Secure Energy Efficiency in Communication Systems Based on Deep Learning
-
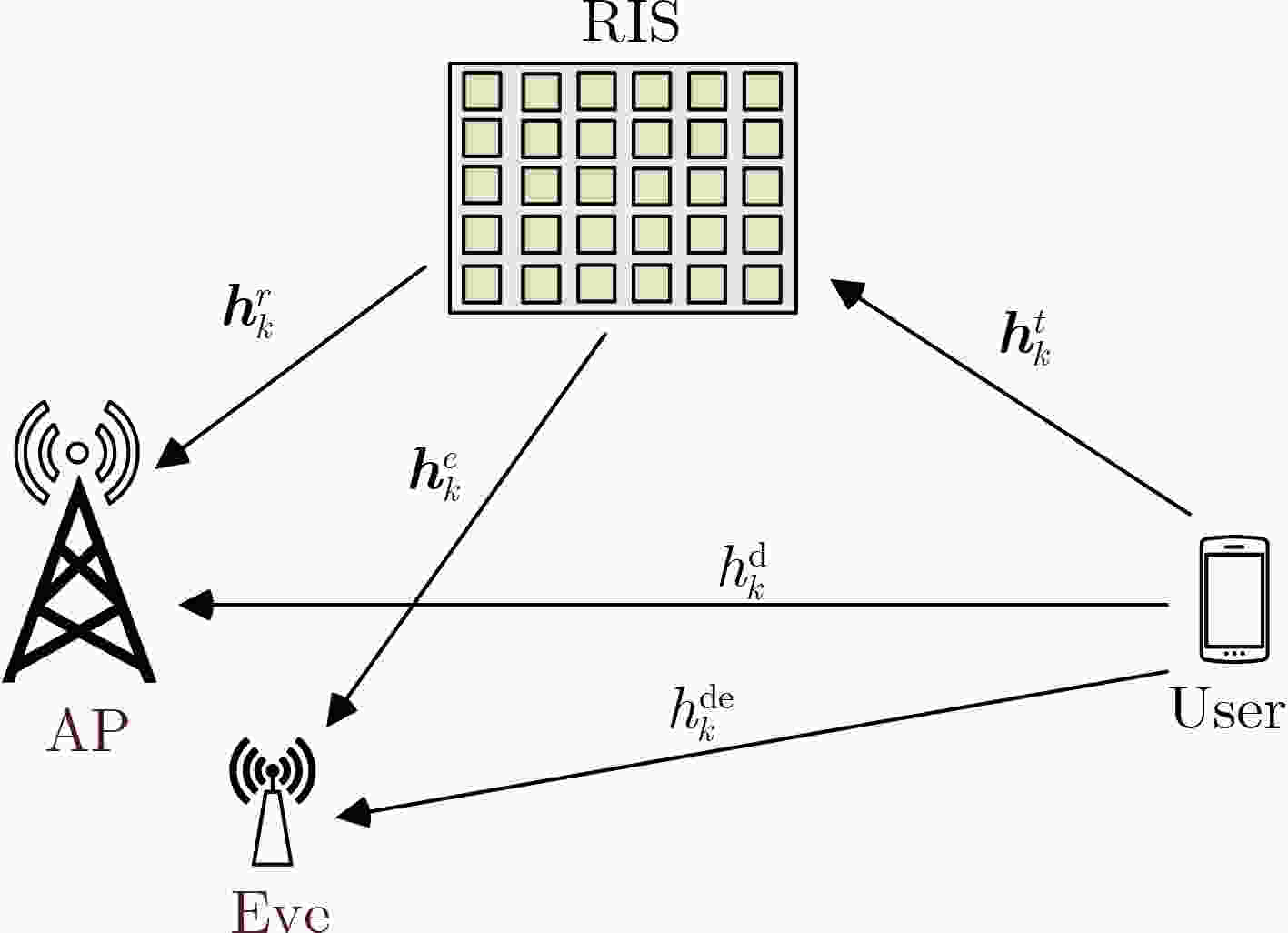
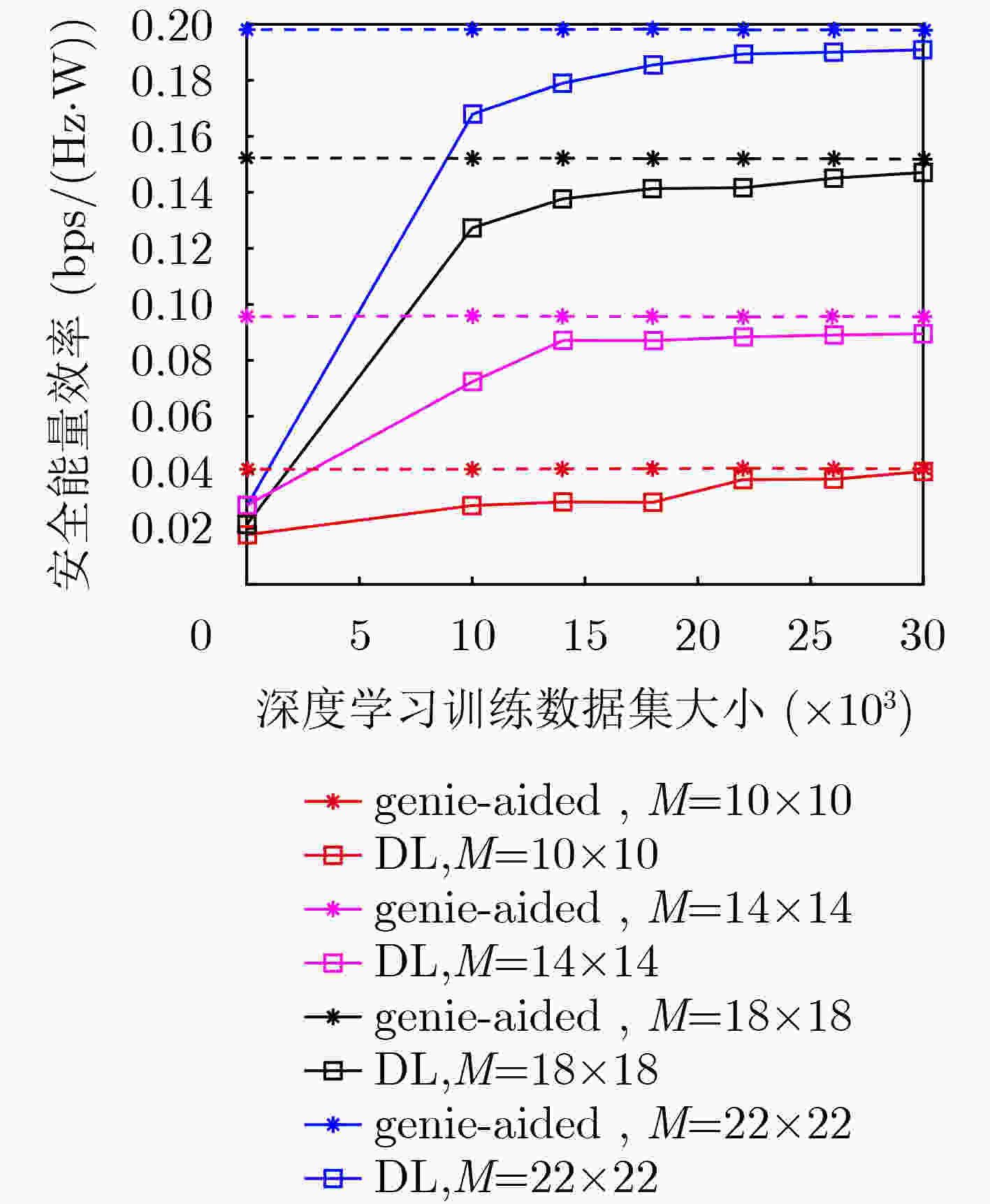
摘要: 该文研究了基于可重构智能超表面(RIS)赋能的无线通信系统的安全传输问题。在研究的模型中,一个用户通过智能超表面连接到接入点,而窃听者窃听了从用户发送到基站的信号。因此,有必要设计一个合适的智能超表面反射向量来解决窃听问题。这个问题被表述为一个优化问题,其目标是通过共同优化智能超表面反射向量和智能超表面元件的数量来最大化安全能效,该安全能效定义为安全速率与系统总能耗的比值。这是一个非凸优化问题,传统方法是难以解决的。为了解决这个问题,提出了一种利用新兴的深度学习(DL)技术的新算法,以找到近似最优的智能超表面反射向量并确定近似最优的genie-aided反射元素数量。仿真结果表明,该方法达到了近似最优算法的最佳安全能效的96%。Abstract: The secure transmission for Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) assisted wireless communication systems is investigated in this paper. In the studied model, one user connects to the access point via a RIS while an eavesdropper eavesdrops on the signal sent from the user to the access point. Therefore, it is necessary to design an appropriate RIS reflection vector to solve the eavesdropping problem. This problem is formulated as an optimization problem whose goal is to maximize the secure energy efficiency which is defined via jointly optimizing the RIS reflection reflector as well as the number of RIS elements, which results in a non-convex optimization problem that is intractable to solve by the traditional methods. To tackle this issue, a new algorithm by leveraging the advance of the emerging Deep Learning (DL) technique is proposed so as to find the near optimal RIS reflection vector and determine the near optimal number of RIS reflection elements. Simulation results show that the proposed method reaches 96% of the near optimal secure energy efficiency of the genie-aided algorithm.
-
表 1 基于深度神经网络的DeepRIS(算法1)
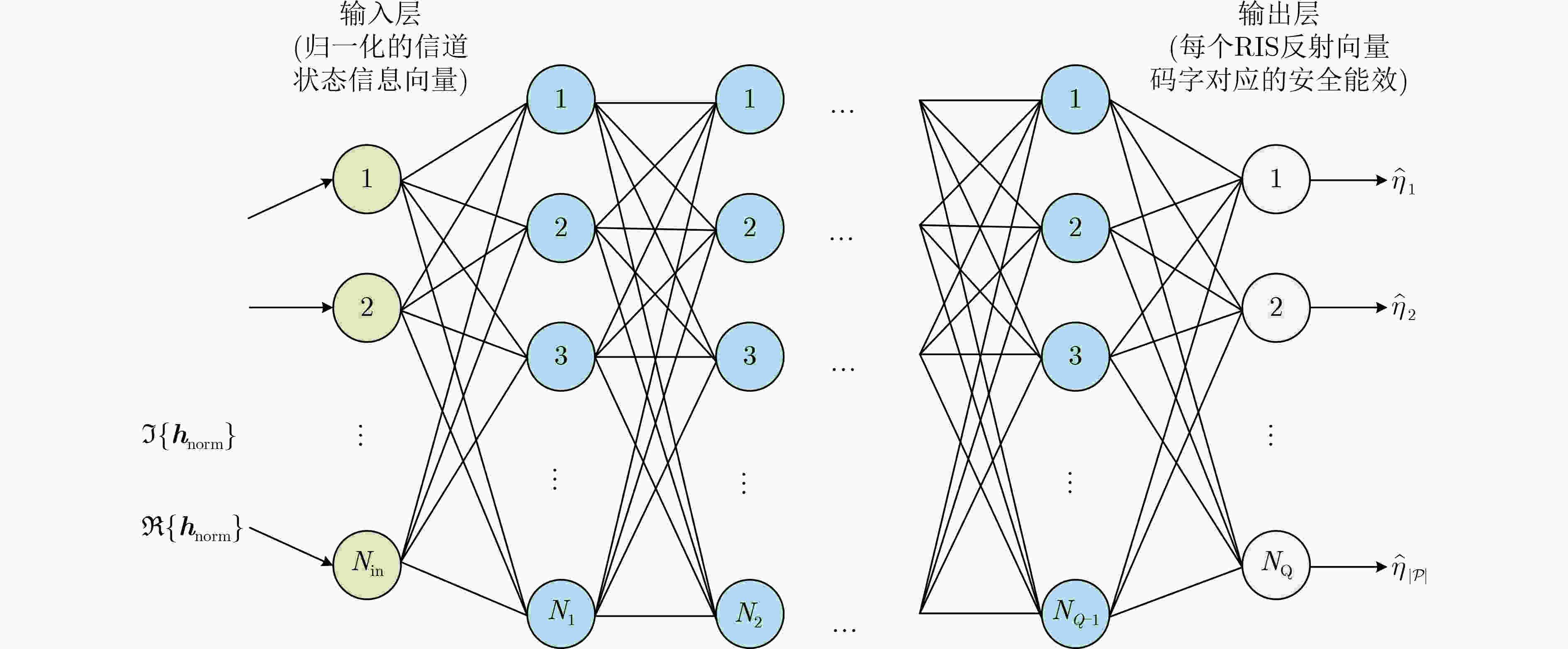
阶段(1):训练阶段 for $s = 1$ to $S$ do //第$s$个信道相干块,$s = 1,2, \cdots ,S$ RIS系统获得信道状态描述符${\mathbf{h}}(s)$ for $n = 1$ to $ \left| \mathcal{P} \right| $ do RIS基于$ {{\mathbf{\theta }}_n} $和RIS激活单元个数$ M $计算出对应的安全能量效率
${\eta _n}(s)$end for RIS构造安全能量效率向量$ {\mathbf{\eta }}(s) = \left[ {{\eta _1}(s),{\eta _2}(s), \cdots ,{\eta _{\left| \mathcal{P} \right|}}(s)} \right] $ 将所获得的数据添加到训练数据集$\mathcal{D} \leftarrow \left\langle {{\mathbf{h}}(s),{\mathbf{\eta }}(s)} \right\rangle $ RIS使用最佳反射向量$ {{\mathbf{\theta }}_{{n^*}}} $($ {n^*} = \arg \mathop {\max }\limits_n {\eta _n}(s) $)传输数据 end for 使用训练数据集$\mathcal{D}$训练深度神经网络 阶段(2):预测阶段 while true do //针对每个信道相干块 RIS系统获得信道状态描述符${\mathbf{h}}$ RIS利用深度神经网络模型预测反射向量
$ {{\mathbf{\theta }}_{{n^{{\text{D}}L}}}} $($ {n^{{\text{DL}}}} = \arg \mathop {\max }\limits_n {\hat \eta _n}(s) $)和激活的反射单元个数
$ {M_{{\text{DL}}}} $($ {M_{{\text{DL}}}} = \arg \mathop {\max }\limits_M \hat \eta _{\max }^M(s) $)RIS使用最佳反射向量$ {{\mathbf{\theta }}_{{n^{{\text{D}}L}}}} $传输数据 end while 表 2 系统及深度MIMO数据集参数
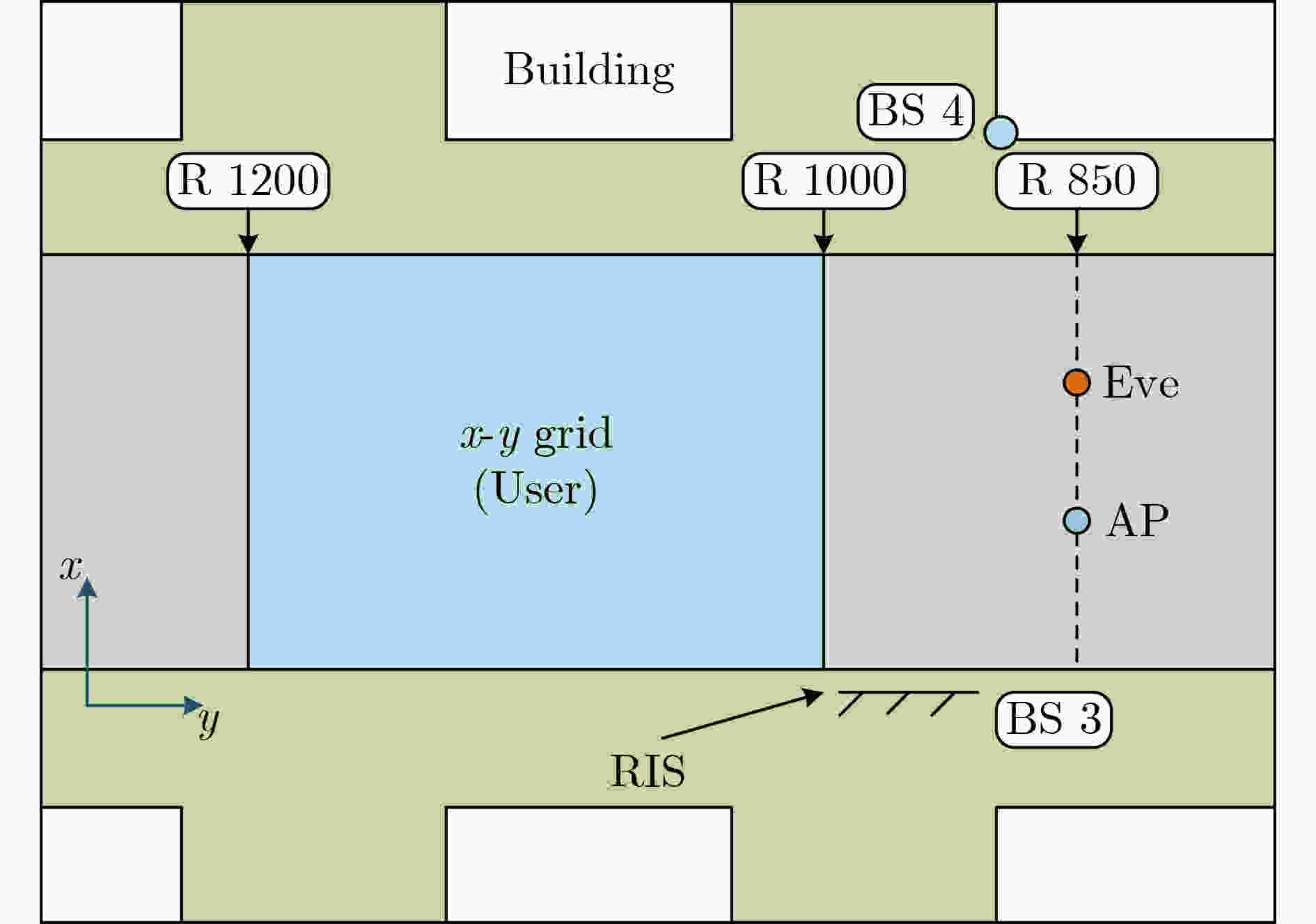
Deep MIMO数据集参数 数值 基站编号(作为RIS) 3 作为发射器的用户 从R1000到R1200的网格范围内 作为AP的用户 R850行,第90列 作为Eve的用户 R850行,第100列 发射器(用户)/接收器(AP/Eve)天线数 均为1 BS天线(RIS单元)数 8×8($ M = 64 $),10×10($ M = 100 $),
12×12($ M = 144 $),14×14($ M = 196 $),
16×16($ M = 256 $),18×18($ M = 324 $),
20×20($ M = 400 $),22×22($ M = 484 $),
24×24($ M = 576 $)系统带宽 100 MHz OFDM子载波数 256 OFDM使用子载波数 4 OFDM采样系数 1 路径数 1 天线间距 0.5 天线单元增益 3 dBi 发射机天线发射功率 35 dBm 用户设备的噪声系数 5 dB 每个RIS单元的功率 0.005W -
[1] TAN Xin, SUN Zhi, JORNET J M, et al. Increasing indoor spectrum sharing capacity using smart reflect-array[C]. 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2016. [2] TAN Xin, SUN Zhi, KOUTSONIKOLAS D, et al. Enabling indoor mobile millimeter-wave networks based on smart reflect-arrays[C]. IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, Honolulu, USA, 2018. [3] HUANG Chongwen, HU Sha, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Holographic MIMO surfaces for 6G wireless networks: Opportunities, challenges, and trends[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2020, 27(5): 118–125. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.1900534 [4] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(8): 4157–4170. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2922609 [5] HUM S V and PERRUISSEAU-CARRIER J. Reconfigurable reflectarrays and array lenses for dynamic antenna beam control: A review[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2014, 62(1): 183–198. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2013.2287296 [6] FOO S. Liquid-crystal reconfigurable metasurface reflectors[C]. 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, San Diego, USA, 2017. [7] LIASKOS C, NIE Shuai, TSIOLIARIDOU A, et al. A new wireless communication paradigm through software-controlled metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(9): 162–169. doi: 10.1109/mcom.2018.1700659 [8] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107 [9] HUANG Chongwen, ZAPPONE A, DEBBAH M, et al. Achievable rate maximization by passive intelligent mirrors[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Calgary, Canada, 2018. [10] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Beamforming optimization for intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Brighton, UK, 2019. [11] HUANG Chongwen, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, ZAPPONE A, et al. Energy efficient multi-user MISO communication using low resolution large intelligent surfaces[C]. 2018 IEEE Globecom Workshops, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018. [12] KHAN S, KHAN K S, and SHIN S Y. Symbol denoising in high order M-QAM using residual learning of deep CNN[C]. The 2019 16th IEEE Annual Consumer Communications & Networking Conference, Las Vegas, USA, 2019. [13] KHAN S and SHIN S Y. Deep learning aided transmit power estimation in mobile communication system[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2019, 23(8): 1405–1408. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2019.2923625 [14] HUANG Chongwen, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, YUEN C, et al. Indoor signal focusing with deep learning designed reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[C]. The 2019 IEEE 20th International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications, Cannes, France, 2019. [15] ALKHATEEB A. DeepMIMO: A generic deep learning dataset for millimeter wave and massive MIMO applications[C]. The Information Theory and Applications Workshop, San Diego, USA, 2019. [16] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network: Joint active and passive beamforming design[C]. 2018 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 2018. [17] SUBRT L and PECHAC P. Intelligent walls as autonomous parts of smart indoor environments[J]. IET Communications, 2012, 6(8): 1004–1010. doi: 10.1049/iet-com.2010.0544 [18] RAPPAPORT T S, SUN Shu, MAYZUS R, et al. Millimeter wave mobile communications for 5g cellular: It will work![J]. IEEE Access, 2013, 1: 335–349. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2013.2260813 [19] IEEE 802.11 ad standard draft d0.1[EB/OL]. www. ieee802. org/11/Reports/tgadupdate. htm, 2012. [20] AKDENIZ M R, LIU Yuanpeng, SAMIMI M K, et al. Millimeter wave channel modeling and cellular capacity evaluation[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32(6): 1164–1179. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2014.2328154 [21] SAMIMI M K and RAPPAPORT T S. Ultra-wideband statistical channel model for non line of sight millimeter-wave urban channels[C]. 2014 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Austin, USA, 2014. [22] SCHNITER P and SAYEED A. Channel estimation and precoder design for millimeter-wave communications: The sparse way[C]. The 2014 48th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, USA, 2014. [23] BOCCARDI F, HEATH R W, LOZANO A, et al. Five disruptive technology directions for 5G[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2014, 52(2): 74–80. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2014.6736746 [24] VA V, CHOI J, and HEATH R W. The impact of beamwidth on temporal channel variation in vehicular channels and its implications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 66(6): 5014–5029. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2016.2622164 [25] RUCK D W, ROGERS S K, KABRISKY M, et al. The multilayer perceptron as an approximation to a Bayes optimal discriminant function[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1990, 1(4): 296–298. doi: 10.1109/72.80266 [26] ALKHATEEB A, ALEX S, VARKEY P, et al. Deep learning coordinated beamforming for highly-mobile millimeter wave systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 37328–37348. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2850226 [27] JIANG Hao, RUAN Chengyao, ZHANG Zaichen, et al. A general wideband non-stationary stochastic channel model for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(8): 5314–5328. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3066806 [28] NI Wanli, LIU Yuanwei, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Federated learning in multi-RIS aided systems[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. To be published. [29] YANG Zhaohui, HU Ye, ZHANG Zhaoyang, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface based orbital angular momentum: Architecture, opportunities, and challenges[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(6): 132–137. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2100223 [30] CHEN Xiao, SHI Jianfeng, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Low-complexity channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-enhanced massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(5): 996–1000. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3054004 [31] XU Yongjun, GAO Zhengnian, WANG Zhengqiang, et al. RIS-enhanced WPCNs: Joint radio resource allocation and passive beamforming optimization[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(8): 7980–7991. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3096603 [32] CHEN Mingzhe, YANG Zhaohui, SAAD W, et al. A joint learning and communications framework for federated learning over wireless networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(1): 269–283. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3024629 [33] YANG Zhaohui, CHEN Mingzhe, SAAD W, et al. Energy efficient federated learning over wireless communication networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(3): 1935–1949. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3037554 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
