Research on Dynamic Topology Model-based Routing Algorithms in 6G Large-scale UAV Networks
-
摘要: 随着无线通信以及无人机(UAV)技术的日益发展,利用无人机移动性、稳定性、广覆盖等优势,建立一个覆盖并连接广袤区域内各种无线终端的大规模“无人机云”,成为未来6G无线通信网络的一个重要的发展方向。如何在无人机云组成的复杂网络拓扑中快速精准地规划出最优路径,成为一个亟待解决的问题。因此,该文利用重力场中的梯度原理设计了一种旨在适用于多种路由方案的新型动态网络拓扑模型,基于此模型实现了复杂拓扑网络下路由路径的计算及选取。这种模型利用梯度本身的特性以实现路径的优化,以适用于未来6G应用中可能出现的高密度高覆盖性无人机群的通信需求。仿真结果表明,该文提出的拓扑模型及路由方法在链路通信质量及平均能耗方面优于目前应用及研究的诸多路由方案。Abstract: With the development of wireless communication and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) technology, the establishment of a large-scale UAV cloud covering and connecting various wireless terminals in a wide area using the advantages of mobility, stability and wide coverage has become an important development direction for future 6G wireless communication networks. How to quickly and accurately plan the optimal path in the complex network topology of the UAV cloud has become an urgent problem to be solved. Therefore, by using the gradient principle in the gravitational field, a new dynamic network topology model designed to be applicable to multiple routing schemes is designed, and the calculation and selection of routing paths under complex topological networks is realized based on this model. This model uses the characteristics of gradient itself in order to achieve path optimization for the communication needs of high-density and high-coverage UAV clouds that may appear in future 6G applications. Simulation results show that the topology model and routing methods proposed in this paper outperform many routing schemes currently applied and studied in terms of link communication quality and average energy consumption.
-
Key words:
- 6G UAV communication /
- Routing /
- Topology model /
- Routing metrics
-
表 1 路由方案α中继节点计算
输入:路径点集合X,源节点S,网络中心D 输出:中继节点集合R (1) while D $ \notin $ R 时 (2) S→R (3) 找到在集合X中的第lockth个元素和集合R中最后一个元素间
的所有节点(4) if不存在节点 (5) lock = lock + 1 (6) 否则计算所有节点的P (7) 找到 min(P) && 节点的能量 > 0 (8) 找到最优的节点作为集合R中的最后一个元素 (9) lock = lock +1 (10) end if (11) end while 表 2 路由方案β中继节点计算
输入:路径点集合X,源节点S,网络中心D,区域集合Z 输出:中继节点集合R (1) while D $ \notin $ R (2) S→R (3) 找到集合X中第lockth个元素所在的网格grid,记作zlock (4) 找到所有在网格gird zlock中的节点 (5) if没有节点存在 (6) lock = lock + 1 (7) else计算所有节点的P值 (8) 找到 min(P) && 节点的能量 > 0 (9) 找到最优的节点作为集合R中的最后一个元素 (10) lock = lock +1 (11) end if (12) end while 表 3 仿真参数表
参数名称 参数值 参数名称 参数值 Pt 11.76 dBm Eelec 100 nJ/bit Gt, Gr 3 εfs 10 pJ/(bit·m2) L 1 εmp 0.0013 pJ/(bit·m4) η 2 EDA 5 nJ/(bit·signal) α 0.05 ε1 100 F 0.06 ε2, ε3 0.01, 1 -
[1] 贾向东, 路艺, 纪澎善, 等. 大规模无人机协助的多层异构网络设计及性能研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(9): 2632–2639. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200443JIA Xiangdong, LU Yi, JI Pengshan, et al. Design of large-scale UAV-assisted multi-tier heterogeneous networks and performance research[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2021, 43(9): 2632–2639. doi: 10.11999/JEIT200443 [2] ZHAO Nan, LU Weidang, SHENG Min, et al. UAV-assisted emergency networks in disasters[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26(1): 45–51. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2018.1800160 [3] KO J, TERZIS A, DAWSON-HAGGERTY S, et al. Connecting low-power and lossy networks to the internet[J]. IEEE Communications Magazine, 2011, 49(4): 96–101. doi: 10.1109/MCOM.2011.5741163 [4] WINTER T, THUBERT P, BRANDT A, et al. RFC 6550 RPL: IPv6 routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks[S]. 2012. [5] YANG Y and WANG J. Design guidelines for routing metrics in multihop wireless networks[C]. The 27th Conference on Computer Communications, Phoenix, USA, 2008: 1615–1623. [6] LAI Xiaohan, JI Xiaoyu, ZHOU Xinyan, et al. Energy efficient link-delay aware routing in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(2): 837–848. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2772321 [7] QIU Ying, LI Shining, LI Zhigang, et al. Multi-gradient routing protocol for wireless sensor networks[J]. China Communications, 2017, 14(3): 118–129. doi: 10.1109/CC.2017.7897328 [8] TANG Fengxiao, MAO Bomin, FADLULLAH Z M, et al. On removing routing protocol from future wireless networks: A real-time deep learning approach for intelligent traffic control[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2018, 25(1): 154–160. doi: 10.1109/MWC.2017.1700244 [9] ZHANG Jiajie, WENG Jian, LUO Weiqi, et al. REMT: A real-time end-to-end media data transmission mechanism in UAV-aided networks[J]. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(5): 118–123. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1700382 [10] LIU Miao, SONG Tiecheng, HU Jing, et al. Deep learning-inspired message passing algorithm for efficient resource allocation in cognitive radio networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(1): 641–653. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2018.2883669 [11] DING Ruijin, XU Yadong, GAO Feifei, et al. Deep reinforcement learning for router selection in network with heavy traffic[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 37109–37120. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2904539 [12] WANG Xiaolin, CHEN Cailian, HE Jianping, et al. Learning-based online transmission path selection for secure estimation in edge computing systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(5): 3577–3587. doi: 10.1109/TII.2020.3012090 [13] HEINZELMAN W B, CHANDRAKASAN A P, and BALAKRISHNAN H. An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2002, 1(4): 660–670. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2002.804190 [14] DE COUTO D S J, AGUAYO D, BICKET J, et al. A high-throughput path metric for multi-hop wireless routing[J]. Wireless Networks, 2005, 11(4): 419–434. doi: 10.1007/s11276-005-1766-z [15] ANCILLOTTI E, BRUNO R, and CONTI M. Reliable data delivery with the IETF routing protocol for low-power and lossy networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2014, 10(3): 1864–1877. doi: 10.1109/TII.2014.2332117 [16] ZHANG Taimin, JI Xiaoyu, and XU Wenyuan. Jamming-resilient backup nodes selection for RPL-based routing in smart grid AMI networks[J/OL]. Mobile Networks and Applications, 2020. [17] MAUVE M, WIDMER J, and HARTENSTEIN H. A survey on position-based routing in mobile ad hoc networks[J]. IEEE Network, 2001, 15(6): 30–39. doi: 10.1109/65.967595 [18] HUANG Haojun, YIN Hao, MIN Geyong, et al. Energy-aware dual-path geographic routing to bypass routing holes in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2018, 17(6): 1339–1352. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2017.2771424 -






 下载:
下载:
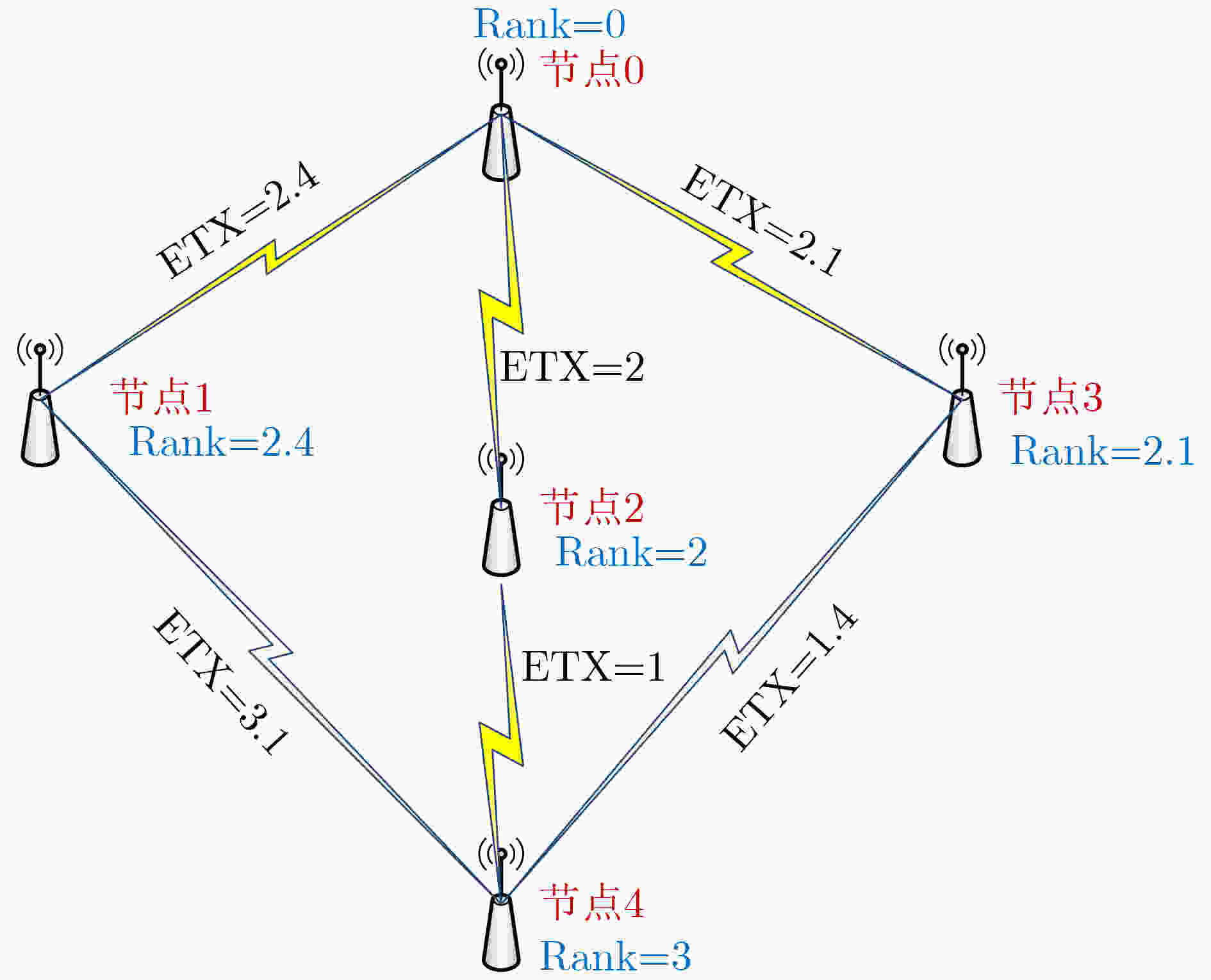
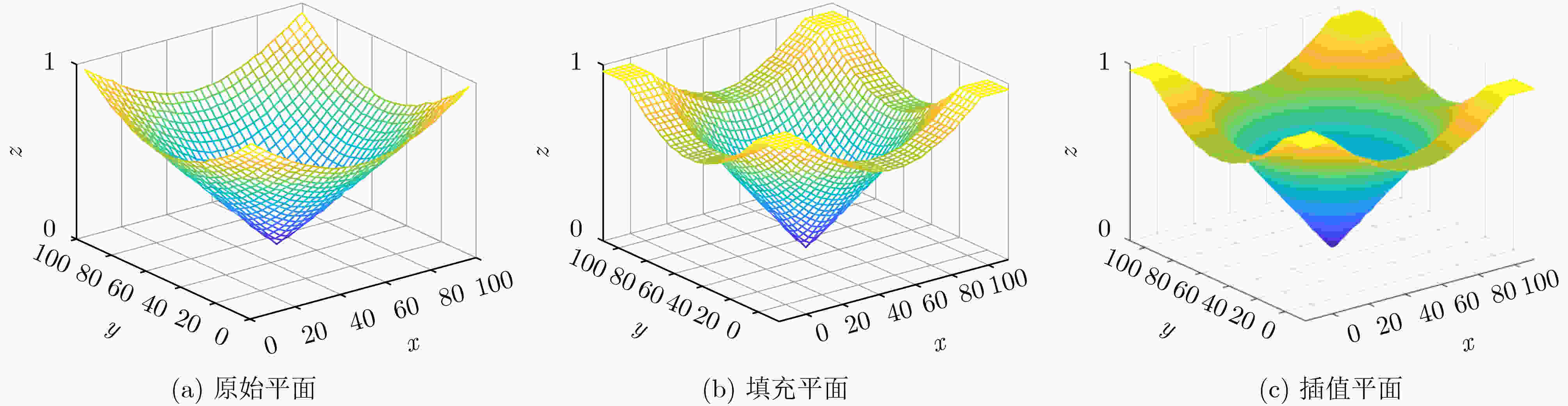
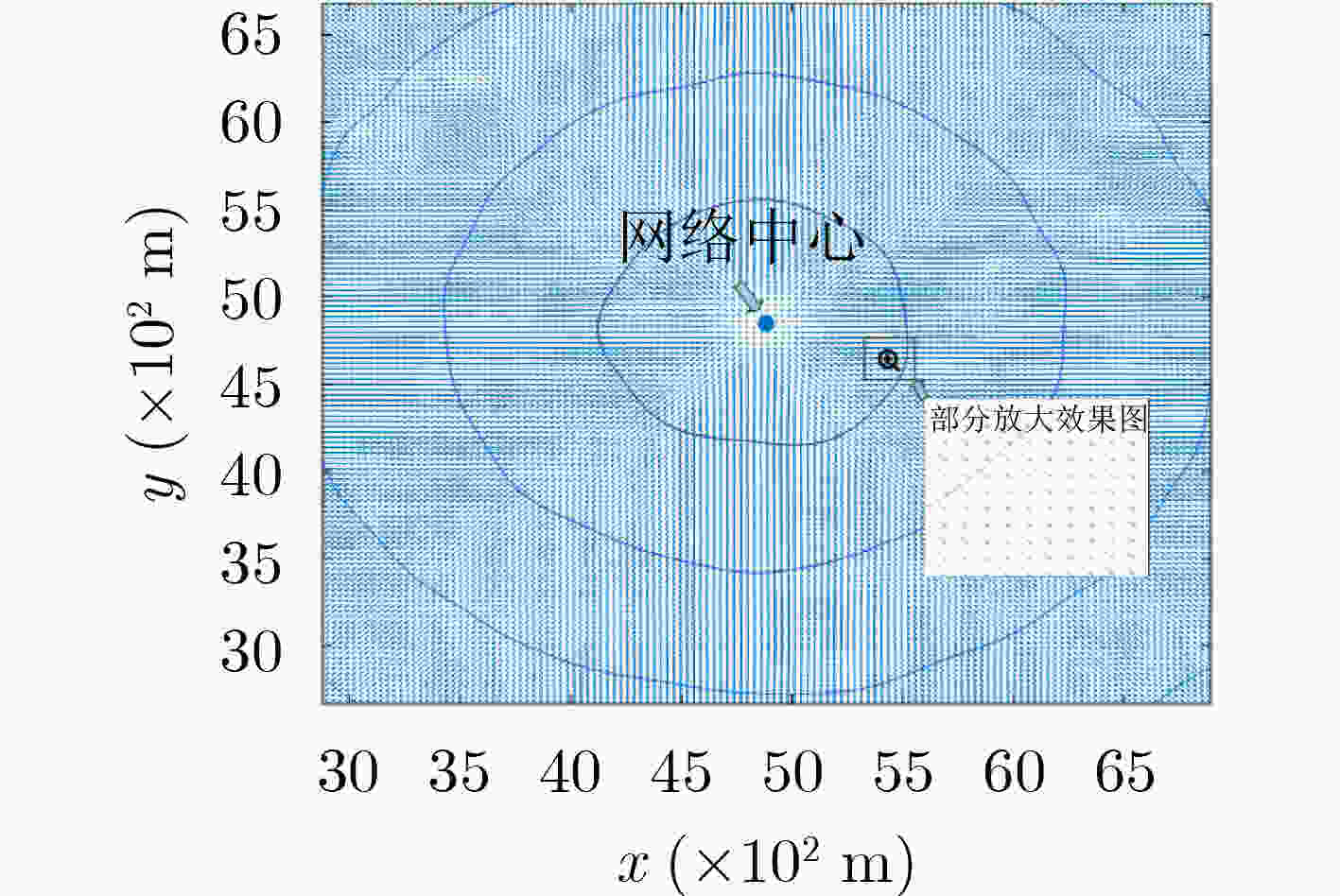
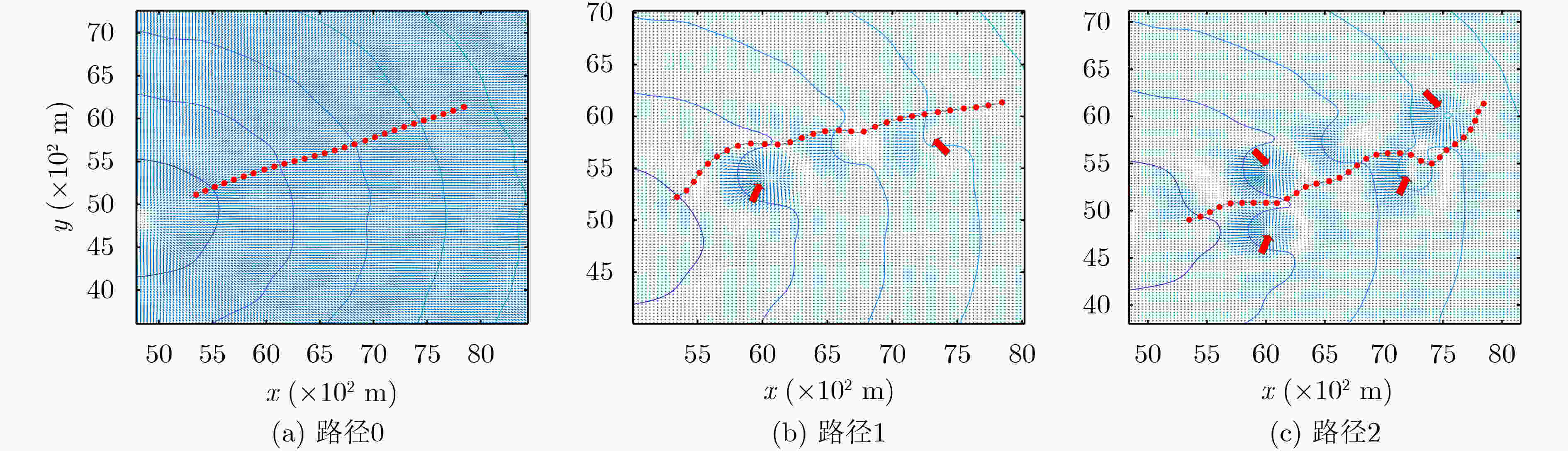
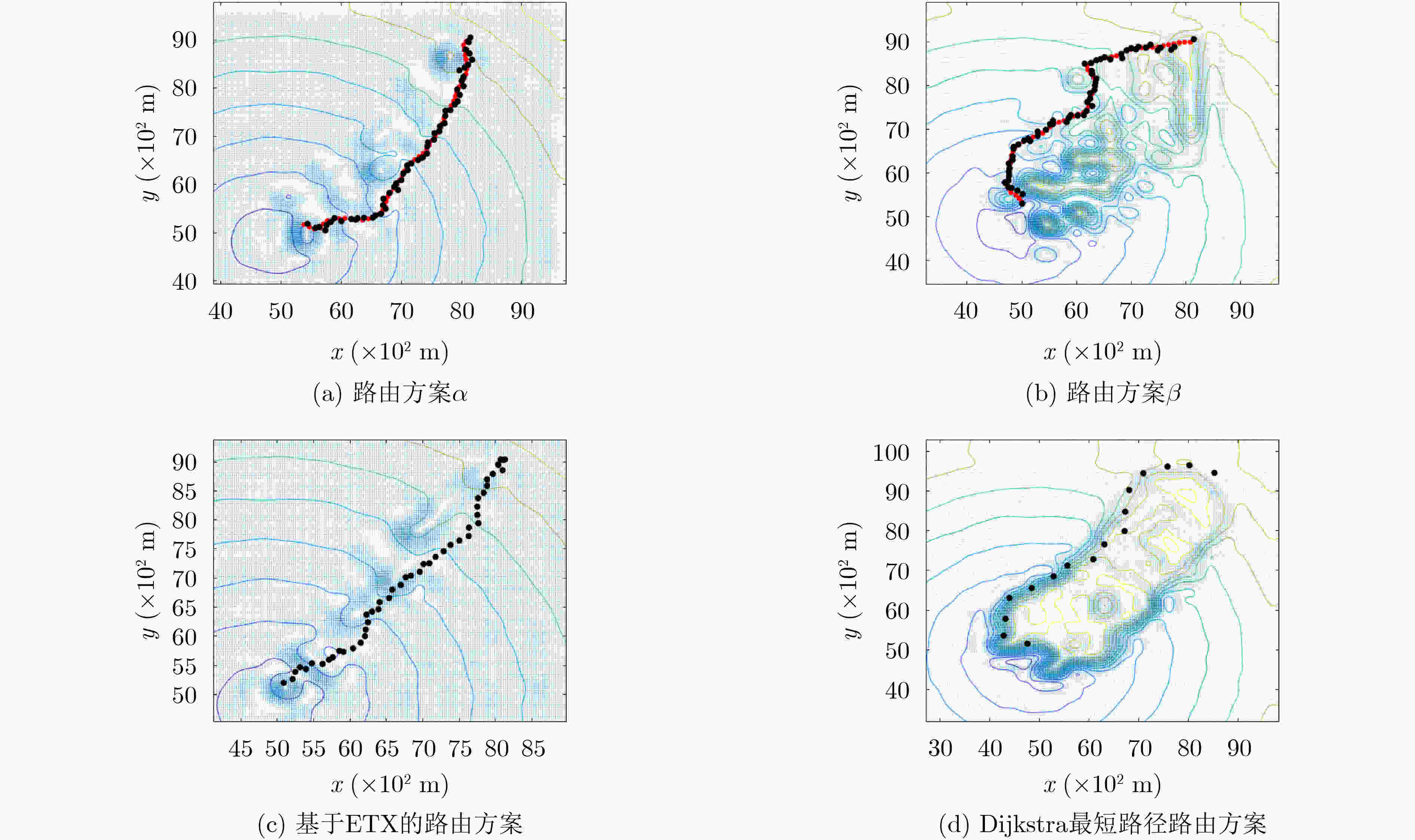
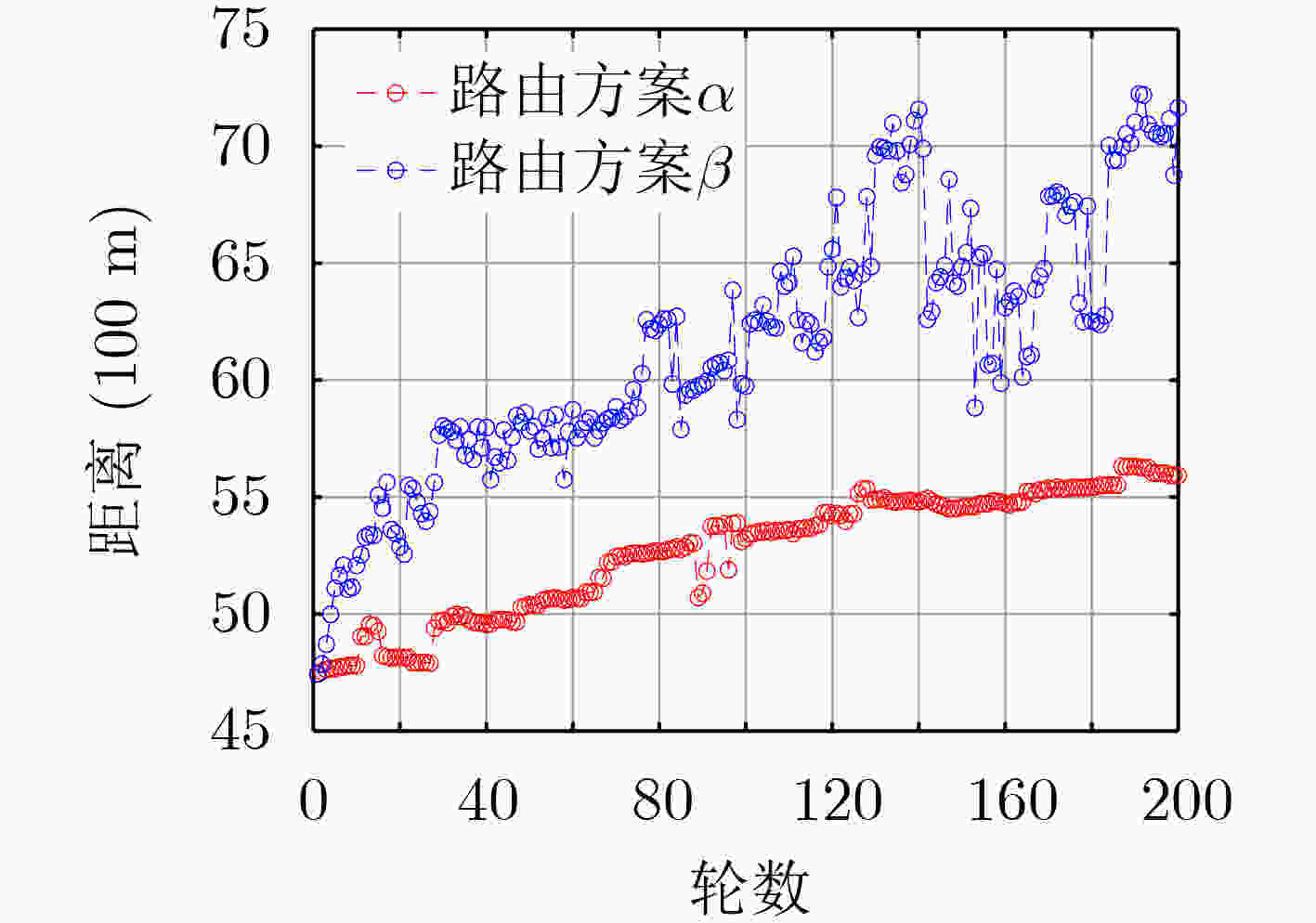
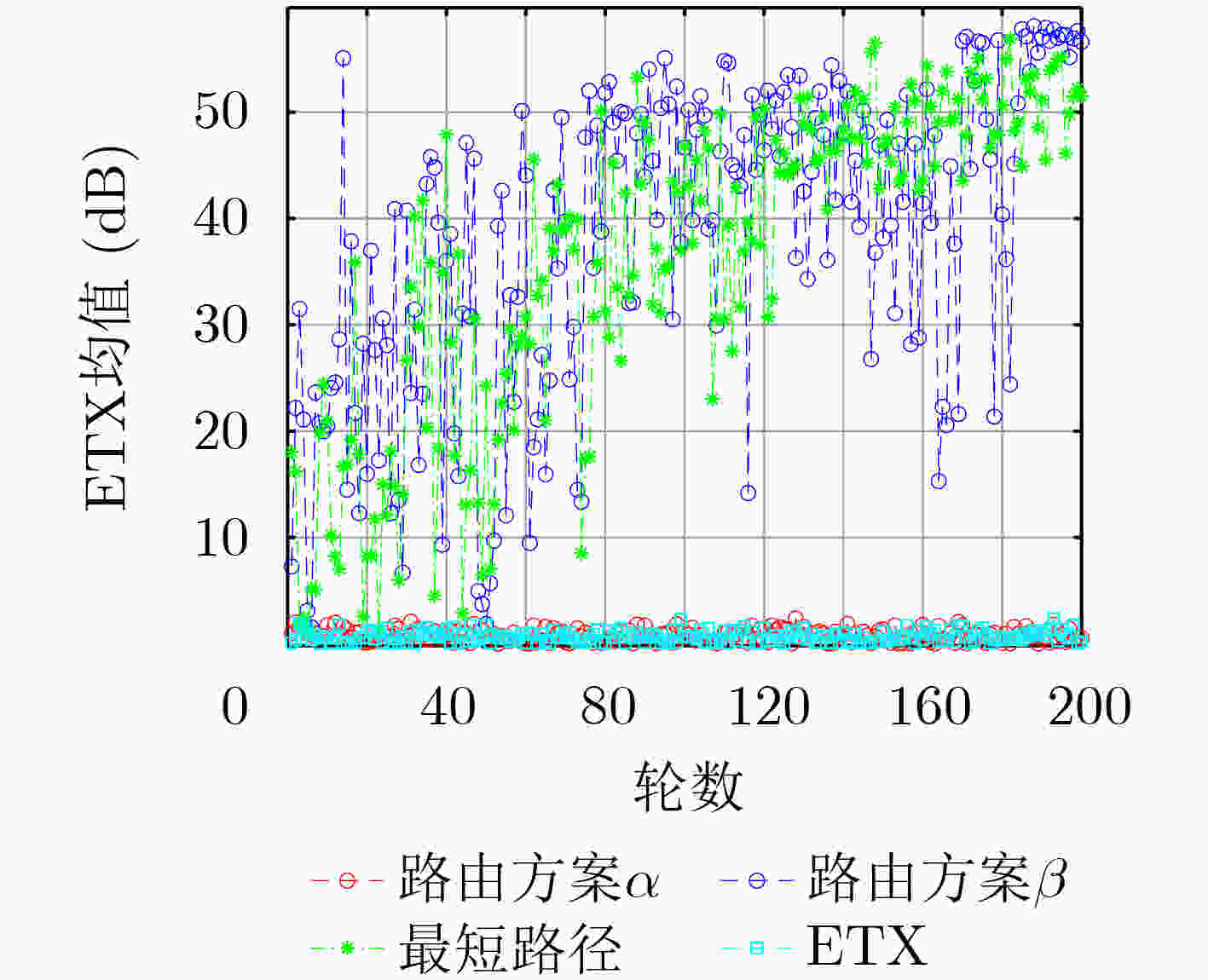
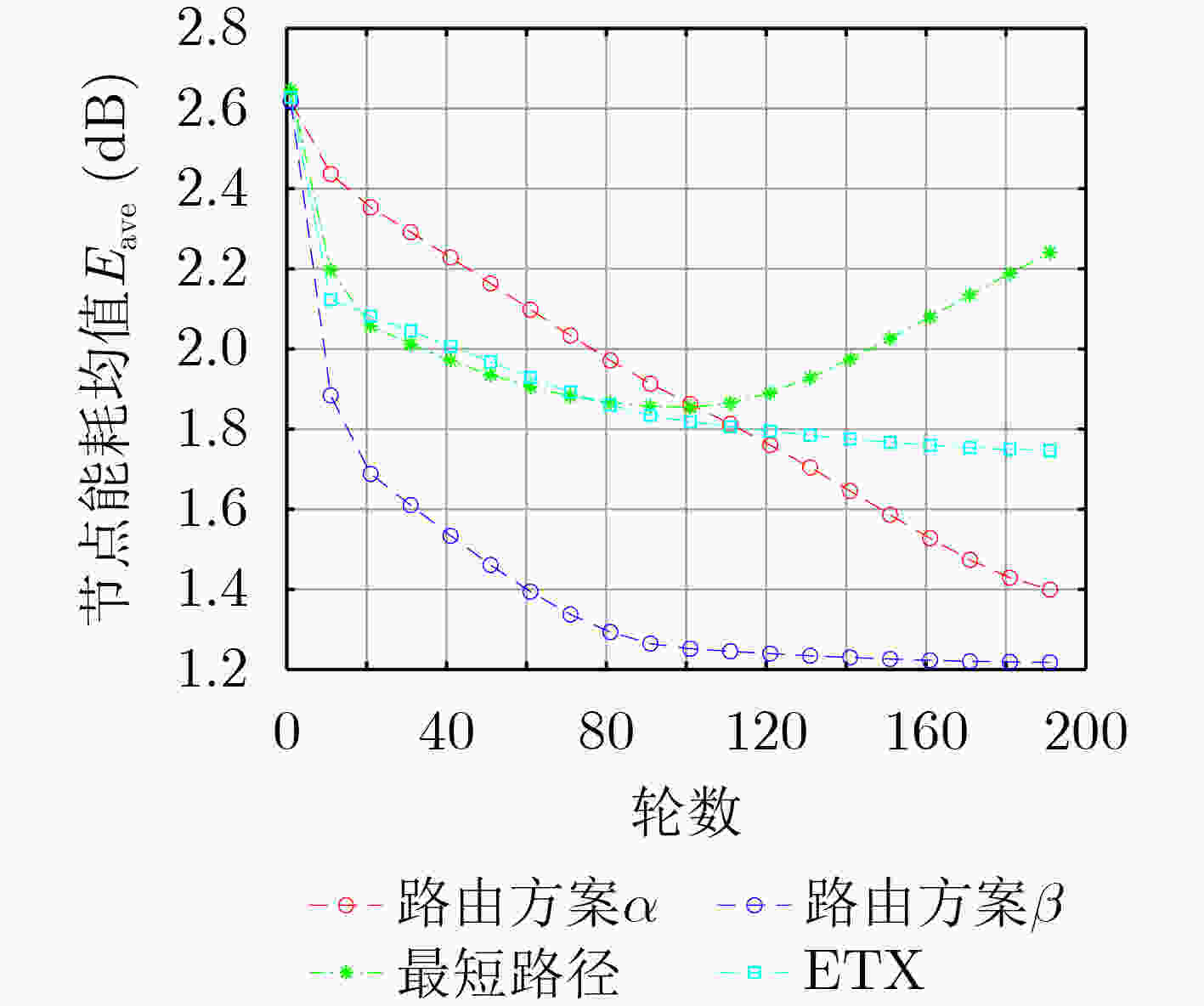


 下载:
下载:
