Digital Twin Empowered Task Offloading for RIS-Assisted Edge Computing Networks
-
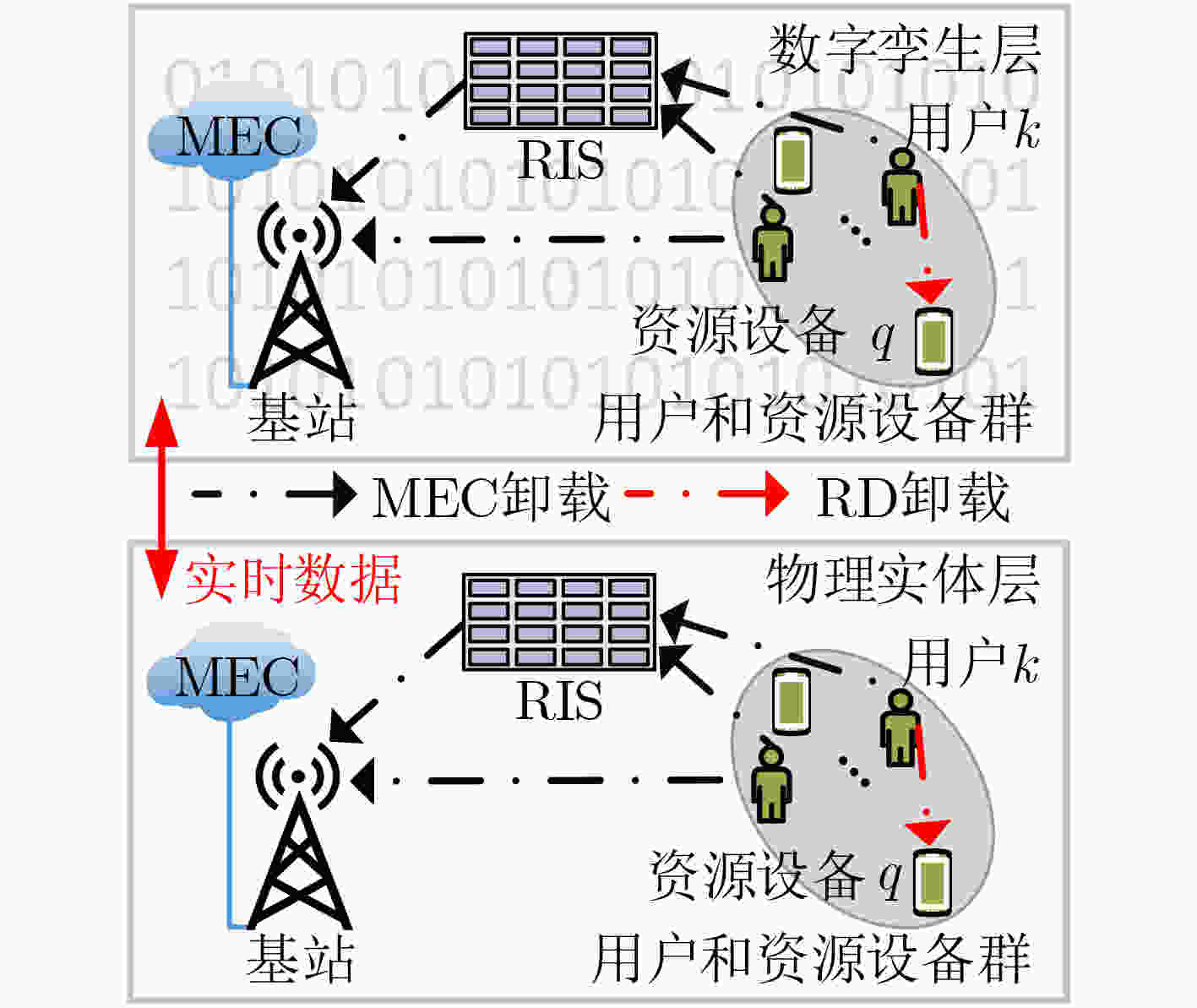
摘要: 针对新兴的计算密集型应用对移动用户高计算性能需求问题,该文提出一种数字孪生(DT)结合智能反射面(RIS)辅助的移动边缘计算(MEC)任务卸载方案。首先,在满足用户传输功率、用户和资源设备能耗、计算资源限制条件下,通过联合优化用户卸载决策、用户传输功率、RIS 相移、波束成形矢量、计算资源分配,建立一个系统能耗最小化问题;其次,将该非凸组合优化问题分解为3个子问题,使用深度双Q网络(DDQN)方法确定用户卸载策略;然后对每个训练时间步进行一次求解,基于交替迭代方法得到问题的优化解。仿真结果表明,基于DDQN的算法训练速度较快,有效降低了系统总能耗。Abstract: In order to meet the high computing demands caused by emerging compute-intensive applications in Mobile Edge Computing (MEC), this paper proposes a Digital Twin (DT)-empowered task offloading scheme where Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) is used to enhance the communication links and extend the coverage. Firstly, the joint optimization of user offloading strategy, RIS phase-shift vector, beamforming vector, transmit power of users and computation capacity allocation are investigated with the aim of minimizing the total energy consumption of users and resource devices under the constraints of communication and computing resources. Then, the formulated non-convex combinational optimization problem is decomposed into three sub-problems, including RIS phase-shift design, binary optimization of transmit power, and computing resource allocation. In addition, the Double Deep Q Network (DDQN) approach is invoked to determine the offloading decisions and an alternating iteration optimization algorithm is designed to achieve the optimal solution. Simulation results show that the DDQN-based algorithm is able to train quickly and reduce effectively the total energy consumption of the system.
-
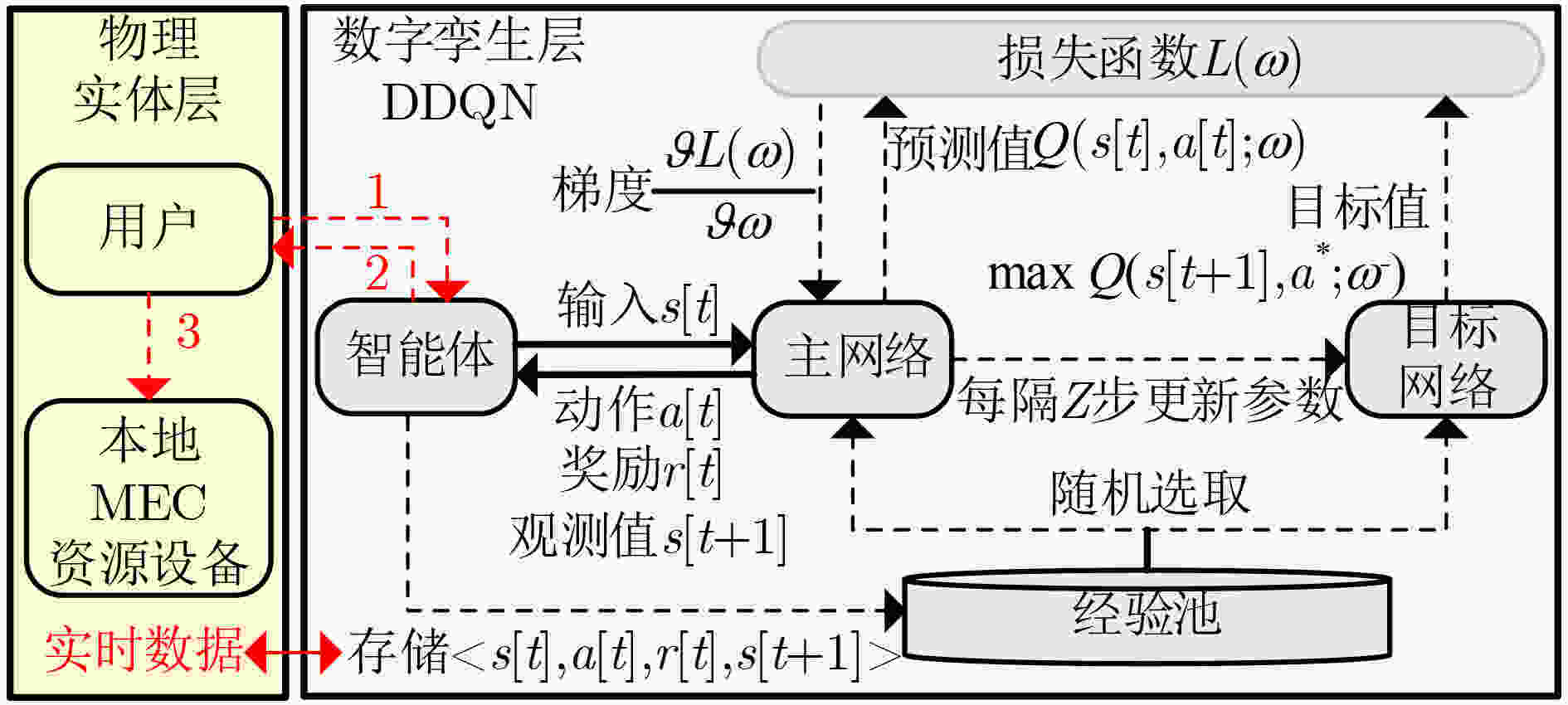
表 1 基于DDQN能耗最小化算法(算法1)
输入:最大回合数E,学习率$\beta $,折扣回报$\gamma $,用户数K,二分法精度$\varepsilon $。 步骤1 初始化主网络参数$\omega $,目标网络参数${\omega ^ - }$,经验数组,用户、基站和资源设备位置,用户任务信息$M_k^t$ 步骤2 for $t = 1:{E}$ 更新$t$时刻用户位置和任务信息; for $ {\text{step}} = {\text{1}}:K $ 根据当前状态$s\left[ t \right]$和策略${\pi _\omega }$选择动作$a\left[ t \right]$; 根据3.2,3.3节讨论和动作$a\left[ t \right]$,使用交替迭代法和二分法求解$ {\theta _{k,n}},{{\mathbf{w}}_k},{p_k},f_k^l,f_{k,q}^r,f_k^e $; 根据奖励函数计算$r\left( t \right)$,观察下一个状态$s\left[ {t + 1} \right]$,并存储$\left\langle {s\left[ t \right],a\left[ t \right],r\left[ t \right],s\left[ {t + 1} \right]} \right\rangle $到经验数组; 从经验回放数组随机取出一组经验,根据式(7)计算损失函数,并更新当前主网络参数$\omega $; 每隔$Z$步更新目标网络参数${\omega ^ - }$; 步骤3 输出任务卸载策略网络参数$\omega $。 表 2 DDQN训练参数
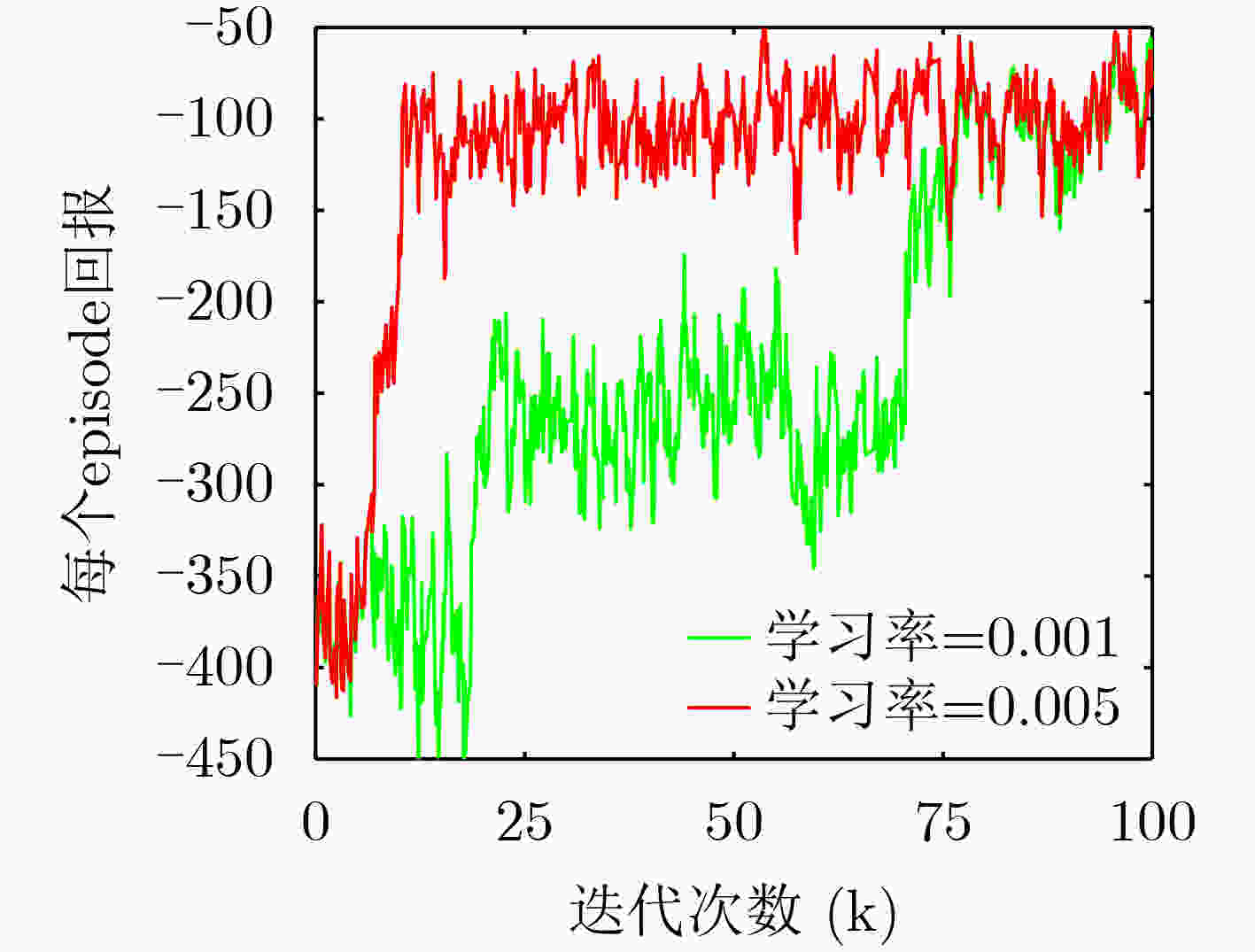
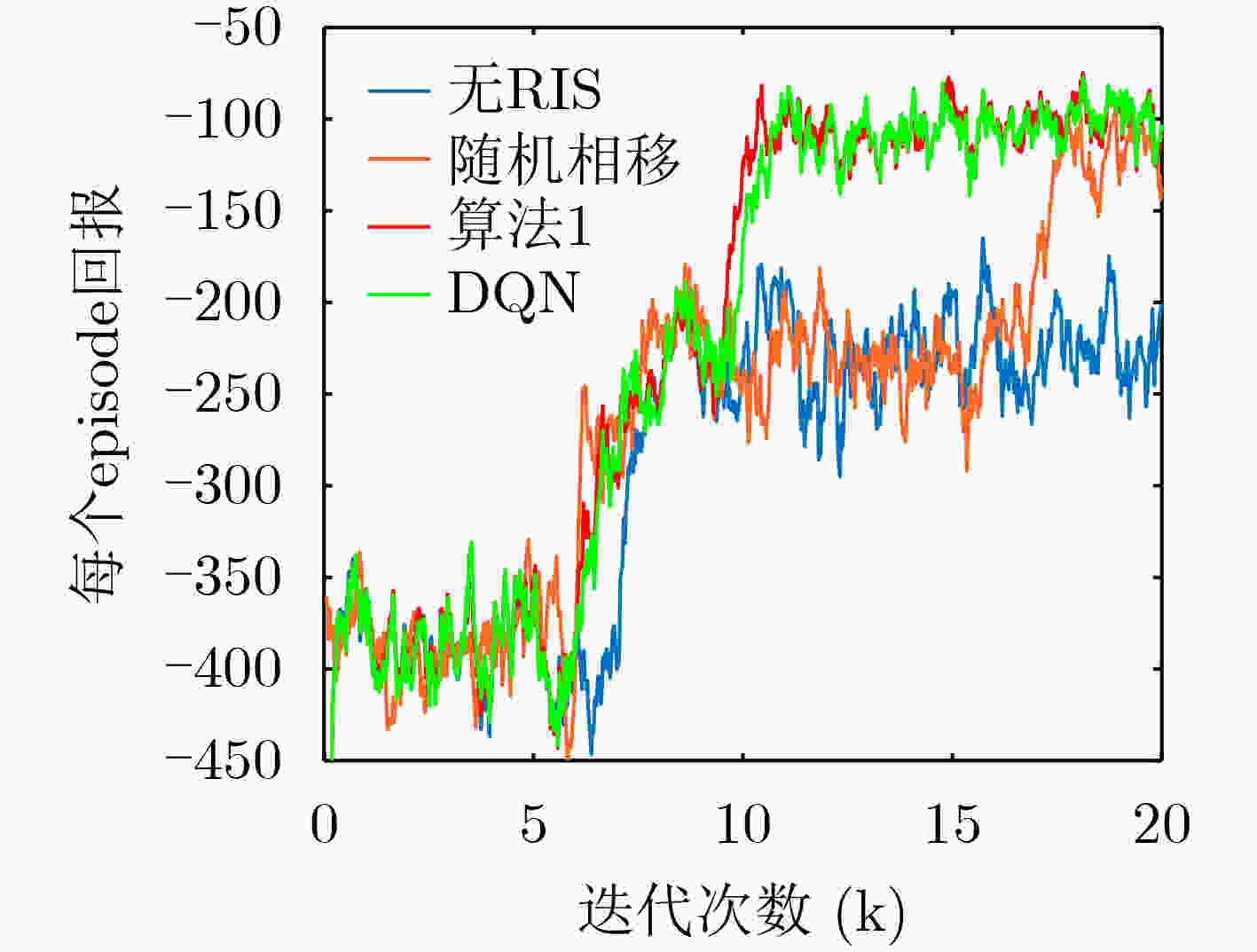
参数 值 参数 值 隐藏层数量$L$ 3 惩罚值$ C $ 100 折扣回报$\gamma $ 0.9 开销值$\vartheta $ (0,1,5) 最大回合数E 100 k 二分法精度$\varepsilon $ 10–6 学习率$\beta $ 5×10–3 经验回放数组大小 215 目标网络更新频率$Z$ 320 贪婪策略比例 0.1 -
[1] ZHANG Jiayi, LIU Heng, WU Qingqing, et al. RIS-aided next-generation high-speed train communications: Challenges, solutions, and future directions[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(6): 145–151. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2100170 [2] 徐勇军, 高正念, 王茜竹, 等. 基于智能反射面辅助的无线供电通信网络鲁棒能效最大化算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 待发表.XU Yongjun, GAO Zhengnian, WANG Qianzhu, et al. Robust energy efficiency maximization algorithm for intelligent reflecting surface-aided wireless powered-communication networks[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, To be published. [3] MAO Yuyi, YOU Changsheng, ZHANG Jun, et al. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2017, 19(4): 2322–2358. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2745201 [4] XU Yongjun, GUI Guan, GACANIN H, et al. A survey on resource allocation for 5G heterogeneous networks: Current research, future trends, and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2021, 23(2): 668–695. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3059896 [5] XU Yongjun, GU Bowen, HU R Q, et al. Joint computation offloading and radio resource allocation in MEC-based wireless-powered backscatter communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(6): 6200–6205. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3077094 [6] CHEN Yuanbin, WANG Ying, ZHANG Jiayi, et al. QoS-driven spectrum sharing for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) aided vehicular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(9): 5969–5985. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3071332 [7] SHI Enyu, ZHANG Jiayi, CHEN Shuaifei, et al. Wireless energy transfer in RIS-aided cell-free massive MIMO systems: Opportunities and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2022, 60(3): 26–32. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.2100671 [8] ZHANG Yan, ZHANG Jiayi, DI RENZO M, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with outdated channel state Information: Centralized vs. distributed deployments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2022, 70(4): 2742–2756. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2022.3146344 [9] JIN Yu, ZHANG Jiayi, HUANG Chongwen, et al. Multiple residual dense networks for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces cascaded channel estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71(2): 2134–2139. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3132305 [10] JIN Yu, ZHANG Jiayi, ZHANG Xiaodan, et al. Channel estimation for semi-passive reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with enhanced deep residual networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(10): 11083–11088. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3109937 [11] YANG Zhaohui, XU Wei, HUANG Chongwen, et al. Beamforming design for multiuser transmission through reconfigurable intelligent surface[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 589–601. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3028309 [12] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609 [13] BAI Tong, PAN Cunhua, DENG Yansha, et al. Latency minimization for intelligent reflecting surface aided mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2666–2682. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007035 [14] CHU Zheng, XIAO Pei, SHOJAFAR M, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted mobile edge computing for internet of things[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(3): 619–623. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3040607 [15] WANG Qun, ZHOU Fuhui, HU Han, et al. Energy-efficient design for IRS-assisted MEC networks with NOMA[C]. 2021 13th International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), Changsha, China, 2021: 1–6. [16] LI Zhiyang, CHEN Ming, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Energy efficient reconfigurable intelligent surface enabled mobile edge computing networks with NOMA[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(2): 427–440. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2021.3068750 [17] HUANG Shanfeng, WANG Shuai, WANG Rui, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted mobile edge computing with heterogeneous learning tasks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2021, 7(2): 369–382. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2021.3056707 [18] WU Yiwen, ZHANG Ke, and ZHANG Yan. Digital twin networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(18): 13789–13804. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3079510 [19] DAI Yueyue, ZHANG Ke, MAHARJAN S, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for stochastic computation offloading in digital twin networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(7): 4968–4977. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3016320 [20] LU Yunlong, HUANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Ke, et al. Low-latency federated learning and blockchain for edge association in digital twin empowered 6G networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(7): 5098–5107. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3017668 [21] SUN Wen, ZHANG Haibin, WANG Rong, et al. Reducing offloading latency for digital twin edge networks in 6G[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 12240–12251. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3018817 [22] LIU Tong, TANG Lun, WANG Weili, et al. Digital-twin-assisted task offloading based on edge collaboration in the digital twin edge network[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(2): 1427–1444. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3086961 [23] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025 [24] HU Xiaoyan, MASOUROS C, WONG K K, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface aided mobile edge computing: From optimization-based to location-only learning-based solutions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(6): 3709–3725. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3066495 -





 下载:
下载:
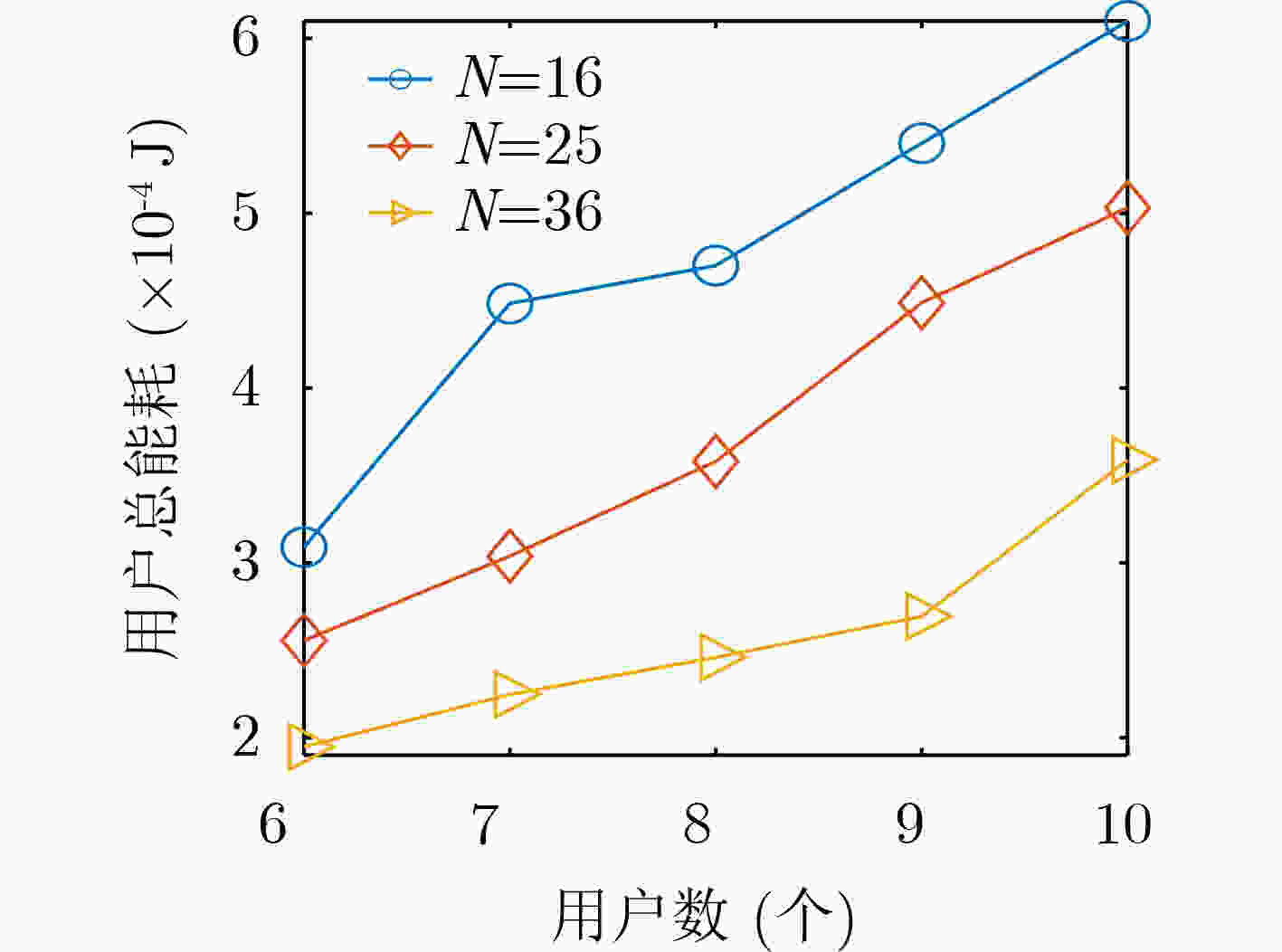
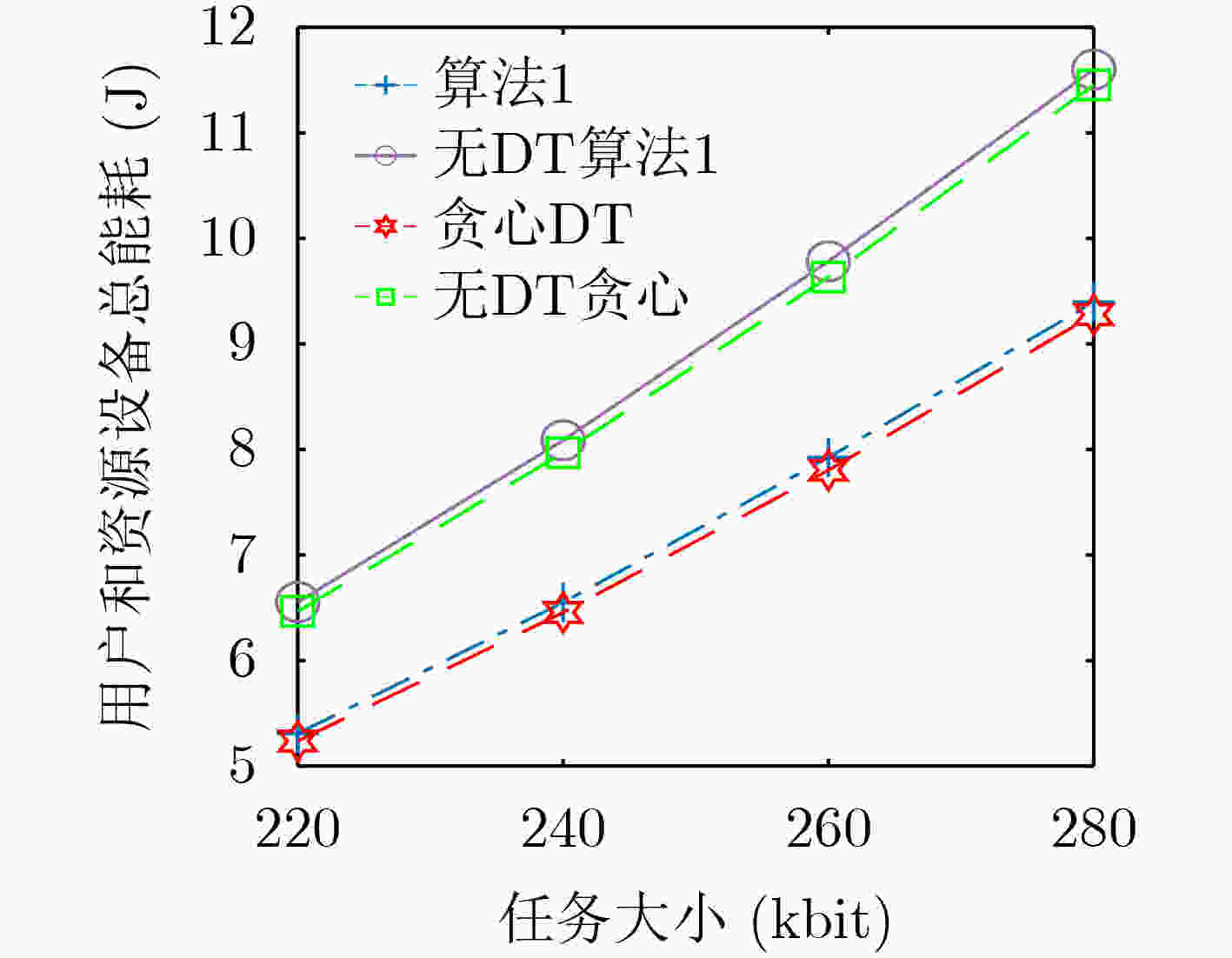


 下载:
下载:
