Irregular Quasi Cyclic Low Density Parity Check Code Construction Based on Basis Matrix Arrangement Optimization Algorithm
-
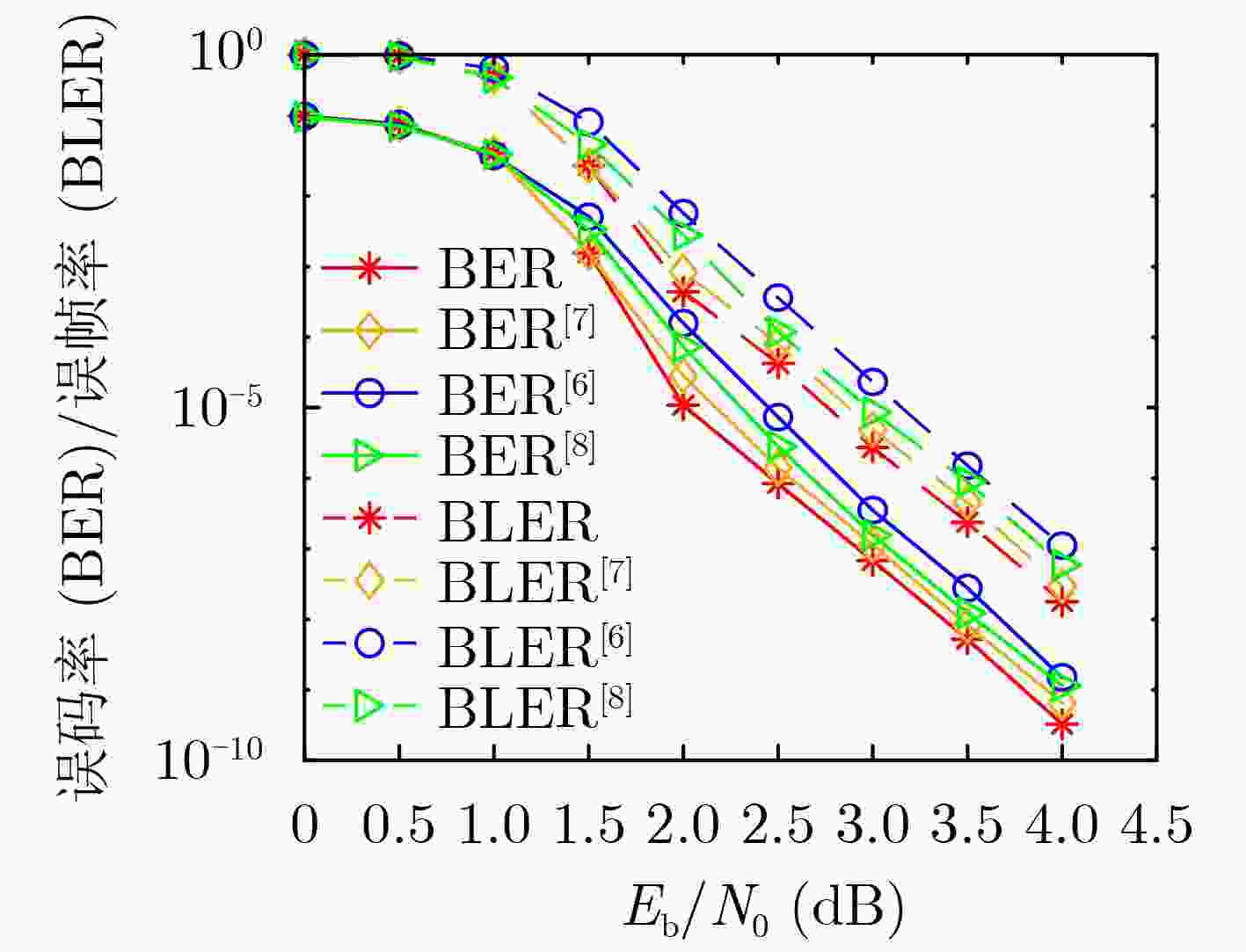
摘要: 为了提升非规则准循环低密度奇偶校验(QC-LDPC)码的误码率性能、降低构造算法的复杂度,该文提出一种基于基矩阵排列优化算法的非规则QC-LDPC码构造方法。首先,利用基于外部信息传递(EXIT)图的阈值分析算法得到满足码率和列重要求的非规则QC-LDPC码的最优度分布,然后将围长和短环数量作为新的约束条件对具有最优度分布的码集进行分析,得到具有最优度分布和最少短环数量的最优基矩阵排列结构,最后,根据得到的基矩阵对规则指数矩阵进行置零操作得到目标非规则QC-LDPC码。该构造方法相对于随机构造方法具有更低的实现复杂度,同时可以通过改变算法的参数值实现码长和码率的灵活设计。仿真结果表明,与现有的一些构造方法相比,所提方法构造的非规则QC-LDPC码在加性高斯白噪声(AWGN)信道上具有更好的误码率性能。
-
关键词:
- 准循环低密度奇偶校验码 /
- 非规则 /
- 基矩阵排列优化算法 /
- 围长 /
- 外部信息传递
Abstract: In order to improve the bit error rate performance of the irregular Quasi-Cyclic Low-Density Parity-Check (QC-LDPC) codes and reduce the complexity of the construction algorithm, an optimization algorithm based on basis matrix arrangement is proposed. Firstly, the optimal degree distribution of irregular QC-LDPC codes satisfying the code rate and column weight requirements is obtained by using the threshold analysis algorithm based on EXtrinsic Information Transfer (EXIT) chart. Then by using the girth and the number of short-cycles as new indicators, a class of codes with the same optimal degree distribution is analyzed. The basic matrix arrangement structure with the optimal degree distribution and the least number of short-cycles is obtained. Finally, according to the obtained base matrix, the corresponding zeroing operation is performed on the regular index matrix to obtain the target irregular QC-LDPC code. Compared with the random construction method, the proposed construction method has lower implementation complexity. At the same time, the code length and code rate can be flexibly changed by changing the parameter values of the algorithm. Simulation results show that, compared with some existing construction methods, the irregular QC-LDPC codes constructed by the proposed method have better bit error rate performance on Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN) channels. -
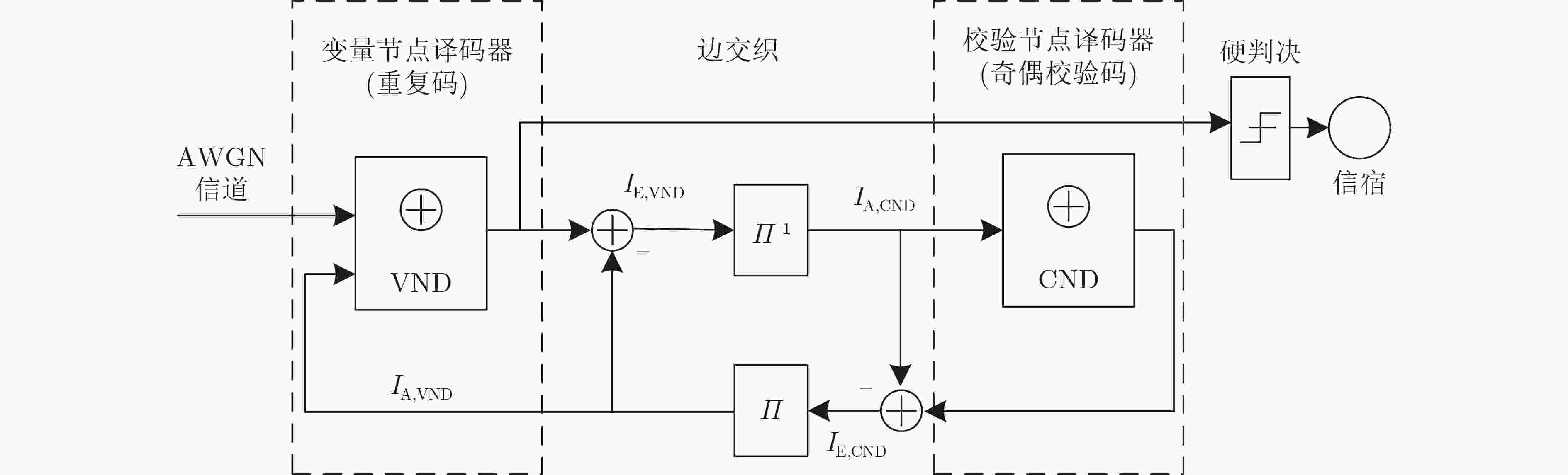
算法1 基于基矩阵结构的度分布多项式对生成算法 输入:基矩阵${\boldsymbol{B}}$ 输出:变量节点度分布多项式$\lambda \left( x \right)$,校验节点度分布多项式$\rho \left( x \right)$ (1) 基矩阵列数$L = {\rm{size} }\left( {{\boldsymbol{B}},1} \right)$,基矩阵行数$J = {\rm{size} }\left( {{\boldsymbol{B}},2} \right)$ (2) ${\rm{for} }{\text{ } }i = 1{\text{ } }{\rm{to}}{\text{ } }L$ (3) ${\rm{for} }{\text{ } }j = 1{\text{ } }{\rm{to}}{\text{ } }J$ (4) ${\rm{if}}{\text{ } }{b_{i,j} } = 1$ (5) 保存当前列的列重,${\rm{col}}\left( i \right) = {\rm{col}}\left( i \right) + 1$ (6) $ {\rm{end}} $ (7) $ {\rm{end}} $ (8) $ {\rm{end}} $ (9) ${\rm{for} }{\text{ } }j = 1{\text{ } }{\rm{to}}{\text{ } }J$ (10) ${\rm{for} }{\text{ } }i = 1{\text{ } }{\rm{to}}{\text{ } }L$ (11) ${\rm{if}}{\text{ } }{b_{i,j} } = 1$ (12) 保存当前行的行权重,${\rm{row}}\left( j \right) = {\rm{row}}\left( j \right) + 1$ (13) $ {\rm{end}} $ (14) $ {\rm{end}} $ (15) $ {\rm{end}} $ (16) 根据列权重记录值计算变量节点的度分布多项式:
$\lambda \left( x \right) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^L {\left( { { { {\rm{col} }\left( i \right)} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { {{\rm{col}}\left( i \right)} {\sum\limits_{i = 1}^L { {\rm{col} }\left( i \right)} } } } \right. } {\sum\limits_{i = 1}^L {{\rm{col}}\left( i \right)} } } } \right)} {x^{ {\rm{col} }\left( i \right) - 1} }$(17) 根据行权重记录值计算校验节点的度分布多项式:
$\rho \left( x \right) = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{j = 1}^J {\left( { { {{\rm{row}}\left( j \right)} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom { {{\rm{row}}\left( j \right)} {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^J {{\rm{row}}\left( j \right)} } } } \right. } {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^J {{\rm{row}}\left( j \right)} } } } \right)} {x^{{\rm{row}}\left( j \right) - 1} }$表 1 相同规则指数矩阵下基矩阵不同排列对应的各短环数量
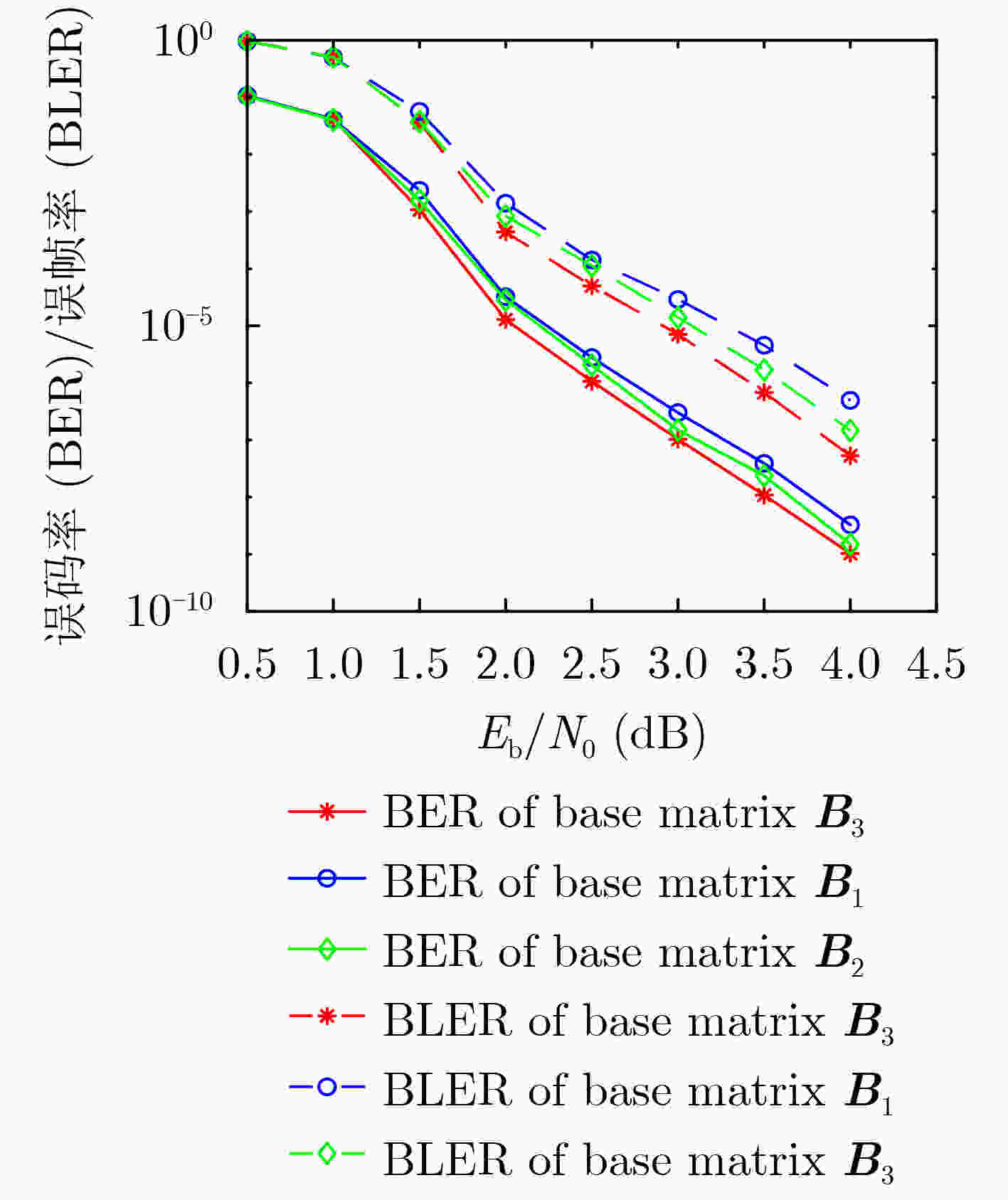
基矩阵 6-cycle 8-cycle 10-cycle 基矩阵 6-cycle 8-cycle 10-cycle ${{\boldsymbol{B}}_1} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } 0&1&1&1&1&0&1&1 \\ 1&0&1&1&0&1&1&1 \\ 0&1&1&1&1&0&1&1 \\ 1&0&1&1&0&1&1&1 \end{array} } \right]$ 0 33P 123P ${{\boldsymbol{B}}_3} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } 1&0&1&0&1&1&1&1 \\ 0&1&0&1&1&1&1&1 \\ 1&0&0&1&1&1&1&1 \\ 0&1&1&0&1&1&1&1 \end{array} } \right]$ 0 16P 59P ${{\boldsymbol{B}}_2} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } 0&1&1&1&0&1&1&1 \\ 1&0&1&1&1&0&1&1 \\ 1&0&1&1&0&1&1&1 \\ 0&1&1&1&1&0&1&1 \end{array} } \right]$ 0 23P 115P ${{\boldsymbol{B}}_4} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c} } 0&1&1&0&1&1&1&1 \\ 1&0&0&1&1&1&1&1 \\ 1&0&1&0&1&1&1&1 \\ 0&1&0&1&1&1&1&1 \end{array} } \right]$ 0 17P 55P -
[1] GALLAGER R G. Low-density parity-check codes[J]. IRE Transactions on Information Theory, 1962, 8(1): 21–28. doi: 10.1109/TIT.1962.1057683 [2] 康婧, 安军社, 王冰冰. 星地高速数传系统低复杂度可重构LDPC编码器设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3727–3734. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200118KANG Jing, AN Junshe, and WANG Bingbing. Low complexity and reconfigurable LDPC encoder for high-speed satellite-to-ground data transmissions[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3727–3734. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200118 [3] 张顺外, 付勇峰. 编码协作系统准循环重复累积码的联合设计与性能分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1298–1305. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190990ZHANG Shunwai and FU Yongfeng. Joint design of QC-RA codes and performance analysis of coded cooperation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1298–1305. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190990 [4] WANG Liqian, WANG Dongdong, NI Yongjing, et al. Design of irregular QC-LDPC code based multi-level coded modulation scheme for high speed optical communication systems[J]. China Communications, 2019, 16(5): 106–120. doi: 10.23919/j.cc.2019.05.009 [5] KHARIN A, DRYAKHLOV A, MIROKHIN E, et al. Irregular QC-LDPC codes generation based on EMD maximization criterion for protograph[C]. 2020 9th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing (MECO), Budva, Montenegro, 2020: 1–4. [6] WANG Dongdong, GUO Yantao, WANG Zhihui, et al. PEG based construction of irregular QC-LDPC codes by jointly optimizing the girth and the number and ACE of short cycles[C]. 2019 18th International Conference on Optical Communications and Networks (ICOCN), Huangshan, China, 2019: 1–3. [7] KARIMI B and BANIHASHEMI A H. Construction of irregular protograph-based QC-LDPC codes with low error floor[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(1): 3–18. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.3028302 [8] WANG Dongdong, WANG Liqian, CHEN Xue, et al. Construction of QC-LDPC codes based on pre-masking and local optimal searching[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22(6): 1148–1151. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2756640 [9] WANG Ruyan, LI Yong, ZHAO Hui, et al. Construction of girth-eight quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check codes with low encoding complexity[J]. IET Communications, 2016, 10(2): 148–153. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2015.0056 [10] 徐恒舟, 朱海, 冯丹, 等. 低秩循环矩阵的构造方法及其关联的多元LDPC码[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 85–91. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200351XU Hengzhou, ZHU Hai, FENG Dan, et al. Construction of low-rank circulant matrices and their associated nonbinary LDPC codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 85–91. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200351 [11] HASHEMI Y and BANIHASHEMI A H. Characterization of elementary trapping sets in irregular LDPC codes and the corresponding efficient exhaustive search algorithms[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2018, 64(5): 3411–3430. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2018.2799627 [12] SARIDUMAN A, PUSANE A E, and TAŞKIN Z C. On the construction of regular QC-LDPC codes with low error floor[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(1): 25–28. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2953058 [13] TEN BRINK S. Convergence behavior of iteratively decoded parallel concatenated codes[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2001, 49(10): 1727–1737. doi: 10.1109/26.957394 [14] TEN BRINK S, KRAMER G, and ASHIKHMIN A. Design of low-density parity-check codes for modulation and detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2004, 52(4): 670–678. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2004.826370 [15] 洪少华, 马文卓, 王琳. 截断式原模图低密度奇偶校验卷积码边扩展优化[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(1): 45–50. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200350HONG Shaohua, MA Wenzhuo, and WANG Lin. Edge spreading optimization for terminated protograph-based low-density parity-check convolutional codes[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(1): 45–50. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200350 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
