Optimal Mean Linear Classifier via Weighted Nuclear Norm and L2,1 Norm
-
摘要: 缺陷检测是智能制造系统的一个重要的环节。在采用传统机器学习算法进行缺陷分类的时候,通常会遇 到数据噪声干扰,降低算法对缺陷类别的预测精度。尽管近几年提出了如鲁棒线性判别分析(RLDA)等强大的算法用于解决数据受稀疏噪声干扰的分类问题,但仍存在一些缺点限制其应用性能。该文提出一种新的基于线性判别分析的最优均值鲁棒线性分类模型(OMRLSA)。不同于以往应对噪声数据的分类方法忽略稀疏噪声具有的拉普拉斯分布特性对数据均值的影响,该文所提出的最优均值鲁棒线性分类模型会自动更新数据的最优均值,从而保证数据的统计特性不会受到噪声的干扰。此外,随后的损失函数中首次在鲁棒分类模型中引入了关于正则化和误差测量的联合L2,1范数最小化和秩压缩的加权核范数最小化方法,从而提高算法的鲁棒性。在具有不同比例损坏的标准数据集上的实验结果说明了该文方法的优越性。Abstract: Defect detection is an important part of intelligent manufacturing system. When traditional machine learning algorithms are used for defect classification, data noise interference is usually encountered, which reduces the algorithm’s prediction accuracy for defect classification. Although powerful algorithms such as Robust Linear Discriminant Analysis (RLDA) have been proposed in recent years to solve classification problems with data disturbed by sparse noise, there are still some drawbacks that limit its application performance. In this paper, a new Optimal Mean-Robust Linear Classification Analyis (OMRLSA) based on linear discriminant analysis is proposed. Different from the previous classification methods dealing with noisy data, ignoring the influence of the Laplace distribution characteristic of sparse noise on the data mean, the optimal mean robust linear classification model proposed in this paper will automatically update the optimal mean of the data. This ensures that the statistical characteristics of the data will not be disturbed by noise. Furthermore, a weighted kernel norm minimization method with joint L2,1 norm minimization and rank compression on regularization and error measurement is introduced for the first time in a robust classification model in the subsequent loss function. Thereby the robustness of the algorithm is improved. Experimental results on standard dataset with different ratio corruption illustrate the superiority of the proposed method.
-
表 1 基于交替方向乘子法求解问题式(12)
开始:正则化每个样本$ \left\{ {{{\boldsymbol{x}}_i}} \right\} $的2范数为1; 初始化:$ \mu = 1.2 $,$ 1 \lt {\rho} \lt 2 $,$ {\boldsymbol{D}} = {\boldsymbol{X}} $,$ {\boldsymbol{E}} = 0 $,
${ {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_1} = \dfrac{ {\boldsymbol{X} } }{ {\left\| {\boldsymbol{X} } \right\|_{\rm{F}}^2} },{ {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_2} = { {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_1},{\mu _{\max } } = {10^6}$;(1) 通过求解$\arg {\min _{\boldsymbol{B} } } = \dfrac{ {\eta} }{2}\left\| { {\boldsymbol{Y} } - { {\boldsymbol{B} }^{\text{T} } }{ {\hat {\boldsymbol{D} } } } } \right\|_{\rm{F}}^2$$ + \dfrac{{\gamma}}{2}{\left\| {\boldsymbol{B}} \right\|_{2,1}} $更新B; (2) 通过求解$\arg {\min _{ { {\hat {\boldsymbol{D} } } } } } = \dfrac{ {\eta} }{2}\left\| { {\boldsymbol{Y} } - { { {\boldsymbol{B} }\hat {\boldsymbol{D} } } } } \right\|_{\rm{F} }^2$
$+\dfrac{ {\gamma} }{2}\left\| { { {\hat {\boldsymbol D} } } - \left[ { {\boldsymbol{D} };{ {\bf{1} }^{\text{T} } } } \right] + \dfrac{ { { {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_2} } }{\mu } } \right\|_{\rm{F} }^2$更新$ {{\hat {\boldsymbol D}}} $;(3) 通过求解$\dfrac{1}{\mu }{\left\| {\boldsymbol{D} } \right\|_*} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\left\| { {\boldsymbol{D} } - {\boldsymbol{P} } } \right\|_{\rm{F}}^2 + \left\| { {\boldsymbol{D} } - {\boldsymbol{Q} } } \right\|_{\rm{F} }^2} \right)$更新
b,D,其中
${\boldsymbol{P} } = {\boldsymbol{X} } - {\boldsymbol{E} } - {\boldsymbol{b} }{ {{{\textit{1}}} }^{\text{T} } } + \dfrac{ { { {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_1} } }{\mu }$, $ {\boldsymbol{Q}} = {\left[ {{{\hat {\boldsymbol D}}} + \dfrac{{{{\boldsymbol{\varGamma }}_2}}}{\mu }} \right]_{\left( {1:{\text{d}}x,:} \right)}} $;(4) 通过求解$\dfrac{ {\text{λ } } }{\mu }{\left\| {\boldsymbol{E} } \right\|_{2,1} } + \dfrac{1}{2}\left\| { {\boldsymbol{E} } - { {\hat {\boldsymbol X} } } } \right\|_{\rm{F}}^2$更新E
其中${ {\hat {\boldsymbol X} } } = {\boldsymbol{X} } - {\boldsymbol{E} } - {\boldsymbol{b} }{ {{{\textit{1}}} }^{\text{T} } } + \dfrac{ { { {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_1} } }{\mu }$;(5) 通过${ {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_1} = { {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_1} + \mu \left( { {\boldsymbol{X} } - {\boldsymbol{D} } - {\boldsymbol{E} } - {\boldsymbol{b} }{ {{{\textit{1}}}}^{\text{T} } } } \right)$
${ {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_2} = { {\boldsymbol{\varGamma } }_2} + \mu \left( { { {\hat {\boldsymbol D} } } - \left[ { {\boldsymbol{D} };{ {{{\textit{1}}} }^{\text{T} } } } \right]} \right)$和
$ \mu = \min \left( {{\rho}\mu ,{\mu _{\max }}} \right) $更新${{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} }_{1},{{\boldsymbol{\varGamma}} }_{2}$和$ \mu $;(6) 判断是否收敛; 输出:B*, D*, E* 表 2 单次迭代计算复杂度分析
加法 乘法 复杂度 计算${\boldsymbol{\varSigma } }$ dx dxc O(dxc) 计算B (dx+1)2 (dx+1)2n+(dx+1)2c O((dx+1)2n) 计算${ {\hat {\boldsymbol{D} } } }$ (dx+1)2 (dx+1)2c+(dx+1)2cn O((dx+1)2c) 计算b dxn dxn O(dxn) 计算D dxn dxn2+dx2n O(dxn2) 计算E n dxn O(dxn) 表 3 各个算法在ORL数据集、AR 数据集和YaleB 数据集的识别率
AR数据集 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% K-NN 46.80±0.94 46.38±0.92 44.75±0.73 44.14±0.76 42.72±0.96 42.22±0.39 41.38±0.58 39.72±0.23 40.22±0.59 LDA 95.91±0.27 95.69±0.26 95.85±0.34 95.06±0.33 94.66±0.53 94.02±0.54 92.09±0.88 91.46±0.79 89.22±0.64 SVM 97.15±0.29 96.89±0.30 96.43±0.34 95.42±0.27 95.45±0.65 95.60±0.53 94.43±0.47 94.03±0.42 92.80±0.41 SRC 79.83±0.59 79.18±0.63 78.48±0.50 78.02±0.43 76.22±0.44 75.54±1.04 75.48±0.96 73.78±0.71 73.80±1.23 RPCA+LDA 96.38±0.36 95.34±0.51 94.02±0.10 91.66±0.77 90.60±1.02 88.69±0.73 86.03±0.46 84.42±1.38 81.88±0.64 RLDA 96.17±0.42 95.95±0.57 95.91±0.53 95.71±0.27 95.68±0.67 95.31±0.41 94.77±0.21 94.68±0.49 93.17±0.44 BDLRR 97.45±0.43 96.22±0.33 96.18±0.42 95.03±0.78 92.81±2.36 90.64±1.77 89.91±1.89 83.24±0.68 80.30±0.27 OMRLDA 97.83±0.29 97.63±0.30 97.62±0.32 97.03±0.14 97.03±0.30 96.35±0.31 95.58±0.43 95.29±0.42 93.45±0.57 ORL数据集 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% K-NN 86.60±1.75 85.30±2.36 83.60±2.95 82.10±2.82 80.80±2.56 79.00±2.67 78.60±2.63 77.00±2.74 75.00±2.87 LDA 92.40±0.82 90.60±0.96 90.10±1.08 88.30±1.64 87.60±1.43 85.80±2.20 85.20±1.82 83.90±2.04 83.30±2.28 SVM 93.80±1.08 92.90±1.56 92.60±0.66 92.30±1.11 92.10±0.84 92.10±0.75 91.70±0.98 91.17±0.42 90.80±0.41 SRC 93.60±1.64 93.00±1.46 91.90±1.78 91.70±1.10 90.90±1.56 90.10±2.82 89.90±2.30 88.90±1.39 88.80±1.40 RPCA+LDA 92.90±1.19 91.30±1.35 91.40±1.02 89.30±1.48 88.60±1.75 86.60±1.56 86.00±1.90 84.70±2.44 84.50±2.26 RLDA 94.10±1.43 93.00±1.27 92.50±1.58 91.80±1.96 89.60±1.52 88.20±1.30 88.60±1.39 87.10±1.92 87.00±2.15 BDLRR 94.20±2.11 92.90±1.64 93.50±1.73 92.60±1.85 92.10±0.89 90.20±1.04 90.30±1.10 90.60±1.19 89.70±1.04 OMRLDA 94.30±1.64 94.30±1.35 94.00±1.77 92.90±1.75 92.80±1.14 92.50±1.20 92.30±0.91 92.30±0.97 91.60±0.74 YaleB数据集 0% 5% 10% 15% 20% 25% 30% 35% 40% K-NN 77.90±0.85 77.34±0.52 76.67±0.97 75.58±0.64 74.69±0.16 74.29±0.76 72.17±0.95 70.63±0.63 70.01±0.53 LDA 88.55±1.12 88.54±0.81 87.70±1.77 87.60±1.60 87.41±1.40 87.28±1.89 87.14±0.92 86.88±2.00 85.59±1.18 SVM 95.83±0.69 94.88±0.75 94.42±0.67 94.32±0.70 93.66±0.73 93.09±0.87 92.20±1.13 92.20±0.96 90.69±1.27 SRC 94.52±0.63 93.47±1.10 93.24±0.79 92.89±0.51 92.53±0.93 92.25±0.89 91.97±0.82 91.52±0.78 91.40±1.01 RPCA+LDA 88.85±1.12 88.52±1.03 88.37±1.59 88.74±1.61 87.79±1.47 87.66±1.78 87.18±0.90 86.95±1.96 85.55±1.28 RLDA 97.07±0.42 96.31±0.65 95.66±0.97 94.98±0.73 93.90±1.08 92.76±0.63 91.75±1.08 91.25±1.24 89.65±1.05 BDLRR 96.92±0.65 96.60±0.68 96.14±0.75 95.73±0.58 95.31±0.56 94.68±0.78 94.12±0.74 93.71±0.54 92.48±0.71 OMRLDA 98.31±0.50 97.37±0.69 96.57±0.90 96.12±0.58 95.36±0.91 94.52±0.68 94.33±0.91 94.11±0.82 93.52±0.88 -
[1] 孙洪宇, 彭丽莎, 屈凯峰, 等. 机器学习在复合绝缘子缺陷超声检测中的应用与展望[J]. 无损检测, 2021, 43(5): 58–63. doi: 10.11973/wsjc202105013SUN Hongyu, PENG Lisha, QU Kaifeng, et al. Application and prospect of machine learning in ultrasonic testing of composite insulator defects[J]. Nondestructive Testing, 2021, 43(5): 58–63. doi: 10.11973/wsjc202105013 [2] 唐伦, 廖皓, 曹睿, 等. 基于深度动态贝叶斯网络的服务功能链故障诊断算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(12): 3588–3596. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200029TANG Lun, LIAO Hao, CAO Rui, et al. Fault diagnosis algorithm of service function chain based on deep dynamic Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(12): 3588–3596. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200029 [3] 王剑, 匡洪宇, 李瑞林, 等. 基于CNN-GAP可解释性模型的软件源码漏洞检测方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 待发表. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210412.WANG Jian, KUANG Hongyu, LI Ruilin, et al. . Software source code vulnerability detection based on CNN-GAP interpretability model[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, To be published. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210412. [4] 刘华祠. 基于传统机器学习与深度学习的图像分类算法对比分析[J]. 电脑与信息技术, 2019, 27(5): 12–15. doi: 10.19414/j.cnki.1005-1228.2019.05.004LIU Huaci. Comparative analysis of image classification algorithms based on traditional machine learning and deep learning[J]. Computer and Information Technology, 2019, 27(5): 12–15. doi: 10.19414/j.cnki.1005-1228.2019.05.004 [5] 刘浩, 陈再良, 张良. 基于机器学习的刀具表面缺陷检测及分类方法[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2021, 29(6): 64–68. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2021.06.014LIU Hao, CHEN Zailiang, and ZHANG Liang. Tool surface defect detection and classification based on machine learning[J]. Computer Measurement &Control, 2021, 29(6): 64–68. doi: 10.16526/j.cnki.11-4762/tp.2021.06.014 [6] 李宇庭, 甘芳吉, 万正军, 等. 基于SVM及电流牵扯效应的金属缺陷分类识别方法[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2015, 47(6): 172–178. doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.2015.06.024LI Yuting, GAN Fangji, WAN Zhengjun, et al. Method for defect classification based on SVM and current drag effect[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition) , 2015, 47(6): 172–178. doi: 10.15961/j.jsuese.2015.06.024 [7] 舒文娉, 刘全香. 基于支持向量机的印品缺陷分类方法[J]. 包装工程, 2014, 35(23): 138–142. doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2014.23.028SHU Wenping and LIU Quanxiang. Classification method of printing defects based on support vector machine[J]. Packaging Engineering, 2014, 35(23): 138–142. doi: 10.19554/j.cnki.1001-3563.2014.23.028 [8] HAGI H, IWAHORI Y, FUKUI S, et al. Defect classification of electronic circuit board using SVM based on random sampling[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2014, 35: 1210–1218. doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2014.08.218 [9] WRIGHT J, YANG A Y, GANESH A, et al. Robust face recognition via sparse representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 31(2): 210–227. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2008.79 [10] CHEN Yudong, CARAMANIS C, and MANNOR S. Robust sparse regression under adversarial corruption[C]. The 30th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, USA, 2013: III-774–III-782. [11] NIE Feiping, HUANG Heng, CAI Xiao, et al. Efficient and robust feature selection via joint ℓ2, 1-norms minimization[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2010: 1813–1821. [12] SHI Xiaoshuang, YANG Yujiu, GUO Zhenhua, et al. Face recognition by sparse discriminant analysis via joint L2, 1-norm minimization[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(7): 2447–2453. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.01.007 [13] VAPNIK V. Statistical Learning Theory[M]. New York, USA: Wiley, 1998. [14] MARONNA R A, MARTIN R D, and YOHAI V J. Robust Statistics: Theory and Methods[M]. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2006. [15] 李松涛, 李维刚, 甘平, 等. 基于Sinkhorn距离特征缩放的多约束非负矩阵分解算法[J/OL]. 电子与信息学报, 待发表. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210946LI Songtao, LI Weigang, GAN Ping, et al. Multi-constrained non-negative matrix factorization algorithm based on sinkhorn distance feature scaling[J/OL]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, To be published. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210946. [16] 李相平, 王明泽, 但波, 等. 基于鲁棒主成分分析的多域联合杂波抑制算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1303–1310. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210676LI Xiangping, WANG Mingze, DAN Bo, et al. The multi-domain union clutter suppression algorithm based on robust principal component analysis[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1303–1310. doi: 10.11999/JEIT210676 [17] 唐红梅, 白梦月, 韩力英, 等. 基于低秩背景约束与多线索传播的图像显著性检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1432–1440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200193TANG Hongmei, BAI Mengyue, HAN Liying, et al. Image saliency detection based on background constraint of low rank and multi-cue propagation[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(5): 1432–1440. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200193 [18] CANDÈS E J, LI Xiaodong, MA Yi, et al. Robust principal component analysis?[J] Journal of the ACM, 2009, 58(3): 11. [19] DING C, ZHOU Ding, HE Xiaofeng, et al. R1-PCA: Rotational invariant L1-norm principal component analysis for robust subspace factorization[C].The 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, New York, USA, 2006: 281–288. [20] YI Shuangyan, HE Zhenyu, and YANG Weiguo. Robust principal component analysis via joint ℓ2, 1-norms minimization[C]. 2017 International Conference on Security, Pattern Analysis, and Cybernetics (SPAC), Shenzhen, China, 2017: 13–18. [21] NIE Feiping, HUANG Heng, and DING Chris HQ. Low-rank matrix recovery via efficient schatten p-norm minimization[C]. The Twenty-Sixth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Toronto, Canada, 2012: 655–661. [22] NIE Feiping, WANG Hua, CAI Xiao, et al. Robust matrix completion via joint schatten p-norm and ℓp-norm minimization[C]. 2012 IEEE 12th International Conference on Data Mining, Brussels, Belgium, 2012: 566–574. [23] HE Ran, HU Baogang, ZHENG Weishi, et al. Robust principal component analysis based on maximum correntropy criterion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2011, 20(6): 1485–1494. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2103949 [24] NIE Feiping, YUAN Jianjun, and HUANG Heng. Optimal mean robust principal component analysis[C]. The 31st International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Beijing, China, 2014: II-1062–II-1070. [25] SHI Xiaoshuang, NIE Feiping, LAI Zhihui, et al. Robust principal component analysis via optimal mean by joint ℓ2, 1 and schatten p -norms minimization[J]. Neurocomputing, 2018, 283: 205–213. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.12.034 [26] LIANG Yiniang, REN Zhigang, WU Zongze, et al. Scalable spectral ensemble clustering via building representative co-association matrix[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 390: 158–167. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.01.055 [27] LIANG Zexiao, GUO Shaozhi, LIU Dakang, et al. Spectral clustering based on high-frequency texture components for face datasets[J]. IET Image Processing, 2021, 15(10): 2240–2246. doi: 10.1049/IPR2.12191 [28] WU Zongze, LIU Sihui, DING C, et al. Learning graph similarity with large spectral gap[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2021, 51(3): 1590–1600. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2899398 [29] WU Zongze, SU Chuncheng, YIN Ming, et al. Subspace clustering via stacked independent subspace analysis networks with sparse prior information[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2021, 146: 165–171. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2021.03.026 [30] GOLDBERG A B, ZHU Xiaojin, RECHT Ben, et al. Transduction with matrix completion: Three birds with one stone[C]. The 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2010: 757–765. [31] CABRAL R, DE LA TORRE F, COSTEIRA J P, et al. Matrix completion for weakly supervised multi-label image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(1): 121–135. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2343234 [32] HUANG Dong, CABRAL R, and DE LA TORRE F. Robust regression[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 363–375. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2448091 [33] ZENG Deyu, WU Zongze, DING C, et al. Labeled-robust regression: Simultaneous data recovery and classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, To be published. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3026101 [34] WRIGHT J, PENG Yigang, MA Yi, et al. Robust principal component analysis: Exact recovery of corrupted low-rank matrices by convex optimization[C]. The 22nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Red Hook, USA, 2009: 2080–2088. [35] LIN Zhouchen, CHEN Minming, WU Leqin, et al. The augmented Lagrange multiplier method for exact recovery of corrupted low rank matrices[R]. UILU-ENG-09–2215, 2009. [36] YIN Ming, ZENG Deyu, GAO Junbin, et al. Robust multinomial logistic regression based on RPCA[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2018, 12(6): 1144–1154. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2018.2872460 [37] GU Shuhang, XIE Qi, MENG Deyu, et al. Weighted nuclear norm minimization and its applications to low level vision[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2017, 121(2): 183–208. doi: 10.1007/s11263-016-0930-5 [38] CAI Jianfeng, CANDÈS E J, and SHEN Zuowei. A singular value thresholding algorithm for matrix completion[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 2008, 20(4): 1956–1982. doi: 10.1137/080738970 [39] ZHANG Zheng, XU Yong, SHAO Ling, et al. Discriminative block-diagonal representation learning for image recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 29(7): 3111–3125. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2712801 -
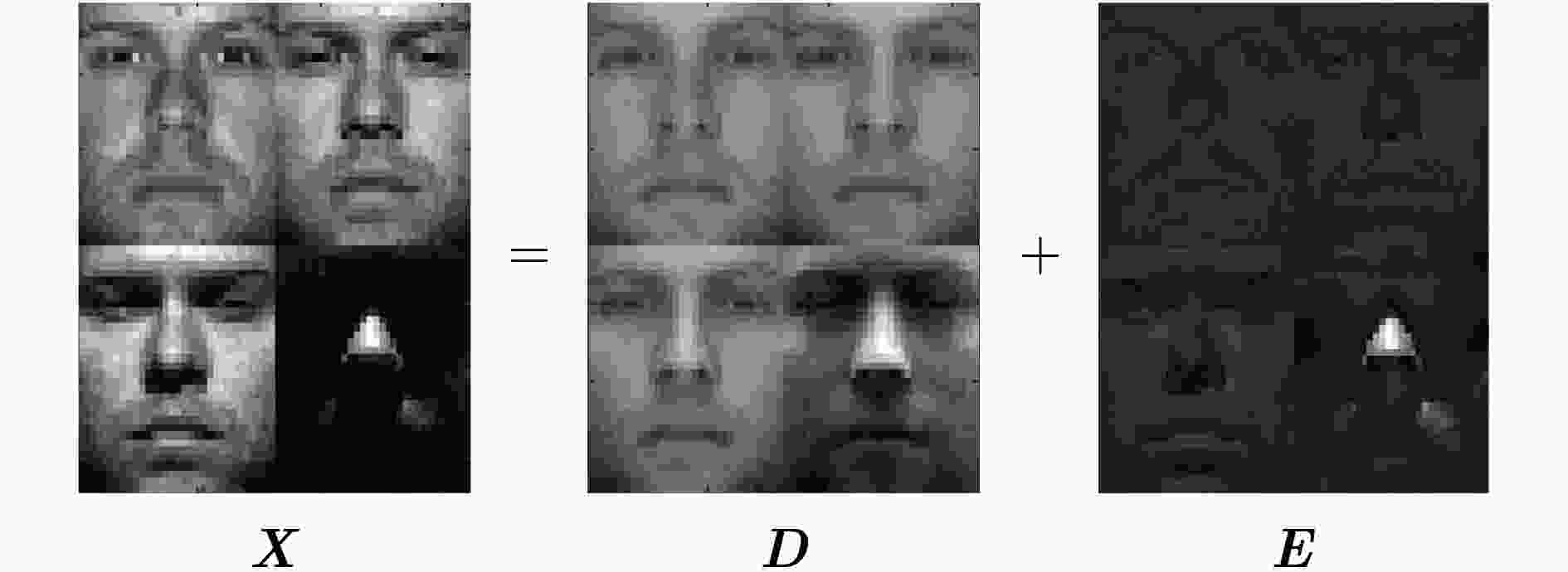






 下载:
下载:
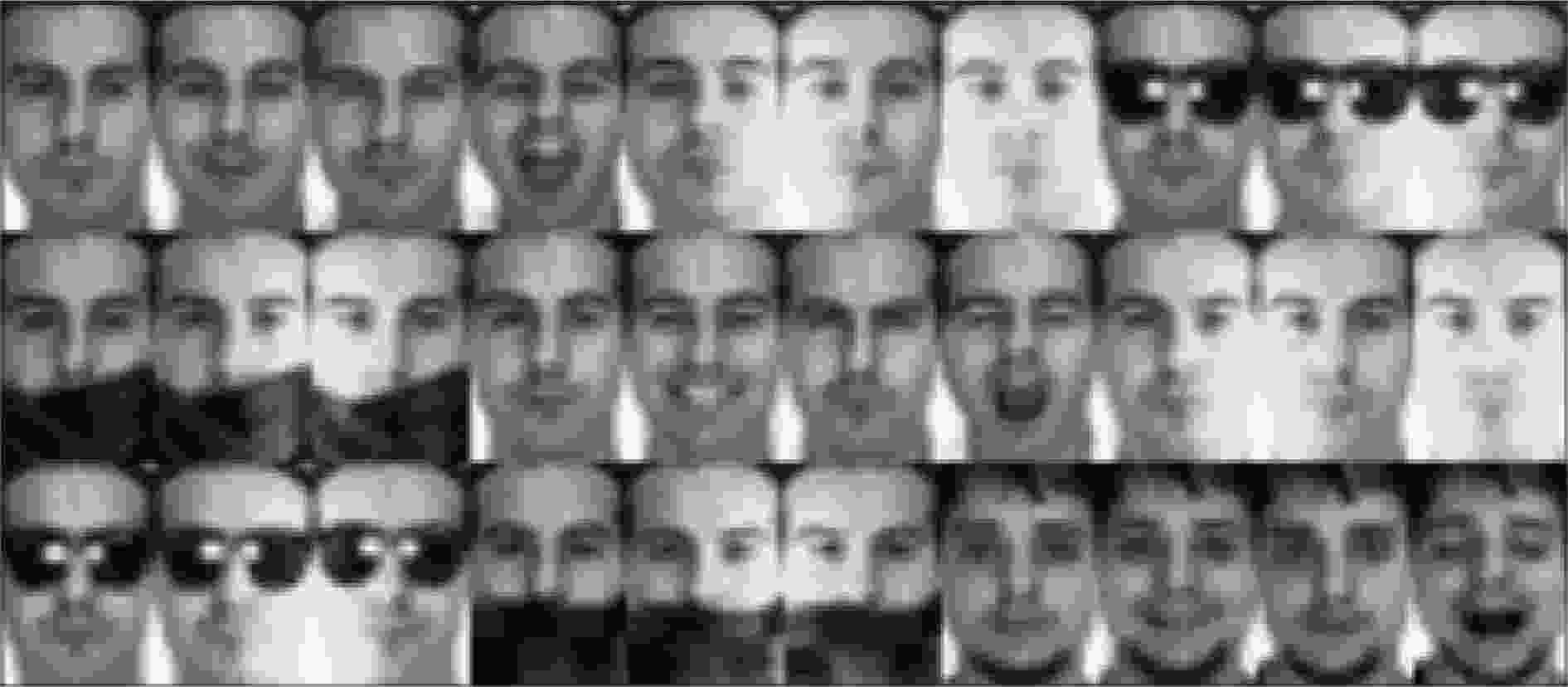
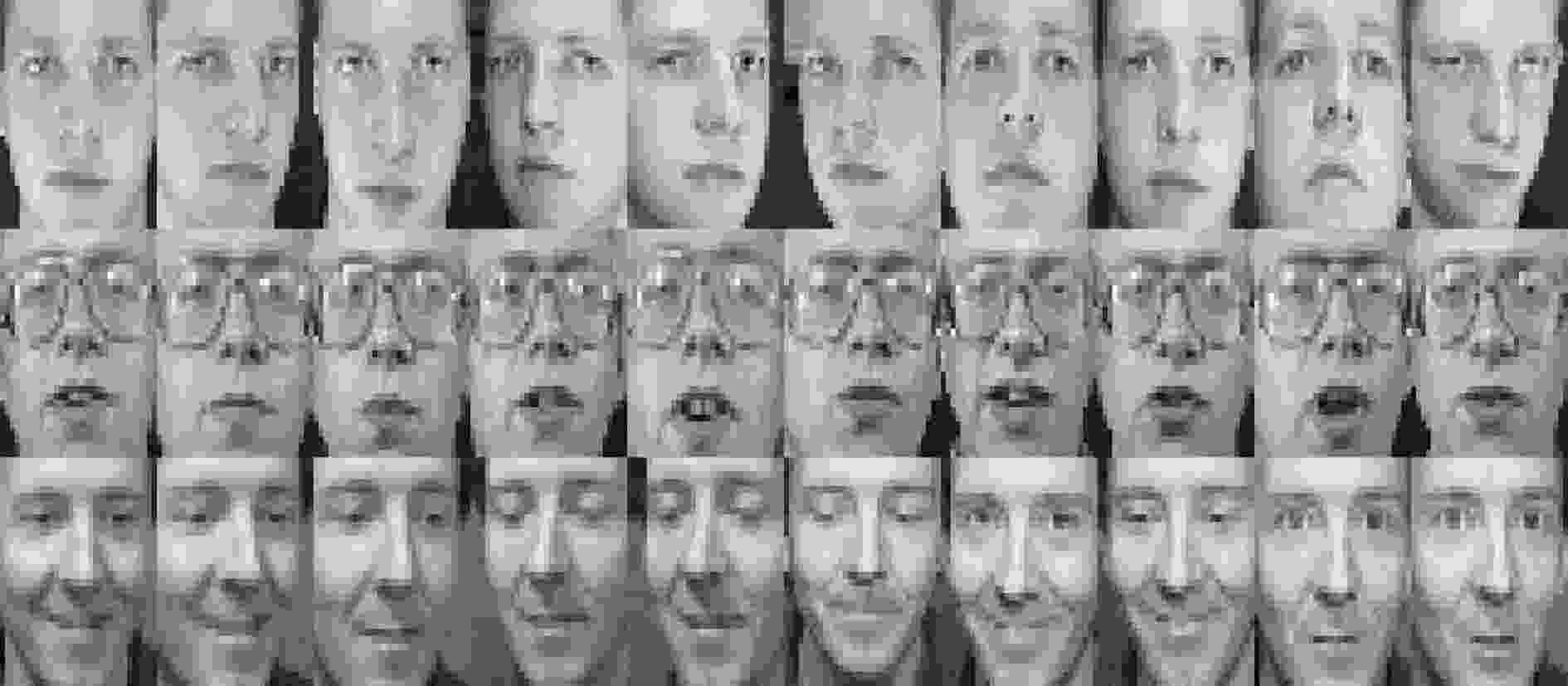






 下载:
下载:
