Variational Bayesian Inference Based Direction Of Arrival Estimation in Presence of Shallow Water Non-Gaussian Noise
-
摘要: 传统基于高斯统计特性的波达角(DOA)估计方法在高斯背景噪声中可以获得较好的估计性能,然而受脉冲噪声影响的浅海环境噪声不再服从高斯分布,若直接利用传统波达角估计方法会引入较大误差。为提升非高斯噪声环境下的波达角估计性能,该文提出一种浅海非高斯噪声下的基于变分贝叶斯推断的波达角估计方法。首先利用信号与脉冲噪声的稀疏性构建多测量向量稀疏信号恢复(SSR)模型;其次,考虑信号的共稀疏特性与脉冲噪声的独立稀疏性,构建层次化贝叶斯估计框架;然后利用变分贝叶斯推断估计信号与噪声的后验概率估计。稀疏信号模型中考虑离网格误差,利用根稀疏贝叶斯估计实现离网格误差修正,解决离网格误差引起的基失配问题;最后通过迭代更新获得较为精确的波达角估计,同时消除脉冲噪声的影响。仿真结果表明:所提方法在非高斯噪声环境下具有较好的波达角估计性能,同时对于脉冲噪声具有较强的抗干扰特性。Abstract: Conventional Direction Of Arrival (DOA) estimators achieve satisfactory performance with the common assumptions of Gaussian noise. However, the impulsive noise exists in the shallow water extensively and does not follow the Gaussian distribution, which induce undesirable biases and degrade the performance of the conventional estimators. In the paper, a new DOA estimation method based on variational Bayesian inference in presence of shallow water non-Gaussian noise is proposed to improve the DOA estimation performance. Firstly, the multiple measurement vectors Sparse Signal Representation (SSR) model is formulated utilizing the sparsity of signal and impulsive noise. After that, the hierarchical Bayesian estimation framework is formulated which considers the common sparsity of signal and the independent sparsity of impulsive noise. Subsequently, the variational Bayesian inference is utilized to achieve the posterior estimations for the signal and impulsive noise. The SSR model incorporates the off-grid bias, and the root sparse Bayesian learning realizes to refine the bias and mitigate the basis mismatches. At last, the accurate DOA estimation is achieved through iterative updates and the effects of impulsive noise are mitigated. Simulations are used to verify that the proposed estimator achieves superior performance compared with state-of-art benchmarks.
-
表 1 浅海噪声参数拟合
噪声模型 参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 ${{{\rm{S}}\alpha {\rm{S}}} }$噪声 $ \alpha $ 1.3401 1.4369 1.3767 1.5134 1.1419 1.6236 $ \chi $ 0.0224 0.0455 0.0308 0.2085 0.0538 -0.0021 $ \gamma $ 0.8838 0.9349 0.9543 0.8637 1.1959 0.6863 $ \psi $ 0.0478 0.0567 0.0376 0.1197 0.1803 -0.0253 GMM噪声 $ \mu $ 0.0828 0.0735 0.0838 0.0962 0.1430 0.0632 $ \sigma _1^2 $ 1.7591 1.8785 1.9661 1.4830 2.9481 1.0192 $ \kappa $ 132 91.2 76.78 35.6 91.32 145 -
[1] WU Wenqian, GAO Xiqi, SUN Chen, et al. Shallow underwater acoustic massive MIMO communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2021, 69: 1124–1139. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2021.3050037 [2] CHEN Wen, ZHANG Wen, WU Yanqun, et al. Joint algorithm based on interference suppression and Kalman filter for bearing-only weak target robust tracking[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 131653–131662. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2940956 [3] ZHANG Xuebo, WU Haoran, SUN Haixin, et al. Multireceiver SAS imagery based on monostatic conversion[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 10835–10853. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3121405 [4] ZHANG Xuebo, YANG Peixuan, TAN Cheng, et al. BP algorithm for the multireceiver SAS[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13(5): 830–838. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2018.5468 [5] ZHANG Xuebo, YANG Peixuan, and DAI Xuntao. Focusing multireceiver SAS data based on the fourth-order legendre expansion[J]. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2019, 38(6): 2607–2629. doi: 10.1007/s00034-018-0982-6 [6] ZHANG Xuebo, YING Wenwei, YANG Peixuan, et al. Parameter estimation of underwater impulsive noise with the Class B model[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(7): 1055–1060. doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2019.0477 [7] ZHANG Xuebo, YING Wenwei, and YANG Bo. Parameter estimation for class a modeled ocean ambient noise[J]. Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences, 2018, 50(3): 330–345. doi: 10.5614/j.eng.technol.sci.2018.50.3.2 [8] ZHOU Mingzhang, WANG Junfeng, FENG Xiao, et al. On generative-adversarial-network-based underwater acoustic noise modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(9): 9555–9559. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3102302 [9] MAHMOOD A, CHITRE M, and VISHNU H. Locally optimal inspired detection in snapping shrimp noise[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2017, 42(4): 1049–1062. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2017.2731058 [10] CHITRE M A, POTTER J R, and ONG S H. Optimal and near-optimal signal detection in snapping shrimp dominated ambient noise[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2006, 31(2): 497–503. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2006.875272 [11] WANG Shuche, HE Zhiqiang, NIU Kai, et al. New results on joint channel and impulsive noise estimation and tracking in underwater acoustic OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19(4): 2601–2612. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2966622 [12] PELEKANAKIS K and CHITRE M. Adaptive sparse channel estimation under symmetric alpha-stable noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13(6): 3183–3195. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2014.042314.131432 [13] TSAKALIDES P and NIKIAS C L. The robust covariation-based MUSIC (ROC-MUSIC) algorithm for bearing estimation in impulsive noise environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1996, 44(7): 1623–1633. doi: 10.1109/78.510611 [14] LIU T H and MENDE J M. A subspace-based direction finding algorithm using fractional lower order statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2001, 49(8): 1605–1613. doi: 10.1109/78.934131 [15] ZENG Wenjun, SO H C, and HUANG Lei. ℓ p-MUSIC: Robust direction-of-arrival estimator for impulsive noise environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(17): 4296–4308. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2013.2263502 [16] 王汗青, 王平波, 王树宗. 基于SαS分布的水声信号自适应波束形成算法[J]. 船海工程, 2012, 41(4): 165–167. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2012.04.045WANG Hanqing, WANG Pingbo, and WANG Shuzong. Adaptive beam-forming algorithm for underwater acoustic signal based on α-Stable distribution[J]. Ship &Ocean Engineering, 2012, 41(4): 165–167. doi: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-7953.2012.04.045 [17] ZHA Daifeng and QIU Tianshuang. Underwater sources location in non-Gaussian impulsive noise environments[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2006, 16(2): 149–163. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2005.04.008 [18] MADADI Z, ANAND G V, and PREMKUMAR A B. 3-D source localization in shallow ocean with non-Gaussian noise using a linear array of acoustic vector sensors[C]. 2012 11th International Conference on Information Science, Signal Processing and their Applications (ISSPA), Montreal, Canada, 2012: 1353–1358. [19] SHI Yunmei, MAO Xingpeng, QIAN Cheng, et al. Robust relaxation for coherent DOA estimation in impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(3): 410–414. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2018.2889913 [20] ZHANG Jiacheng, QIU Tianshuang, and LUAN Shengyang. Robust sparse representation for DOA estimation with unknown mutual coupling under impulsive noise[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2020, 24(7): 1455–1458. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.2983038 [21] SHI Yunmei, MAO Xingpeng, ZHAO Chunlei, et al. Underdetermined DOA estimation for wideband signals via joint sparse signal reconstruction[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2019, 26(10): 1541–1545. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2019.2937381 [22] GEMBA K L, NANNURU S, and GERSTOFT P. Robust ocean acoustic localization with sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2019, 13(1): 49–60. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2019.2900912 [23] TIPPING M E. Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine[J]. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 1: 211–244. doi: 10.1162/15324430152748236 [24] DAS A. Real-valued sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation in ocean acoustics[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2021, 46(1): 172–182. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2020.2981102 [25] DAS A. Deterministic and Bayesian sparse signal processing algorithms for coherent multipath directions-of-arrival (DOAs) estimation[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 44(4): 1150–1164. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2018.2851119 [26] DAS A and SEJNOWSKI T J. Narrowband and wideband off-grid direction-of-arrival estimation via sparse Bayesian learning[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2018, 43(1): 108–118. doi: 10.1109/JOE.2017.2660278 [27] DAI Jisheng and SO H C. Sparse Bayesian learning approach for outlier-resistant direction-of-arrival estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(3): 744–756. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2017.2773420 [28] TZIKAS D G, LIKAS A C, and GALATSANOS N P. The variational approximation for Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2008, 25(6): 131–146. doi: 10.1109/msp.2008.929620 [29] WAN Qian, DUAN Huiping, FANG Jun, et al. Robust Bayesian compressed sensing with outliers[J]. Signal Processing, 2017, 140: 104–109. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2017.05.017 [30] YANG Zai, XIE Lihua, and ZHANG Cishen. Off-grid direction of arrival estimation using sparse Bayesian inference[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2013, 61(1): 38–43. doi: 10.1109/tsp.2012.2222378 [31] DAI Jisheng, BAO Xu, XU Weichao, et al. Root sparse Bayesian learning for off-grid DOA estimation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2017, 24(1): 46–50. doi: 10.1109/lsp.2016.2636319 -





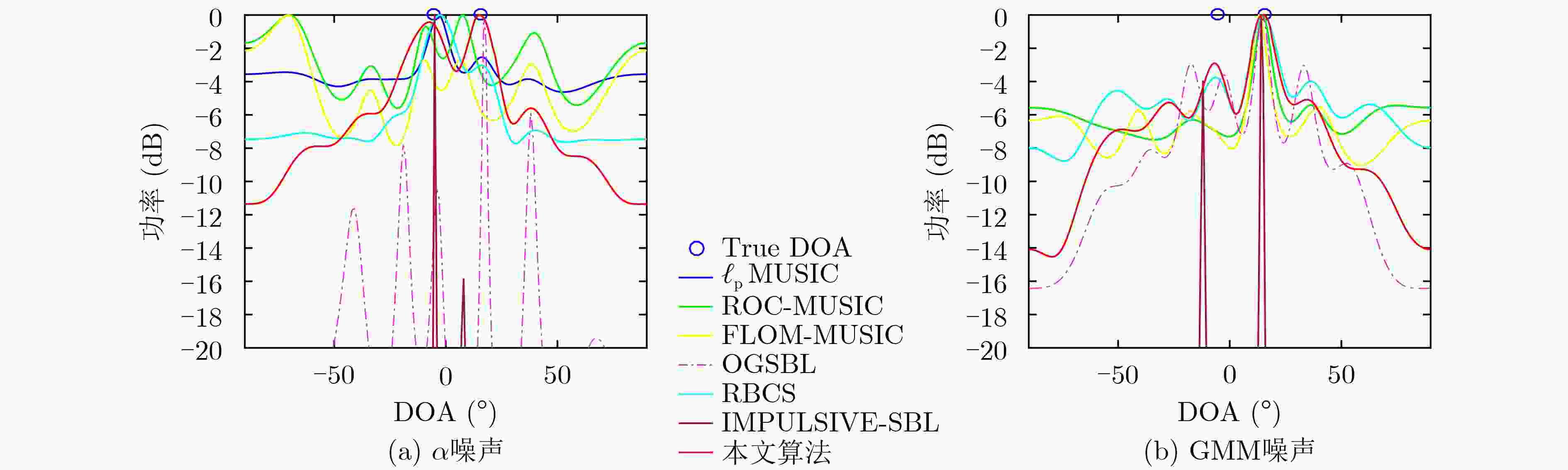
 下载:
下载:
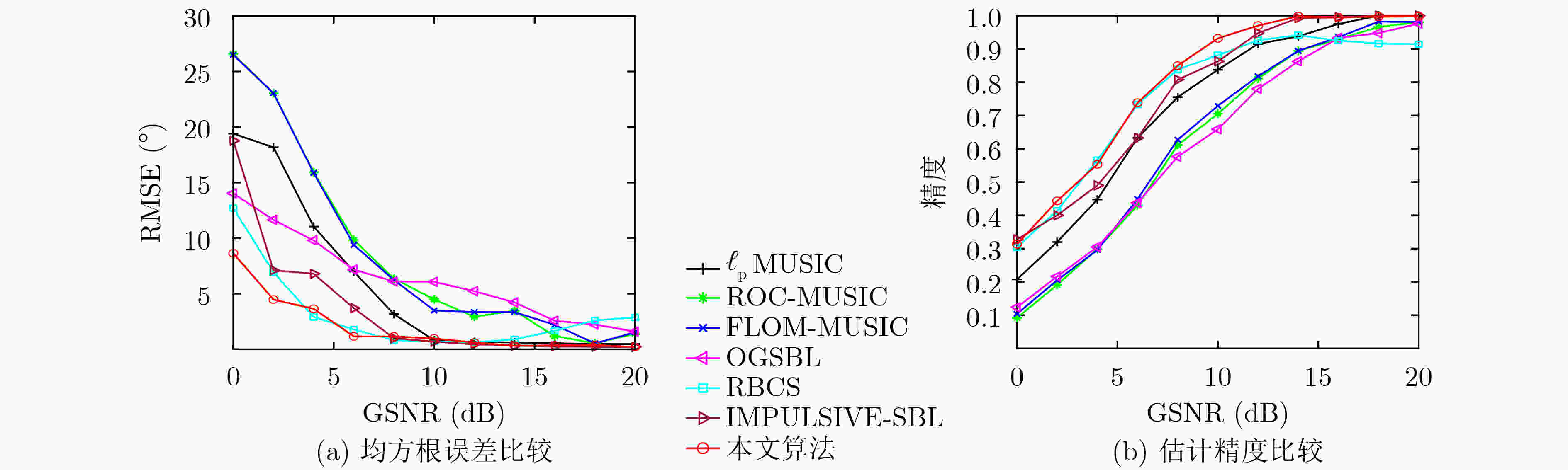
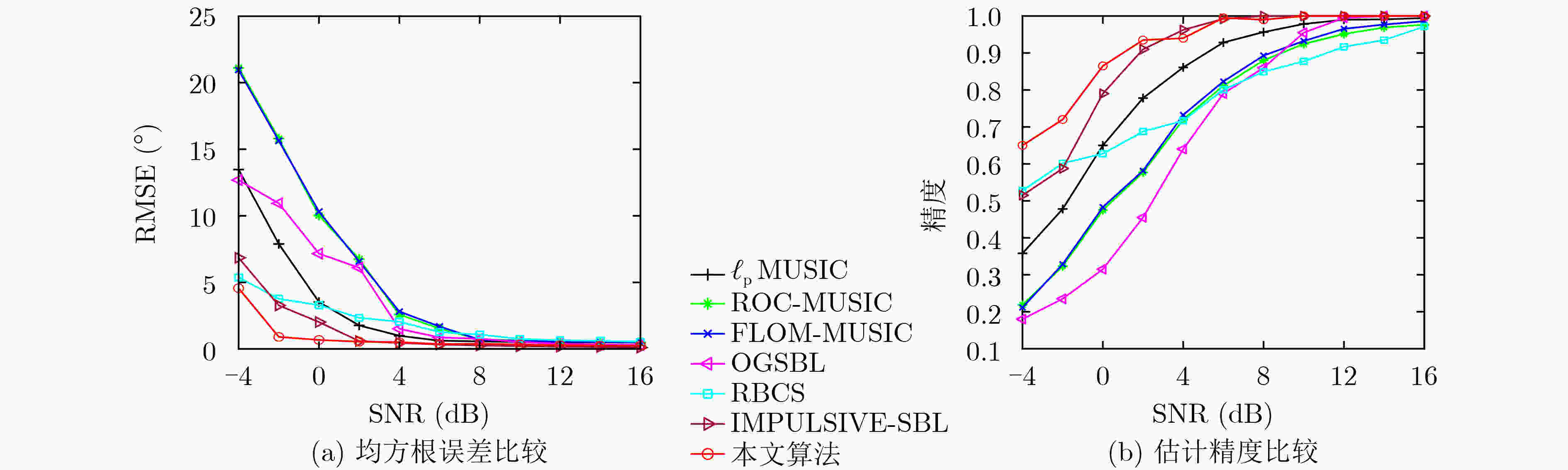



 下载:
下载:
