A Novel Logic-obfuscation Method to Resist Netlist-reverse Attack Based on Genetic Algorithm
-
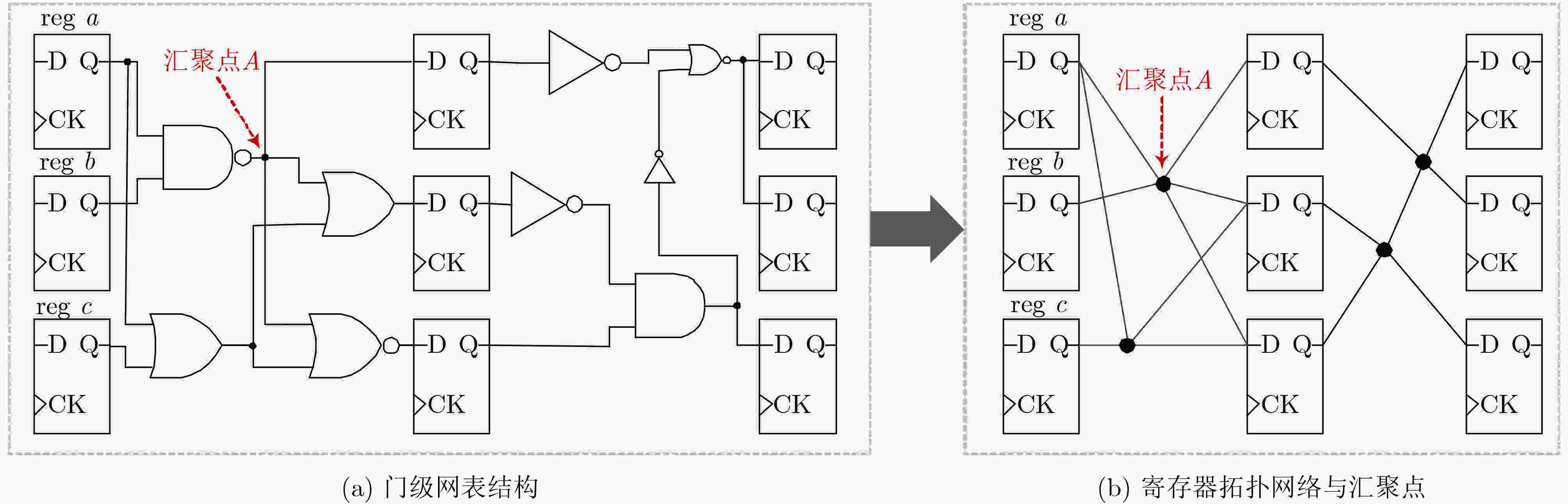
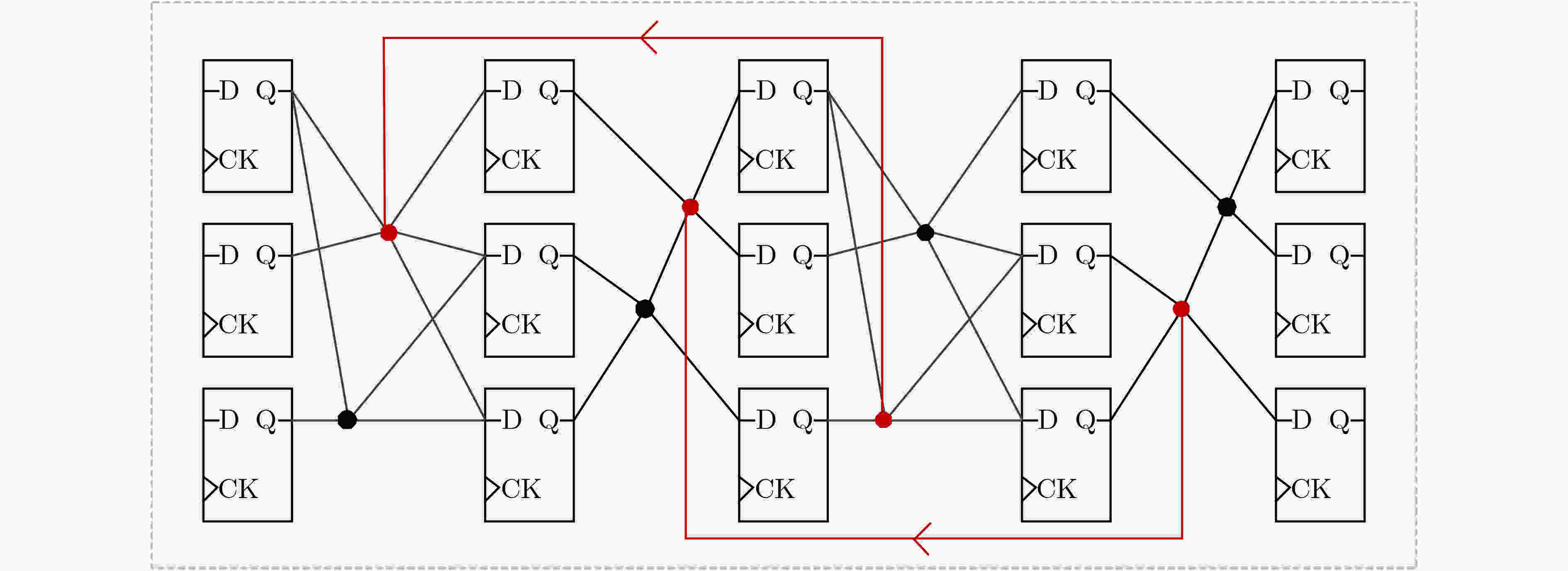
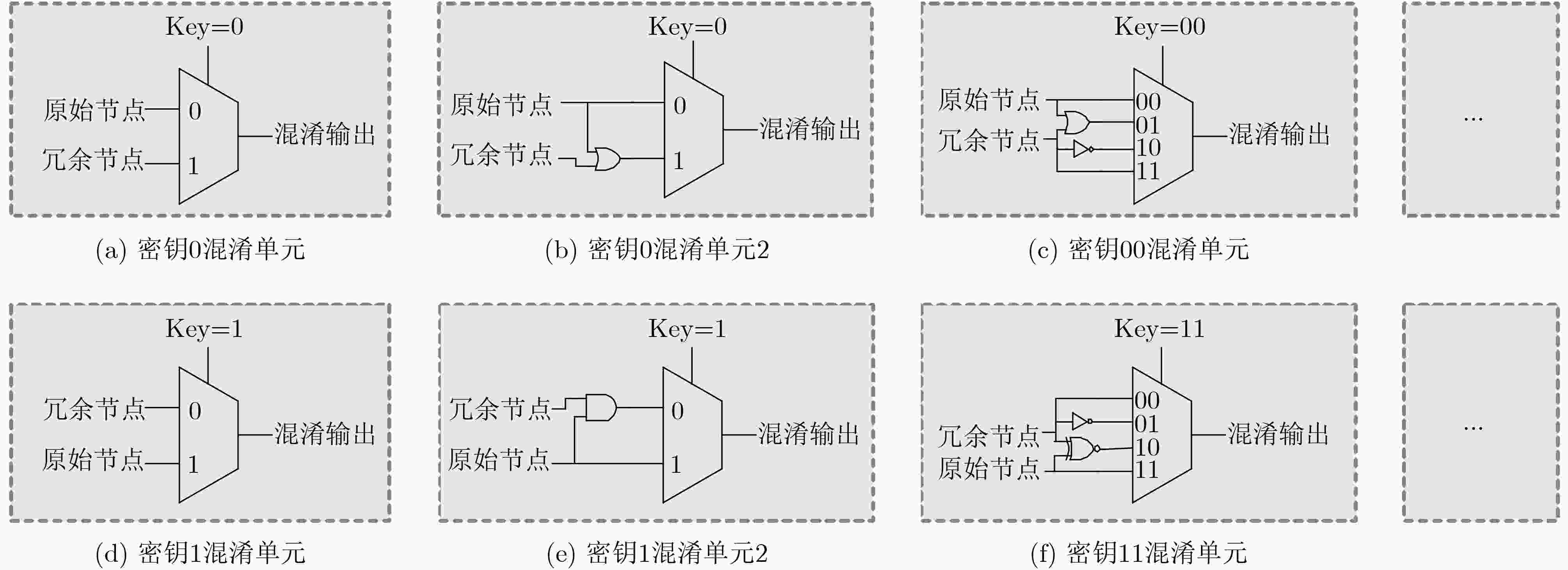
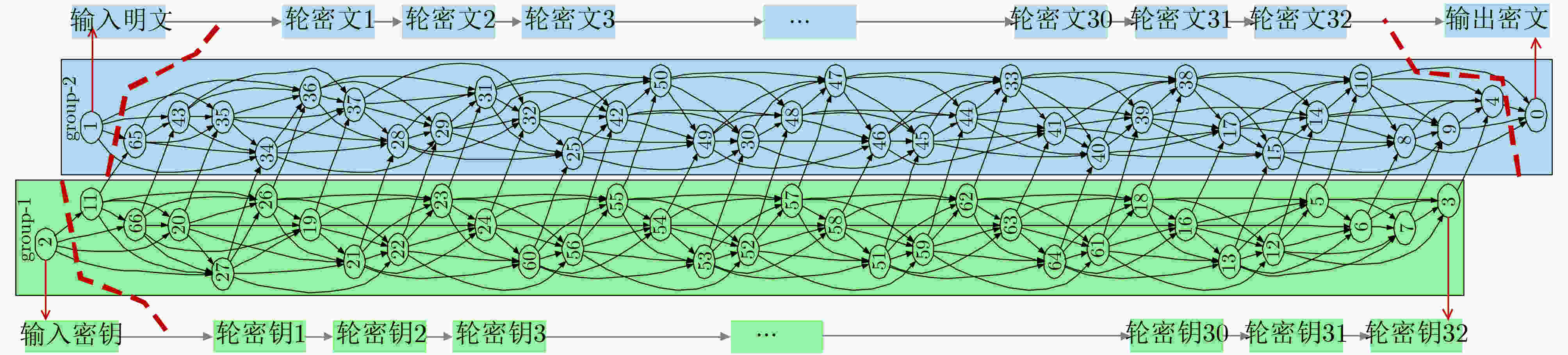
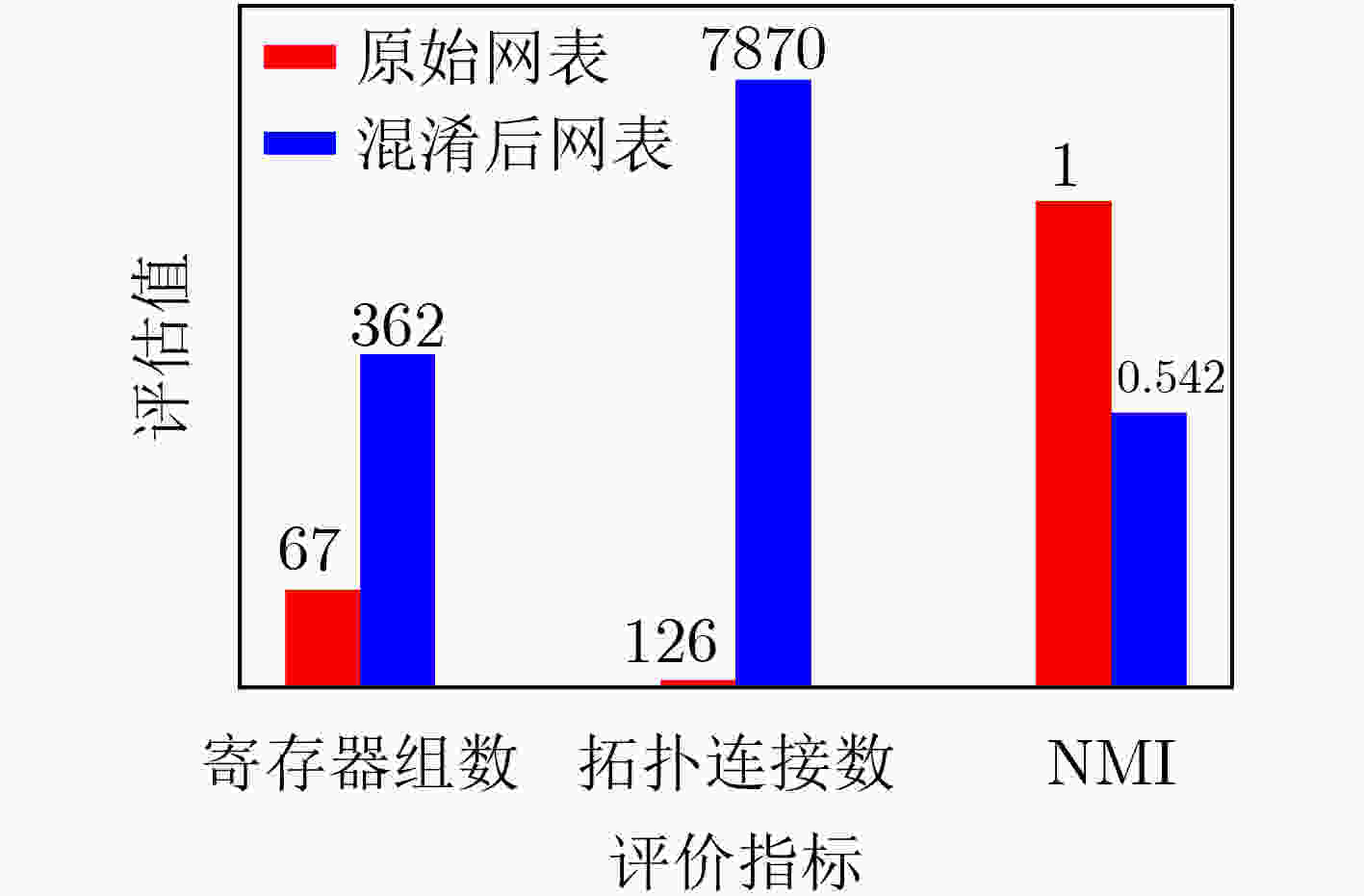
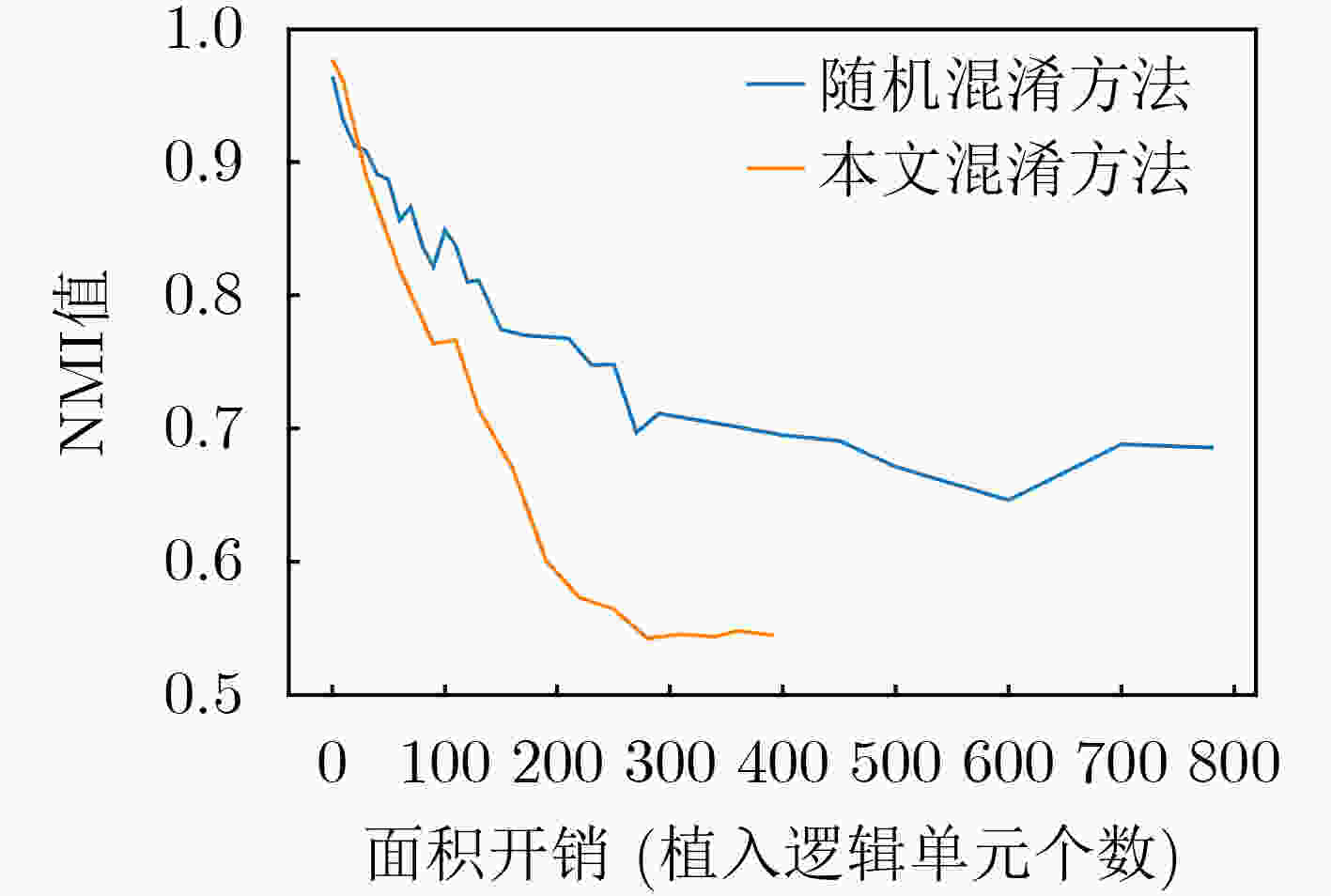
摘要: 随着集成电路(IC)产业进入后摩尔时代,芯片一次性工程成本愈发高昂,而以逆向工程技术为代表的知识产权窃取手段,越来越严重地威胁着芯片信息安全。为了抵抗逆向工程攻击,该文提出一种基于遗传算法的自动化逻辑混淆方法,通过分析网表寄存器的拓扑网络结构,筛选逻辑节点并创建冗余连接,从而混淆词级寄存器的相似性特征,在低开销下防止逆向攻击恢复寄存器传输级的词级变量、控制逻辑与数据通路。基于SM4国密算法基准电路开展验证实验,结果表明:经该文方法混淆后,逆向结果与设计真实情况的标准化互信息相关度下降了46%,拓扑复杂度提升61.46倍,面积额外开销为0.216%;同时相较于随机混淆,该混淆方法效率提升为2.718倍,面积额外开销降低70.8%。Abstract: As the Integrated Circuit (IC) industry enters the post-Moore era, the cost of one-time chip design is getting higher and higher, and threats of reverse engineering to recover the original design increase continually. In order to resist the reverse attacks, an automatic logic obfuscation technology based on genetic algorithm is proposed. By analyzing the topology network of registers in netlist, fan-in and fan-out nets are chosen to create redundant connections between registers, so that obfuscating the similarity among the word-level registers, and at last resist the reverse attacks to recover the word-level variable, control logic and dataflow. Experiments on the SM4 circuit shows, compared to the original netlist, after the proposed method’s obfuscation, the standardized mutual information of reverse attack result is reduced by 46%, and the topology complexity increased by 61.46 times. And compared to random obfuscation, the efficiency of the proposed method is increased to 2.718 times, and the area cost is reduced by 70.8%.
-
Key words:
- Post-Moore era /
- Hardware security /
- Logic obfuscation /
- Reverse engineering /
- Genetic algorithm
-
表 1 面积开销对比
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 NMI值 0.95 0.9 0.85 0.8 0.75 0.7 0.65 0.6 0.55 本文混淆方法开销 13 28 47 70 116 139 169 190 269 随机混淆方法开销 5 35 75 135 228 268 579 – – 本文方法降低面积开销(%) – 20.00↓ 37.33↓ 48.15↓ 49.12↓ 48.13↓ 70.80↓ – – -
[1] BAUMGARTEN A, TYAGI A, and ZAMBRENO J. Preventing IC piracy using reconfigurable logic barriers[J]. IEEE Design & Test of Computers, 2010, 27(1): 66–75. doi: 10.1109/MDT.2010.24 [2] DUPUIS S, BA P S, DI NATALE G, et al. A novel hardware logic encryption technique for thwarting illegal overproduction and Hardware Trojans[C]. 2014 IEEE 20th International On-Line Testing Symposium (IOLTS), Platja d'Aro, Spain, 2014: 49–54. [3] YASIN M, MAZUMDAR B, RAJENDRAN J J V, et al. SARLock: SAT attack resistant logic locking[C]. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), McLean, USA, 2016: 236–241. [4] XIE Yang and SRIVASTAVA A. Anti-SAT: Mitigating SAT attack on logic locking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2019, 38(2): 199–207. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2018.2801220 [5] ZHANG Jiliang. A practical logic obfuscation technique for hardware security[J]. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 2016, 24(3): 1193–1197. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2015.2437996 [6] CHAKRABORTY R S and BHUNIA S. HARPOON: An obfuscation-based SoC design methodology for hardware protection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, 2009, 28(10): 1493–1502. doi: 10.1109/TCAD.2009.2028166 [7] HU Yinghua, YANG Kaixin, NAZARIAN S, et al. SANSCrypt: A sporadic-authentication-based sequential logic encryption scheme[C]. IFIP/IEEE 28th International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration, Salt Lake City, USA, 2020: 129–134, [8] ZHANG Jiliang, LIN Yaping, LYU Yongqiang, et al. A PUF-FSM binding scheme for FPGA IP protection and pay-per-device licensing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2015, 10(6): 1137–1150. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2015.2400413 [9] 张会红, 李憬, 吴秋丰, 等. 基于多级协同混淆的硬件IP核安全防护设计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2458–2465. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210631ZHANG Huihong, LI Jing, WU Qiufeng, et al. Design of hardware IP core security protection based on multi-level co-obfuscation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2458–2465. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210631 [10] LI Wenchao, GASCON A, SUBRAMANYAN P, et al. WordRev: Finding word-level structures in a sea of bit-level gates[C]. 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), Austin, USA, 2013: 67–74. [11] LI Wenchao, WASSON Z, and SESHIA S A. Reverse engineering circuits using behavioral pattern mining[C]. 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware-Oriented Security and Trust, San Francisco, USA, 2012: 83–88. [12] SUBRAMANYAN P, TSISKARIDZE N, PASRICHA K, et al. Reverse engineering digital circuits using functional analysis[C]. 2013 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition, Grenoble, France, 2013: 1277–1280. [13] SUBRAMANYAN P, TSISKARIDZE N, LI Wenchao, et al. Reverse engineering digital circuits using structural and functional analyses[J]. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2014, 2(1): 63–80. doi: 10.1109/TETC.2013.2294918 [14] MEADE T, JIN Yier, TEHRANIPOOR M, et al. Gate-level netlist reverse engineering for hardware security: Control logic register identification[C]. 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2016: 1334–1337. [15] GEIST J, MEADE T, ZHANG Shaojie, et al. RELIC-FUN: Logic identification through functional signal comparisons[C]. 2020 57th ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2020: 1–6. [16] BRUNNER M, BAEHR J, and SIGL G. Improving on state register identification in sequential hardware reverse engineering[C]. 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Hardware Oriented Security and Trust (HOST), McLean, USA, 2019: 151–160. [17] ALBARTUS N, HOFFMANN M, TEMME S, et al. DANA universal dataflow analysis for gate-level netlist reverse engineering[J]. IACR Transactions on Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems, 2020, 2020(4): 309–336. doi: 10.13154/tches.v2020.i4.309-336 [18] RAJENDRAN J, PINO Y, SINANOGLU O, et al. Security analysis of logic obfuscation[C]. The 49th Annual Design Automation Conference, San Francisco, USA, 2012: 83–89. [19] KASARABADA Y, CHEN Suyuan, and VEMURI R. On SAT-based attacks on encrypted sequential logic circuits[C]. 20th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, Santa Clara, USA, 2019: 204–211. [20] MEADE T, ZHANG Shaojie, and JIN Yier. Netlist reverse engineering for high-level functionality reconstruction[C]. 2016 21st Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Macao, China, 2016: 655–660. -





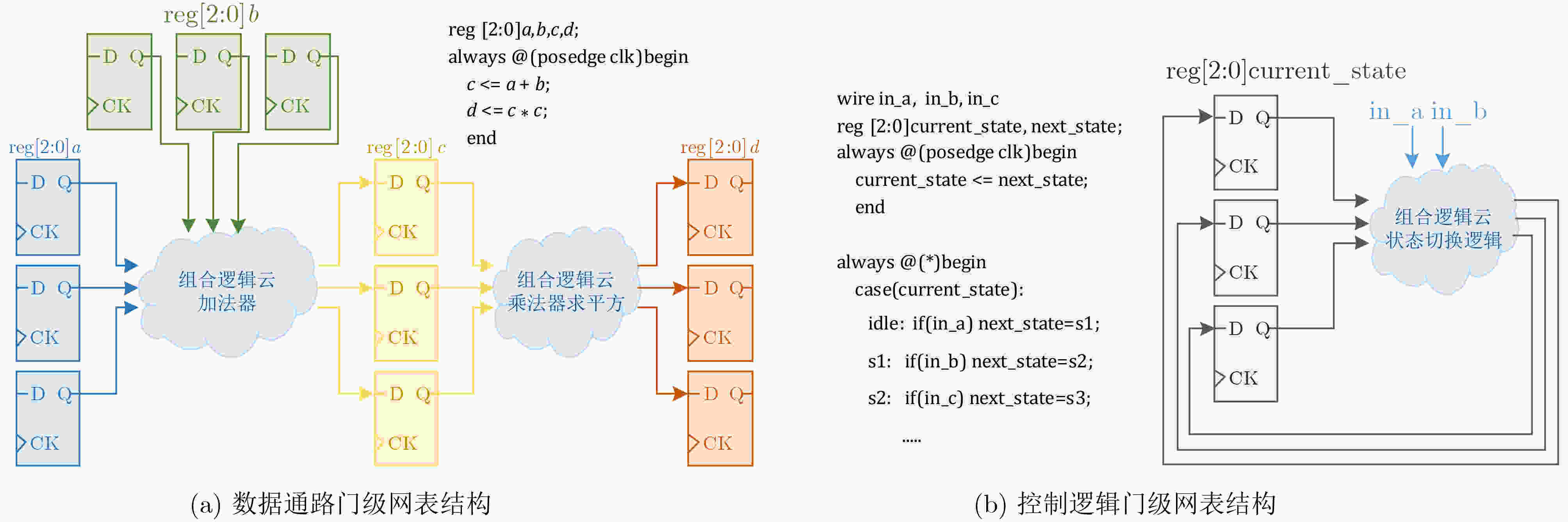
 下载:
下载:
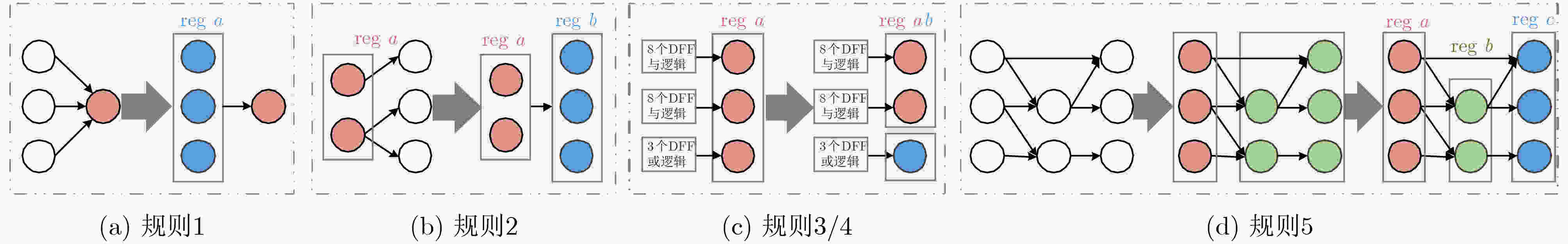
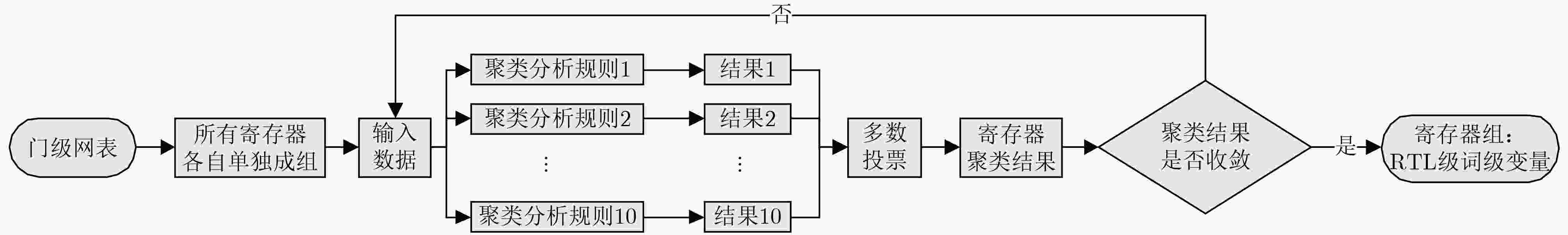
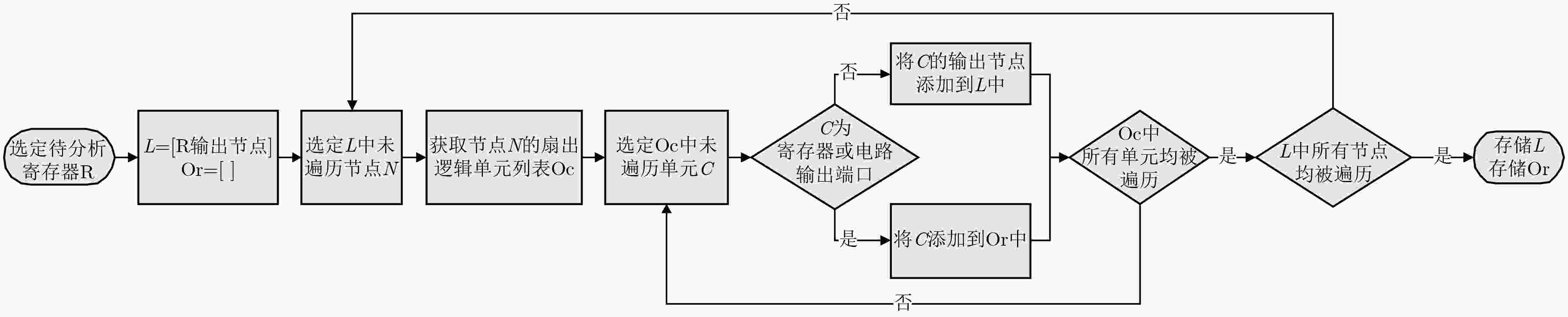


 下载:
下载:
