A Low Complexity Millimeter Wave Channel Estimation Algorithm in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface
-
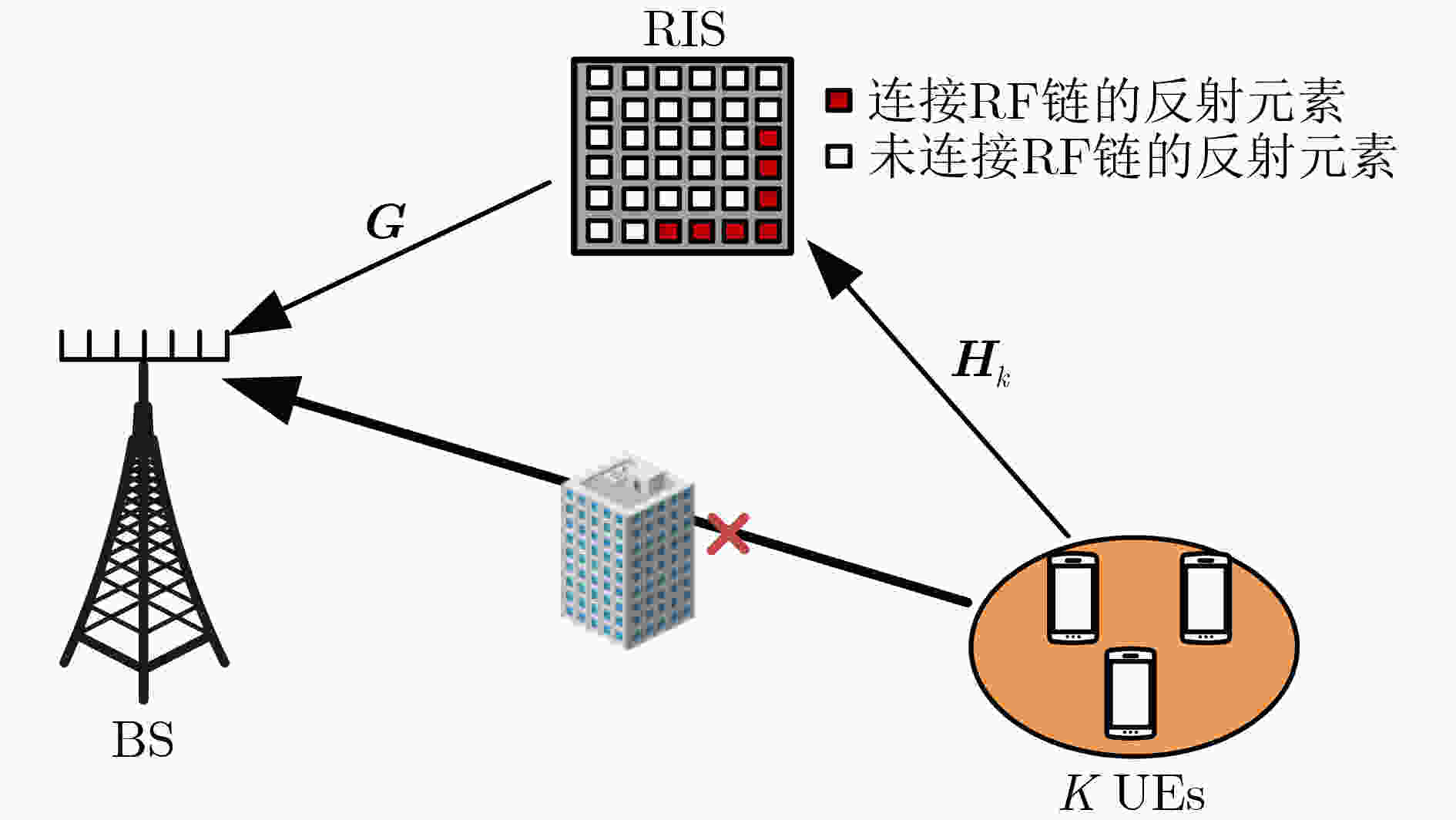
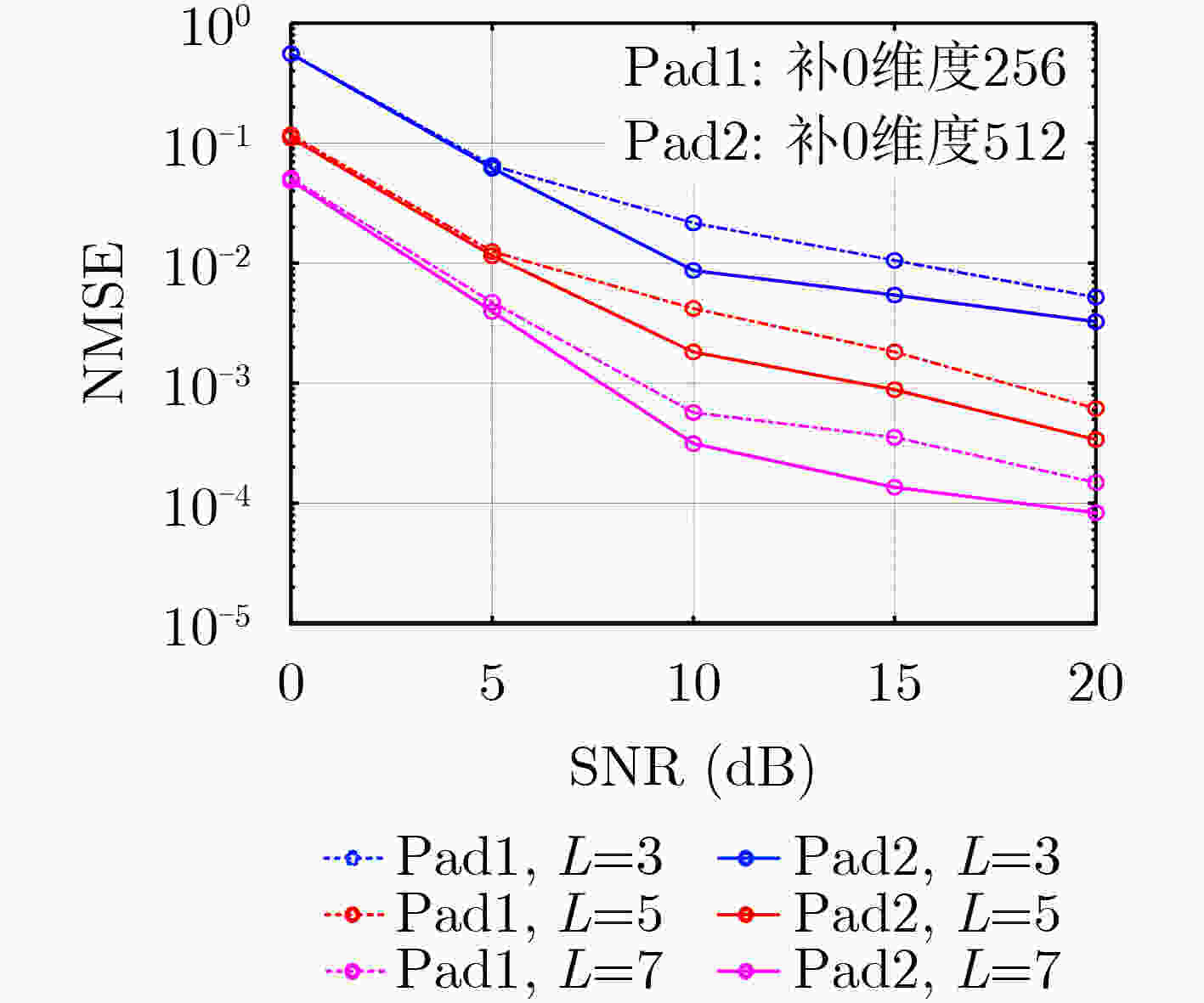
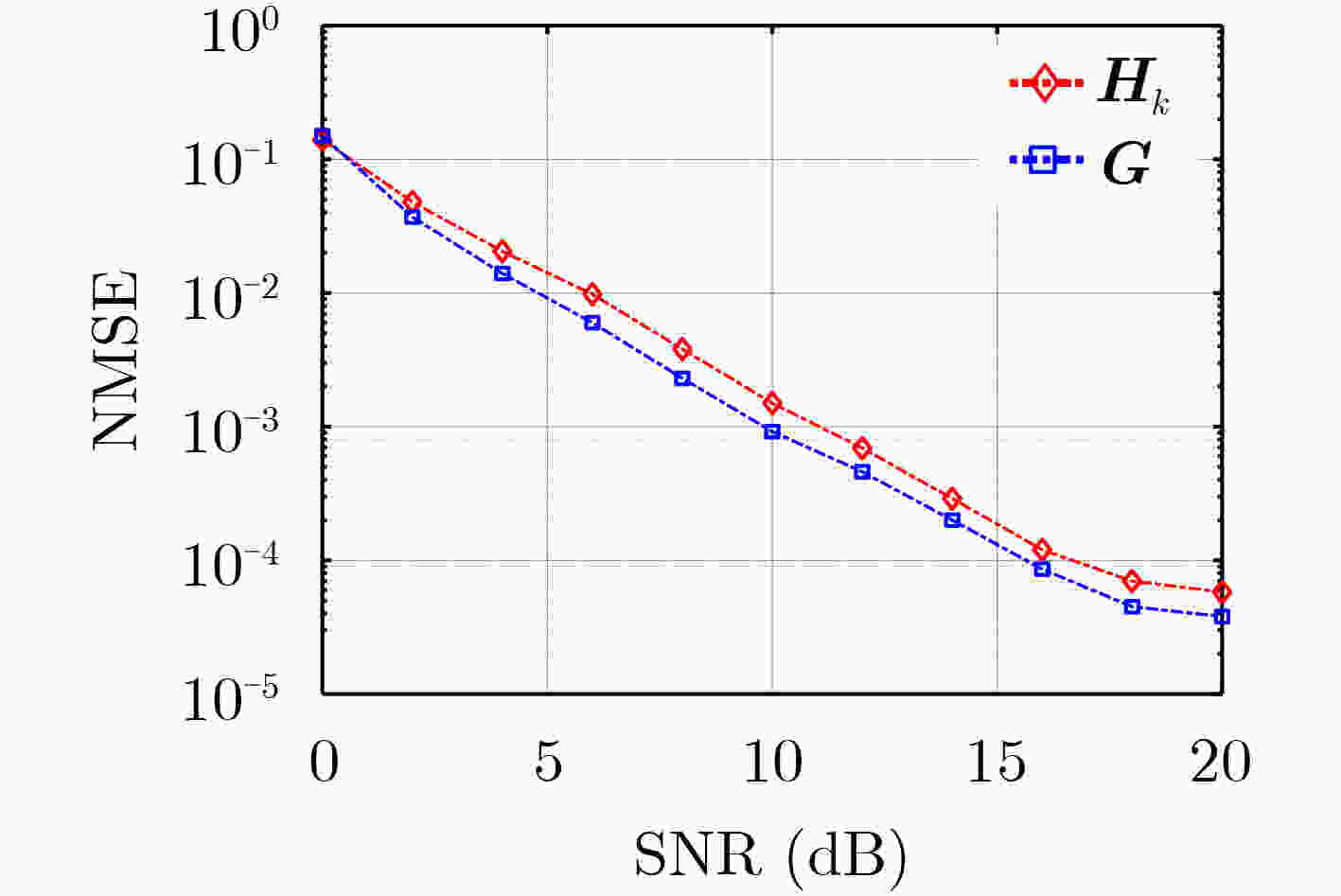
摘要: 针对可重构智能表面(RIS)辅助的大规模多输入多输出(MIMO)毫米波系统中信道估计复杂度高的问题,该文提出一种低复杂度的信道估计算法。在该方案中,将RIS部分元素连接射频(RF)链,分离估计基站/用户和RIS之间的信道,分开获取信道有助于提升用户移动性场景下信道估计的灵活性。在所考虑系统中,首次使用低复杂度的2维快速傅里叶变换(2D-FFT)算法对角度进行估计,并考虑信号补零以获得更加精准的角度估计值,最后利用信号2维空间谱的谱峰和其对应的辐角得到路径增益估计。仿真结果表明,该算法达到了优良的信道估计性能,且在确保信道估计性能的系统参数设置下,该算法具有压倒性的复杂度优势。Abstract: In this paper, a low complexity channel estimation algorithm is proposed, which is used to reduce the computational complexity of the millimeter wave channel estimation in the massive MIMO systems assisted by the Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS). In the proposed scheme, some elements of the RIS are connected to the Radio Frequency (RF) chain to estimate the channel between the base station/user and the RIS separately, which improves the flexibility of channel estimation. The zero-padding two-Dimensional Fast Fourier Transform (2D-FFT) algorithm is used for angle estimation in this scenario for the first time. The path gain estimation is obtained by using the spectral peak of the two-dimensional spatial spectrum of the signal and its corresponding argument. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm achieves excellent channel estimation performance, and based on the system parameter setting to ensure the channel estimation performance, the proposed algorithm has a strong complexity advantage.
-
表 1 本文算法流程表
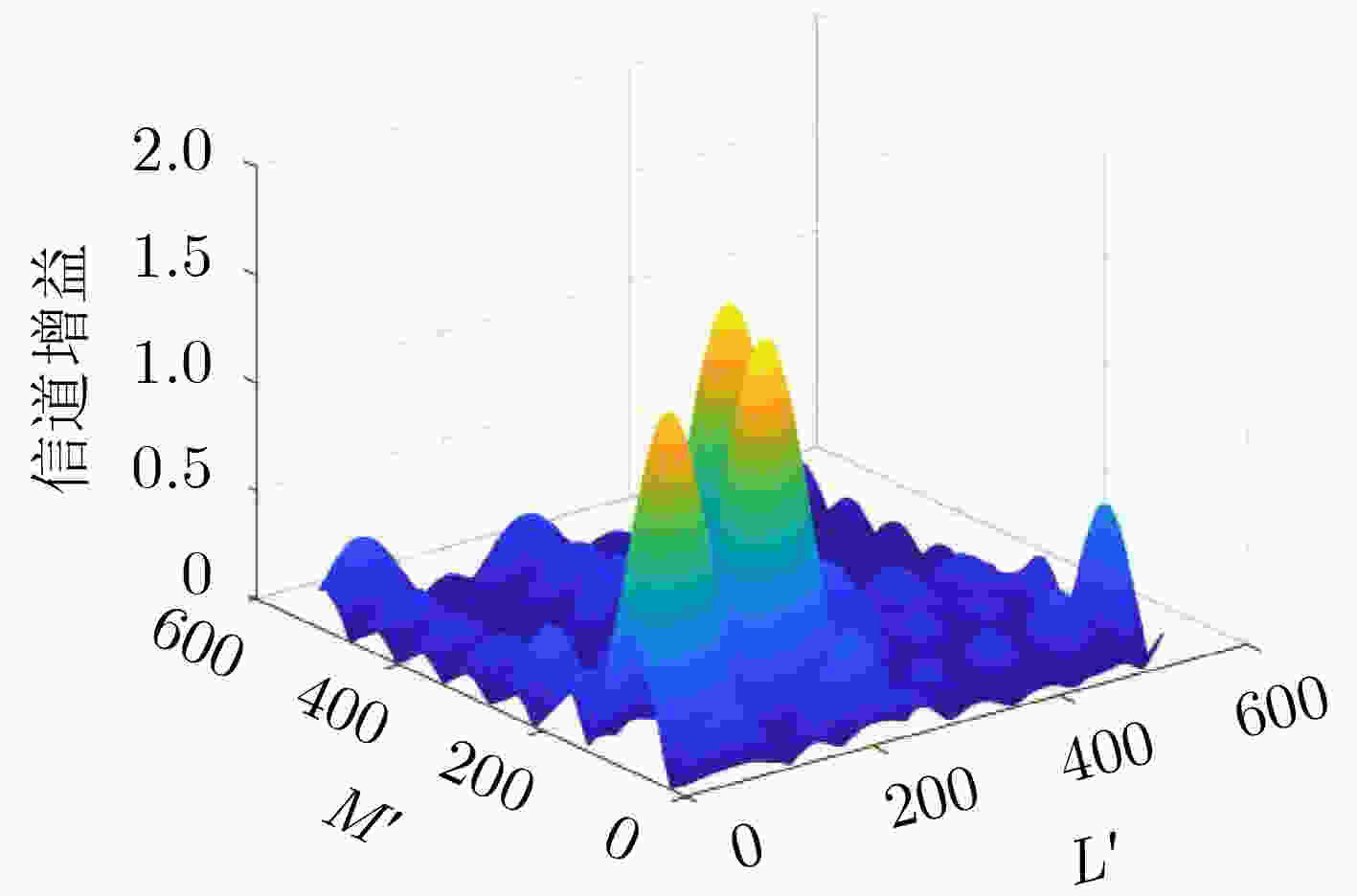
算法:基于2D-FFT的RIS辅助通信系统信道估计 (1) 输入:RIS射频链接收信号:${\boldsymbol{Y}}_k^x$,${\boldsymbol{Y}}_k^y$;BS接收信号:${\boldsymbol{Y}}_{ {\text{BS} } }^x$ ,${\boldsymbol{Y}}_{ {\text{BS} } }^y$;导频: ${\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} _k^{}$,${\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} _{\text{R} }^x$,${\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} _{\text{R} }^y$;反射矩阵:${\boldsymbol{\varPhi}}$ (2) 所有接收信号与导频信号解相关,如${\boldsymbol{Y} }'^x_k = {\boldsymbol{Y} }_k^x{\boldsymbol{\varGamma} } _k^x = {\boldsymbol{H} }_k^x + {\boldsymbol{N} }'^x_k$ (3) 信号补0处理,并对其进行2D-FFT得到峰值点位置。如${\boldsymbol{Y} }'^x_k $补0得到${\boldsymbol{Y}}'^{x,{\text{pad} } }_k$,对其进行2D-FFT变换得到第$l_a $条路径峰值位置$ (m_{l_a}^x,n_{l_a}^x)$ (4) 得到链路对应角度估计值,如 $\hat \phi _{ { {\mathbf{H} }_k} }^{ {l_a} } = \arcsin \left(\dfrac{\lambda }{ { {d_{\text{R} } } } } \cdot \dfrac{ {m_{ {l_a} }^x} }{ {L'} }\right),{\text{ } }\hat \varphi _{ { {\mathbf{H} }_k} }^{ {l_a} } = \arcsin \left(\dfrac{\lambda }{ { {d_{\text{U} } } } } \cdot \dfrac{ {n_{ {l_a} }^x} }{ {M'} }\right)$ 并以相同思路分别得到RIS竖直RF链AOA的仰角估计值$\hat \theta _{{{\mathbf{H}}_k}}^{{l_a}}$,BS端的AoA估计值$\hat \psi_{l_b} $,RIS到BS的仰角和方位角的估计值$\gamma_{l_b} $, $ \hat\varphi_{l_b} $ (5) 依据补0后接收信号空间谱得到路径增益,如$ {\hat a_{{l_a}}}{\text{ = }}{\hat \beta _{{l_a}}}{{\text{e}}^{{\text{j}}{{\hat \alpha }_{{l_a}}}}} $其中 ${\hat \beta _{ {l_a},k} } \approx \dfrac{1}{ {LM} }{\text{|} }\tilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}'^{x,{\text{pad} } }_k(m_{ {l_a} }^x,n_{ {l_a} }^x){\text{|, } }{\hat \alpha _{ {l_a} } } \approx \arctan \dfrac{ { {\text{imag} }(\tilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}'^{x,{\text{pad} } }_k(m_{ {l_a} }^x,n_{ {l_a} }^x))} }{ { {\text{real} }(\tilde {\boldsymbol{Y}}'^{x,{\text{pad} } }_k(m_{ {l_a} }^x,n_{ {l_a} }^x))} }$ 并以相同思路得到RIS到BS端路径增益估计$\hat b_{l_b} $ (6) 输出:依据以上参数估计值,得到信道估计值
${\hat {\boldsymbol{H}}_k} = \displaystyle\sum\limits_{ {l_a} = 0}^{ {L_a} - 1} { { {\hat a}_{ {l_a} } }a_{ {\text{UR} } }^{}(\hat \theta _{ { {\mathbf{H} }_k} }^{ {l_a} },\hat \phi _{ { {\mathbf{H} }_k} }^{ {l_a} })a_{\text{U} }^{\text{H} }(\hat \varphi _{ { {\mathbf{H} }_k} }^{ {l_a} })} {\text{, } }\hat G{\text{ = } }\sum\limits_{ {l_b} = 0}^{ {L_b} - 1} { { {\hat b}_{ {l_b} } }{a_{\text{B} } }({ {\hat \psi }_{ {l_b} } })a_{ {\text{RB} } }^{\text{H} }({ {\hat \gamma }_{ {l_b} } },{ {\hat \varphi }_{ {l_b} } })}$表 2 不同算法计算复杂度对比
信道估计算法 计算复杂度 基于子空间的信道估计算法 $\begin{gathered} {\text{ } }O(\frac{ {32} }{3}({N^3} + {P^3}) + ({P^2} + {N^2})(2T + 2{L_a} - 2) + \\ +PM(2T + 2P - 2) + NP(2T + 2N - 2)) \\ \end{gathered}$ MUSIC+ML $\begin{gathered} {\text{ } }O(\frac{ {52} }{3}({(LT)^3} + {(NT)^3}) + 2({(NT)^2} + {(LT)^2}) + 2{L_a}{D_{ {\text{MUSIC} } } }(8MT - 4T \\ + 4({(LT)^2} + {(NT)^2}) - 4(L{L_a}T + N{L_a}T) + 2T(L + N) - 2) + 12L_a^3 \\ +{\text{2} }L_a^2(4(L + N) + 8T - 6) + 2{L_a}(2 - 2N + 2T(L + N) + 6T(M + L) - 8T)) \\ \end{gathered}$ Root-MUSIC+ML $\begin{gathered} {\text{ } }O(26({(LT)^3} + {(NT)^3}) + 3T({L^2} + {N^2}) + 18L_a^3 + {\text{3} }L_a^2(4(L + N) + 8T - 6) \\ + 3{L_a}(2 - L - N + 2T(N + L) + 6T(M + L) - 8T)) \\ \end{gathered}$ 本文算法 ${\text{ }}2({L^2}(M + N) + 3(M\log (M) + N\log (N)) + 6L\log (L) + 2L(2T - 1)(M + N)$ -
[1] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Beamforming optimization for wireless network aided by intelligent reflecting surface with discrete phase shifts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(3): 1838–1851. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2019.2958916 [2] ZHENG Beixiong, YOU Changsheng, and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface assisted multi-user OFDMA: Channel estimation and training design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(12): 8315–8329. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3021434 [3] 朱政宇, 王梓晅, 徐金雷, 等. 智能反射面辅助的未来无线通信: 现状与展望[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(2): 198–212. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25014ZHU Zhengyu, WANG Zixuan, XU Jinlei, et al. Future wireless communication assisted by intelligent reflecting surface: State of art and prospects[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(2): 198–212. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2021.25014 [4] YUAN Xiaojun, ZHANG Y J A, SHI Yuanming, et al. Reconfigurable-intelligent-surface empowered wireless communications: Challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(2): 136–143. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2000256 [5] LIASKOS C, NIE Shuai, TSIOLIARIDOU A, et al. A new wireless communication paradigm through software-controlled metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2018, 56(9): 162–169. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2018.1700659 [6] BASAR E, DI RENZO M, DE ROSNY J, et al. Wireless communications through reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 116753–116773. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935192 [7] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Towards smart and reconfigurable environment: Intelligent reflecting surface aided wireless network[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2020, 58(1): 106–112. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.001.1900107 [8] LI Lixin, MA Donghui, REN Huan, et al. Enhanced reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted mmWave communication: A federated learning approach[J]. China Communications, 2020, 17(10): 115–128. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2020.10.008 [9] YANG Liang, MENG Fanxu, ZHANG Jiayi, et al. On the performance of RIS-assisted dual-hop UAV communication systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(9): 10385–10390. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3004598 [10] BAI Tong, PAN Cunhua, HAN Chao, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surface aided mobile edge computing[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(6): 80–86. doi: 10.1109/MWC.001.2100142 [11] 朱政宇, 徐金雷, 孙钢灿, 等. 基于IRS辅助的SWIPT物联网系统安全波束成形设计[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(4): 185–193. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021060ZHU Zhengyu, XU Jinlei, SUN Gangcan, et al. Secure beamforming design for IRS-assisted SWIPT internet of things system[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(4): 185–193. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000-436x.2021060 [12] ZHU Zhengyu, LI Zheng, CHU Zheng, et al. Resource allocation for intelligent reflecting surface assisted wireless powered IoT systems with power splitting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2022, 21(5): 2987–2998. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3117346 [13] WU Qingqing and ZHANG Rui. Intelligent reflecting surface enhanced wireless network via joint active and passive beamforming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2019, 18(11): 5394–5409. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2019.2936025 [14] WANG Peilan, FANG Jun, DUAN Huiping, et al. Compressed channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-assisted millimeter wave systems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27: 905–909. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2998357 [15] NADEEM Q U A, ALWAZANI H, KAMMOUN A, et al. Intelligent reflecting surface-assisted multi-user MISO communication: Channel estimation and beamforming design[J]. IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society, 2020, 1: 661–680. doi: 10.1109/OJCOMS.2020.2992791 [16] HU Chen, DAI Linglong, HAN Shuangfeng, et al. Two-timescale channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2021, 69(11): 7736–7747. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2021.3072729 [17] GUAN Xinrong, WU Qingqing, and ZHANG Rui. Anchor-assisted intelligent reflecting surface channel estimation for multiuser communications[C]. 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference, Taipei, China, 2020: 1–6. [18] DE ARAUJO G T and DE ALMEIDA A L F. PARAFAC-based channel estimation for intelligent reflective surface assisted MIMO system[C]. The 2020 IEEE 11th Sensor Array and Multichannel Signal Processing Workshop, Hangzhou, China, 2020: 1–5. [19] LIU Hang, YUAN Xiaojun, and ZHANG Y A. Matrix-calibration-based cascaded channel estimation for reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted multiuser MIMO[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(11): 2621–2636. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3007057 [20] CHEN Xiao, SHI Jianfeng, YANG Zhaohui, et al. Low-complexity channel estimation for intelligent reflecting surface-enhanced massive MIMO[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(5): 996–1000. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3054004 [21] TAHA A, ALRABEIAH M, and ALKHATEEB A. Enabling large intelligent surfaces with compressive sensing and deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 44304–44321. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3064073 [22] 傅友华, 陈栋. 混合智能反射表面结构辅助的毫米波通信信道估计[J]. 通信学报, 2021, 42(10): 189–196. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2021197FU Youhua and CHEN Dong. Channel estimation for hybrid intelligent reflecting surface structure assisted mmWave communications[J]. Journal on Communications, 2021, 42(10): 189–196. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.1000−436x.2021197 [23] FAN Dian, GAO Feifei, WANG Gongpu, et al. Angle domain signal processing-aided channel estimation for indoor 60-GHz TDD/FDD massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2017, 35(9): 1948–1961. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2017.2720938 [24] HU Anzhong, LV Tiejun, and LU Yueming. Subspace-based semi-blind channel estimation for large-scale multi-cell multiuser MIMO systems[C]. The 2013 IEEE 77th Vehicular Technology Conference, Dresden, Germany, 2013: 1–5. -





 下载:
下载:



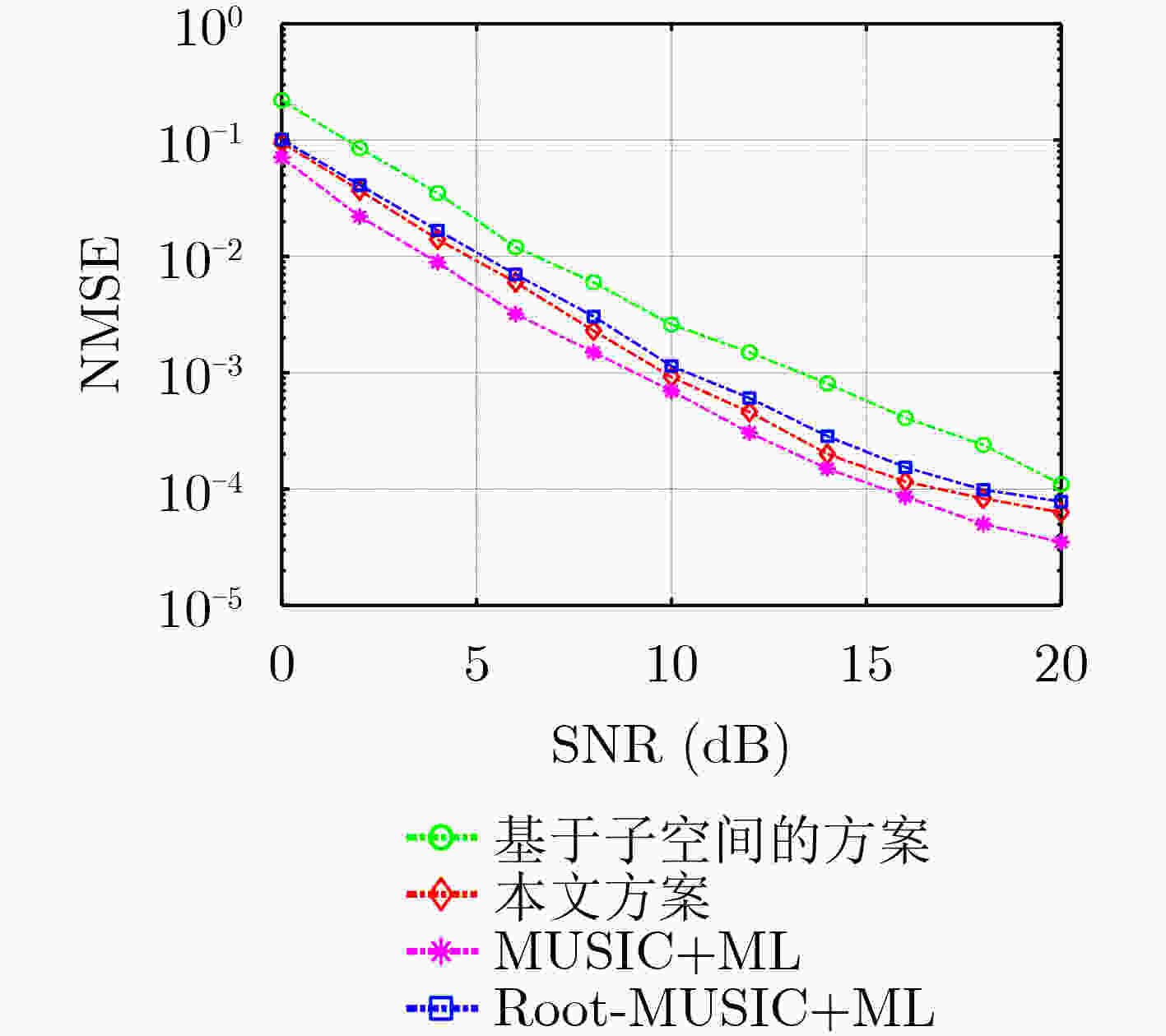



 下载:
下载:
