Classification of Ship Radiated Noise Based on Bi-Logarithmic Scale Spectrum and Convolutional Network
-
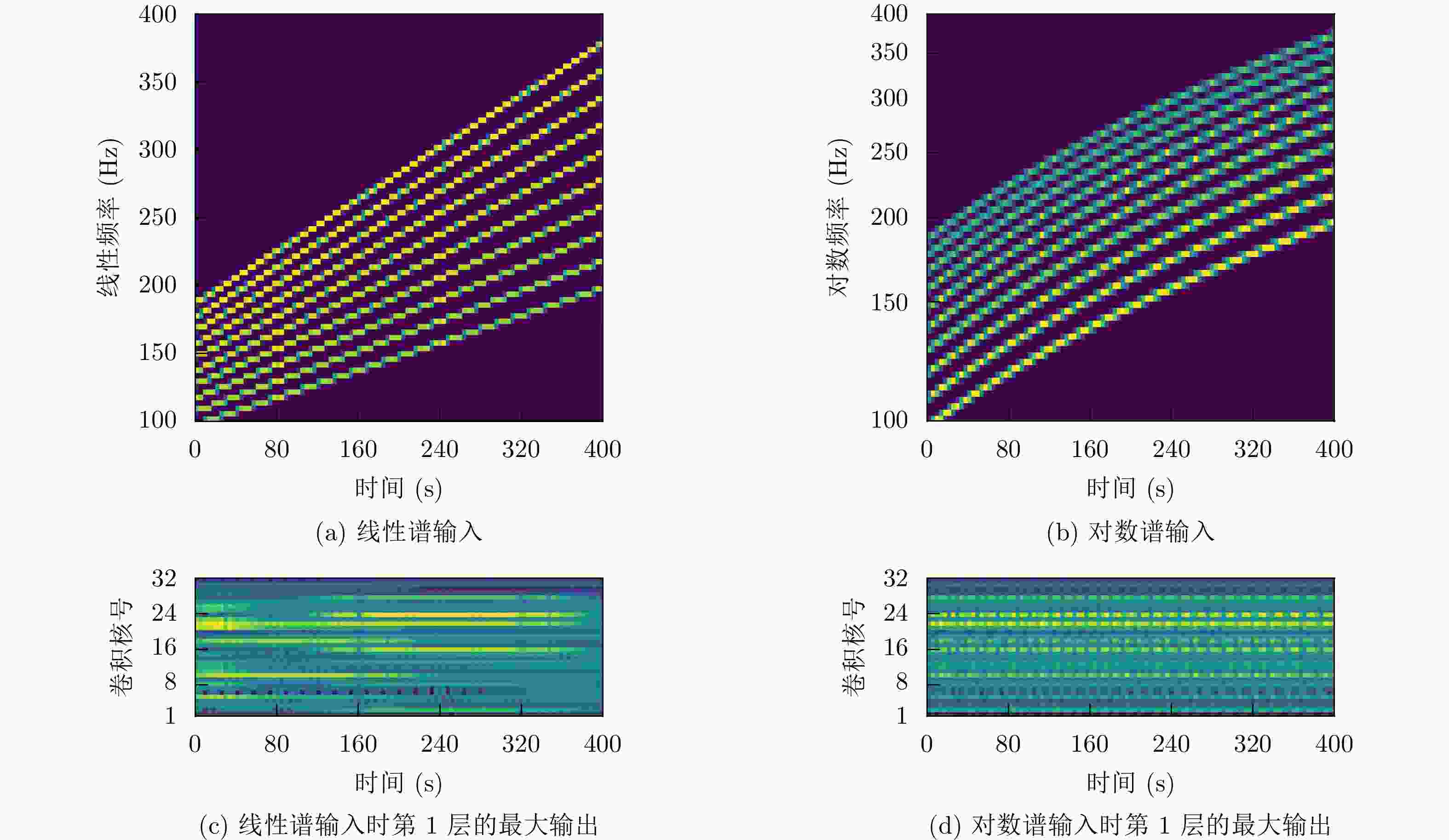
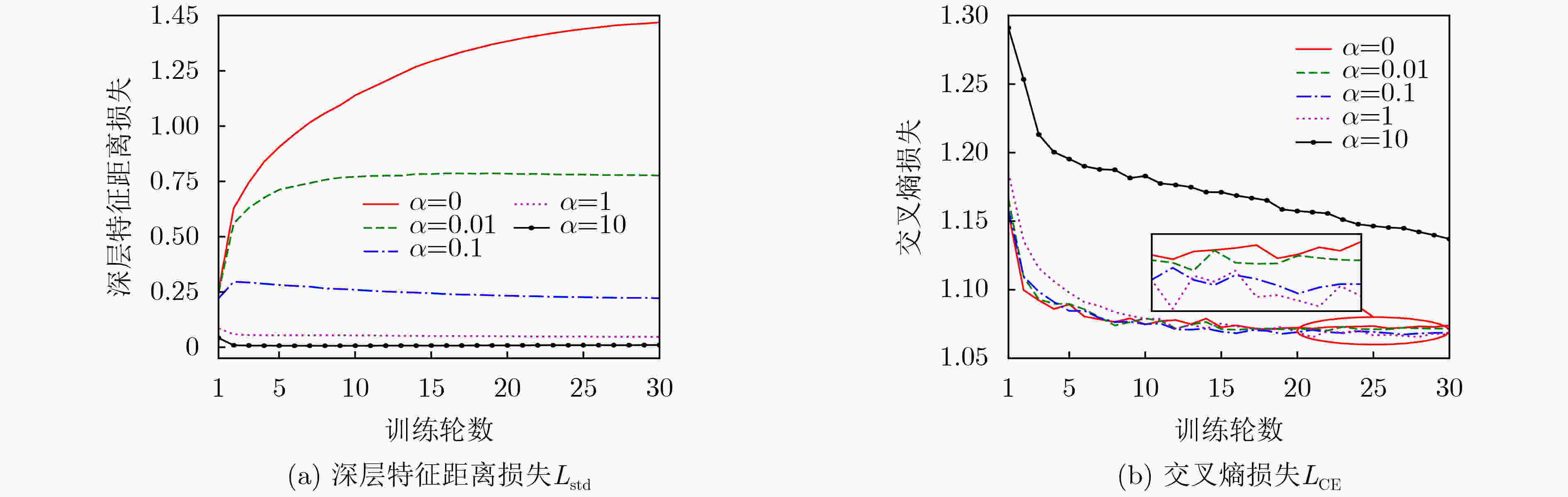
摘要: 卷积层平移等变性与线性谱不适配,卷积网络对高维特征的长距离依赖建模能力不足。该文提出一种双对数谱特征用于船舶辐射噪声分类。双对数谱通过重新排列对数谱频点,保证高频端分辨率的同时,规避使用太深的卷积网络。利用双对数谱各行表征同一目标的先验知识,构建卷积网络和目标函数。DeepShip数据集上的试验结果表明,特征维数相同情况下,提出的算法分类正确率比以线性谱为输入的卷积网络提高2.4%以上。Abstract: The translation equivariance of convolutional layers are not compatible with the linear spectrum. Therefore, the convolutional networks can not carry the long-distance dependency of high-dimensional features. One bi-logarithmic spectrum feature is presented by this paper for classification of ship radiated noise. This bi-logarithmic spectrum rearranges the frequency points of the logarithmic spectrum to ensure the resolution of high frequencies, therefore the substantial deep convolutional network is not necessary. Considering on the prior knowledge that each row of the bi-logarithmic spectrum corresponding to the same one target, a convolutional network as well as an objective function are constructed. Then this network is trained and tested with DeepShip dataset to classify four types of marine vessels, and the results show that, with the same feature dimensions, the classification accuracy of the algorithm proposed by this paper is improved by 2.4% more than the convolutional network with the input feature of linear scale spectrum.
-
表 1 DeepShip 数据集样本统计
类别 记录数 样本数 货轮 109 9580 客轮 191 11544 油轮 240 11048 拖船 69 10112 合计 609 42284 表 2 ACNN 的网络结构参数
层号 层 参数 输入$1 \times I \times J$维 1 Conv2d (32, 1×5) 2 Conv2d+MaxPool2d (64, 1×3), 1×2 3 Conv2d+MaxPool2d (64, 1×3), 1×2 4 Conv2d+MaxPool2d (64, 1×3), 1×2 5 Conv2d+MaxPool2d (64, 1×3), 1×2 6 Conv2d+MaxPool2d (128, 1×3), 1×2 变形为$ 4J \times I $维 7 Conv1d (256, 1) 8 Conv1d (64, 1) 9 Conv1d+AvgPool1d (4, 1), $I$ 表 3 对照组 CNN 结构参数
网络 输入维数 卷积核数 CNN1d 256 32-64-64-64-64-128 1024 16-32-64-64-64-64-128 2048 8-16-32-64-64-64-64-128 CNN2d 4×256 32-64-64-64-64-128 8×256 全连接层均为1024-256-64-4 表 4 分类正确率
网络 特征 维数 正确率(%) CNN1d 线性谱 256 63.62 1024 64.70 2048 64.60 对数谱 256 65.02 1024 66.25 2048 65.31 CNN2d 双对数谱 4×256 66.07 ACNN 66.86 ACNN+约束 67.11 CNN2d 8×256 66.35 ACNN 67.32 ACNN+约束 67.47 -
[1] LECUN Y, BOTTOU L, BENGIO Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278–2324. doi: 10.1109/5.726791 [2] HE Kaiming, ZHANG Xiangyu, REN Shaoqing, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 770–778. [3] 王念滨, 何鸣, 王红滨, 等. 适用于水下目标识别的快速降维卷积模型[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2019, 40(7): 1327–1333. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201805113WANG Nianbin, HE Ming, WANG Hongbin, et al. A fast reduced-dimension convolution model for underwater target recognition[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2019, 40(7): 1327–1333. doi: 10.11990/jheu.201805113 [4] SHEN Sheng, YANG Honghui, LI Junhao, et al. Auditory inspired convolutional neural networks for ship type classification with raw hydrophone data[J]. Entropy, 2018, 20(12): 990. doi: 10.3390/e20120990 [5] HU Gang, WANG Kejun, PENG Yuan, et al. Deep learning methods for underwater target feature extraction and recognition[J]. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, 2018, 2018: 1214301. doi: 10.1155/2018/1214301 [6] LI Junhao and YANG Honghui. The underwater acoustic target timbre perception and recognition based on the auditory inspired deep convolutional neural network[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2021, 182: 108210. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108210 [7] CHEN Yuechao and SHANG Jintao. Underwater target recognition method based on convolution autoencoder[C]. 2019 IEEE International Conference on Signal, Information and Data Processing, Chongqing, China, 2019: 1–5. [8] 王念滨, 何鸣, 王红滨, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的水下目标特征提取方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(6): 1197–1203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506x.2018.06.02WANG Nianbin, HE Ming, WANG Hongbin, et al. Underwater target feature extraction method based on convolutional neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(6): 1197–1203. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506x.2018.06.02 [9] CHEN Jie, HAN Bing, MA Xufeng, et al. Underwater target recognition based on multi-decision LOFAR spectrum enhancement: A deep-learning approach[J]. Future Internet, 2021, 13(10): 265. doi: 10.3390/FI13100265 [10] ZHANG Qi, DA Lianglong, ZHANG Yanhou, et al. Integrated neural networks based on feature fusion for underwater target recognition[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2021, 182: 108261. doi: 10.1016/J.APACOUST.2021.108261 [11] GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, COURVILLE A, 赵申剑, 黎彧君, 符天凡, 等译. 深度学习[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2017: 205–207.GOODFELLOW I, BENGIO Y, COURVILLE A, ZHAO Shenjian, LI Yujun, FU Tianfan, et al. translation. Deep Learning[M]. Beijing: Posts & Telecommunications Press, 2017: 205–207. [12] IRFAN M, ZHENG Jiangbin, ALI S, et al. DeepShip: An underwater acoustic benchmark dataset and a separable convolution based autoencoder for classification[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2021, 183: 115270. doi: 10.1016/J.ESWA.2021.115270 [13] SCHÖRKHUBER C and KLAPURI A. Constant-Q transform toolbox for music processing[C]. The 7th Sound and Music Computing Conference, Barcelona, Spain, 2010. [14] LUO Wenjie, LI Yujia, URTASUN R, et al. Understanding the effective receptive field in deep convolutional neural networks[C]. The 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 2016: 4905–4913. [15] UMESH S, COHEN L, and NELSON D. Fitting the Mel scale[C]. Proceedings of 1999 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Phoenix, USA, 1999: 217–220. [16] 徐源超, 蔡志明. 水声目标分类算法性能评估[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2020, 41(10): 1559–1565. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202007114XU Yuanchao and CAI Zhiming. Performance evaluation on the algorithm of underwater acoustic target classification[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2020, 41(10): 1559–1565. doi: 10.11990/jheu.202007114 -





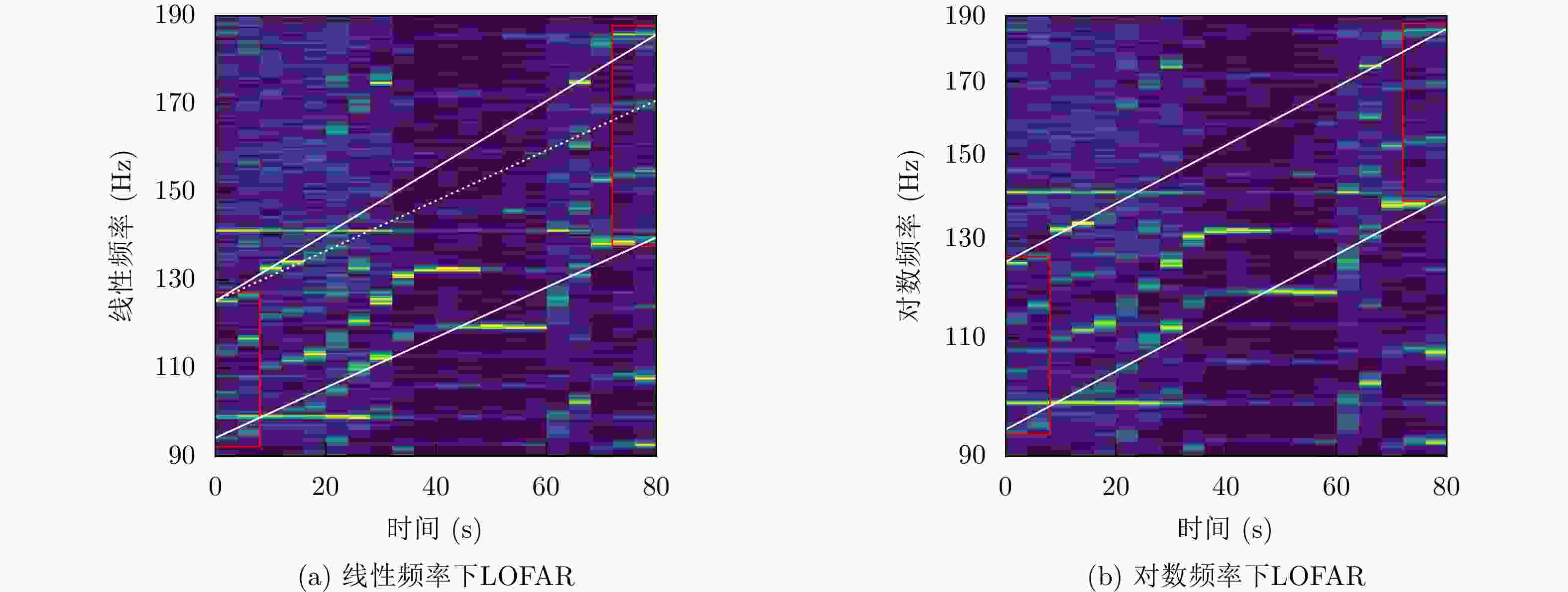
 下载:
下载:
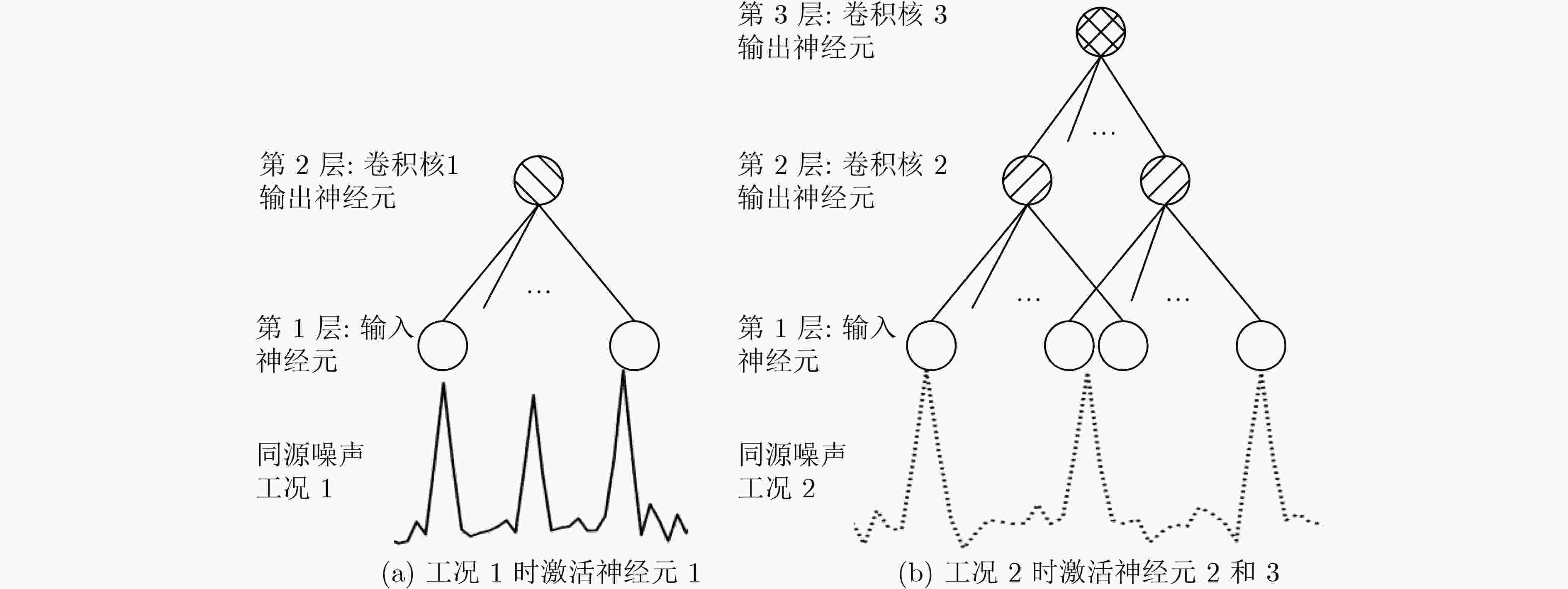
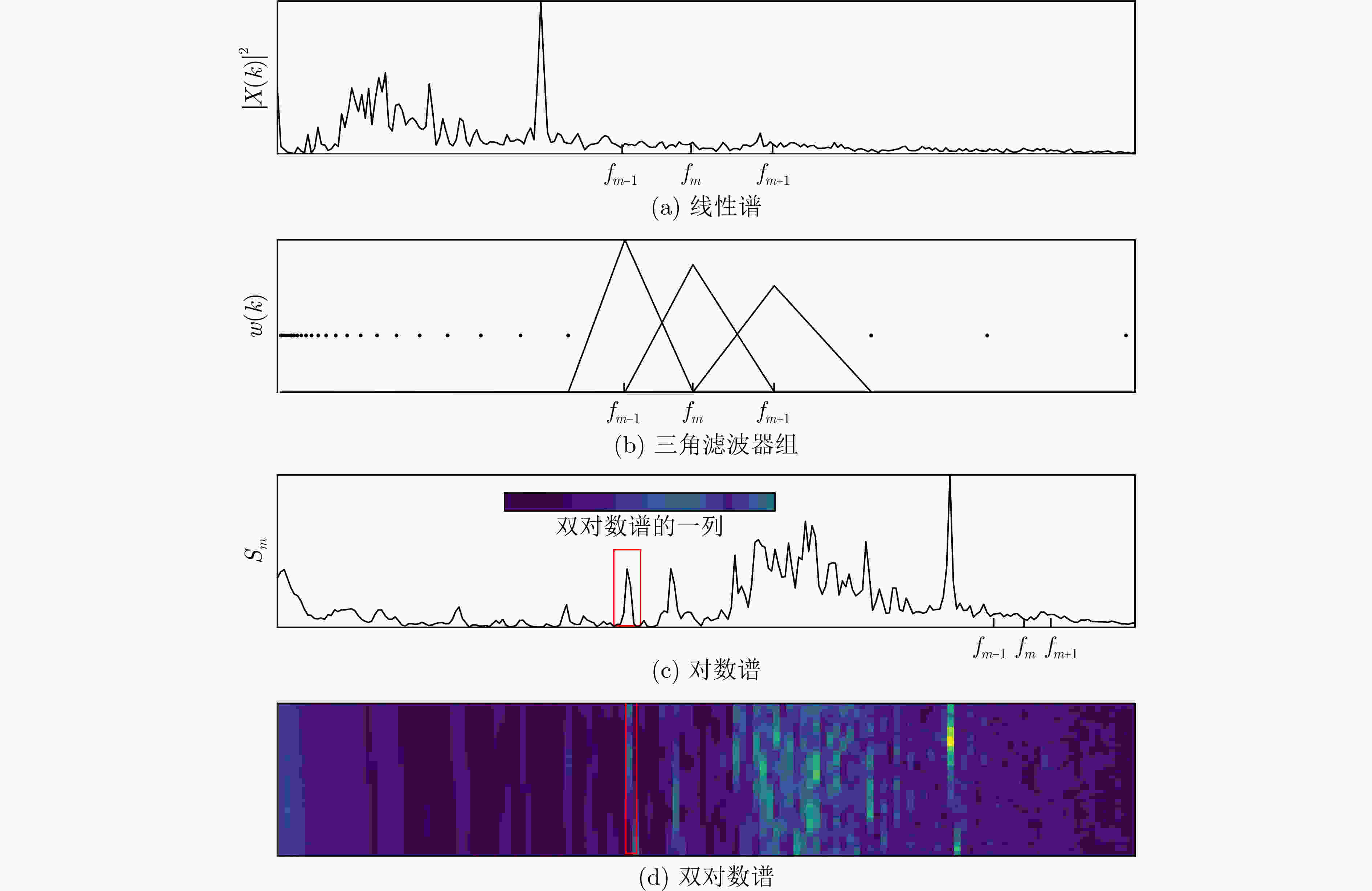
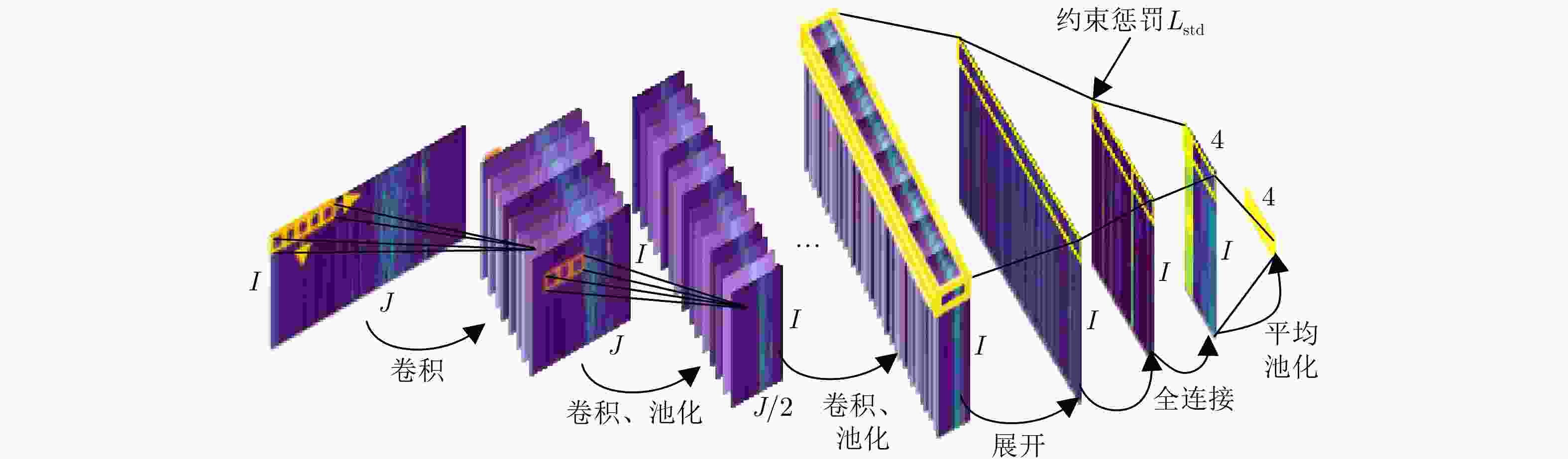


 下载:
下载:
