Feature Fusion Classification for Optical Image and SAR Image Based on Spatial-spectral Attention
-
摘要: 针对多源遥感图像的差异性和互补性问题,该文提出一种基于空间与光谱注意力的光学图像和SAR图像特征融合分类方法。首先利用卷积神经网络分别进行光学图像和SAR图像的特征提取,设计空间注意力和光谱注意力组成的注意力模块分析特征重要程度,生成不同特征的权重进行特征融合增强,同时减弱对无效信息的关注,从而提高光学和SAR图像融合分类精度。通过在两组光学和SAR图像数据集上进行对比实验,结果表明所提方法取得更高的融合分类精度。Abstract: Considering the issue of difference and complementarity of multi-source remote sensing images, this paper proposes a feature fusion classification method for optical image and SAR image based on spatial-spectral attention. Firstly, features of optical image and SAR image are extracted by the convolutional neural network, and an attention module composed of spatial attention and spectral attention is designed to analyze the importance of features. Features can be enhanced by the weights of the attention module, which can reduce the attention to irrelevant information, and thus improve the accuracy of fusion classification for optical and SAR images. Experimental results on two datasets of optical image and SAR image demonstrate that the proposed method is able to yield higher fusion classification accuracy.
-
Key words:
- SAR image /
- Deep learning /
- Feature fusion /
- Attention mechanism
-
表 1 数据集各类别数目
类别 颜色 数据集A 数据集A训练集 数据集A验证集 数据集A测试集 数据集B 数据集B训练集 数据集B验证集 数据集B测试集 建筑 129629 20000 20000 89629 200251 20000 20000 160251 公路 305221 30000 20000 255221 320238 30000 20000 270238 裸土 284388 30000 20000 234388 539888 50000 40000 449888 草坪 695808 70000 60000 565808 263817 20000 20000 223817 树木 84954 10000 10000 64954 175615 20000 20000 135615 总计 – 1500000 160000 130000 1210000 1500000 140000 120000 1240000 表 2 不同识别方法对应的5类数据集A识别正确率(%)及评价指标OA, AA, Kappa值
CNN(S) CNN-ATT(S) CNN(O) CNN-ATT(O) CNN(S+O) Two-branch MDL-Middle TAFFN CNN-ATT(S+O) 建筑公路裸土草坪树木 72.1875.9153.5971.5147.37 75.9776.1154.4971.9243.38 96.9494.7684.1795.5870.50 96.2695.0886.4194.8970.81 95.6994.9586.4094.5980.03 95.5891.5683.1991.4960.90 97.2092.3584.9491.8071.35 94.9894.1787.8193.8478.57 94.9695.6891.9292.7685.91 OA 68.98 69.39 91.58 91.88 92.33 88.46 90.06 92.03 93.06 AA 64.11 64.37 88.39 88.69 90.22 84.55 87.53 89.87 92.25 Kappa 0.5349 0.5415 0.8805 0.8843 0.8897 83.47 85.68 0.8856 0.8997 表 3 不同识别方法对应的5类数据集B识别正确率(%)及评价指标OA, AA, Kappa值
CNN(S) CNN-ATT(S) CNN(O) CNN-ATT(O) CNN(S+O) Two-branch MDL-Middle TAFFN CNN-ATT(S+O) 建筑公路裸土草坪树木 72.7973.1156.8860.0747.58 74.3371.0857.5459.0149.56 97.0591.2288.8683.3377.66 97.9291.1988.2383.8479.86 96.2692.2487.5685.9579.86 93.7386.0381.7979.9971.91 94.7188.9484.4081.6976.42 96.4693.2385.9884.5281.64 96.4192.8288.6787.0184.17 OA 59.67 60.60 88.11 88.30 88.34 82.64 85.21 88.03 89.75 AA 51.74 51.92 73.02 73.42 73.64 68.91 71.03 73.63 74.84 Kappa 44.97 0.4626 0.8436 0.8458 0.8462 77.04 80.48 0.8416 0.8648 表 4 不同识别方法对应的数据集A和B训练和测试时间(s)
数据集 时间 CNN(S) CNN-ATT(S) CNN(O) CNN-ATT(O) CNN(S+O) Two-branch MDL-Middle TAFFN CNN-ATT(S+O) A 训练时间 339.794 492.978 368.404 505.159 534.780 282.893 365.131 440.552 1262.196 测试时间 43.584 56.762 45.952 58.979 58.454 89.591 65.505 129.132 119.097 B 训练时间 285.813 473.852 301.061 462.599 477.815 218.434 299.963 355.166 1060.421 测试时间 42.754 54.065 42.538 66.526 56.818 59.116 66.372 99.237 103.138 表 5 交叉验证数据集介绍
类别 1 2 3 4 5 总计 训练集 10000 20000 30000 22000 9000 91000 测试集 116741 167431 327719 99719 38390 750000 表 6 交叉验证识别正确率(%)及评价指标OA, AA, Kappa值
方法 CNN(S+O) Two-branch MDL-Middle TAFFN CNN-ATT(S+O) 建筑公路裸土草坪树木 91.5470.7987.6445.4949.75 87.9765.4186.9747.7050.21 89.9767.8385.9449.9251.57 92.8066.2987.4549.0057.27 92.4664.6887.4453.1758.04 OA 72.19 71.52 72.64 72.71 73.07 AA 69.04 67.65 69.05 70.56 71.16 Kappa 62.80 61.67 63.00 63.19 63.67 -
[1] SUKAWATTANAVIJIT C, CHEN Jie, and ZHANG Hongsheng. GA-SVM algorithm for improving land-cover classification using SAR and optical remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(3): 284–288. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2628406 [2] 李璐, 杜兰, 何浩男, 等. 基于深度森林的多级特征融合SAR目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 606–614. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200685LI Lu, DU Lan, HE Haonan, et al. Multi-level feature fusion SAR automatic target recognition based on deep forest[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 606–614. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200685 [3] ALONSO-GONZÁLEZ A, LÓPEZ-MARTÍNEZ C, PAPATHANASSIOU K P, et al. Polarimetric SAR time series change analysis over agricultural areas[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(10): 7317–7330. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2981929 [4] ZHANG Hongsheng and XU Ru. Exploring the optimal integration levels between SAR and optical data for better urban land cover mapping in the Pearl River Delta[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 2018, 64: 87–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2017.08.013 [5] KUSSUL N, LAVRENIUK M, SKAKUN S, et al. Deep learning classification of land cover and crop types using remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(5): 778–782. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2681128 [6] ZHANG Xiangrong, WANG Xin, TANG Xu, et al. Description generation for remote sensing images using attribute attention mechanism[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(6): 612. doi: 10.3390/rs11060612 [7] XIE Jie, HE Nanjun, FANG Leyuan, et al. Scale-free convolutional neural network for remote sensing scene classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(9): 6916–6928. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2909695 [8] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, and HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]. Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, USA, 2012: 1097–1105. [9] SIMONYAN K and ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [10] SZEGEDY C, LIU Wei, JIA Yangqing, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]. Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, USA, 2015: 1–9. [11] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]. Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016: 630–645. [12] 周顺杰, 杨学志, 董张玉, 等. 面向特征识别的SAR与可见光图像融合算法研究[J]. 合肥工业大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 41(7): 900–907. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2018.07.008ZHOU Shunjie, YANG Xuezhi, DONG Zhangyu, et al. Fusion algorithm of SAR and visible images for feature recognition[J]. Journal of Hefei University of Technology, 2018, 41(7): 900–907. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2018.07.008 [13] 雷俊杰, 杨武年, 李红, 等. 哨兵光学及SAR卫星影像协同分类研究[J]. 现代电子技术, 2022, 45(2): 135–139. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2022.02.026LEI Junjie, YANG Wunian, LI Hong, et al. Research on cooperative classification of sentinel optical and SAR satellite images[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2022, 45(2): 135–139. doi: 10.16652/j.issn.1004-373x.2022.02.026 [14] KONG Yingying, YAN Biyuan, LIU Yanjuan, et al. Feature-level fusion of polarized SAR and optical images based on random forest and conditional random fields[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13(7): 1323. doi: 10.3390/rs13071323 [15] XU Zhe, ZHU Jinbiao, GENG Jie, et al. Triplet attention feature fusion network for SAR and optical image land cover classification[C]. Proceedings of 2021 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium IGARSS, Brussels, Belgium, 2021: 4256–4259. [16] XU Xiaodong, LI Wei, RAN Qiong, et al. Multisource remote sensing data classification based on convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2018, 56(2): 937–949. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2756851 [17] HONG Danfeng, GAO Lianru, YOKOYA N, et al. More diverse means better: Multimodal deep learning meets remote-sensing imagery classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(5): 4340–4354. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3016820 [18] HU Jie, SHEN Li, and SUN Gang. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]. Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7132–7141. [19] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]. Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 3–19. [20] PARK J, WOO S, LEE J Y, et al. A simple and light-weight attention module for convolutional neural networks[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(4): 783–798. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01283-0 [21] FU Jun, LIU Jing, TIAN Haijie, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]. Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 3141–3149. [22] MISRA D. Mish: A self regularized non-Monotonic neural activation function[J]. arXiv: 1908.08681, 2019. [23] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [24] 徐从安, 吕亚飞, 张筱晗, 等. 基于双重注意力机制的遥感图像场景分类特征表示方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(3): 683–691. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200568XU Cong’an, LÜ Yafei, ZHANG Xiaohan, et al. A discriminative feature representation method based on dual attention mechanism for remote sensing image scene classification[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(3): 683–691. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200568 -





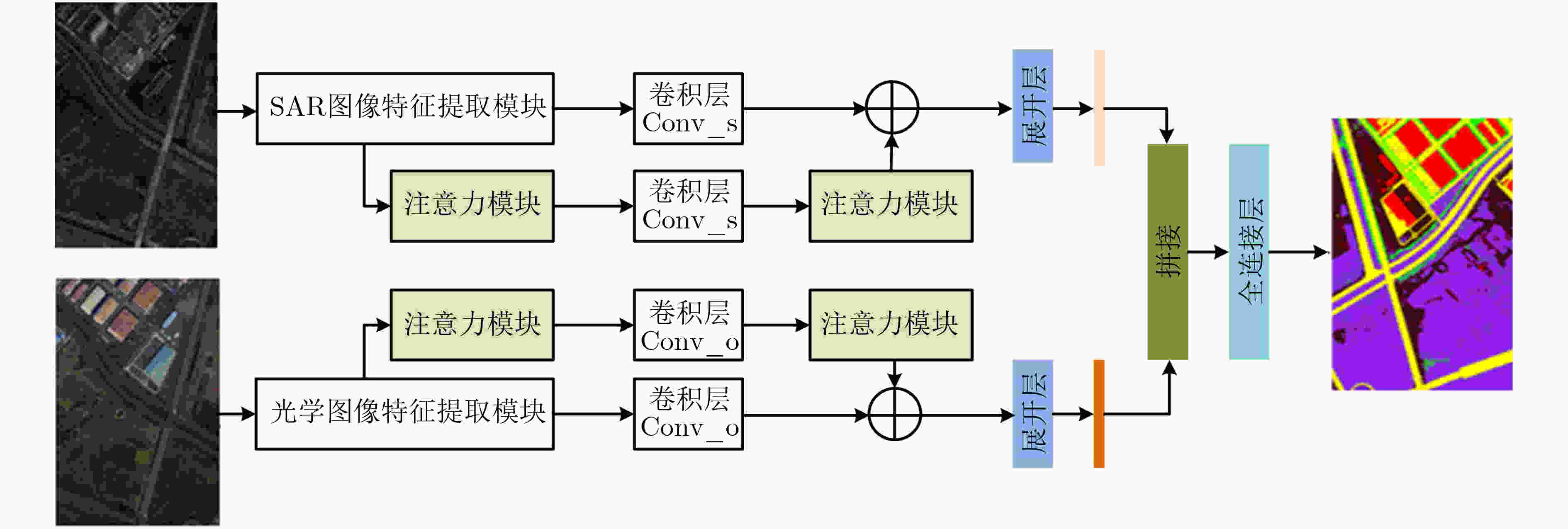
 下载:
下载:
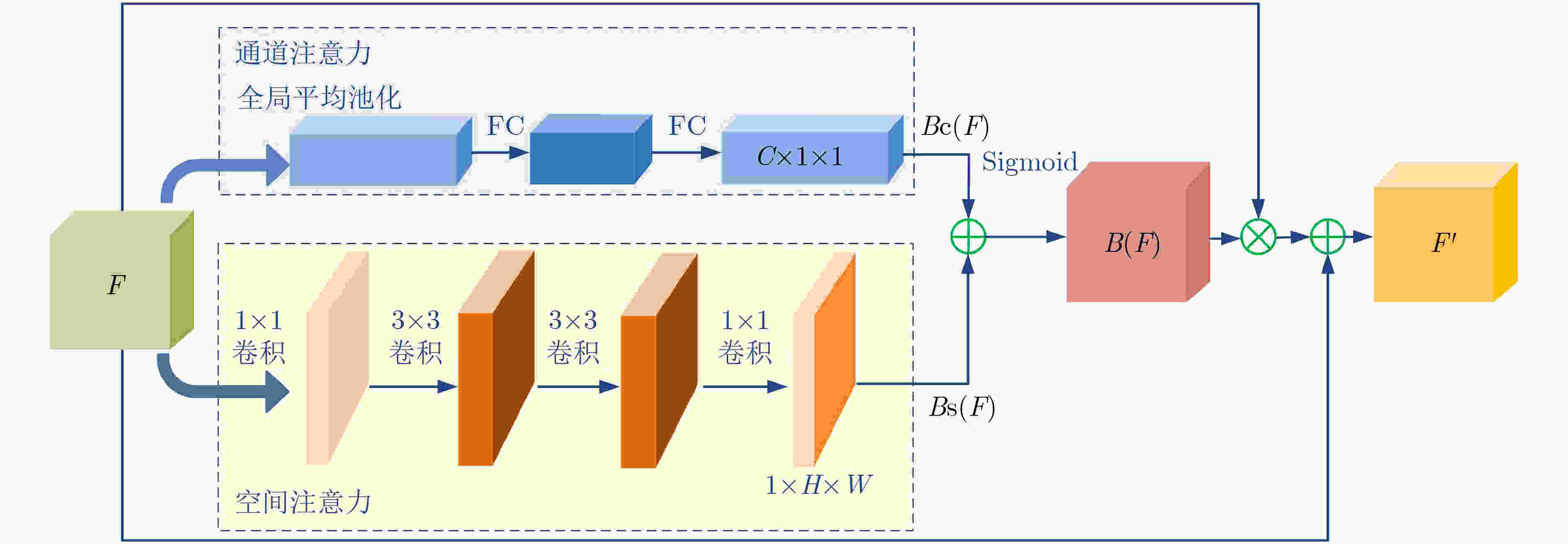
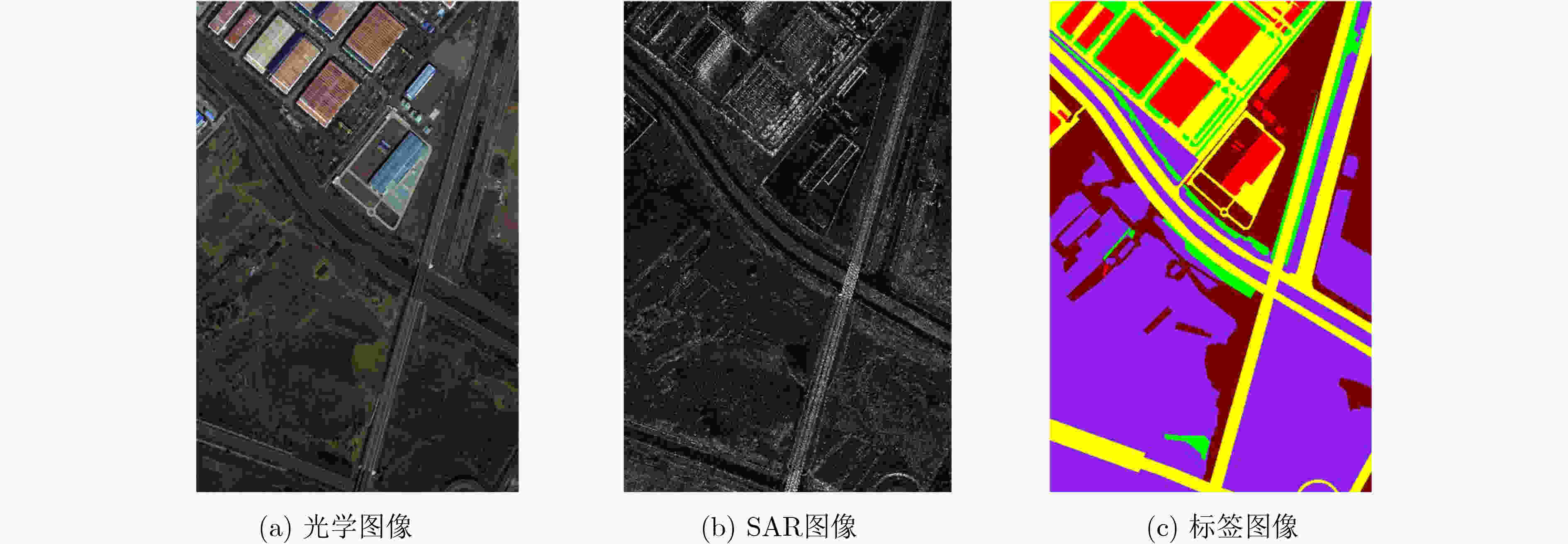
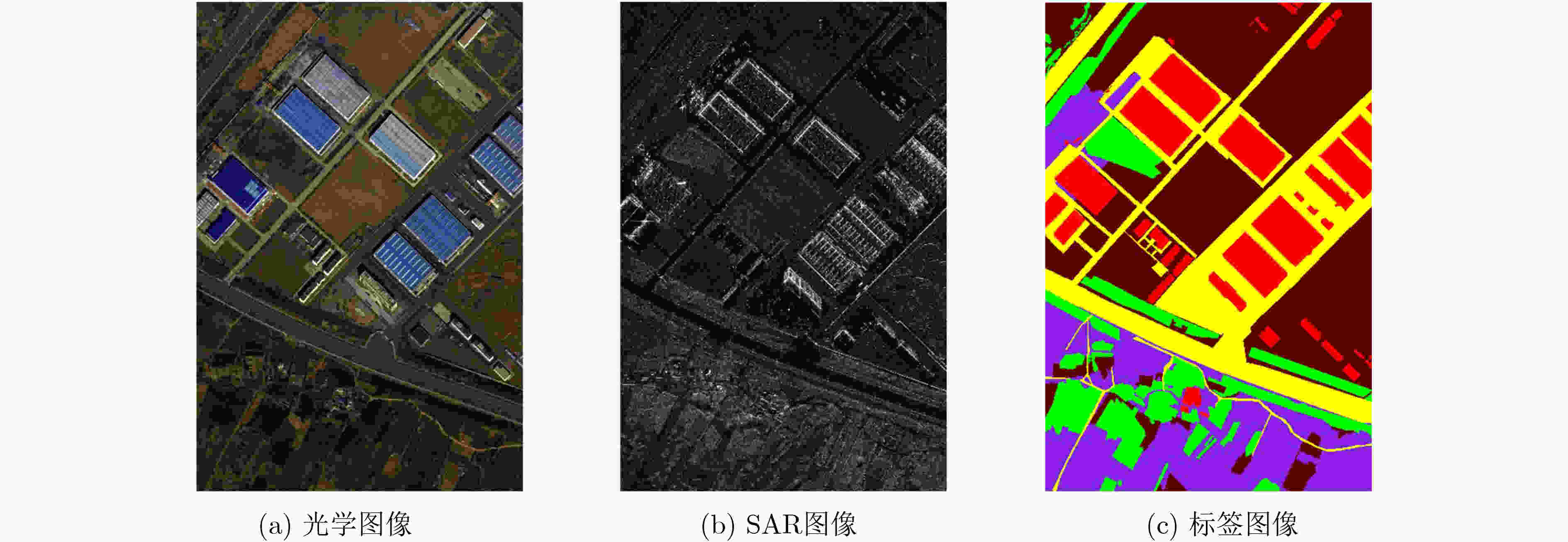
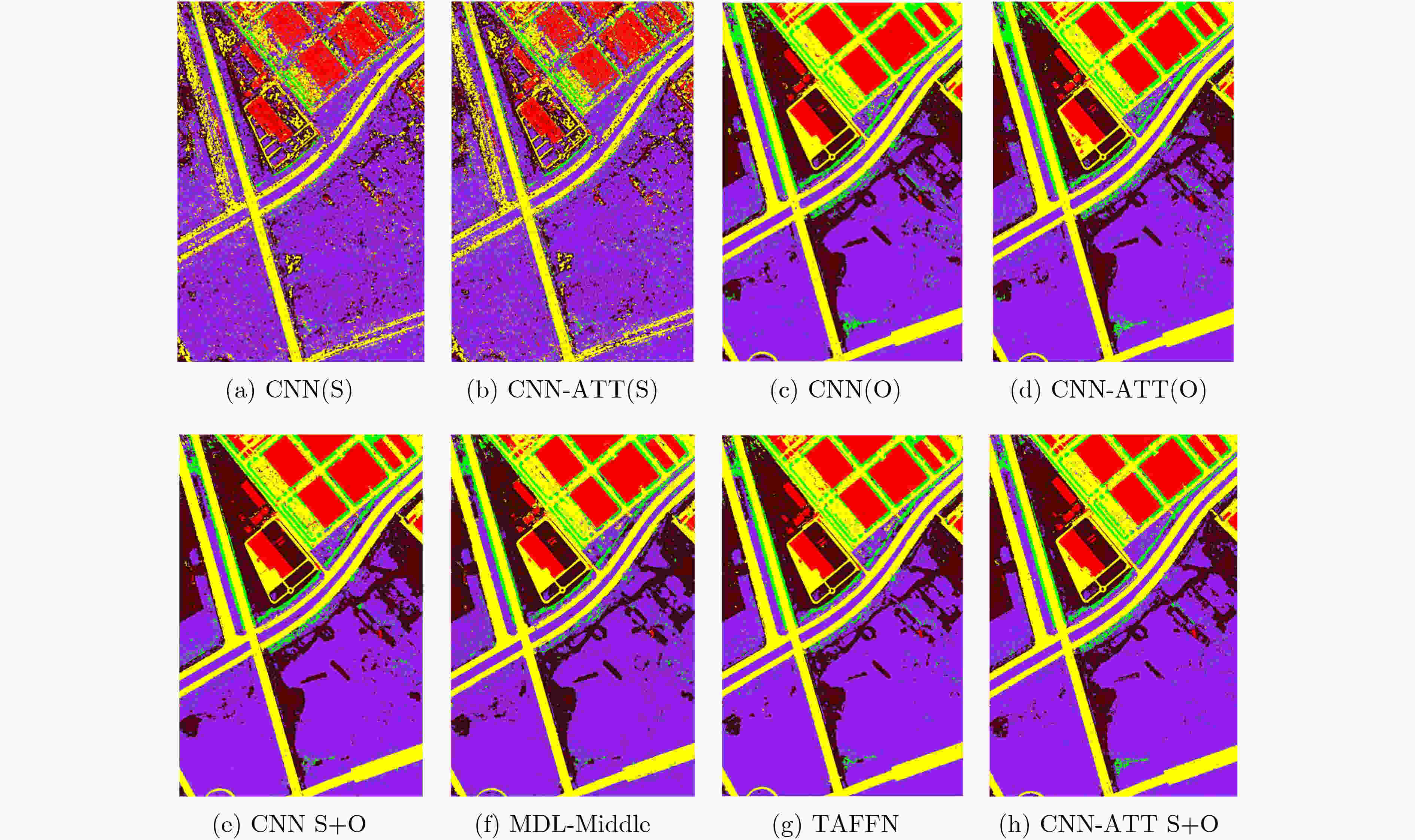
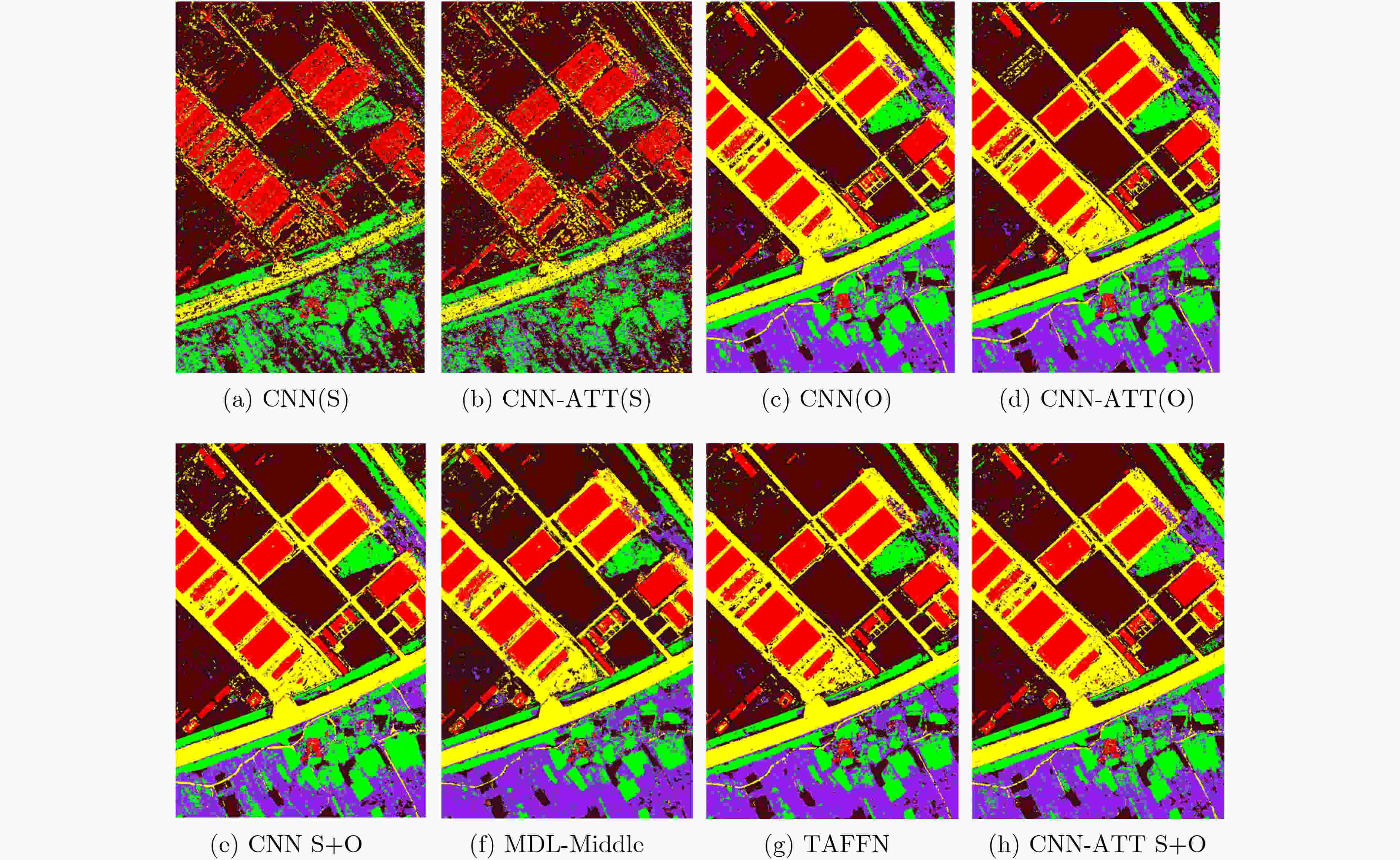
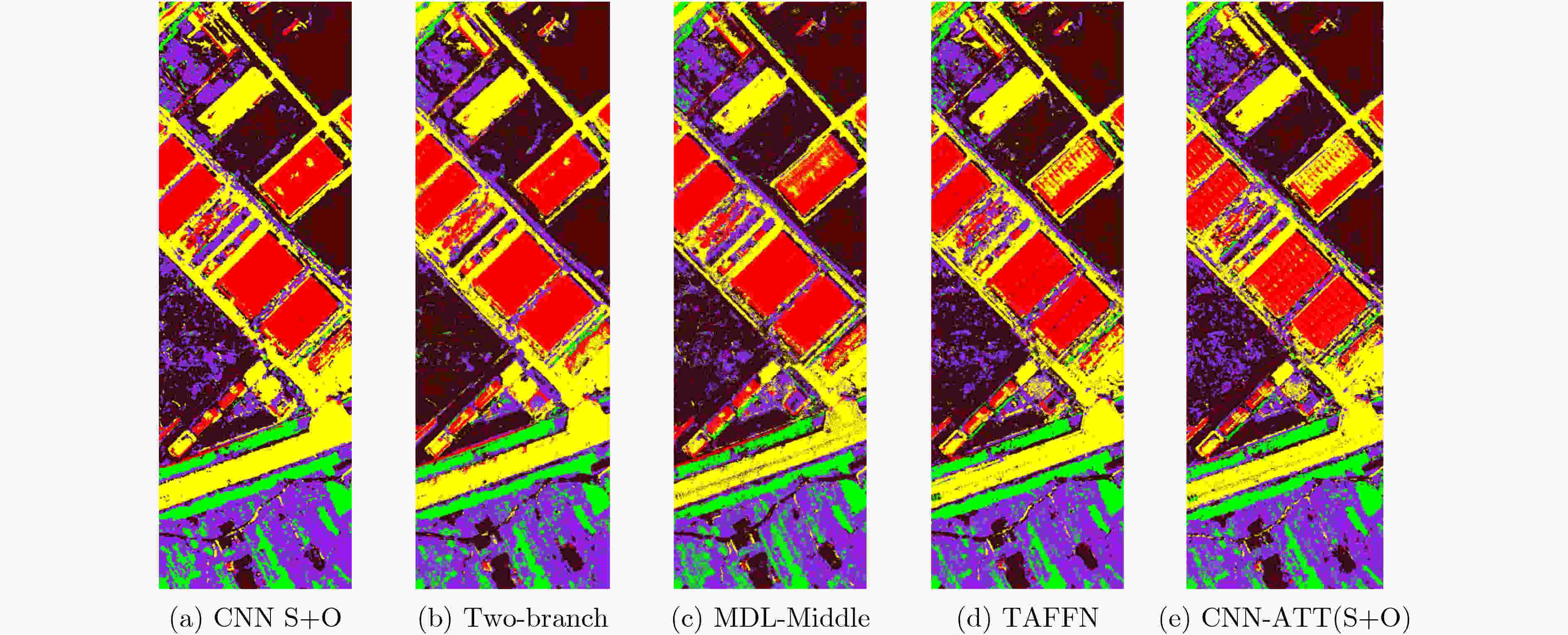


 下载:
下载:
