Image Processing-Driven Spectrum Sensing with Small Training Samples
-
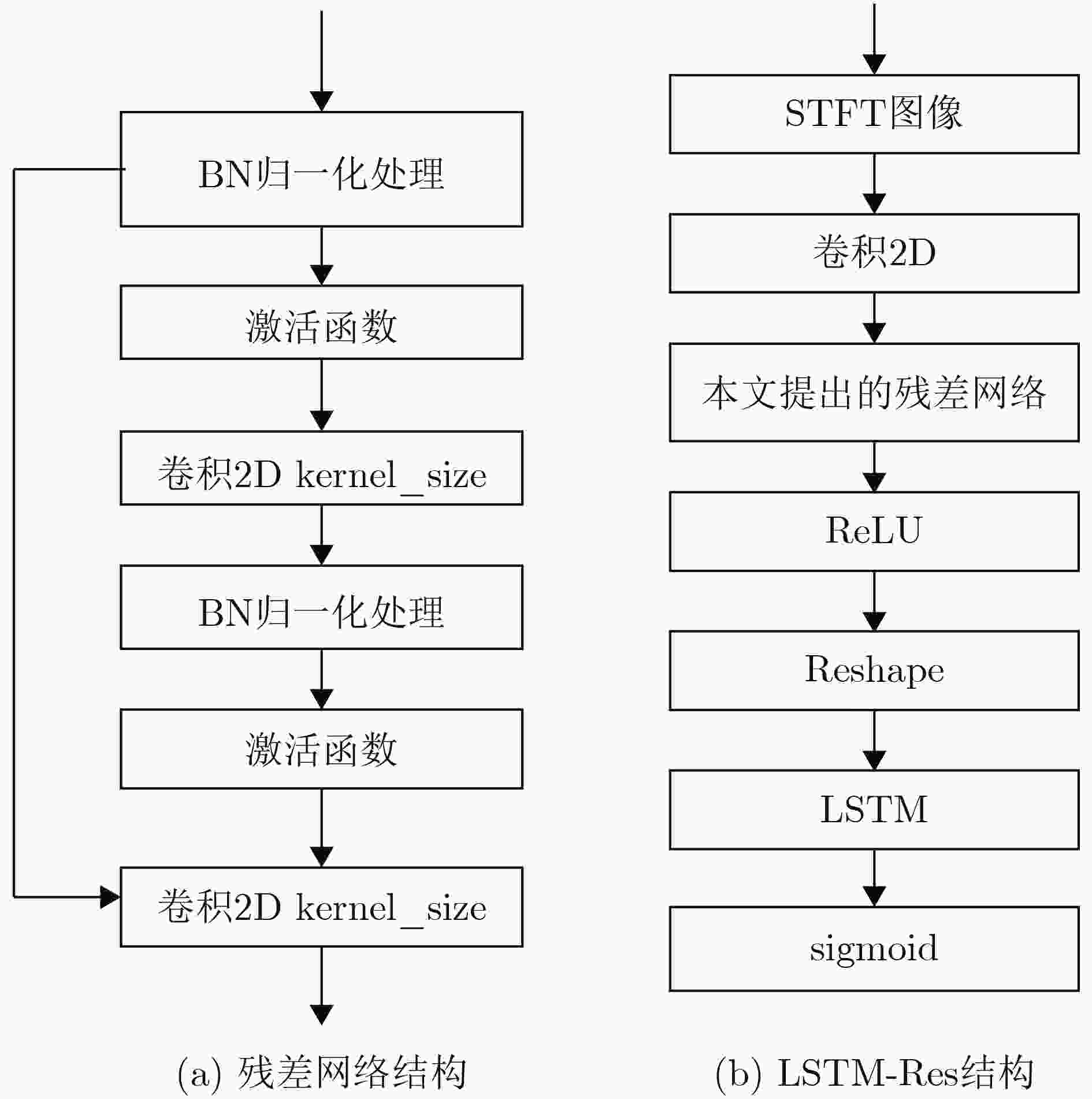
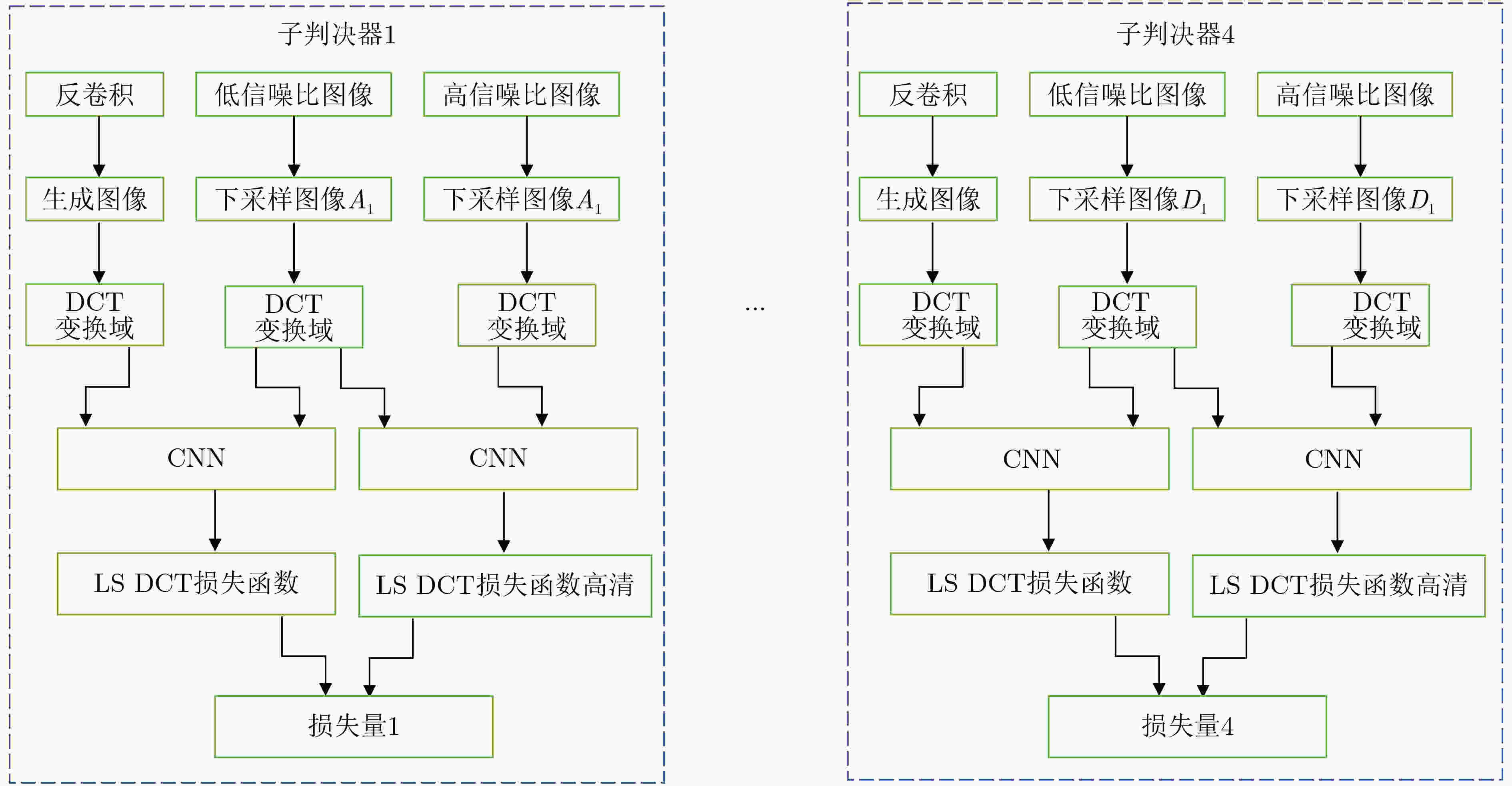
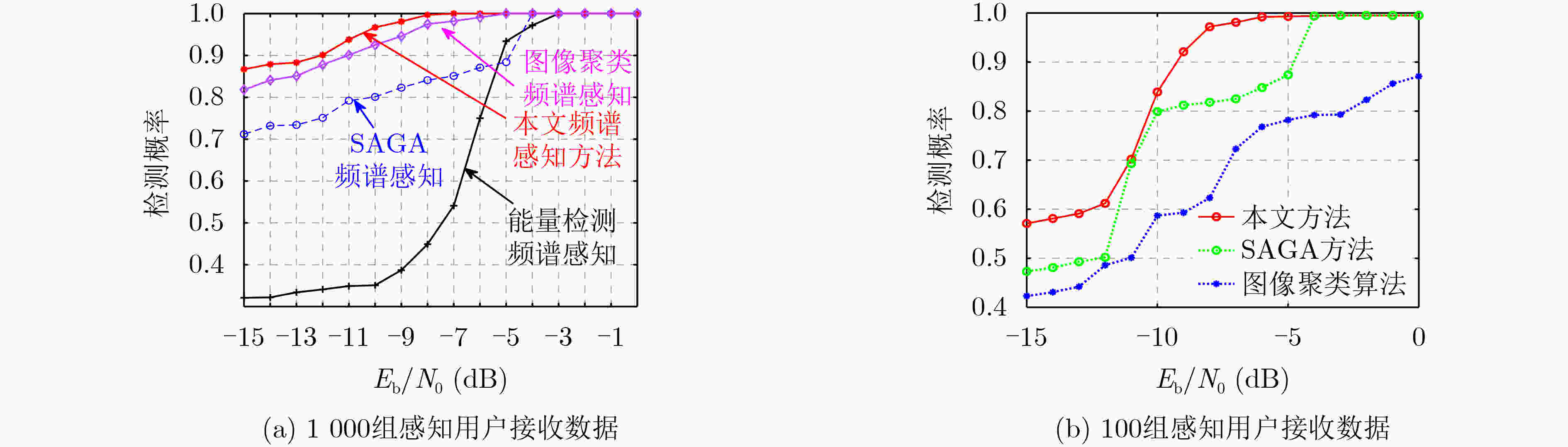
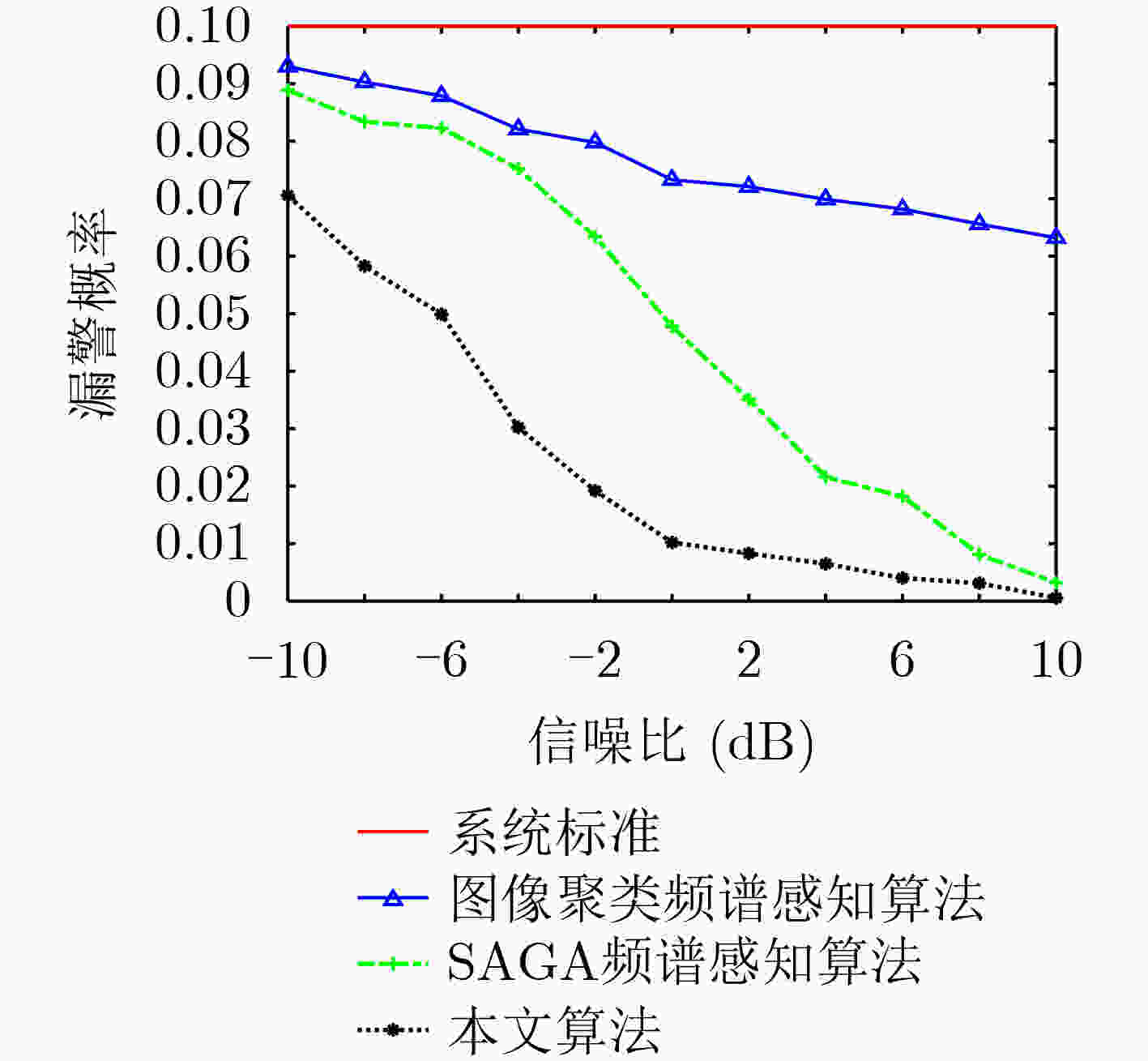
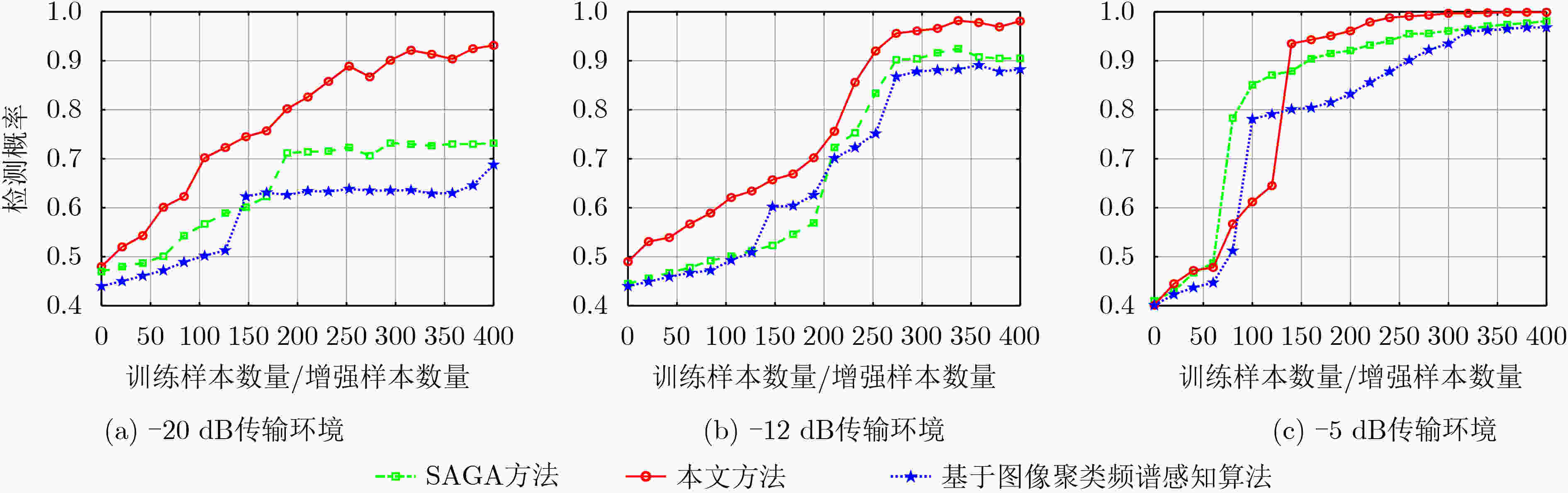
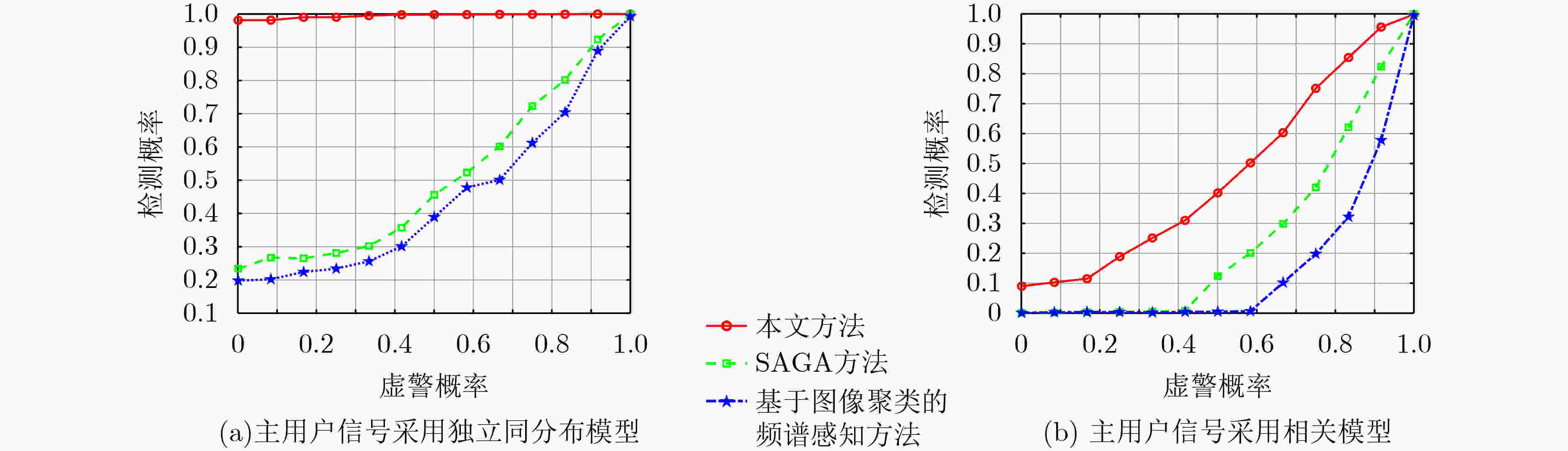
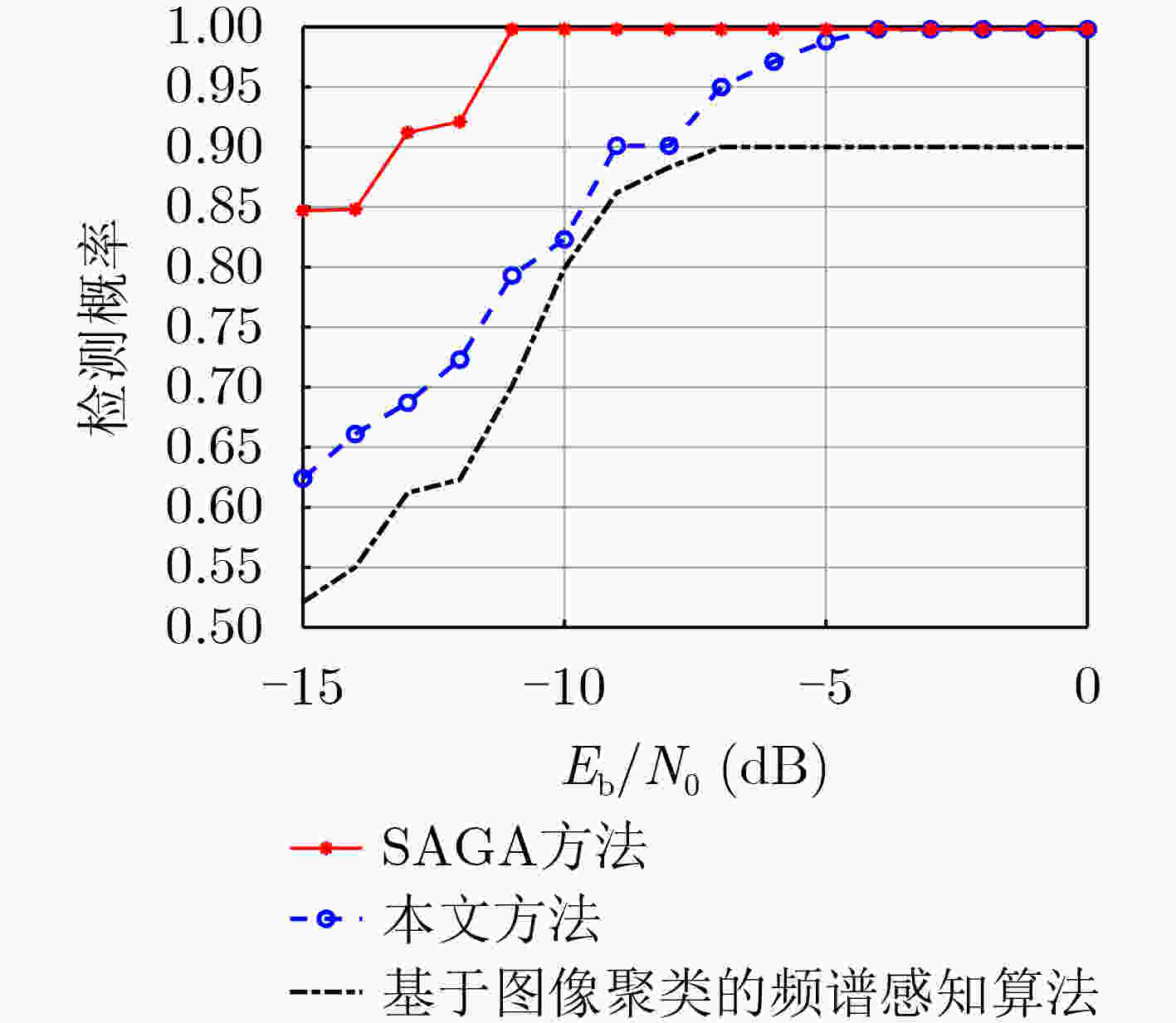
摘要: 针对强噪声环境下频谱感知方法计算复杂度高、难以获取大量标注样本、检测准确率低等问题,该文提出由图像去噪和图像分类思想驱动的频谱感知方法(IDCSS)。首先,对感知用户的接收信号进行时频变换,将无线电数值信号转换为图像。强噪声环境下感知用户接收信号图像与噪声图像相关度高,因此搭建生成对抗网络(GAN)来增加低信噪比下接收信号样本的数量,提高图像的质量。在生成器中,利用残差-长短时记忆网络取代生成网络U-Net结构中的跳跃连接,对图像进行去噪、提取感知用户接收信号图像的多尺度特征、建立基于熵的损失函数来构建网络的抗噪能力;在判决器中,设计适用无线电图像信号的多维度判决器来增强生成图像的质量、保留低信噪比感知用户信号的图像细节。最后利用分类器识别频谱占用状态。仿真结果表明,与现有频谱感知算法相比,所提算法具有较好的检测性能。Abstract: To resolve the problems of high computational complexity in strong noise environment, infeasibility of gaining large number of labeled samples and low detection probability, an Image Denoising and Classification driven Spectrum Sensing (IDCSS) method is proposed. Firstly, time-frequency transformation is employed to convert radio numerical signals into images. Then, as received signals of cognitive users and noise are highly correlated under strong noise environments, a novel Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) is designed to enhance the number and quality of samples of cognitive user signals. In the generator, residual-long-short-term memory network is designed to replace U-Net skip connection, realizing denoising and multi-scale features extraction. Loss function based on entropy is designed to optimize robustness to noise. A multi-dimensional discriminator is designed to enhance the quality of the generated image and retain the image details of the low signal-to-noise ratio cognitive user signals. Finally, the generated high-quality samples are used as labeled data, and the real samples combine to train the classifier to realize the recognition and classification of the spectrum occupancy state. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm has better detection performance by comparing it with the state-of-the-art methods.
-
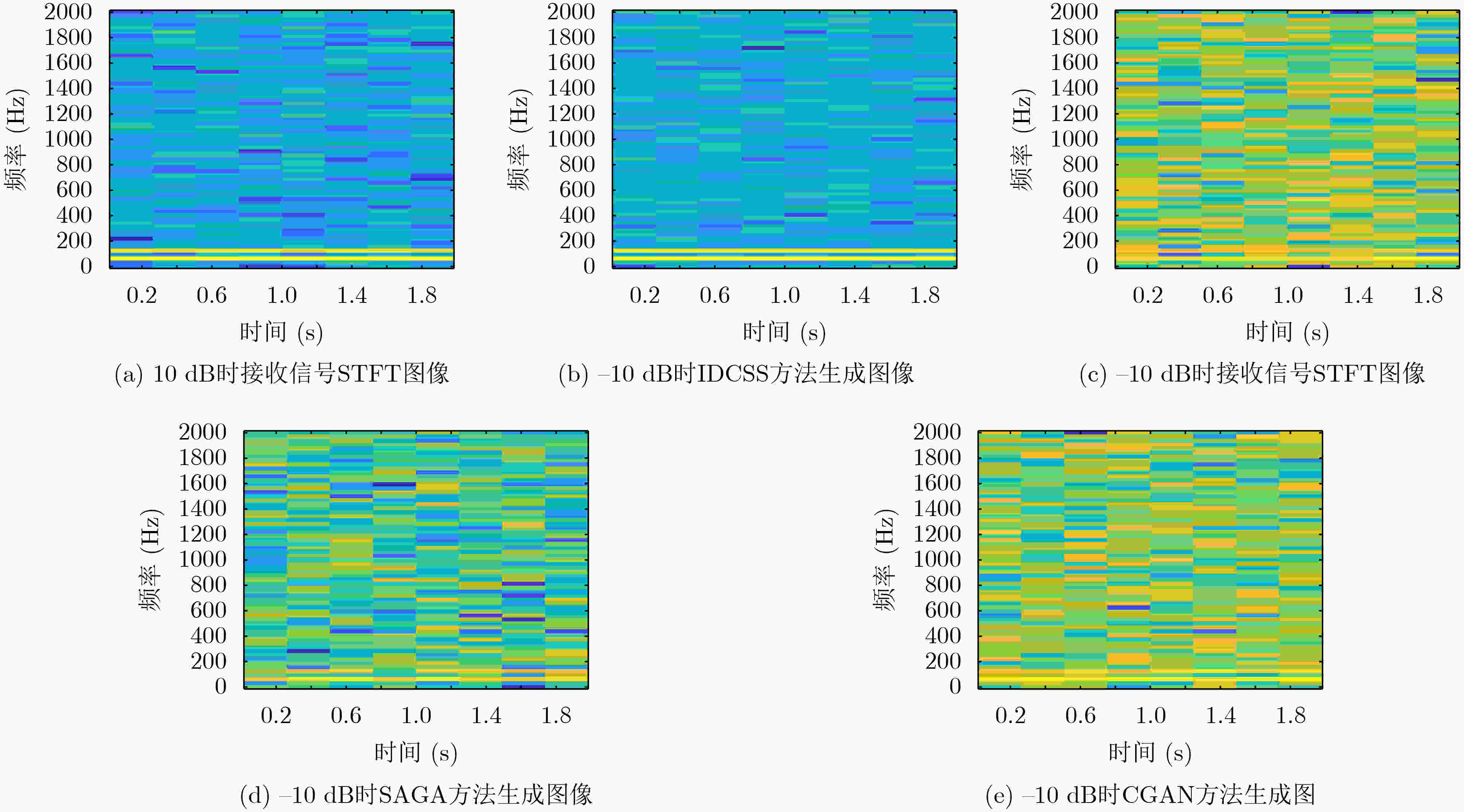
表 1 3种方法生成图像质量比照结果
所用方法 PSNR(dB) SSIM FID CGAN 15.6600 0.6500 87.1200 SAGA 22.3500 0.7200 52.8100 IDCSS 24.2400 0.7900 46.1300 表 2 本文算法生成器时间复杂度
$\sim {O}\left( {4.365 \times {{10}^7}} \right)$ M K Cl–1 Cl M1=8 K1=3 C1=64 C2=128 M2=16 K2=3 C2=128 C3=64 M3=32 K3=3 C3=64 C4=32 M4=64 K4=3 C4=32 C5=1 表 3 本文算法判决器时间复杂度
$ \sim O\left( {5.78 \times {{10}^7}} \right) $ M K Cl–1 Cl M1=64 K1=3 C1=1 C2=32 M2=32 K2=3 C2=32 C3=64 M3=16 K3=3 C3=64 C4=128 M4=8 K4=3 C4=128 C5=256 表 4 训练及感知时间(s)对比
方法 离线训练时间 在线感知时间 图像聚类 40.13 4.01 SAGA 20.05 2.27 本文方法 18.74 1.43 -
[1] 陈勇, 张余, 柳永祥. 电磁频谱战发展剖析与思考[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2018, 4(4): 319–324.CHEN Yong, ZHANG Yu, and LIU Yongxiang. Analysis and thinking on the development of electromagnetic spectrum warfare[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2018, 4(4): 319–324. [2] XIONG Tianyi, YAO Yudong, REN Yujue, et al. Multiband spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks with secondary user hardware limitation: Random and adaptive spectrum sensing strategies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2018, 17(5): 3018–3029. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2018.2805729 [3] 张莹, 滕伟, 韩维佳, 等. 认知无线电频谱感知技术综述[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2015, 41(3): 12–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1131.2015.07.056ZHANG Ying, TENG Wei, HAN Weijia, et al. Review of spectrum sensing techniques in cognitive radio networks[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2015, 41(3): 12–16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1131.2015.07.056 [4] CHEN Hongsong, ZHANG Yongpeng, CAO Yongrui, et al. Security issues and defensive approaches in deep learning frameworks[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2021, 26(6): 894–905. doi: 10.26599/TST.2020.9010050 [5] TANG Hao, LIU Hong, XIAO Wei, et al. When dictionary learning meets deep learning: Deep dictionary learning and coding network for image recognition with limited data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(5): 2129–2141. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2997289 [6] WANG Xi, TANG Fangyao, CHEN Hao, et al. UD-MIL: Uncertainty-driven deep multiple instance learning for OCT image classification[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2020, 24(12): 3431–3442. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2983730 [7] 盖建新, 薛宪峰, 吴静谊, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的协作频谱感知方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(10): 2911–2919. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201005GAI Jianxin, XUE Xianfeng, WU Jingyi, et al. Cooperative spectrum sensing method based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(10): 2911–2919. doi: 10.11999/JEIT201005 [8] 岳文静, 刘文博, 陈志. 基于图像K-means聚类分析的频谱感知算法[J]. 信号处理, 2020, 36(2): 203–209. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.02.006YUE Wenjing, LIU Wenbo, and CHEN Zhi. Spectrum sensing algorithm based on image K-means clustering analysis[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2020, 36(2): 203–209. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2020.02.006 [9] DAVASLIOGLU K and SAGDUYU Y E. Generative adversarial learning for spectrum sensing[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Kansas City, USA, 2018: 1–6. [10] LIU Zheng, JING Xiaojun, ZHANG Ronghui, et al. Spectrum sensing based on deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[C]. 2021 International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, Harbin, China, 2021: 796–801. [11] MAO Xudong, LI Qing, XIE Haoran, et al. Least squares generative adversarial networks[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 2017: 2813–2821. [12] 麻文刚, 张亚东, 郭进. 基于LSTM与改进残差网络优化的异常流量检测方法[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(5): 23–40. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021109MA Wengang, ZHANG Yadong, and GUO Jin. Abnormal traffic detection method based on LSTM and improved residual neural network optimization[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(5): 23–40. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021109 [13] 蒲悦逸, 王文涵, 朱强, 等. 基于CNN-ResNet-LSTM模型的城市短时交通流量预测算法[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2020, 43(5): 9–14. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2019-243PU Yueyi, WANG Wenhan, ZHU Qiang, et al. Urban short-term traffic flow prediction algorithm based on CNN-ResNet-LSTM model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020, 43(5): 9–14. doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2019-243 -





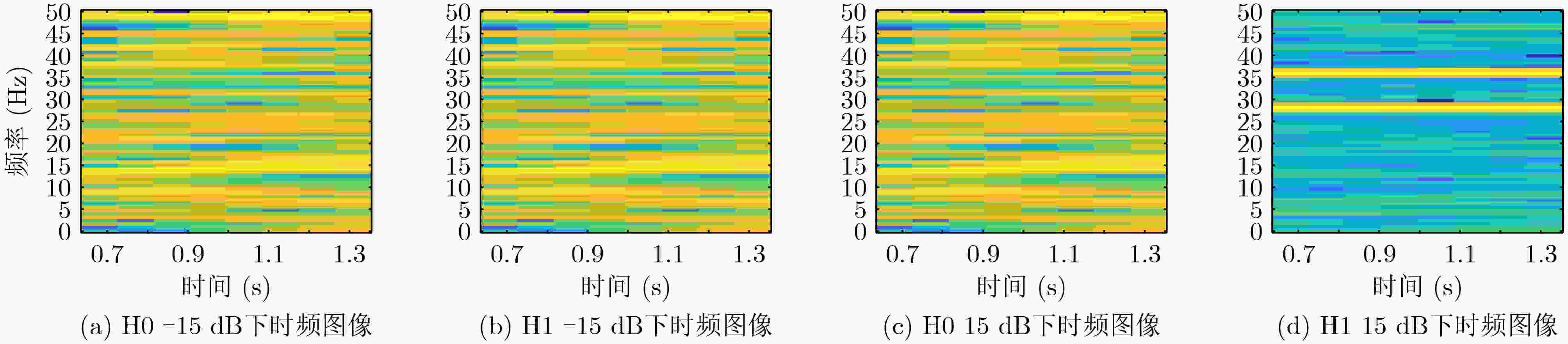
 下载:
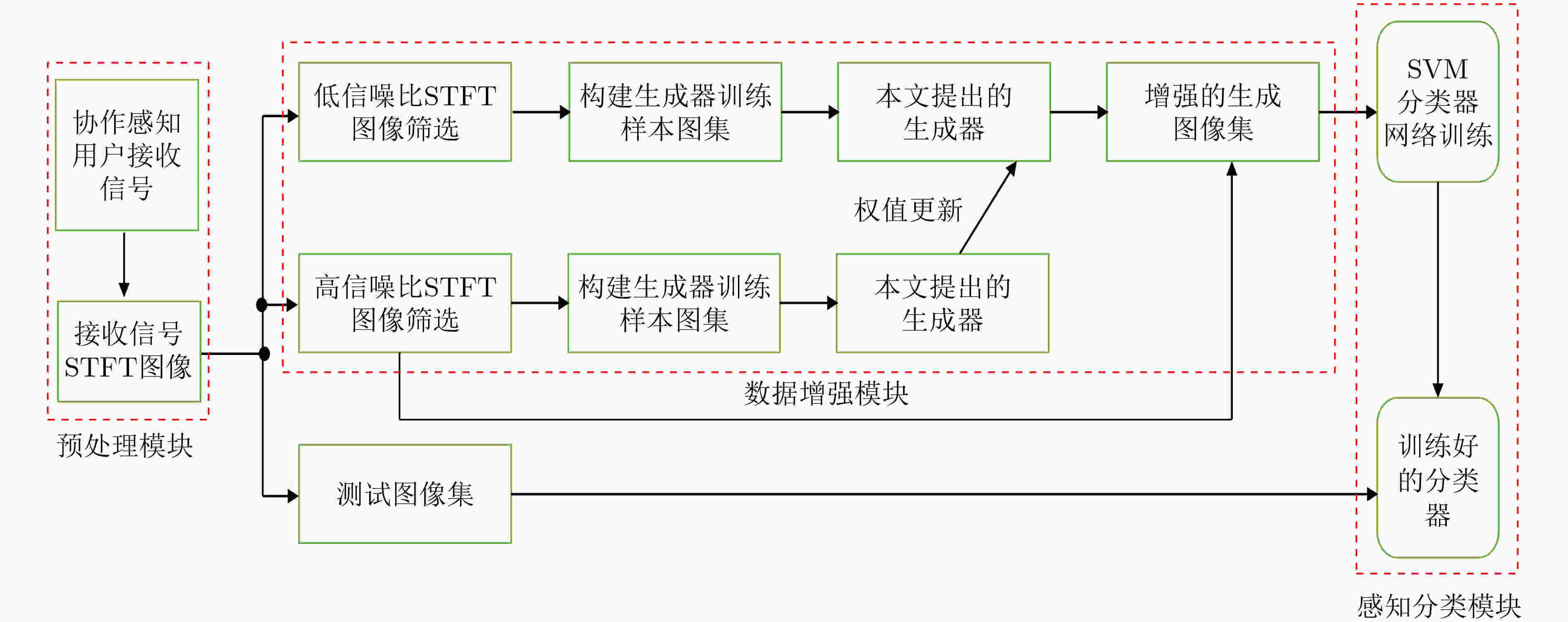
下载:
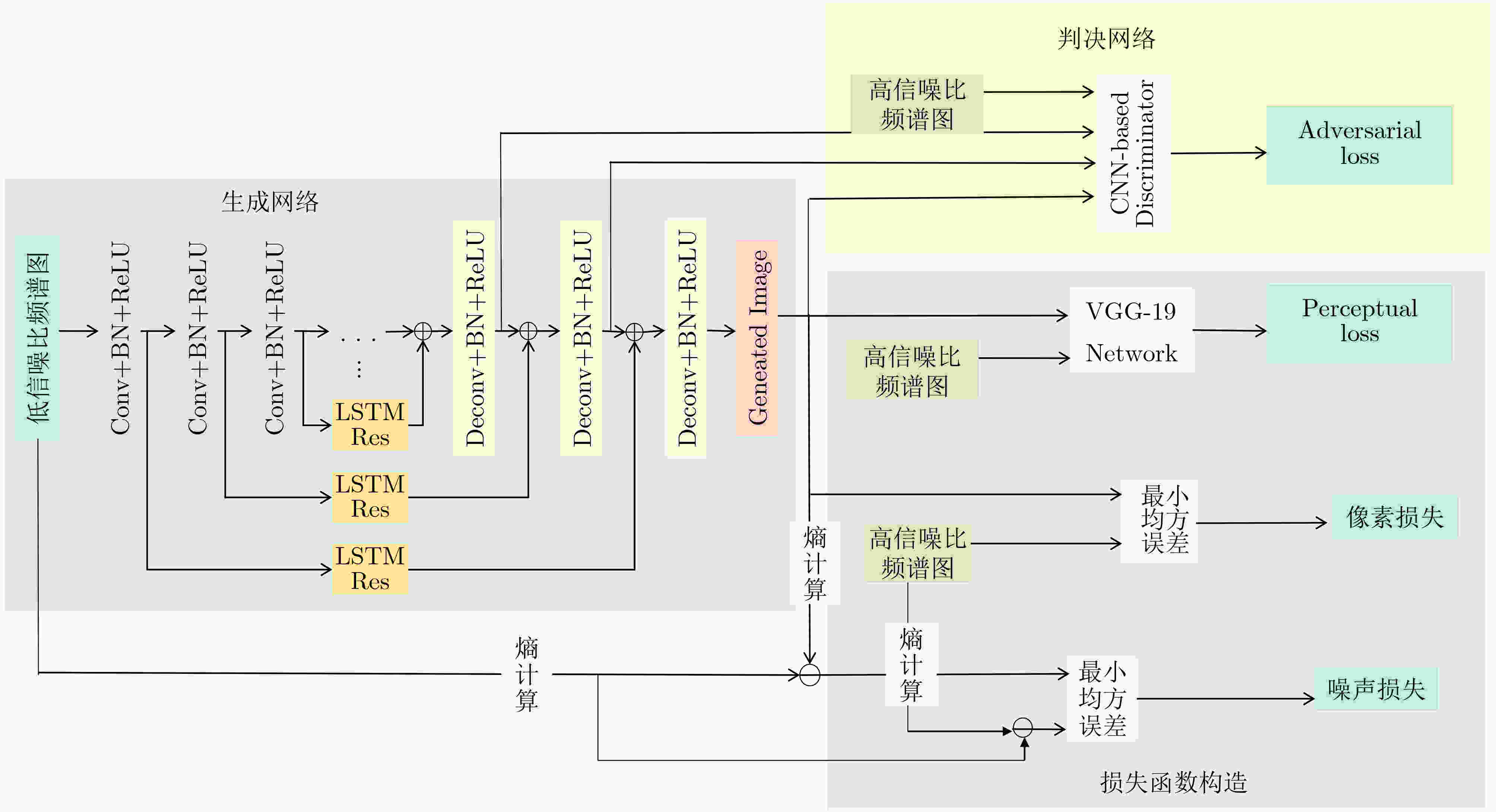




 下载:
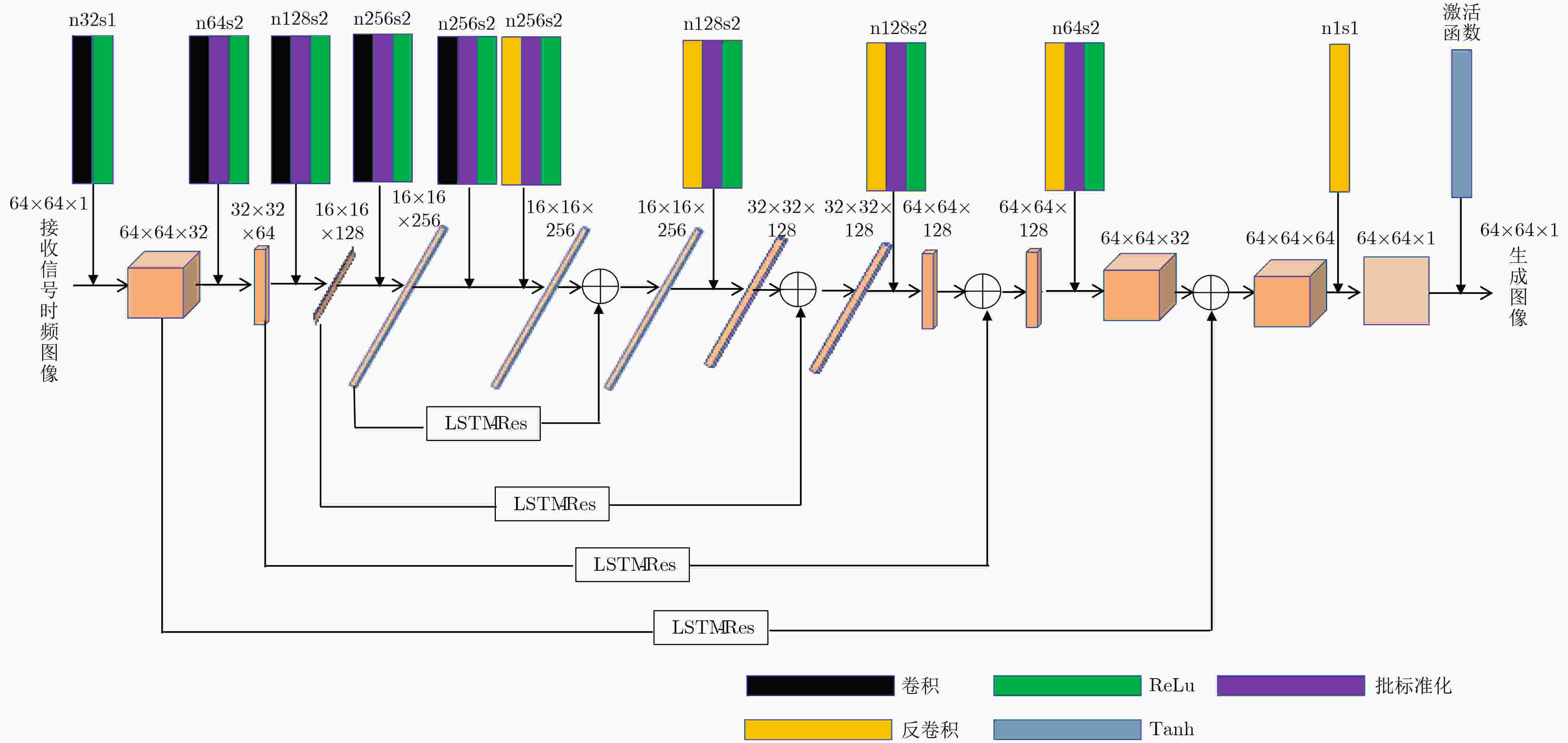
下载:
