Quantum Image Chaotic Cryptography Scheme Based on Arnold Transforms
-
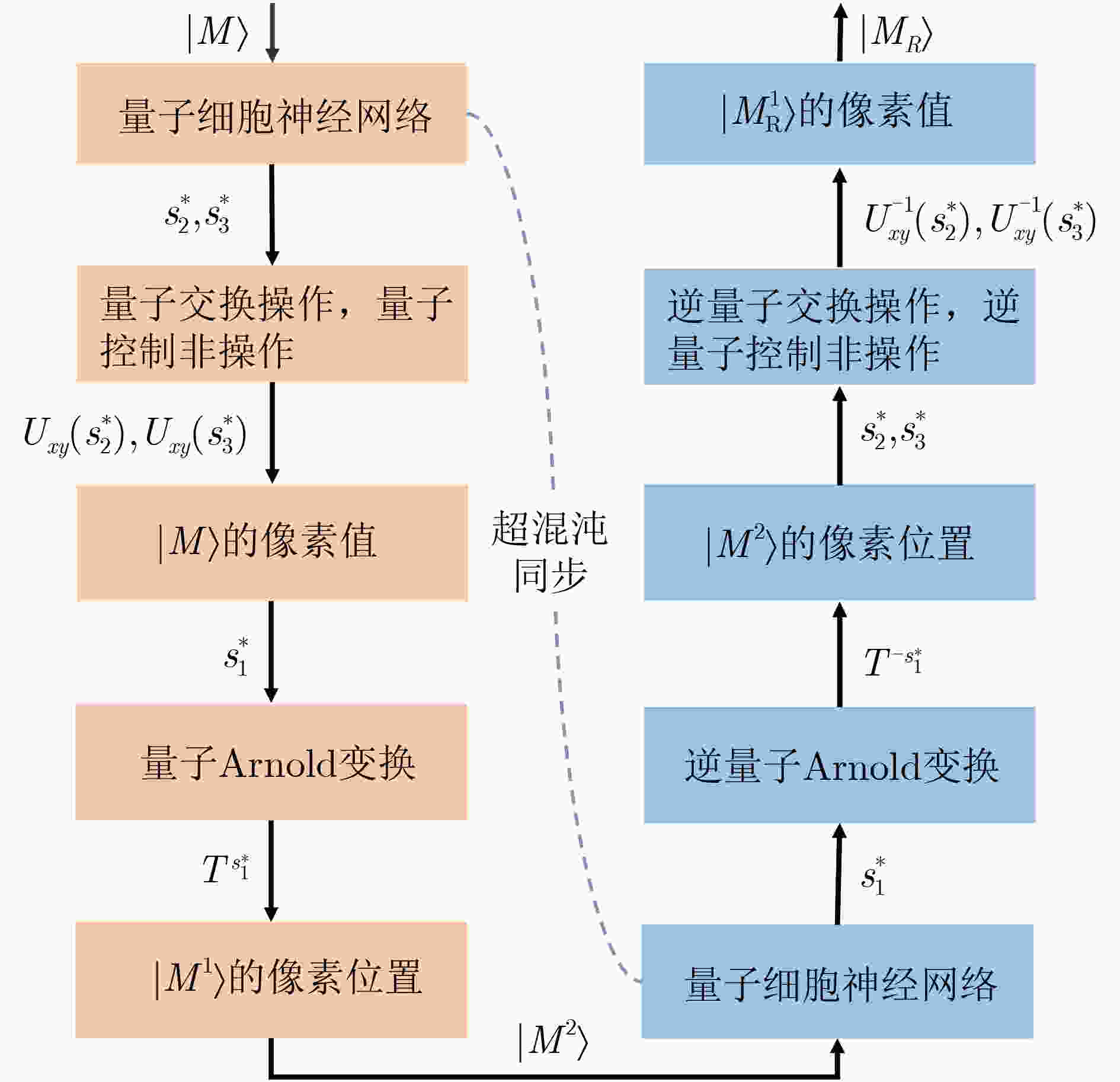
摘要: 在确保量子图像密码算法安全的基础上,为进一步优化解密图像质量及计算复杂度,该文提出一种基于Arnold变换的量子图像混沌加密方案。方案使用量子细胞神经网络产生的混沌信号来控制量子Arnold变换、量子交换(SWAP)和量子控制非操作(CNOT),然后将这些操作作用于量子明文图像中以获得相应的密文图像。研究结果表明:所提量子灰度图像加密方法具有高安全性、高解密图像质量及低计算复杂度的特点。
-
关键词:
- 量子图像密码 /
- 量子细胞神经网络 /
- 量子混沌系统 /
- 量子Arnold变换
Abstract: For improving the resolution of quantum decrypted image and computation complexity under the premise of ensuring quantum image cryptography algorithm security, an approach to quantum image chaotic encryption scheme based on Arnold transforms is proposed. In the paper, the chaotic signals generated by quantum cellular neural network are applied to control quantum Arnold transforms, quantum SWAP and quantum Controlled NOT (CNOT) operations which are utilized to process the plain quantum image to obtain the corresponding cipher image. Theoretical analyses show that the advantages of high security, fine resolution of decrypted images and considerable computation complexity are all presented in the proposed quantum gray image encryption scheme. -
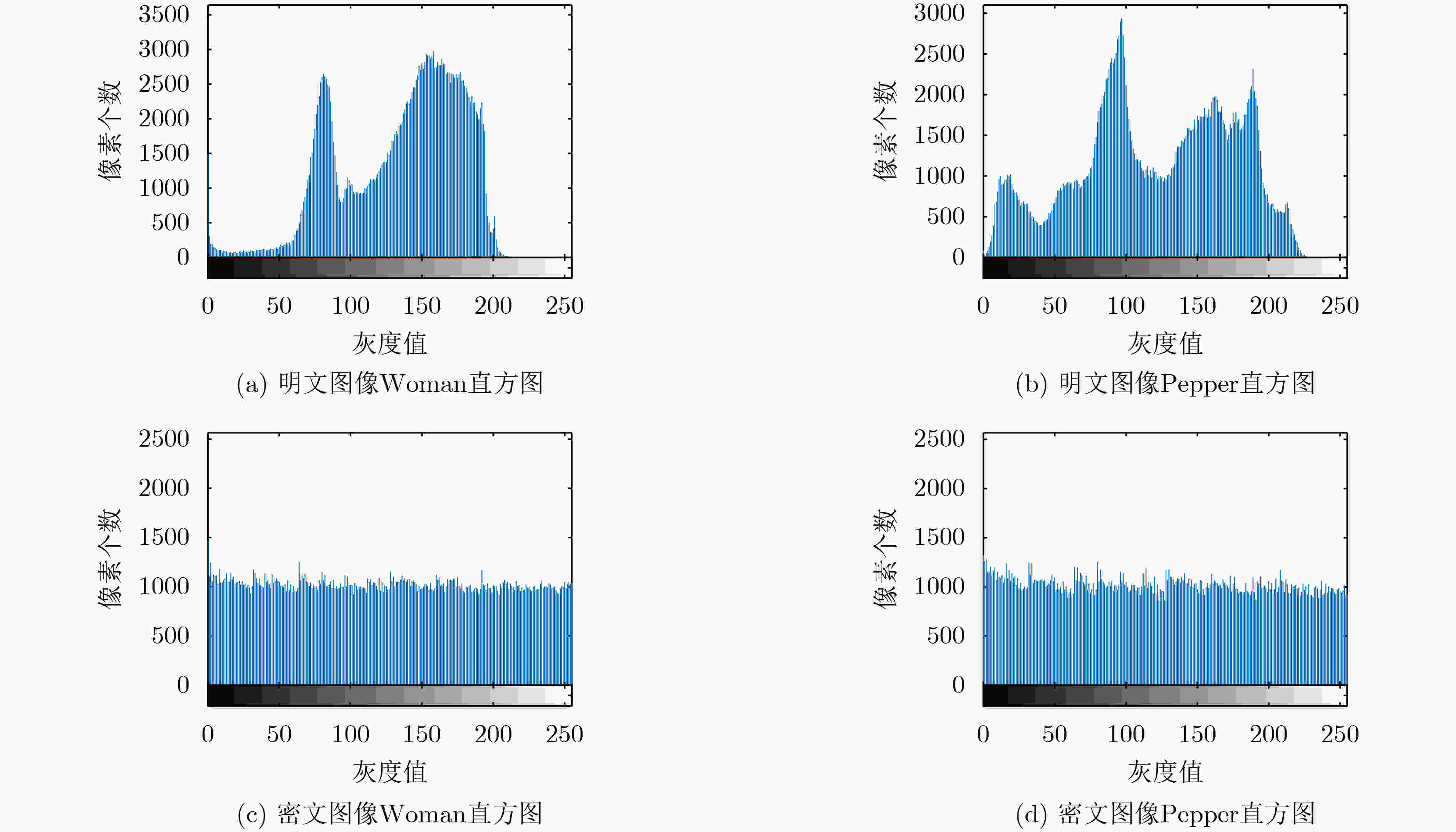
表 1 明文图像及相应密文图像的熵
图像名称 明文信息熵 密文信息熵 Woman 7.1615 7.9976 Pepper 7.5940 7.9957 表 2 明文图像及相应密文图像在水平、垂直、对角方向的相关性
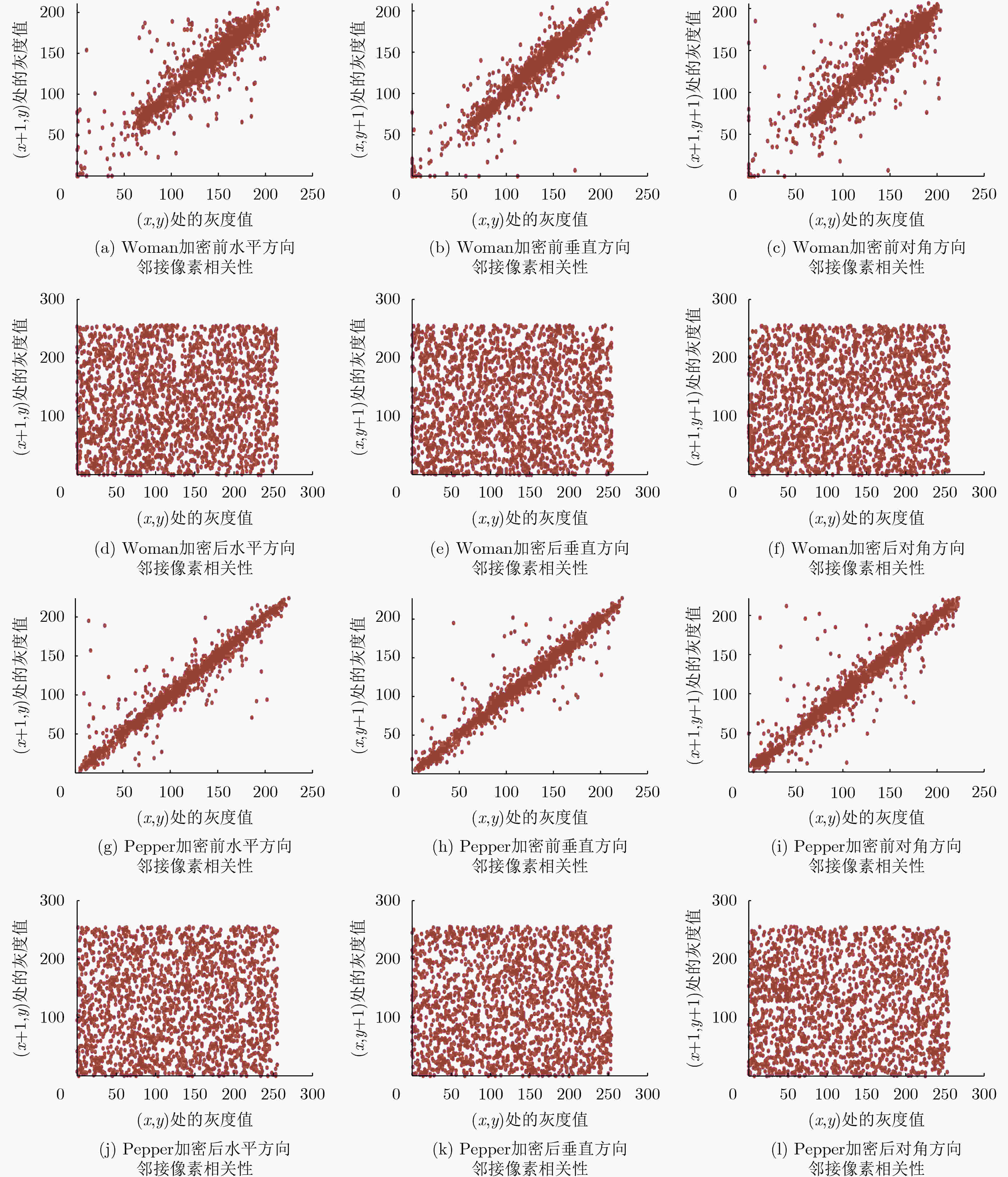
图像名称 明文邻接像素相关性 密文邻接像素相关性 H V D H V D Woman 0.9795 0.9885 0.9230 –0.0076 0.0052 0.0328 Pepper 0.9913 0.9940 0.9670 –0.0141 –0.0481 0.0379 -
[1] GROVER L K. A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search[C]. The Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Philadelphia, USA, 1996: 212–219. [2] SHI Jinjing, CHEN Shuhui, LU Yuhu, et al. An approach to cryptography based on continuous-variable quantum neural network[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 2107. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58928-1 [3] SHOR P W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer[J]. SIAM Review, 1999, 41(2): 303–332. doi: 10.1137/s0036144598347011 [4] 眭晗, 吴文玲. 后量子对称密码的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 287–294. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190667SUI Han and WU Wenling. Research status and development trend of post-quantum symmetric cryptography[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 287–294. doi: 10.11999/JEIT190667 [5] ZHOU Rigui, WU Qian, ZHANG Manqun, et al. Quantum image encryption and decryption algorithms based on quantum image geometric transformations[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2013, 52(6): 1802–1817. doi: 10.1007/s10773-012-1274-8 [6] ZHANG Jinlei, HUANG Zhijie, LI Xiang, et al. Quantum image encryption based on quantum image decomposition[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2021, 60(8): 2930–2942. doi: 10.1007/s10773-021-04862-5 [7] HOU Chengan, LIU Xingbin, and FENG Songyang. Quantum image scrambling algorithm based on discrete Baker map[J]. Modern Physics Letters A, 2020, 35(17): 2050145. doi: 10.1142/S021773232050145X [8] ZHOU Nanrun, HU Yiqun, GONG Lihua, et al. Quantum image encryption scheme with iterative generalized Arnold transforms and quantum image cycle shift operations[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2017, 16(6): 164. doi: 10.1007/s11128-017-1612-0 [9] ZHOU Nanrun, CHEN Weiwei, YAN Xinyu, et al. Bit-level quantum color image encryption scheme with quantum cross-exchange operation and hyper-chaotic system[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2018, 17(6): 137. doi: 10.1007/s11128-018-1902-1 [10] YANG Yuguang, XIA Juan, JIA Xin, et al. Novel image encryption/decryption based on quantum Fourier transform and double phase encoding[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2013, 12(11): 3477–3493. doi: 10.1007/s11128-013-0612-y [11] YE Guodong, JIAO Kaixin, HUANG Xiaoling, et al. An image encryption scheme based on public key cryptosystem and quantum logistic map[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 21044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78127-2 [12] ABD EL-LATIF A A, LI Li, WANG Ning, et al. A new approach to chaotic image encryption based on quantum chaotic system, exploiting color spaces[J]. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(11): 2986–3000. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.03.031 [13] GOGGIN M E, SUNDARAM B, and MILONNI P W. Quantum logistic map[J]. Physical Review A, 1990, 41(10): 5705–5708. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.41.5705 [14] TAN Ruchao, LEI Tong, ZHAO Qingmin, et al. Quantum color image encryption algorithm based on a hyper-chaotic system and quantum Fourier transform[J]. International Journal of Theoretical Physics, 2016, 55(12): 5368–5384. doi: 10.1007/s10773-016-3157-x [15] LIANG Xiyin and QI Guoyuan. Mechanical analysis of Chen chaotic system[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2017, 98: 173–177. doi: 10.1016/j.chaos.2017.03.021 [16] YANG Yuguang, TIAN Ju, LEI He, et al. Novel quantum image encryption using one-dimensional quantum cellular automata[J]. Information Sciences, 2016, 345: 257–270. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.01.078 [17] LIU Xingbin, XIAO Di, and LIU Cong. Double quantum image encryption based on Arnold transform and qubit random rotation[J]. Entropy, 2018, 20(11): 867. doi: 10.3390/e20110867 [18] WANG Jian, GENG Yacong, and LIU Jiqiang. Adaptive quantum image encryption method based on wavelet transform[EB/OL].https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07762, 2019. [19] KHAN M and RASHEED A. Permutation-based special linear transforms with application in quantum image encryption algorithm[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2019, 18(10): 298. doi: 10.1007/s11128-019-2410-7 [20] LIU Xingbin, XIAO Di, and LIU Cong. Quantum image encryption algorithm based on bit-plane permutation and sine logistic map[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2020, 19(8): 239. doi: 10.1007/s11128-020-02739-w [21] LIU Xingbin, XIAO Di, and LIU Cong. Three-level quantum image encryption based on Arnold transform and logistic map[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2021, 20(1): 23. doi: 10.1007/s11128-020-02952-7 [22] YU Shasha, ZHOU Nanrun, GONG Lihua, et al. Optical image encryption algorithm based on phase-truncated short-time fractional Fourier transform and hyper-chaotic system[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 124: 105816. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2019.105816 [23] NIYAT A Y, MOATTAR M H, and TORSHIZ M N. Color image encryption based on hybrid hyper-chaotic system and cellular automata[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2017, 90: 225–237. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2016.10.019 [24] 卢爱平, 李盼池. 基于混沌序列的彩色图像量子加密方案[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2021, 49(4): 692–697,730. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2021.04.017LU Aiping and LI Panchi. Quantum encryption scheme for color images based on chaotic sequences[J]. Computer &Digital Engineering, 2021, 49(4): 692–697,730. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2021.04.017 [25] KARAFYLLIDIS I G. Definition and evolution of quantum cellular automata with two qubits per cell[J]. Physical Review A, 2004, 70(4): 044301. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.70.044301 [26] 蔡理, 马西奎, 王森. 量子细胞神经网络的超混沌特性研究[J]. 物理学报, 2003, 52(12): 3002–3006. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2003.12.013CAI Li, MA Xikui, and WANG Sen. Study of hyperchaotic behavior in quantum cellular neural networks[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2003, 52(12): 3002–3006. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3290.2003.12.013 [27] TÓTH G, LENT C S, TOUGAW P D, et al. Quantum cellular neural networks[J]. Superlattices and Microstructures, 1996, 20(4): 473–478. doi: 10.1006/spmi.1996.0104 [28] KANTZ H. A robust method to estimate the maximal Lyapunov exponent of a time series[J]. Physics Letters A, 1994, 185(1): 77–87. doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(94)90991-1 [29] ZHANG Yi, LU Kai, GAO Yinghui, et al. NEQR: A novel enhanced quantum representation of digital images[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2013, 12(8): 2833–2860. doi: 10.1007/s11128-013-0567-z [30] LI Haisheng, ZHU Qingxin, ZHOU Rigui, et al. Multidimensional color image storage, retrieval, and compression based on quantum amplitudes and phases[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 273: 212–232. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.03.035 [31] 李盼池, 曹梓崎. 基于量子比特相位的彩色图像描述方法及应用[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(2): 489–493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160303LI Panchi and CAO Ziqi. Quantum bits phase based representation and application for color images[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2017, 39(2): 489–493. doi: 10.11999/JEIT160303 [32] HU Wenwen, ZHOU Rigui, LUO Jia, et al. Quantum image encryption algorithm based on Arnold scrambling and wavelet transforms[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2020, 19(3): 82. doi: 10.1007/s11128-020-2579-9 [33] HU Wenwen, ZHOU Rigui, JIANG Shexiang, et al. Quantum image encryption algorithm based on generalized Arnold transform and Logistic map[J]. CCF Transactions on High Performance Computing, 2020, 2(3): 228–253. doi: 10.1007/S42514-020-00043-8 [34] JIANG Nan and WANG Luo. Analysis and improvement of the quantum Arnold image scrambling[J]. Quantum Information Processing, 2014, 13(7): 1545–1551. doi: 10.1007/s11128-014-0749-3 [35] VEDRAL V, BARENCO A, and EKERT A. Quantum networks for elementary arithmetic operations[J]. Physical Review A, 1996, 54(1): 147–153. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.54.147 [36] YANG C H, GE Zhengming, CHANG C M, et al. Chaos synchronization and chaos control of quantum-CNN chaotic system by variable structure control and impulse control[J]. Nonlinear Analysis:Real World Applications, 2010, 11(3): 1977–1985. doi: 10.1016/j.nonrwa.2009.04.019 [37] SUDHEER K S and SABIR M. Adaptive function projective synchronization of two-cell Quantum-CNN chaotic oscillators with uncertain parameters[J]. Physics Letters A, 2009, 373(21): 1847–1851. doi: 10.1016/j.physleta.2009.03.052 [38] WANG Xingyuan, CHEN Feng, and WANG Tian. A new compound mode of confusion and diffusion for block encryption of image based on chaos[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2010, 15(9): 2479–2485. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2009.10.001 -





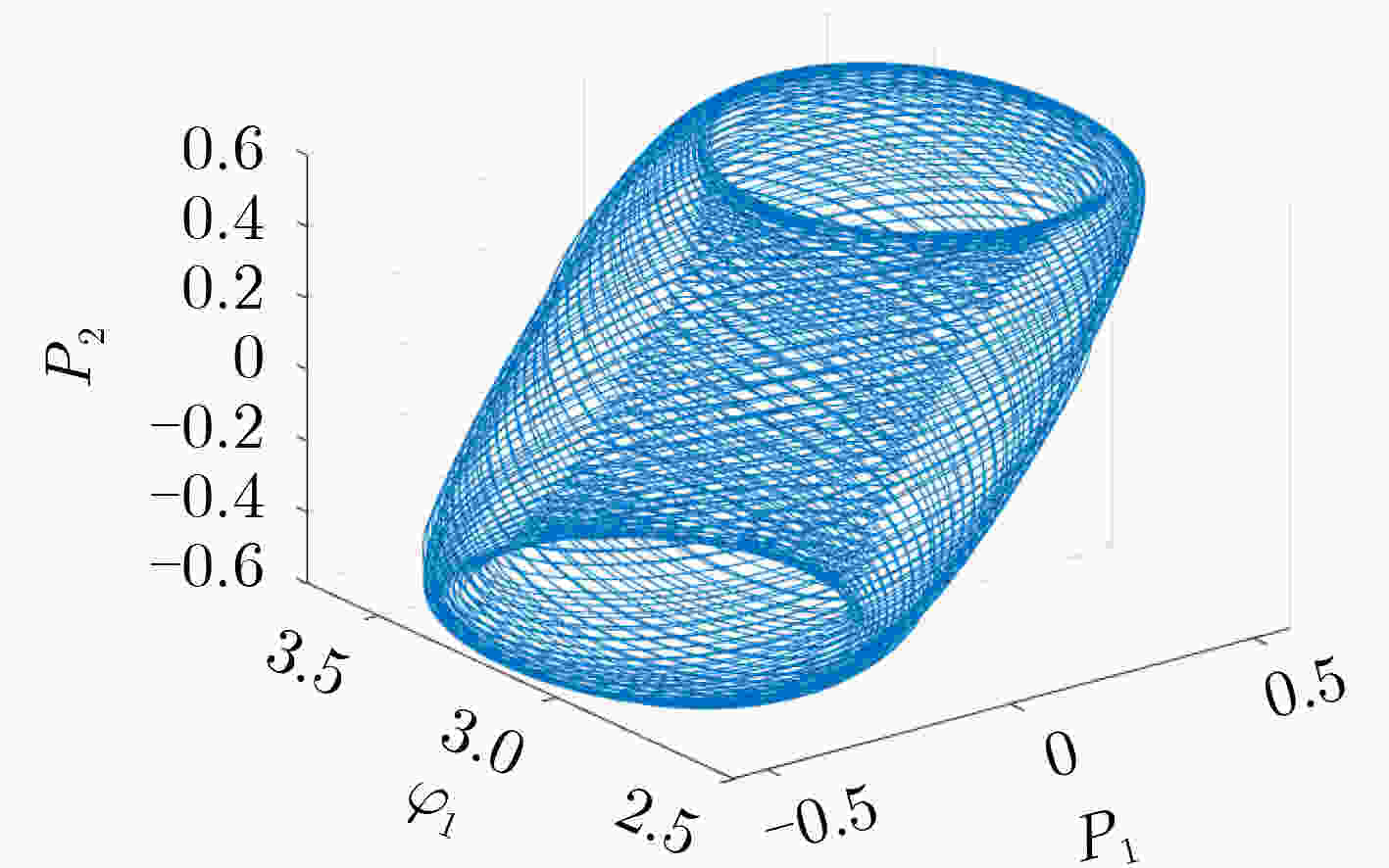



 下载:
下载:
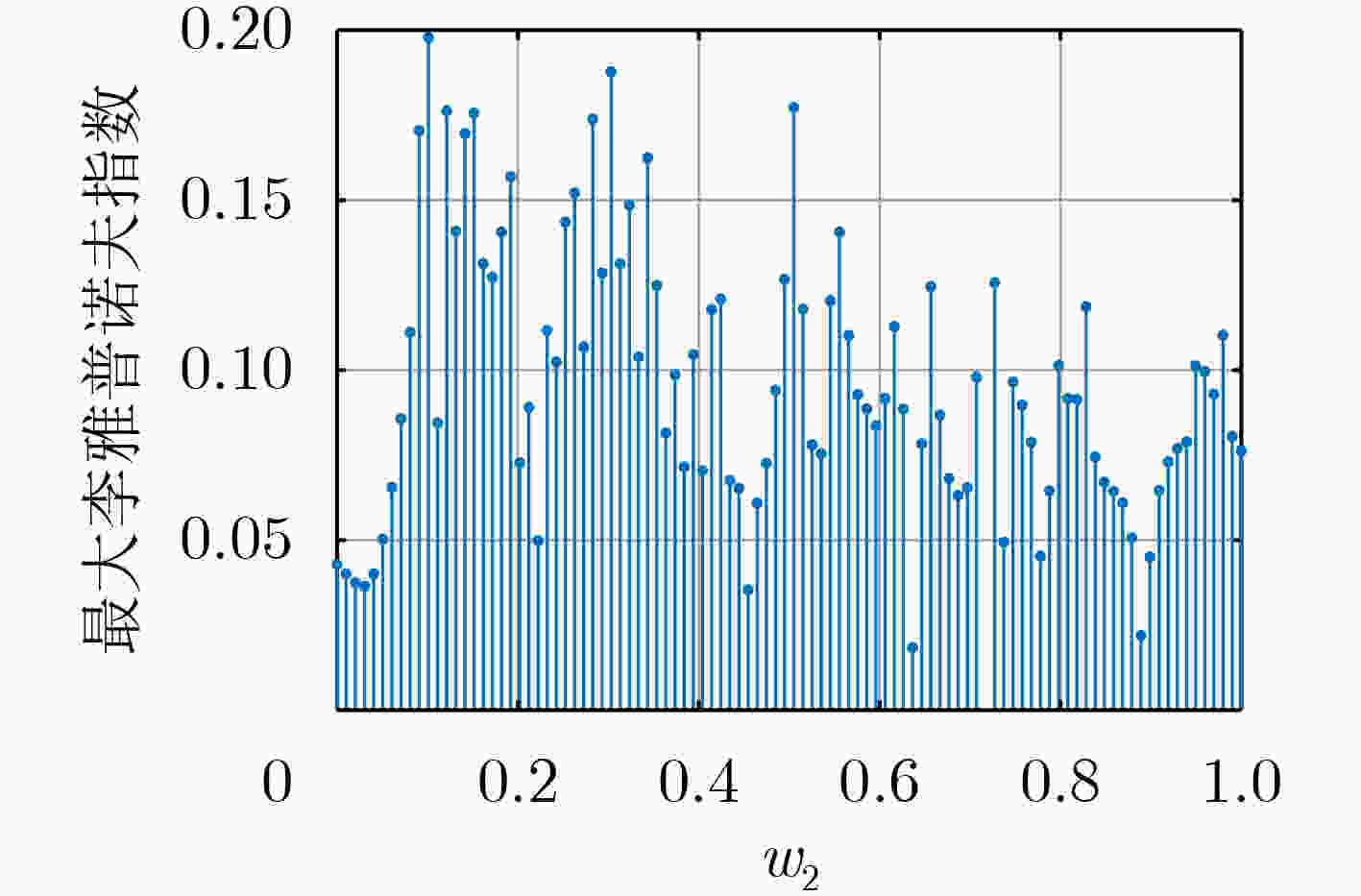
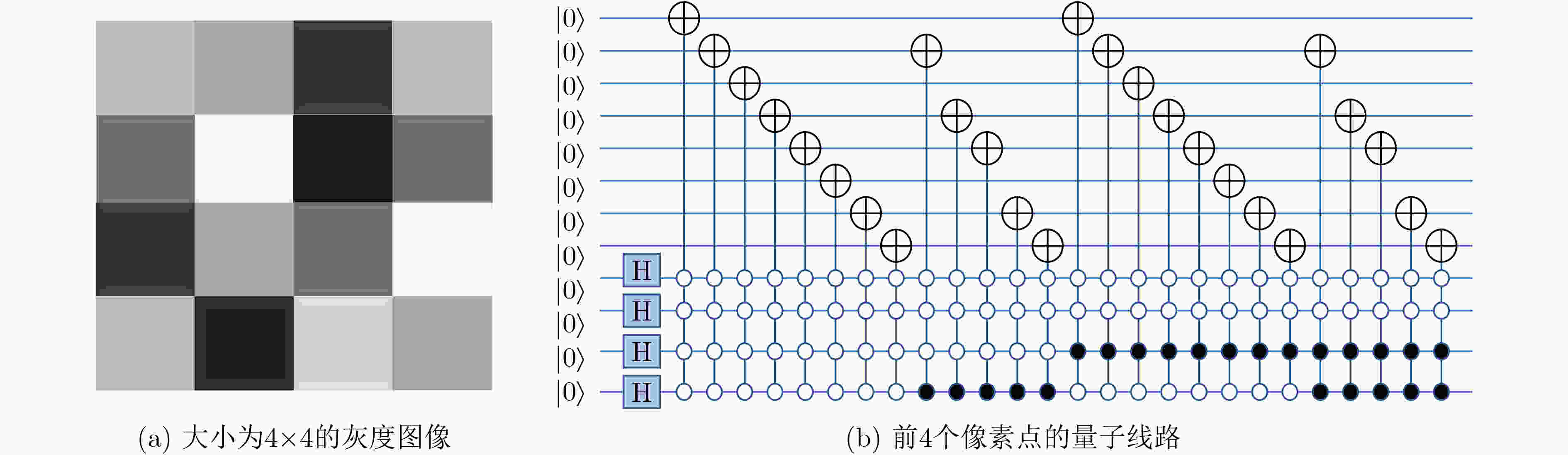
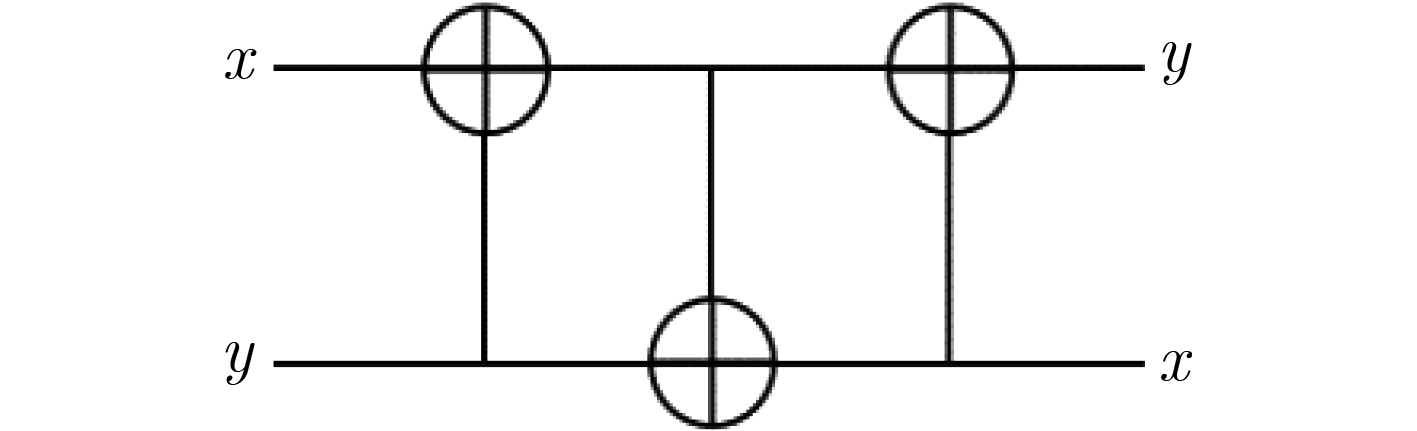




 下载:
下载:
