Dynamic Response of a Class of Hybrid Neuron Model by Electromagnetic Induction and Application of Image Encryption
-
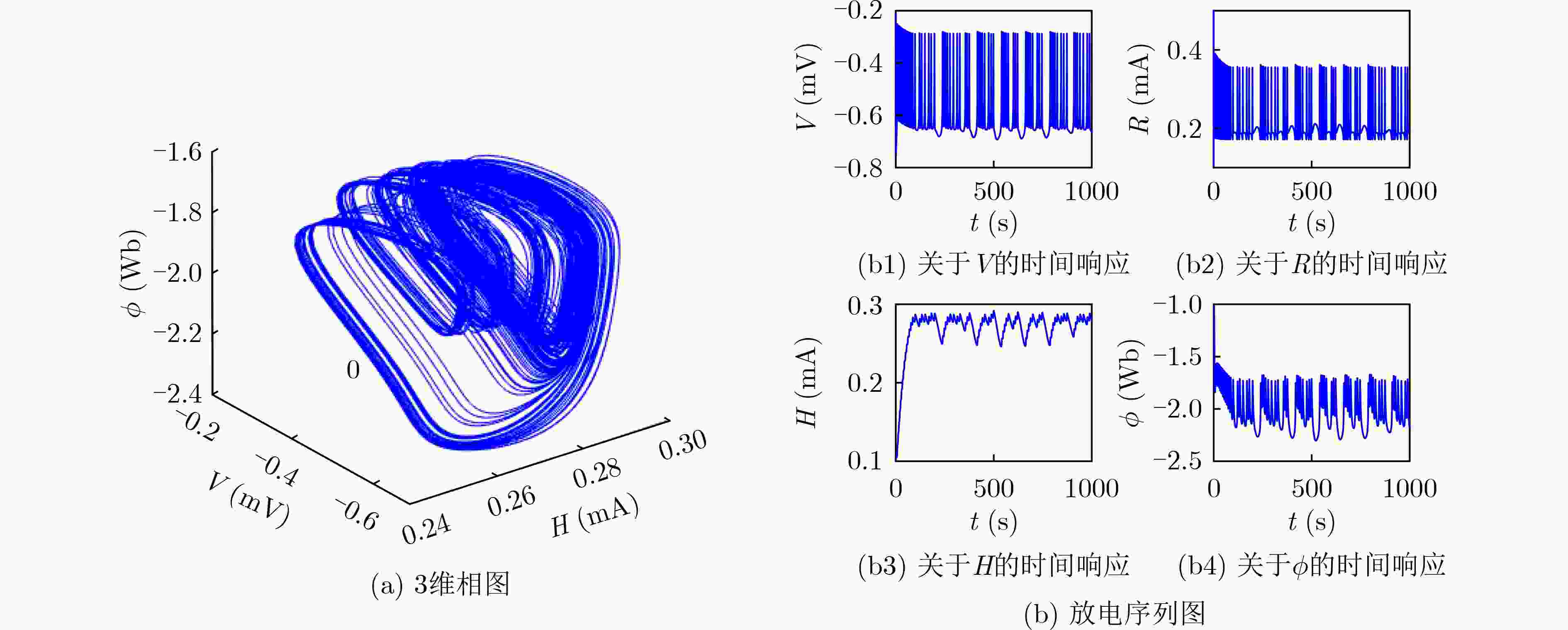
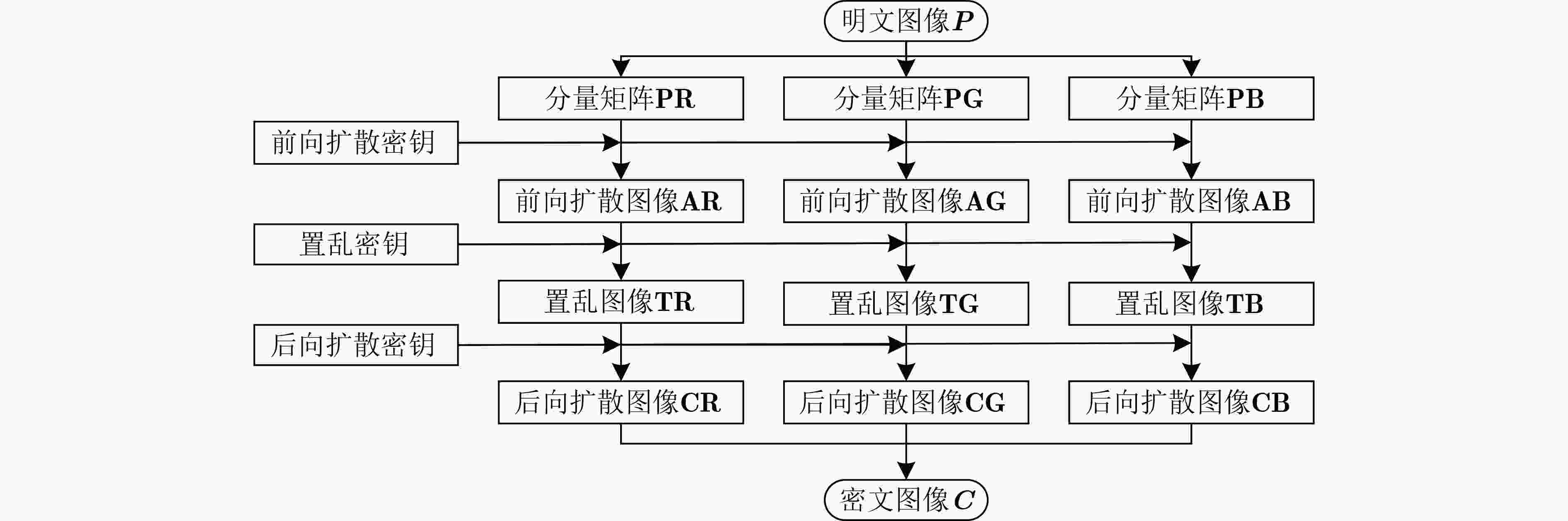
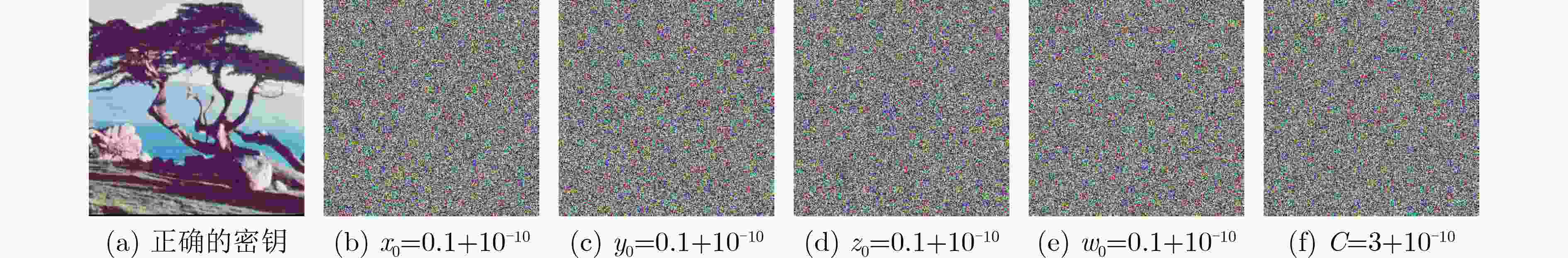
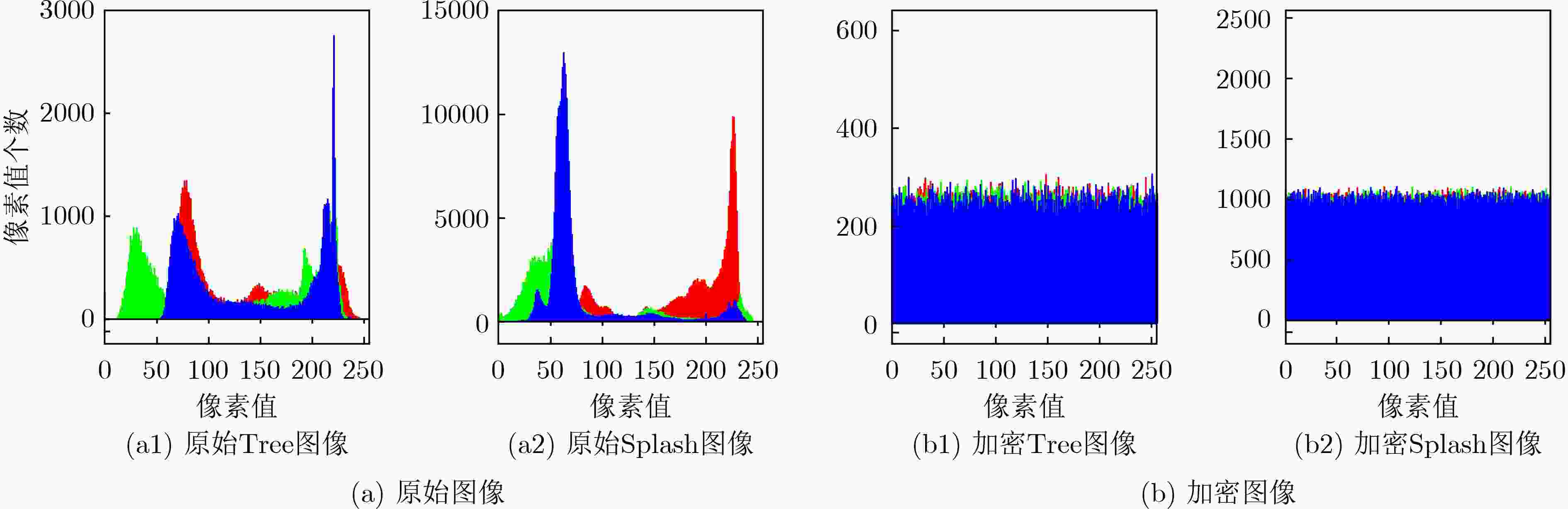
摘要: 在神经元活动的模型建立和分析过程中,应考虑一些生物物理效应。由于神经系统内部细胞内外离子浓度的波动,在集体电活动和神经元集群之间信号传播的过程中需要考虑电磁场的内部波动和跨膜磁通的影响。该文在一类混合神经元中引入磁通变量,通过对膜电位的调制诱发复杂的时变电磁场,运用Xppauto, Matcont和MATLAB等分析工具,探讨了新模型平衡点的存在性、初值敏感性和双参数分岔,发现外界刺激电流和电磁场变化时,可诱发新模型产生丰富的放电模式,如静息态、尖峰放电、周期(或混沌)簇放电,特别是由于磁通变量及忆阻器的引入产生的共存放电、隐藏放电等新现象。通过上述分析,基于电磁感应的神经元模型具有高非线性和较多的敏感参数,可使加密算法具有较大的密钥空间,基于此,该文设计了一种图像加密算法,对明文图像的像素先进行1次扩散再对其位置进行两次置乱。最后,通过一系列数值实验证明所设计的加密算法能有效地加密图像并且具有较高的安全性。该文考虑了神经细胞内外的电磁感应效应,有助于更全面了解神经元之间的信息编码和转迁规律,更多的分岔参数和高复杂性也使所设计的神经元模型在图像加密中具有很好的应用前景。Abstract: During the modeling and analysis of neuronal activity, several biophysical effects should be taken into consideration. Due to fluctuations in intracellular and extracellular ion concentrations within the nervous system, internal fluctuations of electromagnetic fields and the effects of transmembrane magnetic flux need to be considered in the collective electrical activity and signal propagation between neuronal clusters. In this paper, a magnetic flux variable is introduced into a hybrid neuron, and a complex time-varying electromagnetic field is induced by modulating the membrane potential. Using analytical tools such as Xppauto, Matcont and Matlab, the existence and initial value of the equilibrium point of the new model, sensitivity and two-parameter bifurcation are discussed. When the external stimulus current and electromagnetic field change, the new model can be induced to generate abundant discharge modes, such as resting state, spike discharge, periodic (or chaotic) cluster discharge, especially coexisting discharge and hidden discharge benefited from the introduction of magnetic flux variable and memristor. According to the above analysis, the neuron model based on electromagnetic induction has high nonlinearity and more sensitive parameters, which enables the encryption algorithm to have a large key space. Based on this, an image encryption algorithm is designed in this paper. Pixels are first diffused once and then scrambled twice to their positions. Finally, through a series of numerical experiments, it is proved that the designed encryption algorithm can encrypt images effectively and has high security. The research takes into account the electromagnetic induction effect inside and outside the nerve cells, which is helpful for a more comprehensive understanding of the information encoding and transition laws between neurons. More bifurcation parameters and high complexity also make the designed neuron model has a good application prospect in image encryption.
-
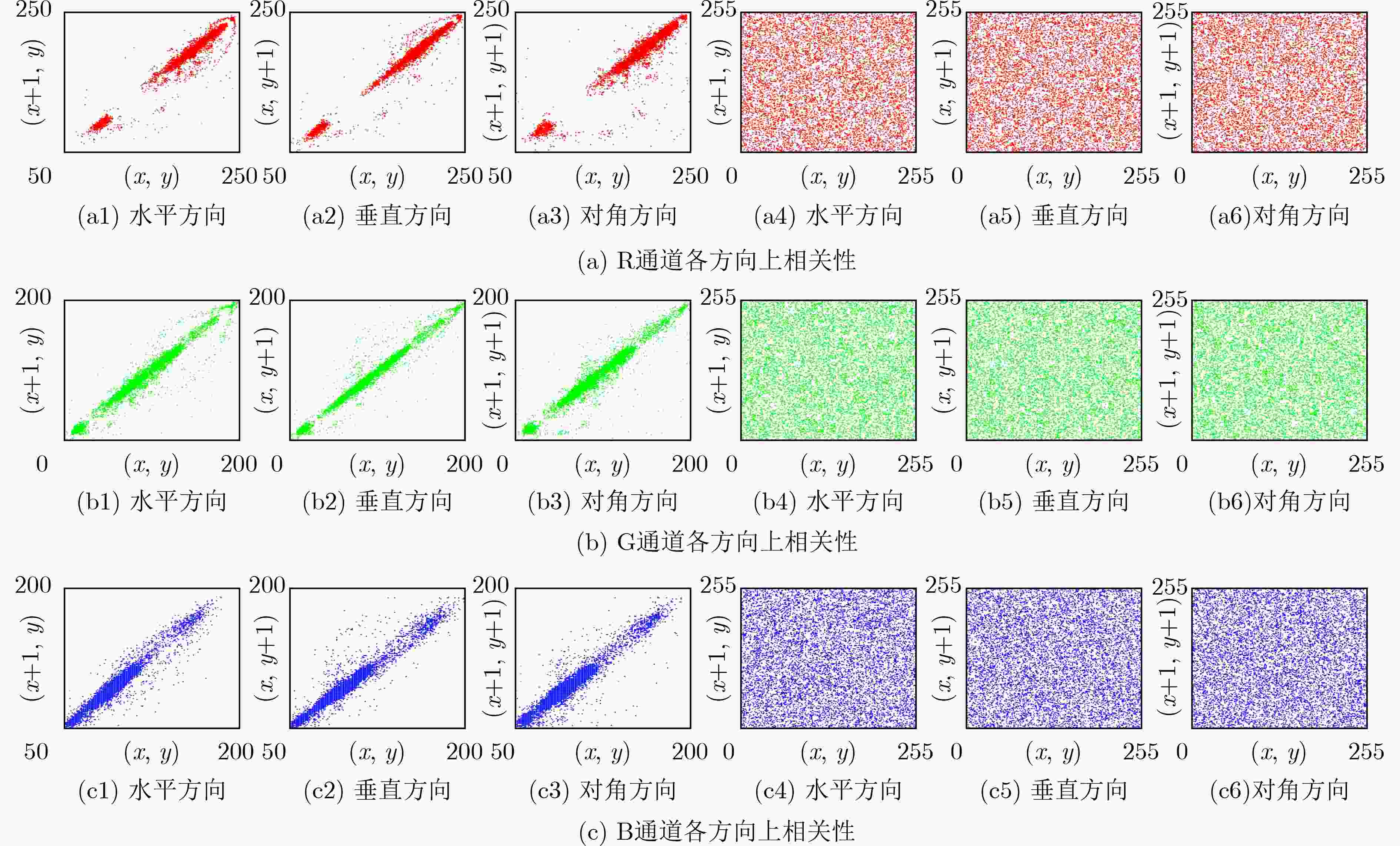
表 1 Lena图像的相关性系数对比
-
[1] BABACAN Y, KAÇAR F, and GÜRKAN K. A spiking and bursting neuron circuit based on memristor[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 203: 86–91. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.03.060 [2] BAO Bocheng, HU Aihuang, BAO Han, et al. Three-dimensional memristive Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model with hidden coexisting asymmetric behaviors[J]. Complexity, 2018, 2018: 3872573. doi: 10.1155/2018/3872573 [3] ZHAO Yong, SUN Xiaoyan, LIU Yang, et al. Phase synchronization dynamics of coupled neurons with coupling phase in the electromagnetic field[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 93(3): 1315–1324. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4261-7 [4] 曹奔, 关利南, 古华光. 兴奋性作用诱发神经簇放电个数不增反降的分岔机制[J]. 物理学报, 2018, 67(24): 240502. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20181675CAO Ben, GUAN Linan, and GU Huaguang. Bifurcation mechanism of not increase but decrease of spike number within a neural burst induced by excitatory effect[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(24): 240502. doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20181675 [5] 李诗玮, 全廷伟, 周航, 等. 神经元形态重建进展及趋势[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(5/6): 532–545. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00998LI Shiwei, QUAN Tingwei, ZHOU Hang, et al. Review of advances and prospects in neuron reconstruction[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(5/6): 532–545. doi: 10.1360/N972018-00998 [6] XU Quan, TAN Xiao, ZHU Dong, et al. Bifurcations to bursting and spiking in the Chay neuron and their validation in a digital circuit[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2020, 141: 110353. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.110353 [7] 徐泠风, 李传东, 陈玲. 神经元模型对比分析[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(24): 240701. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.240701XU Lingfeng, LI Chuandong, and CHEN Ling. Contrastive analysis of neuron model[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2016, 65(24): 240701. doi: 10.7498/aps.65.240701 [8] 彭俊, 王如彬. 神经元膜电位对信息的编码[J]. 动力学与控制学报, 2020, 18(1): 24–32. doi: 10.6052/1672-6553-2020-011PENG Jun and WANG Rubin. Information coding of neuronal membrane potential[J]. Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2020, 18(1): 24–32. doi: 10.6052/1672-6553-2020-011 [9] 王春华, 蔺海荣, 孙晶如, 等. 基于忆阻器的混沌、存储器及神经网络电路研究进展[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821WANG Chunhua, LIN Hairong, SUN Jingru, et al. Research progress on chaos, memory and neural network circuits based on memristor[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(4): 795–810. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190821 [10] RAJAGOPAL K, NAZARIMEHR F, KARTHIKEYAN A, et al. Dynamics of a neuron exposed to integer- and fractional-order discontinuous external magnetic flux[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2019, 20(4): 584–590. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1800389 [11] AN Xinlei and ZHANG Li. Dynamics analysis and Hamilton energy control of a generalized Lorenz system with hidden attractor[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 94(4): 2995–3010. doi: 10.1007/s11071-018-4539-9 [12] MA Jun and TANG Jun. A review for dynamics of collective behaviors of network of neurons[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2015, 58(12): 2038–2045. doi: 10.1007/s11431-015-5961-6 [13] LV Mi, WANG Chunni, REN Guodong, et al. Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2016, 85(3): 1479–1490. doi: 10.1007/s11071-016-2773-6 [14] WU Fuqiang, WANG Chunni, JIN Wuyin, et al. Dynamical responses in a new neuron model subjected to electromagnetic induction and phase noise[J]. Physica A:Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2017, 469: 81–88. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2016.11.056 [15] 安新磊, 张莉. 一类忆阻神经元的电活动多模振荡及Hamilton能量反馈控制[J]. 力学学报, 2020, 52(4): 1174–1188. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-20-035AN Xinlei and ZHANG Li. Multi-mode oscillations and Hamilton energy feedback control of a class of memristor neuron[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2020, 52(4): 1174–1188. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-20-035 [16] 安新磊, 乔帅, 张莉. 基于麦克斯韦电磁场理论的神经元动力学响应与隐藏放电控制[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(5): 050501. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201347AN Xinlei, QIAO Shuai, and ZHANG Li. Dynamic response and control of neuros based on electromagnetic field theory[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(5): 050501. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201347 [17] KAFRAJ M S, PARASTESH F, and JAFARI S. Firing patterns of an improved Izhikevich neuron model under the effect of electromagnetic induction and noise[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2020, 137: 109782. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109782 [18] NJITACKE Z T, DOUBLA I S, MABEKOU S, et al. Hidden electrical activity of two neurons connected with an asymmetric electric coupling subject to electromagnetic induction: Coexistence of patterns and its analog implementation[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2020, 137: 109785. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2020.109785 [19] ZHOU Yicong, HUA Zhongyun, PUN C M, et al. Cascade chaotic system with applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2015, 45(9): 2001–2012. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2014.2363168 [20] ALI D S, ALWAN N A, and AI-SAIDI N M G. Image encryption based on highly sensitive chaotic system[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2019, 2183(1): 080007. doi: 10.1063/1.5136200 [21] SUN Jiayu, LI Chunbiao, LU Tianai, et al. A memristive chaotic system with hypermultistability and its application in image encryption[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 139289–139298. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3012455 [22] YANG Feifei, MOU Jun, MA Chenguang, et al. Dynamic analysis of an improper fractional-order laser chaotic system and its image encryption application[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 129: 106031. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2020.106031 [23] LI Xuejun, MOU Jun, XIONG Li, et al. Fractional-order double-ring erbium-doped fiber laser chaotic system and its application on image encryption[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 140: 107074. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2021.107074 [24] XU Ji, LI Peng, YANG Feifei, et al. High intensity image encryption scheme based on quantum Logistic chaotic map and complex hyperchaotic system[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 167904–167918. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2952140 [25] BAO Han, HUA Zhongyun, LIU Wenbo, et al. Discrete memristive neuron model and its interspike interval-encoded application in image encryption[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2021, 64(10): 2281–2291. doi: 10.1007/s11431-021-1845-x [26] ZHANG Sen, ZHENG Jiahao, WANG Xiaoping, et al. Multi-scroll hidden attractor in memristive HR neuron model under electromagnetic radiation and its applications[J]. Chaos:An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2021, 31(1): 011101. doi: 10.1063/5.0035595 [27] YILDIRIM M. DNA encoding for RGB image encryption with memristor based neuron model and chaos phenomenon[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2020, 104: 104878. doi: 10.1016/j.mejo.2020.104878 [28] TLELO-CUAUTLE E, DÍAZ-MUÑOZ J D, GONZÁLEZ-ZAPATA A M, et al. Chaotic image encryption using Hopfield and Hindmarsh–Rose neurons implemented on FPGA[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(5): 1326. doi: 10.3390/s20051326 [29] SLIMANE N B, AOUF N, BOUALLEGUE K, et al. A novel chaotic image cryptosystem based on DNA sequence operations and single neuron model[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2018, 77(23): 30993–31019. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-6145-8 [30] ZHAO Xuelong, KIM J W, ROBINSON P A, et al. Low dimensional model of bursting neurons[J]. Journal of Computational Neuroscience, 2014, 36(1): 81–95. doi: 10.1007/s10827-013-0468-2 [31] WILSON H R. Simplified dynamics of human and mammalian neocortical neurons[J]. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 1999, 200(4): 375–388. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1999.1002 [32] JAFARI S, SPROTT J C, and NAZARIMEHR F. Recent new examples of hidden attractors[J]. The European Physical Journal Special Topics, 2015, 224(8): 1469–1476. doi: 10.1140/epjst/e2015-02472-1 [33] JIA Bing, GU Huaguang, and XUE Lei. A basic bifurcation structure from bursting to spiking of injured nerve fibers in a two-dimensional parameter space[J]. Cognitive Neurodynamics, 2017, 11(2): 189–200. doi: 10.1007/s11571-017-9422-8 [34] ALVAREZ G and LI Shujun. Some basic cryptographic requirements for chaos-based cryptosystems[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2006, 16(8): 2129–2151. doi: 10.1142/S0218127406015970 [35] WU Xiangjun, WANG Kunshu, WANG Xingyuan, et al. Color image DNA encryption using NCA map-based CML and one-time keys[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 148: 272–287. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.02.028 [36] ZHOU Jie, ZHOU Nanrun, and GONG Lihua. Fast color image encryption scheme based on 3D orthogonal Latin squares and matching matrix[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2020, 131: 106437. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106437 [37] YANG Feifei, MOU Jun, LUO Chunfeng, et al. An improved color image encryption scheme and cryptanalysis based on a hyperchaotic sequence[J]. Physica Scripta, 2019, 94(8): 085206. doi: 10.1088/1402-4896/ab0033 [38] LIU Hongjun, KADIR A, and XU Chengbo. Color image encryption with cipher feedback and coupling chaotic map[J]. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 2020, 30(12): 2050173. doi: 10.1142/S0218127420501734 -





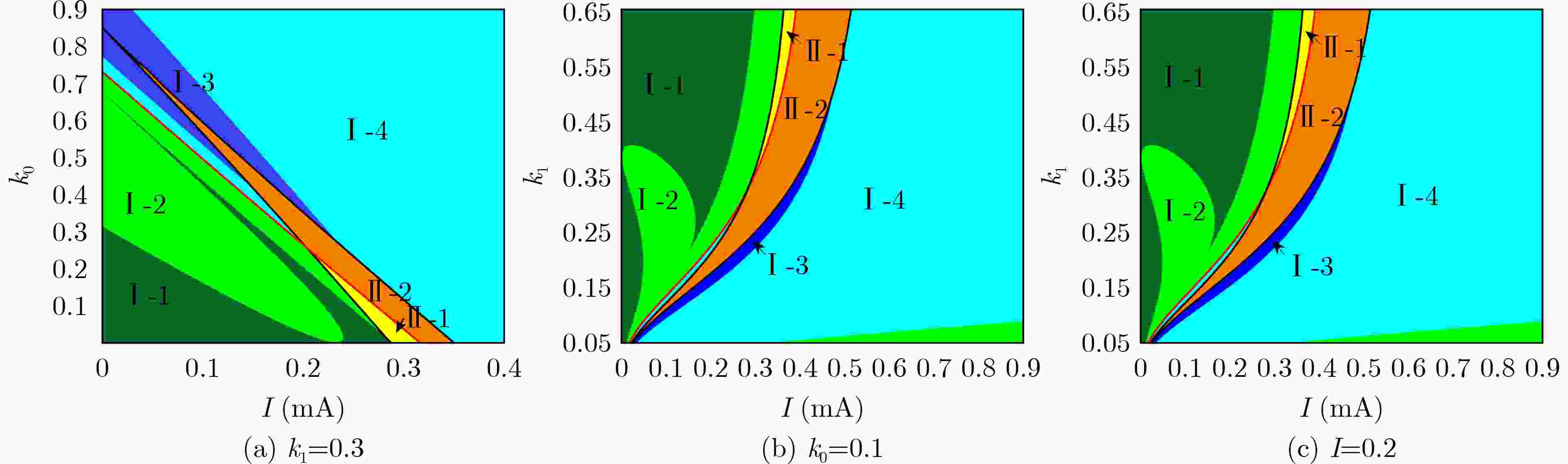
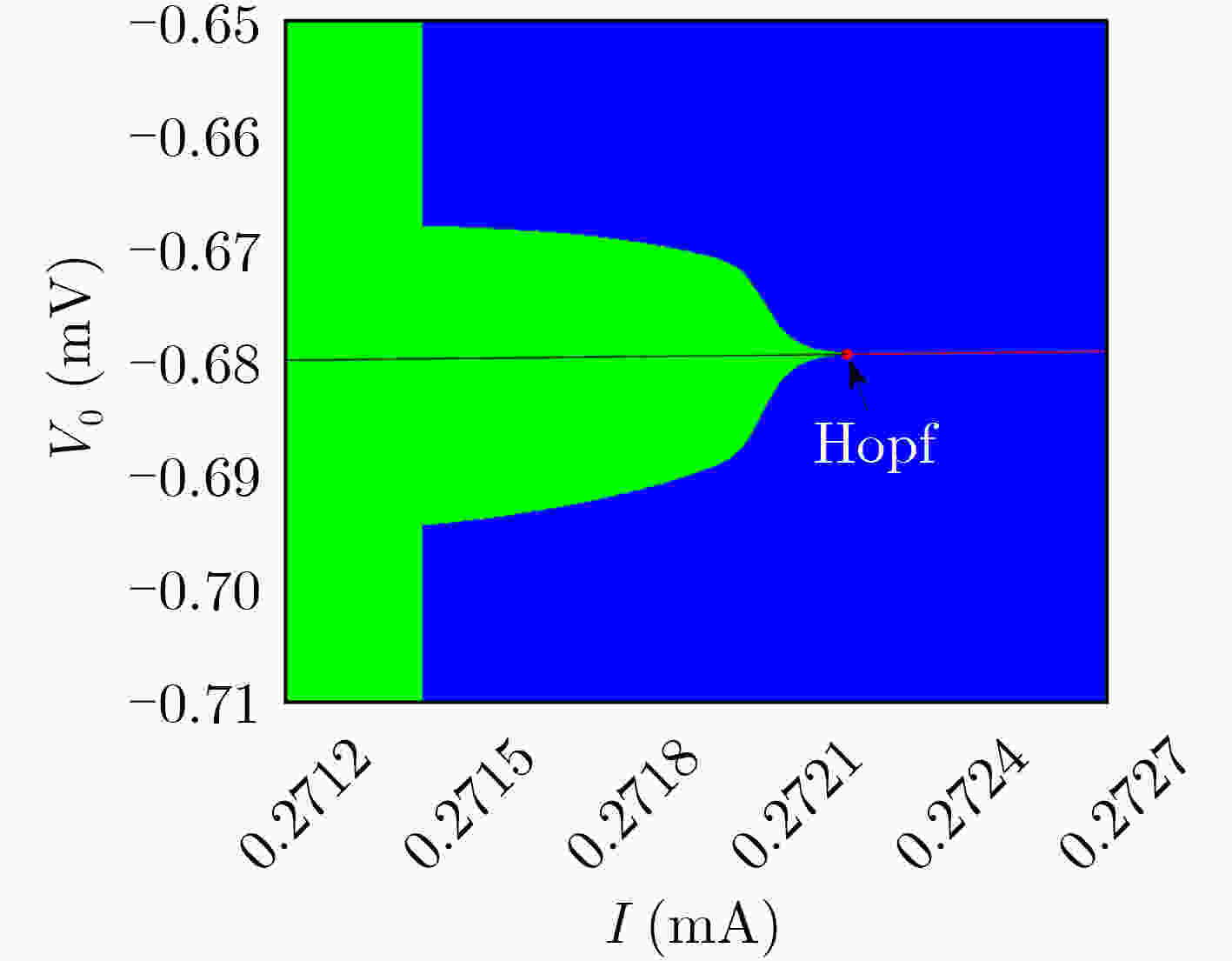
 下载:
下载:


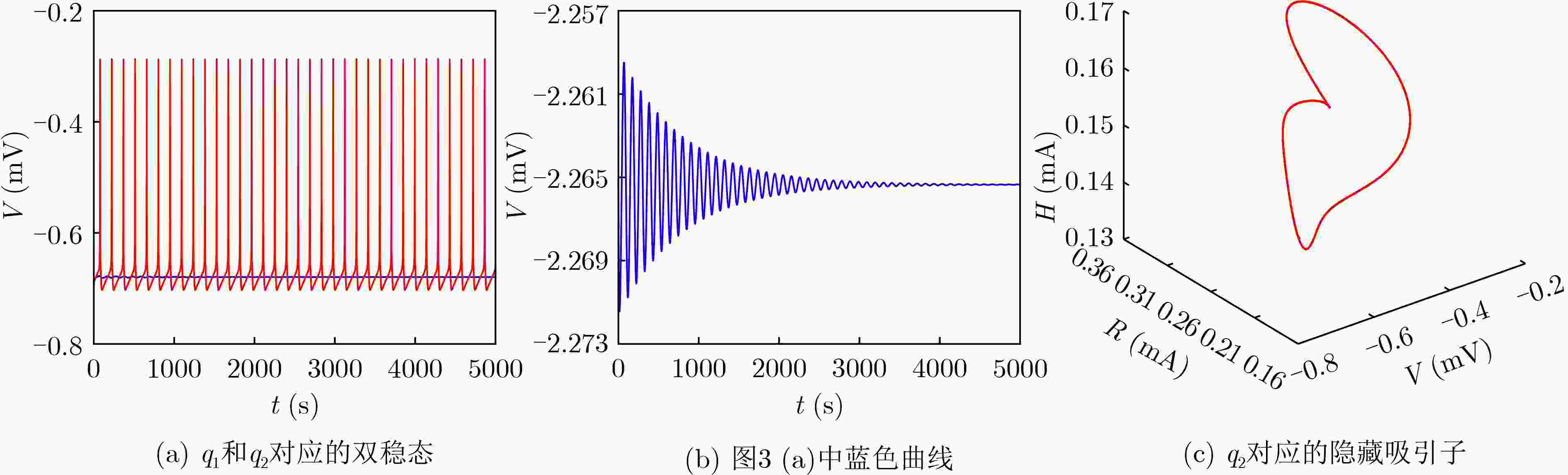

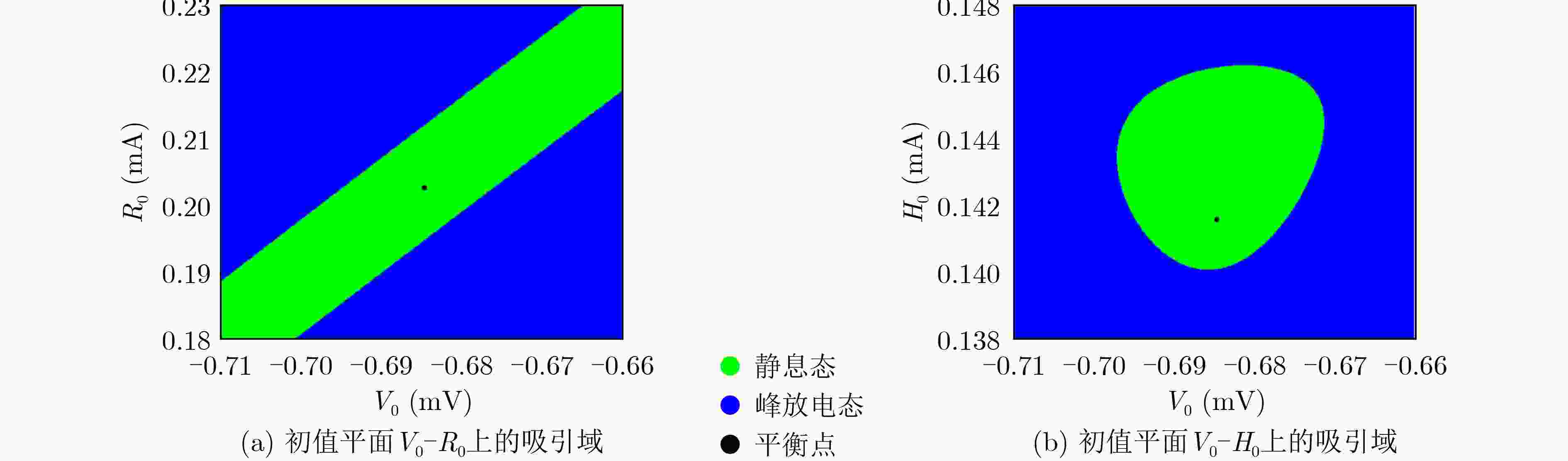
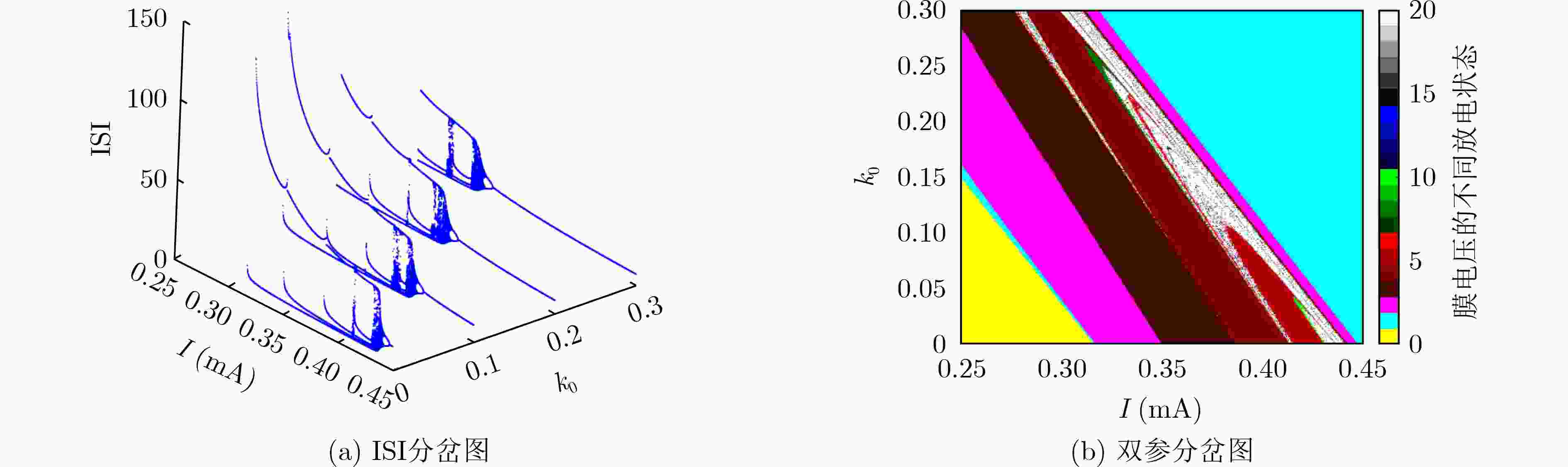


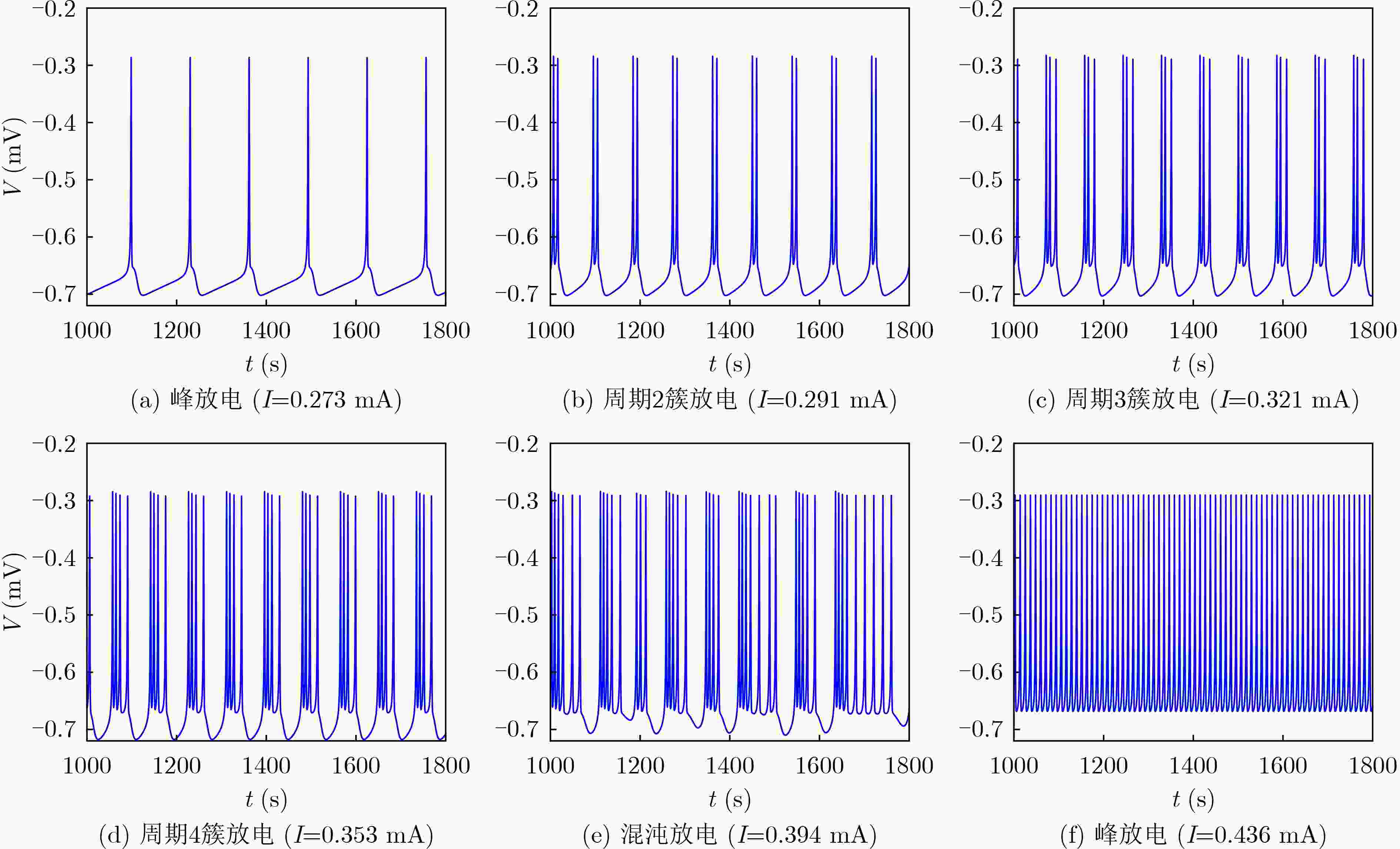


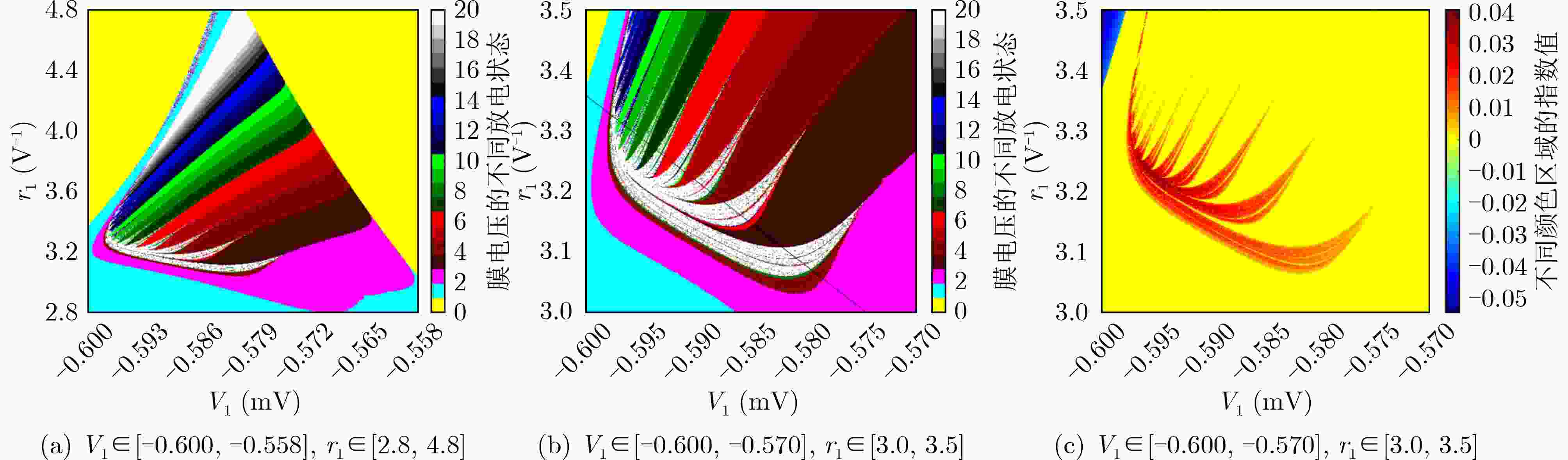


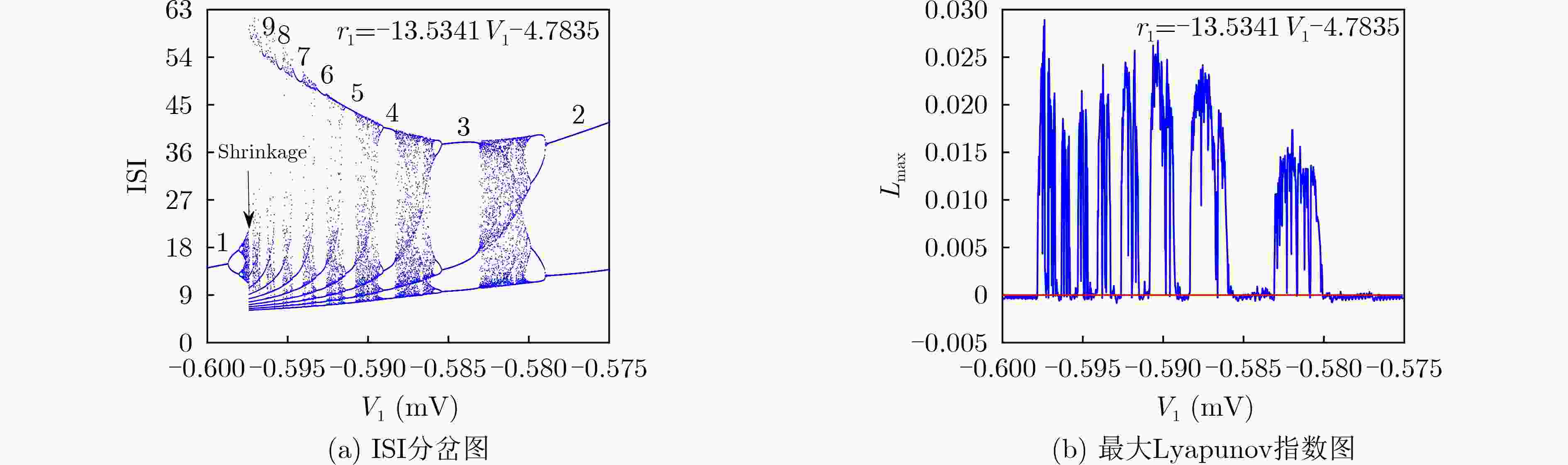




 下载:
下载:
