Semi-supervised SAR Ship Target Detection with Graph Attention Network
-
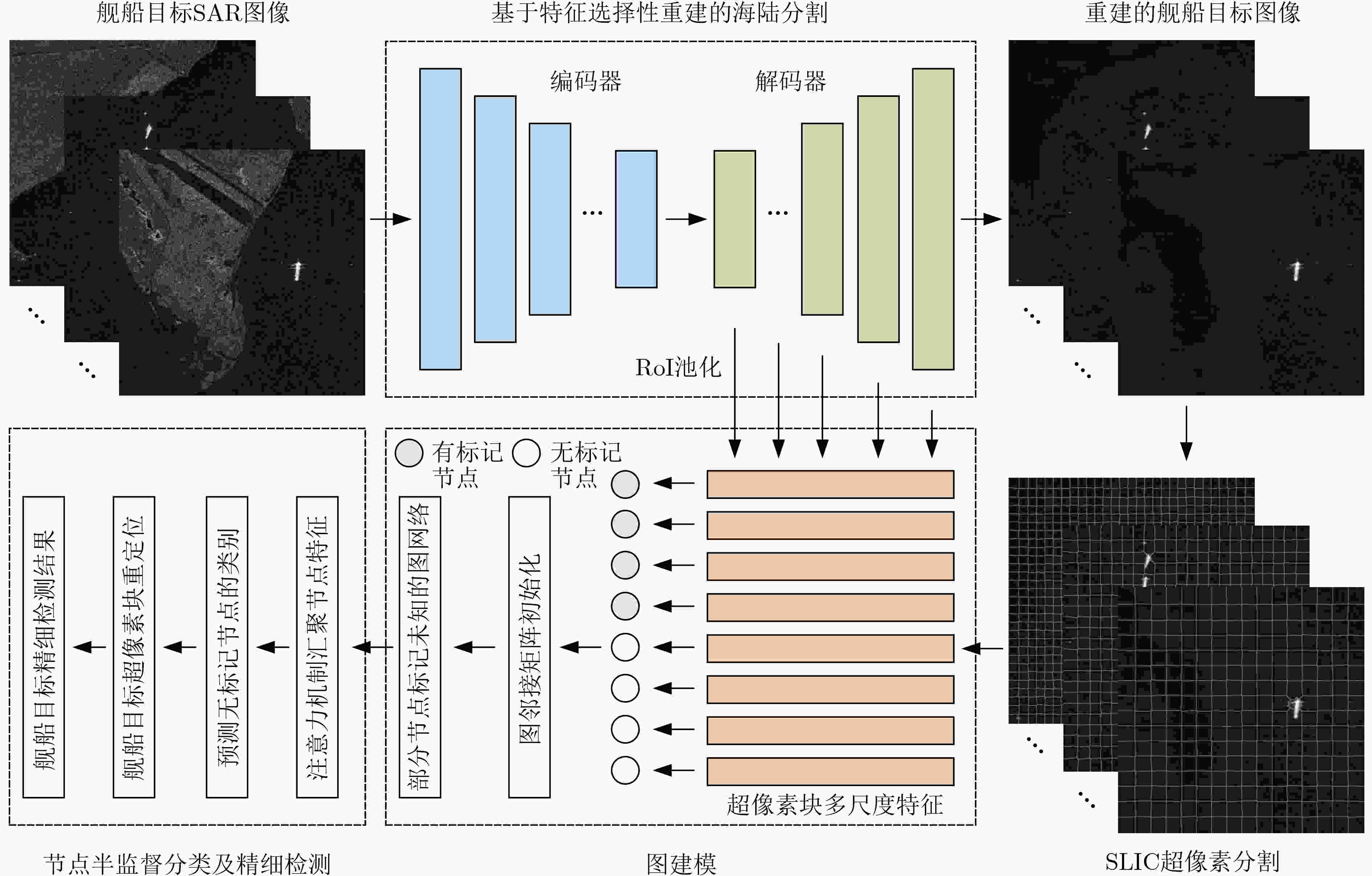
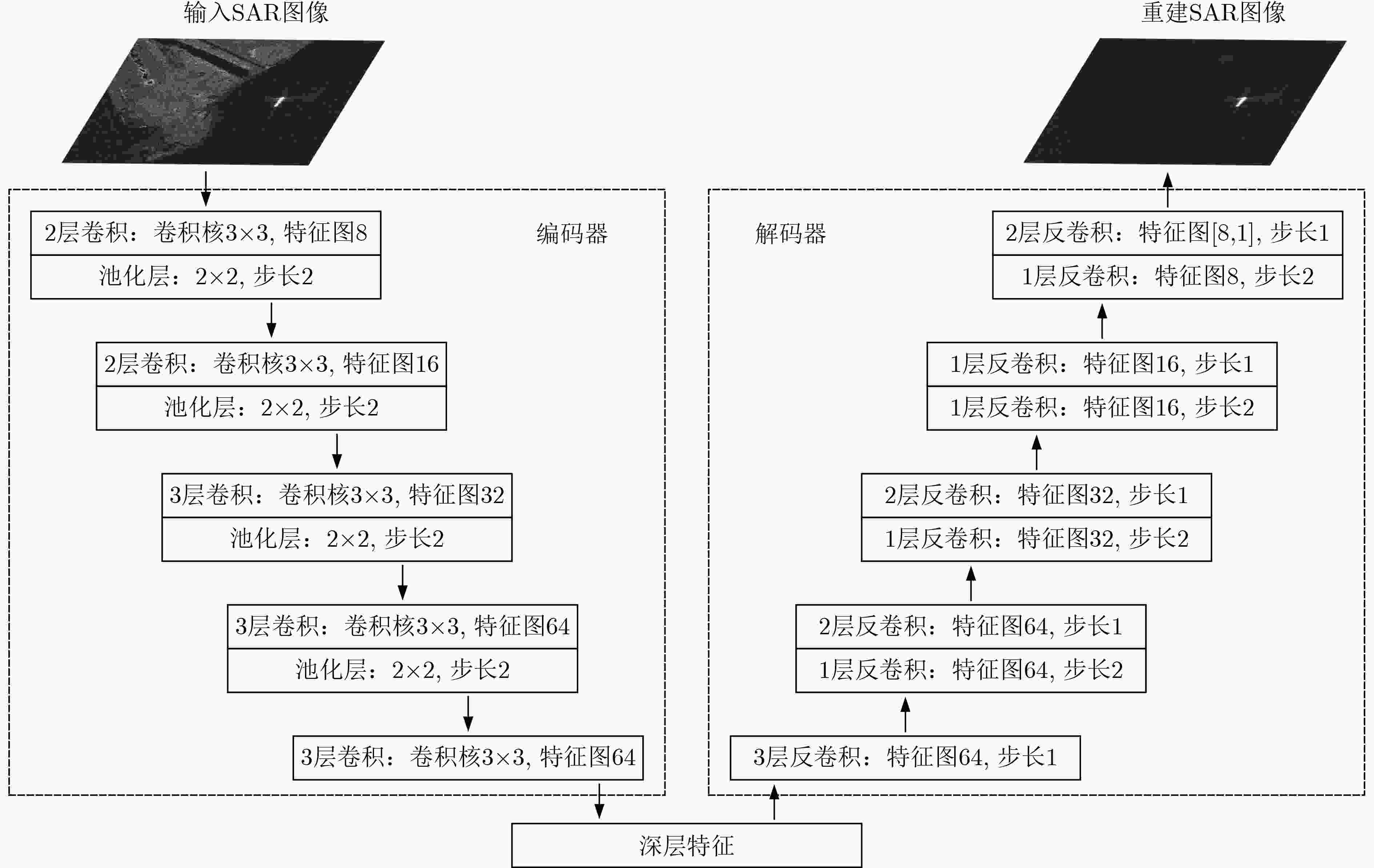
摘要: 基于深度学习的合成孔径雷达(SAR)舰船目标检测近年得到了快速发展。然而,传统有监督学习需要大量的标记样本来训练网络。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于图注意力网络(GAT)的半监督SAR舰船目标检测方法。首先,设计了对称卷积神经网络用于海陆分割。随后,完成超像素分割并将超像素块建模为GAT的节点,利用感兴趣区域池化层提取节点的多尺度特征。GAT采用注意力机制自适应地汇聚邻接节点特征实现对无标记节点的分类。最后,将预测为舰船目标的超像素块定位到SAR图像中并获得精细检测结果。在实测高分辨SAR图像数据集上验证了所提方法。结果表明该方法可以在少量标记样本下,以低虚警率实现对舰船目标的可靠检测。Abstract: Recently, ship target detection in Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery based on deep learning has been widely developed. However, a large number of labeled samples are needed in traditionally supervised learning to train the network. Therefore, a semi-supervised SAR ship target detection approach based on Graph ATtention network (GAT) is proposed. Firstly, a symmetric convolutional neural network is designed to realize land-ocean segmentation. Secondly, the super-pixel segmentation is completed and the super-pixels are modeled as nodes of the GAT. The multi-scale features of a node are extracted by region of interest pooling layer. Attentional mechanisms are used in GAT to concatenate adaptively the neighbor node’s features and classify the unlabeled nodes. Finally, the super-pixels predicted as ship targets are located in SAR image and the fine detection results are obtained. The proposed method is verified on the measured high resolution SAR images dataset. The results show that this method can effectively detect ship targets with low false alarm rate by using a small number of labeled samples.
-
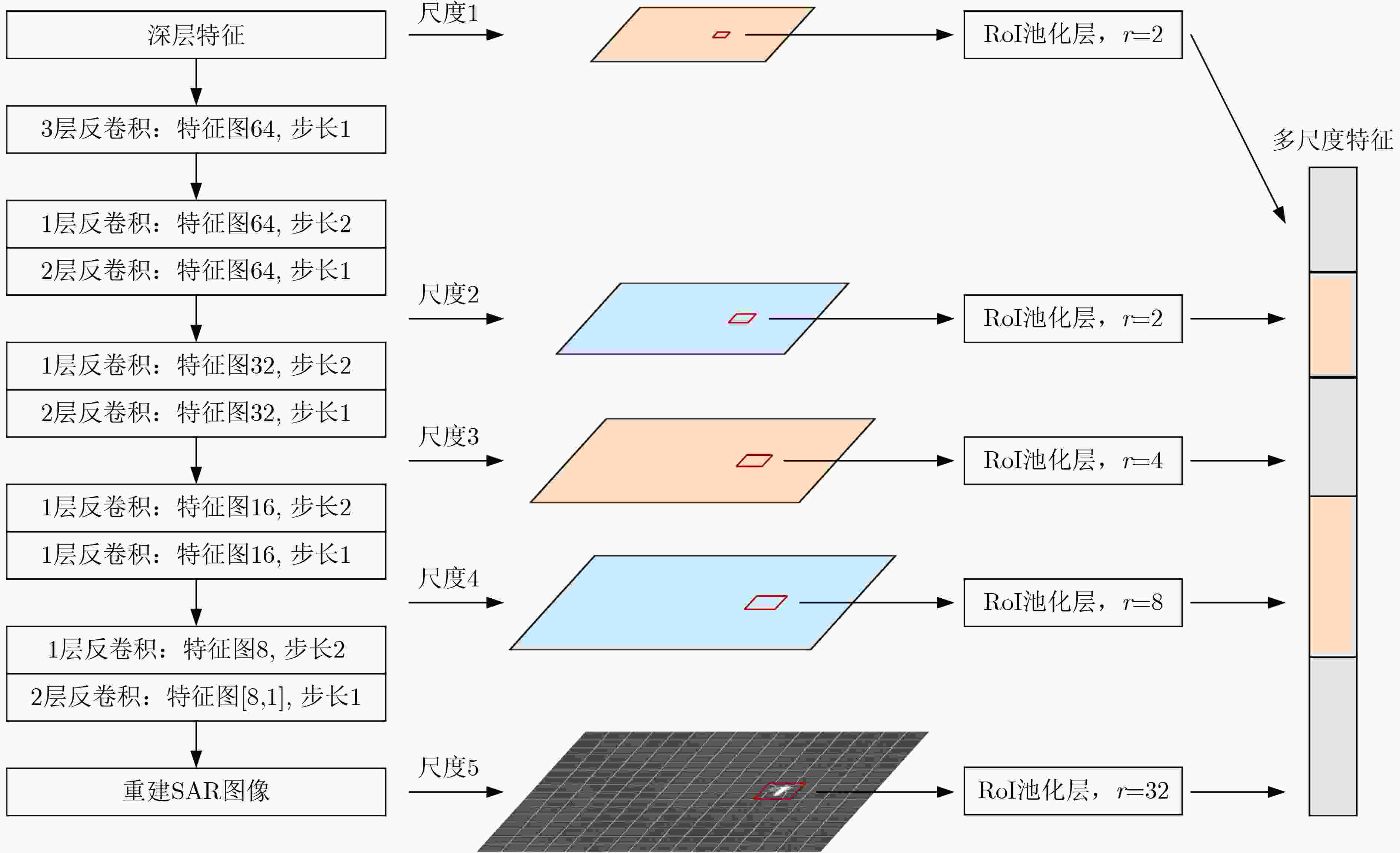
表 1 不同尺度特征图提取的特征维度
尺度 特征图维度 RoI池化尺寸$r$ RoI输出特征维度 不同尺度特征维度 总特征维度 尺度1 50×50×64 2 2×2×64 256 3072 尺度2 100×100×64 2 2×2×64 256 尺度3 200×200×32 4 4×4×32 512 尺度4 400×400×16 8 8×8×16 1024 尺度5 800×800×1 32 32×32×1 1024 算法1 同一类多个超像素块筛选流程 输入:超像素块最小候选区域$ \left\{ {{\delta _i},i = 1,2, \cdots ,P} \right\} $,其中$P$为该类对应的超像素块个数。 (1) 计算超像素块的亮度显著性$ \left\{ {{\eta _i}} \right\} $,其中$ {\eta _i} = {{{M_t}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{M_t}} M}} \right. } M} $,$ {M_t} $为该超像素块中像素值高于门限$ {V_1} $的像素点数量。 (2) 将$ \left\{ {{\eta _i}} \right\} $降序排列得到$ \left\{ {{\kappa _i}} \right\} $,若$ {{{\kappa _j}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{\kappa _j}} {{\kappa _{j + 1}}}}} \right. } {{\kappa _{j + 1}}}} > {V_2} $,则剔除第$ j $个超像素块之后的所有超像素块,其中$ j = 1,2,\cdots,P - 1 $,$ {V_2} $为显著性门限。 输出:筛选后的超像素块。 表 2 图注意力网络的详细建模信息
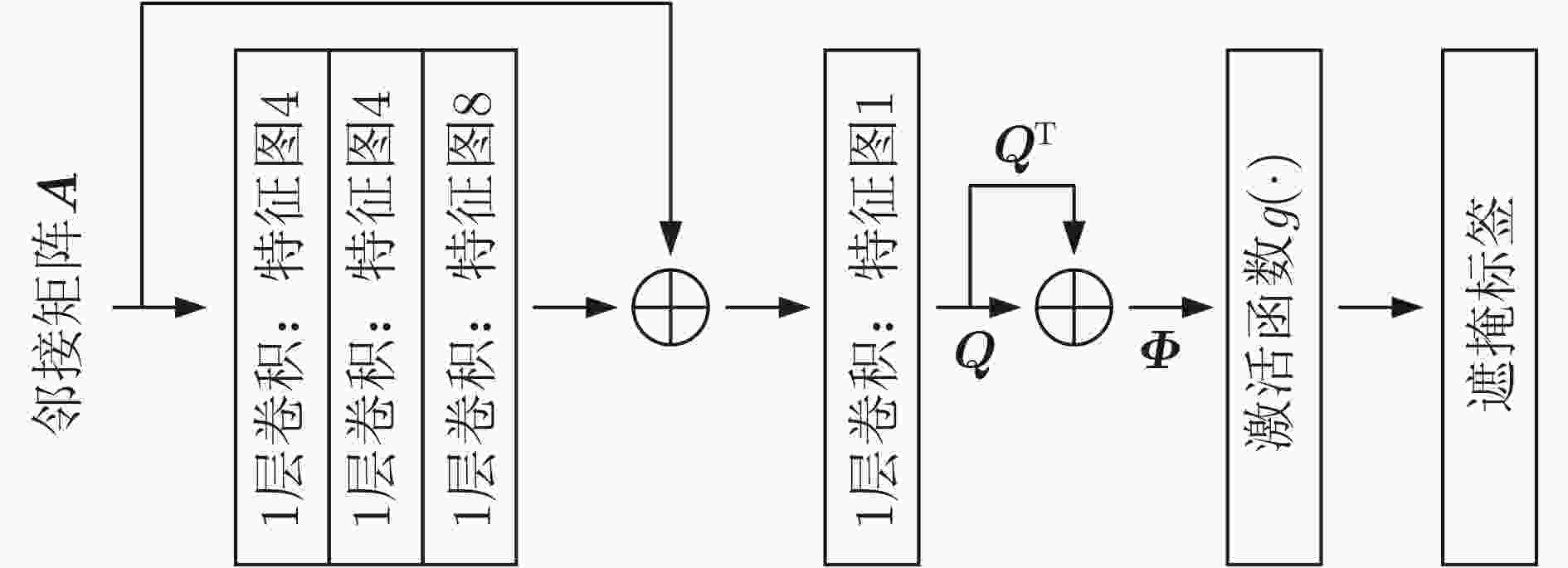
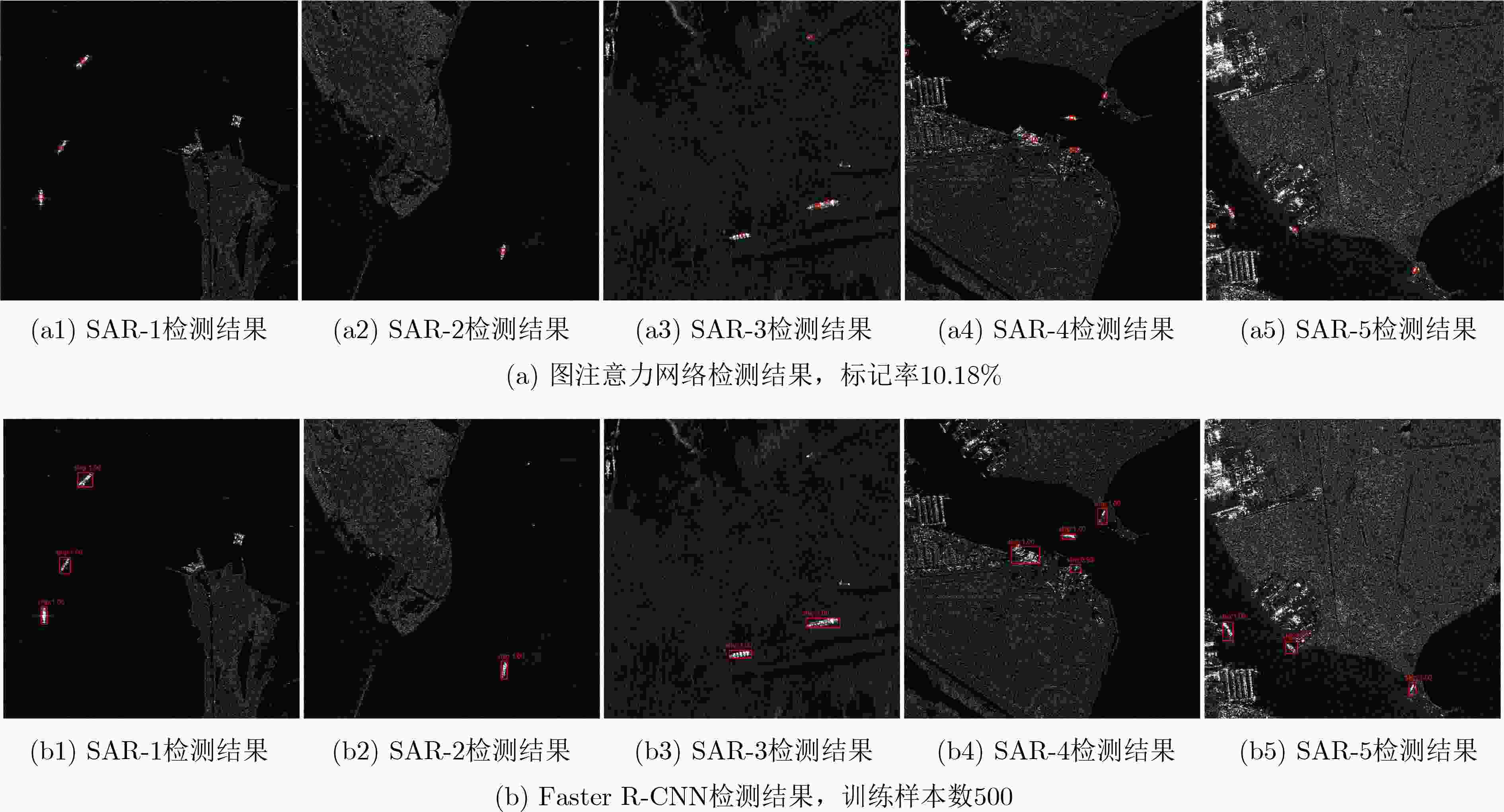
图注意力网络 有标记节点数 无标记节点数 总节点数 标记率(%) G1-1 1 000 (舰船500,杂波500) 4 410 5 410 18.48 G1-2 500 (舰船250,杂波250) 4 910 10.18 G1-3 200 (舰船100,杂波100) 4 610 4.34 表 3 测试集所有SAR图像舰船目标检测性能对比
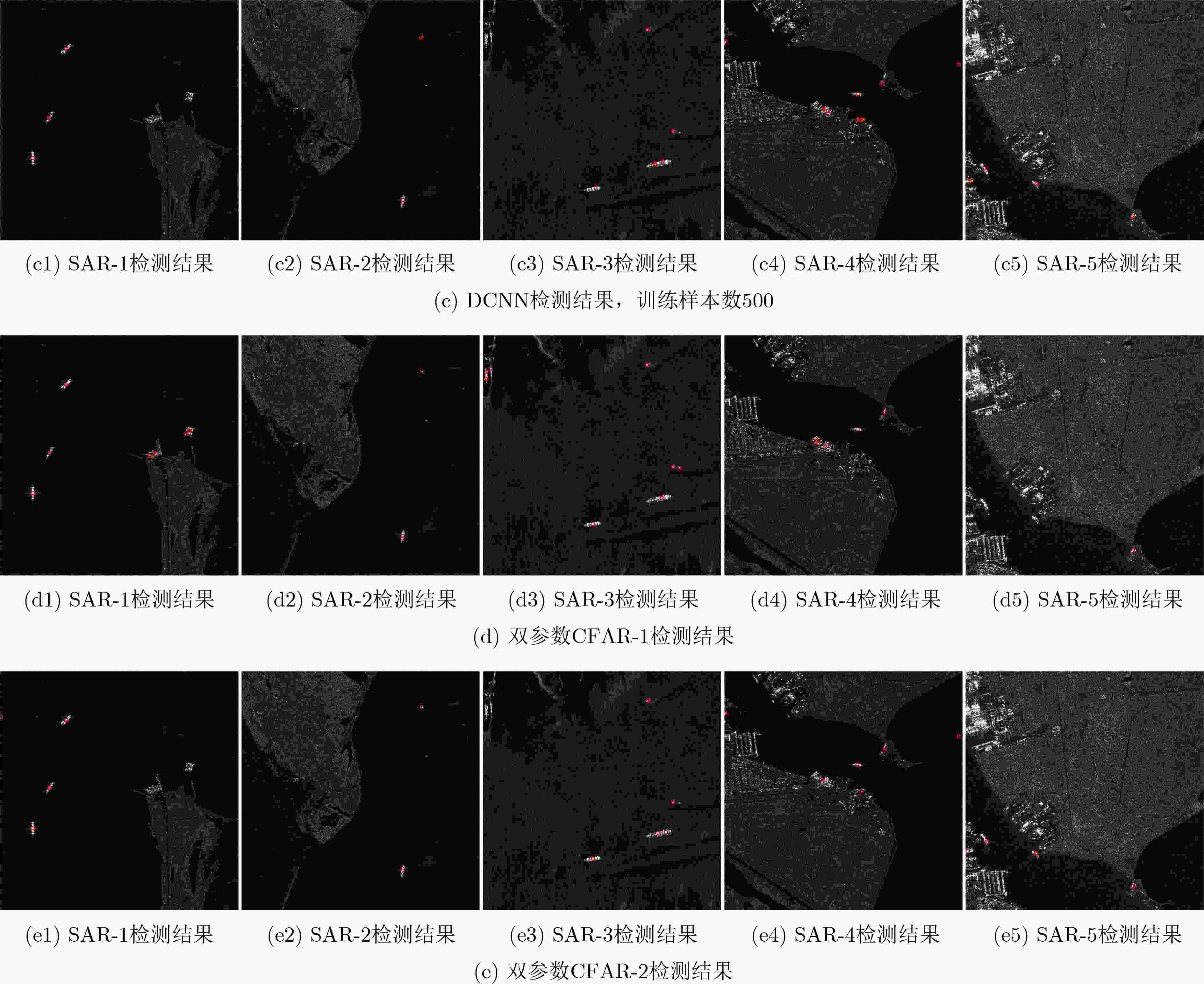
方法 总舰船目标数 漏警 虚警 GAT(标记率分别为18.48%, 10.18%和4.34%) 76 6/7/9 1/1/2 Faster R-CNN(训练样本分别为1000,500和200) 9/10/12 2/1/2 DCNN(训练样本分别为1000,500和200) 8/8/9 9/15/15 双参数CFAR-1 14 15 双参数CFAR-2 9 13 -
[1] 邱宇. 高分辨率SAR图像近海岸舰船目标检测与分类研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.QIU Yu. Nearshore ships detection and classification for high resolution SAR images[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. [2] GAO Gui. A Parzen-window-kernel-based CFAR algorithm for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2011, 8(3): 557–561. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2010.2090492 [3] 杜兰, 王兆成, 王燕, 等. 复杂场景下单通道SAR目标检测及鉴别研究进展综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104DU Lan, WANG Zhaocheng, WANG Yan, et al. Survey of research progress on target detection and discrimination of single-channel SAR images for complex scenes[J]. Journal of Radars, 2020, 9(1): 34–54. doi: 10.12000/JR19104 [4] WANG Xueqian, LI Gang, ZHANG Xiaoping, et al. A fast CFAR algorithm based on density-censoring operation for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 1085–1089. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3082034 [5] AI Jiaqiu, MAO Yuxiang, LUO Qiwu, et al. Robust CFAR ship detector based on bilateral-trimmed-statistics of complex ocean scenes in SAR imagery: A closed-form solution[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(3): 1872–1890. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3050654 [6] 付晓雅, 王兆成. 结合场景分类的近岸区域SAR舰船目标快速检测方法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(12): 2123–2130. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.019FU Xiaoya and WANG Zhaocheng. SAR ship target rapid detection method combined with scene classification in the inshore region[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(12): 2123–2130. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.12.019 [7] HOU Biao, YANG Wei, WANG Shuang, et al. SAR image ship detection based on visual attention model[C]. 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 2013: 2003–2006. [8] WANG Yinghua and LIU Hongwei. A hierarchical ship detection scheme for high-resolution SAR images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(10): 4173–4184. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2012.2189011 [9] LENG Xiangguang, JI Kefeng, ZHOU Shilin, et al. Ship detection based on complex signal kurtosis in single-channel SAR imagery[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6447–6461. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2906054 [10] CHEN Shiyuan, LI Xiaojiang, CHI Shaoquan, et al. Ship target discrimination in SAR images based on BOW model with multiple features and spatial pyramid matching[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 166071–166082. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3022642 [11] YANG Xulei and DING Jie. A computational framework for iceberg and ship discrimination: Case study on Kaggle competition[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 82320–82327. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2990985 [12] ZHAO Yan, ZHAO Lingjun, XIONG Boli, et al. Attention receptive pyramid network for ship detection in SAR images[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2020, 13: 2738–2756. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2020.2997081 [13] WU Zonghan, PAN Shirui, CHEN Fengwen, et al. A comprehensive survey on graph neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems 2021, 32(1): 4–24. [14] VELICKOVIC R, CUCURULL G, CASANOVA A, et al. Graph attention networks[C]. The 6th International Conference on Learning Representations, Vancouver, Canada, 2018. [15] ACHANTA R, SHAJI A, SMITH K, et al. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(11): 2274–2282. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120 [16] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137–1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [17] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [18] WEI Shunjun, ZENG Xiangfeng, QU Qizhe, et al. HRSID: A high-resolution SAR images dataset for ship detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 120234–120254. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005861 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
