FastProtector: An Efficient Federated Learning Method Supporting Gradient Privacy Protection
-
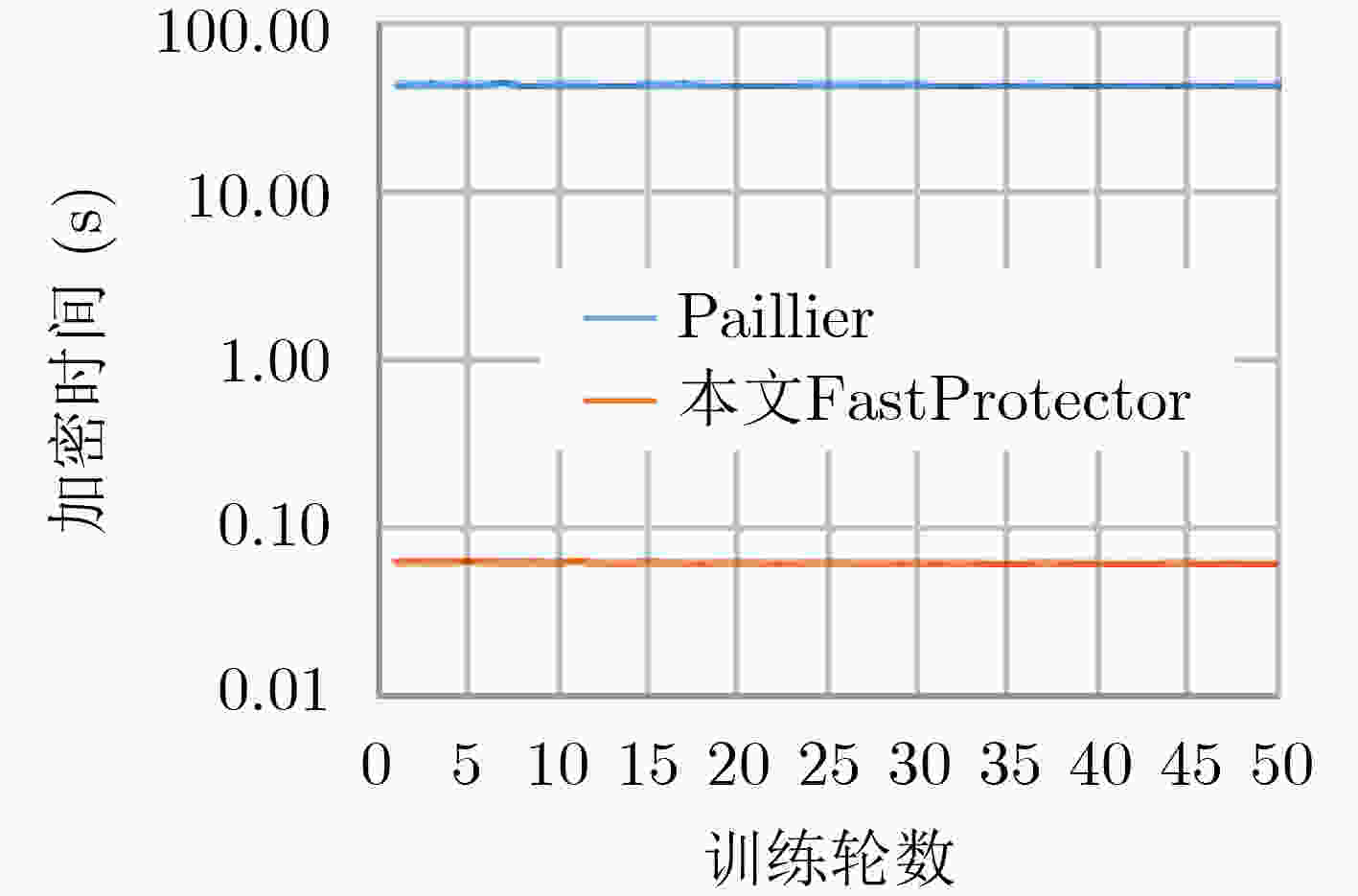
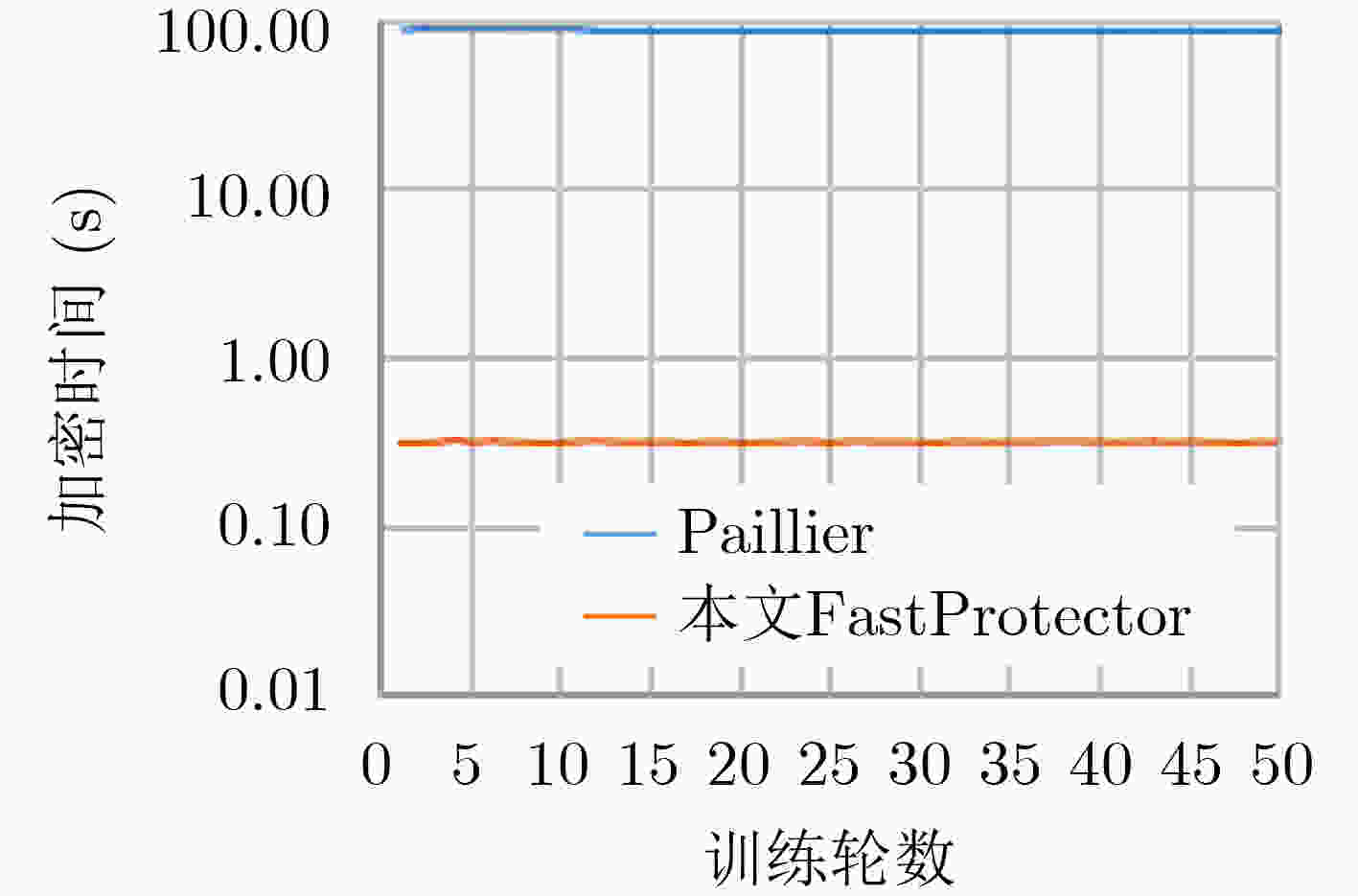
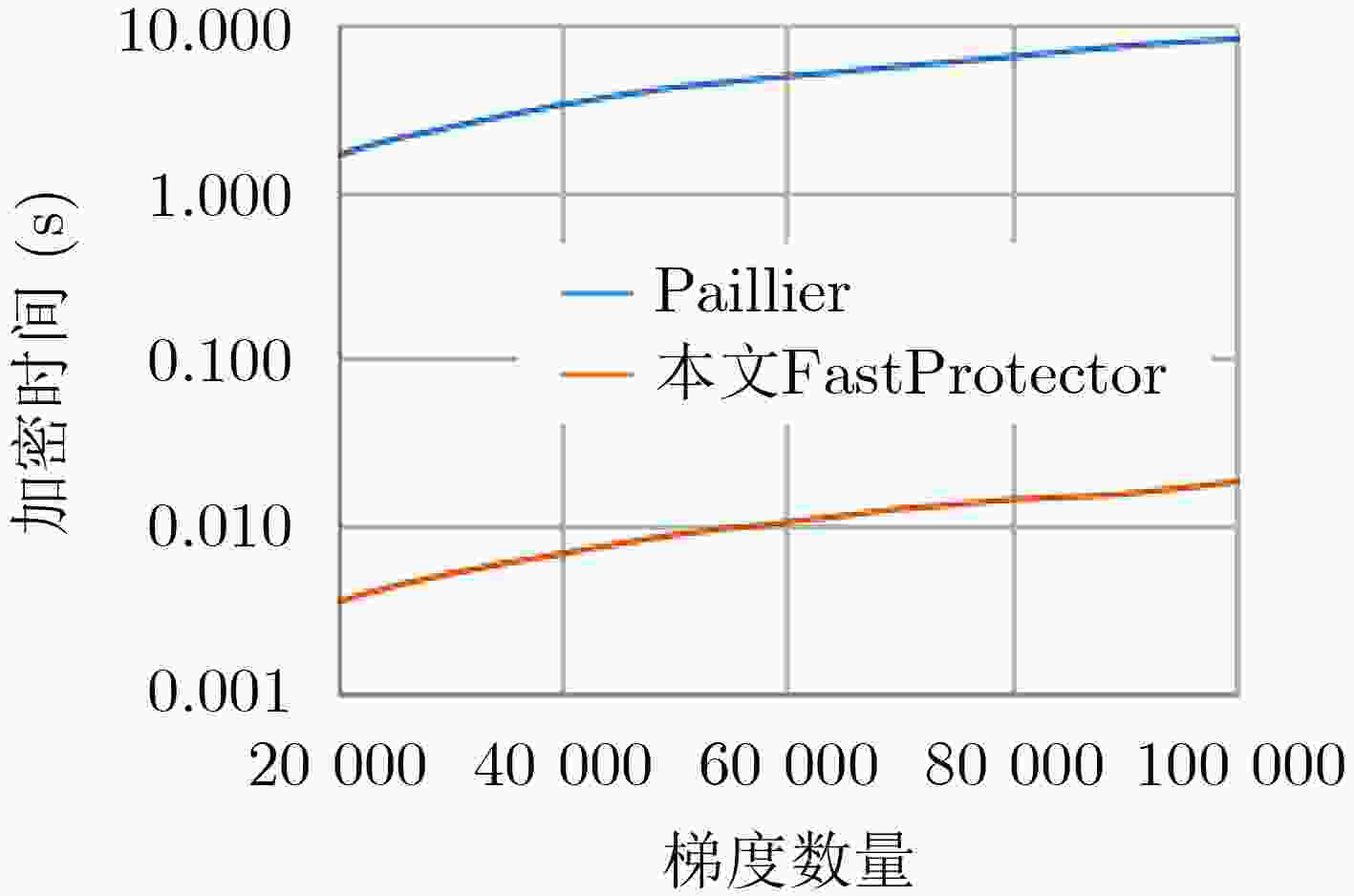
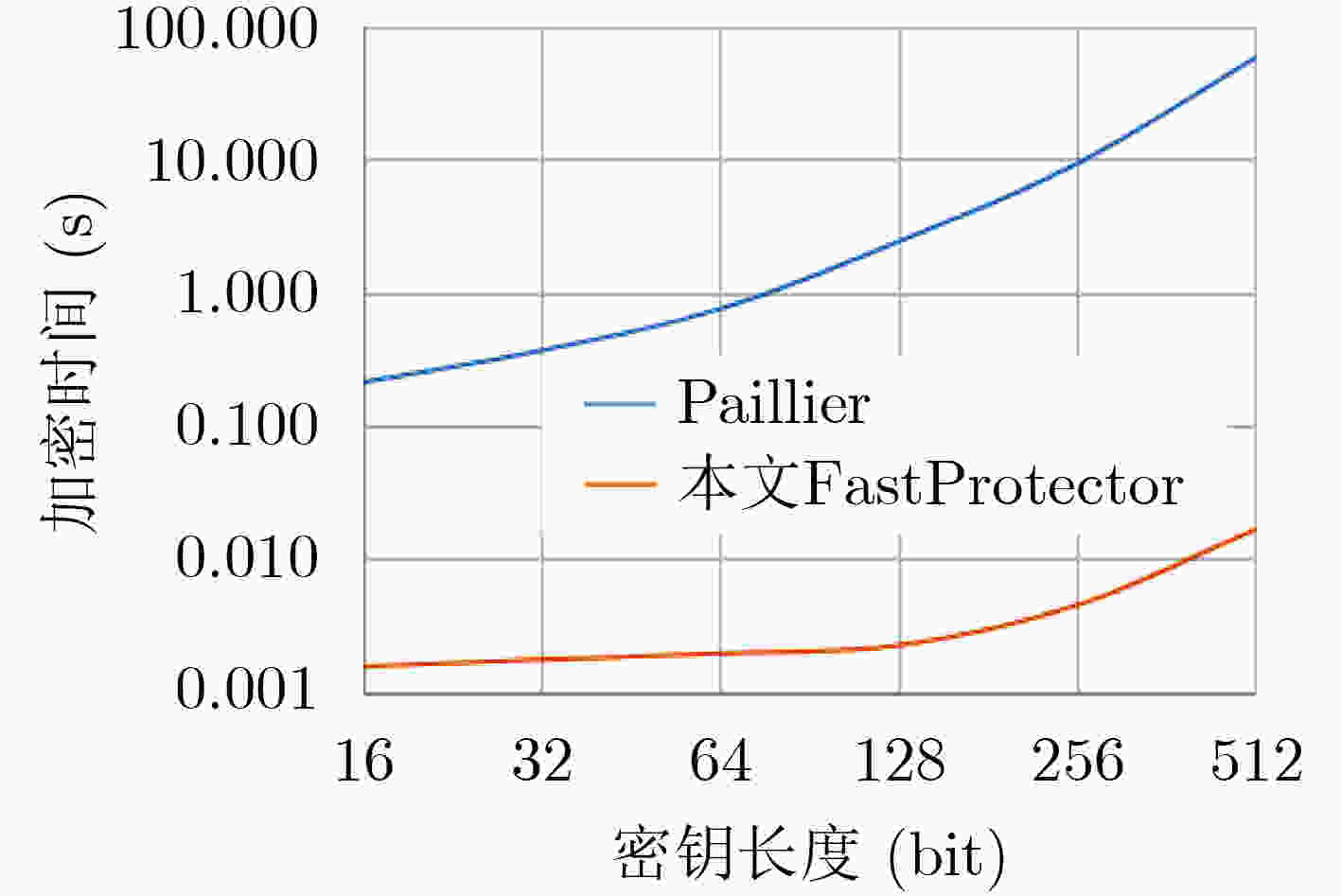
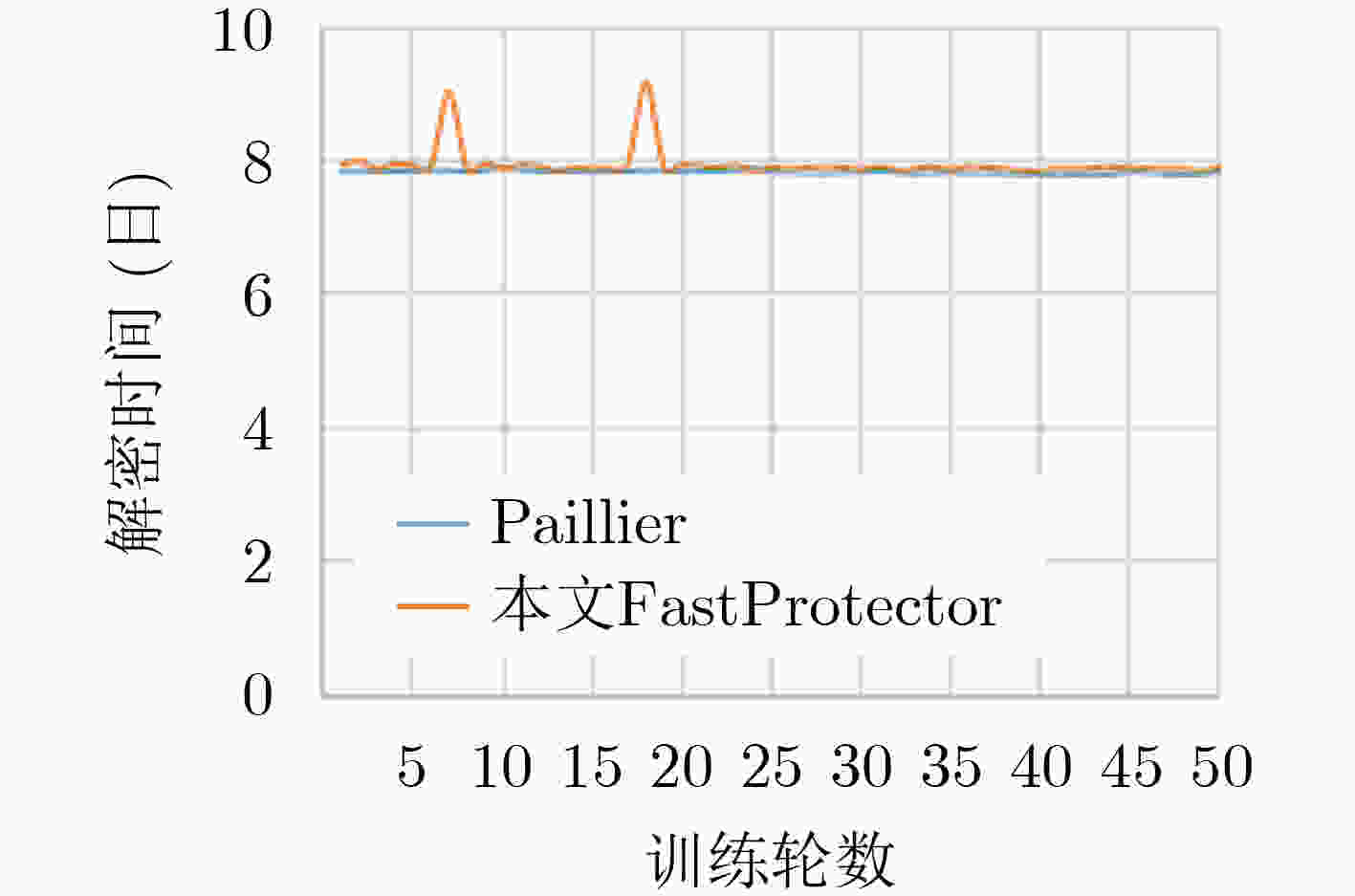
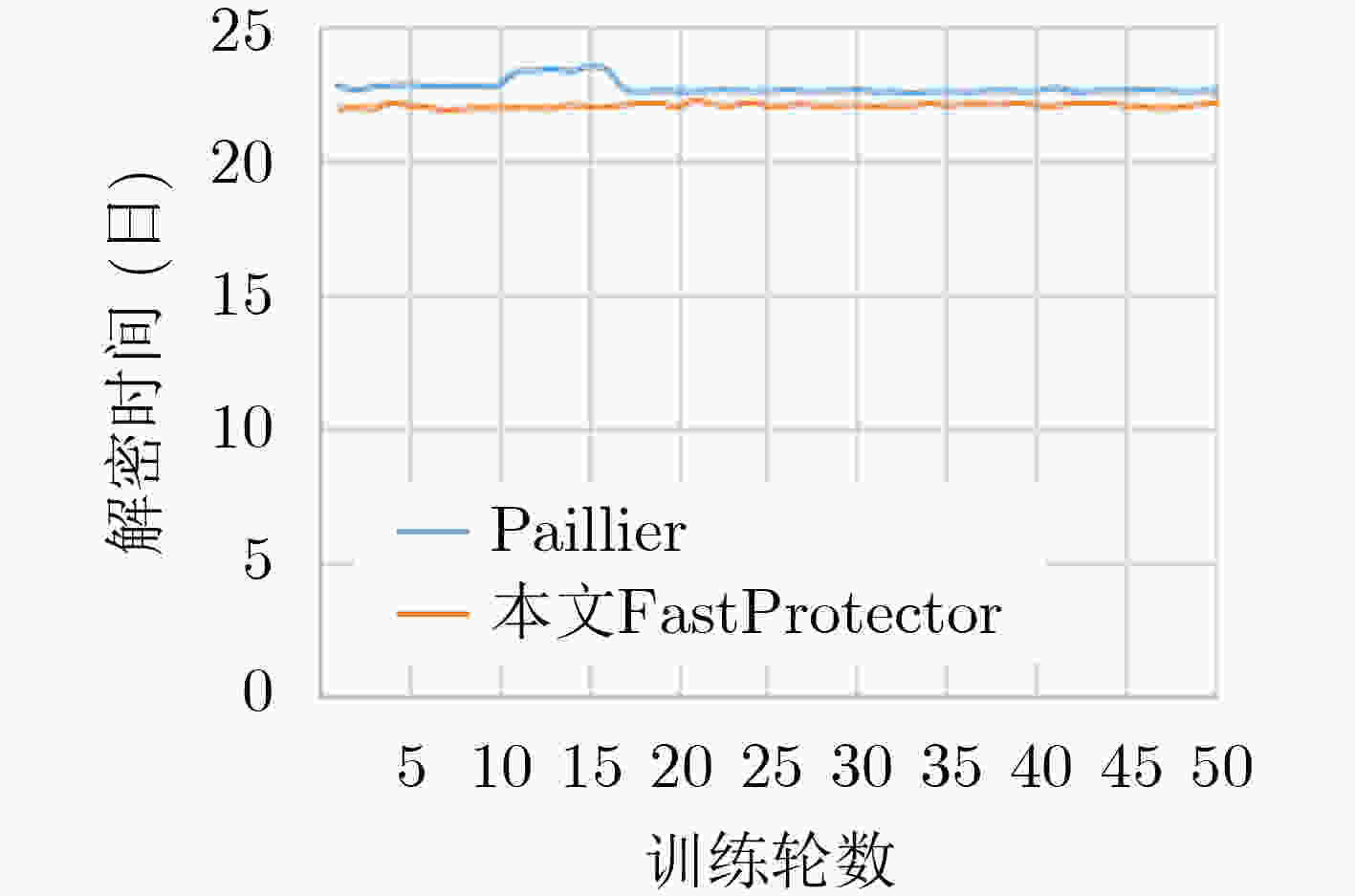
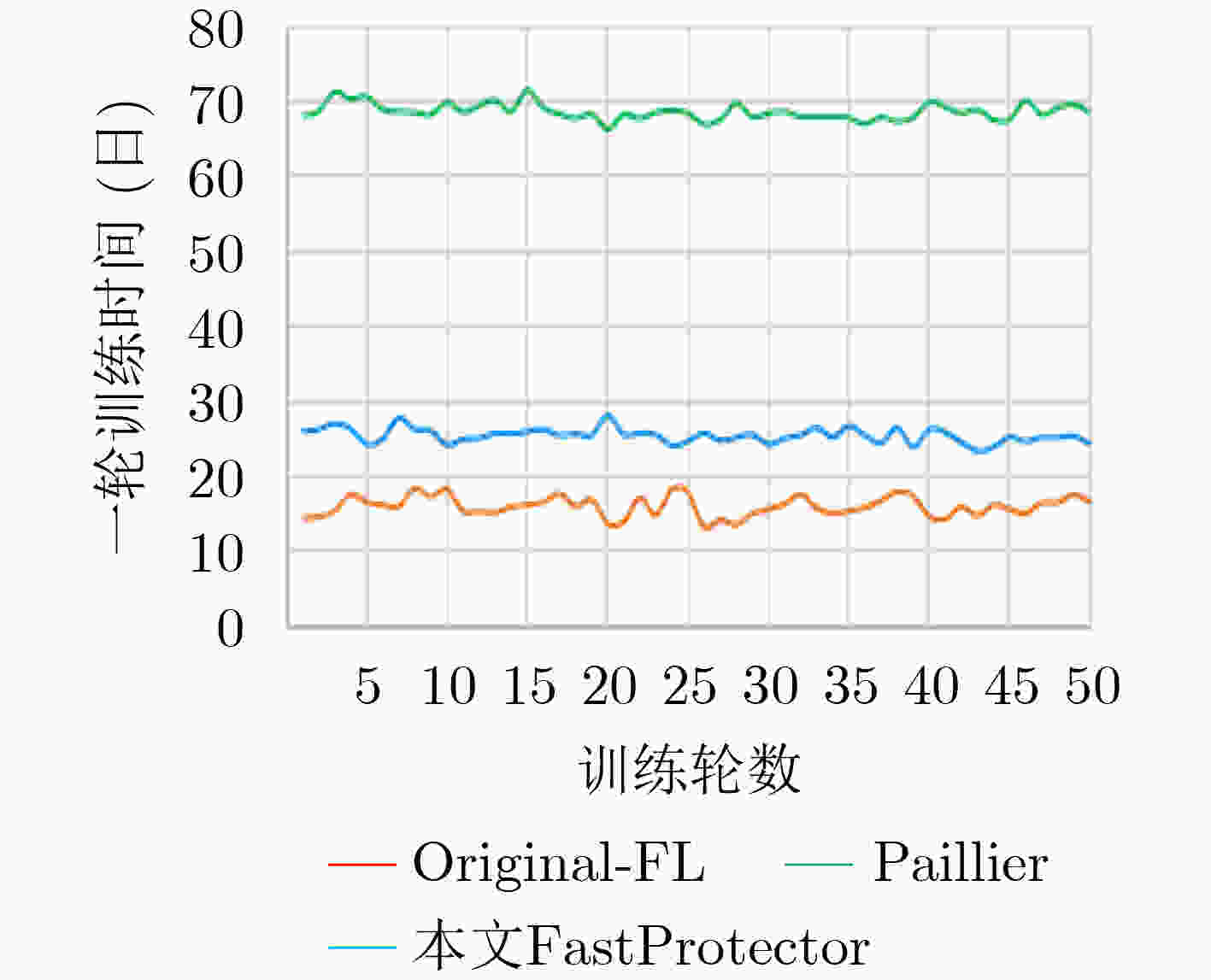
摘要: 联邦学习存在来自梯度的参与方隐私泄露,现有基于同态加密的梯度保护方案产生较大时间开销且潜在参与方与聚合服务器合谋导致梯度外泄的风险,为此,该文提出一种新的联邦学习方法FastProtector,在采用同态加密保护参与方梯度时引入符号随机梯度下降(SignSGD)思想,利用梯度中正负的多数决定聚合结果也能使模型收敛的特性,量化梯度并改进梯度更新机制,降低梯度加密的开销;同时给出一种加性秘密共享方案保护梯度密文以抵抗恶意聚合服务器和参与方之间共谋攻击;在MNIST和CIFAR-10数据集上进行了实验,结果表明所提方法在降低80%左右加解密总时间的同时仍可保证较高的模型准确率。Abstract: Federated learning has the problem of privacy leakage from the gradient. The existing gradient protection schemes based on homomorphic encryption incur a large time cost and the risk of gradient leakage caused by potential collusion between participants and aggregation server. A new federated learning method called FastProtector is proposed, where the idea of SignSGD is introduced when homomorphic encryption is used to protect participant gradients. Exploiting the feature that the majority of positive and negative gradients determine the aggregation result to make the model convergent, the gradient is quantified and the gradient updating mechanism is improved, which can reduce the overhead of gradient encryption. Meanwhile, an additive secret sharing scheme is proposed to protect the gradient ciphertext against collusion attacks between malicious aggregation servers and participants. Experiments on MNIST and CIFAR-10 dataset show that the proposed method can reduce the total encryption and decryption time by about 80% while ensuring high model accuracy.
-
Key words:
- Low encryption overhead /
- Collusion attacks /
- Federated learning /
- Gradient protection
-
表 1 变量符号说明
符号 类型 物理含义 n 标量 参与方个数 m 标量 聚合服务器个数 M 张量 训练模型 α 标量 学习率 epoch 标量 训练轮数 pk 标量 公钥 sk 标量 私钥 Di 张量 参与方i的数据集 Disub 张量 参与方i的数据集的子集 Gi 向量 参与方i的梯度,经过SignSGD方法处理后的梯度 ${\boldsymbol{G}}_j^i $ 向量 参与方i的第j个梯度共享 [[${\boldsymbol{G} }_j^i $]]pk 列表 参与方i的第j个梯度共享密文 [[${\boldsymbol{G} }^j_{\rm{agg}} $]]pk 列表 聚合服务器j的共享加和结果 [[Gagg]]pk 列表 特定聚合服务器下发的聚合梯度密文 pg 标量 正梯度量化的值 ng 标量 负梯度量化的值 算法1 模型训练和基于SignSGD的梯度共享加密 输入:数据集$ {{\boldsymbol{D}}^i} $,模型$ {\boldsymbol{M}} $,训练轮数epoch,正梯度量化的值pg,负梯度量化的值ng,公钥pk; 输出:梯度共享密文${\left[ {\left[ { {\boldsymbol{G} }_{1}^i} \right]} \right]_{ { {\rm{pk} } } }},{\left[ {\left[ { {\boldsymbol{G} }_{ 2}^i} \right]} \right]_{ { {\rm{pk} } } }}, \cdots ,{\left[ {\left[ { {\boldsymbol{G} }_{ {\text{ } }{m} }^i} \right]} \right]_{ { {\rm{pk} } } }}$。 (1) for ep=1 to epoch (2) ${ {\boldsymbol{D} } }^{i}_{ {\rm{sub} } } ={\rm{GetSubset} }\left({ {\boldsymbol{D} } }^{i}\right)$;/*求解${{\boldsymbol{D}}^i}$的随机子集*/ (3) ${ {F} }^{{i} } _{\text{loss} }=\dfrac{1}{{b} }{\displaystyle\sum }_{({{x} }_{\mathrm{l} },{{y} }_{{l} })\in {{D} }^{{i} } _{\mathrm{s}\mathrm{u}\mathrm{b} } }{f}({ {x} }_{ {l} },{M}\text{,}{ {y} }_{ {l} })$;/*计算损失值*/ (4) ${ {\boldsymbol{G} }^i} = \dfrac{ {\delta F^i_{ {\rm{loss} } } }}{ {\delta M} }$;/*计算梯度*/ (5) ${{\boldsymbol{G}}^i} = {\rm{Replace}}\left( {{{\boldsymbol{G}}^i}} \right)$;/*将梯度${ {{G} }^i}$中的正值替换为pg,负值替换为ng*/ (6) ${{\rm{pg}}_{{\rm{share}}}} = {\rm{GetAdditiveShares}}\left( {{\rm{pg}}} \right)$;/*计算得到pg的m份共享*/ (7) ${{\rm{ng}}_{{\rm{share}}}} = {\rm{GetAdditiveShares}}\left( {{\rm{ng}}} \right)$;/*计算得到ng的m份共享*/ (8) ${\left[ {\left[ {{{\rm{pg}}_{{\rm{share}}}}} \right]} \right]_{{\rm{pk}}}} = {\rm{Encrypt}}\left( {{\rm{pk}},{{\rm{pg}}_{{\rm{share}}}}} \right)$;/*加密pg的m份共享*/ (9) ${\left[ {\left[ {{{\rm{ng}}_{{\rm{share}}}}} \right]} \right]_{{\rm{pk}}}} = {\rm{Encrypt}}\left( {{\rm{pk}},{{\rm{ng}}_{{\rm{share}}}}} \right)$;/*加密ng的m份共享*/ (10) ${\boldsymbol{G}}_{ 1}^i = {{\boldsymbol{G}}^i},{\boldsymbol{G}}_{ 2}^i = {{\boldsymbol{G}}^i}, \cdots ,{\boldsymbol{G}}_{ m}^i = {{\boldsymbol{G}}^i}$;/*复制m份相同的${{\boldsymbol{G}}^i}$ */ (11) ${{\boldsymbol{G}}^i_1{'} } = {{\boldsymbol{G}}^i_1{'} }.{\rm{tolist}}(),{{\boldsymbol{G}}^i_2{'} } = {{\boldsymbol{G}}^i_2{'} }.{\rm{tolist}}(), \cdots ,{{\boldsymbol{G}}^i_m{'} } = {{\boldsymbol{G}}^i_m{'} }.{\rm{tolist}}()$;/*将${\boldsymbol{G}}{_{ 1}^i{'} },{\boldsymbol{G}}{_{ 2}^i{'} }, \cdots ,{\boldsymbol{G}}{_{ m}^i{'} }$转换为列表类型*/ (12) ${\rm{datanum}} = {\rm{len}}({{\boldsymbol{G}}^i})$ ;/*获得$ {G^i} $中元素个数*/ (13) for ${\rm{num}} = 0$ to ${\rm{datanum}} - 1$ /*根据$ {G^i} $中的正负将共享密文替换到对应位置*/ (14) if ${{\boldsymbol{G}}^i}\left[ {{\rm{num}}} \right] > 0$ (15) ${G}_{1}^{i}{}^{\prime }\left[{\rm{num}}\right]={\left[\left[{{\rm{pg}}}_{{\rm{share}}}\right]\right]}_{{\rm{pk}}}[0],{G}_{2}^{i}{}^{\prime }\left[{\rm{num}}\right]={\left[\left[{{\rm{pg}}}_{{\rm{share}}}\right]\right]}_{{\rm{pk}}}[1],\cdots ,{G}_{m}^{i}{}^{\prime }[{\rm{num}}]={\left[\left[{{\rm{pg}}}_{{\rm{share}}}\right]\right]}_{{\rm{pk}}}[m-1]$; (16) else (17) ${G}_{1}^{i}{}^{\prime }\left[{\rm{num}}\right]={\left[\left[{{\rm{ng}}}_{{\rm{share}}}\right]\right]}_{{\rm{pk}}}[0],{G}_{2}^{i}{}^{\prime }\left[{\rm{num}}\right]={\left[\left[{{\rm{ng}}}_{{\rm{share}}}\right]\right]}_{pk}[1],\cdots ,{G}_{m}^{i}{}^{\prime }[{\rm{num}}]={\left[\left[n{g}_{{\rm{share}}}\right]\right]}_{{\rm{pk}}}[m-1]$; (18) end if (19) end for (20) ${\left[ {\left[ { {\boldsymbol{G} }_{ 1}^i} \right]} \right]_{ {\rm{pk} } } } = {\boldsymbol{G} }{_{ 1}^i{'} },{\left[ {\left[ { {\boldsymbol{G} }_{ 2}^i} \right]} \right]_{ {\rm{pk} } } } = {\boldsymbol{G} }{_{ 2}^i{'} }, \cdots ,{\left[ {\left[ { {\boldsymbol{G} }_{ m}^i} \right]} \right]_{ {\rm{pk} } } } = {\boldsymbol{G} }{_{ m}^i{'} }$; (21) Return ${\left[ {\left[ {{\boldsymbol{G}}_{ 1}^i} \right]} \right]_{{\rm{pk}}}},{\left[ {\left[ {{\boldsymbol{G}}_{ 2}^i} \right]} \right]_{{\rm{pk}}}}, \cdots ,{\left[ {\left[ {{\boldsymbol{G}}_{{\text{ }} m}^i} \right]} \right]_{{\rm{pk}}}}$; (22)end for 算法2 解密和更新 输入:聚合梯度密文${\left[ {\left[ {{{\boldsymbol{G}}_{{\rm{agg}}}}} \right]} \right]_{{{\rm{pk}}}}} $,公钥pk,私钥sk,模型${\boldsymbol{M}}$,学习率$\alpha $,训练轮数epoch; 输出:更新后的模型${\boldsymbol{M}}$。 (1) for ep=1 to epoch (2) ${G'_{{\rm{agg}}} } = {\rm{Decrypt}}({\rm{pk,sk}},{\left[ {\left[ { {{\boldsymbol{G}}_{{\rm{agg}}} } } \right]} \right]_{ {{\rm{pk}}} } })$;/*聚合梯度密文的解密*/ (3) ${{\boldsymbol{G}}_{{\rm{agg}}} } = {\rm{torch}}. {\rm{tensor}}({{\boldsymbol{G}}_{ {\text{agg} } } }^\prime )$;/*将${\boldsymbol{{G}}_{ {\text{agg} } } }^\prime$转换为张量类型*/ (4) ${\boldsymbol{M}} = {\boldsymbol{M}} - \alpha \cdot {{\boldsymbol{G}}_{{\rm{agg}}} }/n$;/*更新模型*/ (5) Return ${\boldsymbol{M}}$; (6)end for 表 2 MNIST和CIFAR-10数据集上最终模型准确率(%)
方法 MNIST数据集
模型准确率CIFAR-10数据集
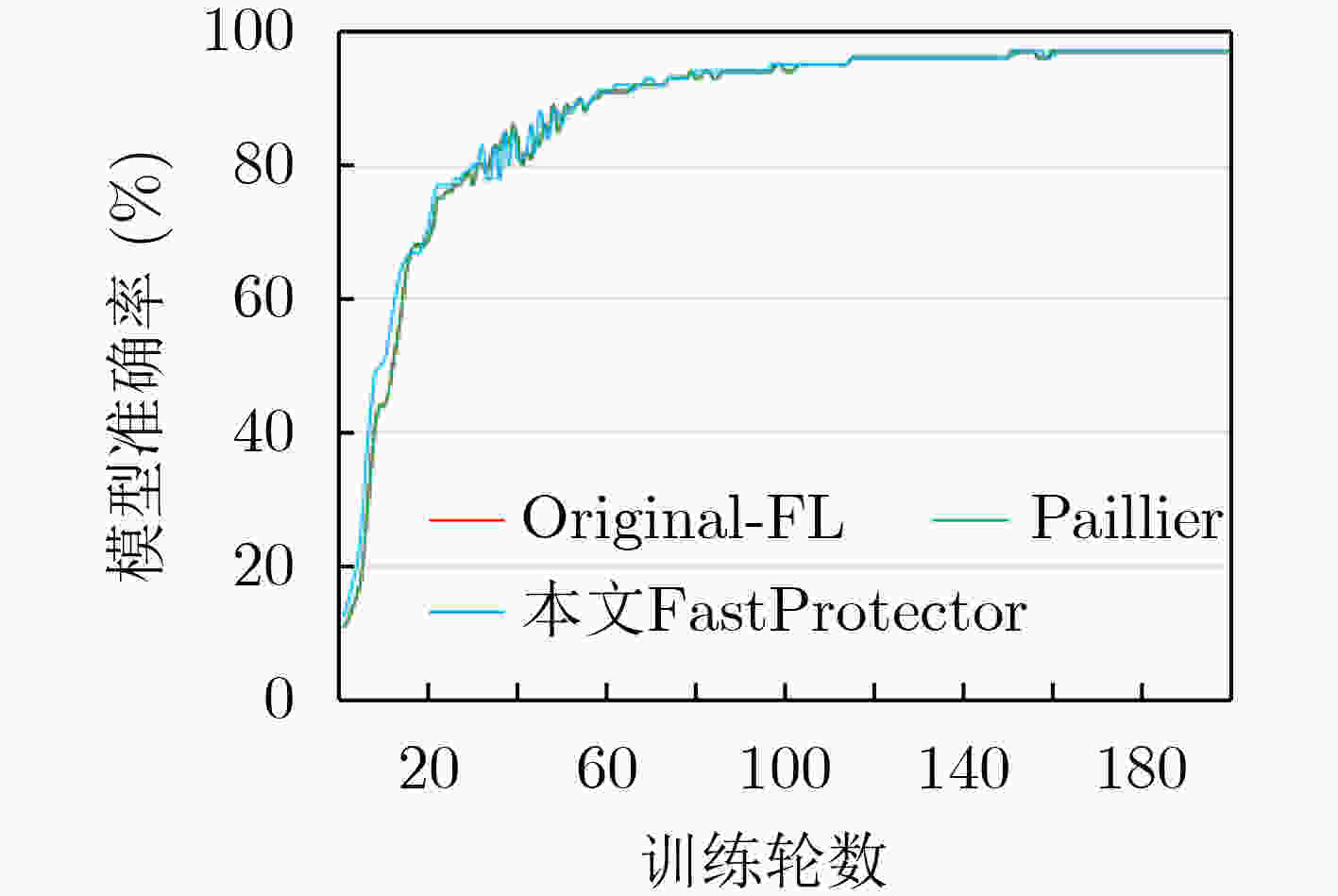
模型准确率Original-FL 99 84 Paillier 99 84 本文FastProtector 99 84 -
[1] JEON J, KIM J, KIM J, et al. Privacy-preserving deep learning computation for geo-distributed medical big-data platforms[C]. 2019 49th IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks-Supplemental Volume, Portland, USA, 2019: 3–4. [2] LIU Yang, MA Zhuo, LIU Ximeng, et al. Privacy-preserving object detection for medical images with faster R-CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17: 69–84. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2019.2946476 [3] VIZITIU A, NIŢĂ C I, PUIU A, et al. Towards privacy-preserving deep learning based medical imaging applications[C]. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications, Istanbul, Turkey, 2019: 1–6. [4] Intersoft consulting. Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 April 2016 on the protection of natural persons with regard to the processing of personal data and on the free movement of such data and repealing Directive 95/46/EC (General Data Protection Regulation) [EB/OL]. https://gdpr-info.eu, 2020. [5] DLA Piper. Data protection laws of the world: Full handbook[EB/OL]. https://www.dlapiperdataprotection.com, 2021. [6] 中华人民共和国网络安全法(全文)[EB/OL]. http://www.zgyq.gov.cn/zwzxrdzt/xfzl/202208/t20220819_76128304.html, 2022.Cybersecurity law of the People's Republic of China[EB/OL]. http://www.zgyq.gov.cn/zwzxrdzt/xfzl/202208/t20220819_76128304.html, 2022. [7] 中华人民共和国数据安全法[EB/OL]. http://www.npc.gov.cn/npc/c30834/202106/7c9af12f51334a73b56d7938f99a788a.shtml, 2021.Data security law of the People's Republic of China[EB/OL]. http://www.npc.gov.cn/npc/c30834/202106/7c9af12f51334a73b56d7938f99a788a.shtml, 2021. [8] 中华人民共和国个人信息保护法[EB/OL]. http://www.npc.gov.cn/npc/c30834/202108/a8c4e3672c74491a80b53a172bb753fe.shtml, 2021.Personal information protection law of the People's Republic of China[EB/OL]. http://www.npc.gov.cn/npc/c30834/202108/a8c4e3672c74491a80b53a172bb753fe.shtml, 2021. [9] MCMAHAN H B, MOORE E, RAMAGE D, et al. Federated learning of deep networks using model averaging[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.05629v1, 2016. [10] ZHU Ligeng, LIU Zhijian, and HAN Song. Deep leakage from gradients[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08935, 2019. [11] MA Chuan, LI Jun, DING Ming, et al. On safeguarding privacy and security in the framework of federated learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.06512, 2019. [12] ZHOU Chunyi, FU Anmin, YU Shui, et al. Privacy-preserving federated learning in fog computing[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(11): 10782–10793. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2987958 [13] PHONG L T, AONO Y, HAYASHI T, et al. Privacy-preserving deep learning via additively homomorphic encryption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2018, 13(5): 1333–1345. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2017.2787987 [14] ZHANG Xianglong, FU Anmin, WANG Huaqun, et al. A privacy-preserving and verifiable federated learning scheme[C]. 2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Dublin, Ireland, 2020: 1–6. [15] LOHANA A, RUPANI A, RAI S, et al. Efficient privacy-aware federated learning by elimination of downstream redundancy[J]. IEEE Design & Test, 2022, 39(3): 73–81. doi: 10.1109/MDAT.2021.3063373 [16] MENG Dan, LI Hongyu, ZHU Fan, et al. FedMONN: Meta operation neural network for secure federated aggregation[C]. 2020 IEEE 22nd International Conference on High Performance Computing and Communications; IEEE 18th International Conference on Smart City; IEEE 6th International Conference on Data Science and Systems (HPCC/SmartCity/DSS), Yanuca Island, Fiji, 2020: 579–584. [17] 董业, 侯炜, 陈小军, 等. 基于秘密分享和梯度选择的高效安全联邦学习[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(10): 2241–2250. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200463DONG Ye, HOU Wei, CHEN Xiaojun, et al. Efficient and secure federated learning based on secret sharing and gradients selection[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(10): 2241–2250. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200463 [18] FANG Minghong, CAO Xiaoyu, JIA Jinyuan, et al. Local model poisoning attacks to Byzantine-Robust federated learning[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.11815, 2021. [19] 夏家骏, 鲁颖, 张子扬, 等. 基于秘密共享与同态加密的纵向联邦学习方案研究[J]. 信息通信技术与政策, 2021, 47(6): 19–26. doi: 10.12267/j.issn.2096-5931.2021.06.003XIA Jiajun, LU Ying, ZHANG Ziyang, et al. Research on vertical federated learning based on secret sharing and homomorphic encryption[J]. Information and Communications Technology and Policy, 2021, 47(6): 19–26. doi: 10.12267/j.issn.2096-5931.2021.06.003 [20] HAO Meng, LI Hongwei, XU Guowen, et al. Towards efficient and privacy-preserving federated deep learning[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Shanghai, China, 2019: 1–6. [21] XIANG Liyao, YANG Jingbo, and LI Baochun. Differentially-private deep learning from an optimization perspective[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2019 - IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Paris, France, 2019: 559–567. [22] BERNSTEIN J, ZHAO J W, AZIZZADENESHELI K, et al. SignSGD with majority vote is communication efficient and fault tolerant[C]. The 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2019: 1–20. -





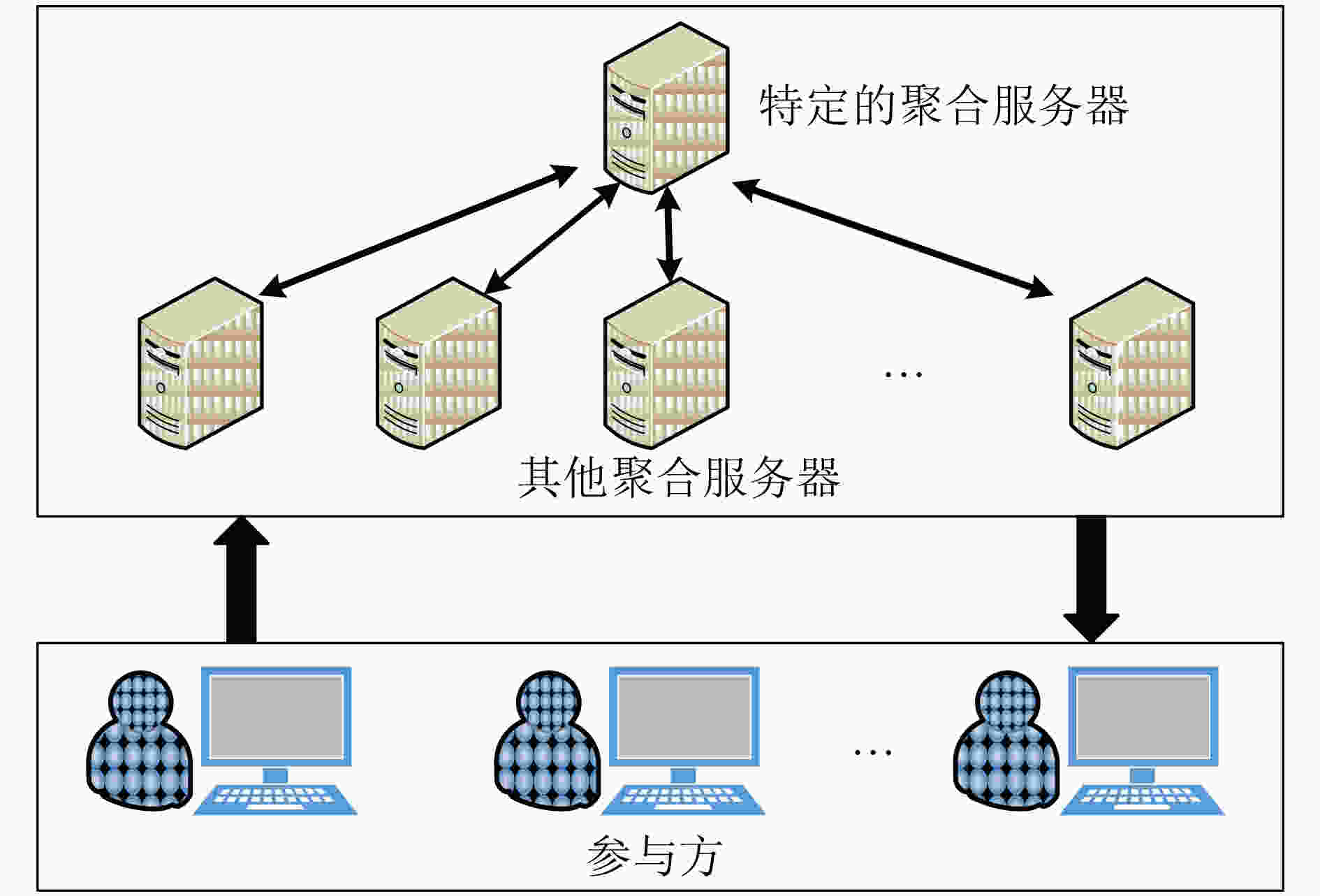
 下载:
下载:
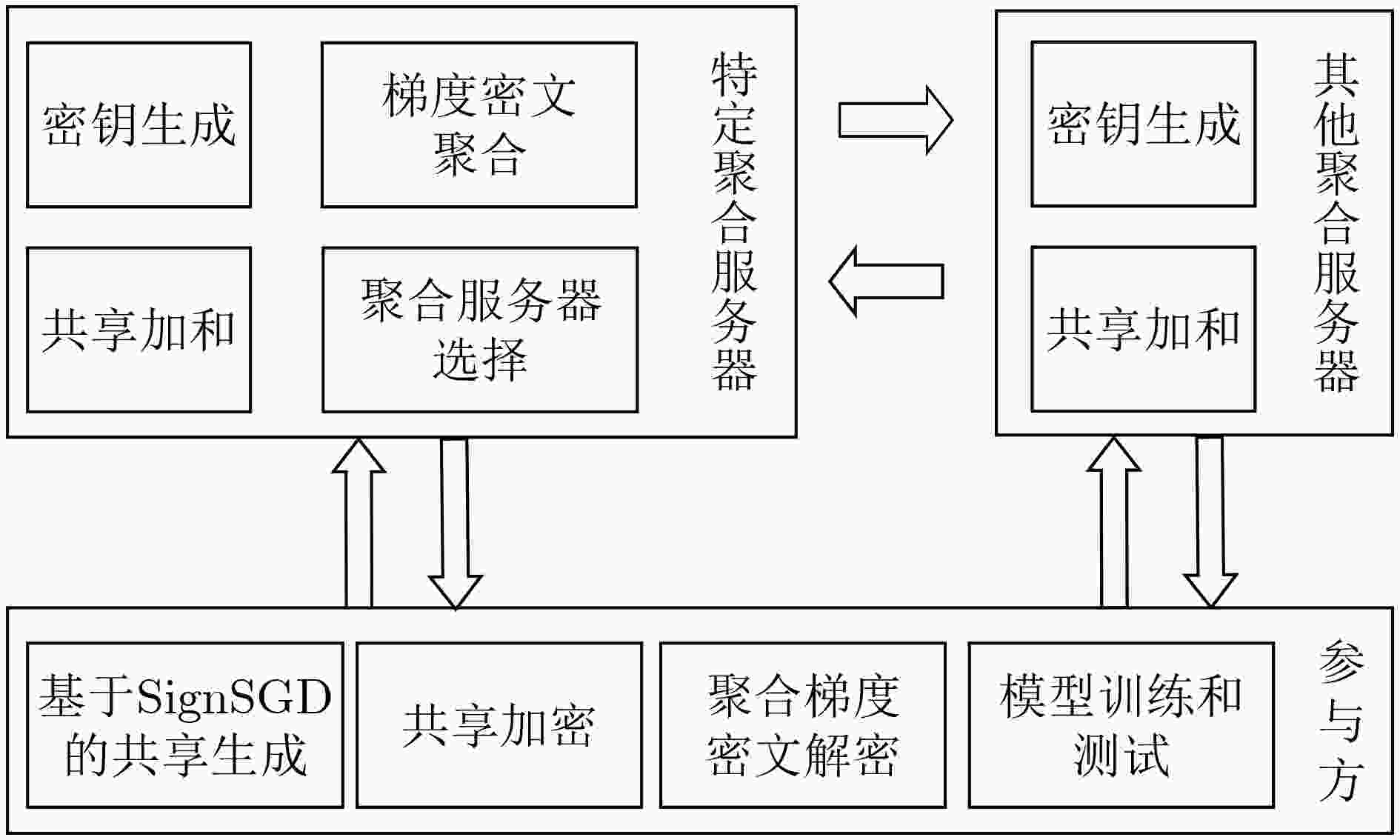
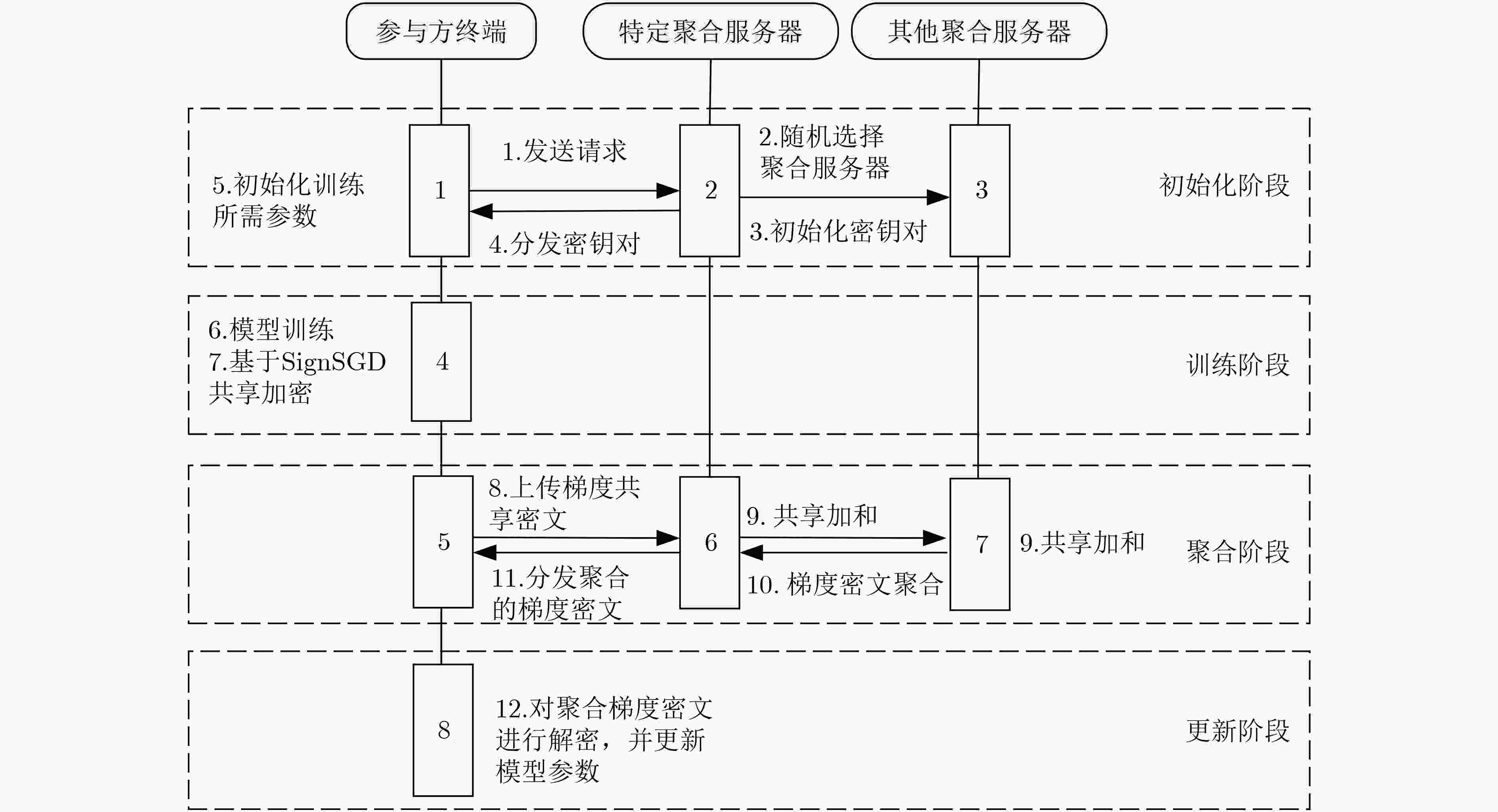
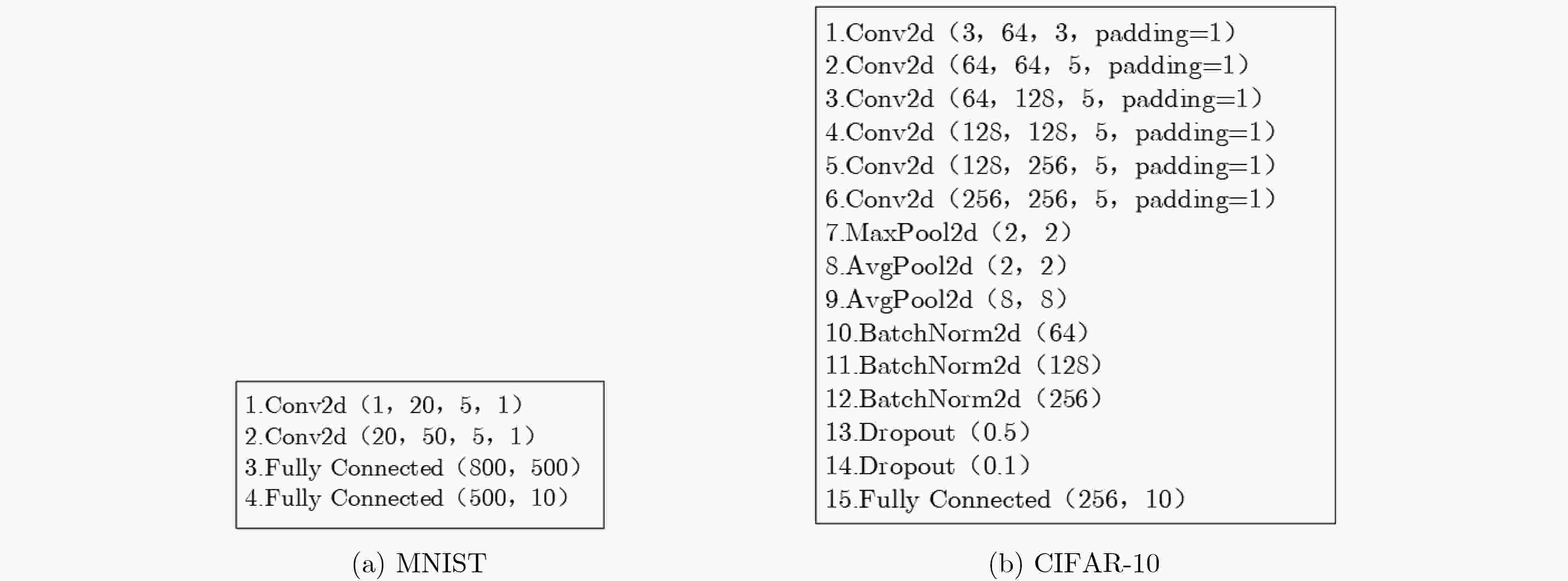



 下载:
下载:
