Unsupervised Underwater Image Enhancement Based on Feature Disentanglement
-
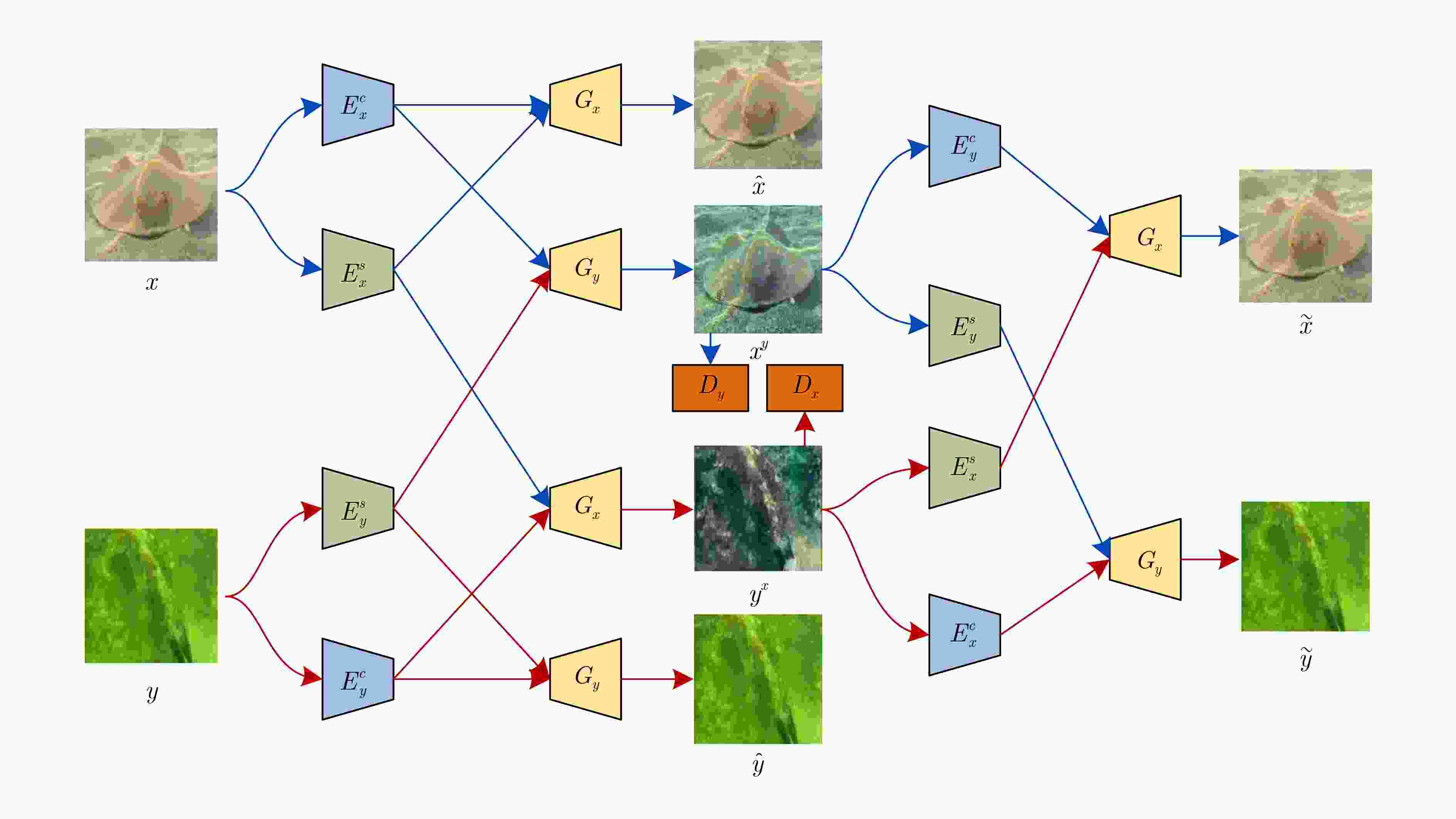
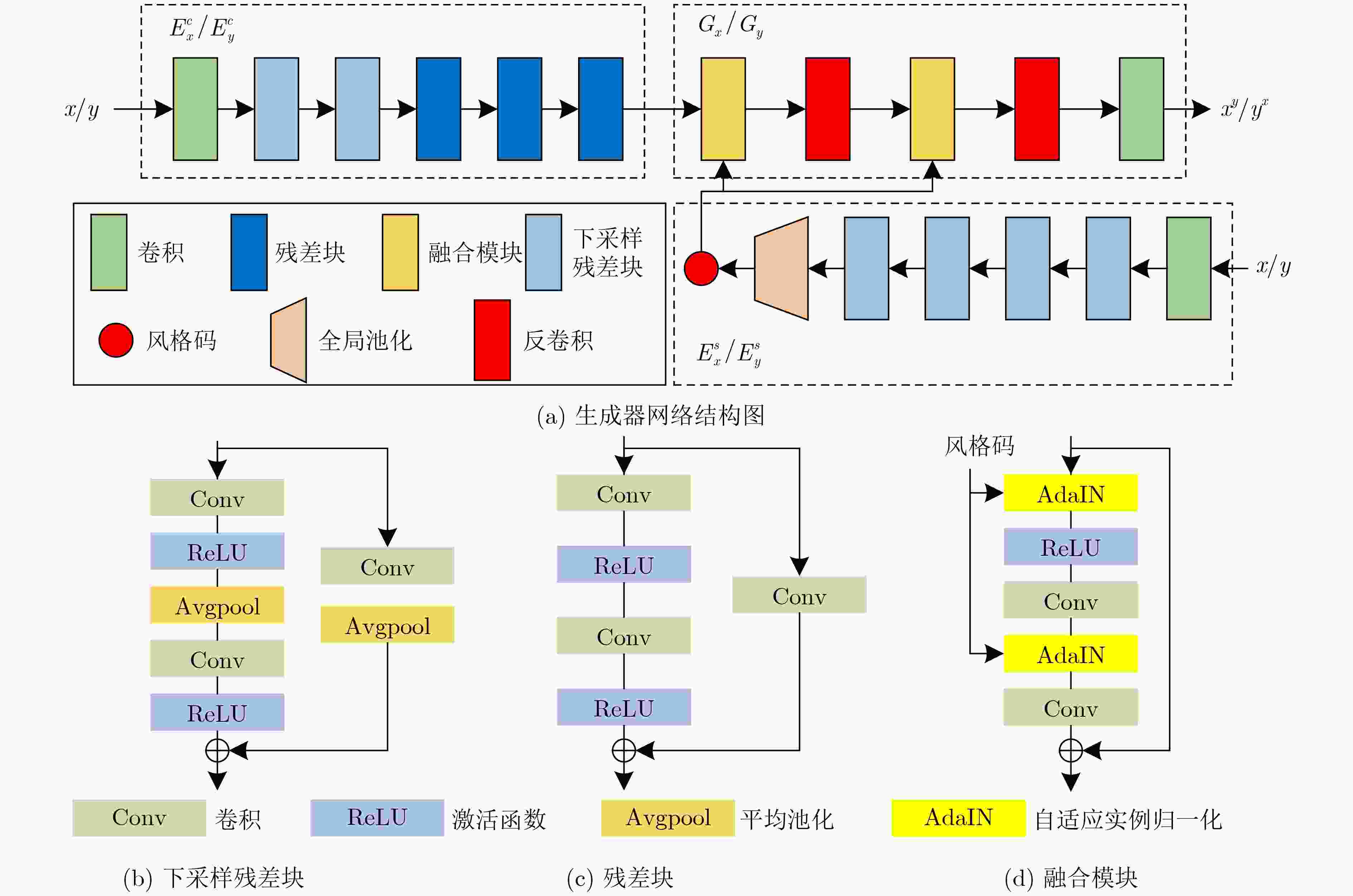
摘要: 水介质的吸收和散射特性致使水下图像存在不同类型的失真,严重影响后续处理的准确性和有效性。目前有监督学习的水下图像增强方法依靠合成的水下配对图像集进行训练,然而由于合成的数据可能无法准确地模拟水下成像的基本物理机制,所以监督学习的方法很难应用于实际的应用场景。该文提出一种基于特征解耦的无监督水下图像增强方法,一方面,考虑获取同一场景下的清晰-非清晰配对数据集难度大且成本高,提出采用循环生成对抗网络将水下图像增强问题转换成风格迁移问题,实现无监督学习;另一方面,结合特征解耦方法分别提取图像的风格特征和结构特征,保证增强前后图像的结构一致性。实验结果表明,该方法可以在非配对数据训练的情况下,能够有效恢复水下图像的颜色和纹理细节。Abstract: The absorption and scattering properties of the water medium cause different types of distortion in underwater images, which affects seriously the accuracy and effectiveness of subsequent processing. At present, underwater image enhancement methods with supervised learning rely on synthetic underwater paired image sets for training. However, the supervised learning methods are challenging to apply to practical application scenarios because the synthetic data may not accurately model the underlying physical mechanisms of underwater imaging. An unsupervised underwater image enhancement based on feature disentanglement is proposed. On the one hand, considering the difficulty and high cost of acquiring clear-unclear paired datasets in the same scene, a cycle generative adversarial network is employed to convert the underwater image enhancement problem into a style transfer problem to achieve unsupervised learning. On the other hand, the feature disentanglement method is combined to extract the style features and structure features separately to ensure the structural consistency of the images before and after enhancement. The experimental results show that the method can effectively recover the color and texture details of underwater images in the case of unpaired data training.
-
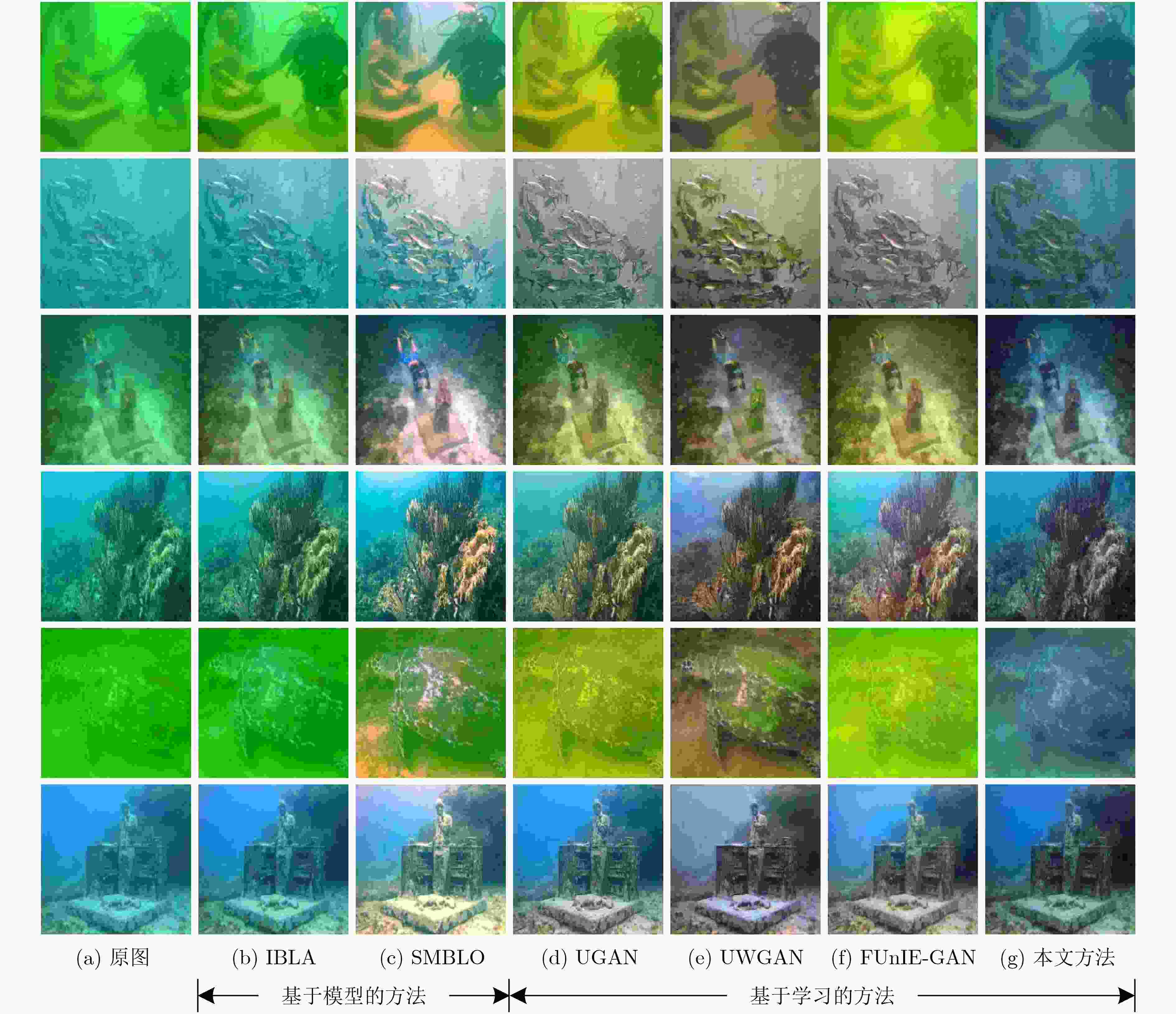
表 1 水下图像定量分析对比
UICM UISM UIConM UIQM UCIQE 原图
IBLA3.1494
5.16395.0460
4.96560.2046
0.12682.3105
2.06544.0049
5.0761SMBLO 9.0997 5.4342 0.1696 2.4677 5.7153 UGAN
UWGAN
FUNIE-GAN
本文方法4.5587
4.4339
4.8336
4.84016.8883
6.5132
6.7341
6.27670.2282
0.2921
0.2425
0.32892.9785
3.0926
2.9919
3.14874.9390
5.2140
5.5505
4.3639 -
[1] GHANI A S A and ISA N A M. Enhancement of low quality underwater image through integrated global and local contrast correction[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 37: 332–344. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.08.033 [2] SINGH K, KAPOOR R, and SINHA S K. Enhancement of low exposure images via recursive histogram equalization algorithms[J]. Optik, 2015, 126(20): 2619–2625. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2015.06.060 [3] ZHANG Shu, WANG Ting, DONG Junyu, et al. Underwater image enhancement via extended multi-scale Retinex[J]. Neurocomputing, 2017, 245: 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.03.029 [4] MERCADO M A, ISHII K, and AHN J. Deep-sea image enhancement using multi-scale retinex with reverse color loss for autonomous underwater vehicles[C]. OCEANS 2017-Anchorage, Anchorage, USA, 2017: 1–6. [5] GHANI A S A. Image contrast enhancement using an integration of recursive-overlapped contrast limited adaptive histogram specification and dual-image wavelet fusion for the high visibility of deep underwater image[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 162: 224–238. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.05.027 [6] LI Chongyi and GUO Jichang. Underwater image enhancement by dehazing and color correction[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2015, 24(3): 033023. doi: 10.1117/1.JEI.24.3.033023 [7] JAFFE J S. Computer modeling and the design of optimal underwater imaging systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1990, 15(2): 101–111. doi: 10.1109/48.50695 [8] AKKAYNAK D and TREIBITZ T. A revised underwater image formation model[C]. The IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 6723–6732. [9] ANWAR S and LI Chongyi. Diving deeper into underwater image enhancement: A survey[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2020, 89: 115978. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2020.115978 [10] SUN Xin, LIU Lipeng, LI Qiong, et al. Deep pixel-to-pixel network for underwater image enhancement and restoration[J]. IET Image Processing, 2018, 13(3): 469–474. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.5237 [11] WANG Yang, ZHANG Jing, CAO Yang, et al. A deep CNN method for underwater image enhancement[C]. 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 2017: 1382–1386. [12] LI Chongyi, GUO Chunle, REN Wenqi, et al. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 4376–4389. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2955241 [13] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]. The 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Cambridge, UK, 2014: 2672–2680. [14] FABBRI C, ISLAM M J, and SATTAR J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 2018: 7159–7165. [15] GULRAJANI I, AHMED F, ARJOVSKY M, et al. Improved training of wasserstein GANs[C]. The 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2017: 5769–5779. [16] GUO Yecai, LI Hanyu, and ZHUANG Peixian. Underwater image enhancement using a multiscale dense generative adversarial network[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45(3): 862–870. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2911447 [17] LI Jie, SKINNER K A, EUSTICE R M, et al. WaterGAN: Unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2017, 3(1): 387–394. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2730363 [18] LU Jingyu, LI Na, ZHANG Shaoyong, et al. Multi-scale adversarial network for underwater image restoration[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 110: 105–113. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.05.048 [19] ZHU Junyan, PARK T, ISOLA P, et al. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2242–2251. [20] ISLAM M J, XIA Youya, and SATTAR J. Fast underwater image enhancement for improved visual perception[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(2): 3227–3234. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.2974710 [21] MIRZA M and OSINDERO S. Conditional generative adversarial nets[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1411.1784, 2014. [22] LEE H Y, TSENG H Y, HUANG Jiabin, et al. Diverse image-to-image translation via disentangled representations[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 36–52. [23] HUANG Xun, LIU Mingyu, BELONGIE S, et al. Multimodal unsupervised image-to-image translation[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 2018: 179–196. [24] LIU Siyuan, THUNG K H, QU Liangqiong, et al. Learning MRI artefact removal with unpaired data[J]. Nature Machine Intelligence, 2021, 3(1): 60–67. doi: 10.1038/s42256-020-00270-2 [25] LOCATELLO F, BAUER S, LUCIC M, et al. Challenging common assumptions in the unsupervised learning of disentangled representations[C]. The 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 4114–4124. [26] LI Chuan and WAND M. Precomputed real-time texture synthesis with markovian generative adversarial networks[C]. 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Holland, 2016: 702–716. [27] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [28] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Hawaii, USA, 2017: 936–944. [29] HUANG Xun and BELONGIE S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 1510–1519. [30] KINGMA D P and WELLING M. Auto-encoding variational bayes[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.6114v10, 2013. [31] KINGMA D P and BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1412.6980v5, 2014. [32] PENG Y T and COSMAN P C. Underwater image restoration based on image blurriness and light absorption[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4): 1579–1594. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2663846 [33] SONG Wei, WANG Yan, HUANG Dongmei, et al. Enhancement of underwater images with statistical model of background light and optimization of transmission map[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2020, 66(1): 153–169. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2019.2960942 [34] LI Chongyi, GUO Jichang, and GUO Chunle. Emerging from water: Underwater image color correction based on weakly supervised color transfer[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2018, 25(3): 323–327. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2792050 [35] YANG Miao and SOWMYA A. An underwater color image quality evaluation metric[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12): 6062–6071. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2491020 [36] PANETTA K, GAO Chen, and AGAIAN S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2016, 41(3): 541–551. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2015.2469915 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
