A Human Target Detection Method under Complex Conditions by Distributed Through-Wall Radar System
-
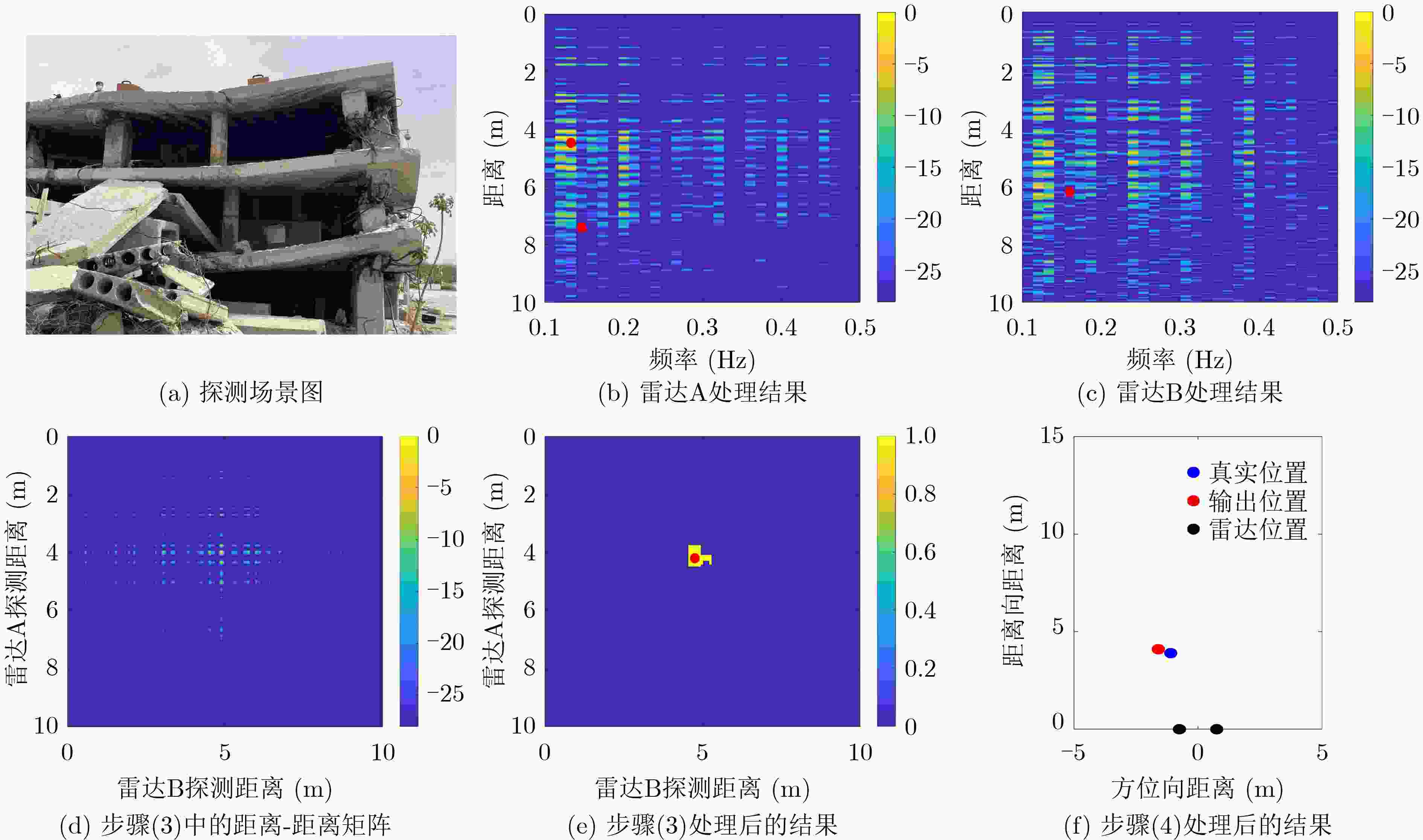
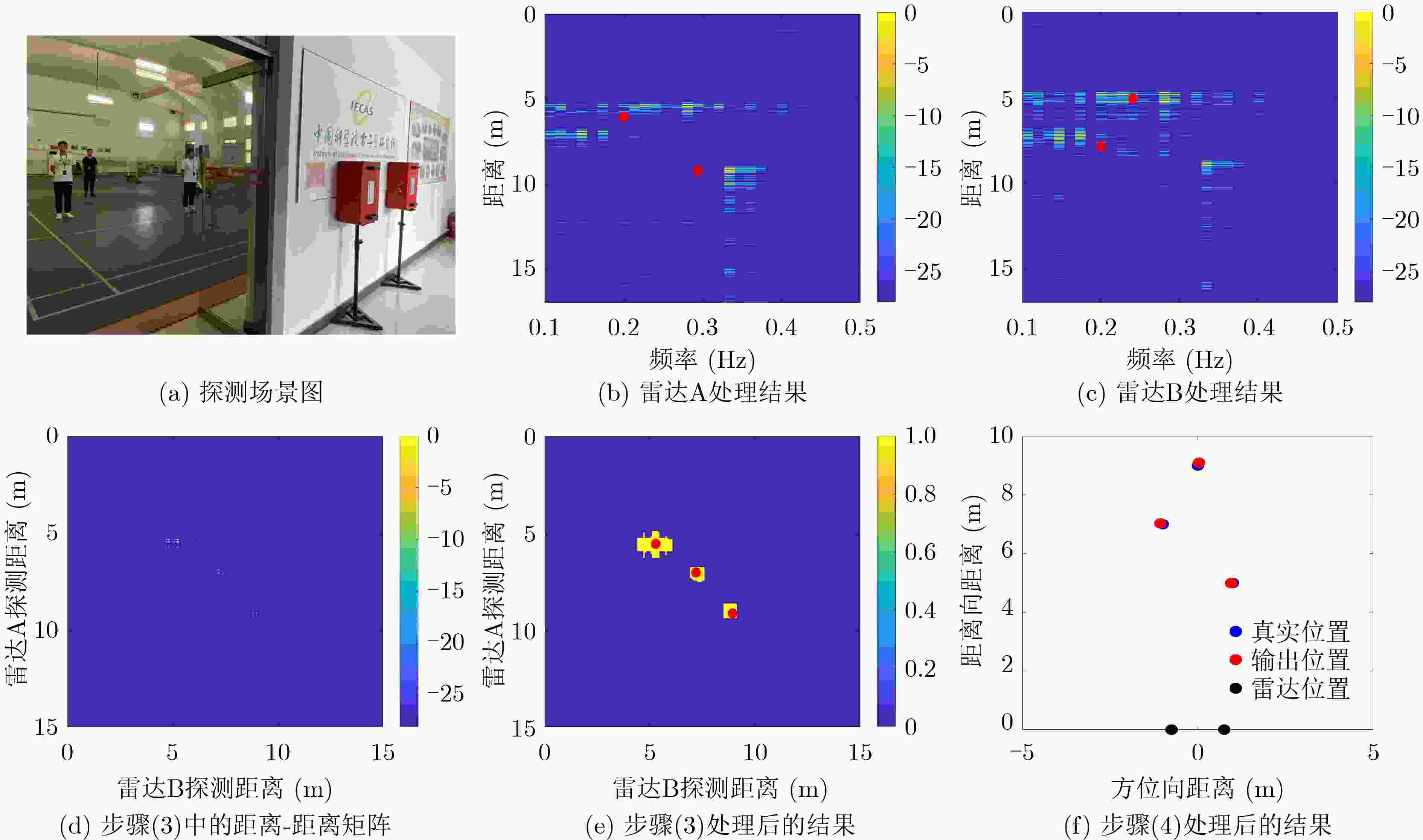
摘要: 超宽带雷达由于具有距离分辨率高、穿透性强等特点,被广泛应用于废墟下的人体救援。然而,在复杂的环境条件下,依靠单台雷达对被困人员进行检测是一个巨大的挑战。该文基于分布式穿墙雷达系统,提出一种低信噪比条件下的人体目标自动检测方法。首先,两台超宽带脉冲雷达分时交替进行工作,从而避免探测时的互相干扰;然后对两台雷达的回波数据进行慢时间维度互相关处理,增强人体呼吸信号;其次,利用适配于分布式穿墙雷达的恒虚警率检测,实现人体呼吸信号的快速、自动检测;最后,通过三角定位方法实现被困人员的2维定位。一系列的实验结果表明,所提方法可以在低信噪比条件下实现人体的检测,其探测性能优于单台雷达。Abstract: Ultra-wideband radar is widely used for human rescue under ruins, due to its high range resolution and high penetration capability. However, it is difficult to rely on a single radar to detect trapped persons, under complex conditions. In this paper, a human respiration detection method under low Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) conditions by distributed through-wall radar is proposed. First, two ultra-wideband impulse radars use time-division multiplexing to prevent mutual interference. Secondly, the slow-time dimension cross-correlation processing is performed on the echo data of the two radars to enhance the human respiration signal. Thirdly, the automatic detection algorithm is improved based on constant false alarm ratio to make it suitable for the distributed through-wall radar and realize automatic and fast detection. Finally, the trilateration algorithm is used to locate the trapped persons. A series of experimental results show that the method proposed can realize human detection under low SNR conditions, and its detection performance is better than that of a single radar.
-
Key words:
- Through-wall radar /
- Distributed radar /
- Target detection
-
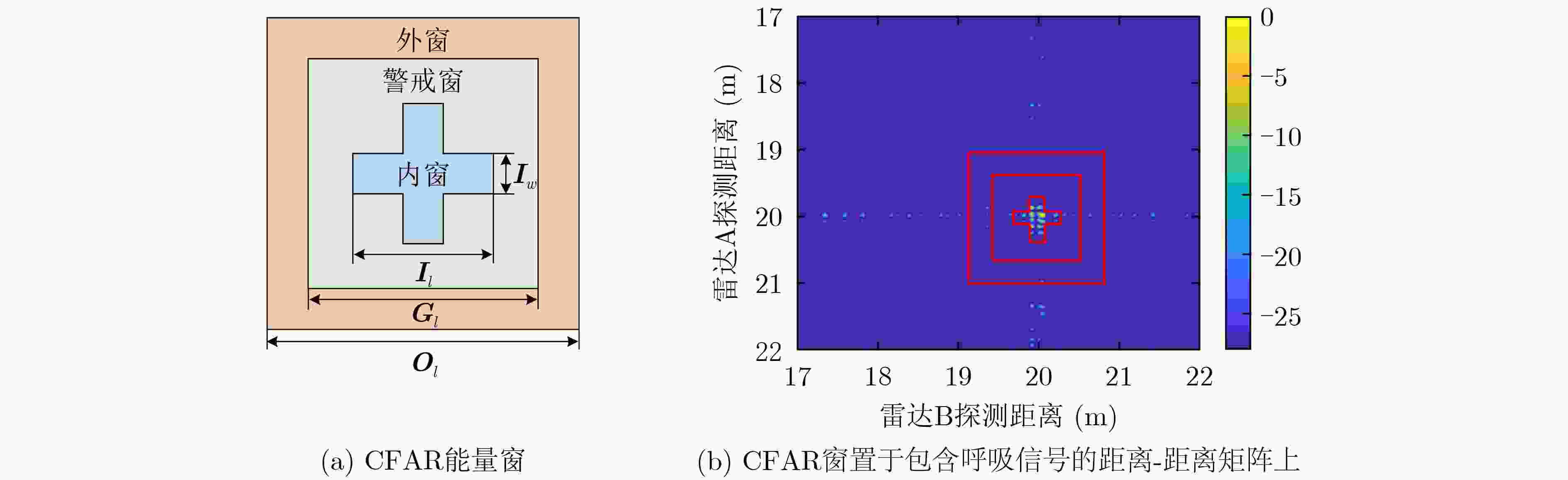
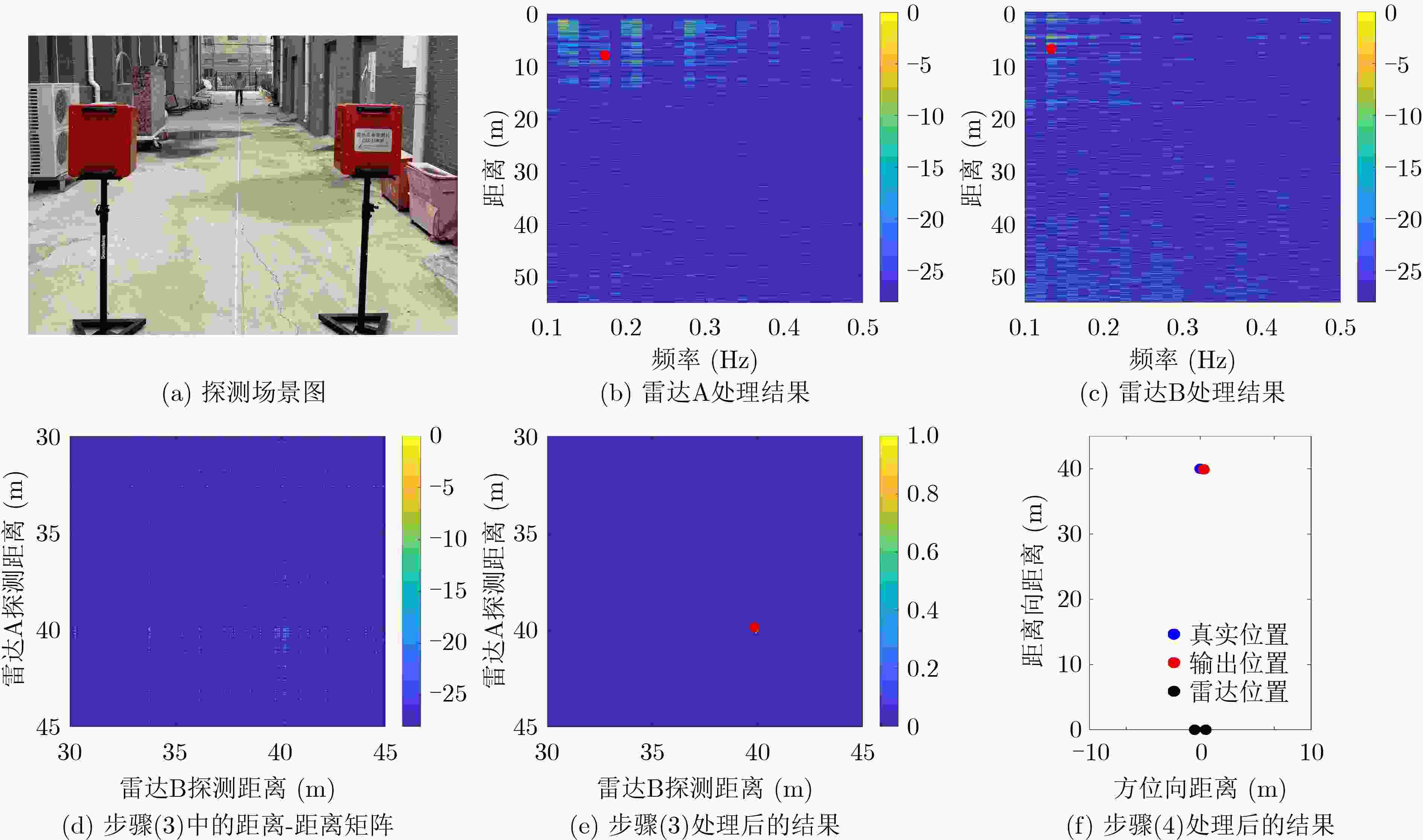
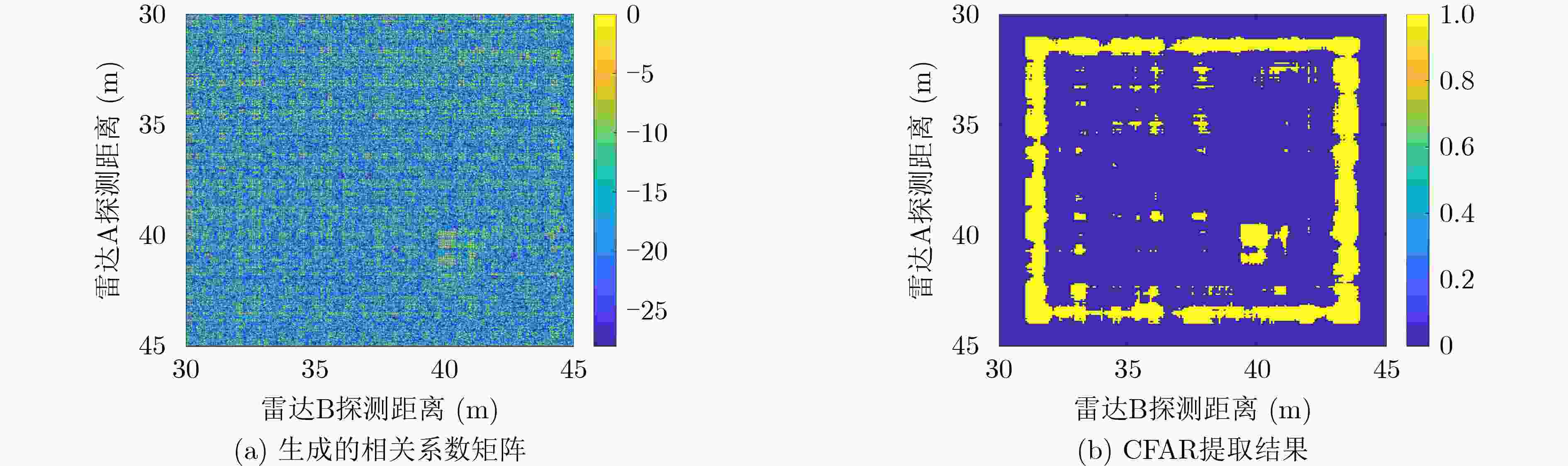
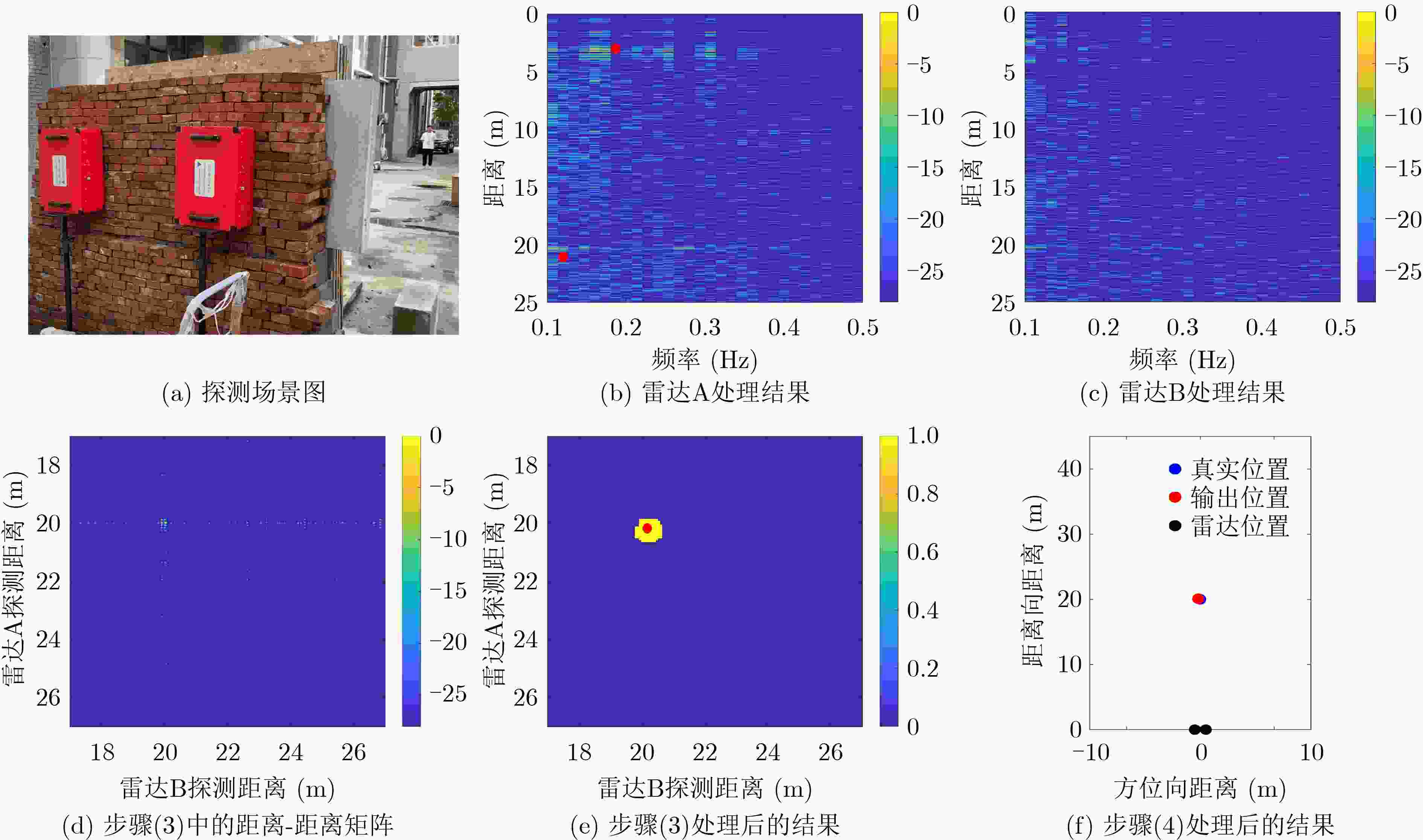
图 7 文献[13]的方法处理结果
表 1 分布式穿墙雷达参数
参数 参数值 脉冲波形 高斯脉冲 中心频率 500 MHz 脉冲重频 32 kHz 快时间采样率 16 GHz 慢时间采样率 8 Hz 采样点数 4096 表 2 不同算法的运行时间对比(s)
文献[13]的算法 算法A 所提算法 运算时间 1.01 112.19 3.27 -
[1] 杨望笑, 窦银科, 稂时楠, 等. 基于改进剥层法的南极冰盖密度反演算法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(4): 1311–1317.YANG Wangxiao, DOU Yinke, LANG Shinan, et al. Antarctic ice sheet density inversion algorithm based on improved layer stripping method[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(4): 1311–1317. [2] 金添, 宋勇平, 崔国龙, 等. 低频电磁波建筑物内部结构透视技术研究进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119JIN Tian, SONG Yongping, CUI Guolong, et al. Advances on penetrating imaging of building layout technique using low frequency radio waves[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10(3): 342–359. doi: 10.12000/JR20119 [3] 金添, 宋勇平. 穿墙雷达人体目标探测技术综述[J]. 电波科学学报, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804JIN Tian and SONG Yongping. Review on human target detection using through-wall radar[J]. Chinese Journal of Radio Science, 2020, 35(4): 486–495. doi: 10.13443/j.cjors.2020040804 [4] ROHMAN B P A, ANDRA M B, and NISHIMOTO M. Through-the-wall human respiration detection using UWB impulse radar on hovering drone[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6572–6584. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3087668 [5] YAN Kun, WU Shiyou, and FANG Guangyou. Detection of quasi-static trapped human being using mono-static UWB life-detection radar[J]. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(7): 3129. doi: 10.3390/app11073129 [6] HARIKESH D, CHAUHAN S S, BASU A, et al. Through the wall human subject localization and respiration rate detection using multichannel Doppler radar[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(2): 1510–1518. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3016755 [7] BROWNE K E, BURKHOLDER R J, and VOLAKIS J L. Through-wall opportunistic sensing system utilizing a low-cost flat-panel array[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2011, 59(3): 859–868. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2010.2103015 [8] LI Zhao, LI Wenzhe, LV Hao, et al. A novel method for respiration-like clutter cancellation in life detection by dual-frequency IR-UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 2013, 61(5): 2086–2092. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2247054 [9] XU Yanyun, DAI Shun, WU Shiyou, et al. Vital sign detection method based on multiple higher order cumulant for ultrawideband radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(4): 1254–1265. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2164928 [10] NEZIROVIC A, YAROVOY A G, and LIGTHART L P. Signal processing for improved detection of trapped victims using UWB radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2010, 48(4): 2005–2014. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2036840 [11] KOCUR D, ŠVECOVÁ M, and ROVŇÁKOVÁ J. Through-the-wall localization of a moving target by two independent ultra wideband (UWB) radar systems[J]. Sensors, 2013, 13(9): 11969–11997. doi: 10.3390/s130911969 [12] NARAYANAN R M, GEBHARDT E T, and BRODERICK S P. Through-wall single and multiple target imaging using MIMO radar[J]. Electronics, 2017, 6(4): 70. doi: 10.3390/electronics6040070 [13] JIA Yong, GUO Yong, YAN Chao, et al. Detection and localization for multiple stationary human targets based on cross-correlation of dual-station SFCW radars[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(12): 1428. doi: 10.3390/rs11121428 [14] NAHAR S, PHAN T, QUAIYUM F, et al. An electromagnetic model of human vital signs detection and its experimental validation[J]. IEEE Journal on Emerging and Selected Topics in Circuits and Systems, 2018, 8(2): 338–349. doi: 10.1109/JETCAS.2018.2811339 [15] ZETIK R, CRABBE S, KRAJNAK J, et al. Detection and localization of persons behind obstacles using M-sequence through-the-wall radar[C]. Proceedings of SPIE 6201, Sensors, and Command, Control, Communications, and Intelligence (C3I) Technologies for Homeland Security and Homeland Defense V, Florida, USA, 2006: 62010I. [16] WU Shiyou, YAO Siqi, LIU Wei, et al. Study on a novel UWB linear array human respiration model and detection method[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2016, 9(1): 125–140. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2519760 [17] XU Yanyun, WU Shiyou, CHEN Chao, et al. A novel method for automatic detection of trapped victims by ultrawideband radar[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2012, 50(8): 3132–3142. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2178248 -





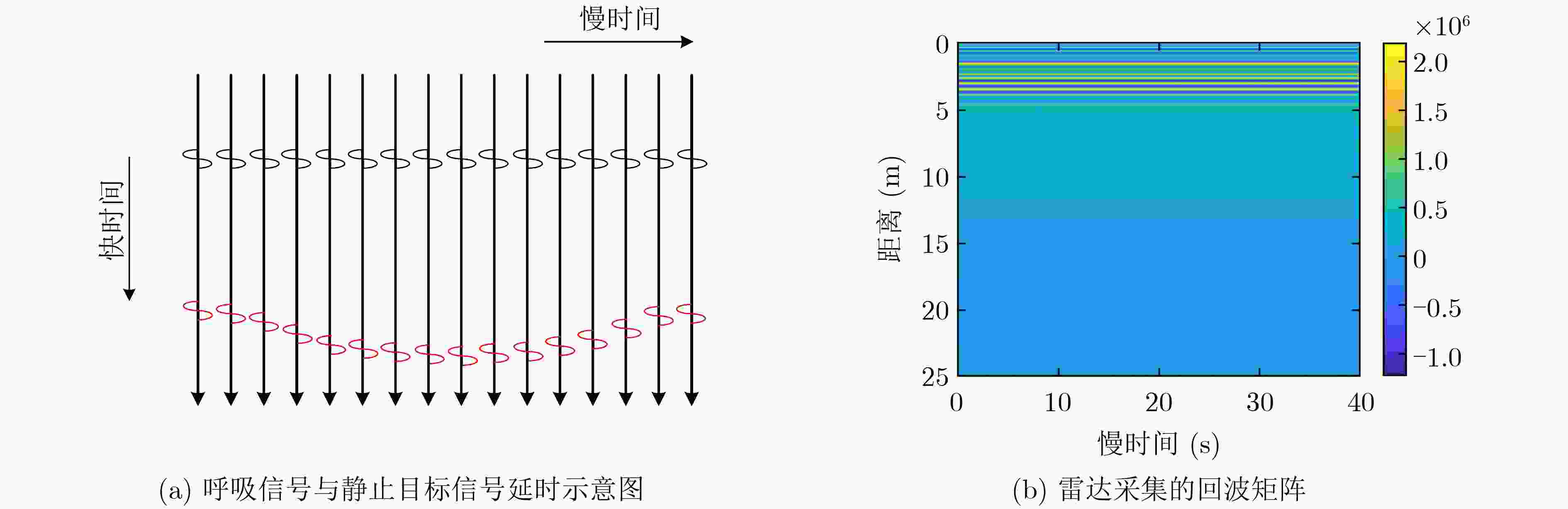
 下载:
下载:
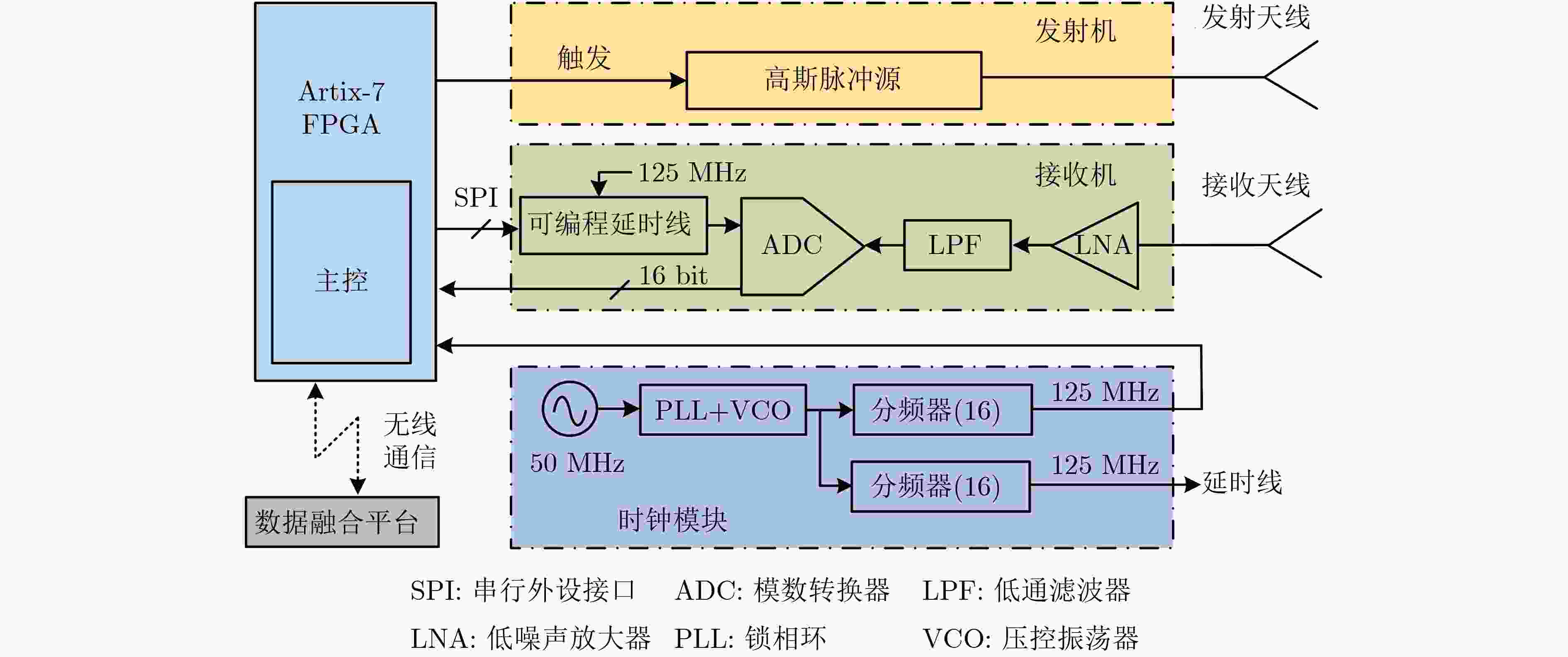
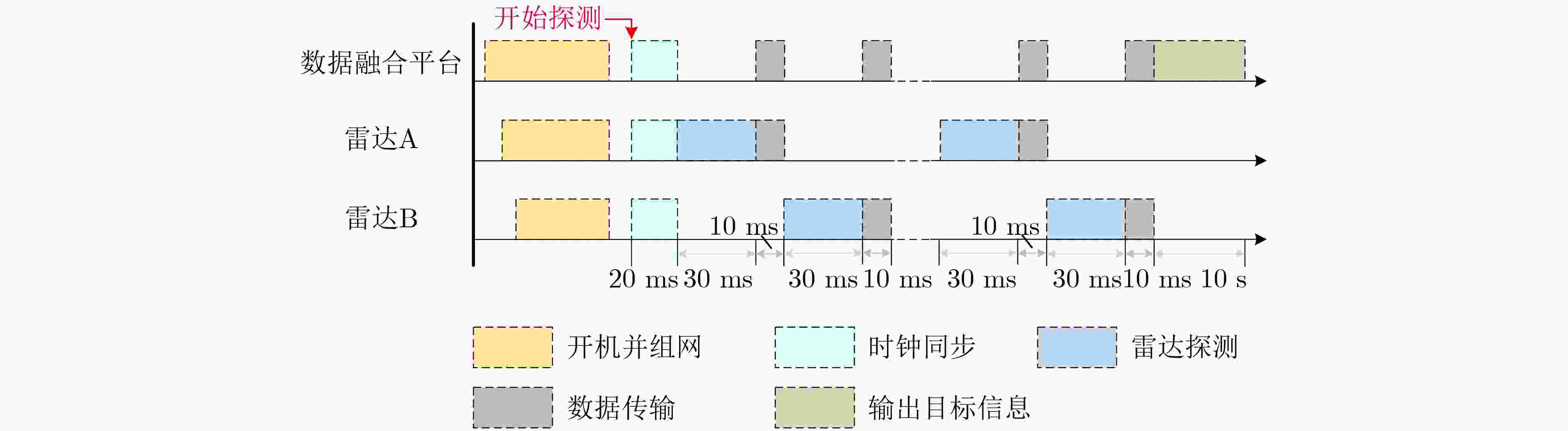
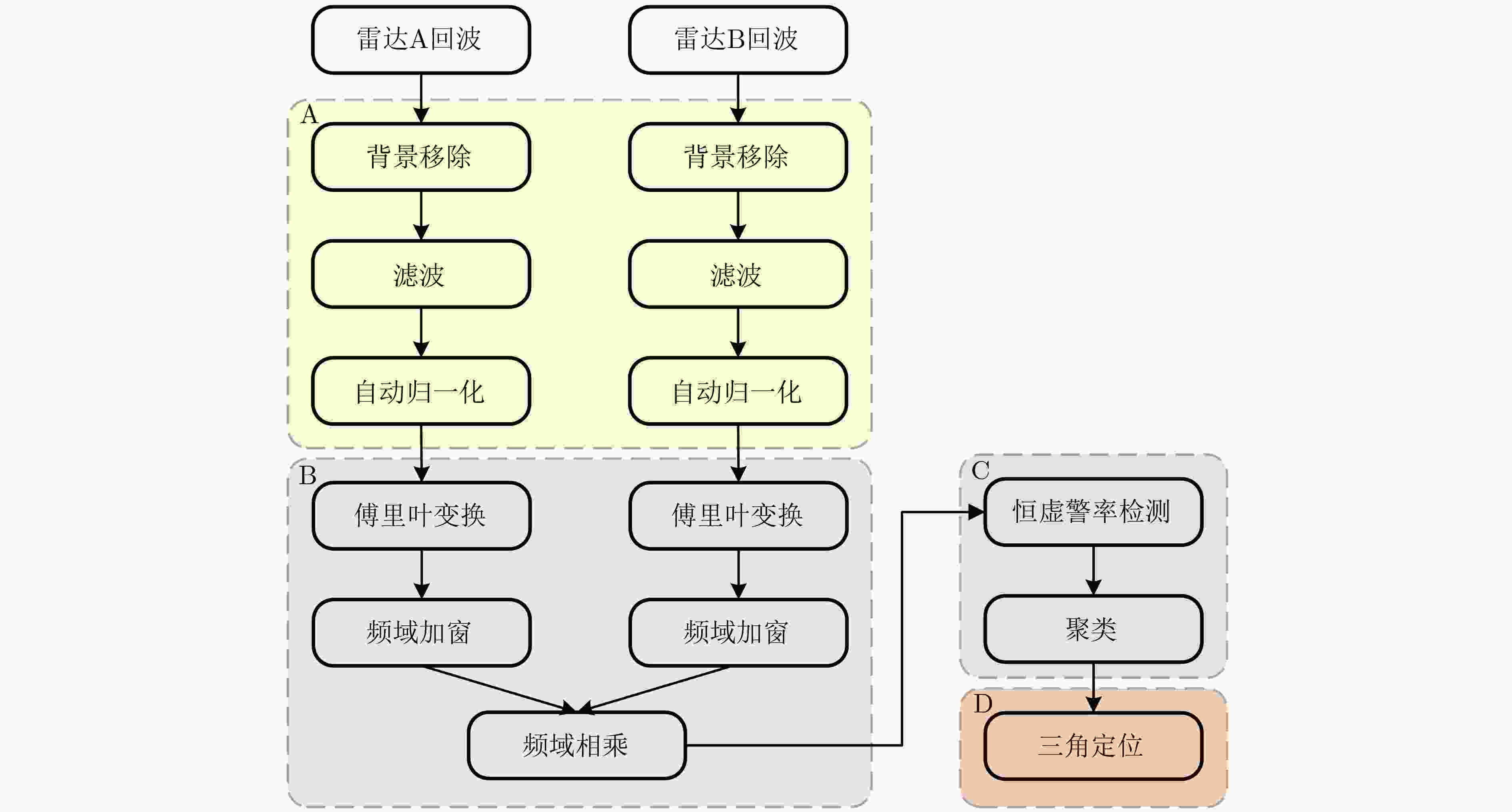


 下载:
下载:
