Two-stage Rain Image Removal Based on Density Guidance
-
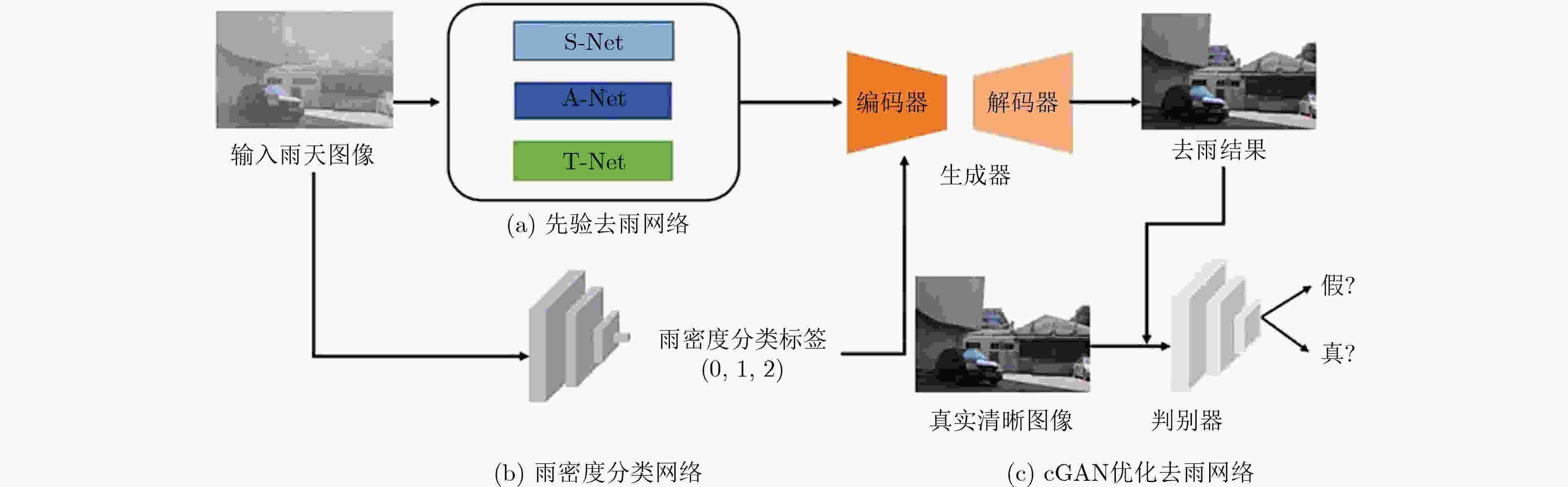
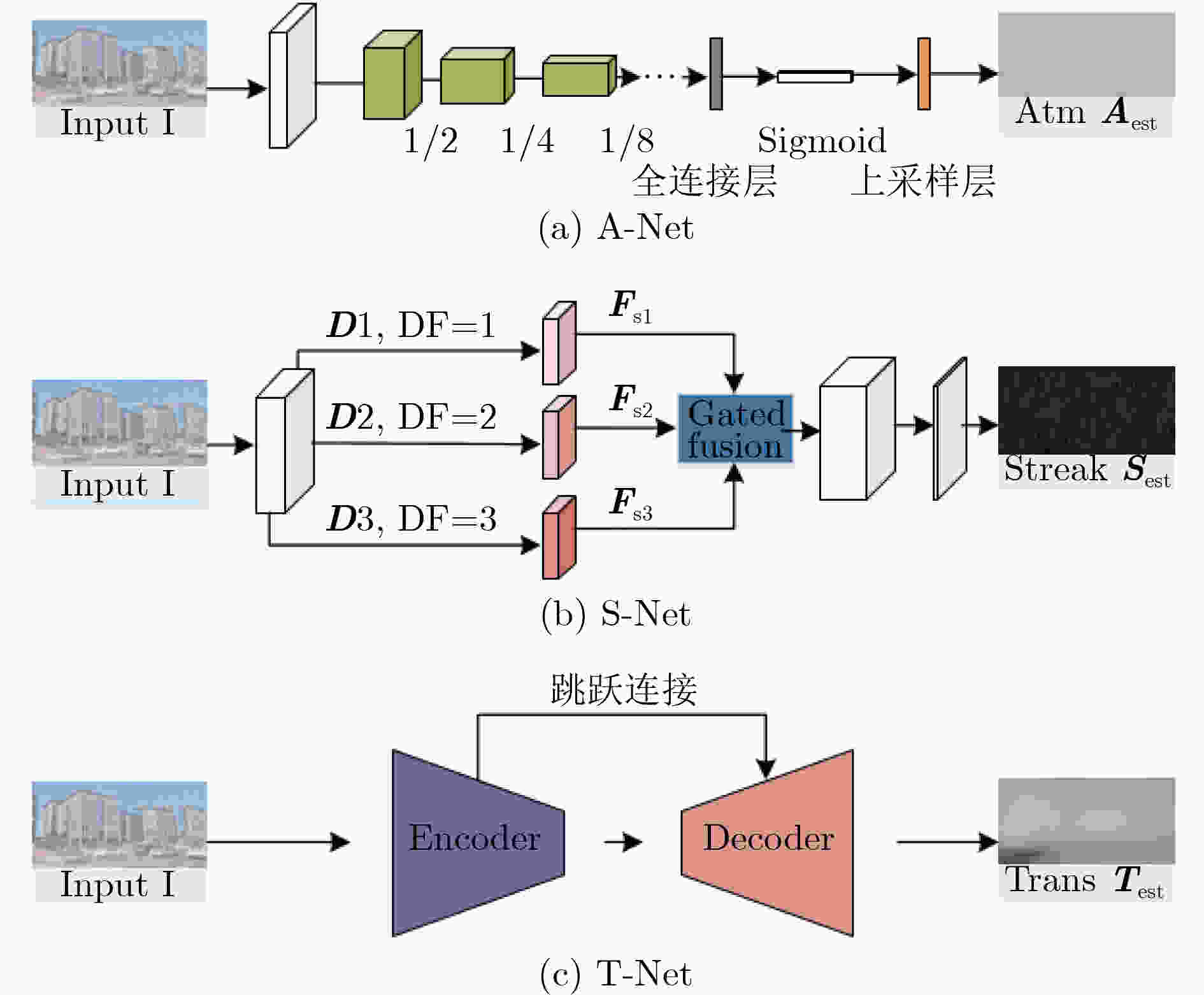
摘要: 雨天作为最常见的恶劣天气,对图像造成的退化效应主要包括雨线对背景的遮挡、雨线累积形成的雨雾效应,从而导致很多为清晰成像条件设计的视觉系统运行效果大打折扣。为了实现雨线和雨雾同时去除、更鲁棒地处理各种真实雨天场景,该文提出了一种雨密度分类引导的双阶段雨天图像复原方法。该方法结合雨天物理模型先验与cGAN网络优化,综合考虑不同模式的雨线与雨雾,利用单独的雨密度分类网络为优化阶段提供引导信息,可以实现不同密度的雨线和雨雾图像复原。在公开合成数据集和真实雨天图像上进行了大量实验,定量和定性的结果均表明了所提方法在去雨有效性和泛化性上的优势。Abstract: As the most common severe weather, rain can degrade the performance of many vision systems designed for clear imaging conditions. In order to realize the simultaneous removal of rain streaks and rain accumulation, and to deal with various real rain scenes, a two-stage rain image restoration method guided by rain density classification is proposed, which integrates physics model and cGAN refinement. Extensive experiments are conducted on representative synthetic rain datasets and realrain scenes. Quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method in terms of effectiveness and generalization ability.
-
Key words:
- Image deraining /
- Physics model /
- cGAN /
- Density-aware /
- Gated fusion
-
表 1 不同方法在OTS-test测试集上的平均PSNR和SSIM结果
方法 PSNR (dB) SSIM DID-MDN 18.97 0.7386 HRR 23.67 0.8720 PReNet 23.86 0.8782 MSPFN 23.69 0.8607 本文方法 25.10 0.8854 表 2 不同方法在Rain100L和Rain100L测试集上的平均PSNR和SSIM结果
方法 Rain100L Rain100H PSNR (dB) SSIM PSNR (dB) SSIM DSC 24.16 0.87 15.66 0.54 LP 29.11 0.88 14.26 0.42 DID-MDN 25.56 0.86 15.95 0.56 HRR 25.40 0.89 22.19 0.78 本文方法 29.21 0.92 24.14 0.83 表 3 不同网络结构OTS-test测试集上的平均PSNR和SSIM结果
方法 PSNR (dB) SSIM DID-MDN 18.97 0.738 6 DID-MDN+优化 19.58 0.754 6 本文方法-分类器 23.92 0.866 6 本文方法 25.10 0.885 4 -
[1] BAHNSEN C H and MOESLUND T B. Rain removal in traffic surveillance: Does it matter?[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 20(8): 2802–2819. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2018.2872502 [2] GARG K and NAYAR S K. Vision and rain[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2007, 75(1): 3–27. doi: 10.1007/s11263-006-0028-6 [3] LI Yu, TAN R T, GUO Xiaojie, et al. Rain streak removal using layer priors[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2736–2744. [4] CHEN Yilei and HSU C T. A generalized low-rank appearance model for spatio-temporally correlated rain streaks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 1968–1975. [5] 王志超, 陈震. 基于小波融合的视频图像去雨(雪)方法[J]. 北华大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 19(1): 135–140. doi: 10.11713/j.issn.1009-4822.2018.01.028WANG Zhichao and CHEN Zhen. Method of removing rain (snow) from video images based on wavelet fusion[J]. Journal of Beihua University:Natural Science, 2018, 19(1): 135–140. doi: 10.11713/j.issn.1009-4822.2018.01.028 [6] FU Xueyang, HUANG Jiabin, DING Xinghao, et al. Clearing the skies: A deep network architecture for single-image rain removal[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(6): 2944–2956. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2691802 [7] 郭继昌, 郭昊, 郭春乐. 多尺度卷积神经网络的单幅图像去雨方法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2018, 50(3): 185–191. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201704075GUO Jichang, GUO Hao, and GUO Chunle. Single image rain removal based on multi-scale convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018, 50(3): 185–191. doi: 10.11918/j.issn.0367-6234.201704075 [8] ZHANG He and PATEL V M. Density-aware single image de-raining using a multi-stream dense network[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 695–704. [9] REN Dongwei, ZUO Wangmeng, HU Qinghua, et al. Progressive image deraining networks: A better and simpler baseline[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3932–3941. [10] JIANG Kui, WANG Zhongyuan, YI Peng, et al. Multi-scale progressive fusion network for single image deraining[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8343–8352. [11] LIN C Y, TAO Zhuang, XU Aisheng, et al. Sequential dual attention network for rain streak removal in a single image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 9250–9265. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.3025402 [12] DENG Sen, WEI Mingqiang, WANG Jun, et al. Detail-recovery image deraining via context aggregation networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 14548–14557. [13] FU Xueyang, QI Qi, ZHA Zhengjun, et al. Rain streak removal via dual graph convolutional network[C]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Palo Alto, USA, 2021: 1352–1360. [14] GUO Qing, SUN Jingyang, JUEFEI-XU F, et al. Uncertainty-aware cascaded dilation filtering for high-efficiency deraining[J]. arXiv: 2201.02366, 2022. [15] ZHENG Shen, LU Changjie, WU Yuxiong, et al. SAPNet: Segmentation-aware progressive network for perceptual contrastive deraining[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Waikoloa, USA, 2022: 52–62. [16] LI Ruoteng, CHEONG L F, and TAN R T. Heavy rain image restoration: Integrating physics model and conditional adversarial learning[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 1633–1642. [17] WEI Yanyan, ZHANG Zhao, WANG Yang, et al. Deraincyclegan: Rain attentive cyclegan for single image deraining and rainmaking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 4788–4801. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3074804 [18] WEI Yanyan, ZHANG Zhao, WANG Yang, et al. Semi-deraingan: A new semi-supervised single image deraining[C]. IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Shenzhen, China, 2021: 1–6. [19] ISOLA P, ZHU Junyan, ZHOU Tinghui, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks[C]. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 5967–5976. [20] JOLICOEUR-MARTINEAU A. The relativistic discriminator: A key element missing from standard GAN[C]. 7th International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, USA, 2018. [21] LI Boyi, REN Wenqi, FU Dengpan, et al. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(1): 492–505. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2867951 [22] BOCHKOVSKIY A, WANG C Y, and LIAO H Y M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J]. arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. -





 下载:
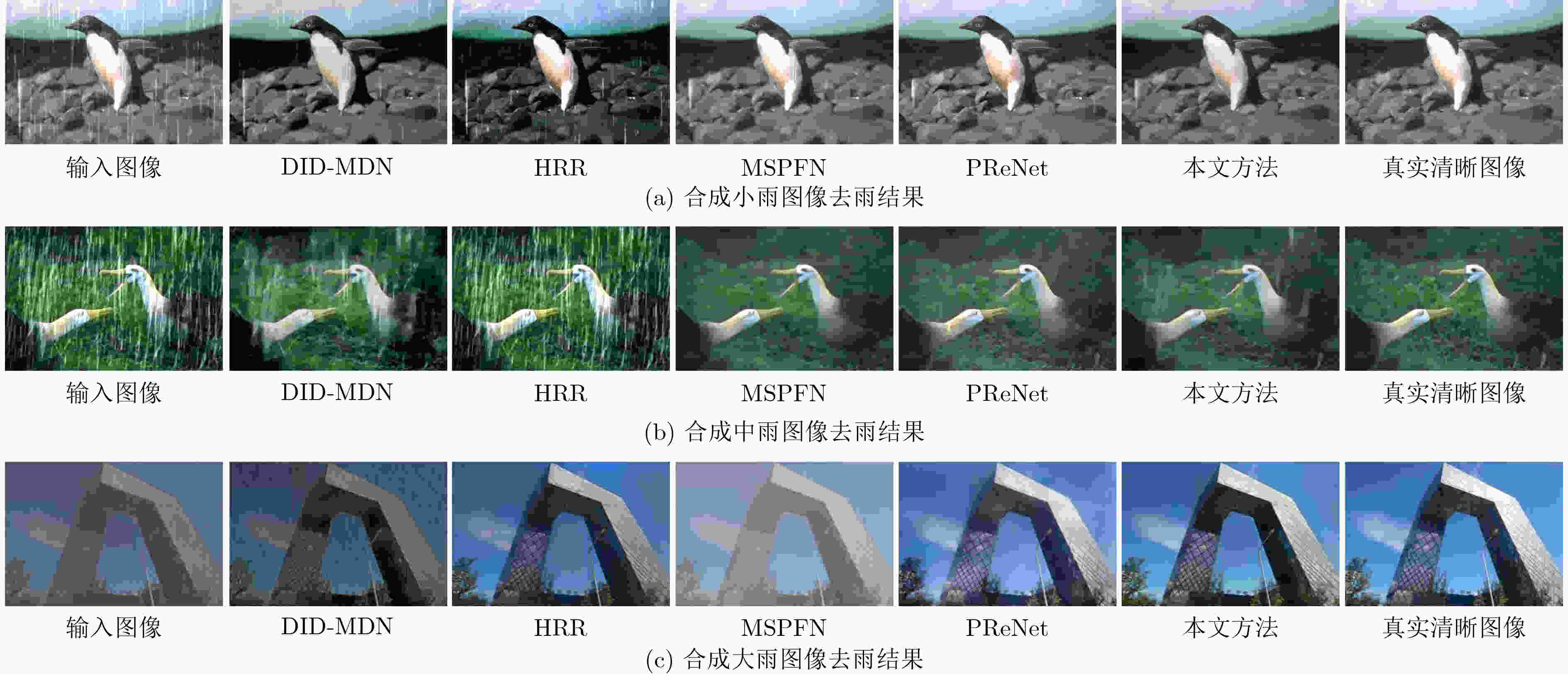
下载:
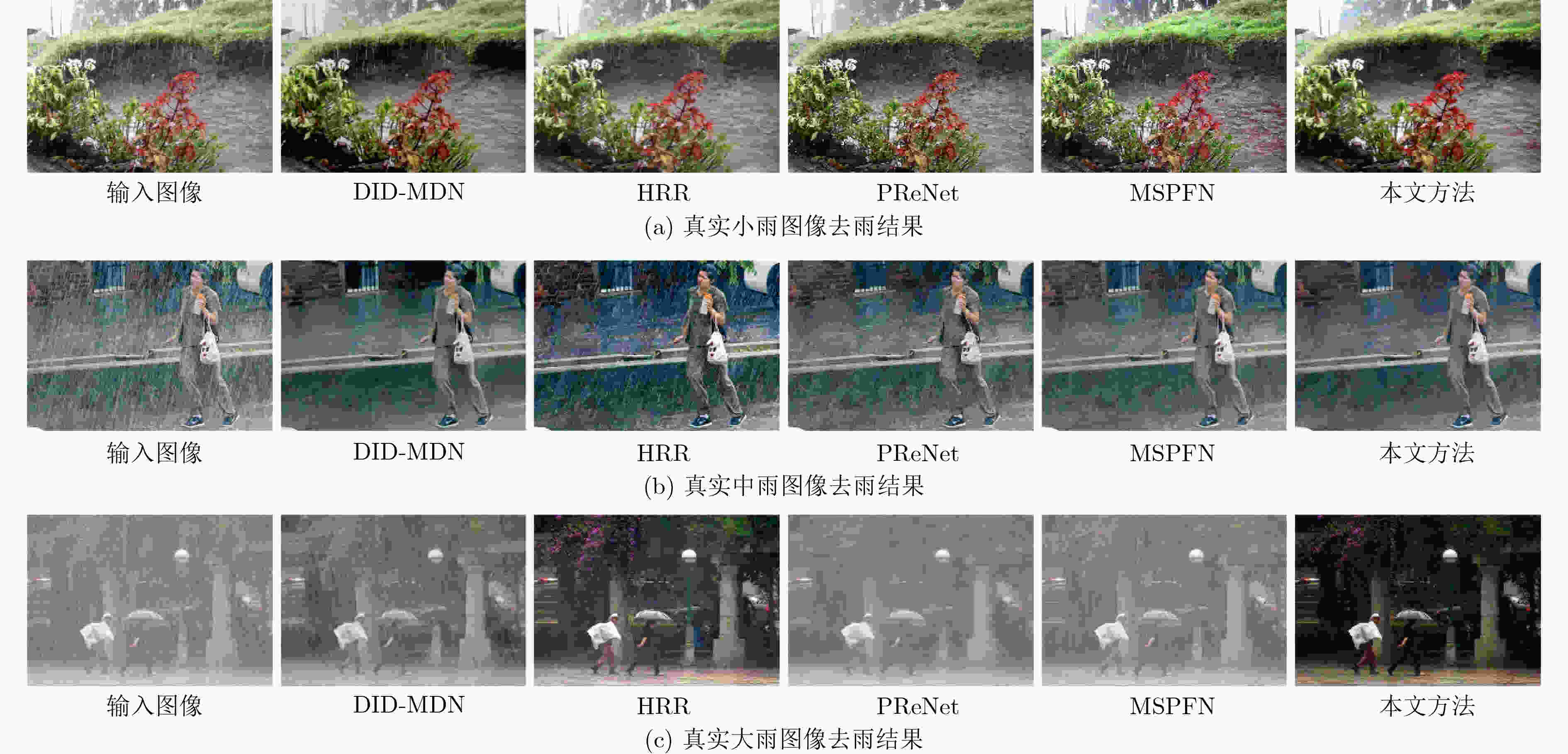






 下载:
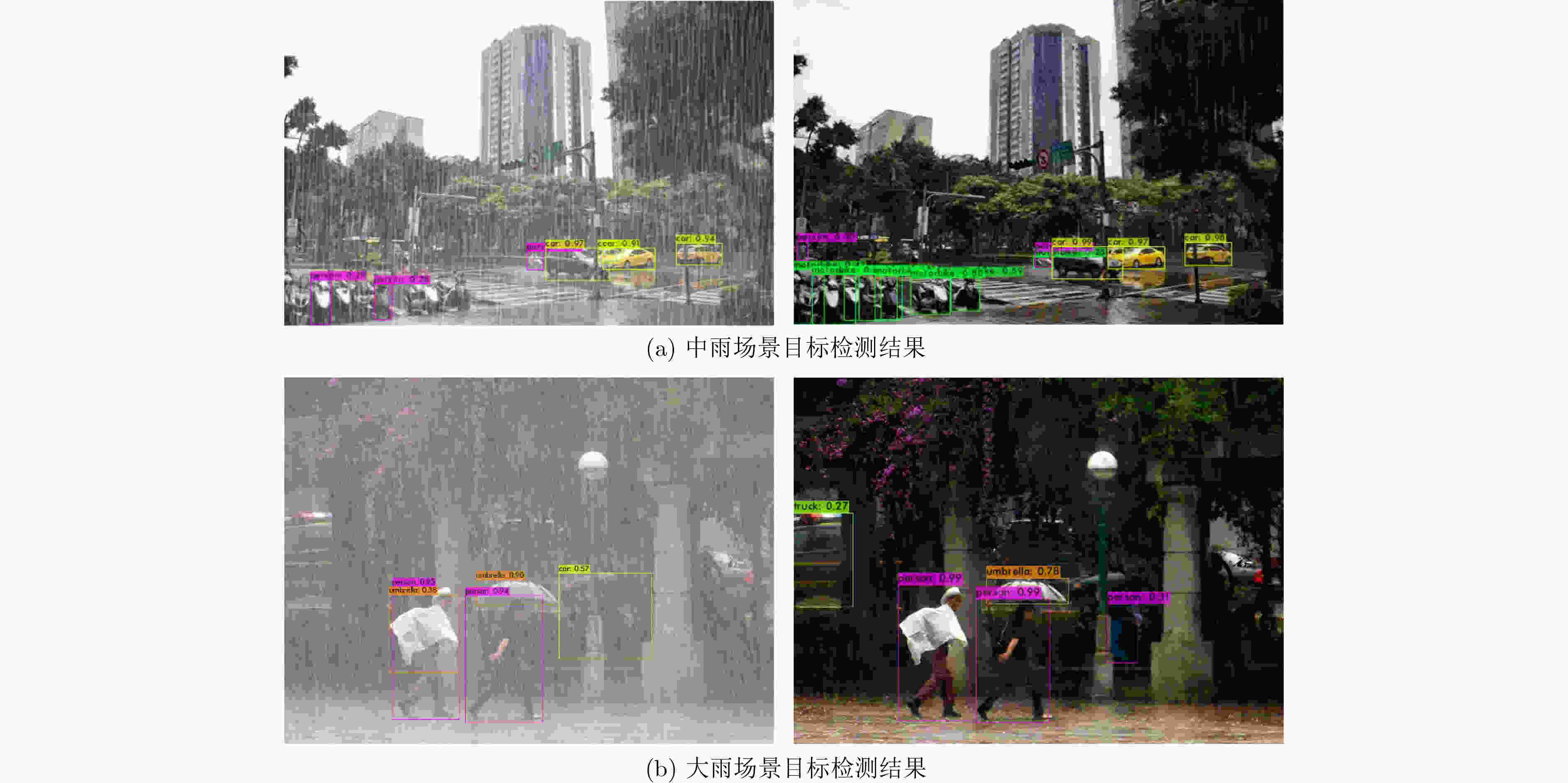
下载:
