Hybrid Geographical Routing Protocol for Internet of Underwater Things
-
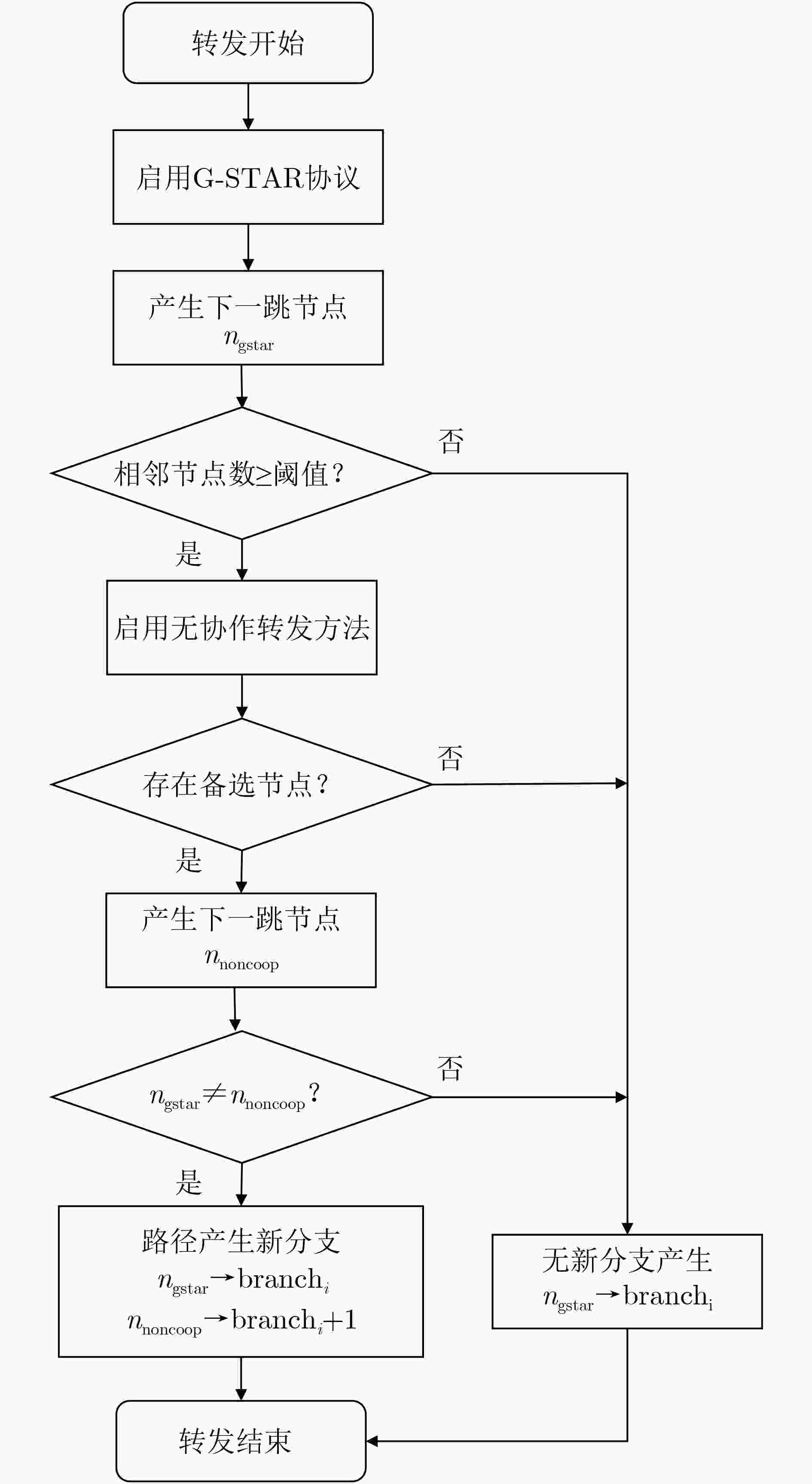
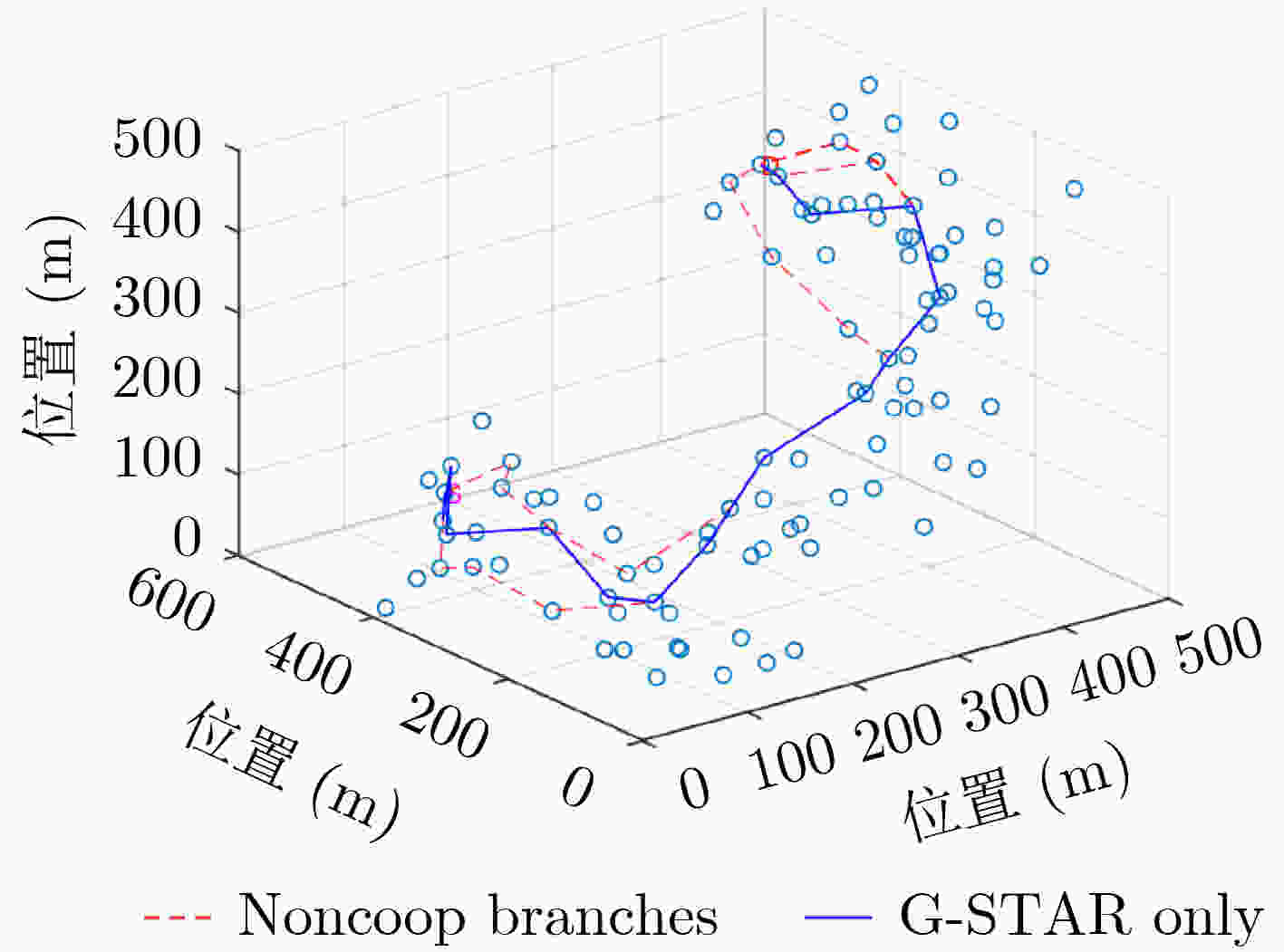
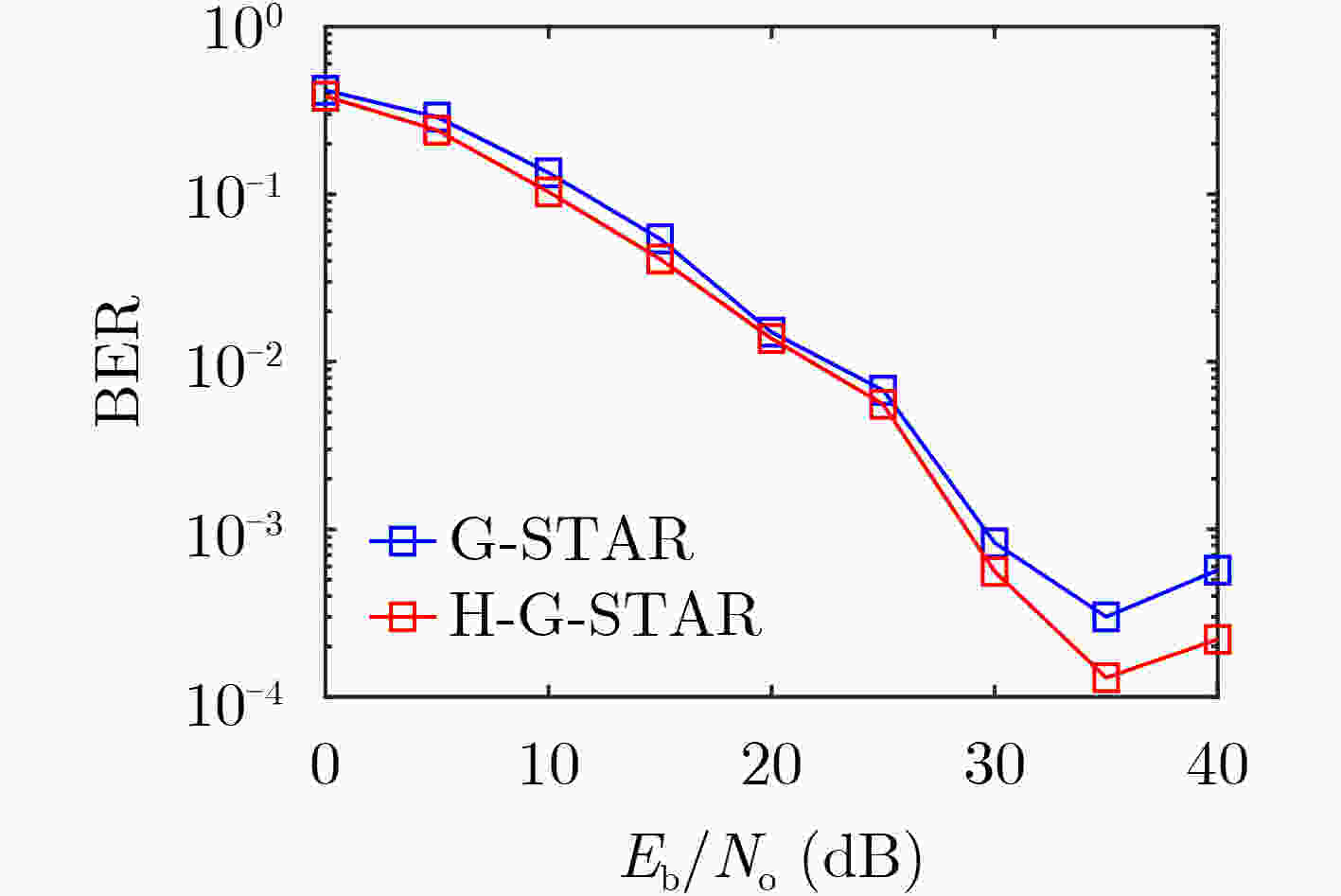
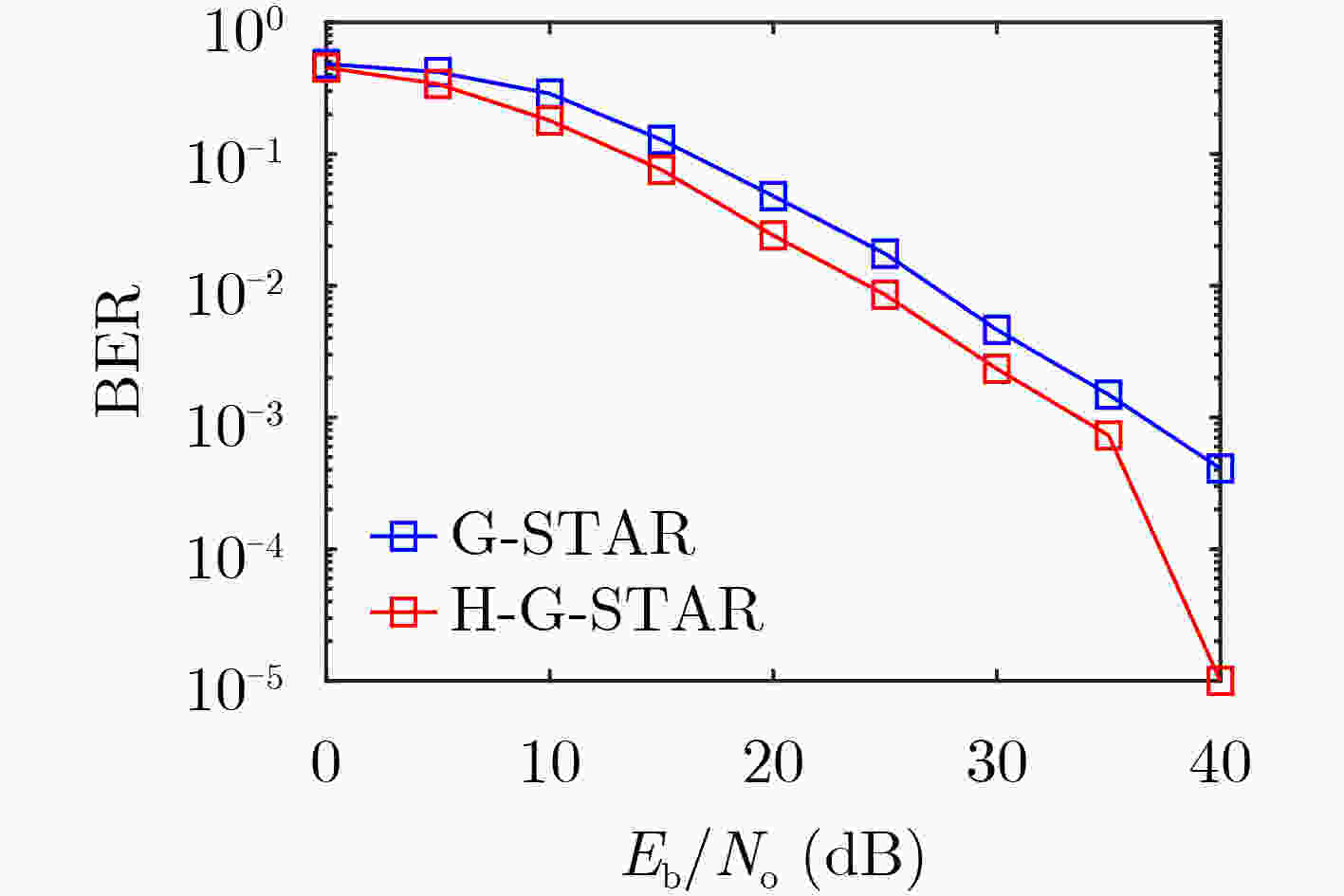
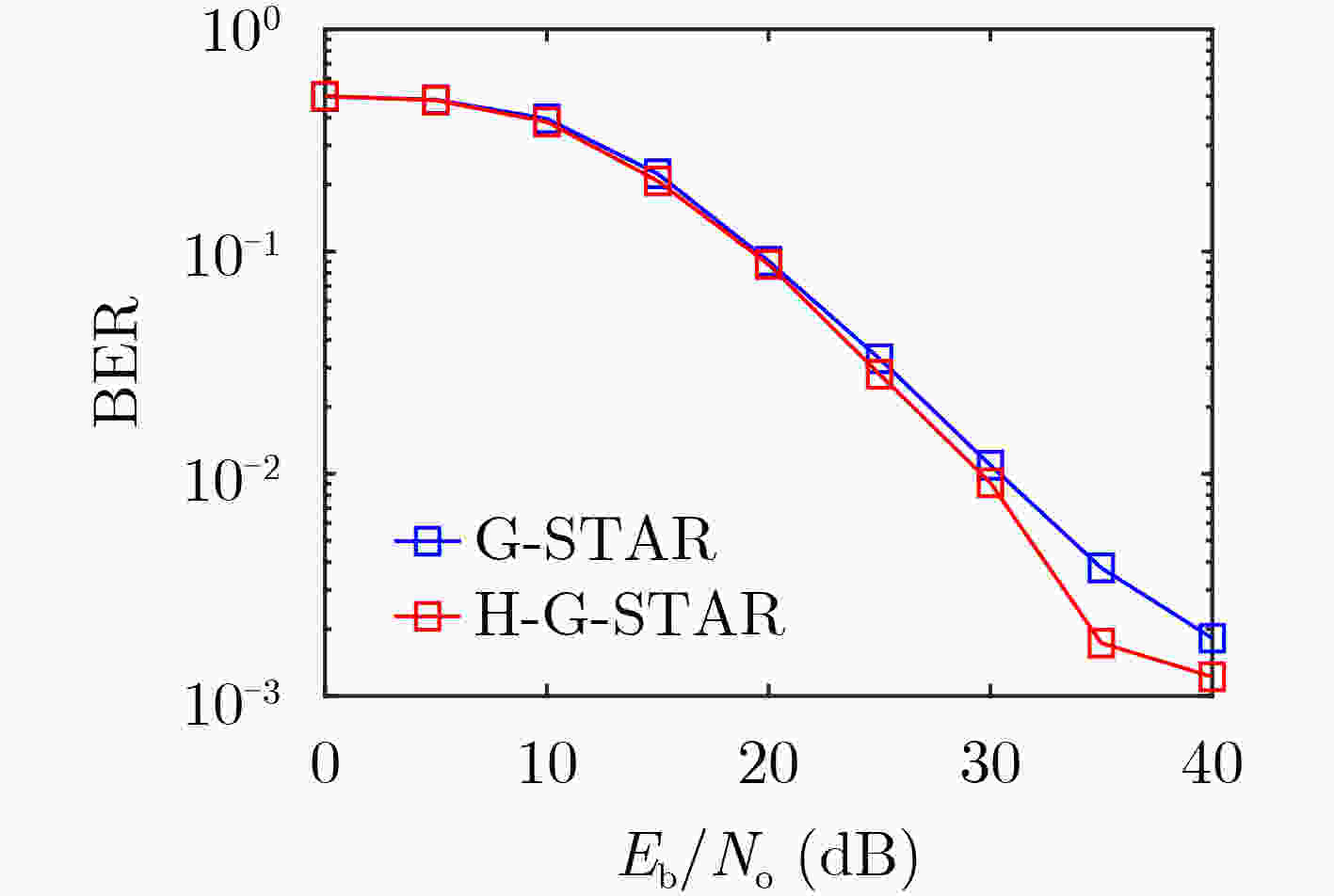
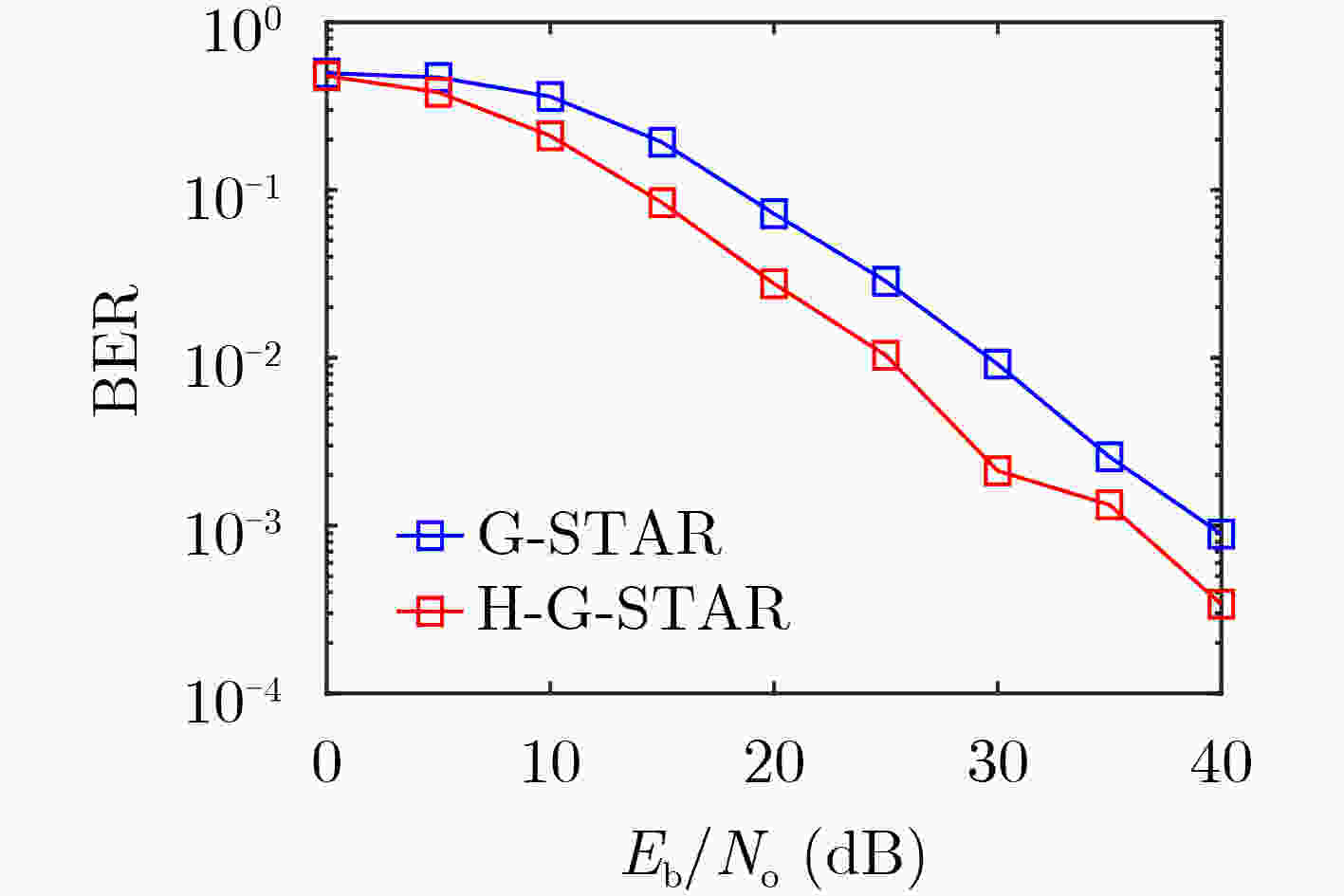
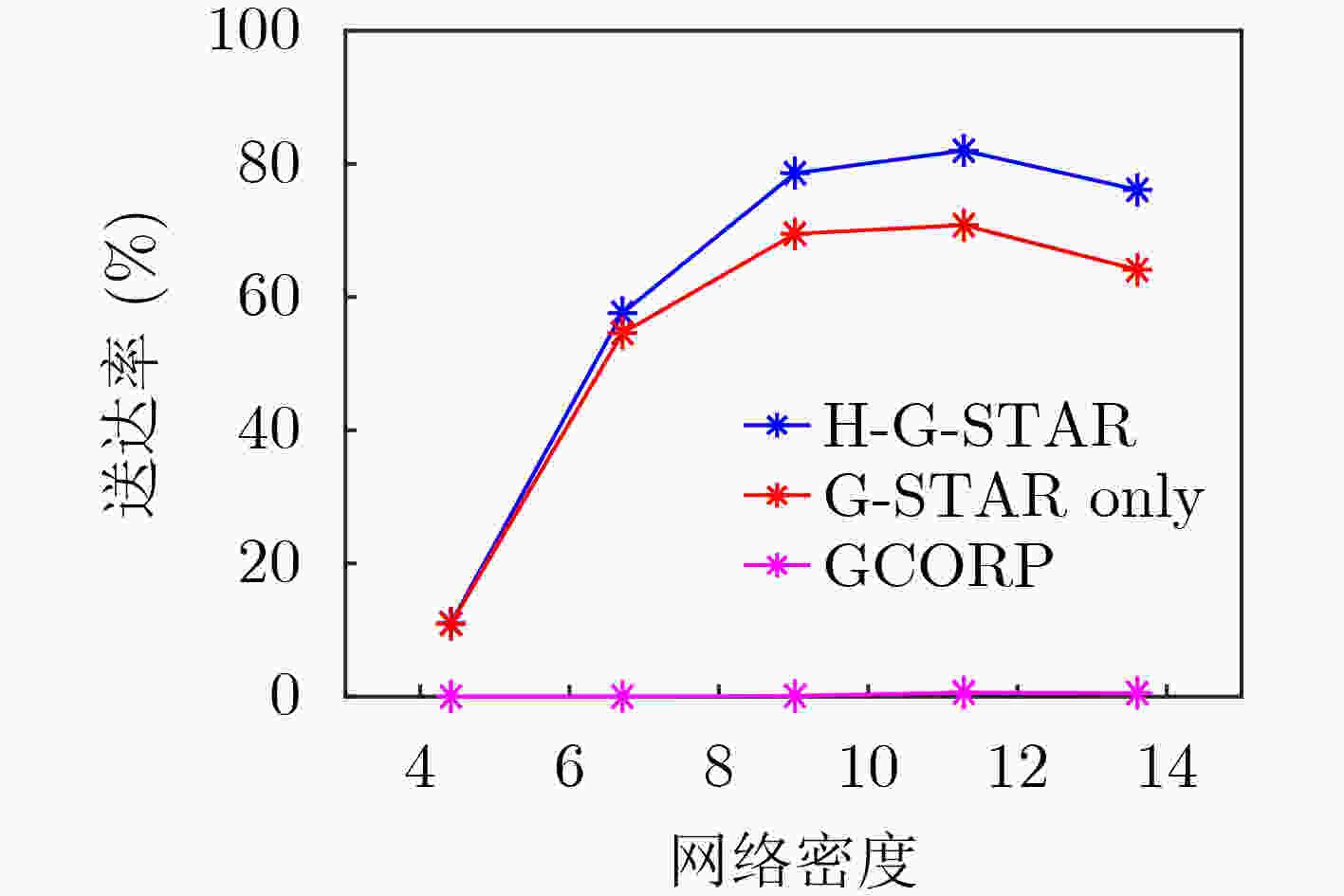
摘要: 该文针对水下物联网(IoUT)数据传输问题设计了一种混合地理路由协议。海洋环境的复杂性严重地限制了IoUT水下物联网节点间的数据传输性能,因此需要一个高效的路由协议以对抗复杂的信道环境。无状态几何路由(G-STAR)是一种采用贪婪转发模式的地理路由协议,在大多数3维物联网情景中能够找到合适的数据传输路径,然而水下环境中存在诸多不利因素制约了G-STAR的性能。对此,该文提出一个混合G-STAR(Hybrid G-STAR, H-G-STAR)协议,在保有G-STAR优势的基础上对协议在水下环境中的适应性进行了针对性设计。通过增加基于信道监听的无协作转发策略,在节点数量足够时自发地选择信道状况最佳的路径进行路由,由此避开贪婪转发在水下环境中可能遭遇的极端劣化信道。仿真结果显示H-G-STAR协议相较于基准G-STAR协议有着更好的路由性能,并且在物理层能够取得更低的误比特率(BER),在水下节点的网络拓扑中更为适用。Abstract: The goal of this paper is to design a routing protocol for IoUT data delivery. It is well known that underwater communication is limited by its channel’s hazardous nature, thus efficient routing protocols are needed to compensate for the challenging environments. Geometric STAteless Routing (G-STAR) is a type of geographical routing protocol that forwards messages in a greedy way and obtains sub-optimal results in most 3-dimensional Internet of Things scenarios. Yet the numerous degrading factors in underwater channels limit severely the performance of the G-STAR protocol. In this paper, a Hybrid G-STAR (H-G-STAR) routing protocol continuing the advantage of G-STAR and specifically adapted for underwater conditions is proposed. By introducing a noncooperative routing tactic based on channel listening, the protocol spontaneously searches for the route with the best channel condition whenever the network condition permits and thus avoiding inferior channels greedy routing might encounter. The simulation results show that the proposed protocol improves the routing performance of the network, obtains a lower Bit Error Rate (BER) in the physical layer than G-STAR and is better adapted for underwater network topologies.
-
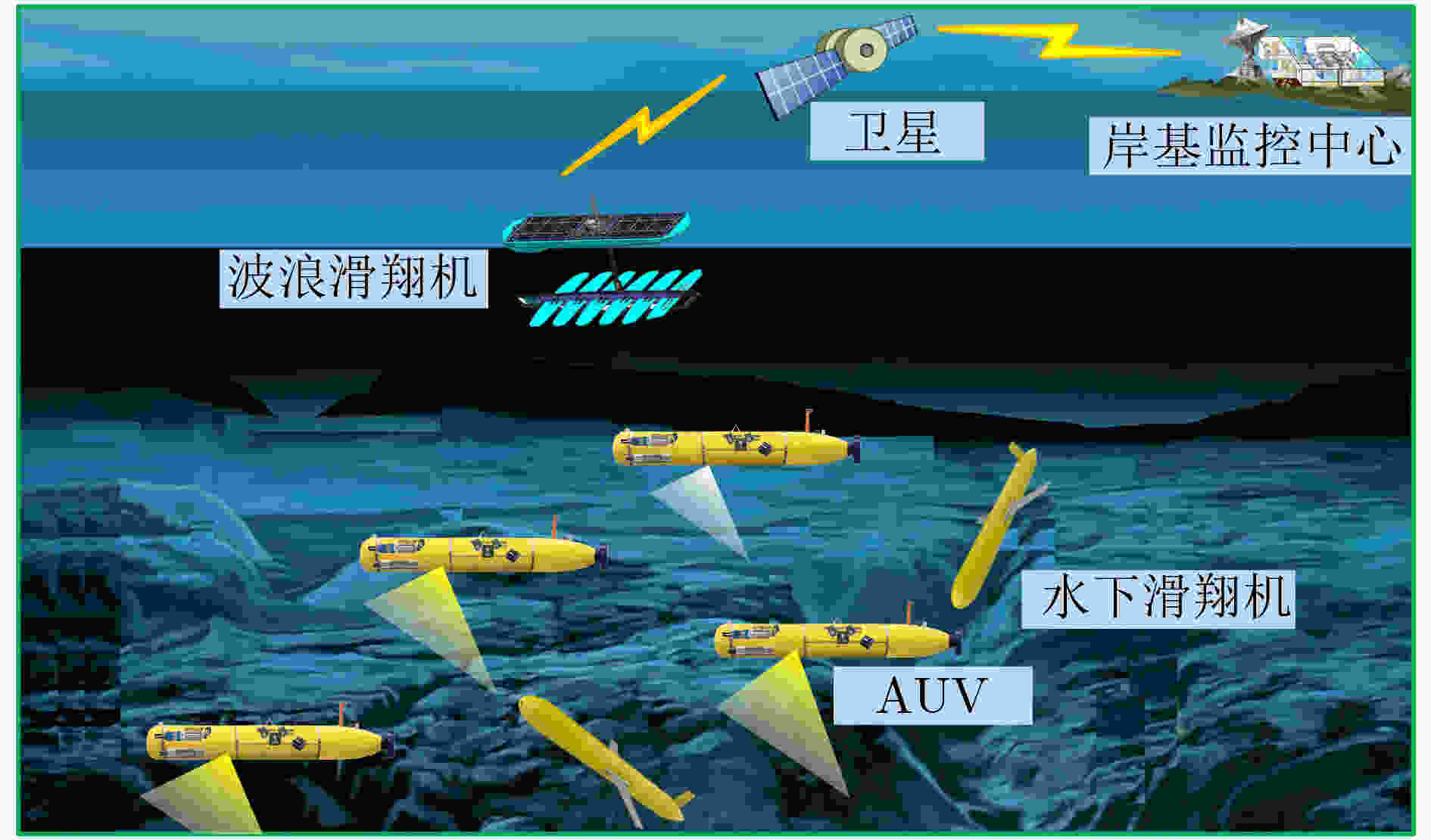
图 1 图l l2-AUV-MN-2.0网络模型的 ICPN[4]
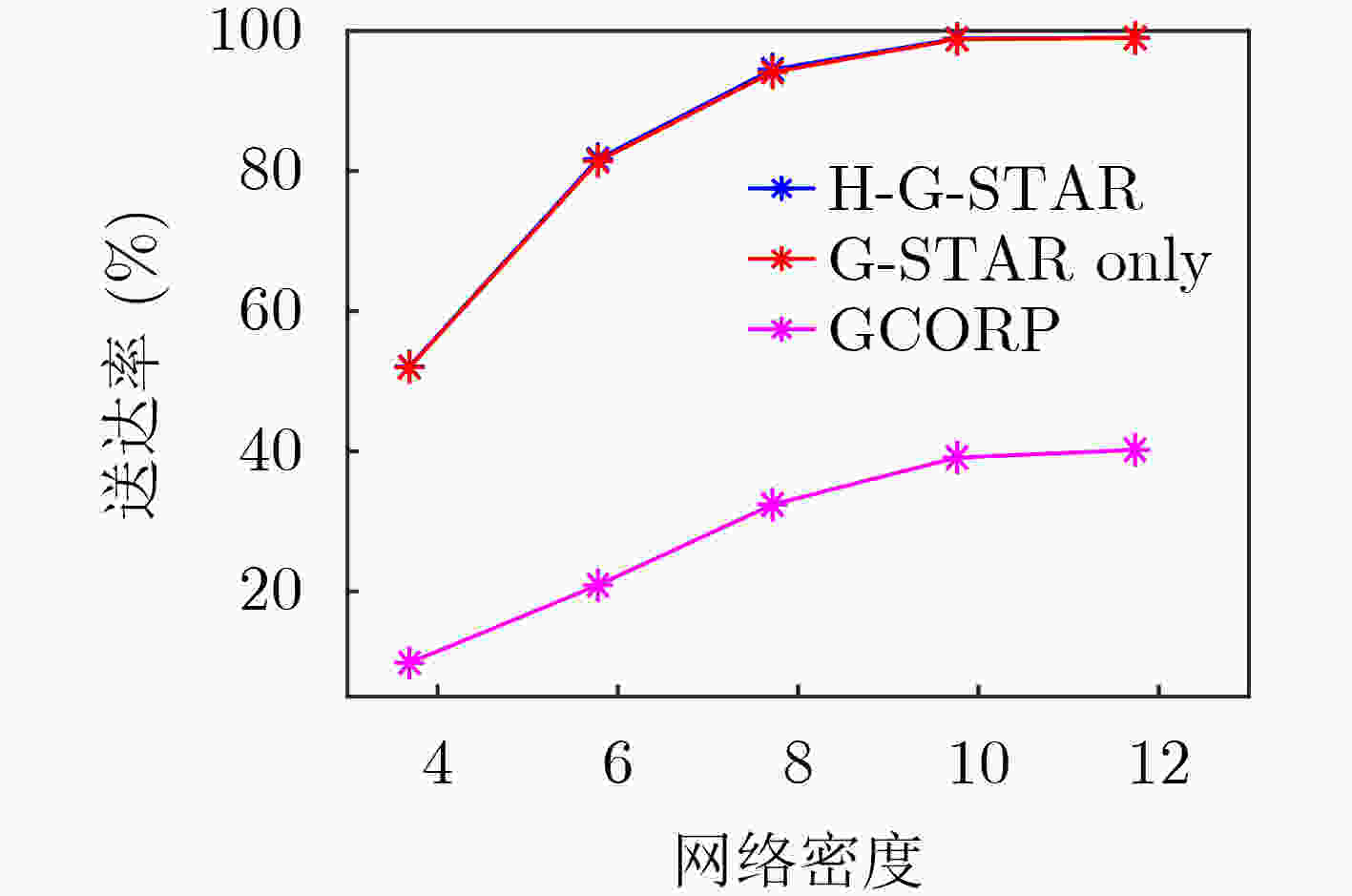
表 1 随机拓扑的误码率
网络密度 4 6 11 G-STAR 0.3780 0.0532 0.0233 H-G-STAR 0.3591 0.0526 0.0231 GCORP 0.9807 0.8453 0.5901 表 2 C型拓扑的误码率
网络密度 10 16 25 G-STAR 0.4062 0.1565 0.0705 H-G-STAR 0.2325 0.1187 0.0515 GCORP – 0.9811 0.9430 -
[1] 徐文, 鄢社锋, 季飞, 等. 海洋信息获取、传输、处理及融合前沿研究评述[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2016, 46(8): 1053–1085. doi: 10.1360/N112016-00064XU Wen, YAN Shefeng, JI Fei, et al. Marine information gathering, transmission, processing, and fusion: Current status and future trends[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2016, 46(8): 1053–1085. doi: 10.1360/N112016-00064 [2] 瞿逢重, 来杭亮, 刘建章, 等. 海洋物联网关键技术研究与应用[J]. 电信科学, 2021, 37(7): 25–33. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2021149QU Fengzhong, LAI Hangliang, LIU Jianzhang, et al. Research and application on key techniques of marine IoT[J]. Telecommunications Science, 2021, 37(7): 25–33. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-0801.2021149 [3] SU Yuhan, LIWANG Minghui, GAO Zhibin, et al. Optimal cooperative relaying and power control for IoUT networks with reinforcement learning[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 8(2): 791–801. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2020.3008178 [4] ZHANG Tongwei, YAN Lei, HAN Guangjie, et al. Fast and accurate underwater acoustic horizontal ranging algorithm for an arbitrary sound-speed profile in the deep sea[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2021, 9(1): 755–769. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3085331 [5] AKYILDIZ I F, POMPILI D, and MELODIA T. Underwater acoustic sensor networks: Research challenges[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2005, 3(3): 257–279. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2005.01.004 [6] CELIK A, SAEED N, SHIHADA B, et al. Opportunistic routing for opto-acoustic internet of underwater things[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2022, 9(3): 2165–2179. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2021.3090301 [7] GUAN Quansheng, JI Fei, LIU Yun, et al. Distance-vector-based opportunistic routing for underwater acoustic sensor networks[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(2): 3831–3839. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2891910 [8] CHEN Yougan, WANG Zhaohui, WAN Lei, et al. OFDM-modulated dynamic coded cooperation in underwater acoustic channels[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2015, 40(1): 159–168. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2014.2304254 [9] CELIK A, SAEED N, SHIHADA B, et al. A software-defined opto-acoustic network architecture for internet of underwater things[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(4): 88–94. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900593 [10] WEI Xiaohui, GUO Hao, WANG Xingwang, et al. Reliable data collection techniques in underwater wireless sensor networks: A survey[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24(1): 404–431. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2021.3134955 [11] LIOU E C, KAO C C, CHANG C H, et al. Internet of underwater things: Challenges and routing protocols[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Applied System Invention, Chiba, Japan, 2018: 1171–1174. [12] KARP B and KUNG H T. GPSR: Greedy perimeter stateless routing for wireless networks[C]. The 6th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, Boston, USA, 2000: 243–254. [13] KUHN F, WATTENHOFER R, ZHANG Yan, et al. Geometric ad-hoc routing: Of theory and practice[C]. The Twenty-Second Annual Symposium on Principles of Distributed Computing, Boston, USA, 2003: 63–72. [14] SUN Minte, SAKAI K, HAMILTON B R, et al. G-STAR: Geometric STAteless routing for 3-D wireless sensor networks[J]. Ad Hoc Networks, 2011, 9(3): 341–354. doi: 10.1016/j.adhoc.2010.07.013 [15] 孙大军, 郑翠娥, 崔宏宇, 等. 水下传感器网络定位技术发展现状及若干前沿问题[J]. 中国科学:信息科学, 2018, 48(9): 1121–1136. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00262SUN Dajun, ZHENG Cuie, CUI Hongyu, et al. Developing status and some cutting-edge issues of underwater sensor network localization technology[J]. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2018, 48(9): 1121–1136. doi: 10.1360/N112017-00262 [16] YAN Hai, SHI Z J, and CUI Junhong. DBR: Depth-based routing for underwater sensor networks[C]. The 7th International IFIP-TC6 Networking Conference on AdHoc and Sensor Networks, Wireless Networks, Next Generation Internet, Singapore, 2008: 72–86. [17] NOH Y, LEE U, LEE S, et al. HydroCast: Pressure routing for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2016, 65(1): 333–347. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2015.2395434 [18] NOH Y, LEE U, WANG P, et al. VAPR: Void-aware pressure routing for underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2013, 12(5): 895–908. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2012.53 [19] RAMEZANI H and LEUS G. Ranging in an underwater medium with multiple isogradient sound speed profile layers[J]. Sensors, 2012, 12(3): 2996–3017. doi: 10.3390/s120302996 [20] PREISIG J. Acoustic propagation considerations for underwater acoustic communications network development[C]. The 1st ACM International Workshop on Underwater Networks, Los Angeles, USA, 2006: 1–5. [21] NGUYEN S T, CAYIRCI E, YAN Liang, et al. A shadow zone aware routing protocol for tactical acoustic undersea surveillance networks[C]. 2009 IEEE Military Communications Conference, Boston, USA, 2009: 1–7. [22] QU F. Underwater acoustic communication and IoUT[R]. 2021. [23] MATHUR S, SAGARI S S, AMIN S O, et al. Demo abstract: CDMA-based IoT services with shared band operation of LTE in 5G[C]. 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops, Atlanta, USA, 2017: 958–959. [24] ZHANG Tongwei, HAN Guangjie, LIN Chuan, et al. Integration of communication, positioning, navigation and timing for deep-sea vehicles[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(2): 121–127. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1900294 [25] ZHANG Tongwei, YAN Lei, HAN Guangjie, et al. Low-cost, long-endurance cooperative navigation based on “light” marine equipment in deep sea[J]. IEEE Network, 2021, 35(2): 222–228. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.2000443 [26] ZHANG Tongwei, HAN Guangjie, YAN Lei, et al. Fast calculation of underwater acoustic horizontal range: A guarantee for B5G ocean mobile networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2021, 8(4): 2922–2933. doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2020.3025571 [27] HAMILTON B R and MA X. Noncooperative routing with cooperative diversity[C]. 2007 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Glasgow, UK, 2007: 4237–4242. [28] MA Xiaoli, SUN Minte, ZHAO Gang, et al. An efficient path pruning algorithm for geographical routing in wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2008, 57(4): 2474–2488. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2007.912332 [29] 陈友淦, 许肖梅. 人工智能技术在水声通信中的研究进展[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2020, 41(10): 1536–1544. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202007110CHEN Yougan and XU Xiaomei. Research progress in artificial intelligence technology for underwater acoustic communications[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2020, 41(10): 1536–1544. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202007110 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
