An Intention Recognition Method Based on Fuzzy Belief-Rule-Base
-
摘要: 针对传统意图识别方法只能处理某种类型不确定性信息的不足,该文结合模糊集和DS证据理论优势提出一种模糊置信规则库(BRB)信息处理方法。首先在置信规则前提部分改进了前提属性的连接关系,根据数据集统计分布特点设计了模糊集分割,选取Cauchy型分布作为隶属度函数,较好地避免置信规则无法被有效激活进而导致系统无有效输出问题;其次融合处理辨识框架内不同类别的置信分布,建立规则权重和特征权重优化模型,构建了特征空间与类别空间之间的输入输出关系;在此基础上,计算未知意图数据在相应规则模糊域的匹配度和激活度,采用置信度最大原则进行识别决策。通过实验验证、参数敏感性及结果分析、时间复杂度分析,表明该文方法可以获得比其他识别方法更高的正确率,尤其是在小样本条件下更能体现出该方法的有效性和可靠性。Abstract: Considering the deficiency that traditional intention recognition methods can only deal with certain types of uncertain information, a new information processing method of fuzzy Belief-Rule-Base (BRB) is proposed, which combines the advantages of fuzzy sets and Dempster-Shafer (DS) theory. Firstly, the connection relation of premise attributes is improved in the premise part of confidence rules, and fuzzy set segmentation is designed according to the statistical distribution characteristics of data sets. Cauchy distribution is selected as membership function to avoid the problem that confidence rules could not be activated effectively, which would lead to no effective output of the system. Secondly, the confidence distribution of different categories in the identification framework is fused, and the optimization model of rule weight and feature weight is established, and the input-output relationship between feature space and category space is constructed. On this basis, the matching degree and activation degree of the unknown intention data are calculated, and the recognition decision is made using the maximum confidence principle. Through experimental verification, sensitive parameter and interpretation of result, time complexity analysis, compared with other methods, the fuzzy belief-rule-base shows high accuracy rate, and effectiveness and reliability under the condition of small samples.
-
Key words:
- Intention recognition /
- Belief-Rule-Base(BRB) /
- Evidential Reasoning (ER) /
- Fuzzy sets
-
表 1 目标各属性边界数据
目标 方位角(°) 距离(km) 水平速度(m/s) 航向角(°) 雷达反射截面积(m2) 意图 1 48.6 281 250 202 3.0 Recon 2 241.2 120 280 52 1.7 Cover 3 240.0 110 300 50 2.1 Cover 4 174.0 290 272 350 5.2 Attack 5 168.0 260 215 260 6.8 Recon 6 139.5 215 320 324 2.8 Attack 7 138 210 300 310 1.2 Attack 表 2 属性模糊划分的数据分割点
序号 属性1分割点 属性2分割点 属性3分割点 属性4分割点 属性5分割点 1 0.0039 0.0740 0.2224 0.0110 0.0634 2 0.0062 0.1098 0.2668 0.1132 0.1248 3 0.0241 0.8034 0.3857 0.5055 0.1683 4 0.5518 0.9321 0.5046 0.7235 0.1995 5 0.9950 – 0.6383 0.9661 0.2616 6 – – 0.7594 – 0.3217 7 – – 0.9359 – 0.8718 统计 5 4 7 5 7 表 3 各类算法的识别正确率对比(%)
SVM BAGC4.5 EBRB BRB-ER 本文 57 87 89 93.5 100 -
[1] 王闯, 李松, 姜浩博, 等. 防空反导智能战场态势估计研究[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2020, 45(3): 7–13,21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2020.03WANG Chuang, LI Song, JIANG Haobo, et al. Research on intelligent battlefield situation assessment of air defense and anti-missile[J]. Fire Control &Command Control, 2020, 45(3): 7–13,21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2020.03 [2] 王海旺, 史红权, 赵晓哲. 目标意图识别方法综述[C]. 2020中国系统仿真与虚拟现实技术高层论坛论文集, 北京, 2020: 186–188.WANG Haiwang, SHI Hongquan, and ZHAO Xiaozhe. A summary of target intention identification methods[C]. 2020 China System Simulation and Virtual Reality Technology High-level Forum, Beijing, China, 2020: 186–188. [3] 高杨, 李东生, 程泽新. 无人机分布式集群态势感知模型研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2018, 40(6): 1271–1278. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170877GAO Yang, LI Dongsheng, and CHENG Zexin. UAV Distributed swarm situation awareness model[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2018, 40(6): 1271–1278. doi: 10.11999/JEIT170877 [4] ZHOU Tongle, CHEN Mou, WANG Yuhui, et al. Information entropy-based intention prediction of aerial targets under uncertain and incomplete information[J]. Entropy, 2020, 22(3): 279. doi: 10.3390/e22030279 [5] 李伟生, 王三民, 王宝树. 基于计划识别的态势估计方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2006, 28(3): 532–536.LI Weisheng, WANG Sanmin, and WANG Baoshu. Study of situation assessment method based on plan recognition theory[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2006, 28(3): 532–536. [6] JIAO Lianmeng, PAN Quan, DENŒUX T, et al. Belief rule-based classification system: Extension of FRBCS in belief functions framework[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 309: 26–49. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.03.005 [7] CHI Zheru, YAN Hong, and PHAM T. Fuzzy Algorithms with Applications to Image Processing and Pattern Recognition[M]. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing Co, 1996. [8] YANG Jianbo, LIU Jun, WANG Jin, et al. Belief rule-based inference methodology using the evidential reasoning approach–RIMER[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A:Systems and Humans, 2006, 36(2): 266–285. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2005.851270 [9] 赵福均, 周志杰, 胡昌华, 等. 基于置信规则库和证据推理的空中目标意图识别方法[J]. 电光与控制, 2017, 24(8): 15–19,50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2017.08.004ZHAO Fujun, ZHOU Zhijie, HU Changhua, et al. Aerial target intention recognition approach based on belief-rule-base and evidential reasoning[J]. Electronics Optics &Control, 2017, 24(8): 15–19,50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2017.08.004 [10] CHANG Leilei, ZHOU Zhijie, YOU Yuan, et al. Belief rule based expert system for classification problems with new rule activation and weight calculation procedures[J]. Information Sciences, 2016, 336: 75–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2015.12.009 [11] ZHOU Zhijie, HU Guanyu, HU Changhua, et al. A survey of belief rule-base expert system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2019, 51(8): 4944–4958. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2019.2944893 [12] UTKIN L V. An imprecise extension of SVM-based machine learning models[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 331: 18–32. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.053 [13] XUE Junjie, ZHU Jie, XIAO Jiyang, et al. Panoramic convolutional long short-term memory networks for combat intension recognition of aerial targets[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 183312–183323. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3025926 [14] ACI M and AVCI M. K nearest neighbor reinforced expectation maximization method[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2011, 38(10): 12585–12591. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.04.046 [15] 张肃, 程启月, 解瑶, 等. 不确定空情信息条件下的意图识别方法[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 9(3): 50–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2008.03.012ZHANG Su, CHENG Qiyue, XIE Yao, et al. A method of inference intention with uncertain aerial information[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 9(3): 50–53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2008.03.012 [16] AFSHAR S, MOSLEH M, and KHEYRANDISH M. Presenting a new multiclass classifier based on learning automata[J]. Neurocomputing, 2013, 104: 97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2012.10.005 [17] ZHUANG Jinhui, YE Jifeng, CHEN Nannan, et al. Extended belief rule-base optimization base on clustering tree and parameter optimization[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 12533–12544. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3051001 [18] DEL AMO A, MONTERO J, FERNANDEZ A, et al. Spectral fuzzy classification: an application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2002, 32(1): 42–48. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2002.1009135 -





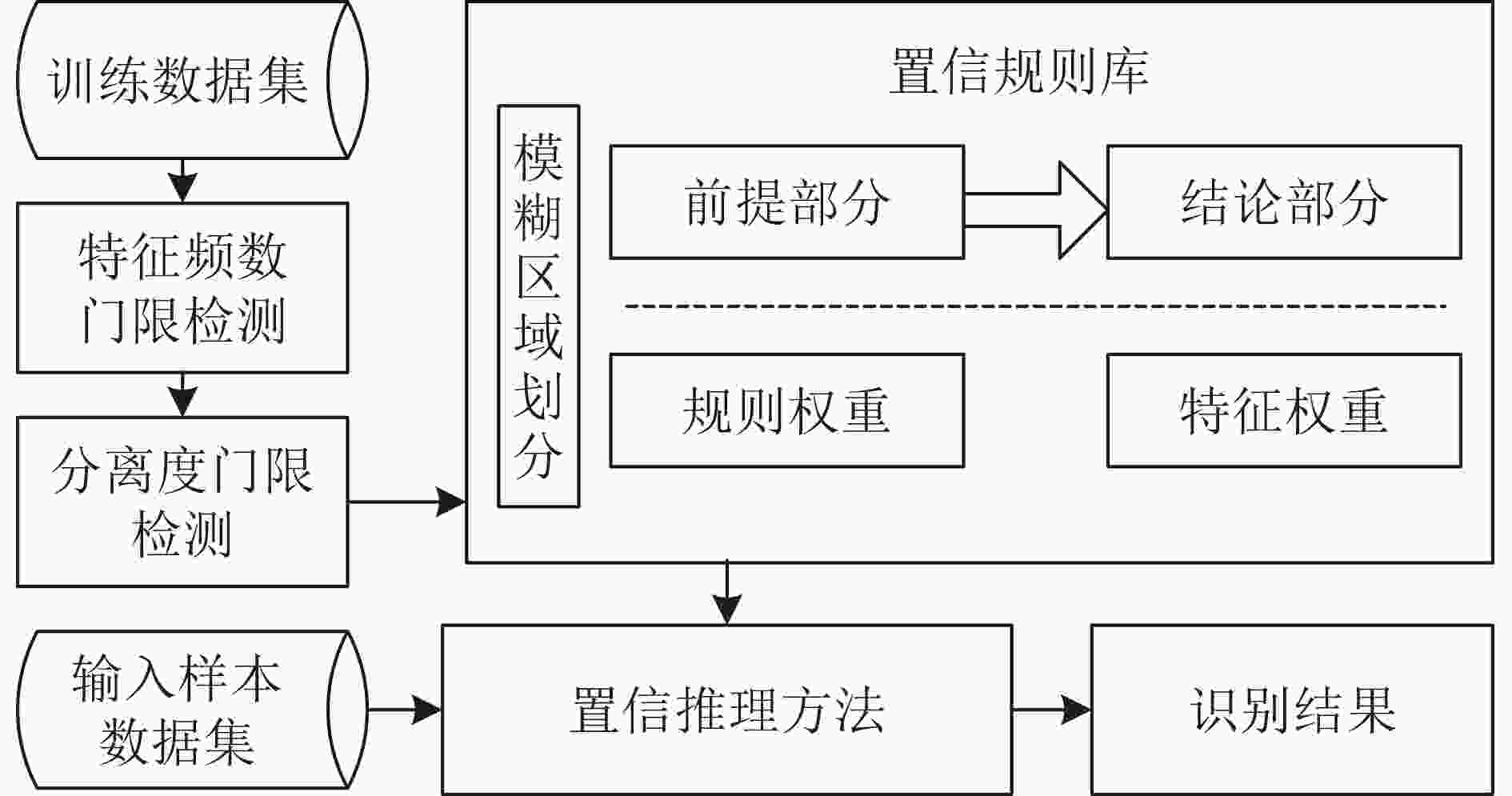
 下载:
下载:
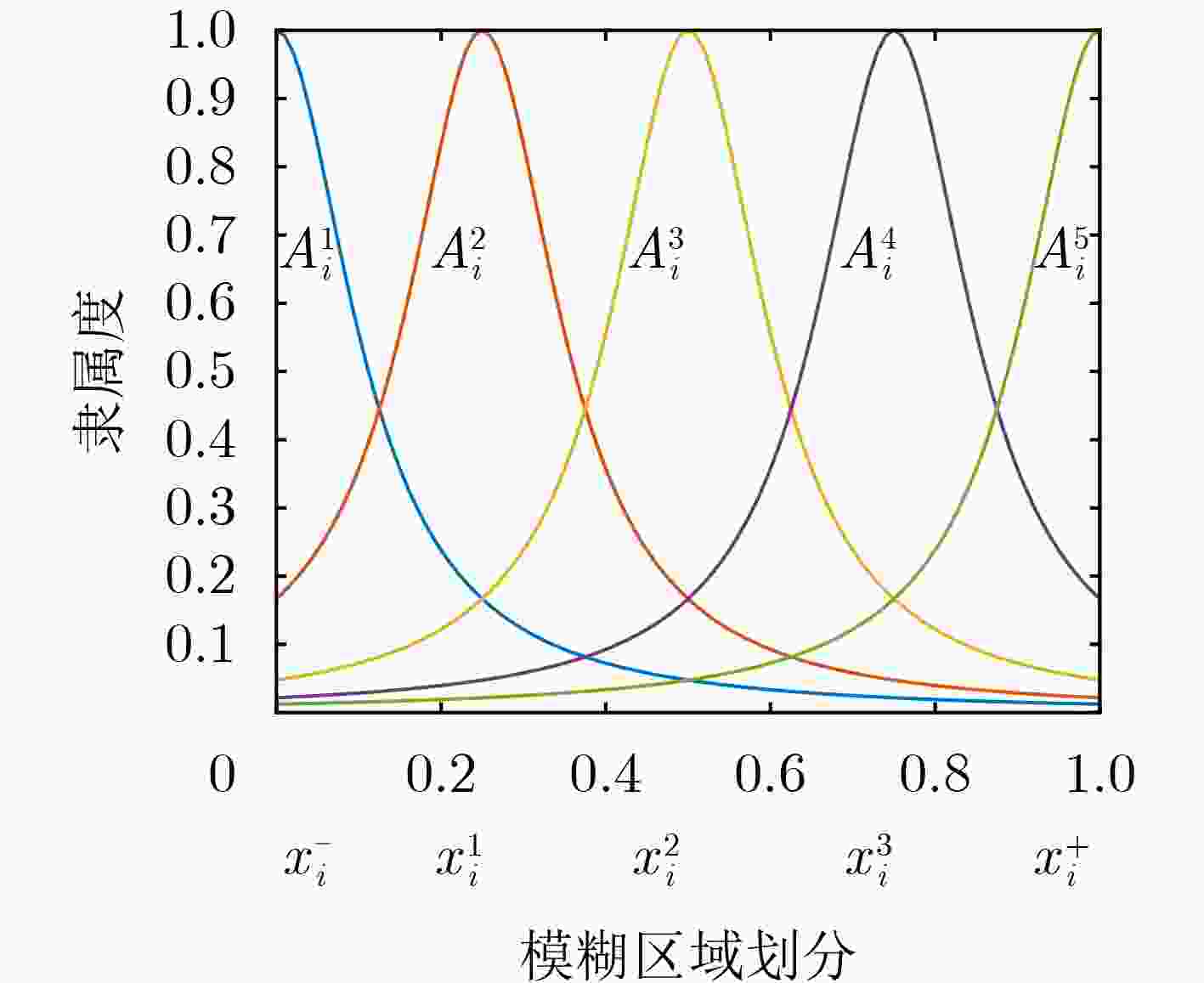
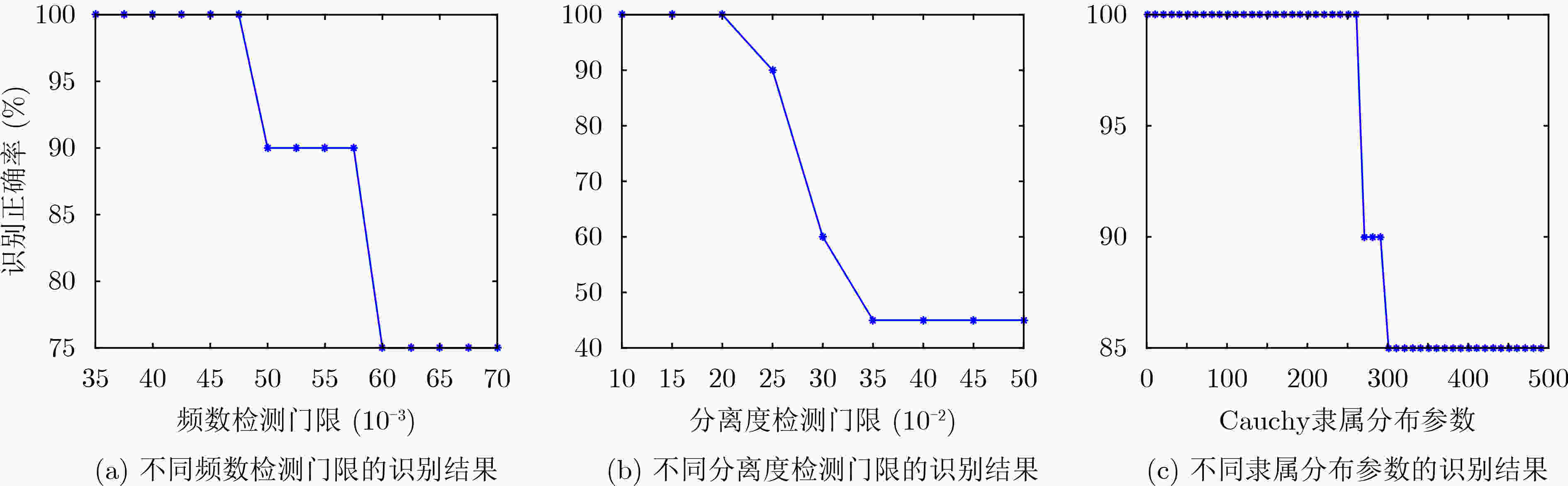


 下载:
下载:
