Attribute-Base Signcryption Scheme Based on Cloud Computing in Mobile Medical Social Network
-
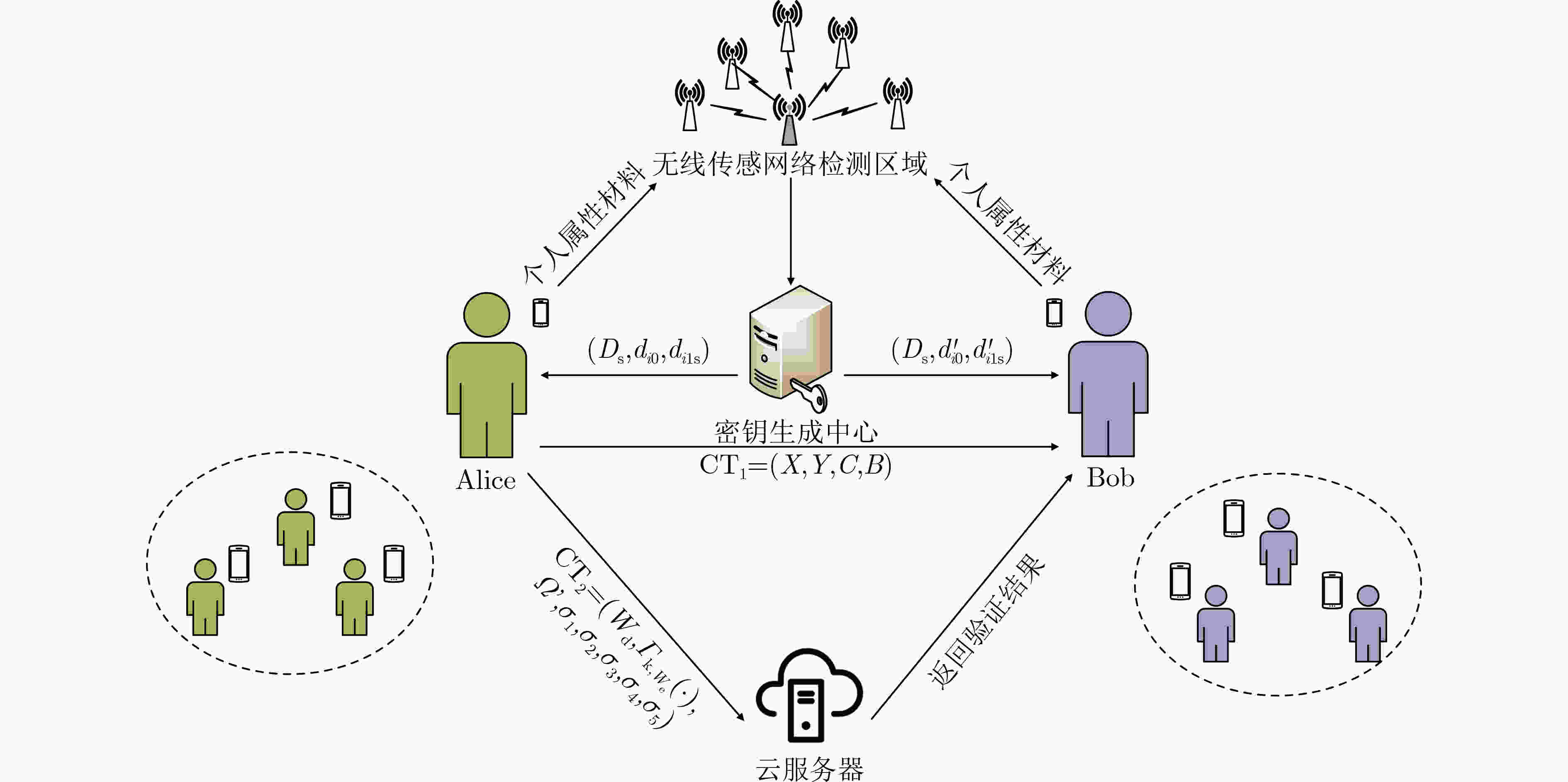
摘要: 移动医疗社交网络的出现为患者之间互相交流病情提供了极大的便利,促进了患者之间高效、高质量的沟通与交流,但与此同时也产生了患者数据的保密性和隐私性问题。针对此问题,该文提出一种基于云计算的属性基签密方案,能够有效地保护患者数据的隐私性。患者将自己的病情信息签密后上传至云服务器,当数据用户要访问患者的信息时,云服务器帮助数据用户进行部分解密并验证数据的完整性,这在一定程度上减少了数据用户的计算量。同时,在随机预言机模型下,证明了该方案满足选择消息攻击下的不可伪造性、选择密文攻击下的不可区分性以及属性隐私安全性。理论分析和数值模拟实验结果表明,该方案在签密和解签密阶段比现存的方案有更高的效率。Abstract: The emergence of mobile medical social networks has greatly facilitated the communication of patients' conditions to each other, promoting efficient and high-quality communication and exchange between patients. However, it also causes problems of confidentiality and privacy of patient data. To solve this problem, an attribute-based signcryption scheme based on cloud-assisted verification is proposed, which can effectively protect the privacy of patient data. Patients signcrypt their health information and upload it to the cloud server. When the data user wants to access the patient's information, the cloud server helps the data user partially decrypt and verify the integrity of the data, which reduces the amount of calculation of the data user to a certain extent. At the same time, under the random oracle model, it is proved that the scheme satisfies the unforgeability under the adaptive selection message, the indistinguishability under the adaptive selection ciphertext attack, and the attribute privacy security. Theoretical analysis and numerical simulation experimental results show that the scheme is more efficient than the existing schemes in the signcryption and unsigncryption phases.
-
表 1 功能特性比较
表 2 计算开销分析
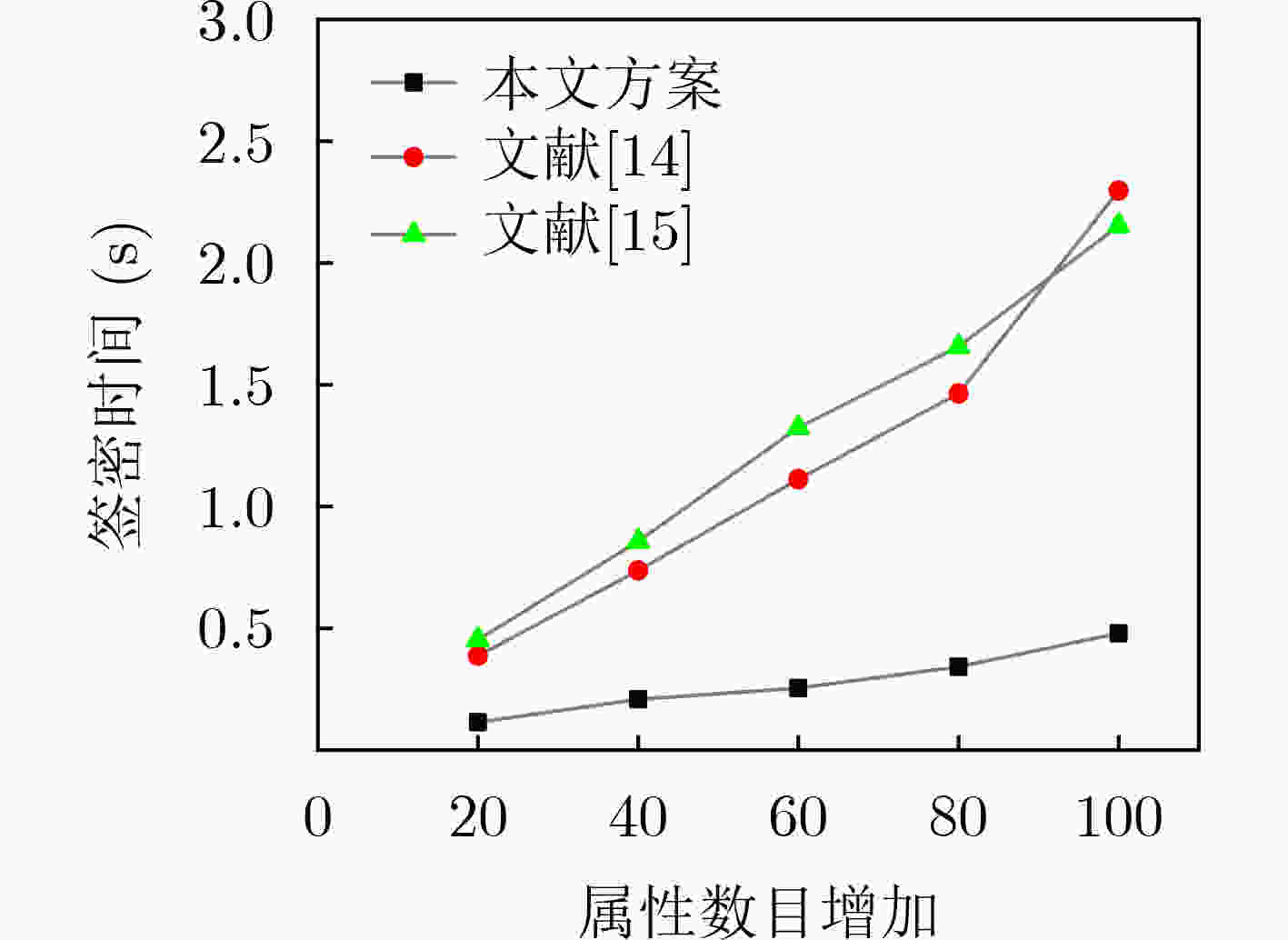
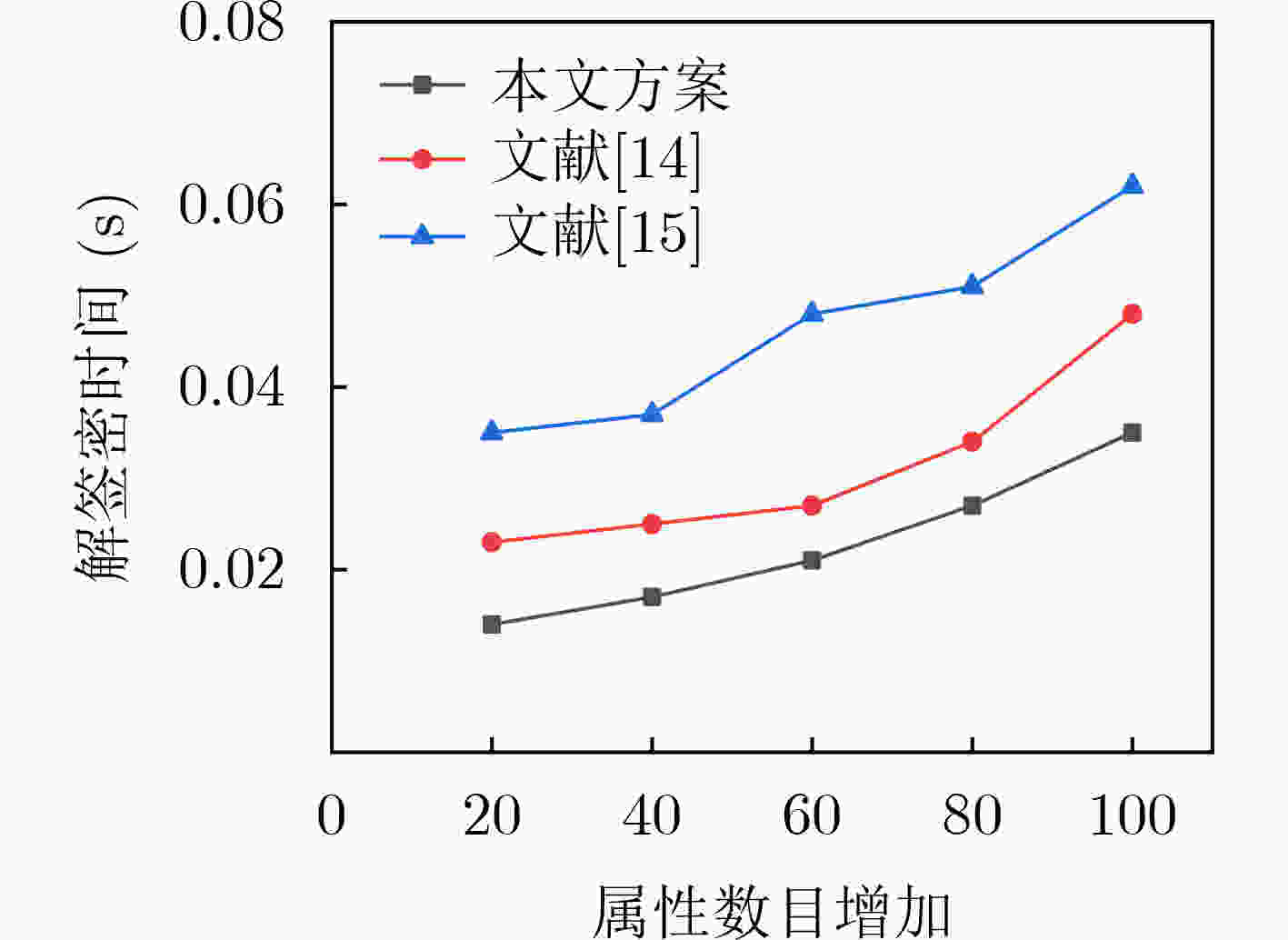
阶段 文献[14] 文献[15] 本文方案 系统初始化 $ 3{T_{\rm e}} + {T_{\rm p}} $ $ {T_{\rm e}} + \left| N \right|{T_{\rm m}} $ $ 2{T_{\rm e}} + {T_{\rm p}} $ 密钥生成 $ 6{T_{\rm e}} + 2\left| N \right|{T_{\rm h}} + 2{T_{\rm m}} $ $ (3\left| N \right|){T_{\rm e}} + (\left| N \right| + 1){T_{\rm m}} $ $ (6\left| N \right| + 1){T_{\rm e}} + 2\left| N \right|{T_{\rm h}} $ 签密 $ (5\left| N \right| + 6){T_{\rm e}} + (2\left| N \right| + 4){T_{\rm m}} $ $ (4\left| N \right| + 4){T_{\rm e}} + {T_{\rm p}} $ $ 8{T_{\rm e}} + (\left| N \right| + 1){T_{\rm h}} + {T_{\rm m}} $ 解签密 $ 2|N|{T_{\rm e}} + 3{T_{\rm h}} + |N|{T_{\rm m}} $ $ (2\left| N \right| + 1){T_{\rm e}} + (4\left| N \right| + 3){T_{\rm p}} + {T_{\rm h}} $ $ \left| N \right|{T_{\rm e}} + 2\left| N \right|{T_{\rm p}} + {T_{\rm h}} $ 表 3 通信开销分析
阶段 文献[14] 文献[15] 本文方案 系统公钥 $ (\left| N \right| + 5)\left| {{Z_{\rm r}}} \right| + (\left| N \right| + 5)\left| G \right| + \left| {{G_{\rm T}}} \right| $ $ (3\left| N \right| + 4)\left| G \right| $ $ 2\left| {{Z_{\rm r}}} \right| + 3\left| G \right| + 4\left| {{G_{\rm T}}} \right| $ 系统主密钥 $ \left| G \right| $ $ \left| {{Z_{\rm r}}} \right| + \left| N \right|\left| G \right| $ $ \left| {{Z_{\rm r}}} \right| $ 用户私钥 $ (2\left| N \right| + 1)\left| G \right| + \left| N \right|\left| {{G_{\rm T}}} \right| $ $ 2\left| N \right|(\left| N \right| + 1)\left| G \right| $ $ 2\left| {{Z_{\rm r}}} \right| + (2\left| N \right| + 1)\left| G \right| $ 加密密文 $ 4\left| {{Z_{\rm r}}} \right| + (3\left| N \right| + 3)\left| G \right| + (\left| N \right| + 1)\left| {{G_{\rm T}}} \right| $ $ 5\left| G \right| + 2(\left| N \right| + 1)\left| {{G_{\rm T}}} \right| $ $ 4\left| {{Z_{\rm r}}} \right| + 6\left| G \right| + (\left| N \right| + 1)\left| {{G_{\rm T}}} \right| $ -
[1] DENG Fuhu, WANG Yali, PENG Li, et al. Revocable cloud-assisted attribute-based signcryption in personal health system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 120950–120960. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2933636 [2] ARFAOUI A, BOUDIA O R M, KRIBECHE A, et al. Context-aware access control and anonymous authentication in WBAN[J]. Computers & Security, 2020, 88: 101496. doi: 10.1016/j.cose.2019.03.017 [3] XU Chang, WANG Jiachen, ZHU Liehuang, et al. Enabling privacy-preserving multi-level attribute based medical service recommendation in eHealthcare systems[J]. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2021, 14(4): 1841–1853. doi: 10.1007/s12083-021-01075-9 [4] 牛淑芬, 刘文科, 陈俐霞, 等. 基于代理重加密的电子病历数据共享方案[J]. 计算机工程, 2021, 47(6): 164–171.NIU Shufen, LIU Wenke, CHEN Lixia, et al. Data sharing scheme of electronic medical record based on proxy Re-encryption[J] Computer Engineering, 2021, 47(6): 164–171. [5] 聂旭云, 鲍阳阳, 孙剑飞, 等. 一个多授权中心的属性基签密方案[J]. 信息安全学报, 2018, 3(5): 15–24. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2018.09.02NIE Xuyun, BAO Yangyang, SUN Jianfei, et al. A multi-authority attribute-based signcryption scheme[J]. Journal of Cyber Security, 2018, 3(5): 15–24. doi: 10.19363/J.cnki.cn10-1380/tn.2018.09.02 [6] SAHAI A and WATERS B. Fuzzy identity-based encryption[C]. The 24th Annual International Conference on Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Aarhus, Denmark, 2005: 457–473. [7] GE Chunpeng, SUSILO W, BAEK J, et al. Revocable attribute-based encryption with data integrity in clouds[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2021, 19(5): 2864–2872. [8] 牛淑芬, 宋蜜, 方丽芝, 等. 智慧医疗中基于属性加密的云存储数据共享[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 107–117. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210858NIU Shufen, SONG Mi, FANG Lizhi, et al. Cloud storage data sharing based on attribute encryption in smart healthcare[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 107–117. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210858 [9] TU Shanshan, WAQAS M, HUANG Fengming, et al. A revocable and outsourced multi-authority attribute-based encryption scheme in fog computing[J]. Computer Networks, 2021, 195: 108196. doi: 10.1016/J.COMNET.2021.108196 [10] CHALLAGIDAD P S and BIRJE M N. Efficient multi-authority access control using attribute-based encryption in cloud storage[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2020, 167: 840–849. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2020.03.423 [11] ZHENG Yuliang. Digital signcryption or how to achieve cost(signature & encryption) << cost(signature) + cost(encryption)[C]. The 17th Annual International Cryptology Conference on Advances in Cryptology, Santa Barbara, USA, 1997: 165–179. [12] DENG Ningzhi, DENG Shaojiang, HU Chunqiang, et al. An efficient revocable attribute-based signcryption scheme with outsourced unsigncryption in cloud computing[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 42805–42815. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2963233 [13] LIU Suhui, CHEN Liquan, WANG Huaqun, et al. O3HSC: Outsourced online/offline hybrid signcryption for wireless body area networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2022, 19(3): 2421–2433. [14] MING Yang and ZHANG Tingting. Efficient privacy-preserving access control scheme in electronic health records system[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3520. doi: 10.3390/s18103520 [15] HAN Yiliang and LU Wanyi. Attribute based generalized signcryption for online social network[C]. 2015 34th Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Hangzhou, China, 2015: 6434–6439. [16] LU Yanfei, WANG Xu, HU Chunqiang, et al. A traceable threshold attribute-based signcryption for mHealthcare social network[J]. International Journal of Sensor Networks, 2018, 26(1): 43–53. doi: 10.1504/IJSNET.2018.088384 [17] BOUCHAALA M, GHAZEL C, and SAIDANE L A. TRAK-CPABE: A novel traceable, revocable and accountable ciphertext-policy attribute-based encryption scheme in cloud computing[J]. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 2021, 61: 102914. doi: 10.1016/j.jisa.2021.102914 [18] BELGUITH S, KAANICHE N, HAMMOUDEH M, et al. PROUD: Verifiable privacy-preserving outsourced attribute based signcryption supporting access policy update for cloud assisted IOT applications[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 111: 899–918. doi: 10.1016/j.future.2019.11.012 [19] OBIRI I A, XIA Qi, XIA Hu, et al. Personal health records sharing scheme based on attribute based signcryption with data integrity verifiable[J]. Journal of Computer Security, 2022, 30(2): 291–324. doi: 10.3233/JCS-210045 [20] YU Jiguo, LIU Suhui, WANG Shengling, et al. LH-ABSC: A lightweight hybrid attribute-based signcryption scheme for cloud-fog-assisted IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2020, 7(9): 7949–7966. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.2992288 [21] PBC Library. The pairing-based cryptography library[EB/OL]. http://crypto.stanford.edu/pbc/, 2015. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
