A Novel Beam Hopping Resource Allocation Scheme of Low Earth Orbit Satellite Based on Transfer Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
摘要: 针对低轨(LEO)卫星场景下,传统资源分配方案容易造成特定小区资源分配无法满足需求的问题,该文提出一种基于迁移深度强化学习(TDRL)的低轨卫星跳波束资源分配方案。首先,该方案联合星上缓冲信息、业务到达情况和信道状态,以最小化卫星上数据包平均时延为目标,建立支持跳波束技术的低轨卫星资源分配优化模型。其次,针对低轨卫星网络的动态多变性,该文考虑动态随机变化的通信资源和通信需求,采用深度Q网络(DQN)算法利用神经网络作为非线性近似函数。进一步,为实现并加速深度强化学习(DRL)算法在其他目标任务中的收敛过程,该文引入迁移学习(TL)概念,利用源卫星学习的调度任务快速寻找目标卫星的波束调度和功率分配策略。仿真结果表明,该文所提出的算法能够优化卫星服务过程中的时隙分配,减少数据包的平均传输时延,并有效提高系统的吞吐量和资源利用效率。Abstract: In the Low Earth Orbit (LEO) scenario, traditional resource allocation schemes can cause unbalanced resource allocation in specific cells. A beam hopping resource allocation scheme of LEO based on Transfer Deep Reinforcement Learning (TDRL) is proposed in this paper. Firstly, considering on-board buffer information, service arrival status and channel status, a LEO resource allocation optimization model that supports beam hopping technology is proposed with the goal of minimizing the average delay of data packets. Secondly, in view of the dynamic variability of the LEO network, the dynamic and random change of communication resources and requirements are considered, then the Deep Q Network (DQN) algorithm is adopted, and its neural network is used as a nonlinear approximation function. Further, to realize and accelerate the convergence process of the Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithm in other target tasks, the concept of Transfer Learning (TL) is introduced in this paper, which uses the scheduling task learned by the source satellite to find quickly the beam scheduling and power allocation strategy of the target satellite. The simulation results demonstrate that the algorithm can optimize the time slot allocation in the satellite service process while decreasing the average delay of data packets and improving the throughput and resource utilization efficiency of the system.
-
算法1 基于TL-DQN的低轨卫星跳波束方案 (1) 初始化多波束低轨卫星网络参数、小区参数、经验回放池${\boldsymbol{D}}$及其容量$ N $ (2) 随机初始化动作-价值函数$ Q $网络中的参数$ w $,初始化动作-价值函数$ {Q^ - } $网络中的参数$ {w^ - } $,并令权重$ {w^ - } = w $ (3) For 学习回合episode=1,2,···,Nepochs do (4) 通过公式$ \varepsilon = 1 - (0.5 + {n_{{\text{epochs}}}}/{N_{{\text{epochs}}}} \times 0.3) $初始化$ \varepsilon $,逐步减小探索概率 (5) 初始化获取状态$ s({t_0}) $,本地策略$ \pi _{{t_0}}^{{\text{tg}}}(s({t_0}),a({t_0})) $和外来迁移策略$ \pi _{{t_0}}^{\text{s}}(s({t_0}),a({t_0})) $ (6) For time i=0,1,···, $ |{\mathbf{T}}| - 1 $ do (7) 随机生成概率$ p $ (8) If $p \le \varepsilon$: (9) 低轨卫星随机选取满足限制条件的$ a({t_i}) $ (10) Else (11) 由式(26)得到整体策略,根据$ \pi _{{t_0}}^{{\text{tg}}}(s({t_0}),a({t_0})) $选择动作$ a({t_i}) = \arg {\max _{a({t_i})}}Q(s({t_i}),a({t_i});\omega ) $,实现低轨卫星波束调度和资
源分配,而后更新环境状态$ s({t_{i + 1}}) $,并立即得到奖励$ r({t_i}) $(12) 将4元组$ (s({t_i}),a({t_i}),r({t_i}),s({t_{i + 1}})) $存储在${\boldsymbol{D}}$中 (13) 从${\boldsymbol{D}}$中随机抽取一小批量的样本$ (s({t_i}),a({t_i}),r({t_i}),s({t_{i + 1}})) $ (14) 利用式(19)计算损失函数 (15) 指数加权平均数的1阶矩和2阶矩可以分别通过式(21)和式(22)得到 (16) 利用Adam算法,计算式(23)和式(24)分别得出1阶矩和2阶矩的偏差修正项 (17) 利用式(25)更新估值网络$ Q $的权重参数$ w $ (18) 每隔一定步数$ G $用$ Q $网络参数$ w $替换更新目标$ {Q^ - } $网络参数$ {w^ - } $ (19) End for (20) End for 表 1 低轨卫星场景设置参数
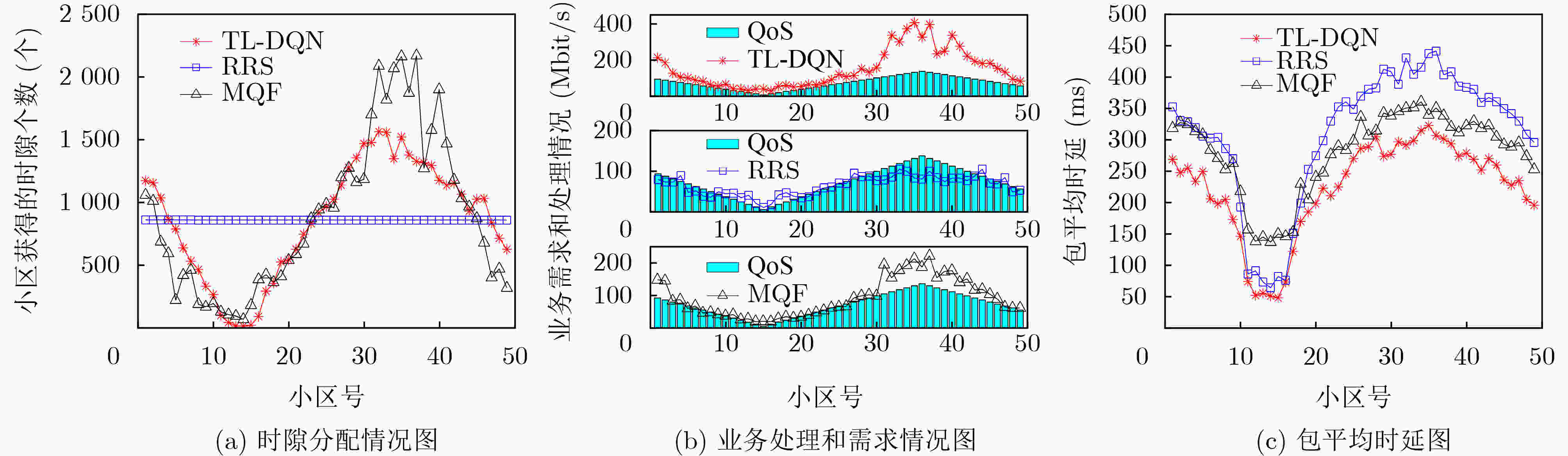
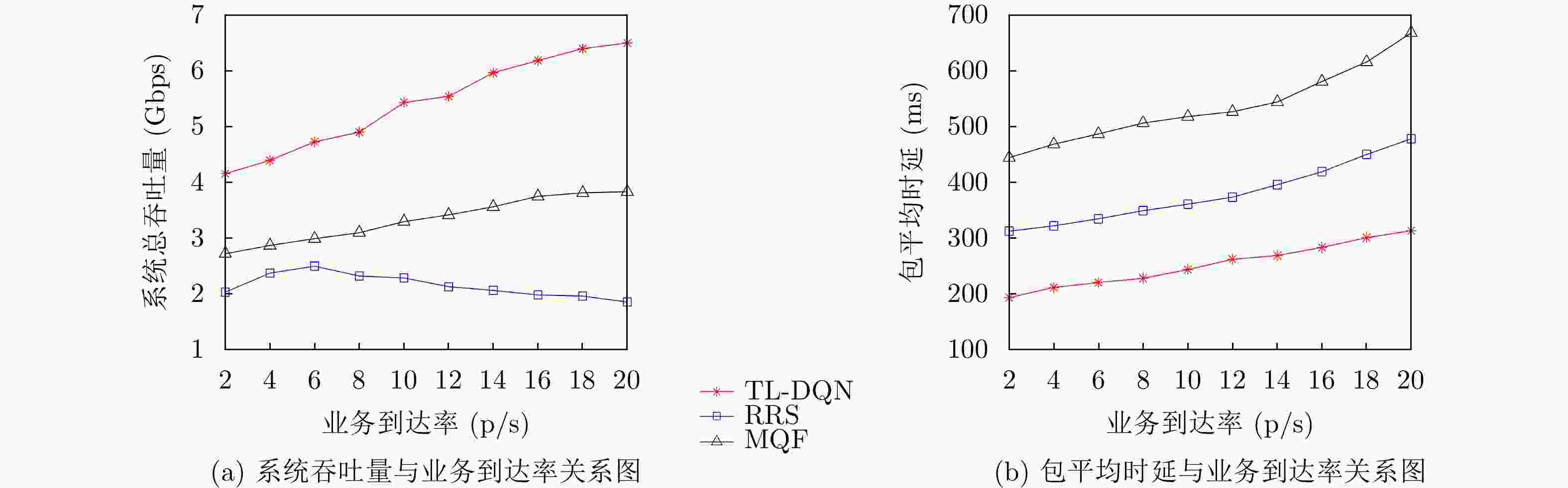
低轨卫星网络参数 取值 低轨卫星网络参数 取值 卫星轨道高度h 781 km 用户的接收天线增益Gr 20 dBi 卫星波束个数K 7 噪声功率密度N0 –174 dBm/Hz 服务小区总数N 49 卫星最大发射功率Ptot 20 dBW 小区直径D 667 km 单波束的最大发射功率Pmax 18 dBW 信道总带宽Bw 250 MHz 多波束天线半波束角$ {\theta _\alpha } $ $ {2^ \circ } $ 下行链路工作频率f 20 GHz 数据包大小M 50 kbit 卫星发射的最大天线增益Gm 41.6 dBi 业务数据包到达率$ {\lambda _{{c_n}}}(t) $ [1,21] 表 2 TL-DQN算法参数设置
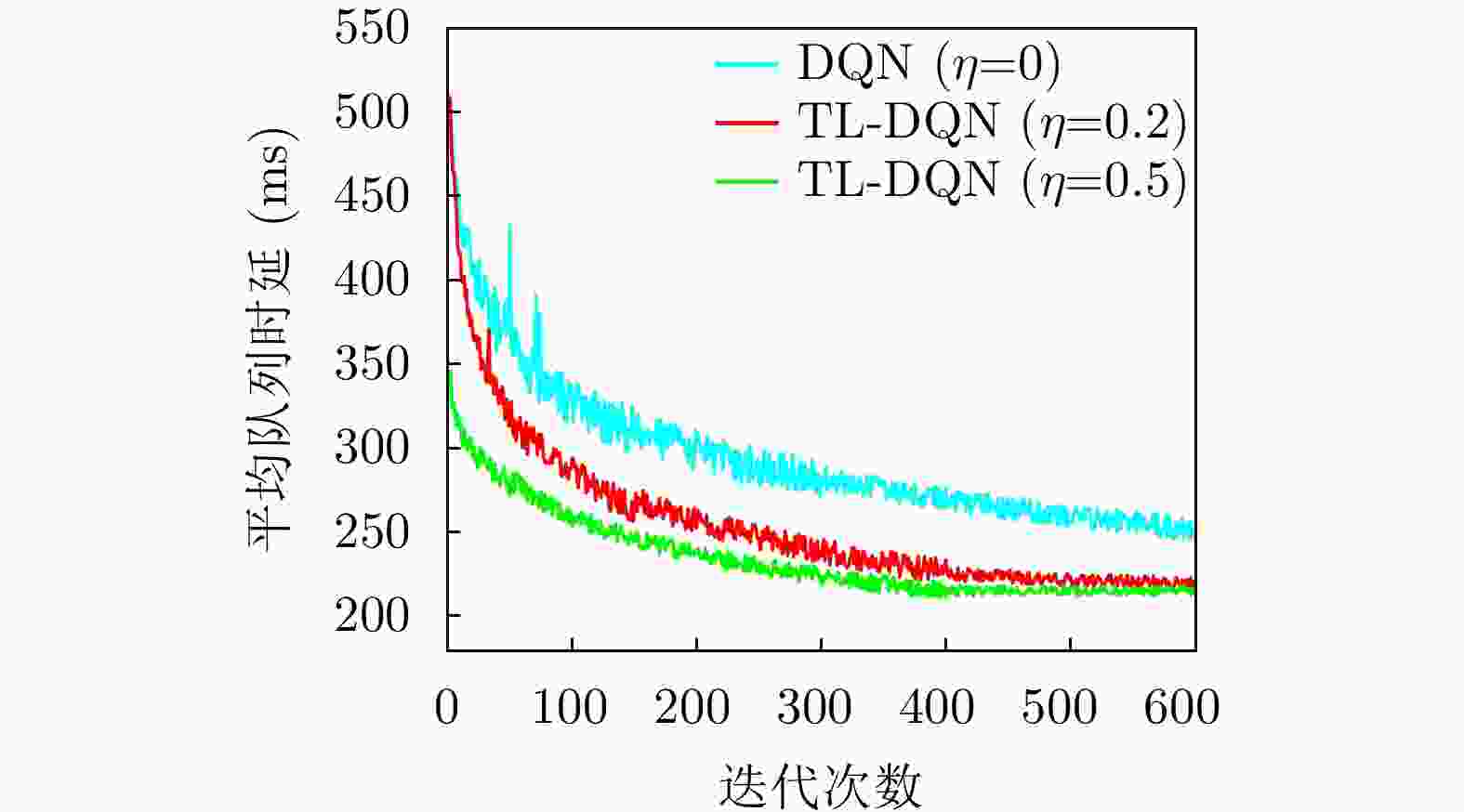
TL-DQN算法参数 取值 TL-DQN算法参数 取值 训练周期Nepochs 600 Adam优化器中$ {\beta _1} $ 0.9 每周期的时隙数|T| 6000 Adam优化器中$ {\beta _2} $ 0.999 经验池容量 5000 随机失活比例 0.2 折扣因子$ \gamma $ 0.9 目标$ {Q^ - } $网络的更新频率G 100 学习率$ \alpha $ 0.0001 激活函数 ReLU 批量训练数目Nt 10 探索概率$ \varepsilon $ (0.2,0.5) 优化器算法 Adam 迁移率因子$ \eta $ {0,0.2,0.5} -
[1] RADTKE J, KEBSCHULL C, and STOLL E. Interactions of the space debris environment with mega constellations—using the example of the OneWeb constellation[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2017, 131: 55–68. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2016.11.021 [2] NI Shuang, LIU Junyu, SHENG Min, et al. Joint optimization of user association and resource allocation in cache-enabled terrestrial-satellite integrating network[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64(8): 182306. doi: 10.1007/s11432-020-3083-5 [3] XIE Renchao, TANG Qinqin, WANG Qiuning, et al. Satellite-terrestrial integrated edge computing networks: Architecture, challenges, and open issues[J]. IEEE Network, 2020, 34(3): 224–231. doi: 10.1109/MNET.011.1900369 [4] PANTHI S, BREYNAERT D, MCLAIN C, et al. Beam hopping-a flexible satellite communication system for mobility[C]. The 35th AIAA International Communications Satellite Systems Conference, Trieste, Italy, 2017: 16–19. [5] WANG Libing, HU Xin, MA Shijun, et al. Dynamic beam hopping of multi-beam satellite based on genetic algorithm[C]. 2020 IEEE Intl Conf on Parallel & Distributed Processing with Applications, Big Data & Cloud Computing, Sustainable Computing & Communications, Social Computing & Networking (ISPA/BDCloud/SocialCom/SustainCom), Exeter, UK, 2020: 1364–1370. [6] LEI Jiang, HAN Zhu, VÁZQUEZ-CASTRO M Á, et al. Secure satellite communication systems design with individual secrecy rate constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2011, 6(3): 661–671. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2011.2148716 [7] HAN Han, ZHENG Xueqiang, HUANG Qinfei, et al. QoS-equilibrium slot allocation for beam hopping in broadband satellite communication systems[J]. Wireless Networks, 2015, 21(8): 2617–2630. doi: 10.1007/S11276-015-0934-Z [8] LIZARRAGA J, ANGELETTI P, ALAGHA N, et al. Flexibility performance in advanced Ka-band multibeam satellites[C]. 2014 IEEE International Vacuum Electronics Conference, Monterey, USA, 2014: 45–46. [9] ALEGRE R, ALAGHA N, and VÁZQUEZ-CASTRO M A. Heuristic algorithms for flexible resource allocation in beam hopping multi-beam satellite systems[C]. The 29th AIAA International Communications Satellite Systems Conference, Nara, Japan, 2011: 6–20. [10] SHI Shengchao, LI Guangxia, LI Zhiqiang, et al. Joint power and bandwidth allocation for beam-hopping user downlinks in smart gateway multibeam satellite systems[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2017, 13(5): 155014771770946. [11] LEI Lei, LAGUNAS E, YUAN Yaxiong, et al. Deep learning for beam hopping in multibeam satellite systems[C]. The 2020 IEEE 91st Vehicular Technology Conference, Antwerp, Belgium, 2020: 1–5. [12] LEI Lei, LAGUNAS E, YUAN Yaxiong, et al. Beam illumination pattern design in satellite networks: Learning and optimization for efficient beam hopping[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 136655–136667. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3011746 [13] International Telecommunication Union-Radio(ITU-R). Rec. ITU-R S. 1528 Satellite antenna radiation patterns for non-geostationary orbit satellite antennas operating in the fixed-satellite service below 30 GHz[S]. 2001. [14] 管令进. 基于深度强化学习的异构云无线接入网资源分配算法研究[D]. [硕士论文], 重庆邮电大学, 2020.GUAN Lingjin. Deep reinforcement learning-based resource allocation algorithm research for heterogeneous cloud access network[D]. [Master dissertation], Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020. [15] 王艺鹏. 多波束卫星通信系统中的动态波束调度技术研究[D]. [硕士论文], 北京邮电大学, 2019.WANG Yipeng. Research on dynamic beam scheduling technology in multi-beam satellite communication system[D]. [Master dissertation], Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2019. [16] JUSTESEN N, BONTRAGER P, TOGELIUS J, et al. Deep learning for video game playing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Games, 2020, 12(1): 1–20. doi: 10.1109/TG.2019.2896986 [17] 陈前斌, 管令进, 李子煜, 等. 基于深度强化学习的异构云无线接入网自适应无线资源分配算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(6): 1468–1477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190511CHEN Qianbin, GUAN Lingjin, LI Ziyu, et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive wireless resource allocation algorithm for heterogeneous cloud wireless access network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(6): 1468–1477. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190511 [18] ŞEN S Y and ÖZKURT N. Convolutional neural network hyperparameter tuning with adam optimizer for ECG classification[C]. 2020 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 2020: 1–6. [19] KOUSHI A M, HU Fei, and KUMAR S. Intelligent spectrum management based on transfer actor-critic learning for rateless transmissions in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(5): 1204–1215. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2744620 [20] 唐伦, 贺小雨, 王晓, 等. 基于迁移演员-评论家学习的服务功能链部署算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(11): 2671–2679. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190542TANG Lun, HE Xiaoyu, WANG Xiao, et al. Deployment algorithm of service function chain based on transfer actor-critic learning[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(11): 2671–2679. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190542 [21] PRATT S R, RAINES R A, FOSSA C E, et al. An operational and performance overview of the IRIDIUM low earth orbit satellite system[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys, 1999, 2(2): 2–10. doi: 10.1109/COMST.1999.5340513 [22] HU Xin, ZHANG Yuchen, LIAO Xianglai, et al. Dynamic beam hopping method based on multi-objective deep reinforcement learning for next generation satellite broadband systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 2020, 66(3): 630–646. doi: 10.1109/TBC.2019.2960940 -





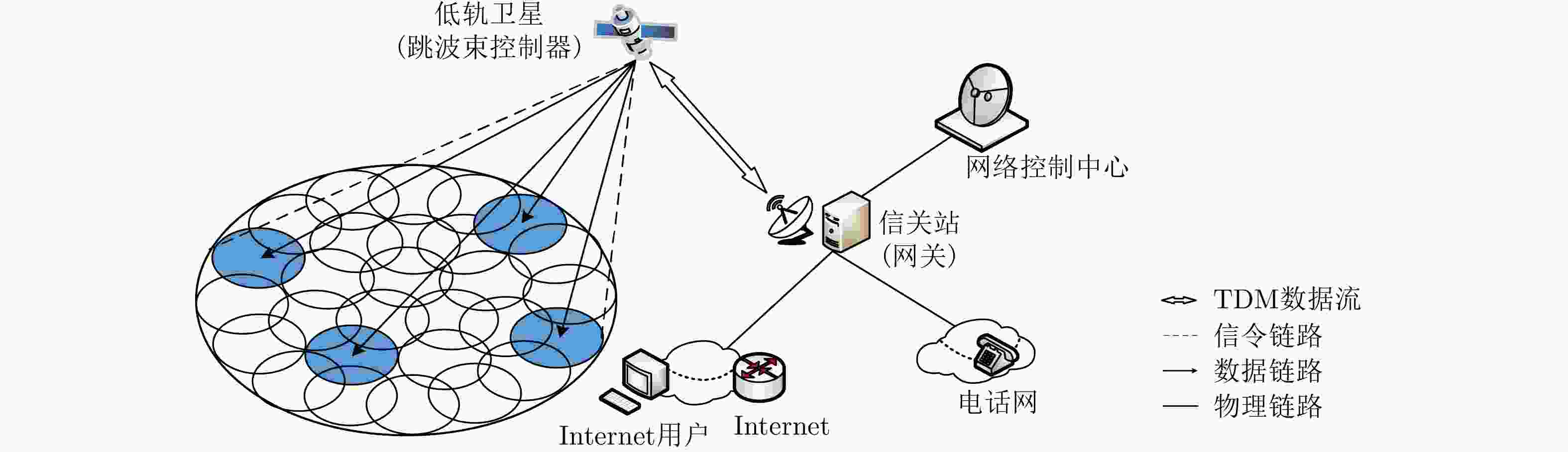
 下载:
下载:
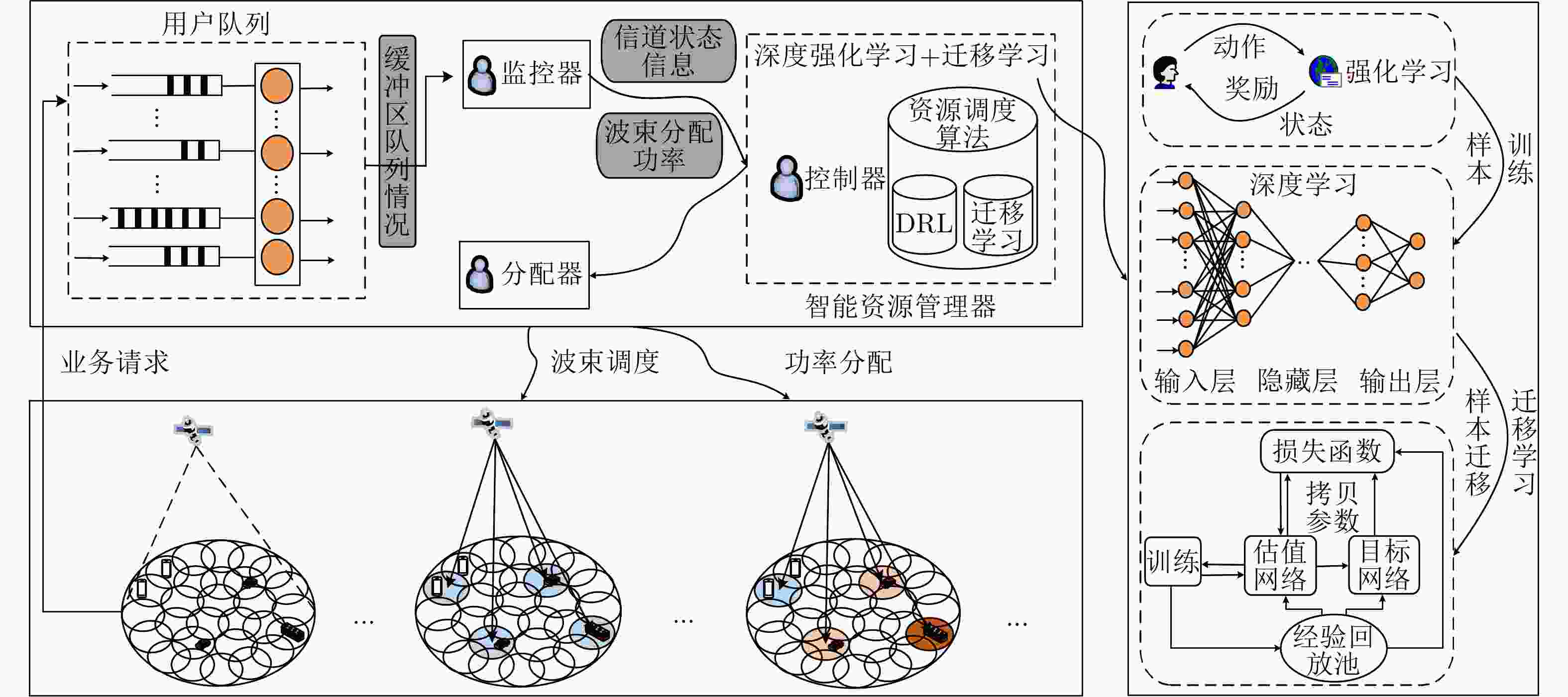
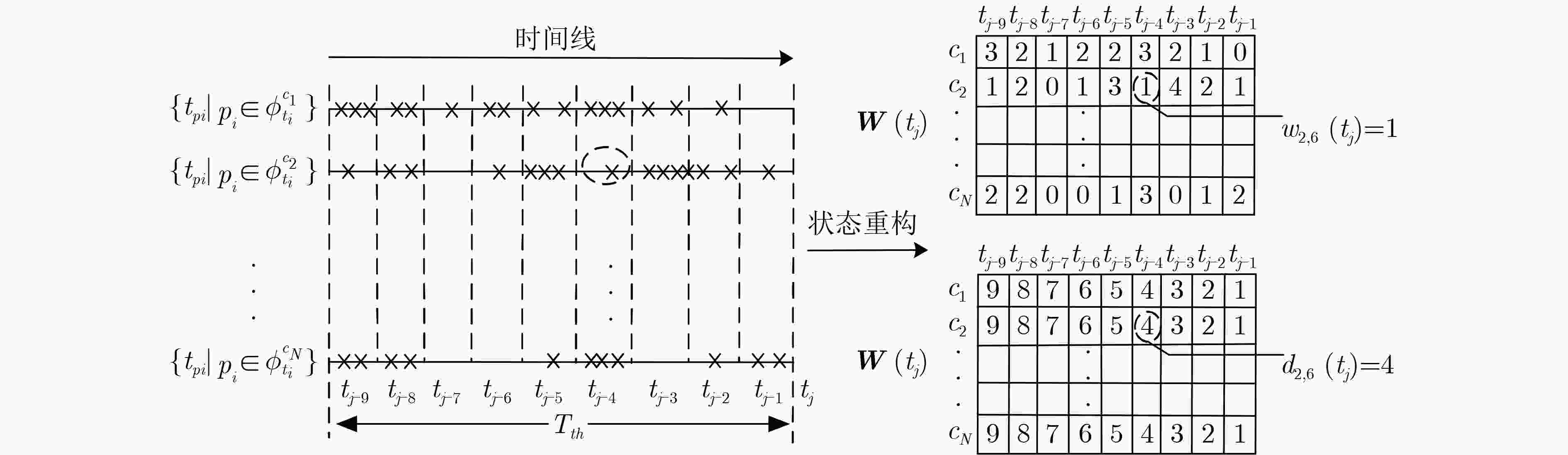
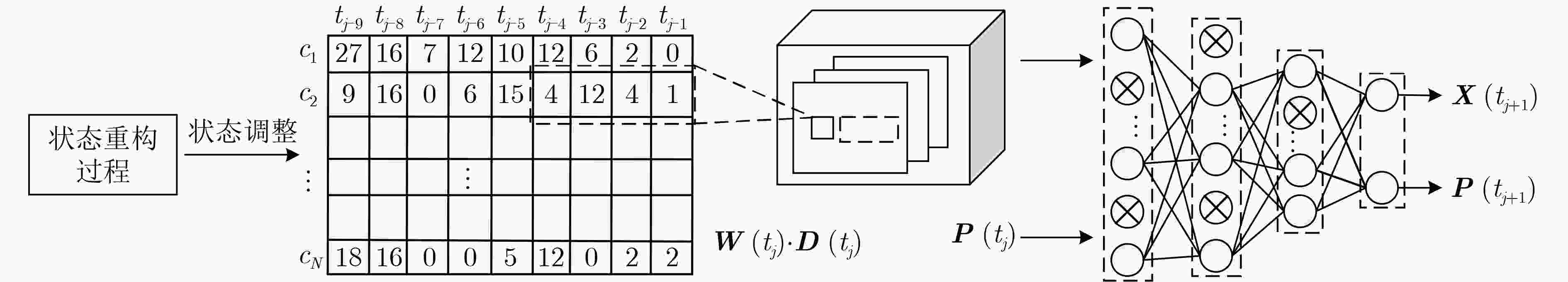


 下载:
下载:
