Occluded Object Segmentation Based on Bilayer Decoupling Strategy and Attention Mechanism
-
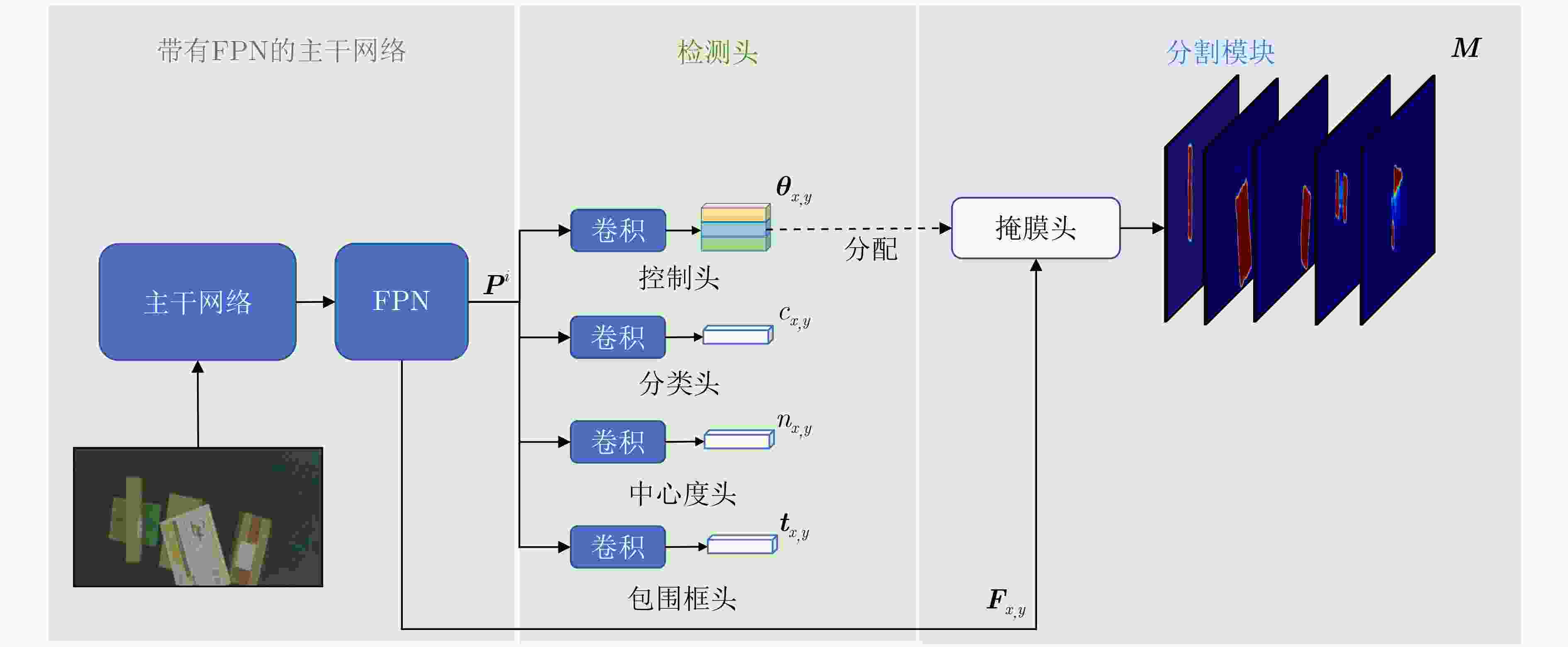
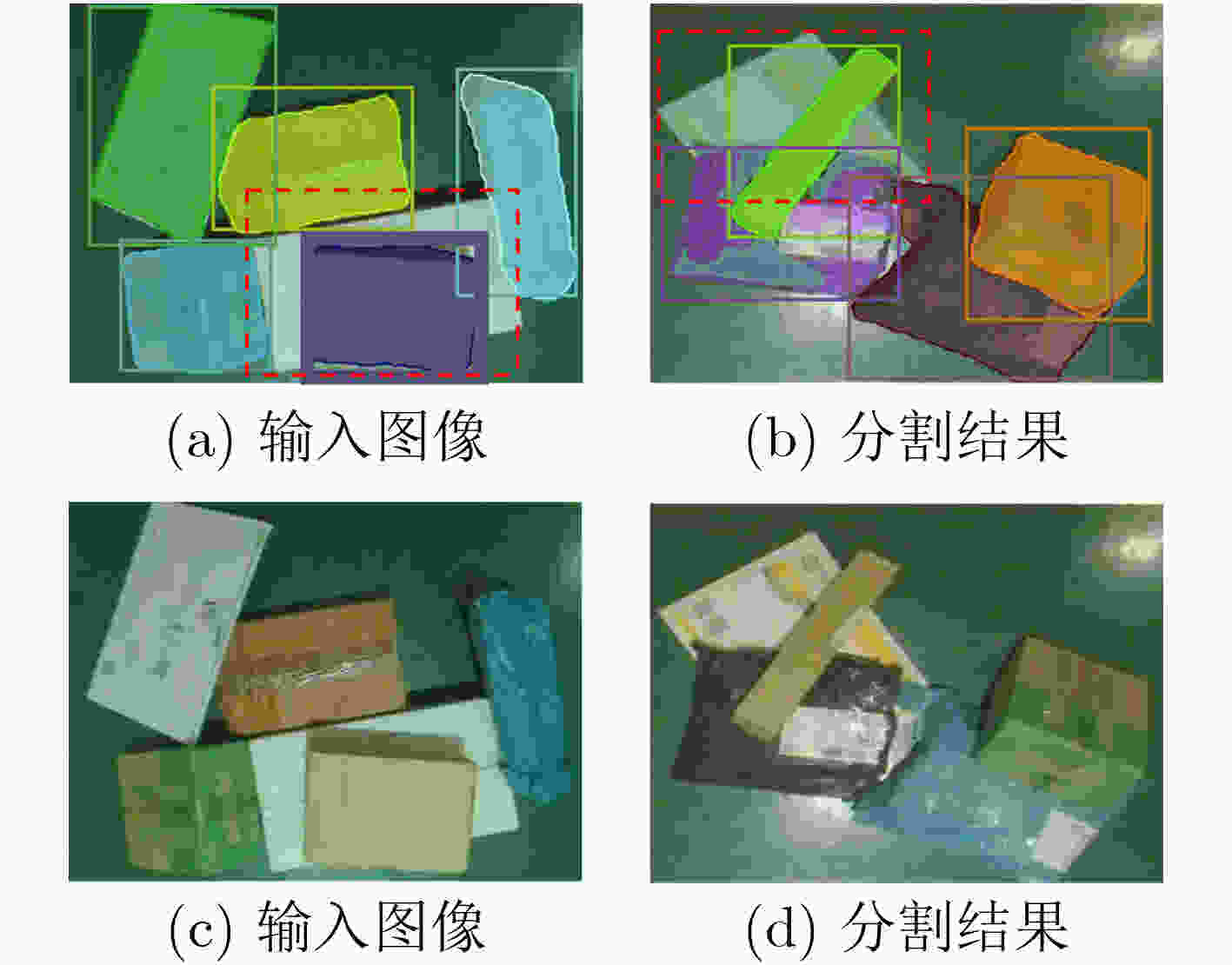
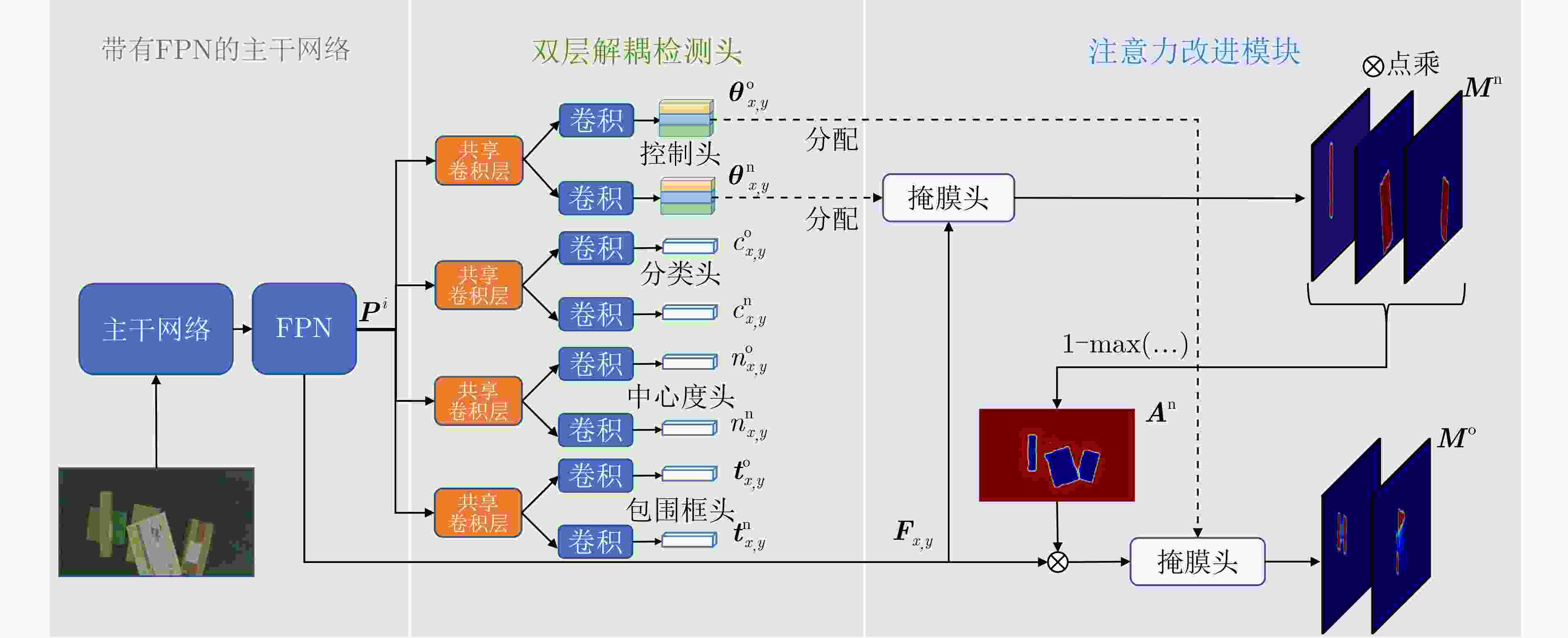
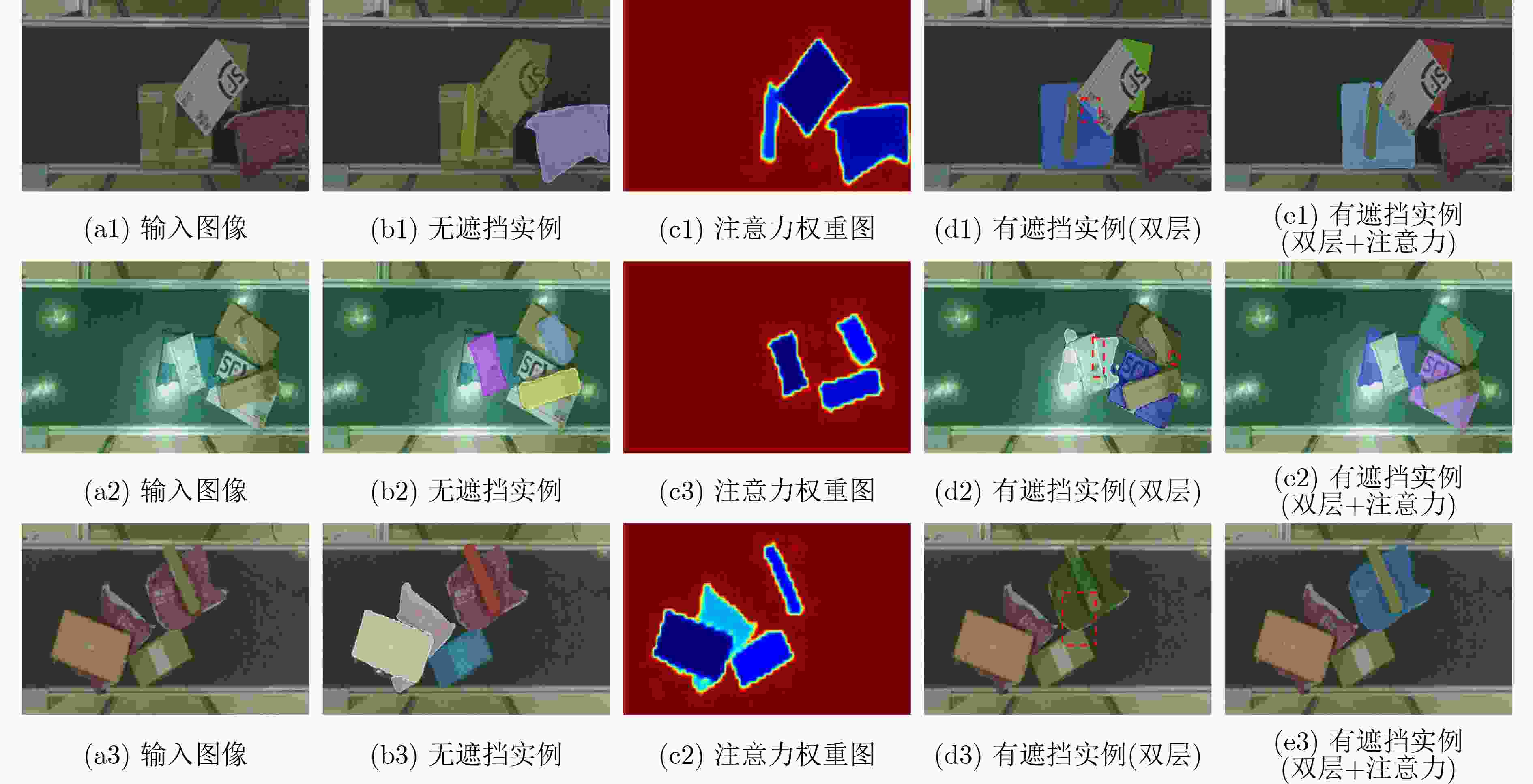
摘要: 遮挡目标分割是实例分割中的一个难点,但在多个应用领域有很强的实用价值,例如物流传输线上堆叠快递包裹的分割。针对快递包裹目标遮挡导致难以分割的问题,该文提出一种基于双层解耦策略和注意力机制的遮挡目标分割方法。该方法首先利用带有特征金字塔(FPN)的主干网络提取图像特征;然后,利用双层解耦检测头自动预测实例的重心是否被遮挡并使用不同的分支对两类不同遮挡类型的实例进行检测;接下来,利用注意力改进模块得到无遮挡实例的预测掩模并将这些掩模合成为一个注意力权重图;最后,注意力改进模块利用该注意力权重图帮助有遮挡实例得到分割结果。该研究采集了一个遮挡快递包裹实例分割数据集,并在该数据集上进行实验。实验结果表明,该方法的平均精度(AP)、召回率(Recall)和漏检率(MR–2)指标分别达到了95.66%, 97.17%和11.78%,较其他方法具有更优的分割性能。Abstract: Occluded object segmentation is a difficult problem in instance segmentation, but it has great practical value in many industrial applications such as stacked parcel segmentation on logistics automatic sorting. In this paper, an occluded object segmentation method based on bilayer decoupling strategy and attention mechanism is proposed to improve the segmentation performance of occluded parcels. Firstly, the image features are extracted through a backbone network with a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN); Secondly, the bilayer decoupling head is used to predict whether the mass centers of instances are occluded, and different occlusion types of instances are predicted through different branches; Thirdly, attention refinement module is used to obtain predicted masks of non-occluded instances and generate an attention map by combining these masks; Finally, this attention map is used to help the prediction of occluded instances. A dataset is provided for occluded parcel segmentation. Our method is tested on this dataset. The experimental results show that the proposed network achieves 95,66% Average Precision(AP), 97.17% Recall, and 11.78% Miss Rate(MR–2). It indicates that this method has better segmentation performance than other methods.
-
Key words:
- Image segmentation /
- Attention mechanism /
- Occluded object /
- Bilayer decoupling strategy
-
表 1 不同方法与不同NMS策略的分割结果(%)
NMS策略 方法 AP Recall MR–2 Box-NMS Mask RCNN 92.21 93.75 16.79 CondInst 92.17 93.27 15.96 CondInst+双层 92.83 94.38 18.96 CondInst+双层+注意力 94.94 96.00 15.47 Matrix-NMS Mask RCNN 91.12 91.54 16.94 CondInst 91.49 92.53 16.01 CondInst+双层 95.14 96.85 12.75 CondInst+双层+注意力 95.66 97.17 11.78 表 2 与遮挡目标检测方法比较的结果(%)
方法 AP Recall MR–2 CondInst+Soft-NMS 94.88 97.67 20.55 CrowdDet 94.22 96.00 17.85 本文方法(基于掩模) 94.72 96.74 14.82 本文方法(基于包围框头) 95.33 97.72 14.38 表 3 针对有遮挡实例和无遮挡实例的分割结果(%)
方法 无遮挡实例 有遮挡实例 AP AR AP AR CondInst 94.62 94.70 69.03 77.93 CondInst+双层 96.52 95.59 83.57 91.80 CondInst+双层+注意力 96.62 95.70 84.47 92.52 表 4 共享卷积层的数量对模型性能的影响
共享卷积层的数量 AP(%) Recall(%) MR–2(%) 4 95.12 97.11 17.45 3 95.22 96.53 12.87 2 95.66 97.17 11.78 1 95.42 96.87 10.87 0 95.32 96.78 11.23 表 5 不同置信度阈值
$ \sigma $ 对模型性能的影响置信度阈值$ \sigma $ AP(%) Recall(%) MR–2(%) 0.50 95.27 96.45 12.41 0.60 95.32 96.48 12.10 0.65 95.66 97.17 11.78 0.70 95.31 96.32 12.07 0.90 94.26 95.68 14.79 1.00 94.21 95.60 14.79 -
[1] HE Kaiming, GKIOXARI G, DOLLÁR P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 2980–2988. [2] PENG Sida, JIANG Wen, PI Huaijin, et al. Deep snake for real-time instance segmentation[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 8530–8539. [3] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]. The 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 91–99. [4] TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, and CHEN Hao. Conditional convolutions for instance segmentation[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 282–298. [5] XIE Enze, SUN Peize, SONG Xiaoge, et al. PolarMask: Single shot instance segmentation with polar representation[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 12190–12199. [6] WANG Xinlong, KONG Tao, SHEN Chunhua, et al. SOLO: Segmenting objects by locations[C]. The 16th European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 2020: 649–665. [7] WANG Xinlong, ZHANG Rufeng, KONG Tao, et al. SOLOv2: Dynamic and fast instance segmentation[C/OL]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020: 17721–17732. [8] ZHANG Rufeng, TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, et al. Mask encoding for single shot instance segmentation[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 10223–10232. [9] ZHANG Shifeng, WEN Longyin, BIAN Xiao, et al. Occlusion-aware R-CNN: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd[C]. The 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 2018: 657–674. [10] WANG Xinlong, XIAO Tete, JIANG Yuning, et al. Repulsion loss: Detecting pedestrians in a crowd[C]. The 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA, 2018: 7774–7783. [11] BODLA N, SINGH B, CHELLAPPA R, et al. Soft-NMS—improving object detection with one line of code[C]. The 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 2017: 5562–5570. [12] HE Yihui, ZHU Chenchen, WANG Jianren, et al. Bounding box regression with uncertainty for accurate object detection[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 2883–2892. [13] HOSANG J, BENENSON R, and SCHIELE B. Learning non-maximum suppression[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 6469–6477. [14] QI Lu, LIU Shu, SHI Jianping, et al. Sequential context encoding for duplicate removal[C]. The 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montréal, Canada, 2018: 2053–2062. [15] HOSANG J, BENENSON R, and SCHIELE B. A convnet for non-maximum suppression[C]. The 38th German Conference on Pattern Recognition, Hannover, Germany, 2016: 192–204. [16] LIU Songtao, HUANG Di, and WANG Yunhong. Adaptive NMS: Refining pedestrian detection in a crowd[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA, 2019: 6452–6461. [17] STEWART R, ANDRILUKA M, and NG A Y. End-to-end people detection in crowded scenes[C]. The 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA, 2016: 2325–2333. [18] RUKHOVICH D, SOFIIUK K, GALEEV D, et al. IterDet: Iterative scheme for object detection in crowded environments[C]. Joint IAPR International Workshops on Statistical Techniques in Pattern Recognition (SPR) and Structural and Syntactic Pattern Recognition (SSPR), Padua, Italy, 2021: 344–354. [19] CHU Xuangeng, ZHENG Anlin, ZHANG Xiangyu, et al. Detection in crowded scenes: One proposal, multiple predictions[C]. The 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, USA, 2020: 12211–12220. [20] LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]. The 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA, 2017: 936–944. [21] TIAN Zhi, SHEN Chunhua, CHEN Hao, et al. FCOS: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection[C]. The 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 2019: 9626–9635. [22] DOLLAR P, WOJEK C, SCHIELE B, et al. Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(4): 743–761. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.155 -





 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
