Optimal Manipulation Mixing Optimization Control Method for Injection Speed During Injection Molding Process
-
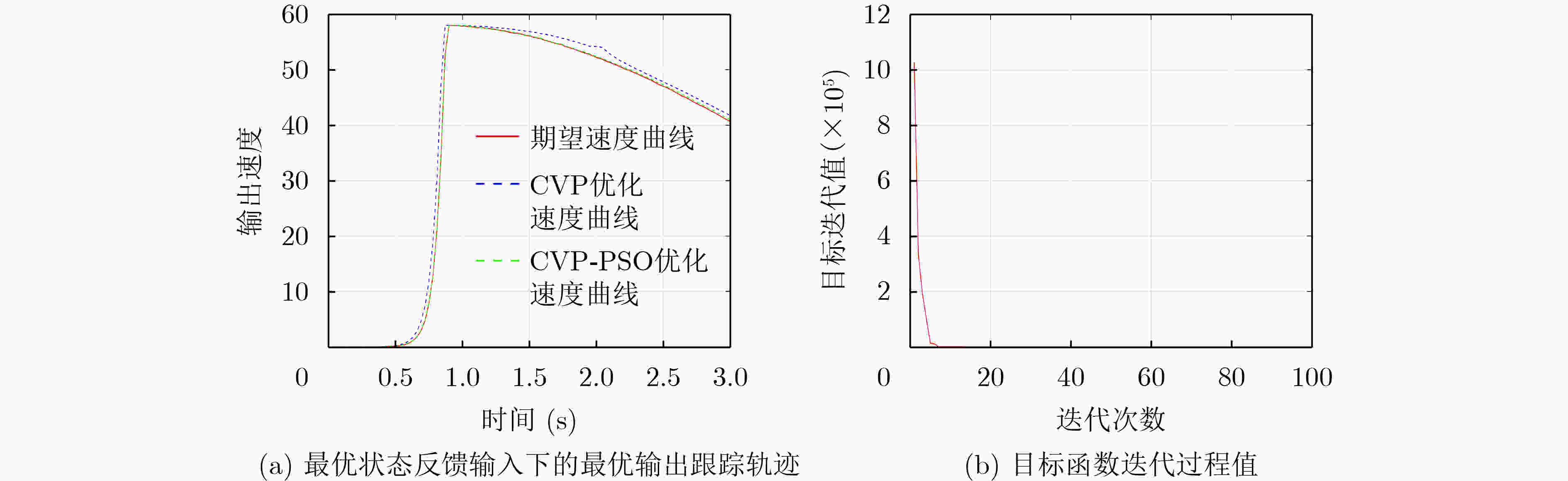
摘要: 在注塑工艺过程中,注射速度控制是其重要环节之一,实现注射速度的快速可靠优化控制对于注塑产品的高效生产具有重要意义。该文针对一类典型的注塑装备中的伺服电机驱动恒泵液压系统,研究了注塑机工作过程中的注射速度最优跟踪控制问题,提出一种高效的基于控制参数化与粒子群优化相结合的混合智能优化控制方法,分别设计实现了开环最优控制器和状态反馈最优控制器,将控制器设计问题转化为一序列最优参数选择问题,实现了在给定时间内对所期望的注射速度跟踪控制的高效求解。最后通过实验仿真结果验证了所提出的混合优化控制算法对于求解注塑工艺过程中注射速度的动态优化问题的可行性和有效性。Abstract: In the process of injection molding, the injection speed control is one of the important aspects, and it is important to achieve fast and reliable optimal control of the injection speed for the efficient production of injection molded products. In this paper, an efficient hybrid intelligent optimal control method based on the combination of control parameterization and particle swarm optimization is proposed, and an open-loop optimal controller and a state feedback optimal controller are designed and implemented, respectively. The controller design problem is transformed into a sequence of optimal parameter selection problems to achieve an efficient solution for the desired injection speed tracking control in a given time. Finally, the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed hybrid optimal control algorithm for solving the dynamic optimization problem of the injection speed in the injection molding process are verified by experimental simulation results.
-
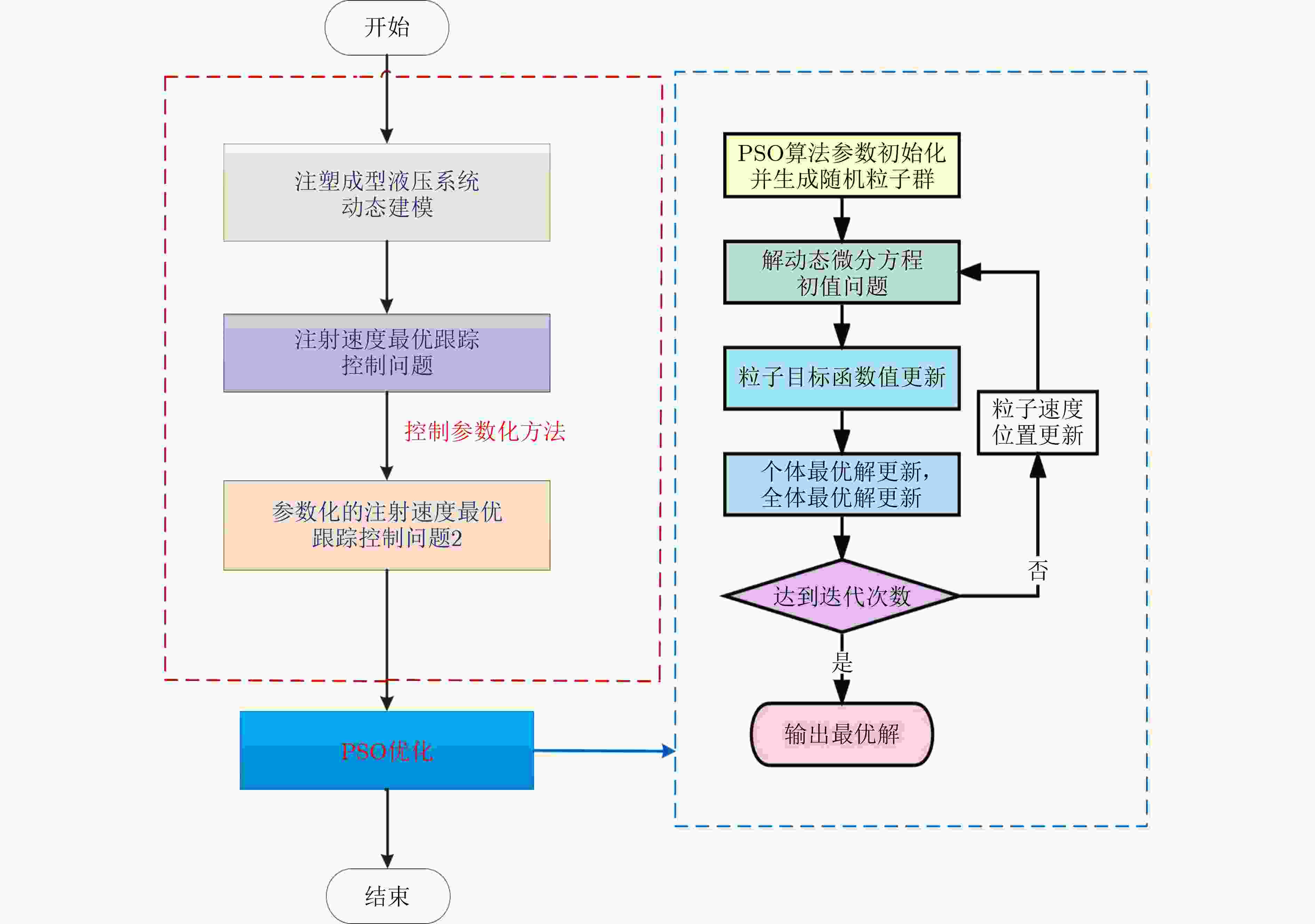
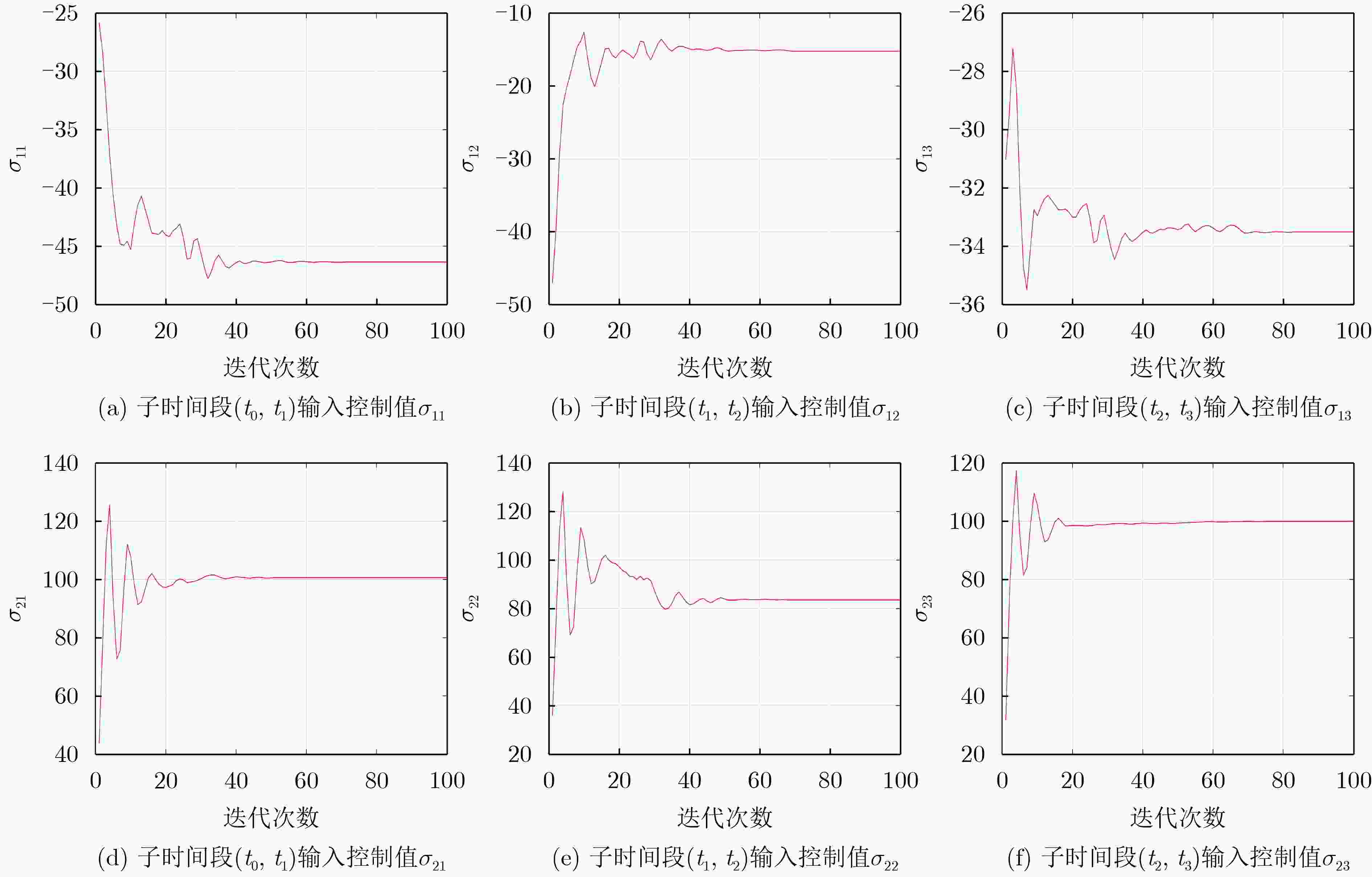
表 1 CVP-PSO混合优化控制策略算法过程
步骤1:将控制变量时间域平均分为N段,并将控制器$ u\left(t\right) $参数
化$\boldsymbol{\sigma }=\left[{\sigma }_{1},{\sigma }_{2},\cdots ,{\sigma }_{n}\right]\in {R}^{n}$;将原始注塑速度最优跟踪
问题转化为N个参数优化问题;步骤2:PSO算法参数初始化:设置生成粒子数${\boldsymbol{\sigma } }^{i}$,粒子迭代
次数${\rm{GEN}}$,粒子维度${\rm{Dim}}$,粒子影响系数$ {c}_{1} $,$ {c}_{2} $,以
及惯性权重$ w $,随机生成粒子初始位置,以及粒子初
始速度;步骤3:求解参数化动态微分方程组式(16b)和式(16c); 步骤4:粒子目标函数值更新,根据步骤3求得的动态微分方程,
计算目标函数值式(16a),并衡量粒子当前位置适应度值;步骤5:判断是否达到迭代次数,如果达到迭代次数,则输出最
优解,包括个体最优解pbest和全体最优解gbest,如果
未达到迭代次数,使$ k=k+1 $,继续进行步骤6;步骤6:粒子速度和位置更新:通过对自身最优解信息的获取和
与群体交流共享获取的全体最优解信息,更新粒子速度
和位置状态,返回步骤3。表 2 注塑系统动态模型关键参数设定值
参数名称 参数符号 参数设定值 电机时间常数 $ {\tau }_{s} $ 0.0263 电机扭矩增益 $ {k}_{s} $ 0.012 螺钉质量 $ M $ 8.663 液缸横截面积 $ {A}_{1} $ 3342.2 桶横截面积 $ {A}_{2} $ 201.06 聚合物熔体的幂指数倒数 $ s $ 1.112 液压流体体积模量 $ {\beta }_{1} $ 1120 注油侧的油量 $ {\alpha }_{10} $ 17045.3 泵流量 $ {Q}_{1} $ 7920 喷嘴体积弹性模量 $ {\beta }_{2} $ 1120 桶内聚合物的体积 $ {\alpha }_{20} $ 11678.38 聚合物熔体流动速率 $ {Q}_{2} $ 16.67 -
[1] ZHENG Rong, TANNER R I, and FAN Xijun. Injection Molding: Integration of Theory and Modeling Methods[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2011. [2] ZHOU Huamin. Computer Modeling for Injection Molding: Simulation, Optimization, and Control[M]. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2013: 47. [3] FERNANDES C, PONTES A J, VIANA J C, et al. Modeling and optimization of the injection-molding process: A review[J]. Advances in Polymer Technology, 2018, 37(2): 429–449. doi: 10.1002/adv.21683 [4] GAO Huang, ZHANG Yun, ZHOU Xundao, et al. Intelligent methods for the process parameter determination of plastic injection molding[J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 13(1): 85–95. doi: 10.1007/s11465-018-0491-0 [5] FROEHLICH C, KEMMETMÜLLER W, and KUGI A. Control-oriented modeling of servo-pump driven injection molding machines in the filling and packing phase[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling of Dynamical Systems, 2018, 24(5): 451–474. doi: 10.1080/13873954.2018.1481870 [6] GUO Fei, ZHOU Xiaowei, LIU Jiahuan, et al. A reinforcement learning decision model for online process parameters optimization from offline data in injection molding[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 85: 105828. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105828 [7] KHOSRAVANI M R and NASIRI S. Injection molding manufacturing process: Review of case-based reasoning applications[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2020, 31(4): 847–864. doi: 10.1007/s10845-019-01481-0 [8] CHO Y J, CHO H S, and LEE C O. Optimal open-loop control of the mould filling process for injection moulding machines[J]. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 1983, 4(1): 1–12. doi: 10.1002/oca.4660040102 [9] HUANG Sunan, TAN K K, and LEE T H. Predictive control of ram velocity in injection molding[J]. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Engineering, 1999, 38(2): 285–303. doi: 10.1080/03602559909351578 [10] YAO Ke and GAO Furong. Optimal start-up control of injection molding barrel temperature[J]. Polymer Engineering & Science, 2007, 47(3): 254–261. doi: 10.1002/pen.20701 [11] REITER M, STEMMLER S, HOPMANN C, et al. Model predictive control of cavity pressure in an injection moulding process[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2014, 47(3): 4358–4363. doi: 10.3182/20140824-6-ZA-1003.02505 [12] HOPMANN C, RESSMANN A, REITER M, et al. A self-optimising injection moulding process with model-based control system parameterisation[J]. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2016, 29(11): 1190–1199. doi: 10.1080/0951192X.2015.1066035 [13] HAZWAN M H M, SHAYFULL Z, NAWI M A M, et al. Warpage optimization on battery cover using genetic algorithm (GA)[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2019, 2129(1): 020195. doi: 10.1063/1.5118203 [14] STEMMLER S, VUKOVIC M, AY M, et al. Quality control in injection molding based on norm-optimal iterative learning cavity pressure control[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(2): 10380–10387. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.2777 [15] XU Jiahong, REN Zhigang, XIE Shengli, et al. Deep learning-based optimal tracking control of flow front position in an injection molding machine[J]. Optimal Control Applications and Methods, To be published. doi: 10.1002/oca.2787 [16] LI Qiuli, BU Leping, LUO Hui, et al. Optimization of injection molding of display panel based on PSO-BP neural network[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series, 2021, 1986: 012076. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1986/1/012076 [17] LIN Qun, LOXTON R, and TEO K L. The control parameterization method for nonlinear optimal control: A survey[J]. Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization, 2014, 10(1): 275–309. doi: 10.3934/jimo.2014.10.275 [18] REN Zhigang, CHEN Tehuan, and WU Zongze. Optimal matching control of a low energy charged particle beam in particle accelerators[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(2): 460–470. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2018.7511270 [19] 刘平, 李国栋, 杨金凤, 等. 集装箱装卸摆动最优控制快速数值求解算法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2019, 36(8): 1275–1282. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80352LIU Ping, LI Guodong, YANG Jinfeng, et al. Fast optimal control numerical approach for the swing control of container load[J]. Control Theory &Applications, 2019, 36(8): 1275–1282. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.80352 [20] CHO Y J, CHO H, and LEE C. Optimal Control of the Molding Process in the Injection Molding Machine[M]. Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, 1983. [21] CHEN Tehuan, LOU Junqiang, YANG Yiling, et al. Vibration suppression of a high-speed macro–micro integrated system using computational optimal control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(9): 7841–7850. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2941136 [22] 梁海燕, 任志刚, 许超, 等. 翼伞系统最优归航轨迹设计的敏感度分析方法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(8): 1003–1011. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.40855LIANG Haiyan, REN Zhigang, XU Chao, et al. Optimal homing trajectory design for parafoil systems using sensitivity analysis approach[J]. Control Theory &Applications, 2015, 32(8): 1003–1011. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2015.40855 [23] LOXTON R C, TEO K L, REHBOCK V, et al. Optimal control problems with a continuous inequality constraint on the state and the control[J]. Automatica, 2009, 45(10): 2250–2257. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.05.029 [24] LOXTON R, LIN Qun, REHBOCK V, et al. Control parameterization for optimal control problems with continuous inequality constraints: New convergence results[J]. Numerical Algebra, Control and Optimization, 2012, 2(3): 571–599. doi: 10.3934/naco.2012.2.571 [25] SENGUPTA S, BASAK S, and PETERS II R A. Particle swarm optimization: A survey of historical and recent developments with hybridization perspectives[J]. Machine Learning & Knowledge Extraction, 2019, 1(1): 157–191. doi: 10.3390/make1010010 [26] DORIGO M, DE OCA M A M, and ENGELBRECHT A. Particle swarm optimization[J]. Scholarpedia, 2008, 3(11): 1486. doi: 10.4249/scholarpedia.1486 -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
