Prediction of Evolution Results of Urban Rail Transit Emergencies Based on Knowledge Graph
-
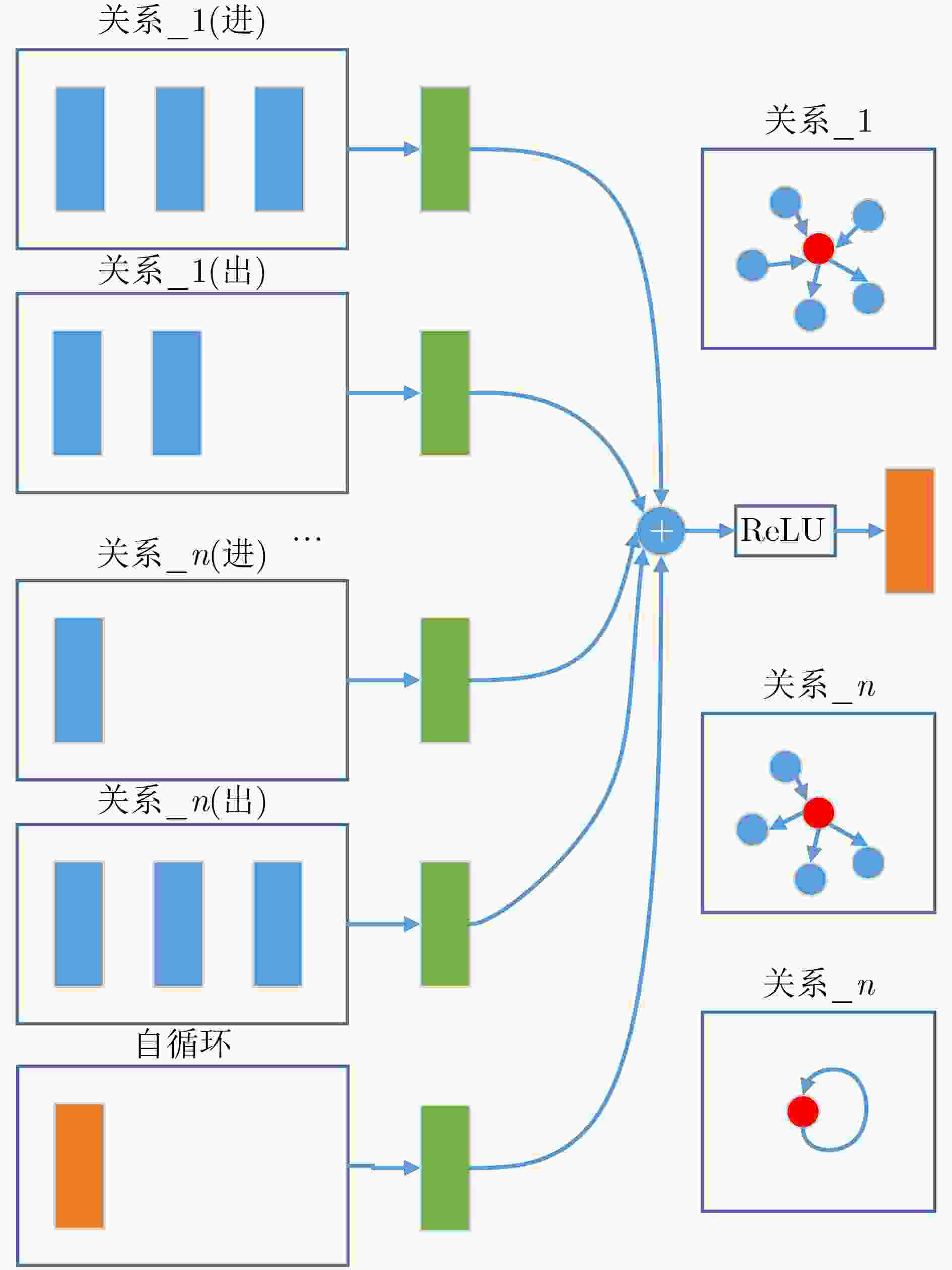
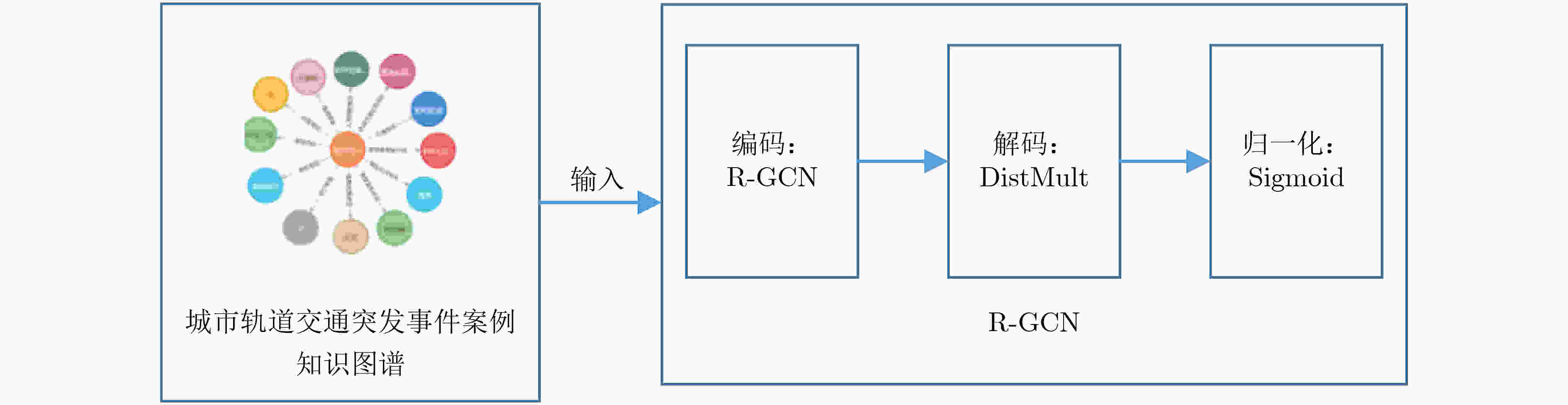
摘要: 准确预测突发事件的演化结果,对城市轨道交通系统制定应急方案、保障安全运营,具有重要的参考意义。目前突发事件演化结果预测方法智能化程度不高,过分依赖决策者主观设定的特征权重、检索模板,复杂、准确性低且应用性较弱。该文基于知识图谱(KG)和关系图卷积神经网络(R-GCN)模型提出一种城市轨道交通突发事件演化结果预测方法。首先,构建城市轨道交通突发事件知识图谱,将与事件相关的场景信息进行结构化处理;其次,基于关系图卷积神经网络模型构建城市轨道交通突发事件结果的预测模型;最后,利用城市轨道交通突发事件案例库进行验证。实验结果表明,所提预测方法具有较好的准确率、较强的普适性,可为轨道交通应急管理提供方法和技术支持。Abstract: Accurately predicting the evolution process and results of emergencies is of great reference to formulate the emergency response plans of the urban rail transit system and safeguard its secure operation. However, the prediction methods of emergency evolution results are lack of high intelligence, and excessively depend on the feature weighting and retrieval template set subjectively by policymakers, which is complicated, inaccurate, and short of applicability. Based on Knowledge Graph(KG) and Relational-Graph Convolution Neural network(R-GCN), a predicting method of evolution result of urban rail transit emergencies is proposed. A knowledge graph of urban rail transit emergencies is constructed to combine with contextual information related to the emergency for structured processing. Firstly, the knowledge graph of urban rail transit emergencies is constructed to combine with contextual information related to the emergency for structured processing. Then the predicting model of urban rail transit emergencies is constructed based on the relational-graph convolution neural network to achieve the result prediction of urban rail transit emergency. Finally, the verification is conducted via case base of urban rail transit emergency. The experimental result demonstrates that the predicting method proposed in this paper is of high accuracy and applicability, which can provide consolidated data and decision support for rail transit emergency management.
-
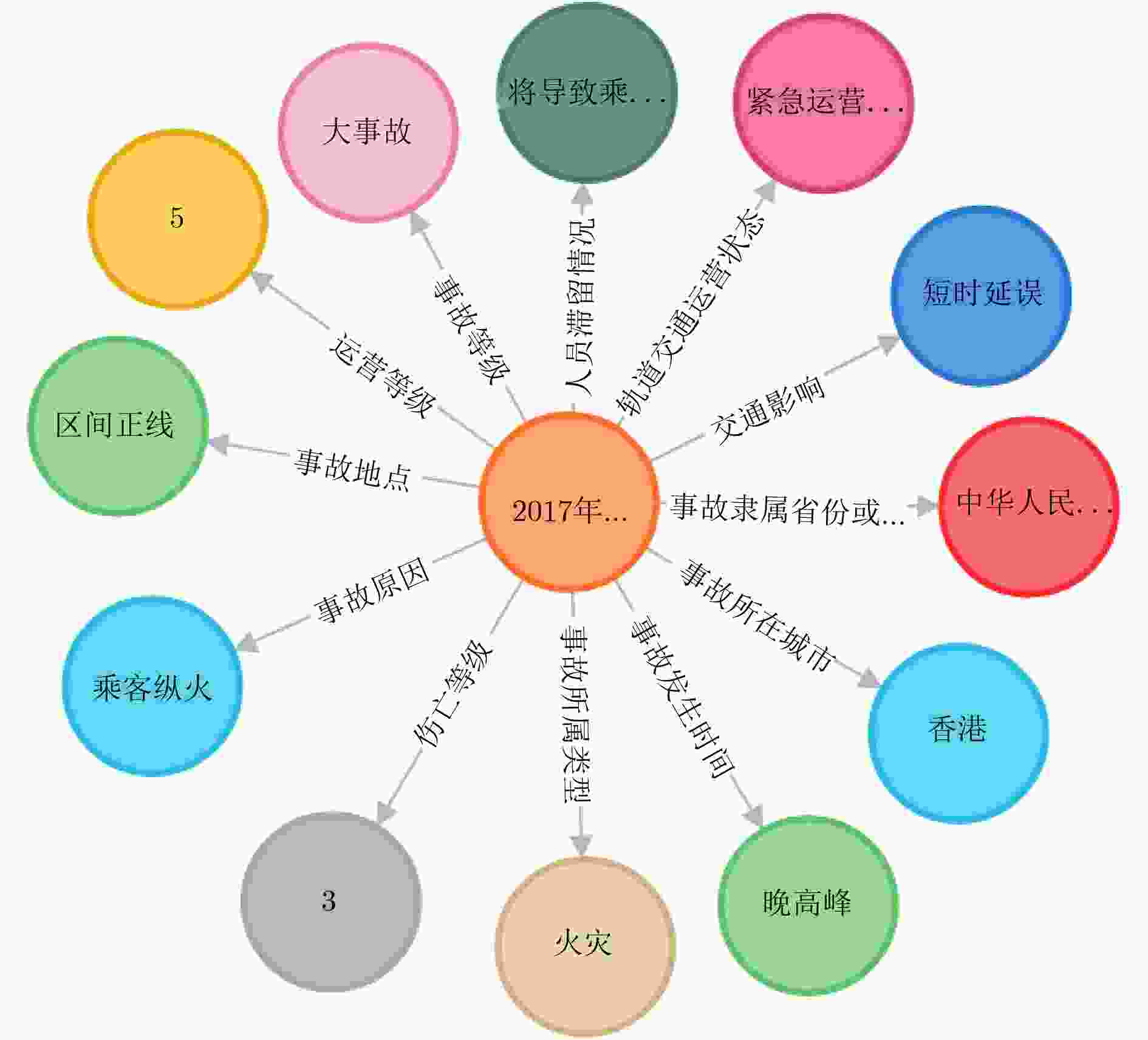
表 1 城轨突发事件特征信息定义及描述
特征信息 描述 事故原因 人员因素、设备因素、管理因素、环境因素、其他 事故地点 区间正线、车站正线、车站内 事故类型 火灾、脱轨、停电、踩踏、自然灾害、相撞、恐怖袭击、设备故障、其他事故 表 2 城轨突发事件结果信息定义及描述
结果信息 描述 交通影响 停运(特长时间停运、长时间停运、暂时停运、短时停运)、延误(特长时间延误、长时间延误、
暂时延误、短时延误)、运营秩序正常人员滞留情况 将导致乘客滞留、未导致乘客滞留 衍生灾害 无衍生灾害、车站内踩踏、车站内火灾、隧道内毒气、隧道内火灾、隧道内浓烟、隧道内踩踏、车站内浓烟、
列车相撞、车厢内浓烟、乘客滞留隧道、踩踏等事故等级 重大事故、一般事故、险性事故、特大事故、大事故 运营等级 1,2,3,4,5 轨道交通运营状态 紧急运营状态、正常运营状态、非正常运营状态 伤亡等级 0,1,2,3,4,5 表 3 城轨突发事件预测结果(%)
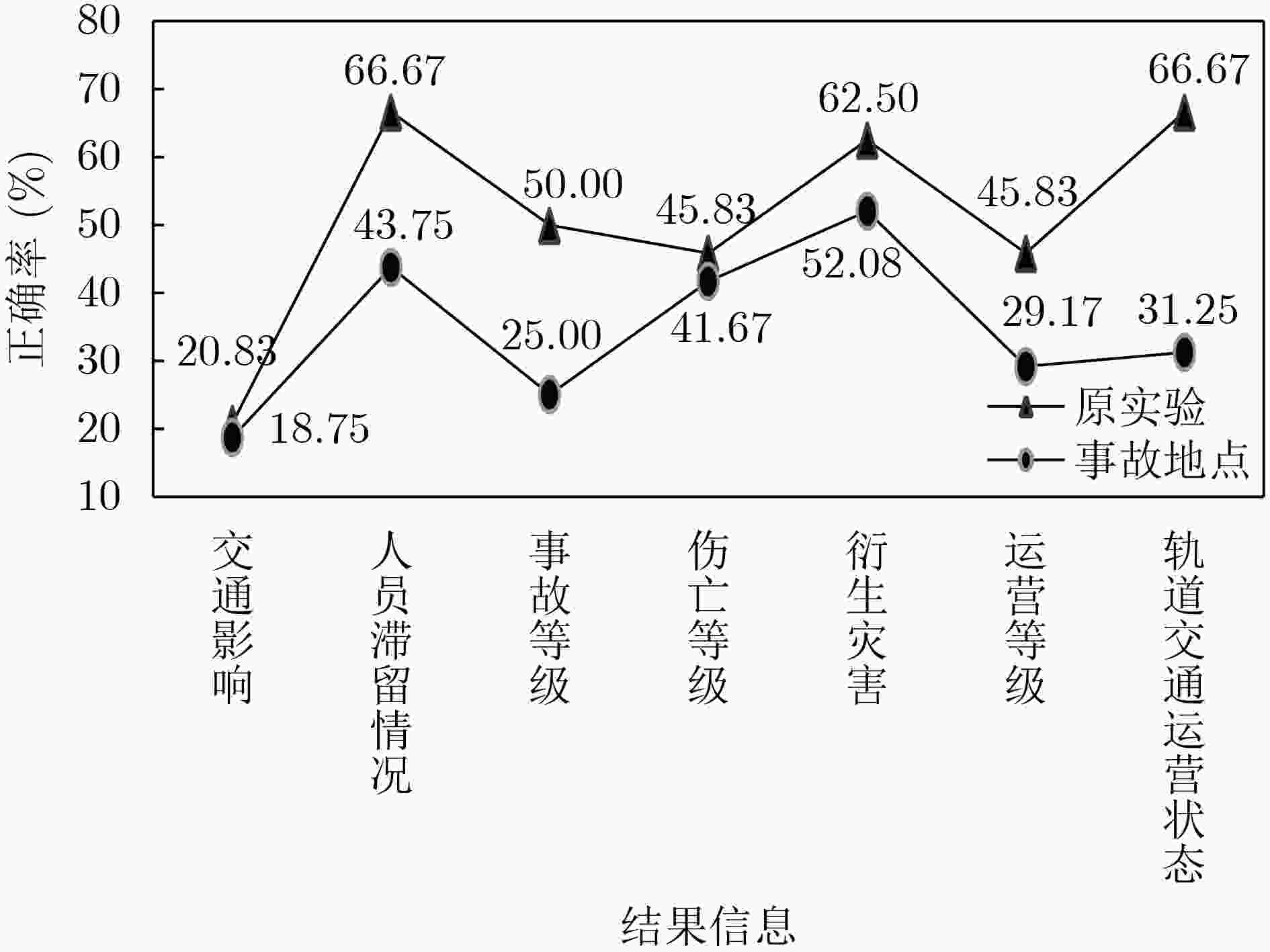
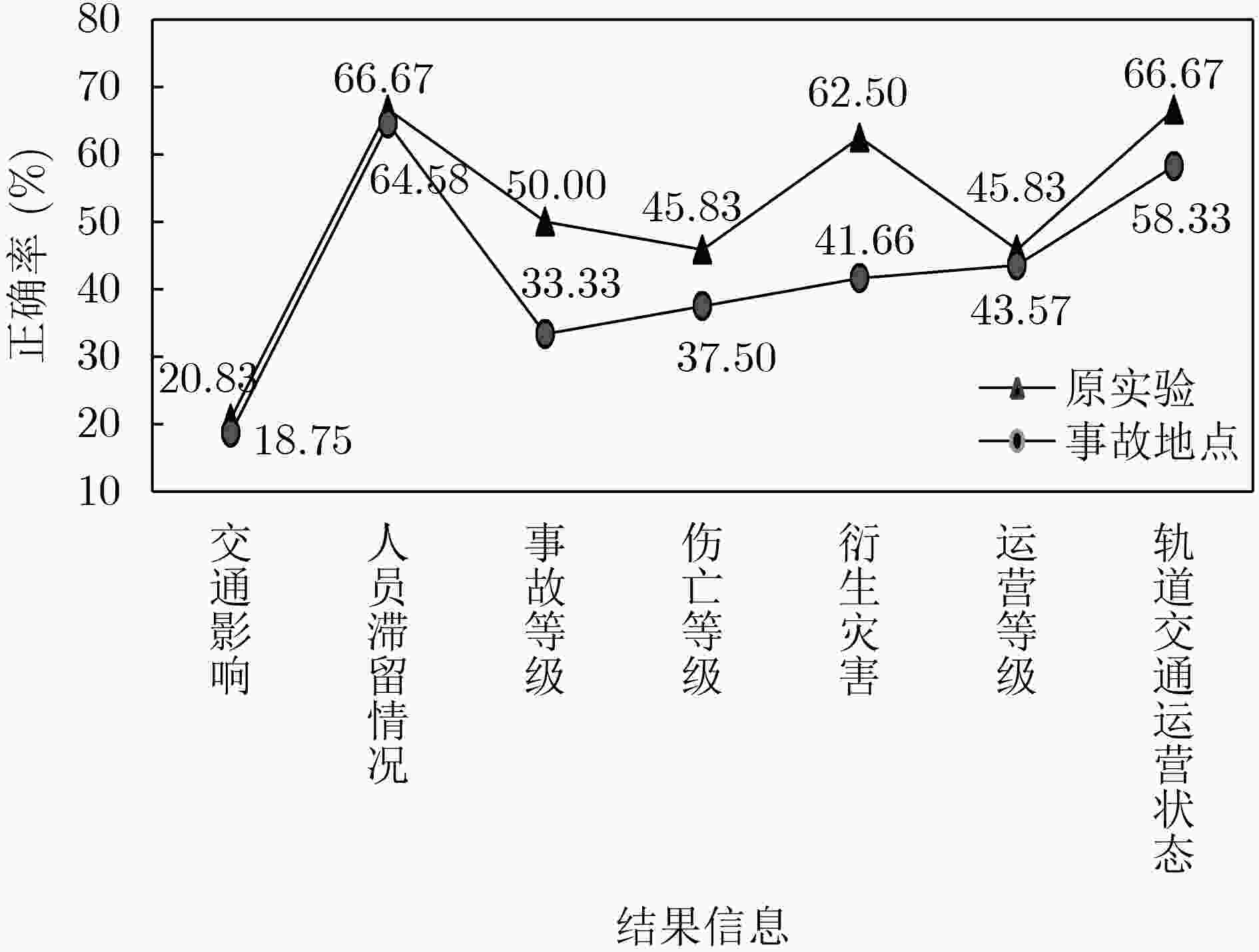
结果信息 正确率 结果信息 正确率 交通影响 20.83 衍生灾害 62.50 人员滞留情况 66.67 运营等级 45.83 事故等级 50.00 轨道交通运营状态 66.67 伤亡等级 45.83 -
[1] 封超, 杨乃定, 桂维民, 等. 基于案例推理的突发事件应急方案生成方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2016, 31(8): 1526–1530. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2015.0696FENG Chao, YANG Naiding, GUI Weimin, et al. Method for generating emergency alternative based on case-based reasoning[J]. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(8): 1526–1530. doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2015.0696 [2] 张力菠, 韩玉启, 陈杰, 等. 供应链管理的系统动力学研究综述[J]. 系统工程, 2005, 23(6): 8–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4098.2005.06.002ZHANG Libo, HAN Yuqi, CHEN Jie, et al. A review: The application of system dynamics in supply chain management[J]. Systems Engineering, 2005, 23(6): 8–15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4098.2005.06.002 [3] 马骁. 基于系统动力学的城市轨道交通车站客流仿真与控制研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京交通大学, 2019.MA Xiao. Research on passenger flow simulation and control of urban rail transit station based on system dynamics[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing Jiaotong University, 2019. [4] 董士浩, 李稚. 基于系统动力学的国际供应链金融风险预测[J]. 财会月刊, 2019(12): 170–176. doi: 10.19641/j.cnki.42-1290/f.2019.12.022DONG Shihao and LI Zhi. Forecasting of financial risks in international supply chain by system dynamics method[J]. Finance and Accounting Monthly, 2019(12): 170–176. doi: 10.19641/j.cnki.42-1290/f.2019.12.022 [5] 王其藩. 系统动力学[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1994: 41–45.WANG Qifan. System Dynamics[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 1994: 41–45. [6] 李肖冰. 基于系统动力学的中国能源供求预测模型研究[D]. [硕士论文], 内蒙古科技大学, 2015.LI Xiaobing. The research of energy demand and supply forecast model of China based on system dynamics[D]. [Master dissertation], Inner Mongolia University of Science & Technology, 2015. [7] 徐曼, 沈江, 余海燕. 数据驱动的医疗与健康决策支持研究综述[J]. 工业工程与管理, 2017, 22(1): 1–13. doi: 10.19495/j.cnki.1007-5429.2017.01.001XU Man, SHEN Jiang, and YU Haiyan. A review on data-driven healthcare decision-making support[J]. Industrial Engineering and Management, 2017, 22(1): 1–13. doi: 10.19495/j.cnki.1007-5429.2017.01.001 [8] 强韶华, 罗云鹿, 李玉鹏, 等. 基于RBR和CBR的金融事件本体推理研究[J]. 数据分析与知识发现, 2019, 3(8): 94–104. doi: 10.11925/infotech.2096-3467.2018.1137QIANG Shaohua, LUO Yunlu, LI Yupeng, et al. Ontology reasoning for financial affairs with RBR and CBR[J]. Data Analysis and Knowledge Discovery, 2019, 3(8): 94–104. doi: 10.11925/infotech.2096-3467.2018.1137 [9] 官赛萍, 靳小龙, 贾岩涛, 等. 面向知识图谱的知识推理研究进展[J]. 软件学报, 2018, 29(10): 2966–2994. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005551GUAN Saiping, JIN Xiaolong, JIA Yantao, et al. Knowledge reasoning over knowledge graph: A survey[J]. Journal of Software, 2018, 29(10): 2966–2994. doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005551 [10] 王萌, 王靖婷, 江胤霖, 等. 人机混合的知识图谱主动搜索[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2020, 57(12): 2501–2513. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200750WANG Meng, WANG Jingting, JIANG Yinlin, et al. Hybrid human-machine active search over knowledge graph[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2020, 57(12): 2501–2513. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2020.20200750 [11] 曹明宇, 李青青, 杨志豪, 等. 基于知识图谱的原发性肝癌知识问答系统[J]. 中文信息学报, 2019, 33(6): 88–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2019.06.013CAO Mingyu, LI Qingqing, YANG Zhihao, et al. A question answering system for primary liver cancer based on knowledge graph[J]. Journal of Chinese Information Processing, 2019, 33(6): 88–93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0077.2019.06.013 [12] 董丽丽, 程炯, 张翔, 等. 融合知识图谱与深度学习的疾病诊断方法研究[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2020, 14(5): 815–824. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.1908018DONG Lili, CHENG Jiong, ZHANG Xiang, et al. Research on disease diagnosis method combining knowledge graph and deep learning[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2020, 14(5): 815–824. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.1908018 [13] 林海舟. 基于知识图谱的航空安全事件推理方法的研究[D]. [硕士论文], 中国民航大学, 2020.LIN Haizhou. Research on reasoning method of aviation safety events based on knowledge graph[D]. [Master dissertation], Civil Aviation University of China, 2020. [14] 虞凤萍. 基于知识图谱的可解释临床事件预测方法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 山东师范大学, 2021.YU Fengping. Interpretable predicting methods of clinical events based on knowledge graph[D]. [Master dissertation], Shandong Normal University, 2021. [15] 张善文, 王振, 王祖良. 结合知识图谱与双向长短时记忆网络的小麦条锈病预测[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(12): 172–178. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.12.021ZHANG Shanwen, WANG Zhen, and WANG Zuliang. Prediction of wheat stripe rust disease by combining knowledge graph and bidirectional long short term memory network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(12): 172–178. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.12.021 [16] SEKINE S. NYU: Description of the Japanese NE system used for MET-2[C]. Seventh Message Understanding Conference, Fairfax, USA, 1998. [17] 徐增林, 盛泳潘, 贺丽荣, 等. 知识图谱技术综述[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2016, 45(4): 589–606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.012XU Zenglin, SHENG Yongpan, HE Lirong, et al. Review on knowledge graph techniques[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2016, 45(4): 589–606. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0548.2016.04.012 [18] 李世宝, 张益维, 刘建航, 等. 基于知识图谱共同邻居排序采样的推荐模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3522–3529. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200735LI Shibao, ZHANG Yiwei, LIU Jianhang, et al. Recommendation model based on public neighbor sorting and sampling of knowledge graph[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3522–3529. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200735 [19] 刘峤, 李杨, 段宏, 等. 知识图谱构建技术综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(3): 582–600. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20148228LIU Qiao, LI Yang, DUAN Hong, et al. Knowledge graph construction techniques[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(3): 582–600. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2016.20148228 [20] SCHLICHTKRULL M, KIPF T N, BLOEM P, et al. Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks[C]. 15th International Conference on the Semantic Web, Heraklion, Greece, 2018: 593–607. [21] KIP T N and WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[C]. 5th International Conference on Learning Representations, Toulon, France, 2017. [22] 向敏, 饶华阳, 张进进, 等. 基于图卷积神经网络的软件定义电力通信网络路由控制策略[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(2): 388–395. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190971XIANG Min, RAO Huayang, ZHANG Jinjin, et al. Software-defined power communication network routing control strategy based on graph convolution network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(2): 388–395. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190971 [23] 王汝言, 陶中原, 赵容剑, 等. 多交互图卷积网络用于方面情感分析[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(3): 1111–1118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210459WANG Ruyan, TAO Zhongyuan, ZHAO Rongjian, et al. Multi-interaction graph convolutional networks for aspectlevel sentiment analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technologyy, 2022, 44(3): 1111–1118. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210459 [24] 李玉格. 营养学知识图谱构建及补全技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020.LI Yuge. Research on construction and completion technology of nutrition knowledge graph[D]. [Master dissertation], Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. [25] DEFFERRARD M, BRESSON X, and VANDERGHEYNST P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 3844–3852. [26] HAMMOND D K, VANDERGHEYNST P, and GRIBONVAL R. Wavelets on graphs via spectral graph theory[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2011, 30(2): 129–150. doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2010.04.005 [27] 张金斗. 知识图谱分布式表示学习方法及应用研究[D]. [博士论文], 中国科学技术大学, 2021.ZHANG Jindou. Learning methods and application of knowledge graph distributed representation[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], University of Science and Technology of China, 2021. [28] 蔡毅, 邢岩, 胡丹. 敏感性分析综述[J]. 北京师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2008, 44(1): 9–16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0476-0301.2008.01.003CAI Yi, XING Yan, and HU Dan. On sensitivity analysis[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University:Natural Science, 2008, 44(1): 9–16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0476-0301.2008.01.003 -






 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
