Transmit Power Allocation Method of Frequency Diverse Array-Multi Input and Multi Output Radar Based on Reinforcement Learning
-
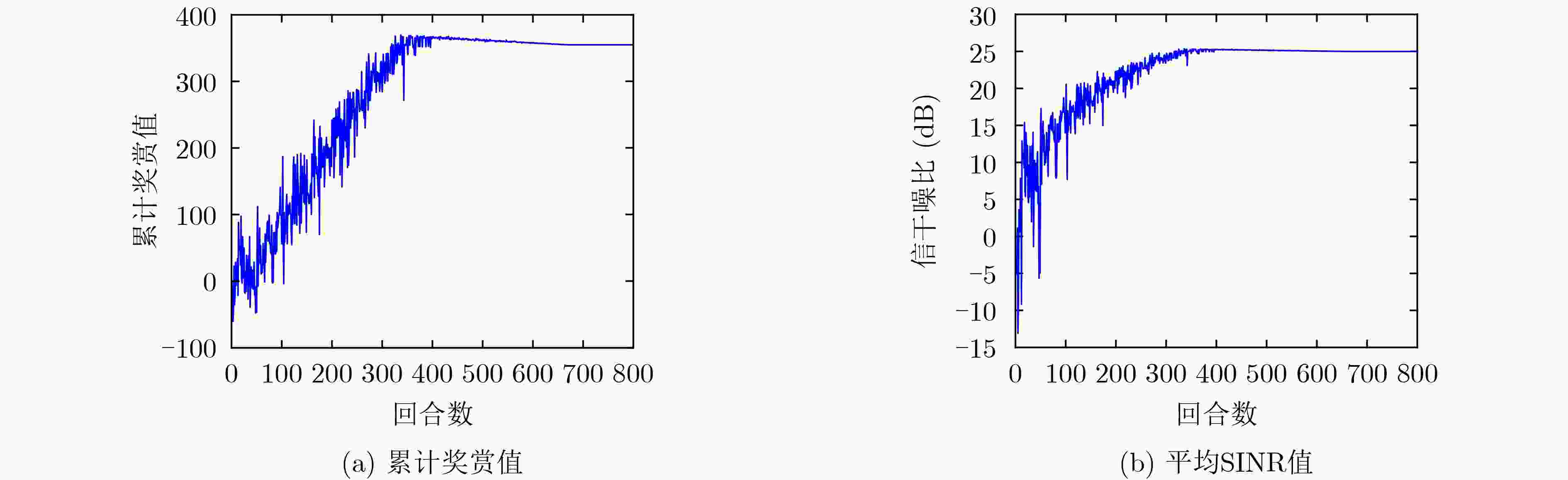
摘要: 当前电磁环境日益复杂多变,新式干扰手段层出不穷,对雷达系统带来了极大的挑战和威胁。该文引入频谱干扰模型并提出了一种在频控阵-多输入多输出(FDA-MIMO)雷达与干扰机动态博弈框架下基于强化学习(RL)的发射功率分配优化方法,使雷达系统能够获得最大的信干噪比(SINR)。在此基础上,构造了频谱干扰模型。其次,雷达和干扰机之间存在一种Stackelberg博弈关系,且将雷达作为领导者,干扰机作为跟随者,建立动态博弈框架下的发射功率分配优化模型。采用深度确定性策略梯度(DDPG)算法,结合功率约束设计了奖赏函数,对雷达发射功率进行实时分配来获得最大的输出SINR。最后,仿真结果表明,在雷达与干扰机博弈的框架下,所提优化算法能够有效地对雷达发射功率进行优化,使雷达具备较好的抗干扰性能。Abstract: In recent years, the electromagnetic environment has been becoming increasingly complex and changeable, and new jamming methods emerge one after another, which brings great challenges and threats to the radar system. In this paper, the spectrum interference model is introduced and a transmit power allocation optimization method based on Reinforcement Learning (RL) under the dynamic game framework of Frequency Diverse Array Multi Input and Multi Output (FDA-MIMO) radar and the spectrum interference is proposed, so that the radar system can obtain the maximum output Signal-to-Interference plus Noise Ratio (SINR). Firstly, the mathematical model of FDA-MIMO radar is established, and on this basis, the spectrum interference model is constructed. Secondly, there is a Stackelberg game relationship between radar and jammer. Taking radar as the leader and jammer as the follower, the transmit power allocation optimization model under the framework of dynamic game is established. Using the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG) algorithm and power constraints, a reward function is designed to allocate the radar transmit power in real time to obtain the maximum output SINR. Finally, the simulation results show that under the framework of the game between radar and interference, the proposed optimization algorithm can effectively optimize the radar transmit power and make the radar have better anti-jamming performance.
-
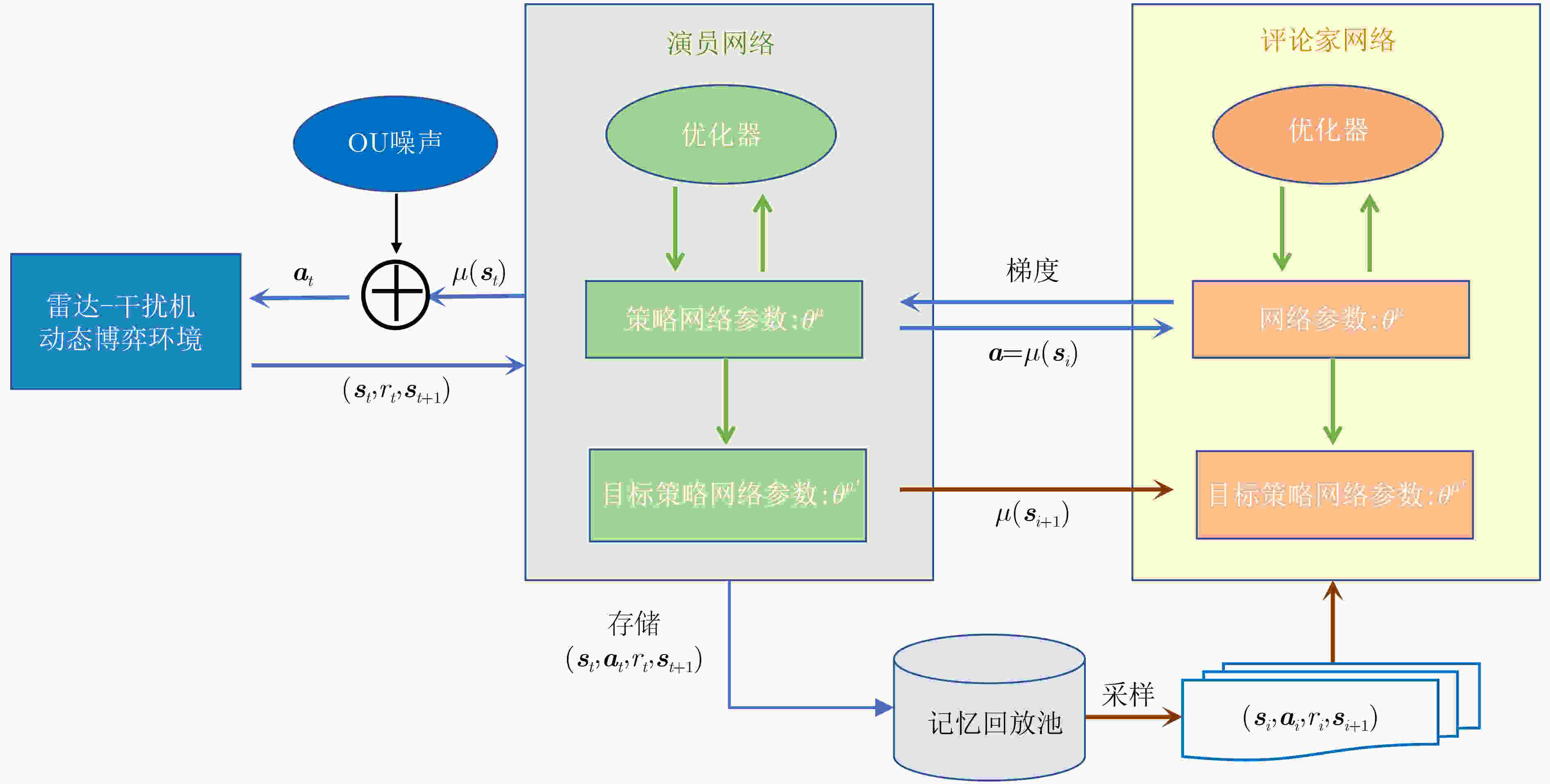
算法1 DDPG算法 随机初始化评论家网络$ Q\left(·|{\theta }^{Q}\right) $和演员网络$ \mu \left(·|{\theta }^{\mu }\right) $的网络参
数$ {\theta ^Q} $, $ {\theta ^\mu } $初始化目标评论家和演员网络的参数$ {\theta ^{Q'}} \leftarrow {\theta ^Q} $, $ {\theta ^{\mu '}} \leftarrow {\theta ^\mu } $ 初始化回放记忆池$ B $ FOR 回合数=1:L do 在动作探索策略中初始化随机过程$ \mathcal{O} $ 接收初始观测状态${{\boldsymbol{s}}_1}$ FOR t=1:T do 根据当前策略和随机噪声选择动作${a_t} = \mu \left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_t}|{\theta ^\mu } } \right) + {\mathcal{O}_t}$ 执行动作$ {a_t} $并且获得奖赏值$ {r_t} $,得到新状态${{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t + 1} }$, 保存传递样本组合$\left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_t},{r_t},{{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t + 1} } } \right)$到回放记忆池$ B $ 从回放记忆池$ B $中随机采样生成H维数据库
$\left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_t},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_t},{r_t},{{\boldsymbol{s}}_{t + 1} } } \right)$根据评论家网络$ Q\left(·|{\theta }^{Q}\right) $,计算目标值 ${y_i} = {r_i} + \varepsilon Q'\left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_{i + 1} },\mu '\left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_{i + 1} }|{\theta ^\mu } } \right)|{\theta ^Q} } \right)$ 通过最小化损失函数更新评论家网络:
$\dfrac{1}{H}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^H { { {\left( { {y_i} - Q\left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_i},{{\boldsymbol{a}}_i}|{\theta ^Q} } \right)} \right)}^2} }$计算评论家网络的策略梯度:
${ {\text{∇} } _{\boldsymbol{a}}}Q\left( {{\boldsymbol{s}},{\boldsymbol{a}}|{\theta ^Q} } \right){|_{a = \mu \left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_{i + 1} }|{\theta ^\mu } } \right),{\boldsymbol{s}} = {{\boldsymbol{s}}_j} } }$使用样本的策略梯度更新演员网络参数$ {\theta ^\mu } $:
$\dfrac{1}{H}\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^H { { {\text{∇} } _a} } Q\left( { {\boldsymbol{s} },{\boldsymbol{a} }|{\theta ^Q} } \right){|_{a = \mu \left( { {{\boldsymbol{s}}_{i + 1} }|{\theta ^\mu } } \right),{\boldsymbol{s} } = { {\boldsymbol{s} }_i} } } \cdot { {\text{∇} }_{ {\theta ^\mu } } }\mu \left( { {\boldsymbol{s} }|{\theta ^\mu } } \right){|_{ {\boldsymbol{s} } = { {\boldsymbol{s} }_i} } }$评论家和演员目标网络参数更新: $ {\theta ^{Q'}} \leftarrow \tau {\theta ^Q} + \left( {1 - \tau } \right){\theta ^{Q'}} $, $ {\theta ^{\mu '}} \leftarrow \tau {\theta ^\mu } + \left( {1 - \tau } \right){\theta ^{\mu '}} $, 其中,$ \tau $($ 0 < \tau < 1 $)为参数更新速率 END FOR END FOR 表 1 频谱干扰信号在工作时间段内的参数变化情况
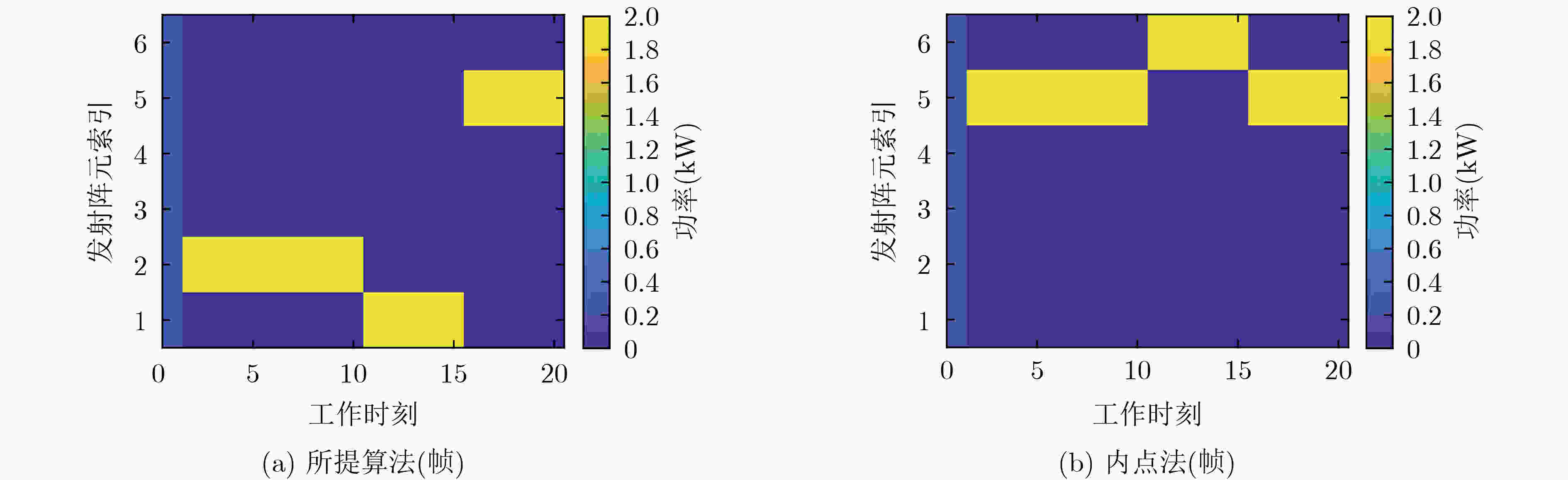
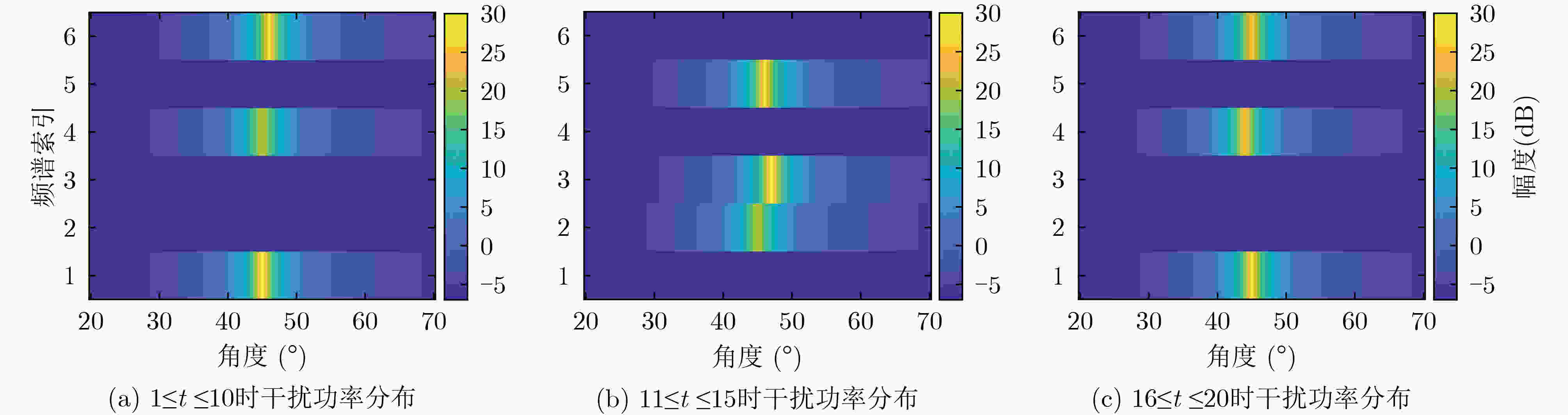
参数 ${\text{1} } \le t \le 10$ ${\text{11} } \le t \le {\text{15} }$ ${\text{16} } \le t \le {\text{2} }0$ 干扰功率 (dB) 30, 20, 30 20, 30, 30 30, 25, 25 干扰频谱索引 1, 4, 6 2, 3, 5 1, 4, 6 干扰角度 (°) 45, 45, 46 45, 47, 46 45, 44, 45 表 2 算法复杂度
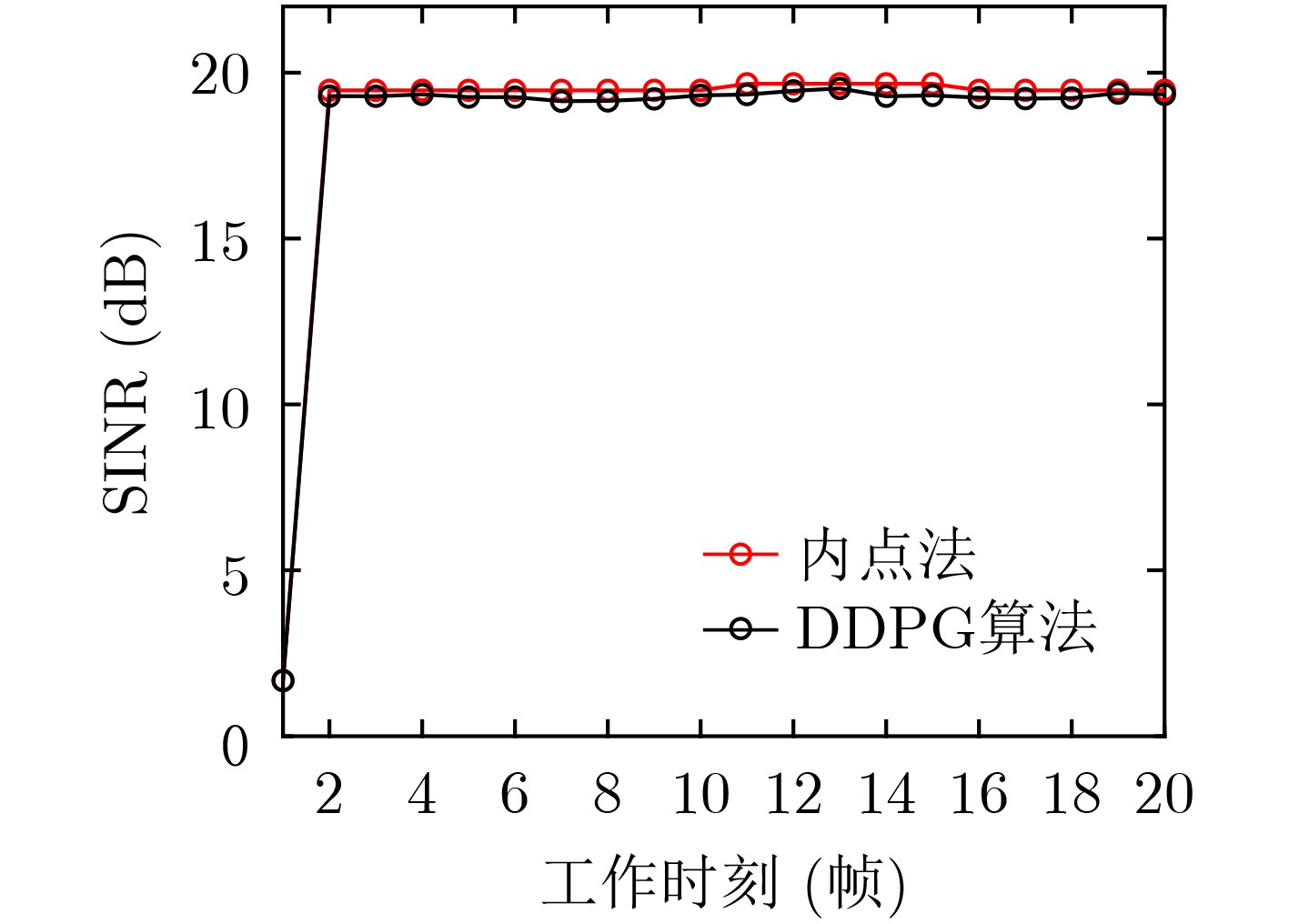
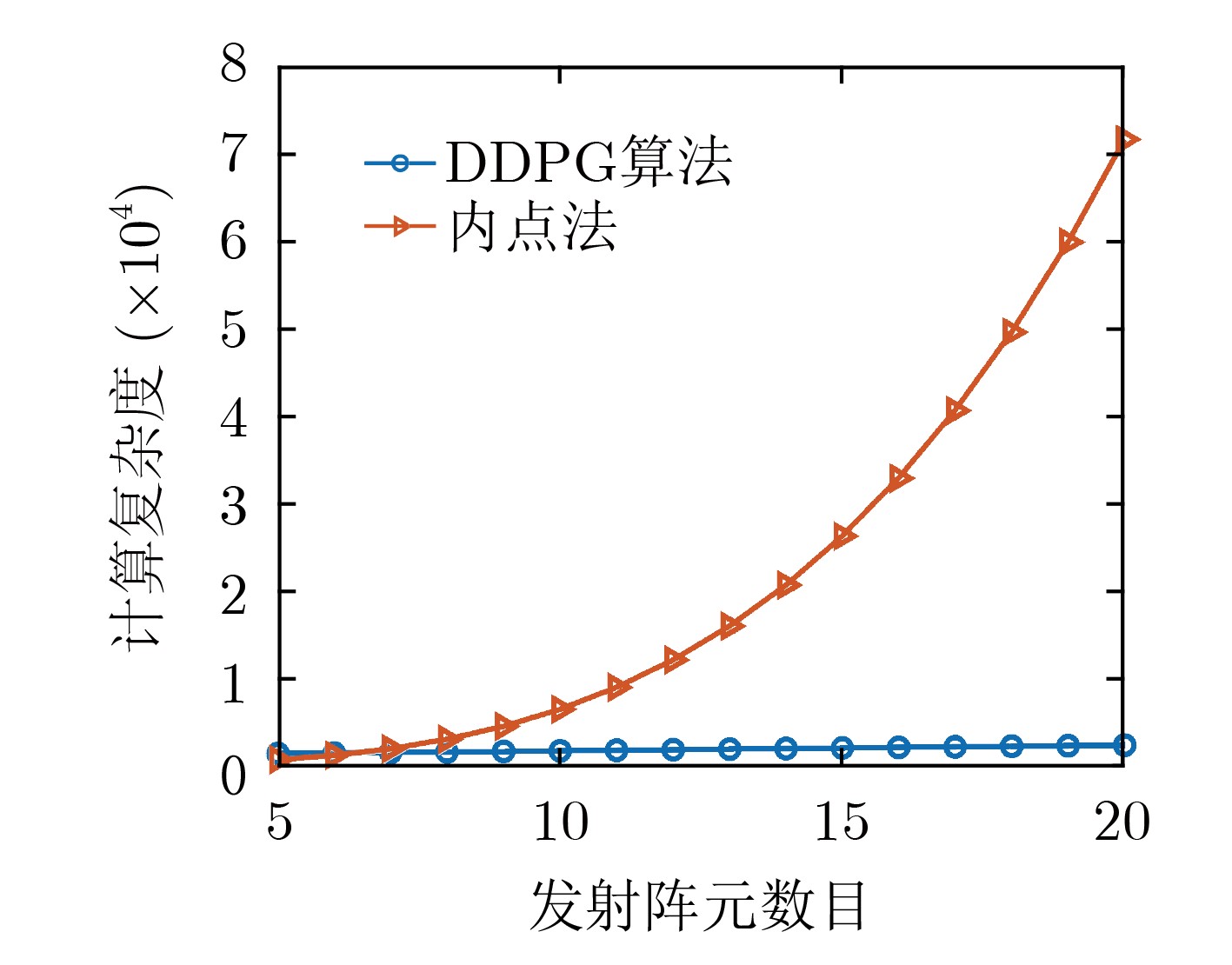
所提算法 内点法[20] 计算复杂度 $\mathcal{O}\left( { {N_{ {\text{input} } } }{N_1} + {N_1}{N_2} + {N_2}{N_{ {\text{output} } } }} \right)$ $\mathcal{O}\left( { { {\left( { {N_{ {\text{input} } } } } \right)}^{3.5} }\lg \left( {1/\varepsilon } \right)} \right)$ -
[1] ANTONIK P, WICKS M C, GRIFFITHS H D, et al. Frequency diverse array radars[C]. The 2006 IEEE Conference on Radar, Verona, Italy, 2006: 215–217. [2] WANG Wenqing. Overview of frequency diverse array in radar and navigation applications[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10(6): 1001–1012. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2015.0464 [3] WANG Wenqing and SHAO Huaizong. Range-angle localization of targets by a double-pulse frequency diverse array radar[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(1): 106–114. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2013.2285528 [4] DING Zihang, XIE Junwei, WANG Bo, et al. Robust adaptive null broadening method based on FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 177976–177983. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3025602 [5] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Joint range and angle estimation using MIMO radar with frequency diverse array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(13): 3396–3410. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2422680 [6] WANG Bo, XIE Junwei, ZHANG Jing, et al. Dot-shaped beamforming analysis of subarray-based sin-FDA[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2019, 20(10): 1429–1444. doi: 10.1631/FITEE.1800722 [7] XIONG Jie, WANG Wenqing, SHAO Huaizong, et al. Frequency diverse array transmit beampattern optimization with genetic algorithm[J]. IEEE Antennas Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 16: 469–472. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2584078 [8] SAMMARTINO P F, BAKER C J, and GRIGGITHS H D. Frequency diverse MIMO techniques for radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(1): 201–222. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6404099 [9] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, ZHU Shengqi, et al. Deceptive jamming suppression with frequency diverse MIMO radar[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 113: 9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.01.014 [10] LAN Lan, XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, et al. Suppression of mainbeam deceptive jammer with FDA-MIMO radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69(10): 11584–11598. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2020.3014689 [11] LAN Lan, LIAO Guisheng, XU Jingwei, et al. Transceive beamforming with accurate nulling in FDA-MIMO radar for imaging[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 58(6): 4145–4159. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2961324 [12] XU Jingwei, ZHU Shengqi, and LIAO Guisheng. Space-time-range adaptive processing for airborne radar systems[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2015, 15(3): 1602–1610. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2014.2364594 [13] XU Jingwei, LIAO Guisheng, HUANG Lei, et al. Robust adaptive beamforming for fast-moving target detection with FDA-STAP radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(4): 973–984. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2628340 [14] 赫彬, 苏洪涛. 认知雷达抗干扰中的博弈论分析综述[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1199–1211. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200843HE Bin and SU Hongtao. A review of game theory analysis in cognitive radar anti-jamming[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1199–1211. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200843 [15] 吴家乐, 时晨光, 周建江. 博弈论在雷达系统中的应用研究综述[J]. 飞航导弹, 2021(9): 59–66.WU Jiale, SHI Chenguang, and ZHOU Jianjiang. A review of game theory application in radar system[J]. Aerodynamic Missile Journal, 2021(9): 59–66. [16] SONG Xiufeng, WILLETT P, ZHOU Shengli, et al. The MIMO radar and jammer games[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Process, 2012, 6(2): 687–699. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2169251 [17] DELIGIANNIS A, PANOUI A, LAMBOTHARAN S, et al. Game-theoretic power allocation and the NASH equilibrium analysis for a multistatic MIMO radar network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2017, 65(24): 6397–6408. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2755591 [18] GODRICH H, PETROPULU A P, and POOR H V. Power allocation strategies for target localization in distributed multiple-radar architectures[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(7): 3226–3240. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2144976 [19] DING Zihang and XIE Junwei. Joint transmit and receive beamforming for cognitive FDA-MIMO radar with moving target[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(18): 20878–20885. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3100332 [20] LUO Zhiquan, MA W K, SO A M C, et al. Semidefinite relaxation of quadratic optimization problems[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2010, 27(3): 20–34. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2010.936019 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
