Minimum Spanning Tree Segmentation and Extract with Image Edge Weight Optimization
-
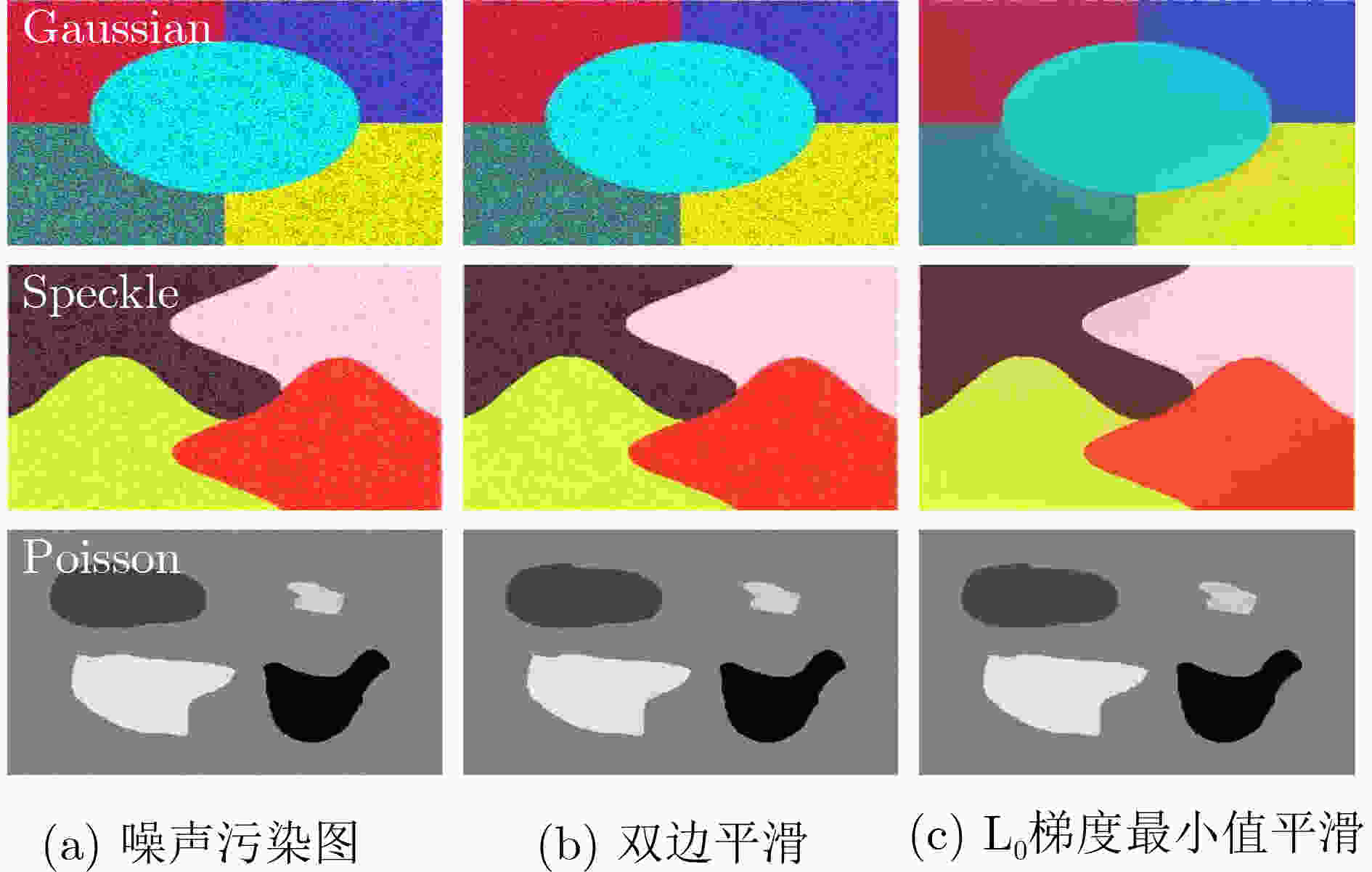
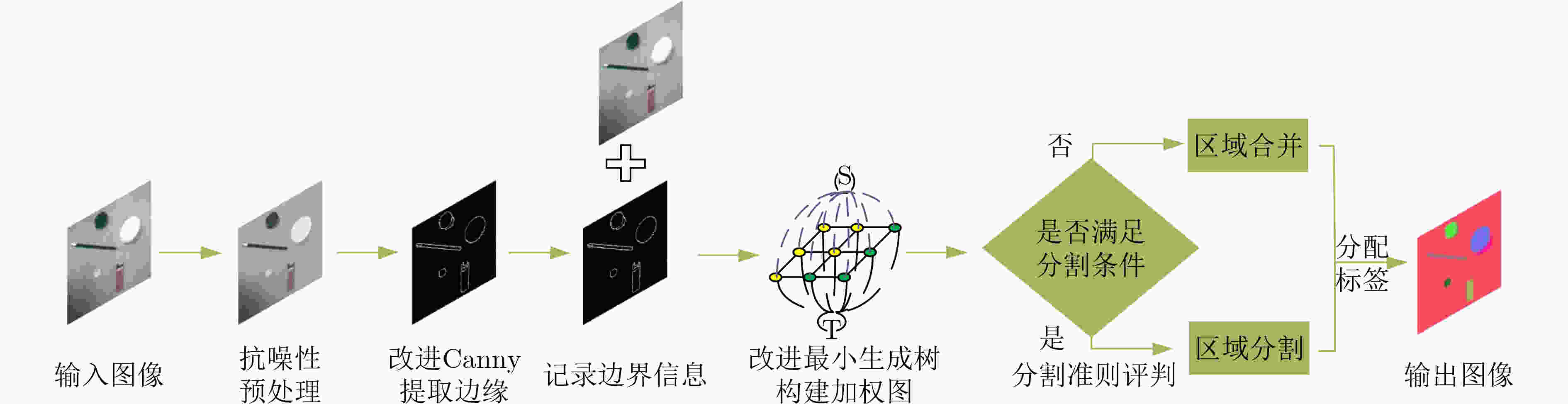
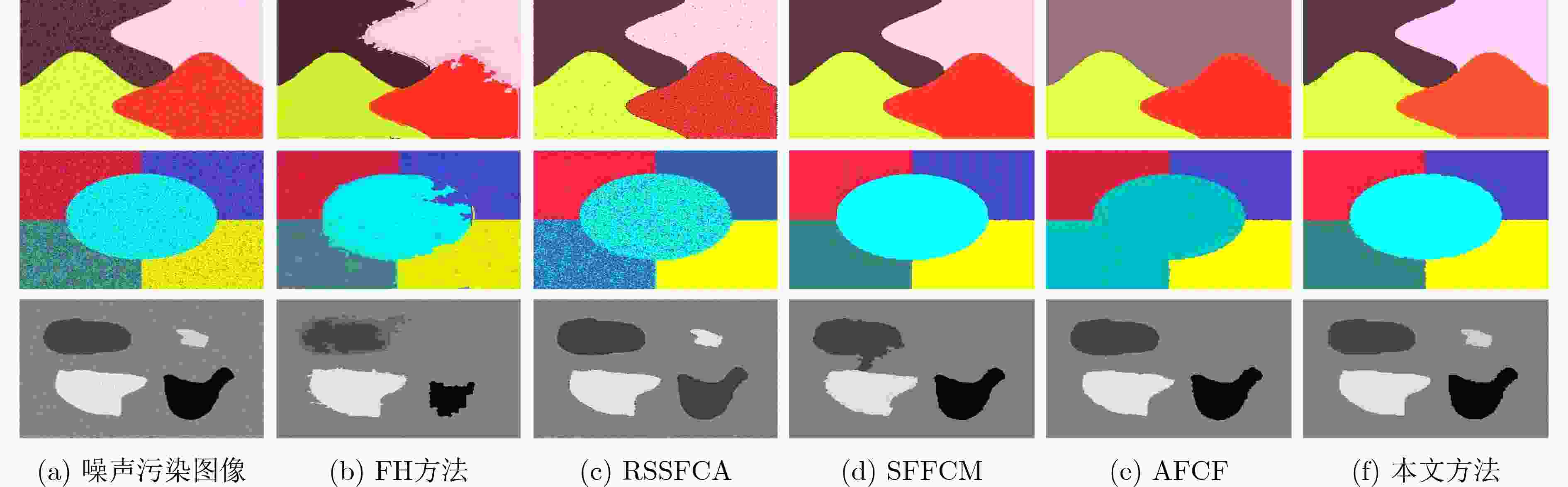
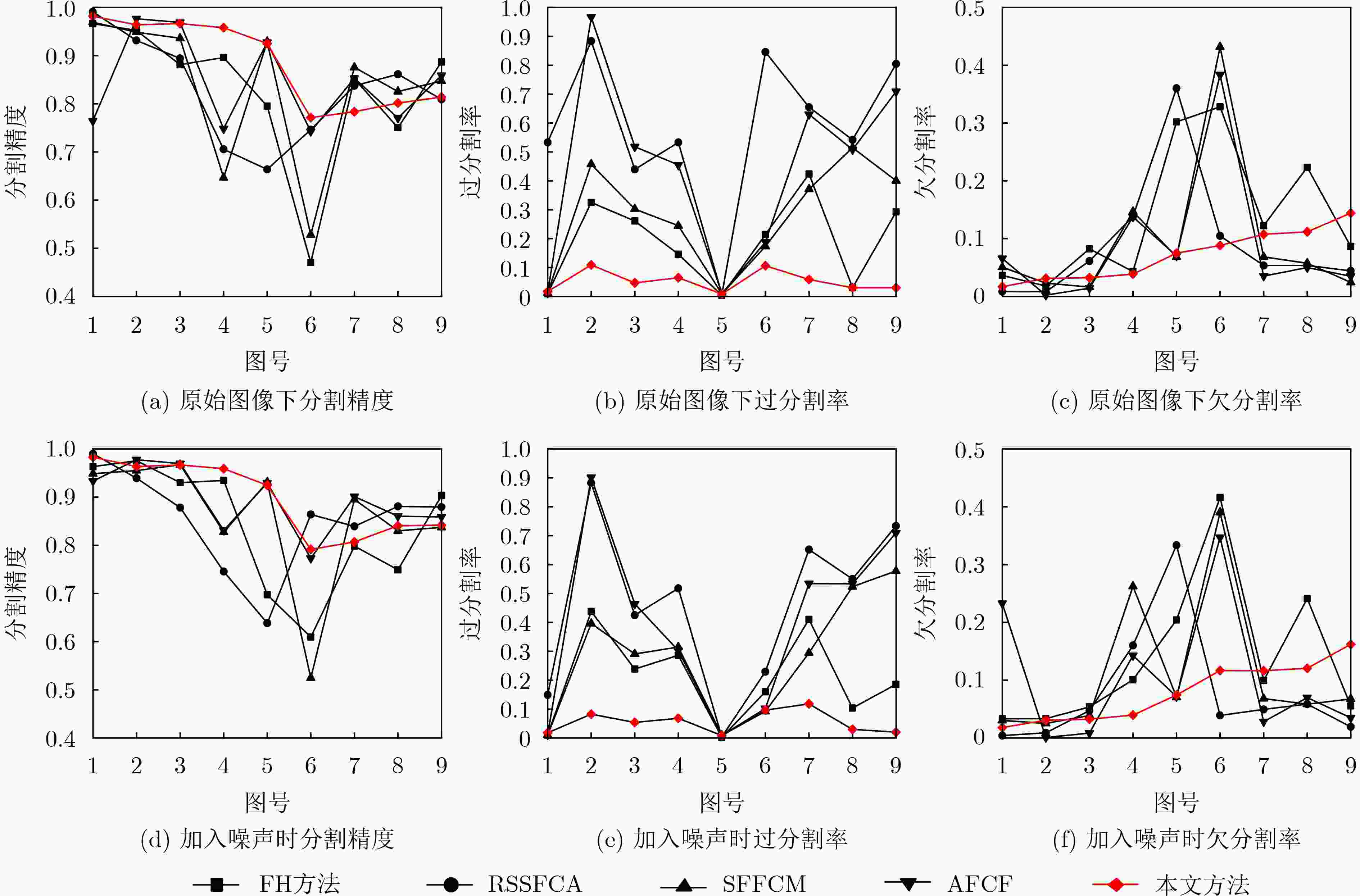
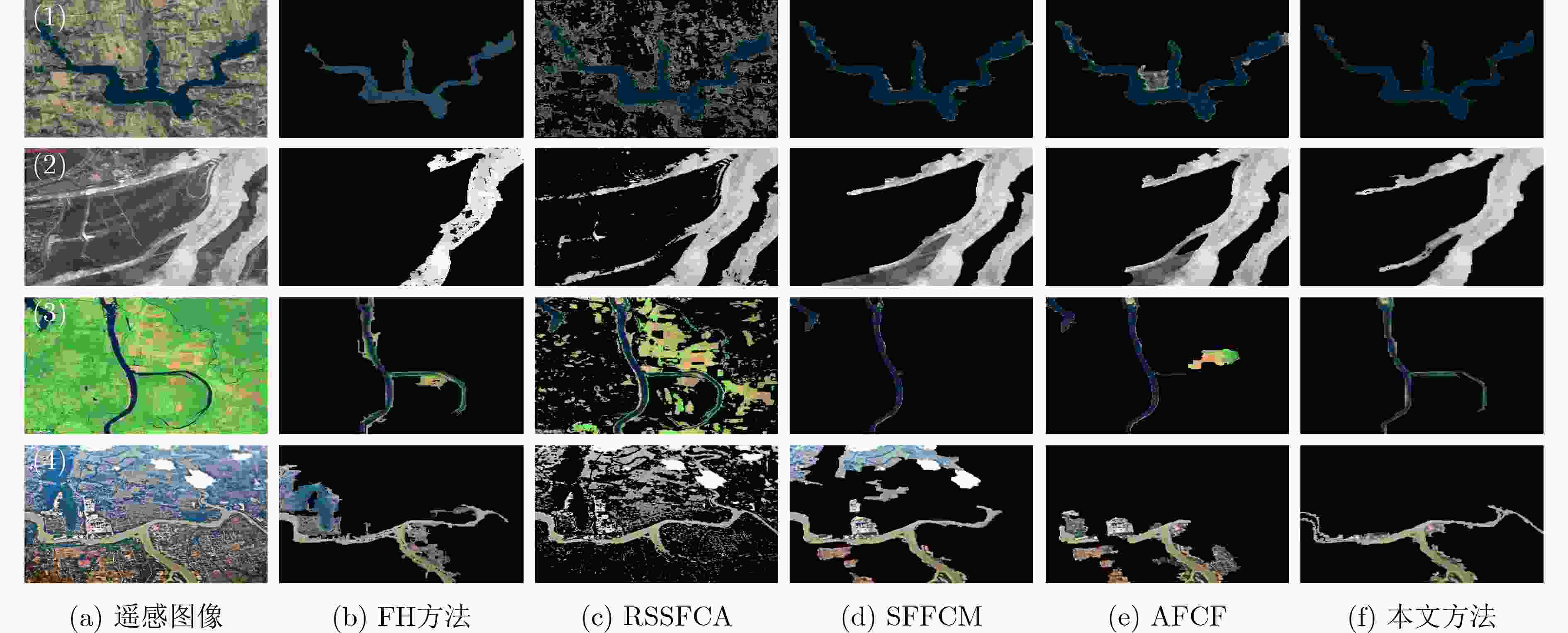
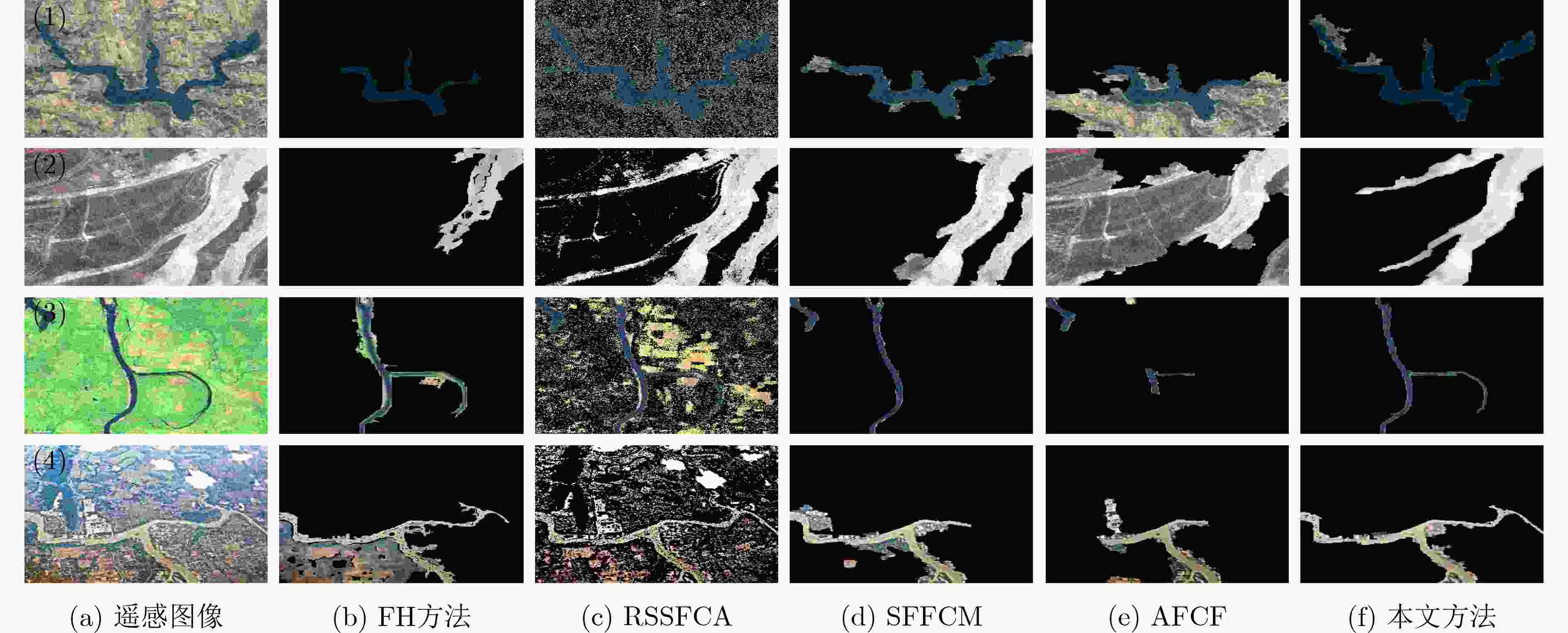
摘要: 针对无监督图像分割方法对噪声敏感而导致图像建模困难、分割结果准确率低等问题,该文提出一种图像边缘权重优化的最小生成树分割提取方法。首先,利用L0梯度最小值平滑处理噪声再结合Otsu优化Canny边缘检测,得到更加准确的边缘信息;其次,重新设计权重函数,采用更加合理的色差空间构建加权图,通过改进分割准则优化物体合并与区分过程;最后,选择不同类型图片进行抗噪性、分割效果实验。实验结果表明:相对于其他算法,该文算法的抗噪性能优秀,分割精度平均提升5.15%,过分割率平均下降32.07%,欠分割率平均下降2.69%。将其运用在实际航空遥感图像的河道湖泊提取中,所得结果相比其他主流算法结构更加完整,无关信息更少,抗噪性能更好。Abstract: The unsupervised image segmentation method is sensitive to noise, leading to difficult building image model and poor accuracy of segmentation results. In this paper, a minimum spanning tree segmentation and extract with image edge weight optimization is proposed. Firstly, L0 gradient minimum is used to smooth the noise. The Canny edge detection with Otsu is optimized to obtain more accurate edge information. Secondly, the weight function is redesigned and the weighted graph by using more reasonable color difference space is constructed. The segmentation criterion is improved to optimize the process of object merging and distinguishing. Finally, different types of images are chosen to conduct experiments with noise resistance and segmentation effect. Experimental comparing results show that the proposed algorithm has excellent anti-noise performance, and the segmentation accuracy is improved by 5.15% on average, the over-segmentation rate is decreased by 32.07% on average, and the under-segmentation rate is decreased by 2.69% on average. Moreover, this method is applied to the river and lake extraction of aviation and remote sensing images, and the result has more complete structure, less irrelevant information and better anti-noise performance.
-
Key words:
- Image segmentation /
- Image edge /
- Minimum spanning tree /
- Image extraction /
- Airborne remote sensing
-
表 1 合成图像分割结果峰值信噪比/平均结构相似性 (dB / %)
噪声比例 FH方法 RSSFCA SFFCM AFCF 本文方法 高斯5% 18.21 / 81.96 26.48 / 94.59 26.04 / 95.77 13.78 / 84.17 27.63 / 96.61 高斯10% 20.71 / 87.06 21.06 / 68.20 21.68 / 94.33 13.67 / 83.82 23.72 / 94.97 高斯15% 15.67 / 79.36 17.90 / 41.14 19.07 / 92.48 13.41 / 83.27 21.79 / 94.11 乘性5% 23.54 / 85.72 24.57 / 74.67 32.55 / 97.84 32.49 / 97.56 33.23 / 97.89 乘性10% 22.84 / 84.76 20.44 / 51.69 32.57 / 97.24 20.20 / 94.70 32.76 / 97.43 乘性15% 19.33 / 80.71 19.87 / 48.79 32.44 / 96.91 22.62 / 92.84 28.18 / 97.23 泊松 21.31 / 82.03 25.08 / 82.21 27.92 / 92.83 28.49 / 93.76 34.84 / 96.94 -
[1] GANGLOFF H, COURBOT J B, MONFRINI E, et al. Unsupervised image segmentation with spatial triplet Markov trees[C]. ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Toronto, Canada, 2021: 1790–1794. [2] HUANG Quanwei, ZHOU Yuezhi, TAO Linmi, et al. A Chan-Vese model based on the Markov chain for unsupervised medical image segmentation[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2021, 26(6): 833–844. doi: 10.26599/TST.2020.9010042 [3] GANGLOFF H, MORALES K, and PETETIN Y. A general parametrization framework for pairwise Markov models: An application to unsupervised image segmentation[C]. 2021 IEEE 31st International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing, Gold Coast, Australia, 2021: 1–6. [4] ZHANG Ling, LIU Jianchao, SHANG Fangxing, et al. Robust segmentation method for noisy images based on an unsupervised denosing filter[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2021, 26(5): 736–748. doi: 10.26599/TST.2021.9010021 [5] 赵凤, 孙文静, 刘汉强, 等. 基于近邻搜索花授粉优化的直觉模糊聚类图像分割[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 1005–1012. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190428ZHAO Feng, SUN Wenjing, LIU Hanqiang, et al. Intuitionistic fuzzy clustering image segmentation based on flower pollination optimization with nearest neighbor searching[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 1005–1012. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190428 [6] 徐金东, 赵甜雨, 冯国政, 等. 基于上下文模糊C均值聚类的图像分割算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(7): 2079–2086. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200263XU Jindong, ZHAO Tianyu, FENG Guozheng, et al. Image segmentation algorithm based on context fuzzy C-means clustering[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(7): 2079–2086. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200263 [7] LI Zhimei, ZHANG Wanzhen, and YANG Hua. Color image segmentation based on wavelet transform and fuzzy kernel clustering[C]. 2020 International Conference on Virtual Reality and Intelligent Systems, Zhangjiajie, China, 2020: 411–414. [8] JIN Can, YE Zhiwei, YAN Lingyu, et al. Image segmentation using fuzzy C-means optimized by ant lion optimization[C]. 2019 10th IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications, Metz, France, 2019: 388–393. [9] GUO Li, CHEN Long, LU Xiliang, et al. Membership affinity lasso for fuzzy clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(2): 294–307. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2905114 [10] LEI Tao, LIU Peng, JIA Xiaohong, et al. Automatic fuzzy clustering framework for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 28(9): 2078–2092. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2019.2930030 [11] YANG Tingting, ZHOU Suyin, XU Aijun, et al. A method for tree image segmentation combined adaptive mean shifting with image abstraction[J]. Journal of Information Processing Systems, 2020, 16(6): 1424–1436. doi: 10.3745/JIPS.02.0151 [12] PARK H. α-MeanShift++: Improving MeanShift++ for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 131430–131439. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3114223 [13] XIA Kaijian, GU Xiaoqing, and ZHANG Yudong. Oriented grouping-constrained spectral clustering for medical imaging segmentation[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2020, 26(1): 27–36. doi: 10.1007/S00530-019-00626-8 [14] NAIK S S. A hybrid approach towards color image segmentation[C]. 2021 International Conference on Intelligent Technologies, Hubli, India, 2021: 1–5. [15] 刘仲民, 李战明, 李博皓, 等. 基于稀疏矩阵的谱聚类图像分割算法[J]. 吉林大学学报:工学版, 2017, 47(4): 1308–1313. doi: 10.13229/J.CNKI.JDXBGXB201704042LIU Zhongmin, LI Zhanming, LI Bohao, et al. Spectral clustering image segmentation based on sparse matrix[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Engineering and Technology Edition, 2017, 47(4): 1308–1313. doi: 10.13229/J.CNKI.JDXBGXB201704042 [16] HE Wenjing, SONG Hongjun, and YAO Yuanyuan. An improved region merging approach for SAR complex water area segmentation[C]. 2019 6th Asia-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Xiamen, China, 2019: 1–5. [17] LONG Xiaodong and SUN Jian. Image segmentation based on the minimum spanning tree with a novel weight[J]. Optik, 2020, 221: 165308. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2020.165308 [18] BOGACH I V, LUPIAK D D, IVANOV Y Y, et al. Analysis and experimental research of modifications of the image segmentation method using graph theory[C]. 2019 International Siberian Conference on Control and Communications, Tomsk, Russia, 2019: 1–4. [19] FELZENSZWALB P F and HUTTENLOCHER D P. Efficient Graph-based image segmentation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 59(2): 167–181. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000022288.19776.77 [20] XU Li, LU Cewu, XU Yi, et al. Image smoothing via L0 gradient minimization[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2011, 30(6): 1–12. doi: 10.1145/2070781.2024208 [21] 杨振亚, 王勇, 杨振东, 等. RGB颜色空间的矢量-角度距离色差公式[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2010, 46(6): 154–156. doi: 10.3778/J.ISSN.1002-8331.2010.06.044YANG Zhenya, WANG Yong, YANG Zhendong, et al. Vector-Angular distance color difference formula in RGB color space[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2010, 46(6): 154–156. doi: 10.3778/J.ISSN.1002-8331.2010.06.044 [22] JIA Xiaohong, LEI Tao, DU Xiaogang, et al. Robust self-sparse fuzzy clustering for image segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 146182–146195. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3015270 [23] LEI Tao, JIA Xiaohong, ZHANG Yanning, et al. Superpixel-based fast fuzzy C-means clustering for color image segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 27(9): 1753–1766. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2018.2889018 -





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
