云龙, 等. 雷达海杂波测量试验回顾与展望[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006DING Hao, LIU Ningbo, DONG Yunlong, et al. Overview and prospects of radar sea clutter measurement experiments[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(3): 281–302. doi: 10.12000/JR19006 [19] 刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011LIU Ningbo, DING Hao, HUANG Yong, et al. Annual progress of the sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(1): 173–182. doi: 10.12000/JR21011 [20] LI Dongchen and SHUI Penglang. Floating small target detection in sea clutter via normalised Hurst exponent[J]. Electronics Letters, 2014, 50(17): 1240–1242. doi: 10.1049/el.2014.1569 [21] DILLARD G M and SUMMERS B F. Mean-level detection in the frequency domain[J]. IEE Proceedings - Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 1996, 143(5): 307–312. doi: 10.1049/ip-rsn:19960457 -





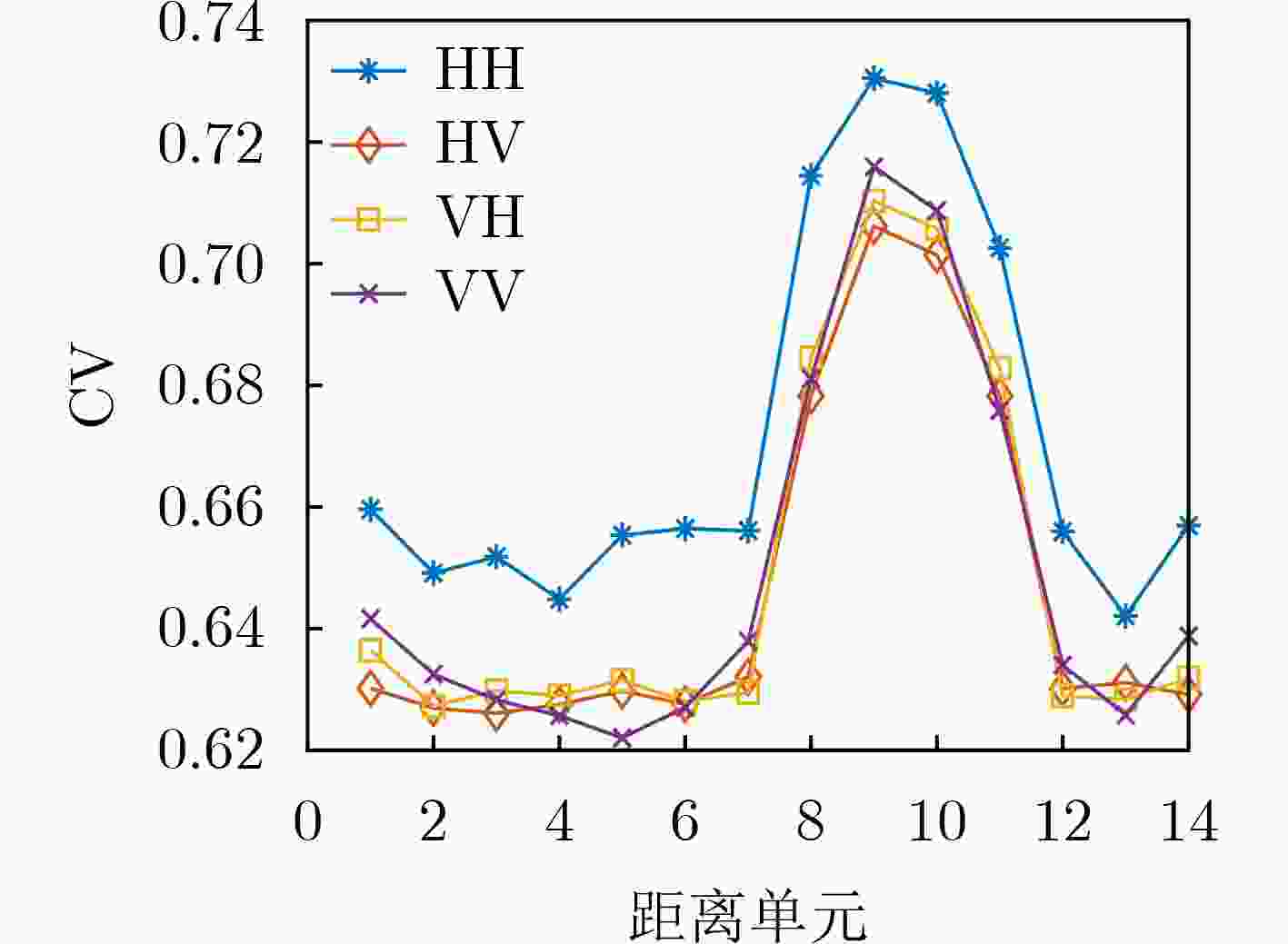
 下载:
下载:
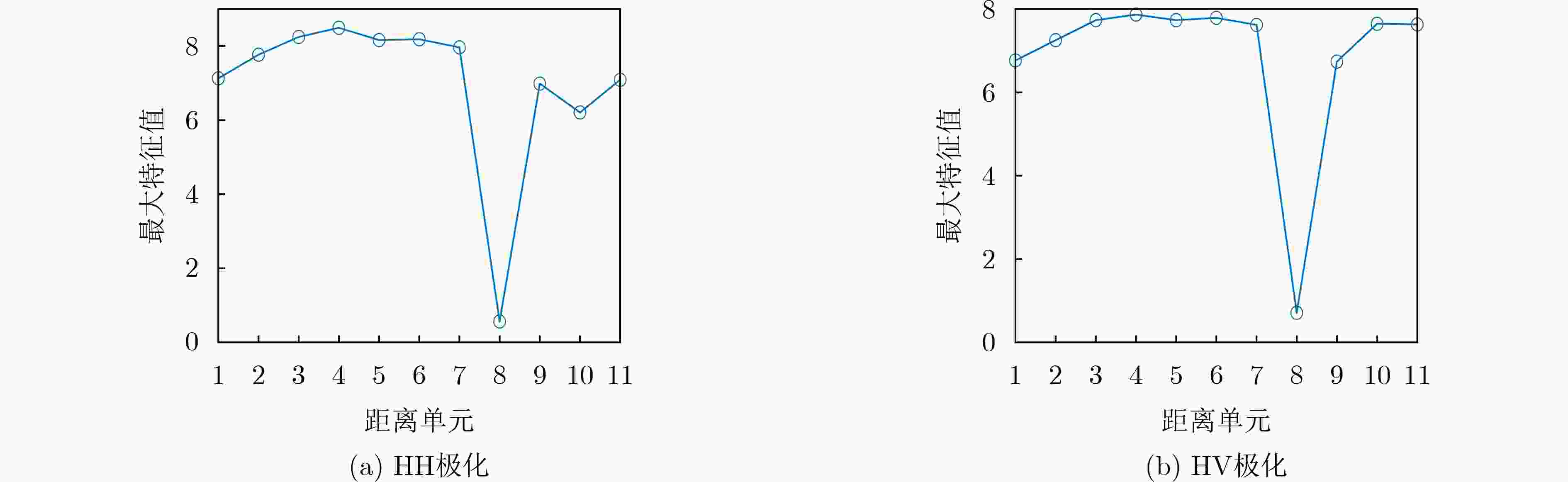
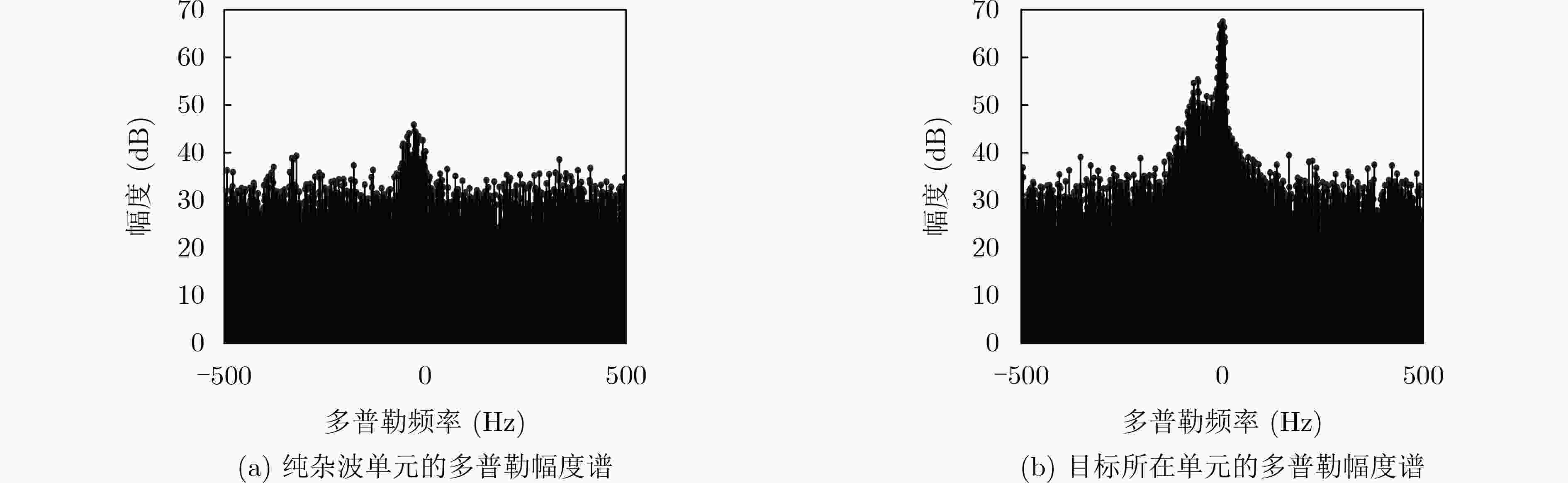


 下载:
下载:
