Cryptoanalysis on the Forward Security of Two Authenticated Key Protocols
-
摘要: 目前,网络安全及隐私受到广泛关注。前向安全性是Günther在1989年提出的一种认证密钥协商协议( AKA)的安全属性(doi: 10.1007/3-540-46885-4_5),该性质经过30年的蓬勃发展已经成为研究领域的热点之一。该文主要分析了MZK20和VSR20两个AKA协议。首先在启发式分析的基础上,利用BAN逻辑分析了MZK20协议不具有弱前向安全性;其次利用启发式分析和Scyther工具证明了VSR20协议不具备前向安全性。最后,在分析VSR20协议设计缺陷的基础上,提出了改进方案,并在eCK模型下证明了改进后协议的安全性;并且,结合Scyther软件证明了改进VSR20协议与VSR20协议相比明显提高了安全性。
-
关键词:
- 安全协议形式化工具分析 /
- 认证密钥协商协议 /
- 前向安全性
Abstract: At present, network security and privacy have attracted extensive attention. Forward security is a security attribute of Authenticated Key Agreement protocol (AKA) proposed by Günther in 1989. Since then, this property has become one of the hot topics. This paper analyzes the security properties of two AKA protocols, MZK20 and VSR20. First, based on heuristic analysis and BAN logic, MZK20 protocol is proved that it does not satisfy weak forward security. Second, using heuristic analysis and Scyther, it is proved that VSR20 protocol does not fulfill forward security. Finally, the enhanced VSR20 protocol is designed and proved more secure than VSR20. The security of the modified VSR20 is verified both by the use of security reduction under eCK model and Scyther. -
表 1 BAN逻辑分析MZK20协议
MZK20协议期望达成的目标如下(参与双方用$ {{\text{S}}_j} $和$ {{\text{U}}_u} $表示,$ {K_{uj}} $表示双方达成的会话密钥):
G1. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{uj}} $;
G2. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{uj}}) $;
G3. $ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{uj}} $;
G4. $ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{uj}}) $.消息:
$ {\text{Message}}\,{\text{1}}\quad {{\text{U}}_u} \to {{\text{S}}_j}: < {\{ {\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}\} _{{K_u}}},{\{ {C_u}\} _{{K_S}}} > $;
$ {\text{Message}}\,{\text{2}}\quad {{\text{S}}_j} \to {{\text{U}}_u}: < {D_j}{ > _{ < {\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}{ > _{{K_{{\text{RC}}}}}}}} $;假设:
A1.$ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{\text{fresh}}({C_u}) $,$ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;{\text{fresh}}({D_j}) $;
A2.$ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{C_u} $,$ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;{D_j} $;
A3.$ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\mathop \Leftrightarrow \limits^{{K_u}} {{\text{S}}_j}) $,$ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\mathop \Leftrightarrow \limits^{{K_u}} {{\text{S}}_j}) $;
A4.$ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{controls}}\;{K_{uj}}) $,$ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{controls}}\;{K_{uj}}) $;
A5.$ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{{\text{RC}}}} $,$ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{{\text{RC}}}} $.推理过程:
F1. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{sees}}\; < {\{ {\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}\} _{{K_u}}},{\{ {C_u}\} _{{K_S}}} > $;
F2. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{sees}}\;{\{ I{D_u}\} _{{K_u}}} $,$ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{sees}}\;{\{ {C_u}\} _{{K_s}}} $;
F3. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{said}}\;{\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}) $,$ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{said}}\;{C_u}) $($ {\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u} = {C_u}P \oplus {\text{PI}}{{\text{D}}_u} $, $ {X_u} = h({\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}||{\text{p}}{{\text{k}}_{{\text{RC}}}}) $且$ {\text{PI}}{{\text{D}}_u} = {\{ {\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}\} _{{K_u}}} $);
F4. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{C_u}) $,$ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{X_u}) $;
F5. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{uj}}) $($ {K_{uj}} = {\text{S}}{{\text{K}}_{uj}} = h({\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}||{C_u}P||{D_j}||{X_u}||{\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_j}) $);
F6. $ {{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{believes}}\;{K_{uj}} $;
F7. $ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{sees}}\; < {D_j}{ > _{ < {\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}{ > _{{K_{{\text{RC}}}}}}}} $;
F8. $ {{\text{U}}_u}\;{\text{believes}}\;({{\text{S}}_j}\;{\text{said}}\;{D_j}) $($ {K_{uj}} = {\text{S}}{{\text{K}}_{uj}} = h({\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_u}||{C_u}P||{D_j}||{X_u}||{\text{I}}{{\text{D}}_j}) $). -
[1] GÜNTHER C G. An identity-based key-exchange protocol[C]. Workshop on the Theory and Application of of Cryptographic Techniques, Houthalen, Belgium, 1989: 29–37. [2] MATSUMOTO T, TAKASHIMA Y, and IMAI H. On seeking smart public-key-distribution systems[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Electronics and Communication Engineers of Japan Section E, 1986, 69(2): 99–106. [3] JEONG I R, KATZ J, and LEE D H. One-round protocols for two-party authenticated key exchange[C]. The 2nd International Conference on Applied Cryptography and Network Security, Yellow Mountain, China, 2004: 220–232. [4] KRAWCZYK H. HMQV: A high-performance secure Diffie-Hellman protocol[C]. The 25th Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, USA, 2005: 546–566. [5] BOYD C and NIETO J G. On forward secrecy in one-round key exchange[C]. The 13th IMA International Conference on Cryptography and Coding, Oxford, UK, 2011: 451–468. [6] 曹晨磊, 刘明奇, 张茹, 等. 基于层级化身份的可证明安全的认证密钥协商协议[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2014, 36(12): 2848–2854. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2014.00684CAO Chenlei, LIU Mingqi, ZHANG Ru, et al. Provably secure authenticated key agreement protocol based on hierarchical identity[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2014, 36(12): 2848–2854. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1146.2014.00684 [7] 杨孝鹏, 马文平, 张成丽. 一种新型基于环上带误差学习问题的认证密钥交换方案[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2015, 37(8): 1984–1988. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141506YANG Xiaopeng, MA Wenping, and ZHANG Chengli. New authenticated key exchange scheme based on ring learning with errors problem[J]. Journal of Electronics &Information Technology, 2015, 37(8): 1984–1988. doi: 10.11999/JEIT141506 [8] 熊婧, 王建明. 基于HASH函数的RFID安全双向认证协议研究[J]. 中国测试, 2017, 43(3): 87–90,96. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2017.03.018XIONG Jing and WANG Jianming. Based on HASH function of RFID security authentication protocol and analysis[J]. China Measurement &Test, 2017, 43(3): 87–90,96. doi: 10.11857/j.issn.1674-5124.2017.03.018 [9] LI Xiong, PENG Jieyao, OBAIDAT M S, et al. A secure three-factor user authentication protocol with forward secrecy for wireless medical sensor network systems[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 14(1): 39–50. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2019.2899580 [10] SALEEM M A, SHAMSHAD S, AHMED S, et al. Security analysis on “A secure three-factor user authentication protocol with forward secrecy for wireless medical sensor network systems”[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(4): 5557–5559. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2021.3073537 [11] YANG Zheng, HE Jun, TIAN Yangguang, et al. Faster authenticated key agreement with perfect forward secrecy for industrial internet-of-things[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(10): 6584–6596. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2963328 [12] CHANG C C and LE H D. A provably secure, efficient, and flexible authentication scheme for ad hoc wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2016, 15(1): 357–366. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2473165 [13] GOPE P and HWANG T. A realistic lightweight anonymous authentication protocol for securing real-time application data access in wireless sensor networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(11): 7124–7132. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2585081 [14] 王晨宇, 汪定, 王菲菲, 等. 面向多网关的无线传感器网络多因素认证协议[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(4): 683–700. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00683WANG Chenyu, WANG Ding, WANG Feifei, et al. Multi-factor user authentication scheme for multi-gateway wireless sensor networks[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(4): 683–700. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00683 [15] QIU Shuming, WANG Ding, XU Guoai, et al. Practical and provably secure three-factor authentication protocol based on extended chaotic-maps for mobile lightweight devices[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure Computing, 2022, 19(2): 1338–1351. doi: 10.1109/TDSC.2020.3022797 [16] SHAMSHAD S, SALEEM M A, OBAIDAT M S, et al. On the security of a lightweight privacy-preserving authentication protocol for VANETs[C]. 2021 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Systems (ICAIS), Coimbatore, India, 2021: 1766–1770. [17] RESCORLA E.Internet Engineering Task Force. RFC 8446-The Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol version 1.3[S]. 2018. [18] BOYD C and GELLERT K. A modern view on forward security[J]. The Computer Journal, 2021, 64(4): 639–652. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/bxaa104 [19] LAMACCHIA B, LAUTER K, and MITYAGIN A. Stronger security of authenticated key exchange[C]. The 1st International Conference on Provable Security, Wollongong, Australia, 2007: 1–16. [20] CANETTI R and KRAWCZYK H. Analysis of key-exchange protocols and their use for building secure channels[C]. International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, Innsbruck, Austria, 2001: 453–474. [21] MOHAMED M I, WANG Xiaofen, and ZHANG Xiaosong. Adaptively-secure authenticated key exchange protocol in standard model[J]. International Journal of Network Security, 2018, 20(2): 345–358. doi: 10.6633/IJNS.201803.20(2).16 [22] BURROWS M, ABADI M, and NEEDHAM R M. A logic of authentication[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society A:Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1989, 426(1871): 233–271. doi: 10.1098/rspa.1989.0125 [23] CREMERS C J F. The scyther tool: Verification, falsification, and analysis of security protocols[C]. International Conference on Computer Aided Verification, Princeton, USA, 2008: 414–418. [24] AKRAM M A, GHAFFAR Z, MAHMOOD K, et al. An anonymous authenticated key-agreement scheme for multi-server infrastructure[J]. Human-centric Computing and Information Sciences, 2020, 10(1): 22. doi: 10.1186/s13673-020-00227-9 [25] SURESHKUMAR V, ANANDHI S, AMIN R, et al. Design of robust mutual authentication and key establishment security protocol for cloud-enabled smart grid communication[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2021, 15(3): 3565–3572. doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2020.3039402 -





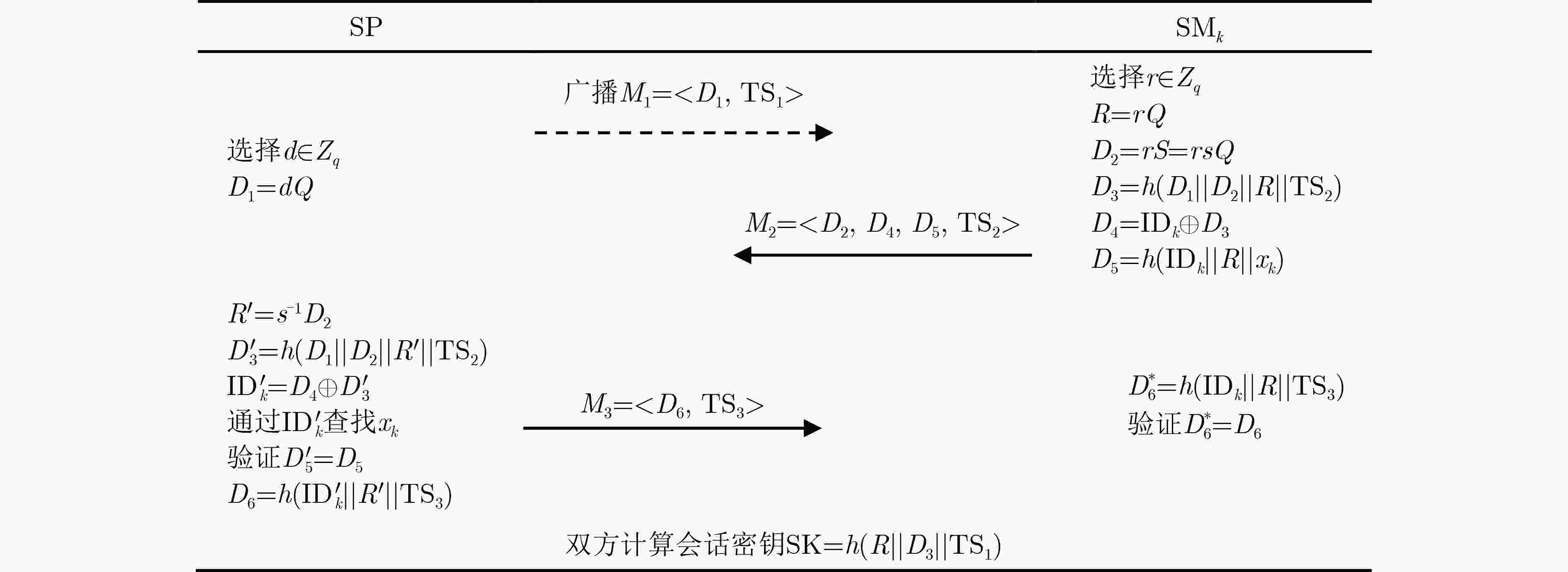
 下载:
下载:
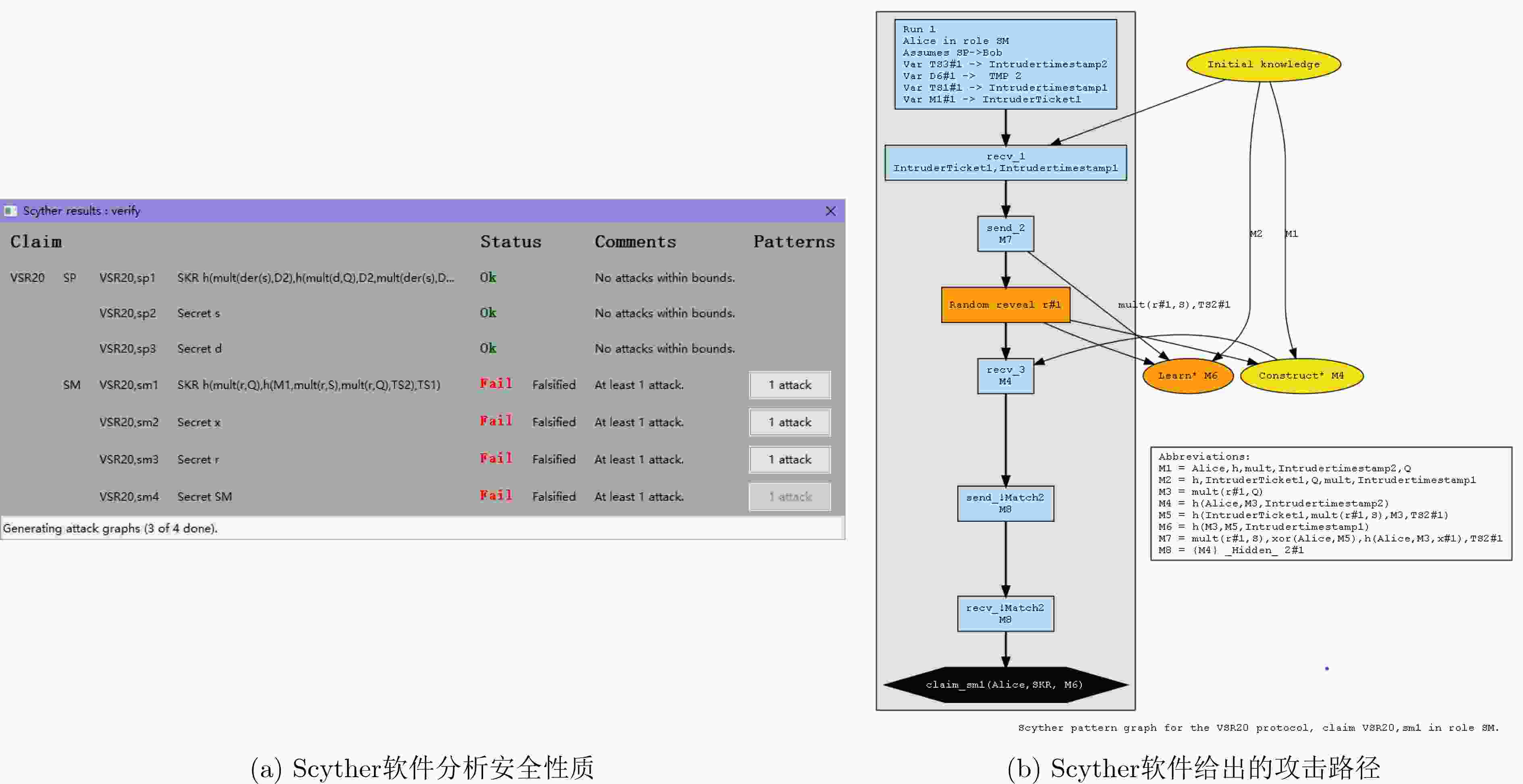
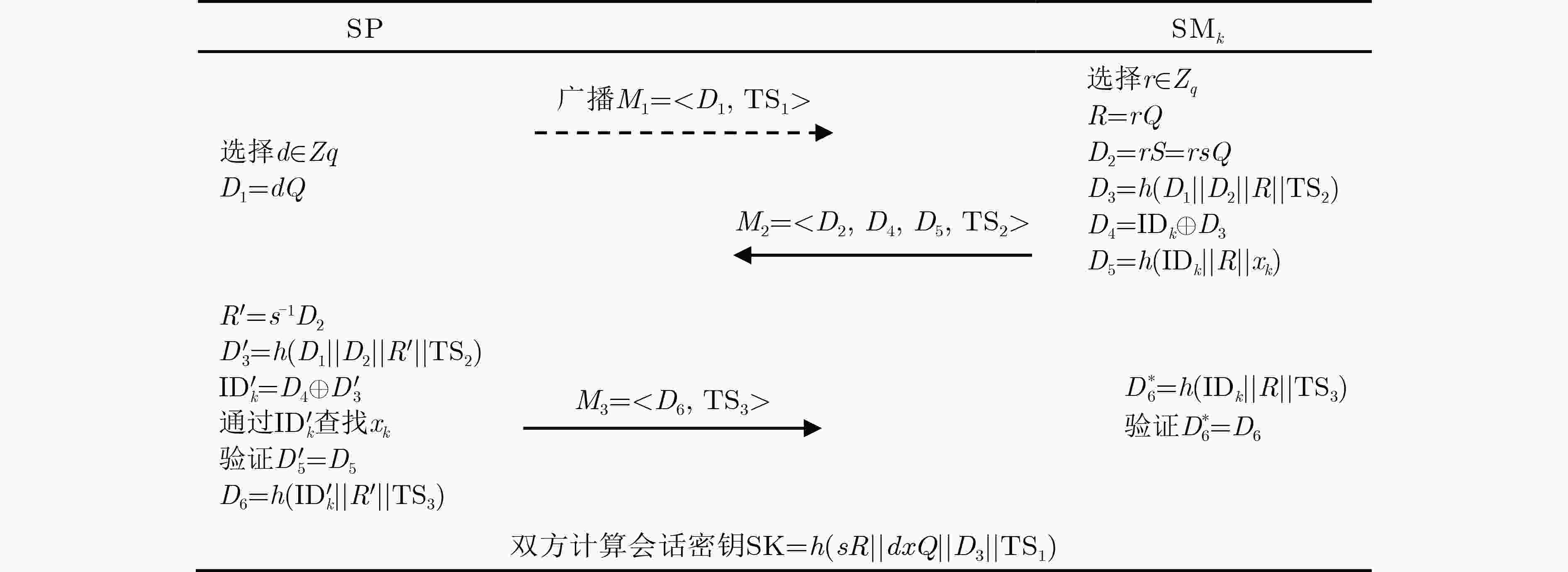
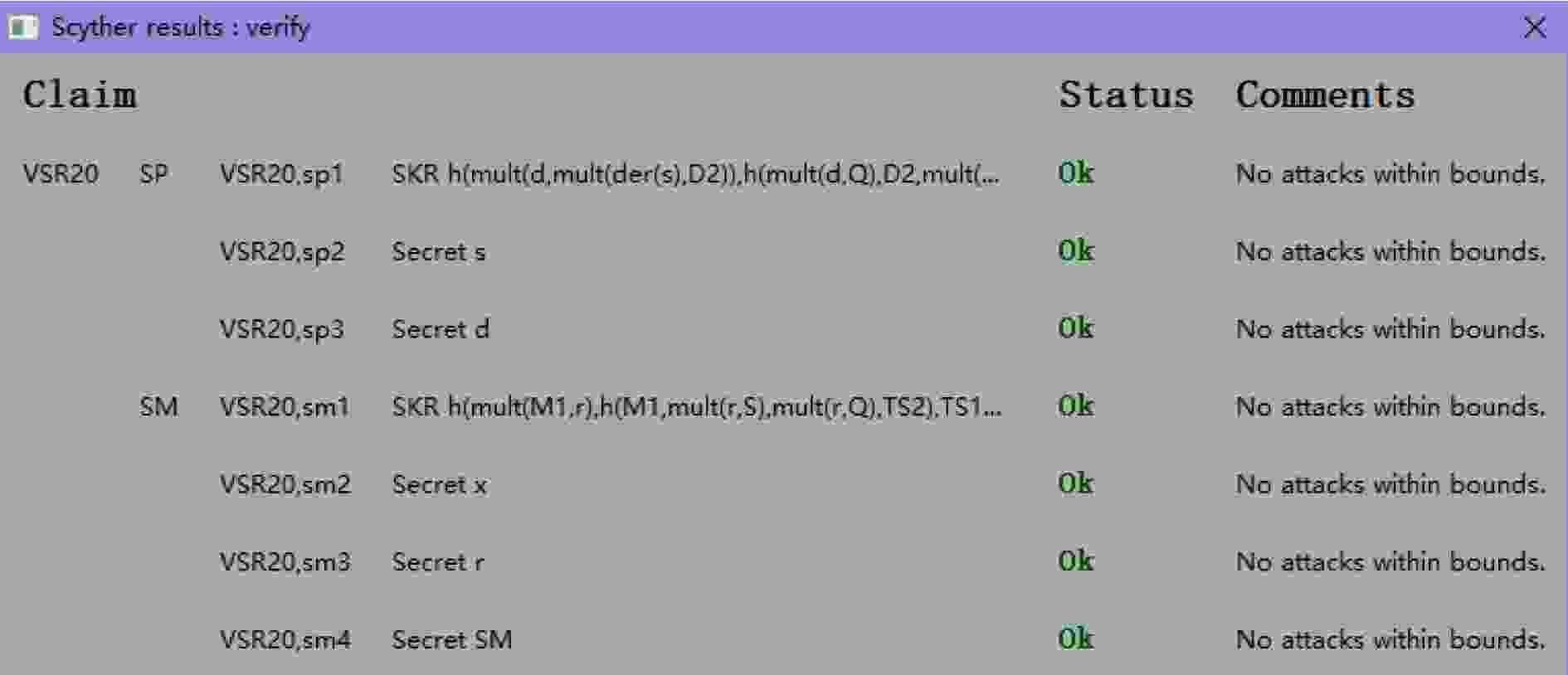


 下载:
下载:
