Performance Analysis and Optimization of Multi-antenna Dense Heterogeneous Network Based on Stochastic Geometry Theory
-
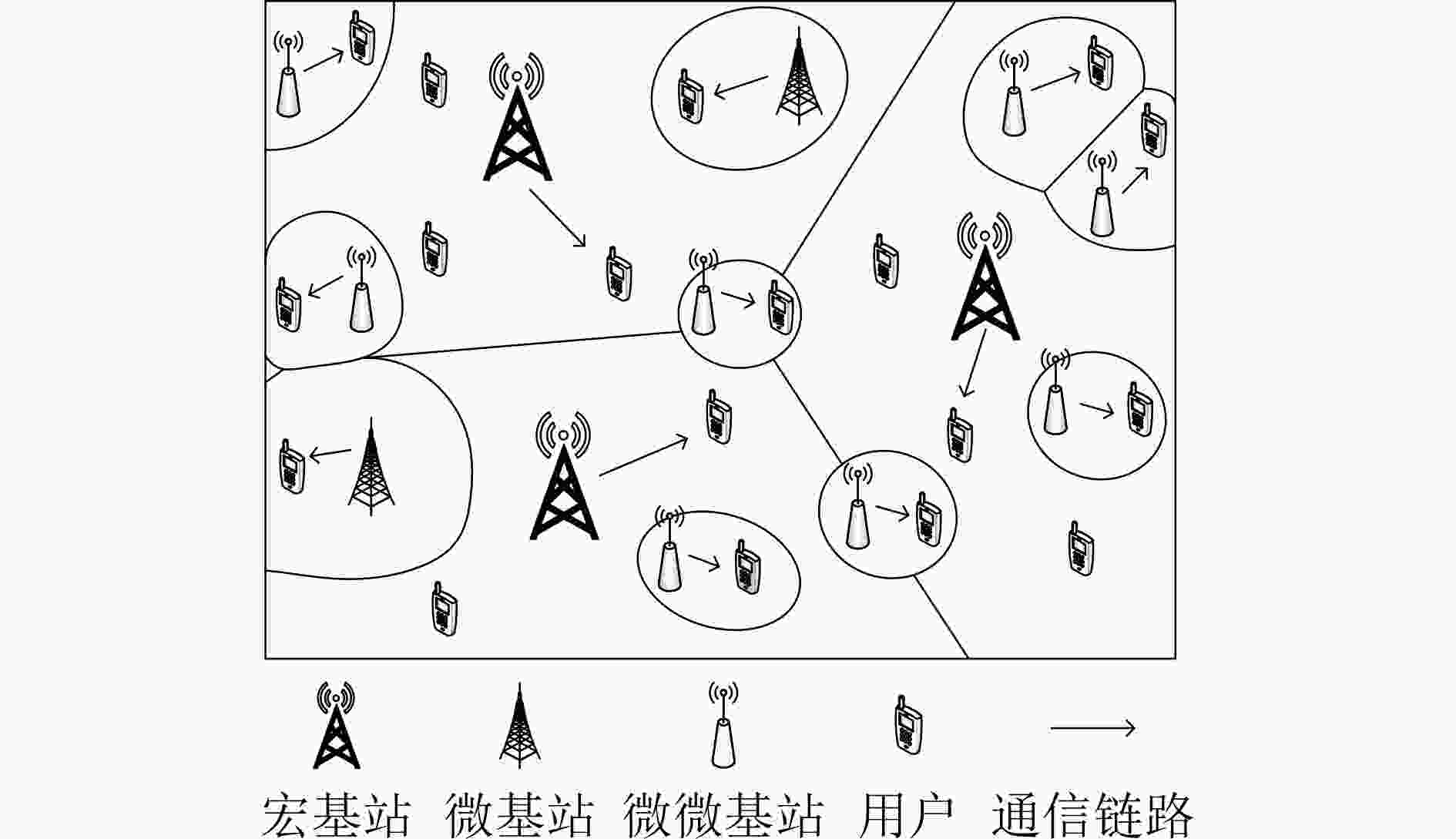
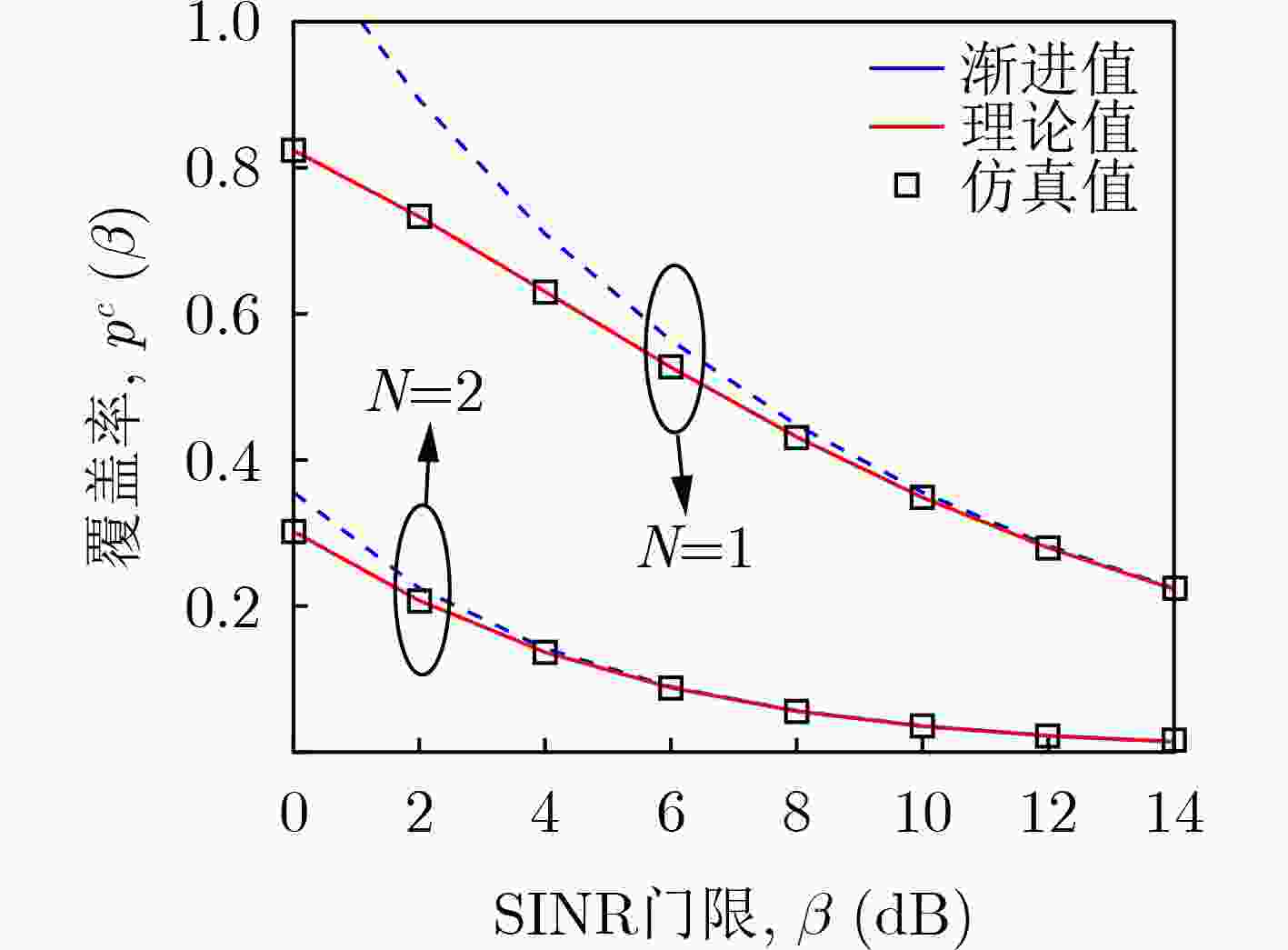
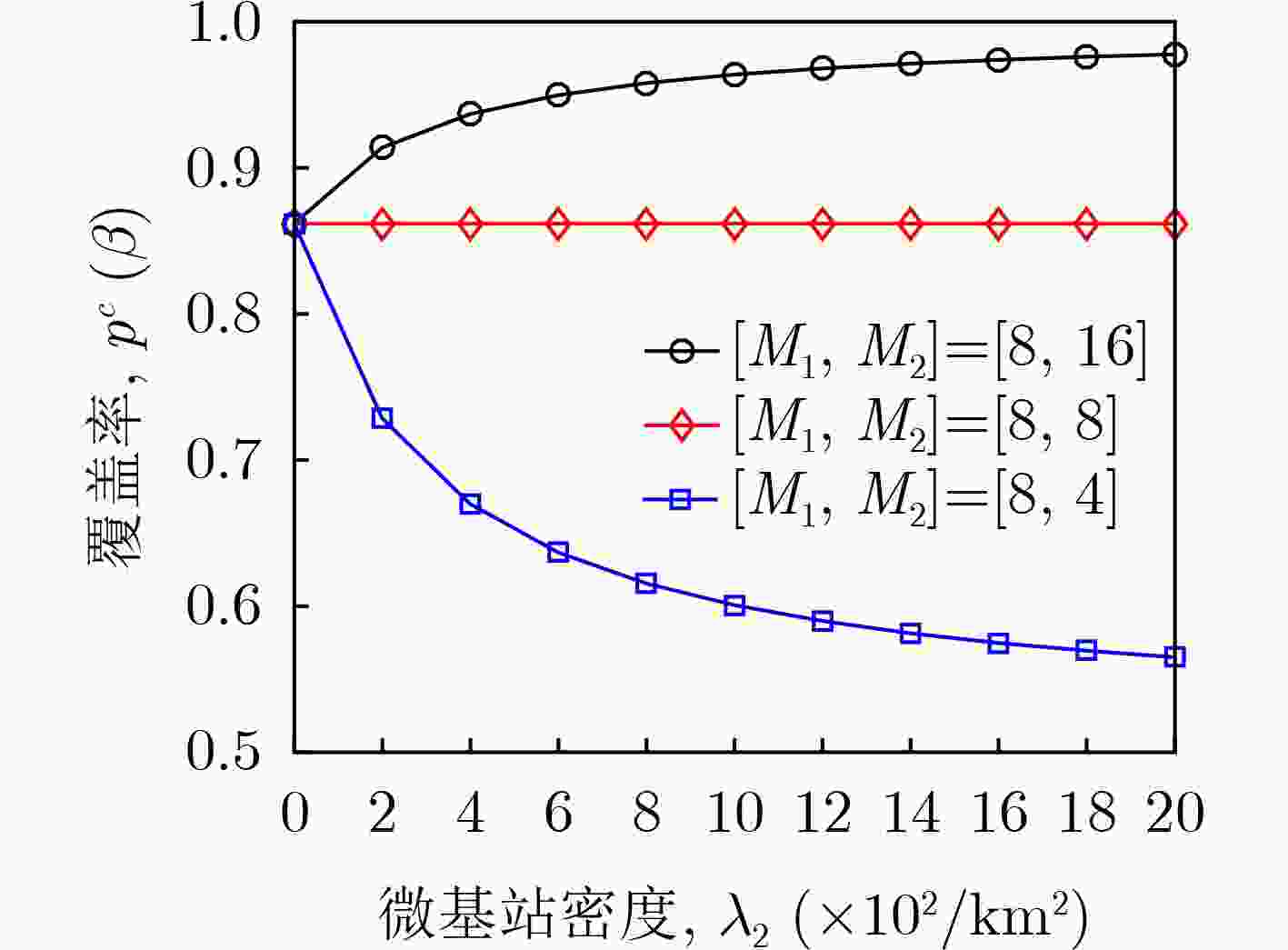
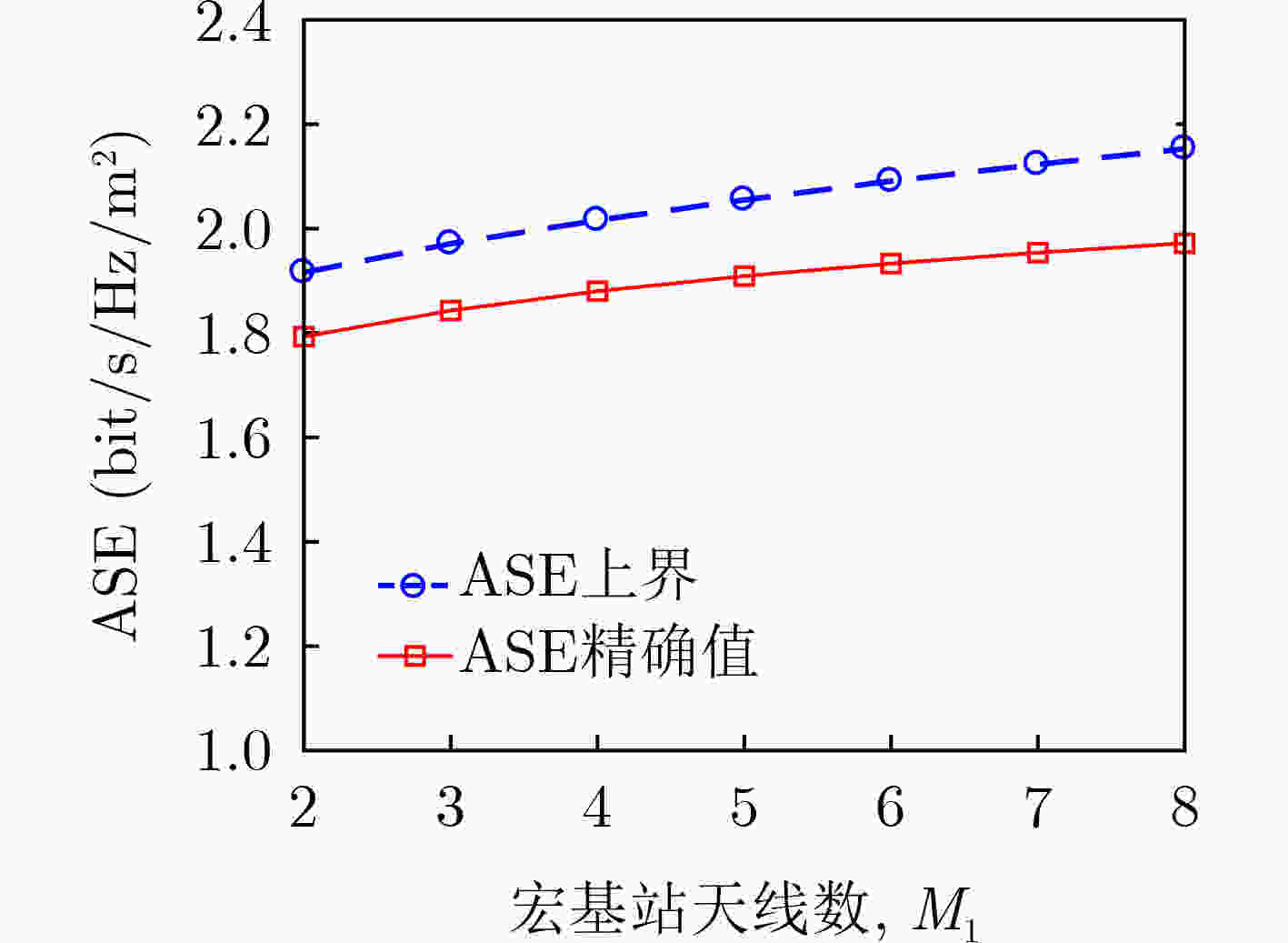
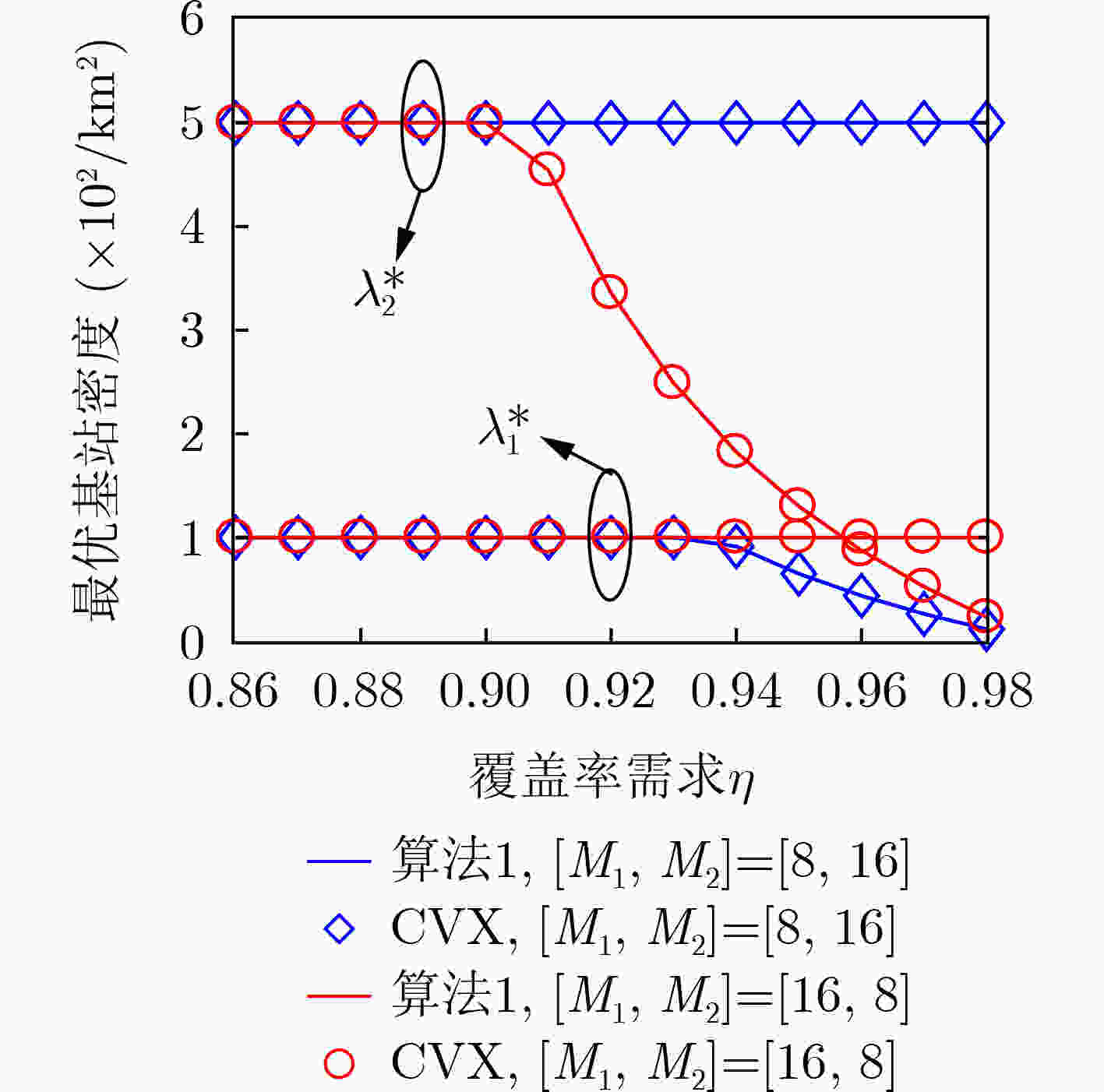
摘要: 无线网络的异构化、密集化部署极大地提高了系统容量,可满足用户日益增长的数据流量需求,但是复杂的网络结构、近乎随机的基站分布不利于系统的性能评估和参数设计。针对这一问题,该文提出一种适用于多天线密集异构网络的性能分析框架。首先,利用随机几何模型推导了覆盖率的闭合表达式并给出了优化方案。为了直观地观察关键系统参数对覆盖率的影响,还给出了一种渐近表达式。其次,推导了区域频谱效率(ASE)的积分表达式,为了减小计算复杂度,给出了一种ASE的上界。最后,还提出了一种有效的算法来设计最优的基站(BSs)部署密度,以在满足覆盖率需求的前提下最大化ASE。仿真结果验证了理论分析的正确性和所提优化算法的有效性。该文的研究成果不但可以为复杂网络的性能分析提供理论依据,还可为系统的优化与设计提供可行性方案。Abstract: The heterogeneous and intensive deployment of wireless network improves greatly the system capacity, which can meet the increasing data traffic demand of users. However, the complex network structure and almost random base station distribution are not conducive to the performance evaluation and parameter design of systems. Considering this problem, a performance analysis framework for multi-antenna dense heterogeneous networks is proposed. Firstly, resorting to stochastic geometry model, the closed-form expression of coverage probability is derived, and the optimization scheme is proposed. In order to observe intuitively the effects of key system parameters on coverage probability, an asymptotic expression is also given. Secondly, the integral expression of Area Spectral Efficiency (ASE) is derived. In order to reduce the computational complexity, an upper bound of ASE is provided. Finally, an effective algorithm is proposed to design the optimal active Base Stations (BSs) densities, maximizing the ASE with appropriate requirements of coverage probability. The simulation results verify the correctness of the theoretical analysis and the effectiveness of the proposed optimization algorithm. The research results of this paper can not only provide theoretical basis for the performance analysis of complex networks, but also provide feasible schemes for the optimization and design of systems.
-
表 1 最优基站部署方案求解算法(算法1)
输入:覆盖率需求$ \eta $ 输出:最优解$ {\lambda ^ * } $ (1) if $ \eta \mathop {\max }\limits_{k \in \mathcal{K}} p_k^{\rm{c}} \left( \beta \right)$ then (2) 没有可行解 (3) else (4) $ {\lambda ^ * } \leftarrow {\lambda ^{\max }} $ (5) while ${\boldsymbol{c}}{\lambda ^ * } < 0$且$\mathcal{K} \ne \varnothing$ do
(6) $ i = \arg \mathop {\min }\limits_{i \in \mathcal{K}} \dfrac{{{c_i}}}{{{b_i}}} $(7) $ \lambda _i^ * \leftarrow 0 $ (8) if ${\boldsymbol{c}}{\lambda ^ * } > 0$ then (9) $\lambda _i^ * \leftarrow - \dfrac{ {{\boldsymbol{c}}{\lambda ^ * } } }{ { {c_i} } }$ (10) end if (11) $ \mathcal{K}\leftarrow \mathcal{K}/\left\{i\right\} $ (12) end while (13) end if -
[1] LIU Guangyi, HUANG Yuhong, LI Na, et al. Vision, requirements and network architecture of 6G mobile network beyond 2030[J]. China Communications, 2020, 17(9): 92–104. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2020.09.008 [2] CHEN Shanzhi, SUN Shaohui, and KANG Shaoli. System integration of terrestrial mobile communication and satellite communication—the trends, challenges and key technologies in B5G and 6G[J]. China Communications, 2020, 17(12): 156–171. doi: 10.23919/JCC.2020.12.011 [3] ANDREEV S, PETROV V, DOHLER M, et al. Future of ultra-dense networks beyond 5G: Harnessing heterogeneous moving cells[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2019, 57(6): 86–92. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2019.1800056 [4] TENG Yinglei, LIU Mengting, YU F R, et al. Resource allocation for ultra-dense networks: A survey, some research issues and challenges[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2019, 21(3): 2134–2168. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2018.2867268 [5] 赵东来, 王钢, 郑黎明, 等. 超密集网络中非合作博弈的功率分配算法[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2020, 52(5): 30–34. doi: 10.11918/201910027ZHAO Donglai, WANG Gang, ZHENG Liming, et al. Optimal power allocation strategy in ultra-dense networks with non-cooperative game[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020, 52(5): 30–34. doi: 10.11918/201910027 [6] XIAO Jia, YANG Chungang, ANPALAGAN A, et al. Joint interference management in ultra-dense small-cell networks: A multi-domain coordination perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2018, 66(11): 5470–5481. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2851215 [7] ANDREWS J G, BACCELLI F, and GANTI R K. A tractable approach to coverage and rate in cellular networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2011, 59(11): 3122–3134. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2011.100411.100541 [8] DHILLON H S, GANTI R K, BACCELLI F, et al. Modeling and analysis of K-tier downlink heterogeneous cellular networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2012, 30(3): 550–560. doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2012.120405 [9] JO H S, SANG Y J, XIA Ping, et al. Heterogeneous cellular networks with flexible cell association: A comprehensive downlink SINR analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2012, 11(10): 3484–3495. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2012.081612.111361 [10] ZHAO Donglai, WANG Gang, JIA Shaobo, et al. Performance analysis of K-tier ultra-dense networks over Nakagami-m fading channels[C]. 2021 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), Nanjing, China, 2021: 1–6. [11] KHAN K S and JAMALIPOUR A. Coverage analysis for multi-request association model (MRAM) in a caching ultra-dense network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(4): 3882–3889. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2896604 [12] FILO M, FOH C H, VAHID S, et al. Performance analysis of ultra-dense networks with regularly deployed base stations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(5): 3530–3545. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2974729 [13] 贾向东, 路艺, 纪澎善, 等. 大规模无人机协助的多层异构网络设计及性能研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2632–2639. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200443JIA Xiangdong, LU Yi, JI Pengshan, et al. Design of large-scale UAV-assisted multi-tier heterogeneous networks and performance research[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2632–2639. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200443 [14] ZHANG Ruoyu, SHIM B, and ZHAO Honglin. Downlink compressive channel estimation with phase noise in massive MIMO systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2020, 68(9): 5534–5548. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2020.2998141 [15] LI Chang, ZHANG Jun, and LETAIEF K B. Throughput and energy efficiency analysis of small cell networks with multi-antenna base stations[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(5): 2505–2517. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.031714.131020 [16] DI RENZO M, GUIDOTTI A, and CORAZZA G E. Average rate of downlink heterogeneous cellular networks over generalized fading channels: A stochastic geometry approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 2013, 61(7): 3050–3071. doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2013.050813.120883 [17] WANG Rui, ZHANG Jun, SONG S H, et al. Average throughput analysis of downlink cellular networks with multi-antenna base stations[C]. The IEEE 25th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communication (PIMRC), Washington, USA, 2014: 1892–1896. [18] HEATH JR R W, WU Tao, KWON Y H, et al. Multiuser MIMO in distributed antenna systems with out-of-cell interference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2011, 59(10): 4885–4899. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2161985 [19] HE Anqi, WANG Lifeng, CHEN Yue, et al. Massive MIMO in K-tier heterogeneous cellular networks: Coverage and rate[C]. 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), San Diego, USA, 2015: 1–6. [20] BACCELLI F and BLASZCZYSZYN B. Stochastic Geometry and Wireless Networks[M]. Hanover: Now Publishers, 2009: 6–14. [21] GRADSHTEYN I S and RYZHIK I M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products[M]. 7th ed. San Diego: Academic Press, 2007: 1008–1009. -





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
