Research on Underwater Source Ranging Algorithm Based on Joint Distribution Adaptation
-
摘要: 水下声源被动测距基于接收数据中声源辐射的声压信号,通过特定方法在空域中搜索声源位置参数,是一个参数估计问题。对于参数估计问题,机器学习方法通常将其转化为分类问题,相比于传统匹配场处理(MFP)具有更准确的估计能力,并且无需先验的声场环境信息。但当训练数据和测试数据的概率密度函数服从不同的分布或者训练数据严重不足时,传统机器学习方法下的分类器预测效果通常较差。因此,该文提出基于联合分布适配(JDA)的水下声源测距算法,该算法使用JDA寻找恰当的变换矩阵进行数据映射,从而减小不同数据域间分布差异,实现源域到目标域的迁移。对经过JDA后数据进行实验的结果表明,JDA可以有效降低在不同时间和不同方位的水声场中获取航迹数据之间的差异,使得基于源域训练的分类器对目标域预测结果的均方根误差(RMSE)和平均绝对误差(MAE)降低了超过30%,从而实现对声源更准确的距离估计。Abstract: Underwater source passive ranging is based on the pressure radiated by the source in the received data. It is a parameter estimation problem to search for source position parameters in the airspace through the method. Parameter estimation problems are usually converted into classification problems by machine learning methods, which have more accurate estimation capabilities than traditional Matched Field Processing (MFP) and with needless prior sound field information. However, when the probability density of training data and test data follow different distributions or the training data is insufficient, the effect of the classifier under traditional machine learning methods is usually poor. Therefore, an underwater target source ranging algorithm based on Joint Distribution Adaptation (JDA) is proposed to find an appropriate transformation matrix for data mapping, thereby reducing the distribution differences and realizing the migration between source and target. The experimental results indicate that JDA can effectively reduce the differences between the track data obtained in the underwater acoustic field at different times and orientations, thus target could be predicted by classifier based on the source training. The resulting Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) are reduced by more than 30%, enabling more accurate distance estimates.
-
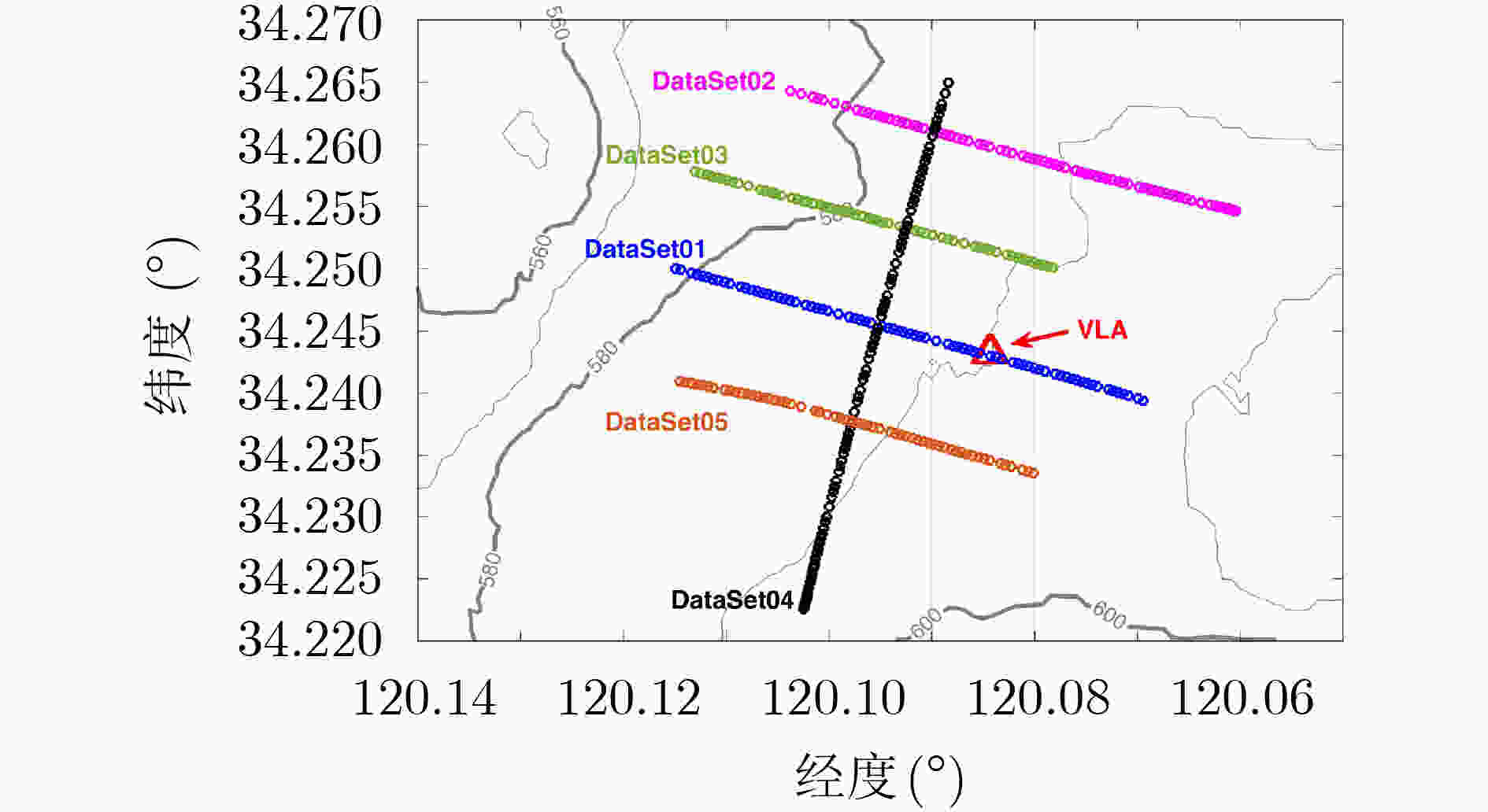
表 1 源域和目标域划分及其规模和维度
实验任务 实验1 实验2 实验3 源域(距离范围) DataSet2345(960 m,3080 m) DataSet1245(0 m,2960 m) DataSet1235(0 m,2960 m) 源域规模和维度 (3105,7200) (3345,7200) (2985,7200) 目标域(距离范围) DataSet01(960 m,2960 m) DataSet03(960 m,2960 m) DataSet04(1000 m,2840 m) 目标域规模和维度 (523,7200) (650,7200) (1010,7200) -
[1] BAGGEROER A B, KUPERMAN W A, and MIKHALEVSKY P N. An overview of matched field methods in ocean acoustics[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 1993, 18(4): 401–424. doi: 10.1109/48.262292 [2] MICHALOPOULOU Z H, GERSTOFT P, and CAVIEDES-NOZAL D. Matched field source localization with Gaussian processes[J]. JASA Express Letters, 2021, 1(6): 064801. doi: 10.1121/10.0005069 [3] BUCKER H P. Use of calculated sound fields and matched-field detection to locate sound sources in shallow water[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1976, 59(2): 368–373. doi: 10.1121/1.380872 [4] FIZELL R G and WALES S C. Source localization in range and depth in an Arctic environment[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1985, 78(S1): S57–S58. doi: 10.1121/1.2022889 [5] GINGRAS D F and GERSTOFT P. Inversion for geometric and geoacoustic parameters in shallow water: Experimental results[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1995, 97(6): 3589–3598. doi: 10.1121/1.412442 [6] 杨剑锋, 乔佩蕊, 李永梅, 等. 机器学习分类问题及算法研究综述[J]. 统计与决策, 2019, 35(6): 36–40. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2019.06.008YANG Jianfeng, QIAO Peirui, LI Yongmei, et al. A review of machine-learning classification and algorithms[J]. Statistics and Decision, 2019, 35(6): 36–40. doi: 10.13546/j.cnki.tjyjc.2019.06.008 [7] 牛海强, 李整林, 王海斌, 等. 水声被动定位中的机器学习方法研究进展综述[J]. 信号处理, 2019, 35(9): 1450–1459. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.09.002NIU Haiqiang, LI Zhenglin, WANG Haibin, et al. Overview of machine learning methods in underwater source localization[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2019, 35(9): 1450–1459. doi: 10.16798/j.issn.1003-0530.2019.09.002 [8] CHEN R and SCHMIDT H. Model-based convolutional neural network approach to underwater source-range estimation[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2021, 149(1): 405–420. doi: 10.1121/10.0003329 [9] LIU Wenxu, YANG Yixin, XU Mengqian, et al. Source localization in the deep ocean using a convolutional neural network[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 147(4): EL314–EL319. doi: 10.1121/10.0001020 [10] NAKADAI K, MASAKI S, KOJIMA R, et al. Sound source localization based on von-Mises-Bernoulli deep neural network[C]. 2020 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration (SII), Honolulu, USA, 2020: 658–663. [11] HUANG Zhaoqiong, XU Ji, GONG Zaixiao, et al. A deep neural network based method of source localization in a shallow water environment[C]. 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Calgary, Canada, 2018: 3499–3503. [12] HAVYARIMANA V, XIAO Zhu, SEMONG T, et al. Achieving reliable intervehicle positioning based on Redheffer weighted least squares model under multi-GNSS outages[J/OL]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021. [13] LIU Bin, CHEN Hongyang, ZHONG Ziguo, et al. Asymmetrical round trip based synchronization-free localization in large-scale underwater sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2010, 9(11): 3532–3542. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2010.090210.100146 [14] CHEN Hobgyang, WANG Gang, WANG Zizhuo, et al. Non-line-of-sight node localization based on semi-definite programming in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(1): 108–116. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011.110811.101739 [15] NIU Haiqiang, OZANICH E, and GERSTOFT P. Ship localization in Santa Barbara channel using machine learning classifiers[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2017, 142(5): EL455–EL460. doi: 10.1121/1.5010064 [16] NIU Haiqiang, REEVES E, and GERSTOFT P. Source localization in an ocean waveguide using supervised machine learning[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2017, 142(3): 1176–1188. doi: 10.1121/1.5000165 [17] NIU Haiqiang, GONG Zaixiao, OZANICH E, et al. Deep-learning source localization using multi-frequency magnitude-only data[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2019, 146(1): 211–222. doi: 10.1121/1.5116016 [18] LIU Yining, NIU Haiqiang, and LI Zhenglin. A multi-task learning convolutional neural network for source localization in deep ocean[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 148(2): 873–883. doi: 10.1121/10.0001762 [19] CHI Jing, LI Xiaolei, WANG Haozhong, et al. Sound source ranging using a feed-forward neural network trained with fitting-based early stopping[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2019, 146(3): EL258–EL264. doi: 10.1121/1.5126115 [20] LIU Yining, NIU Haiqiang, and LI Zhenglin. Source ranging using ensemble convolutional networks in the direct zone of deep water[J]. Chinese Physics Letters, 2019, 36(4): 044302. doi: 10.1088/0256-307X/36/4/044302 [21] WANG Yun and PENG Hua. Underwater acoustic source localization using generalized regression neural network[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2018, 143(4): 2321–2331. doi: 10.1121/1.5032311 [22] 邓晋, 潘安迪, 肖川, 等. 基于迁移学习的水声目标识别[J]. 计算机系统应用, 2020, 29(10): 255–261. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.007538DENG Jin, PAN Andi, XIAO Chuan, et al. Transfer learning for acoustic target recognition[J]. Computer Systems &Applications, 2020, 29(10): 255–261. doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.007538 [23] 雷波, 何兆阳, 张瑞. 基于迁移学习的水下目标定位方法仿真研究[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(22): 183–192. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20210277LEI Bo, HE Zhaoyang, and ZHANG Rui. Simulation study of underwater intruder localization based on transfer learning[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2021, 70(22): 183–192. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20210277 [24] LONG Mingsheng, WANG Jianmin, DING Guiguang, et al. Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation[C]. 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, Australia, 2013: 2200–2207. [25] 龙明盛. 迁移学习问题与方法研究[D]. [博士论文], 清华大学, 2014.LONG Mingsheng. Transfer learning: Problems and methods[D]. [Ph. D. dissertation], Tsinghua University, 2014. [26] BYUN S H, VERLINDEN C M A, and SABRA K G. Blind deconvolution of shipping sources in an ocean waveguide[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2017, 141(2): 797–807. doi: 10.1121/1.4976046 -





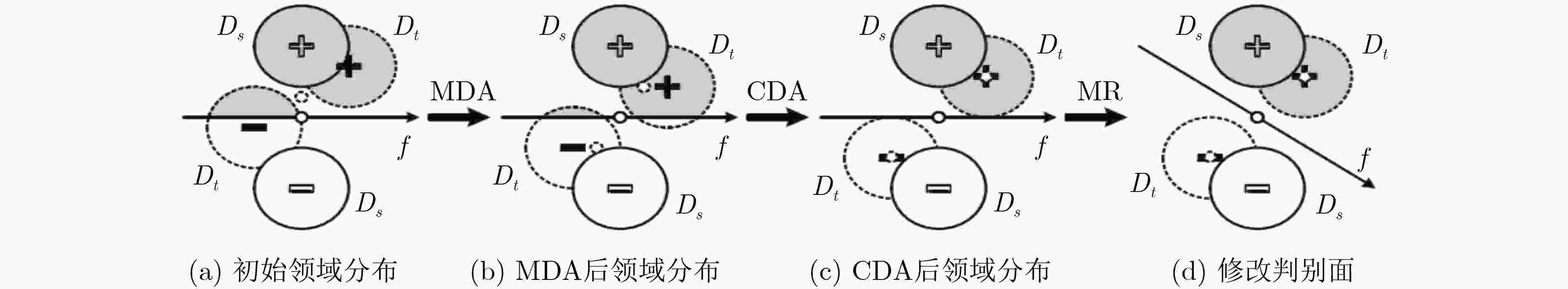
 下载:
下载:
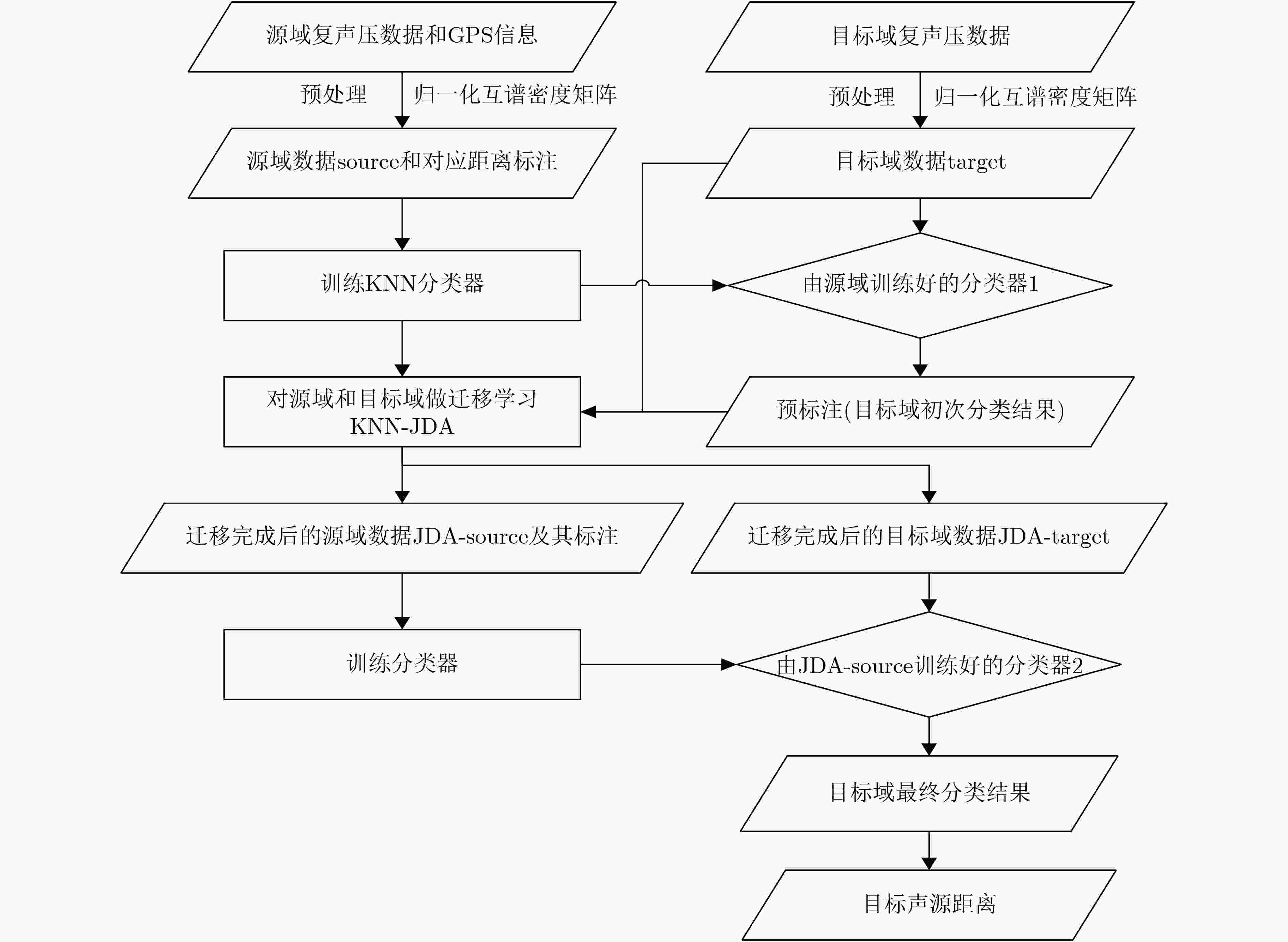

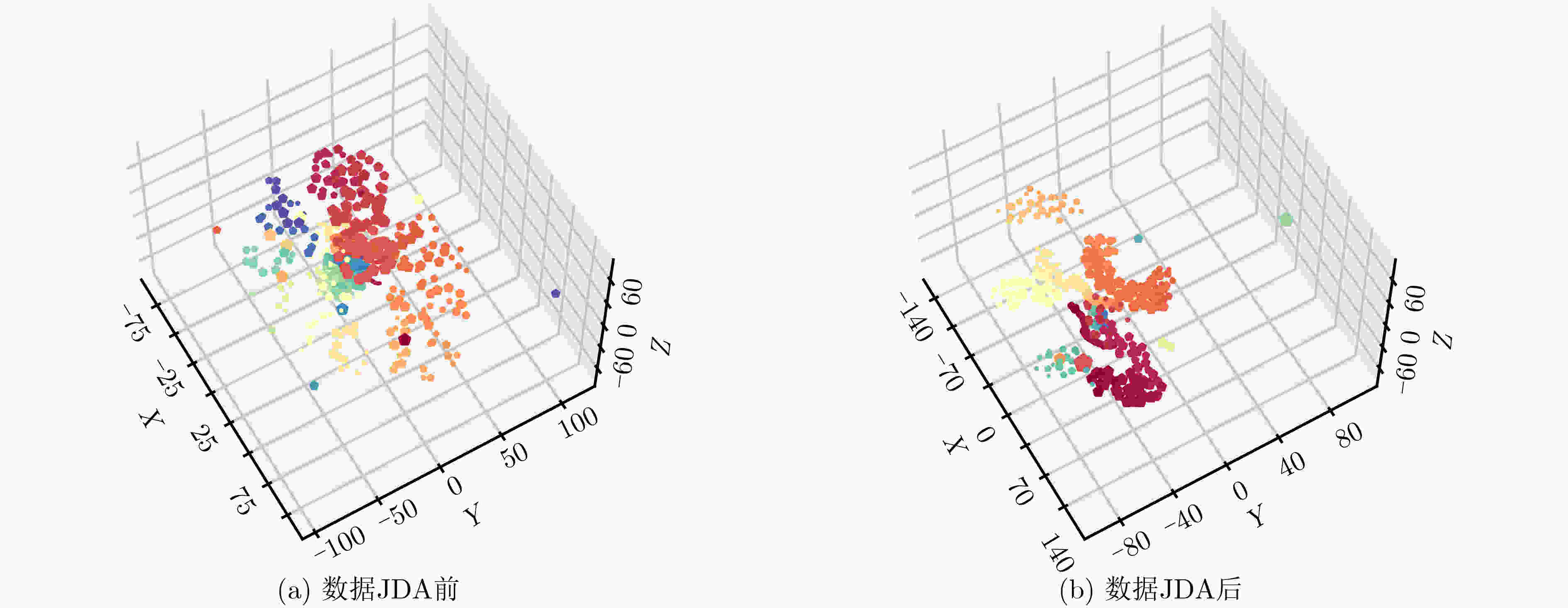
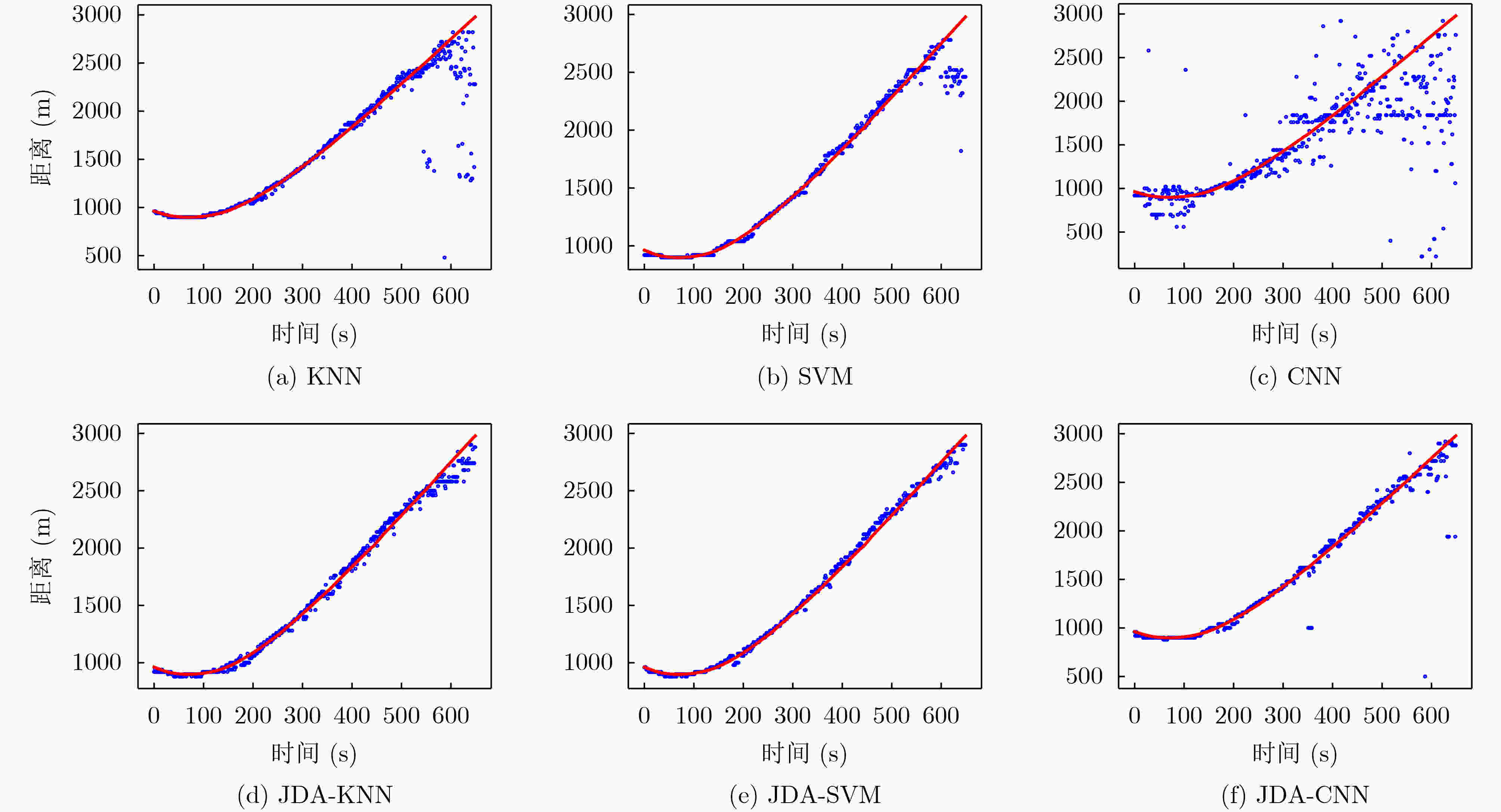
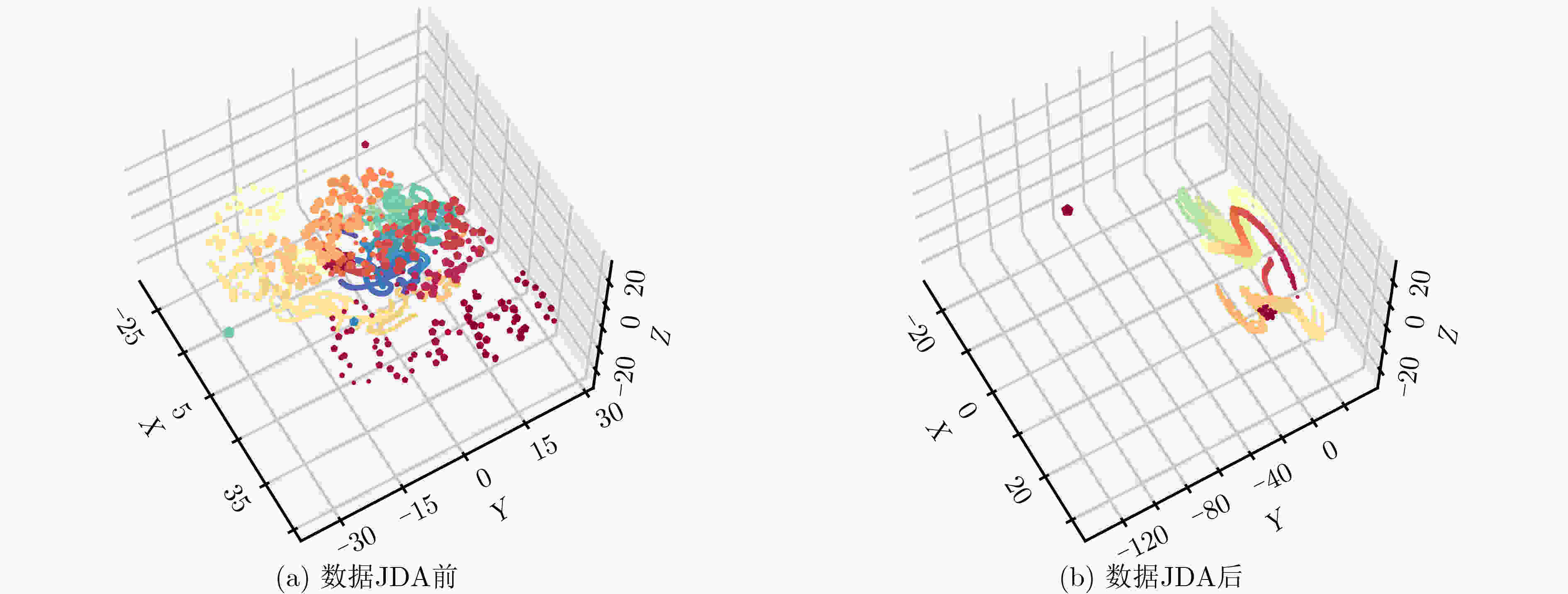
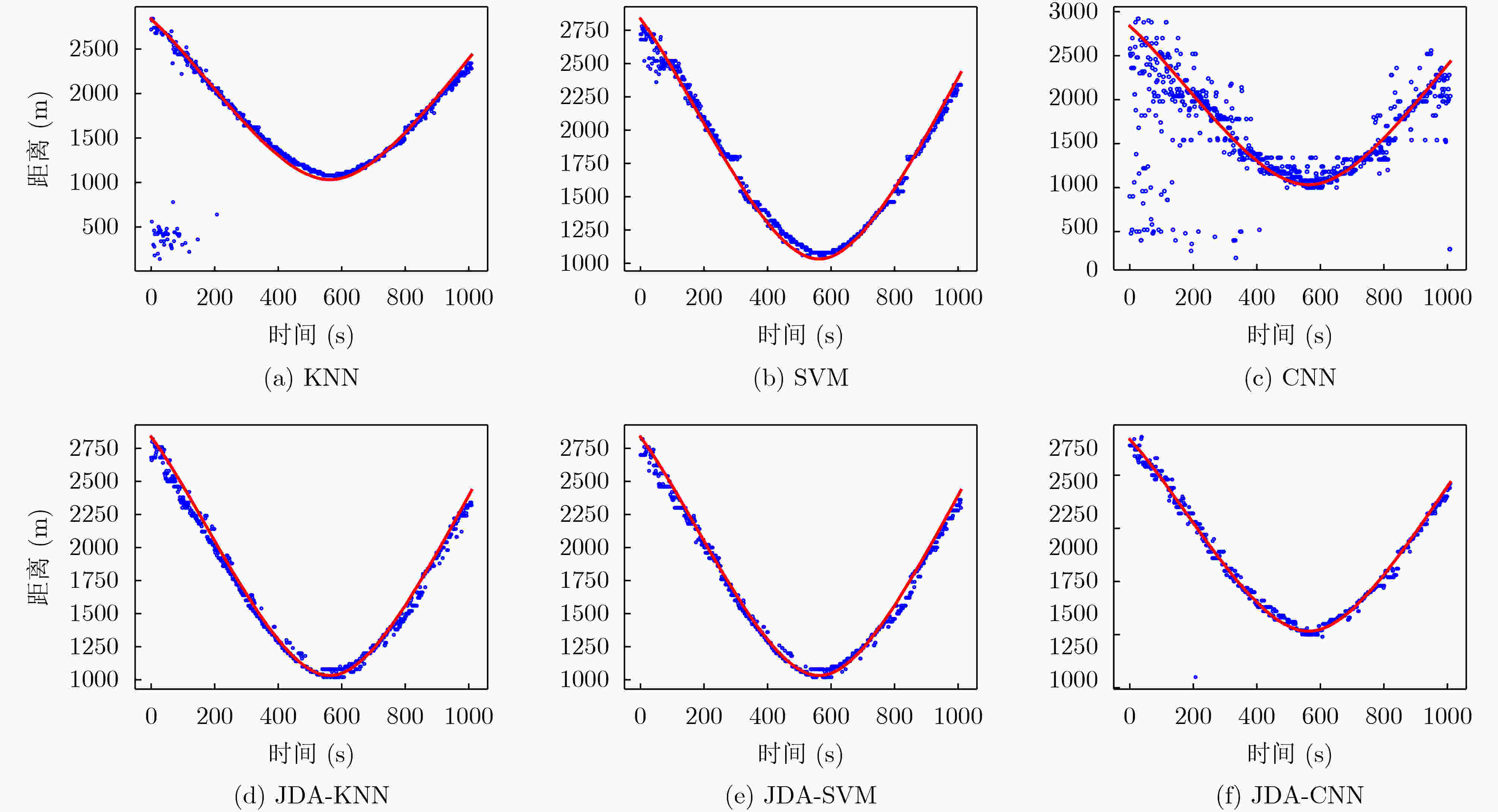
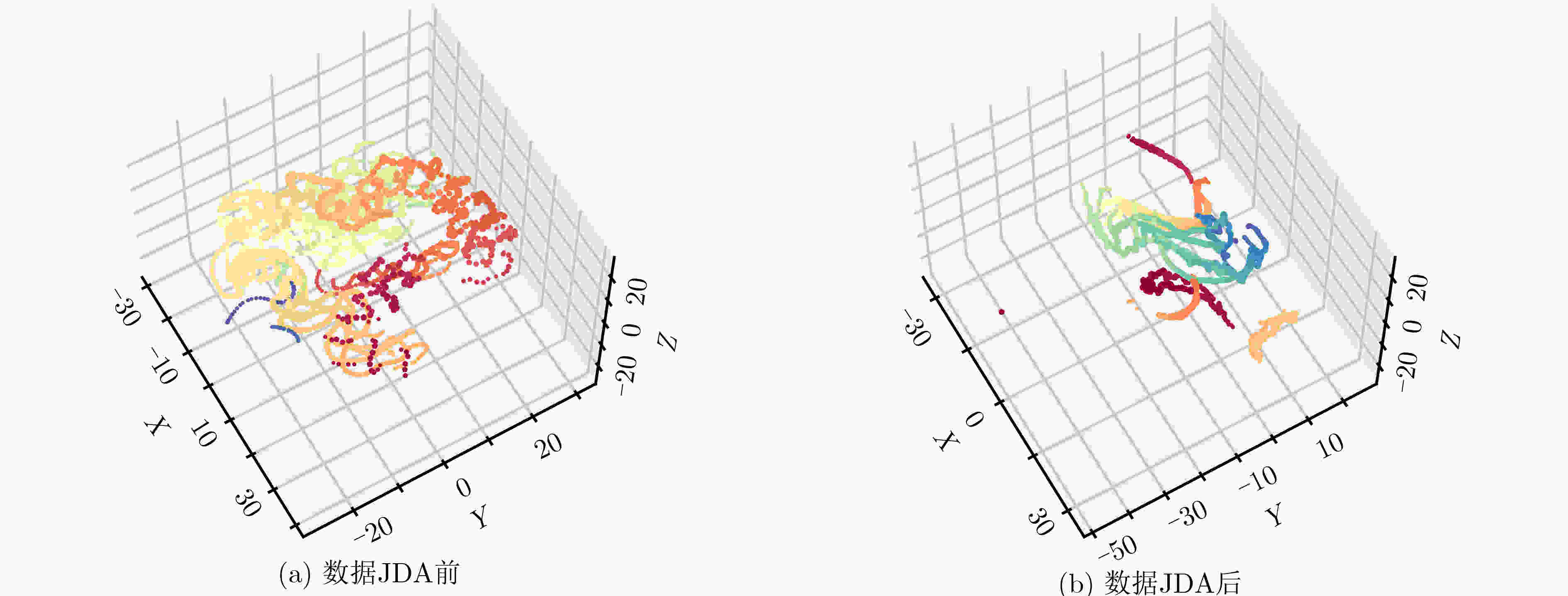
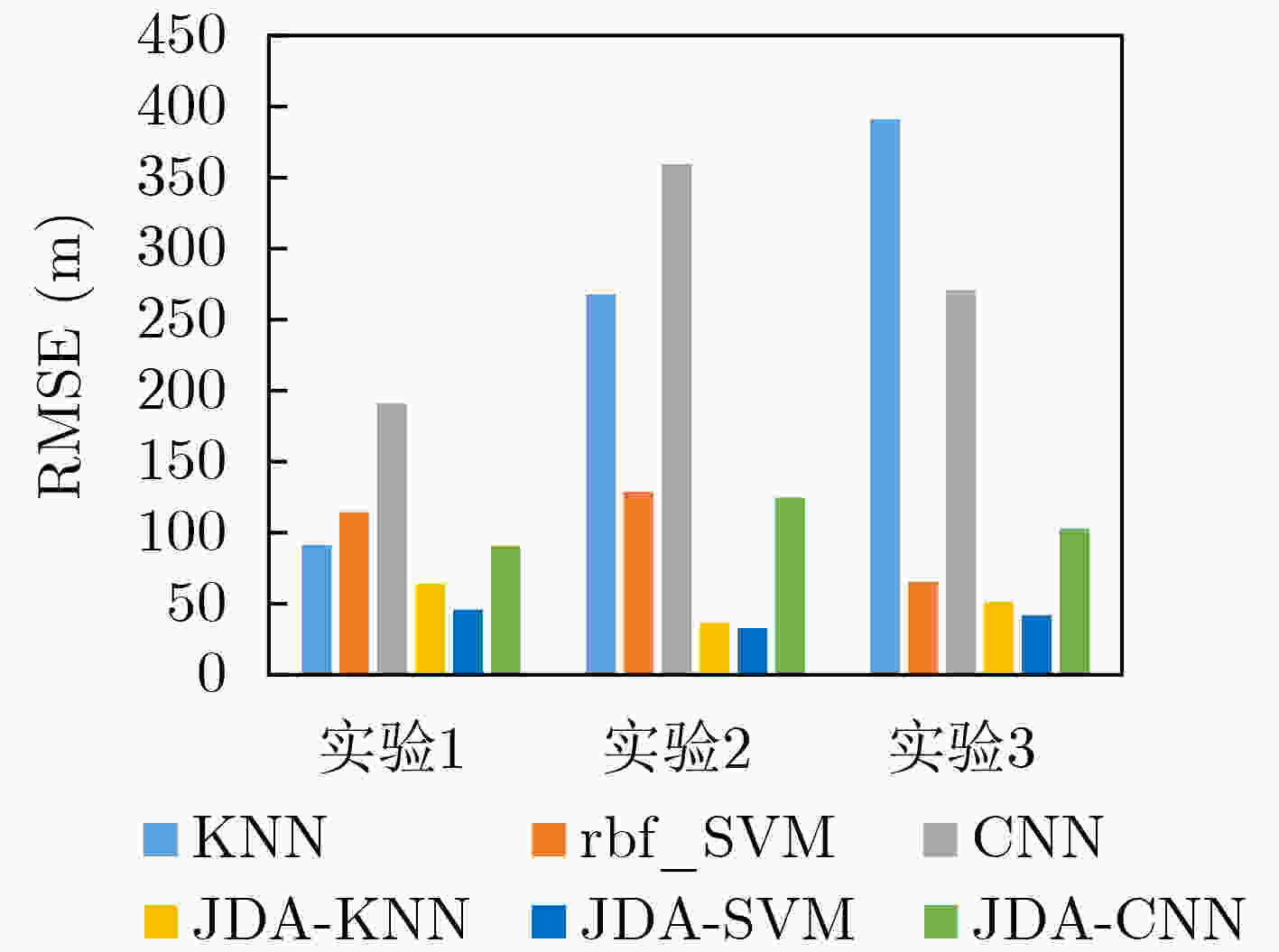
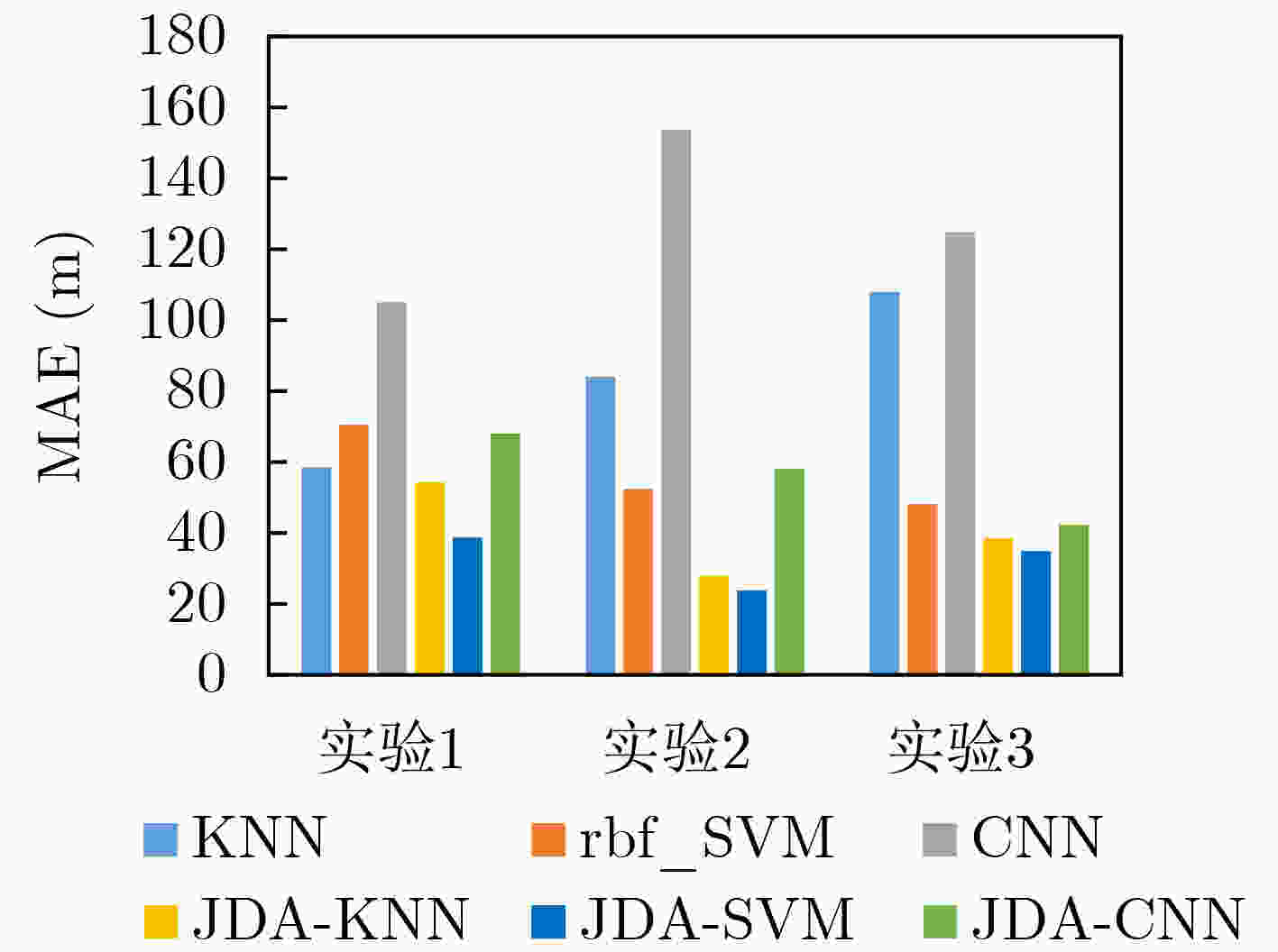


 下载:
下载:
