Signal Detection Algorithm of RIS-Assisted SIMO Communication System with Index Modulation
-
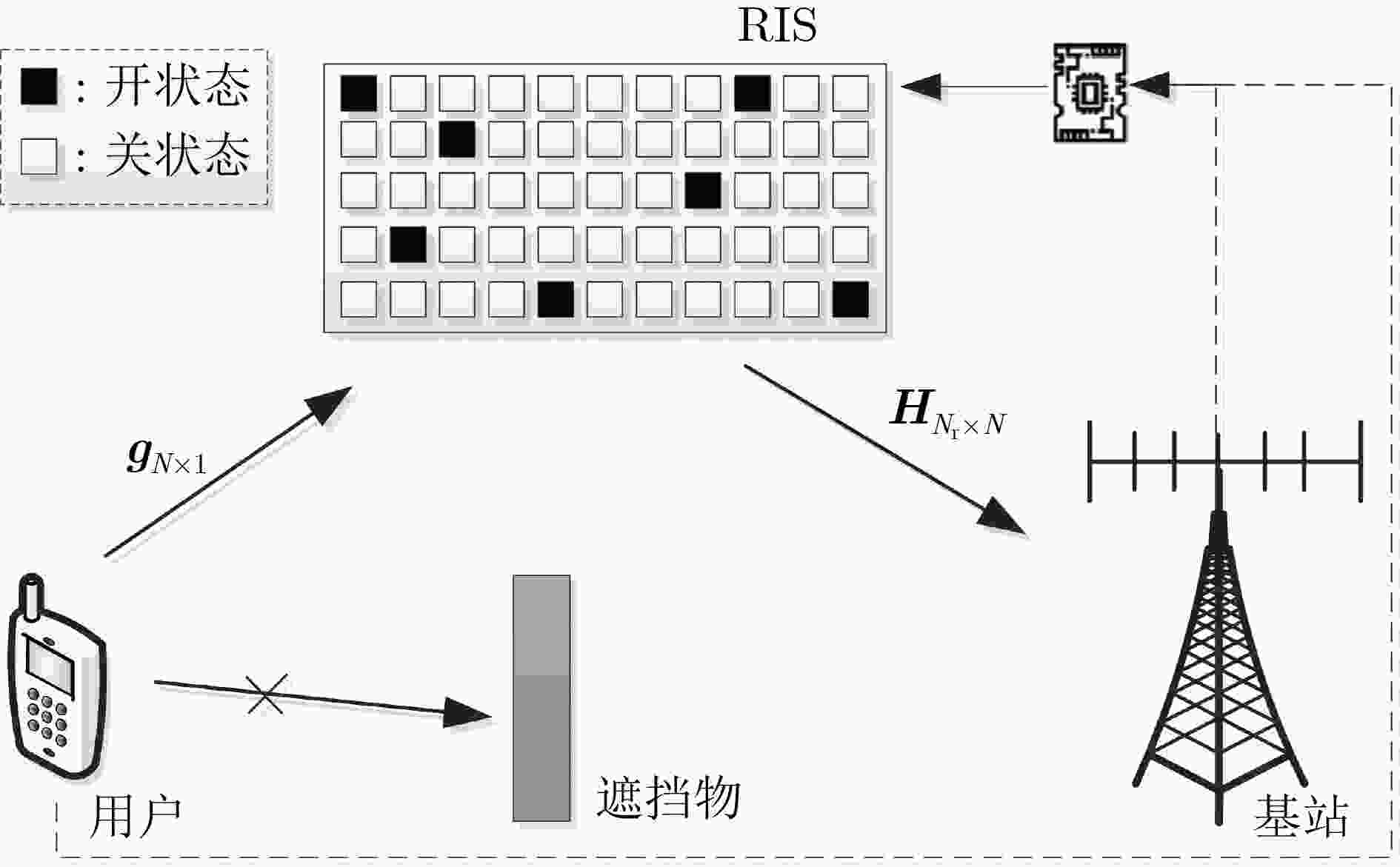
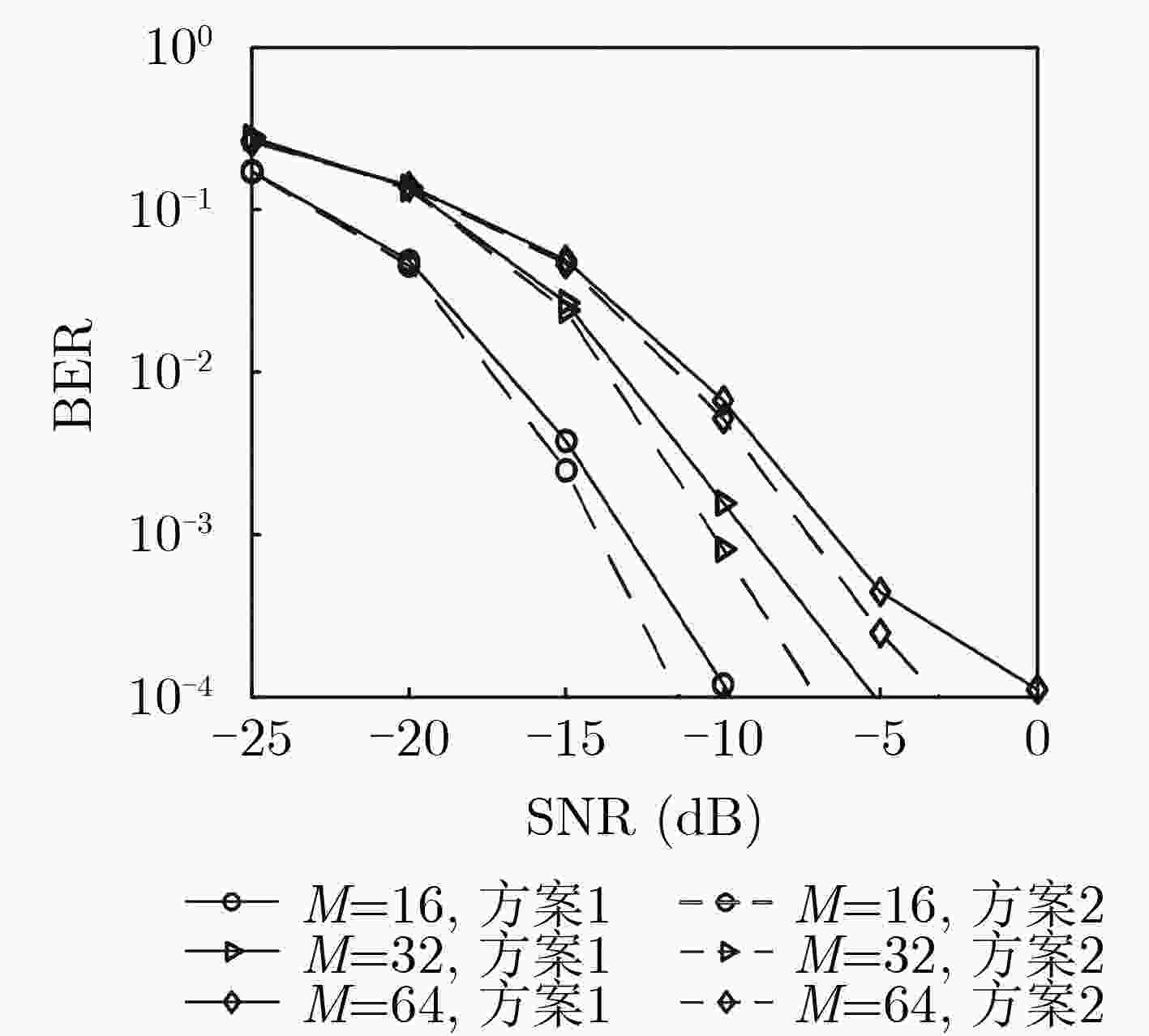
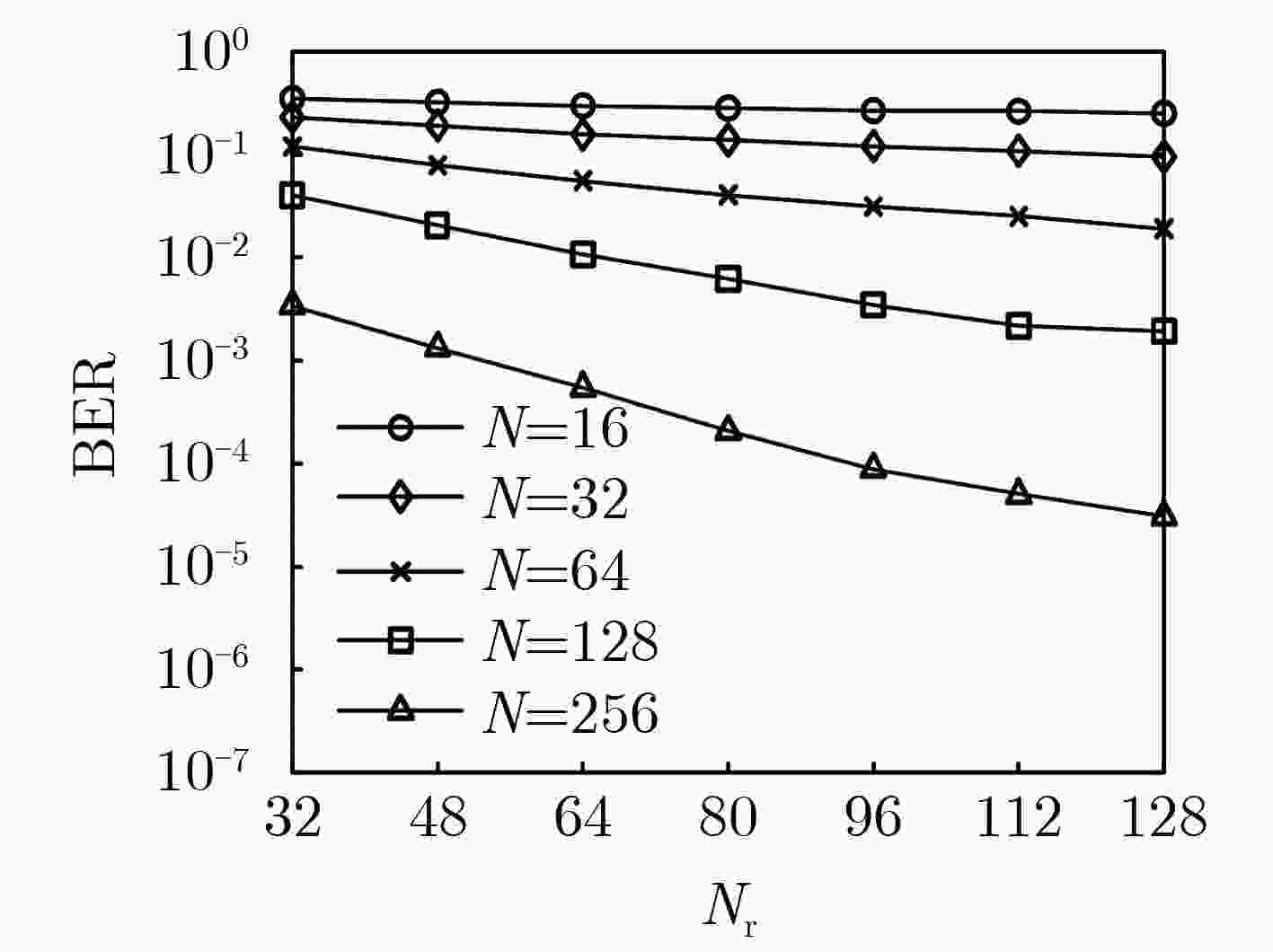
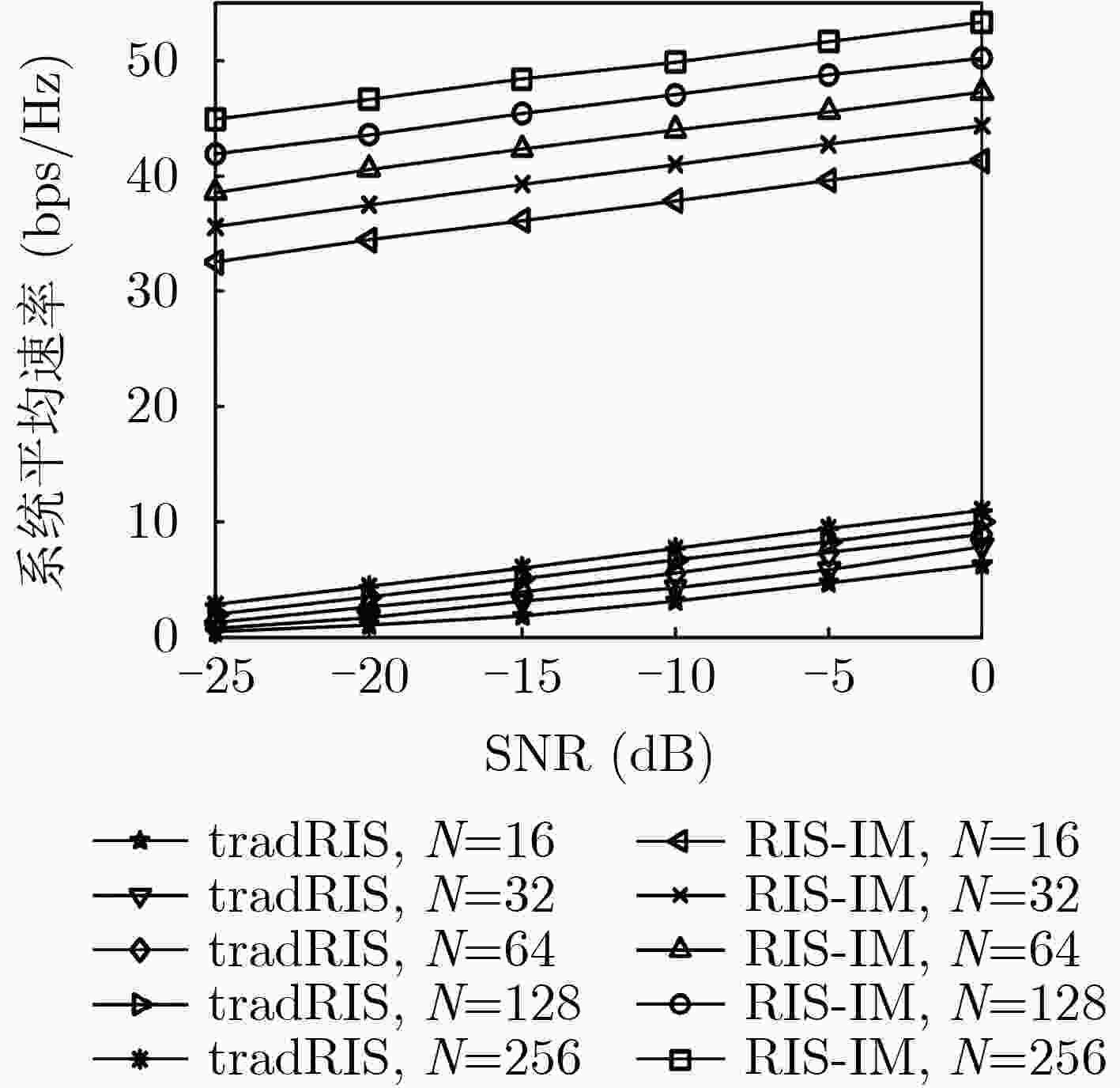
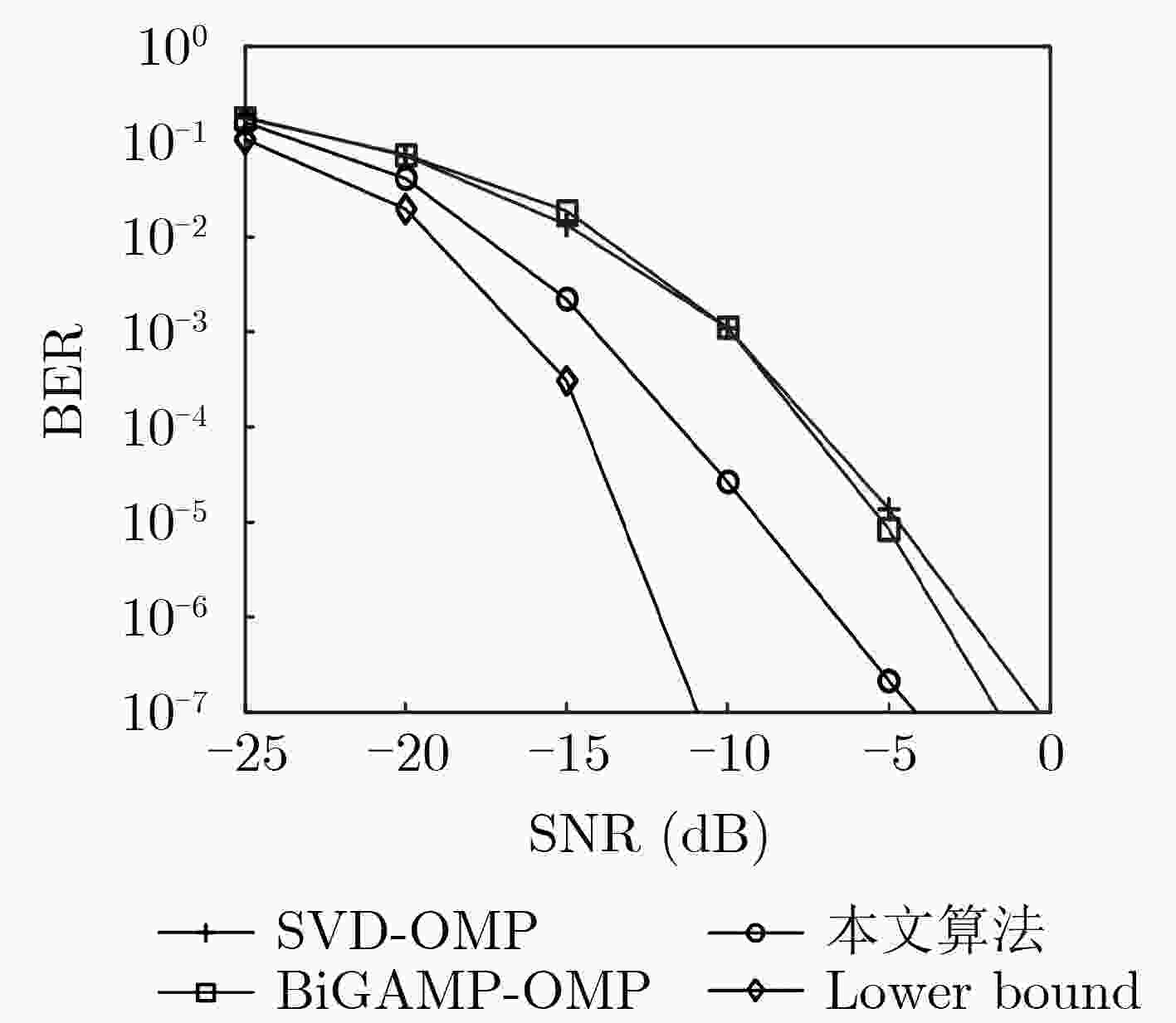
摘要: 面对未来无线移动通信对通信质量和频谱效率的更高要求,该文融合索引调制(IM)与可重构智能表面(RIS)技术,建立基于IM的RIS辅助单输入多输出(SIMO)通信系统架构,并提出一种基于变分贝叶斯推断(VBI)的信号检测算法。首先,在该系统中,RIS单元被划分为若干子块,利用RIS子块的激活状态传递附加信息;接着,利用VBI给出激活RIS子块对应的相移矢量与待检测信号的近似后验分布;最后,利用RIS相移矢量近似后验分布的对数零梯度值结合正交匹配追踪算法(OMP)恢复出索引信息比特,进而利用待检测信号对数零梯度值,恢复出发送信号。同时,从理论上推导了基于IM的RIS辅助SIMO系统平均速率。仿真结果表明,与传统RIS辅助的SIMO通信系统相比,基于IM的RIS辅助SIMO系统具有更高的系统平均速率;并且与现有算法相比,该文算法具有更低的误比特率。Abstract: For the higher requirements of communication quality and spectrum efficiency in future wireless mobile communication systems, this paper combines Index Modulation (IM) and Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface (RIS) technologies to establish the RIS-assisted Single-Input Multiple-Output (SIMO) communication systems with IM, and the Variational Bayes Inference (VBI)-based signal detection algorithm is proposed. Firstly, in the system, the RIS units are divided into a number of sub-blocks, and the activation state of the RIS sub-block is used to transmit additional information. Then, the VBI is used to calculate the approximate posterior distribution of the phase shift vector corresponding to the activated RIS sub-block and the signal vector for detection. Finally, the index information bits are recovered by using the logarithmic zero gradient value of the approximate posterior distribution of the RIS phase shift vector combined with the Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (OMP) algorithm, and taking advantage of the logarithmic zero gradient value of the signal to be detected, the transmitted symbols are recovered. Meanwhile, the system average rate is theoretically deduced. The simulation results show that compared with the traditional RIS-assisted SIMO communication systems, the RIS -assisted SIMO systems with IM has a higher system average rate; and in contrast to existing algorithms, the proposed one has lower bit errors rate.
-
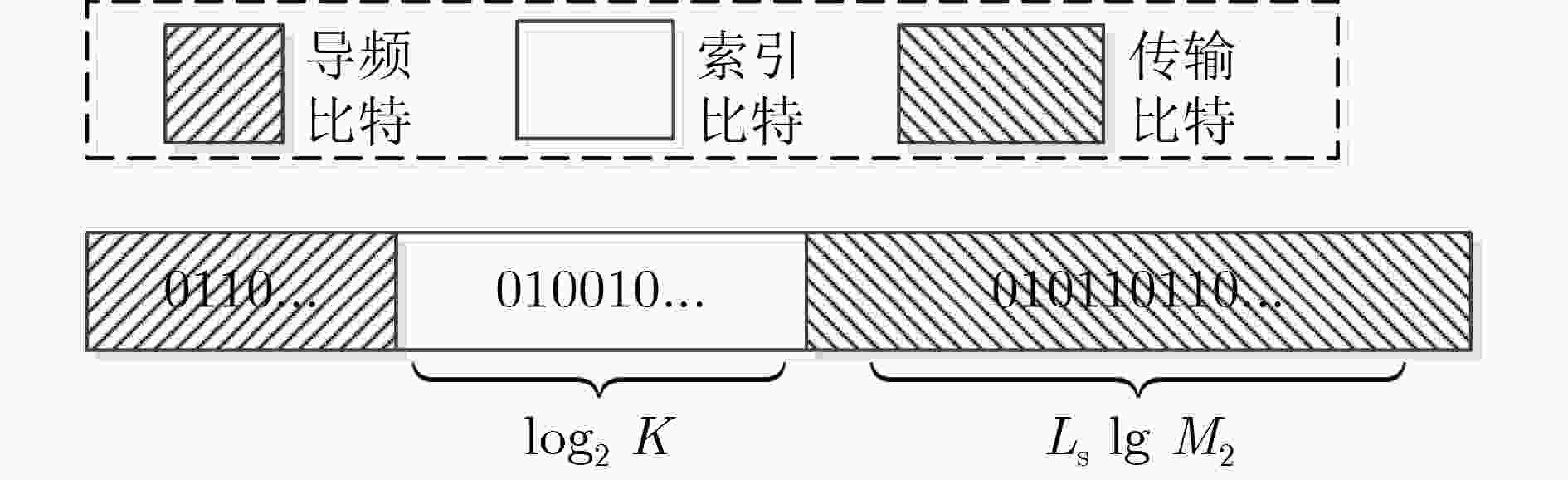
表 1 索引比特对应两种分组原则下RIS相移矩阵
索引比特 组索引$ k $ 与分组方案1对应的${{\boldsymbol{\theta}} _k}$ 与分组方案2对应的${{\boldsymbol{\theta}} _k}$ $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0 \end{array}} \right] $ 1 $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\theta _1}}&{{\theta _2}}&0&0&0&0&0&0 \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&{{\theta _2}}&0&0&0&0&0&{{\theta _8}} \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&1 \end{array}} \right] $ 2 $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0&{{\theta _3}}&{{\theta _4}}&0&0&0&0 \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{\theta _1}}&0&0&{{\theta _4}}&0&0&0&0 \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&0 \end{array}} \right] $ 3 $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0&0&0&{{\theta _5}}&{{\theta _6}}&0&0 \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0&{{\theta _3}}&0&0&0&{{\theta _7}}&0 \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ $ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 1&1 \end{array}} \right] $ 4 $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0&0&0&0&0&{{\theta _7}}&{{\theta _8}} \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ $ {\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&0&0&0&{{\theta _5}}&{{\theta _6}}&0&0 \end{array}} \right]^{\text{T}}} $ -
[1] DI RENZO M, DEBBAH M, PHAN-HUY D T, et al. Smart radio environments empowered by reconfigurable AI meta-surfaces: An idea whose time has come[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2019, 2019(1): 129. doi: 10.1186/s13638-019-1438-9 [2] SAAD W, BENNIS M, and CHEN Mingzhe. A vision of 6G wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(3): 134–142. doi: 10.1109/MNET.001.1900287 [3] LIN Shaoe, ZHENG Beixiong, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces with reflection pattern modulation: Beamforming design and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(2): 741–754. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.3028198 [4] WANG Xinyi, FEI Zesong, GUO Jing, et al. RIS-assisted spectrum sharing between MIMO radar and MU-MISO communication systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10(3): 594–598. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.3039369 [5] PANG Xiaowei, SHENG Min, ZHAO Nan, et al. When UAV meets IRS: Expanding air-ground networks via passive reflection[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2021, 28(5): 164–170. doi: 10.1109/MWC.010.2000528 [6] BASAR E. Index modulation techniques for 5G wireless networks[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2016, 54(7): 168–175. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2016.7509396 [7] CANBILEN A E, BASAR E, and IKKI S S. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted space shift keying[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2020, 9(9): 1495–1499. doi: 10.1109/LWC.2020.2994930 [8] FENG Lei, QUE Xiaoyu, YU Peng, et al. IRS assisted multiple user detection for uplink URLLC non-orthogonal multiple access[C]. IEEE INFOCOM 2020-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications Workshops (INFOCOM WKSHPS), Toronto, Canada, 2020: 1314–1315. [9] LI Wei, HUANG Chongwen, ALEXANDROPOULOS G C, et al. Joint channel estimation and signal recovery in RIS-assisted multi-user MISO communications[C]. 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–6. [10] ALBINSAID H, SINGH K, BANSAL A, et al. Multiple antenna selection and successive signal detection for SM-based IRS-aided Communication[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 813–817. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3071981 [11] KHAN S, KHAN K S, HAIDER N, et al. Deep-learning-aided detection for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces[EB/OL]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.09136, 2020. [12] MESLEH R Y, HAAS H, SINANOVIC S, et al. Spatial modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2008, 57(4): 2228–2241. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2007.912136 [13] IDOWU-BISMARK O, OYELEKE O, and ILESANMI O. Index modulation-aided orthogonal frequency division multiplexing and its applications[J]. International Journal of Networks and Communications, 2019, 9(3): 97–102. doi: 10.5923/j.ijnc.20190903.02 [14] KADDOUM G, AHMED M F A, and NIJSURE Y. Code index modulation: A high data rate and energy efficient communication system[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2015, 19(2): 175–178. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2385054 [15] MESLEH R, HAAS H, AHN C W, et al. Spatial modulation-a new low complexity spectral efficiency enhancing technique[C]. 2006 First International Conference on Communications and Networking in China, Beijing, China, 2006: 1–5. [16] JEGANATHAN J, GHRAYEB A, and SZCZECINSKI L. Spatial modulation: Optimal detection and performance analysis[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2008, 12(8): 545–547. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2008.080739 [17] BAI Guo, CHENG Yufan, TANG Wanbin, et al. An innovative low-complexity detection algorithm for spatial modulation[C]. 2017 IEEE 17th International Conference on Communication Technology (ICCT), Chengdu, China, 2017: 38–42. [18] WANG Jintao, JIA Shuyun, and SONG Jian. Generalised spatial modulation system with multiple active transmit antennas and low complexity detection scheme[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(4): 1605–1615. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.030512.111635 [19] ZHENG Jianping and LIU Qin. Low-complexity soft-decision detection of coded OFDM with index modulation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2018, 67(8): 7759–7763. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2822943 [20] WEI Li and ZHENG Jianping. Approximate message passing-aided iterative channel estimation and data detection of OFDM-IM in doubly selective channels[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 133410–133420. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941233 [21] BASAR E. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-based index modulation: A new beyond MIMO paradigm for 6G[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(5): 3187–3196. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2971486 [22] WINN J and BISHOP C M. Variational message passing[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2005, 6: 661–694. [23] 申滨, 吴和彪, 崔太平, 等. 基于最优索引广义正交匹配追踪的非正交多址系统多用户检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(3): 621–628. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190270SHEN Bin, WU Hebiao, CUI Taiping, et al. An optimal number of indices aided gOMP algorithm for multi-user detection in NOMA system[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(3): 621–628. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190270 [24] PARKER J T, SCHNITER P, and CEVHER V. Bilinear generalized approximate message passing—part II: Applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(22): 5854–5867. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2357773 [25] BJORNSON E, MATTHAIOU M, and DEBBAH M. A new look at dual-hop relaying: Performance limits with hardware impairments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(11): 4512–4525. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.100913.130282 -





 下载:
下载:

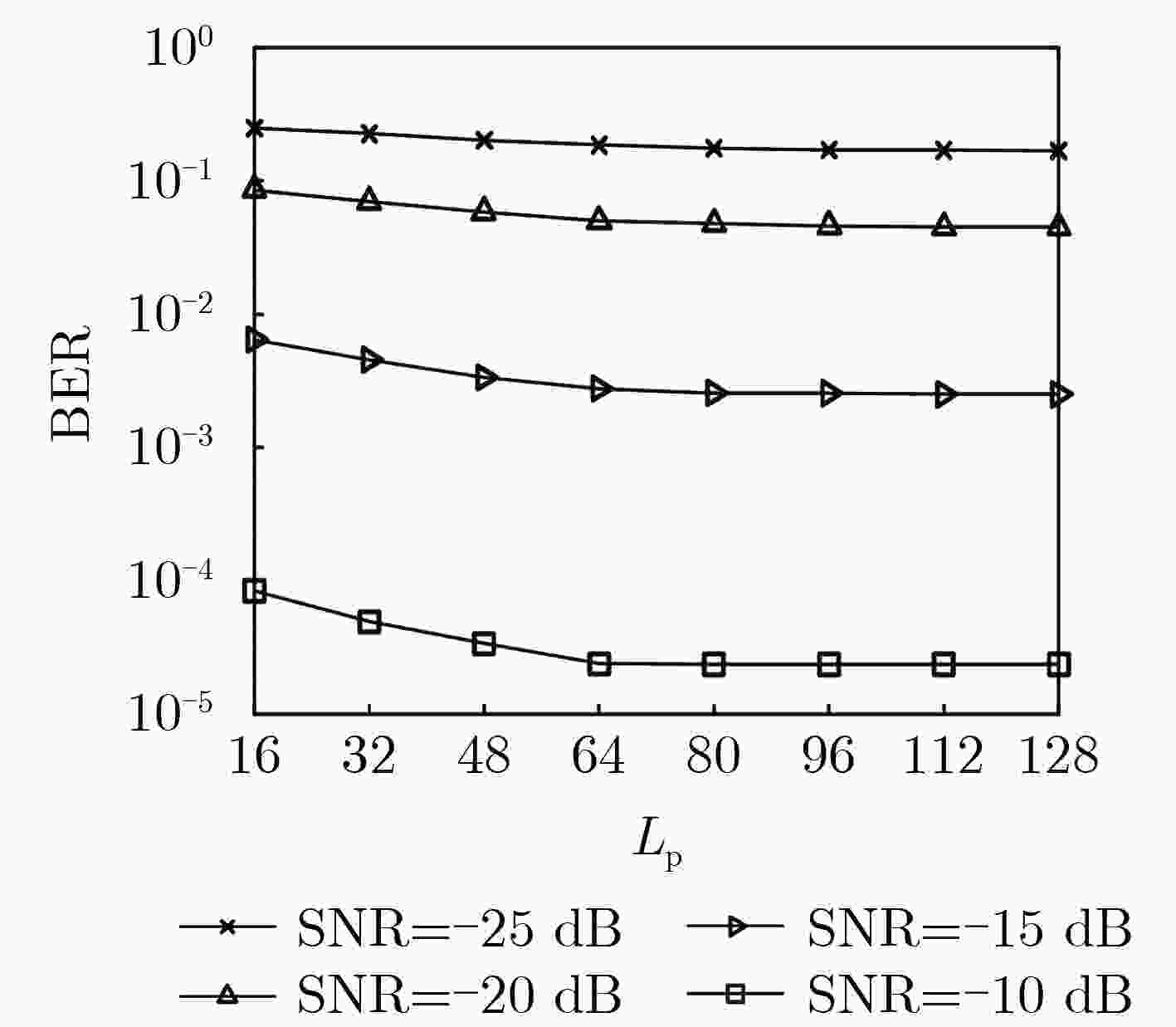

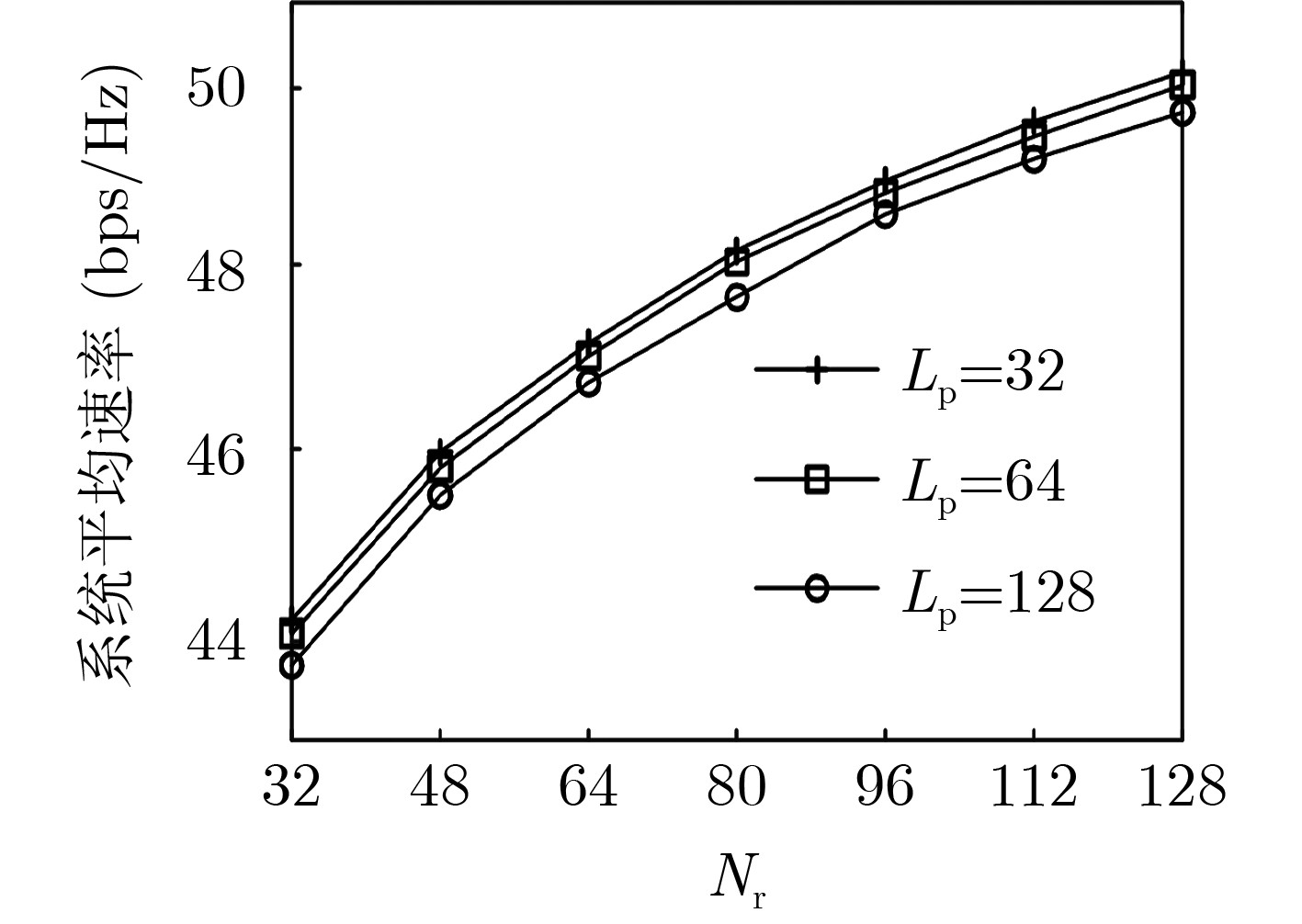


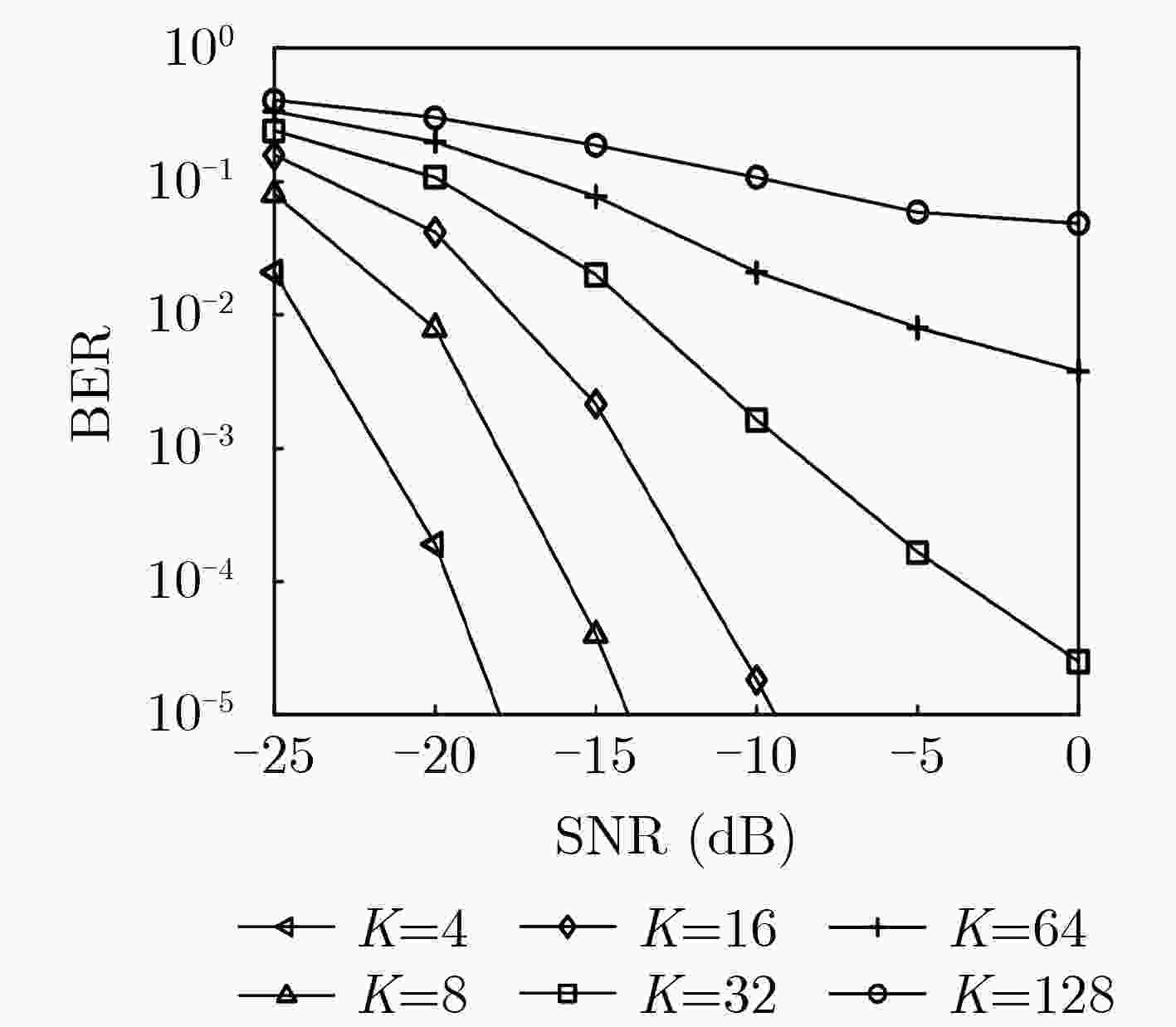
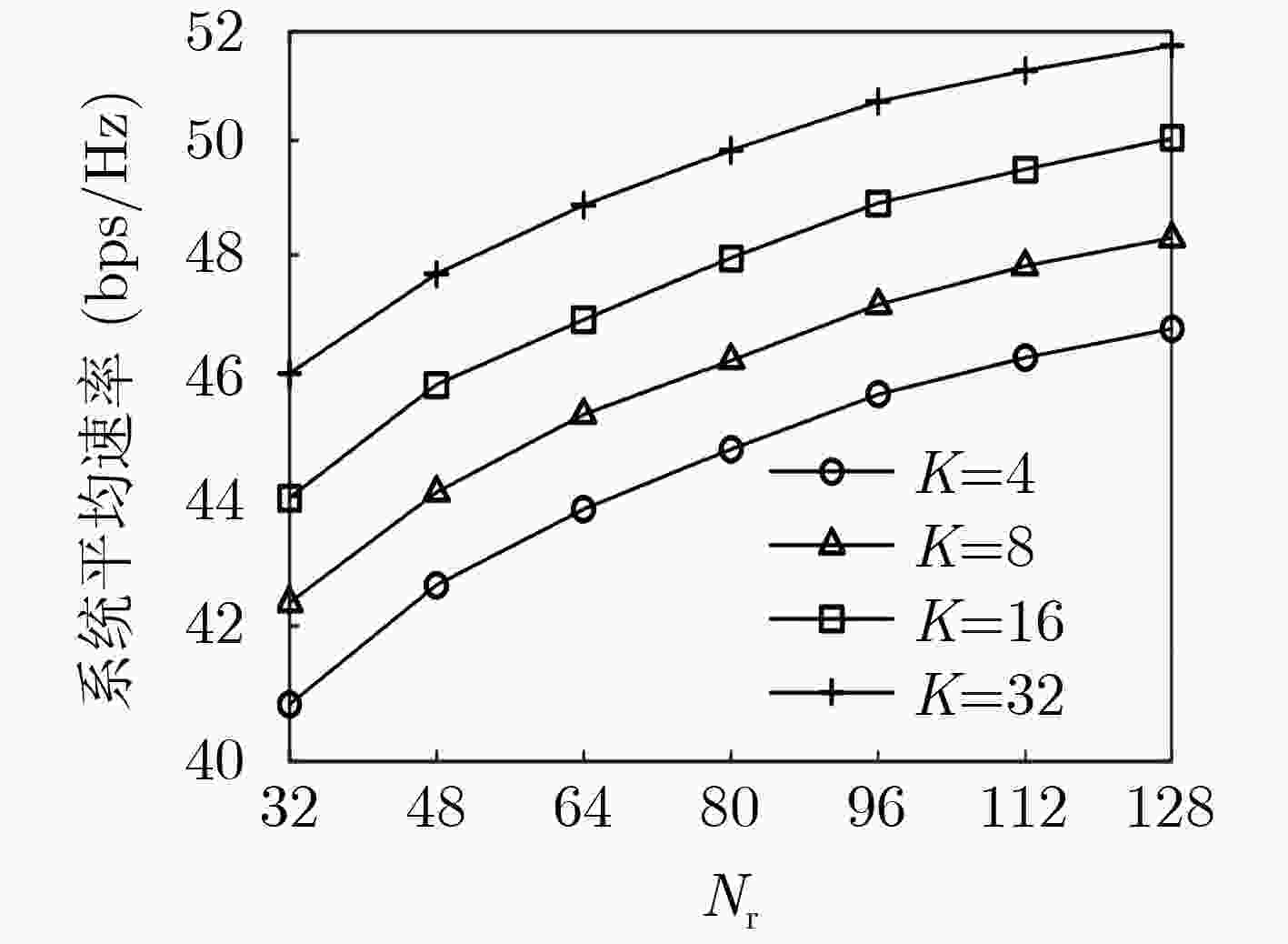


 下载:
下载:
