A Survey on FPGA Electronic Design Automation Technology Based on Machine Learning
-
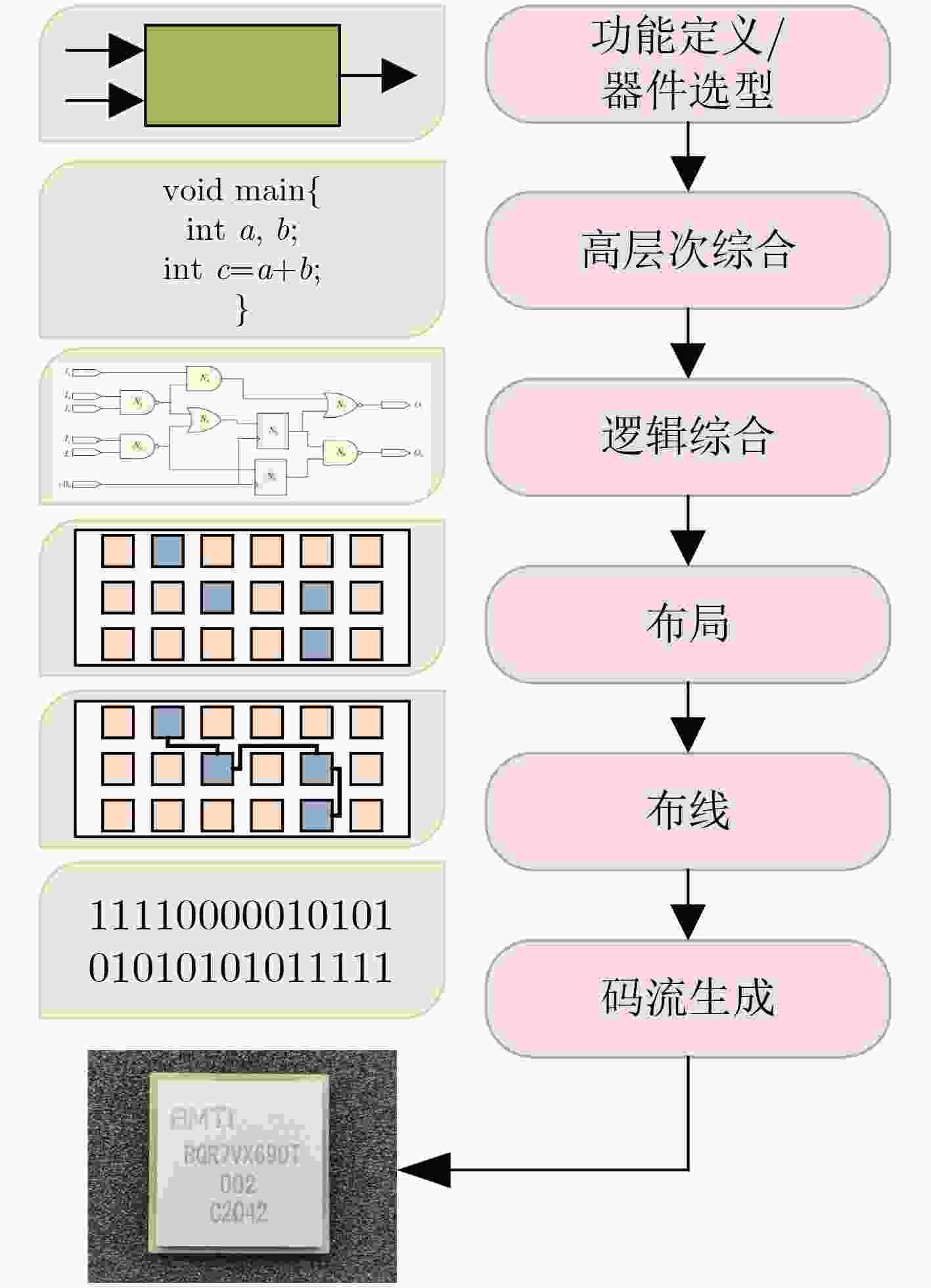
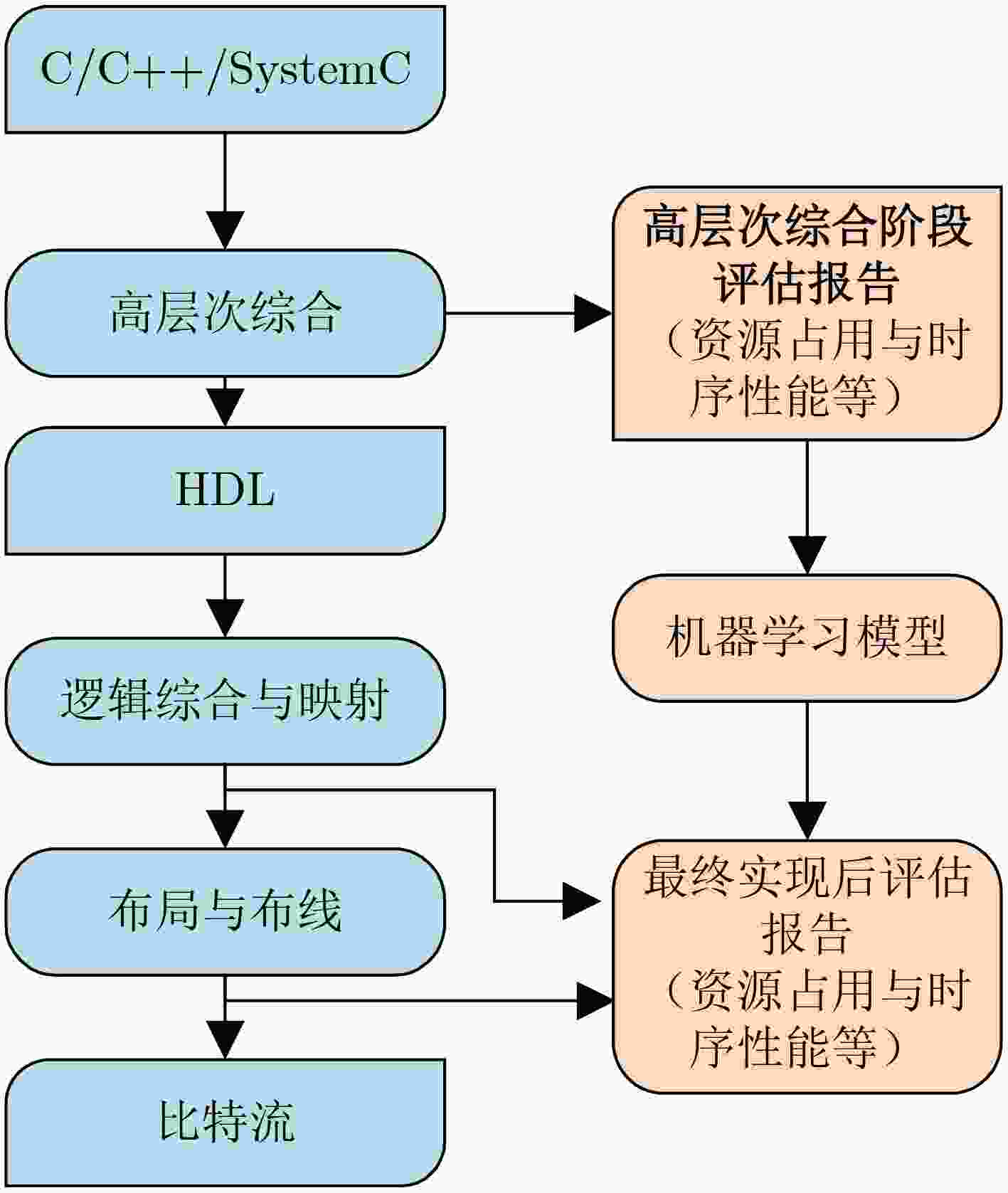
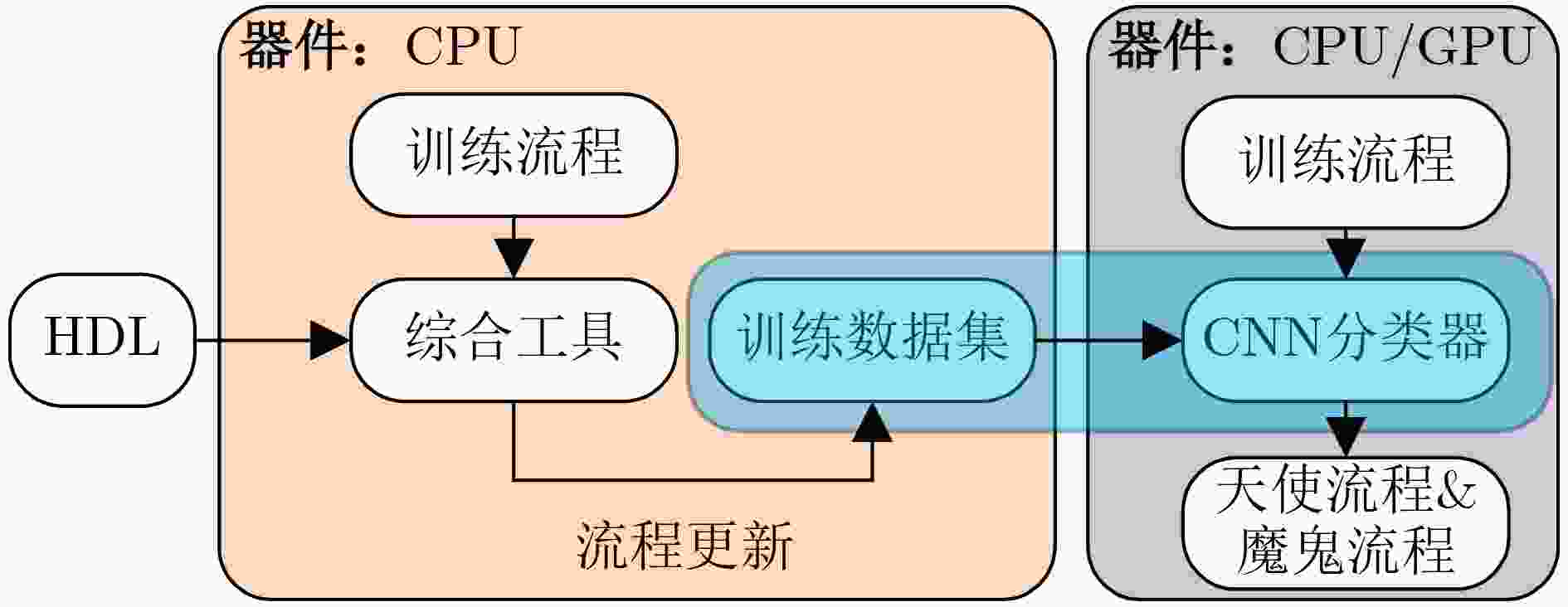
摘要: 随着后摩尔时代的来临,现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)凭借其灵活的重复可编程特性、开发成本低的特点,现已被广泛应用于物联网 (IoTs)、5G通信、航空航天以及武器装备等各个领域。作为FPGA设计开发过程中所必备的手段,FPGA电子设计自动化(EDA)技术的研究在各界得到了广泛的关注。尤其是在机器学习方法的推动下,FPGA EDA工具的运行效率和结果质量(QoR)得到了很大的提升。该文首先对FPGA EDA技术与机器学习技术的概念内涵进行了简要概述,随后综述了机器学习技术在FPGA EDA高层次综合(HLS)、逻辑综合、布局与布线等各个不同阶段应用的研究现状。最后,对基于机器学习的FPGA EDA技术的发展进行了展望。以期为本领域及相关领域的专家和学者提供参考,为后摩尔时代我国集成电路产业的发展提供技术支持。Abstract: With the advent of the post-Moore era, Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) is widely used in various fields such as Internet of Things (IoTs), 5G communication, aerospace, weapons and equipment because of its flexible repetitive programmable characteristics and low development cost. As a necessary means in the process of FPGA design and development, FPGA Electronic Design Automation (EDA) has received extensive attention from industry and academia. Especially driven by machine learning, the running efficiency and Quality of Result (QoR) have been significantly improved. A brief overview of the conceptual connotation of FPGA EDA and machine learning is presented at first, Then, the application of machine learning to different FPGA EDA stages such as High Level Synthesis (HLS), logic synthesis, placement and routing is summarized. Finally, the development of FPGA EDA technology based on machine learning is prospected. It is expected to provide reference for experts and scholars in this field and related fields, and provide technical support for the development of China’s integrated circuit industry in the post-Moore era.
-
表 1 机器学习在FPGA EDA高层次综合技术中的应用
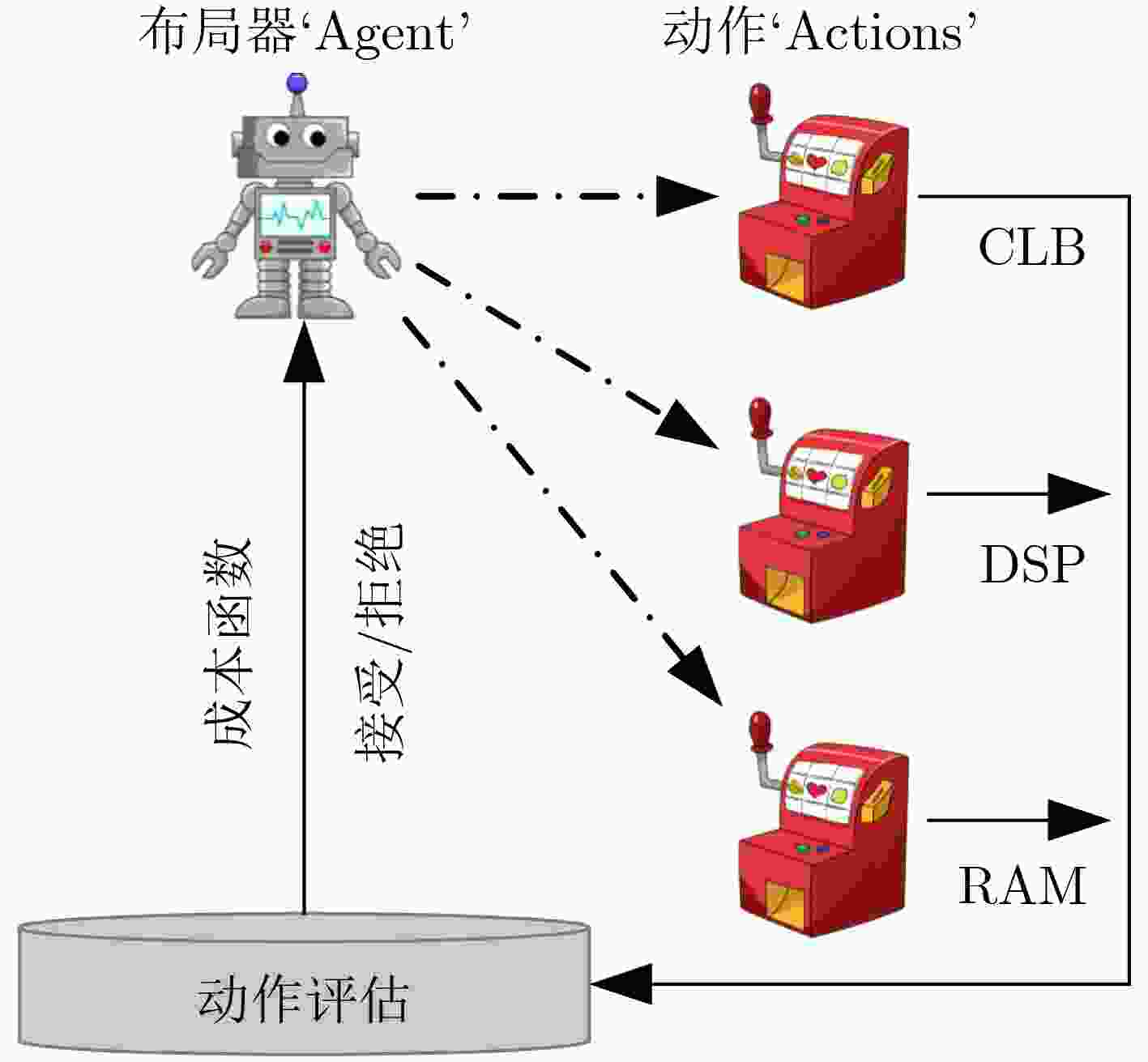
表 2 机器学习在FPGA EDA布局技术中的应用
-
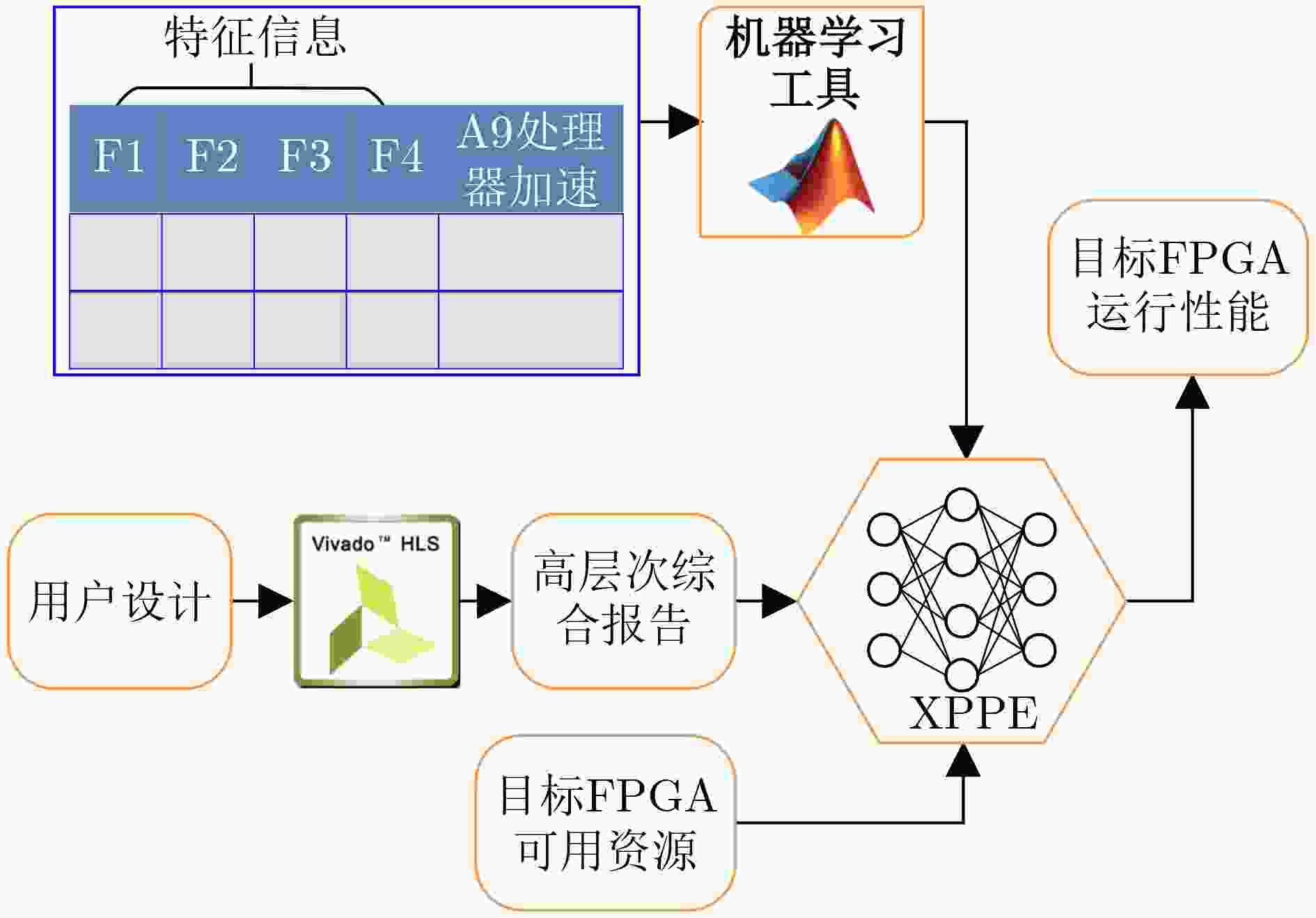
[1] MEINDL J D. Beyond Moore's Law: The interconnect era[J]. Computing in Science & Engineering, 2003, 5(1): 20–24. doi: 10.1109/MCISE.2003.1166548 [2] YOSHIMURA C, HAYASHI M, OKUYAMA T, et al. FPGA-based annealing processor for ising model[C]. 2016 Fourth International Symposium on Computing and Networking (CANDAR), Hiroshima, Japan, 2017: 436–442. [3] MONMASSON E and CIRSTEA M N. FPGA design methodology for industrial control systems—a review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2007, 54(4): 1824–1842. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2007.898281 [4] FUJII N and KOIKE N. IoT remote group experiments in the cyber laboratory: A FPGA-based remote laboratory in the hybrid cloud[C]. 2017 International Conference on Cyberworlds (CW), Chester, UK, 2017: 162–165. [5] HUANG Hai, XIA Jingjing, and BOUMAIZA S. Parallel-processing-based digital predistortion architecture and FPGA implementation for wide-band 5G transmitters[C]. 2019 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Conference on Hardware and Systems for 5G and Beyond (IMC-5G), Atlanta, USA, 2019: 1–3. [6] MEIER J and RAMESH T. Intelligent sensor fabric computing on a chip - a technology path for intelligent network computing[C]. 2007 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, USA, 2007: 1–7. [7] CHEN Yingrui, WANG Teng, WANG Xin’an, et al. Implementation of an embedded dual-core processor for portable medical electronics applications[C]. The 10th International Conference on ASIC, Shenzhen, China, 2013: 1–4. [8] DONG Yang, YANG Aibing, and LI Zhuolun. Design of weapons training simulator of the audio transmission system based on FPGA platform[C]. 2011 International Conference of Information Technology, Computer Engineering and Management Sciences, Nanjing, China, 2011: 7–10. [9] HAMOLIA V and MELNYK V. A survey of machine learning methods and applications in electronic design automation[C]. The 11th International Conference on Advanced Computer Information Technologies (ACIT), Deggendorf, Germany, 2021: 757–760. [10] 涂开辉, 黄志洪, 侯峥嵘, 等. 基于配置模式匹配和层次化映射结构的高效FPGA码流生成系统研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(11): 2585–2591. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190143TU Kaihui, HUANG Zhihong, HOU Zhengrong, et al. Research on efficient FPGA bitstream generation system based on mode matching and hierarchical mapping[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2019, 41(11): 2585–2591. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190143 [11] XILINX. VIRTEX UltraScale+ VU19P FPGA product brief[EB/OL]. https://www.xilinx.com/content/dam/xilinx/publications/product-briefs/virtex-ultrascale-plus-vu19p-product-brief.pdf, 2020. [12] INTEL. Intel® Stratix® 10 GX 10M FPGA product specifications[EB/OL]. https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/products/sku/210290/intel-stratix-10-gx-10m-fpga/specifications.html, 2020. [13] HUANG Guyue, HU Jingbo, HE Yifan, et al. Machine learning for electronic design automation: A survey[J]. ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems, 2021, 26(5): 40. doi: 10.1145/3451179 [14] LU Mei and LI Fanzhang. Survey on lie group machine learning[J]. Big Data Mining and Analytics, 2020, 3(4): 235–258. doi: 10.26599/BDMA.2020.9020011 [15] BABIC D and HU A J. Integration of supercubing and learning in a SAT solver[C]. The ASP-DAC 2005. Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Shanghai, China, 2005: 438–444. [16] ELFADEL I M, BONING D S, and LI Xin. Machine Learning in VLSI Computer-Aided Design[M]. Cham: Springer, 2019. [17] DHAR S, SINGHAL L, IYER M, et al. FPGA accelerated FPGA placement[C]. The 29th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Barcelona, Spain, 2019: 404–410. [18] DU Boyang, STERPONE L, and CODINACHS D M. A new EDA flow for the mitigation of SEUs in dynamic reconfigurable FPGAs[C]. The 21th IEEE European Test Symposium (ETS), Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2016: 1–2. [19] CONG J, LIU Bin, NEUENDORFFER S, et al. High-level synthesis for FPGAs: From prototyping to deployment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2011, 30(4): 473–491. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2011.2110592 [20] NANE R, SIMA V M, PILATO C, et al. A survey and evaluation of FPGA high-level synthesis tools[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2016, 35(10): 1591–1604. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2015.2513673 [21] SARKER A L and LEE M H. Synthesis of VHDL code for FPGA design flow using Xilinx PlanAhead tool[C]. The International Conference on Education and e-Learning Innovations, Sousse, Tunisia, 2012: 1–5. [22] AL-HYARI A, ABUOWAIMER Z, MAAROUF D, et al. An effective FPGA placement flow selection framework using machine learning[C]. The 30th International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), Sousse, Tunisia, 2018: 164–167. [23] LUO Ruiqi, CHEN Xiaolei, and HA Yajun. Optimization of FPGA routing networks with time-multiplexed interconnects[C]. The 11th Latin American Symposium on Circuits & Systems (LASCAS), San Jose, Costa Rica, 2020: 1–4. [24] 姜园, 张朝阳, 仇佩亮, 等. 用于数据挖掘的聚类算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2005, 27(4): 655–662.JIANG Yuan, ZHANG Zhaoyang, QIU Peiliang, et al. Clustering algorithms used in data mining[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2005, 27(4): 655–662. [25] SUN Lili and WANG Xizhao. A survey on active learning strategy[C]. 2010 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Qingdao, China, 2010: 161–166. [26] CHEN Jingsong, KUANG Jian, ZHAO Guowei, et al. PROS: A plug-in for routability optimization applied in the state-of-the-art commercial EDA tool using deep learning[C]. 2020 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), San Diego, USA, 2020: 1–8. [27] LEE C K. Deep learning creativity in EDA[C]. 2020 International Symposium on VLSI Design, Automation and Test (VLSI-DAT), Hsinchu, China, 2020. [28] DAI S, ZHOU Yuan, ZHANG Hang, et al. Fast and accurate estimation of quality of results in high-level synthesis with machine learning[C]. The 26th Annual International Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines (FCCM), Boulder, USA, 2018: 129–132. [29] MAKRANI H M, FARAHMAND F, SAYADI H, et al. Pyramid: Machine learning framework to estimate the optimal timing and resource usage of a high-Level synthesis design[C]. The 29th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Barcelona, Spain, 2019: 397–403. [30] FARAHMAND F, FEROZPURI A, DIEHL W, et al. Minerva: Automated hardware optimization tool[C]. 2017 International Conference on ReConFigurable Computing and FPGAs (ReConFig), Cancun, Mexico, 2017: 1–8. [31] USTUN E, DENG Chenhui, PAL D, et al. Accurate operation delay prediction for FPGA HLS using graph neural networks[C]. The 39th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Diego, USA, 2020: 87. [32] MAKRANI H M, SAYADI H, MOHSENIN T, et al. XPPE: Cross-platform performance estimation of hardware accelerators using machine learning[C]. The 24th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Tokyo, Japan, 2019: 727–732. [33] O’NEAL K, LIU M, TANG H, et al. HLSPredict: Cross platform performance prediction for FPGA high-level synthesis[C]. 2018 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Diego, USA, 2018: 1–8. [34] LIU Dong and SCHAFER B C. Efficient and reliable High-Level Synthesis design space explorer for FPGAs[C]. The 26th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Lausanne, Switzerland, 2016: 1–8. [35] LIU H Y and CARLONI L P. On learning-based methods for design-space exploration with high-level synthesis[C]. The 50th Annual Design Automation Conference, Austin, USA, 2013: 50. [36] MENG Pingfan, ALTHOFF A, GAUTIER Q, et al. Adaptive threshold non-pareto elimination: Re-thinking machine learning for system level design space exploration on FPGAs[C]. 2016 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 2016: 918–923. [37] NETO W L, AUSTIN M, TEMPLE S, et al. LSOracle: A logic synthesis framework driven by artificial intelligence: Invited paper[C]. 2019 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Westminster, USA, 2019: 1–6. [38] BRAYTON R and MISHCHENKO A. ABC: An academic industrial-strength verification tool[C]. The 22nd International Conference on Computer Aided Verification, Edinburgh, UK, 2010: 24–40. [39] YU Cunxi, XIAO Houping, and DE MICHELI G. Developing synthesis flows without human knowledge[C]. The 55th ACM/ESDA/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, USA, 2018: 1–6. [40] WU N, LEE J, XIE Yuan, et al. Hybrid graph models for logic optimization via spatio-temporal information[J]. arXiv: 2201.08455, 2022. [41] PERUVEMBA Y V, RAI S, AHUJA K, et al. RL-guided runtime-constrained heuristic exploration for logic synthesis[C]. 2021 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer Aided Design (ICCAD), Munich, Germany, 2021: 1–9. [42] HAASWIJK W, COLLINS E, SEGUIN B, et al. Deep learning for logic optimization algorithms[C]. 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 2018: 1–4. [43] HOSNY A, HASHEMI S, SHALAN M, et al. DRiLLS: Deep reinforcement learning for logic synthesis[C]. The 25th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Beijing, China, 2020: 581–586. [44] YANG Chenghao, XIA Yinshui, CHU Zhufei, et al. Logic synthesis optimization sequence tuning using RL-based LSTM and graph isomorphism network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II:Express Briefs, 2022, 69(8): 3600–3604. doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2022.3168344 [45] YU Cunxi. FlowTune: Practical multi-armed bandits in Boolean optimization[C]. The 39th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Diego, USA, 2020: 130. [46] GROSNIT A, MALHERBE C, TUTUNOV R, et al. BOiLS: Bayesian optimisation for logic synthesis[C]. 2022 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Antwerp, Belgium, 2022: 1193–1196. [47] BETZ V and ROSE J. VPR: A new packing, placement and routing tool for FPGA research[C]. The 7th International Workshop on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, London, UK, 1997: 213–222. [48] CHEN Gang and CONG J. Simultaneous placement with clustering and duplication[J]. ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems, 2006, 11(3): 740–772. doi: 10.1145/1142980.1142989 [49] MURRAY K E and BETZ V. Adaptive FPGA placement optimization via reinforcement learning[C]. 2019 ACM/IEEE 1st Workshop on Machine Learning for CAD (MLCAD), Canmore, Canada, 2019: 1–6. [50] ELGAMMA M A, MURRAY K E, and BETZ V. Learn to place: FPGA placement using reinforcement learning and directed moves[C]. 2020 International Conference on Field-Programmable Technology (ICFPT), Maui, USA, 2020: 85–93. [51] ELGAMMA M A, MURRAY K E, and BETZ V. RLPlace: Using reinforcement learning and smart perturbations to optimize FPGA placement[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2022, 41(8): 2532–2545. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2021.3109863 [52] XU Yonghong and KHALID M A S. QPF: Efficient quadratic placement for FPGAs[C]. The International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications, Tampere, Finland, 2005: 555–558. [53] GOPALAKRISHNAN P, LI Xin, and PILEGGI L. Architecture-aware FPGA placement using metric embedding[C]. The 43rd annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2006: 460–465. [54] GORT M and ANDERSON J H. Analytical placement for heterogeneous FPGAs[C]. 22nd International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Oslo, Norway, 2012: 143–150. [55] GESSLER F, BRISK P, and STOJILOVIČ M. A shared-memory parallel implementation of the RePlAce global cell placer[C]. The 33rd International Conference on VLSI Design and 2020 19th International Conference on Embedded Systems (VLSID), Bangalore, India, 2020: 78–83. [56] LIN T H, BANERJEE P, and CHANG Y W. An efficient and effective analytical placer for FPGAs[C]. The 50th Annual Design Automation Conference, Austin, USA, 2013: 10. [57] CHEN Yuchen, CHEN S Y, and CHANG Yaowen. Efficient and effective packing and analytical placement for large-scale heterogeneous FPGAs[C]. 2014 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), San Jose, USA, 2014: 647–654. [58] MENG Yibai, LI Wuxi, LIN Yibo, et al. elfPlace: Electrostatics-based placement for large-scale heterogeneous FPGAs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2022, 41(1): 155–168. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2021.3053191 [59] LU Jingwei, CHEN Pengwen, CHANG C C, et al. ePlace: Electrostatics based placement using Nesterov's method[C]. The 51st Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2014: 1–6. [60] LI Wuxi, DHAR S, and PAN D Z. UTPlaceF: A routability-driven FPGA placer with physical and congestion aware packing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(4): 869–882. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2729349 [61] CHEN Gengjie, PUI C W, CHOW W K, et al. RippleFPGA: Routability-driven simultaneous packing and placement for modern FPGAs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2018, 37(10): 2022–2035. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2017.2778058 [62] ABUOWAIMER Z, MAAROUF D, MARTIN T, et al. GPlace3.0: Routability-driven analytic placer for UltraScale FPGA architectures[J]. ACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic Systems, 2018, 23(5): 66. doi: 10.1145/3233244 [63] RAJARATHNAM R S, ALAWIEH M B, JIANG Zixuan, et al. DREAMPlaceFPGA: An open-source analytical placer for large scale heterogeneous FPGAs using deep-learning toolkit[C]. The 27th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Taipei, China, 2022: 300–306. [64] PUI C W, CHEN Gengjie, MA Yuzhe, et al. Clock-aware ultrascale FPGA placement with machine learning routability prediction: (Invited paper)[C]. 2017 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD), Irvine, USA, 2017: 929–936. [65] MAAROUF D, ALHYARI A, ABUOWAIMER Z, et al. Machine-learning based congestion estimation for modern FPGAs[C]. The 28th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), Dublin, Ireland, 2018: 4270–4277. [66] YU Cunxi and ZHANG Zhiru. Painting on placement: Forecasting routing congestion using conditional generative adversarial nets[C]. The 56th Annual Design Automation Conference 2019, Las Vegas, USA, 2019: 219. [67] ALAWIEH M B, LI Wuxi, LIN Yibo, et al. High-definition routing congestion prediction for large-scale FPGAs[C]. The 25th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC), Beijing, China, 2020: 26–31. [68] XILINX. ML-based routing congestion and delay estimation in Vivado ML edition[EB/OL]. https://semiengineering.com/ml-based-routing-congestion-and-delay-estimation-in-vivado-ml-edition, 2021. [69] 田春生, 陈雷, 王源, 等. 面向FPGA的布局与布线技术研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2022, 50(5): 1243–1254. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210637TIAN Chunsheng, CHEN Lei, WANG Yuan, et al. Review on technology of placement and routing for the FPGA[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2022, 50(5): 1243–1254. doi: 10.12263/DZXB.20210637 [70] MCMURCHIE L and EBELING C. PathFinder: A negotiation-based performance-driven router for FPGAs[C]. The Third International ACM Symposium on Field-Programmable Gate Arrays, Napa Valley, USA, 1995: 111–117. [71] FAROOQ U, HASAN N U, BAIG I, et al. Efficient FPGA routing using reinforcement learning[C]. The 12th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS), Valencia, Spain, 2021: 106–111. [72] 赵佳琦, 周勇, 何欣, 等. 基于深度学习的点云分割研究进展分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022,, 44(12): 4426–4440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210972ZHAO Jiaqi, ZHOU Yong, HE Xin, et al. Research progress analysis of point cloud segmentation based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022,, 44(12): 4426–4440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210972 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
